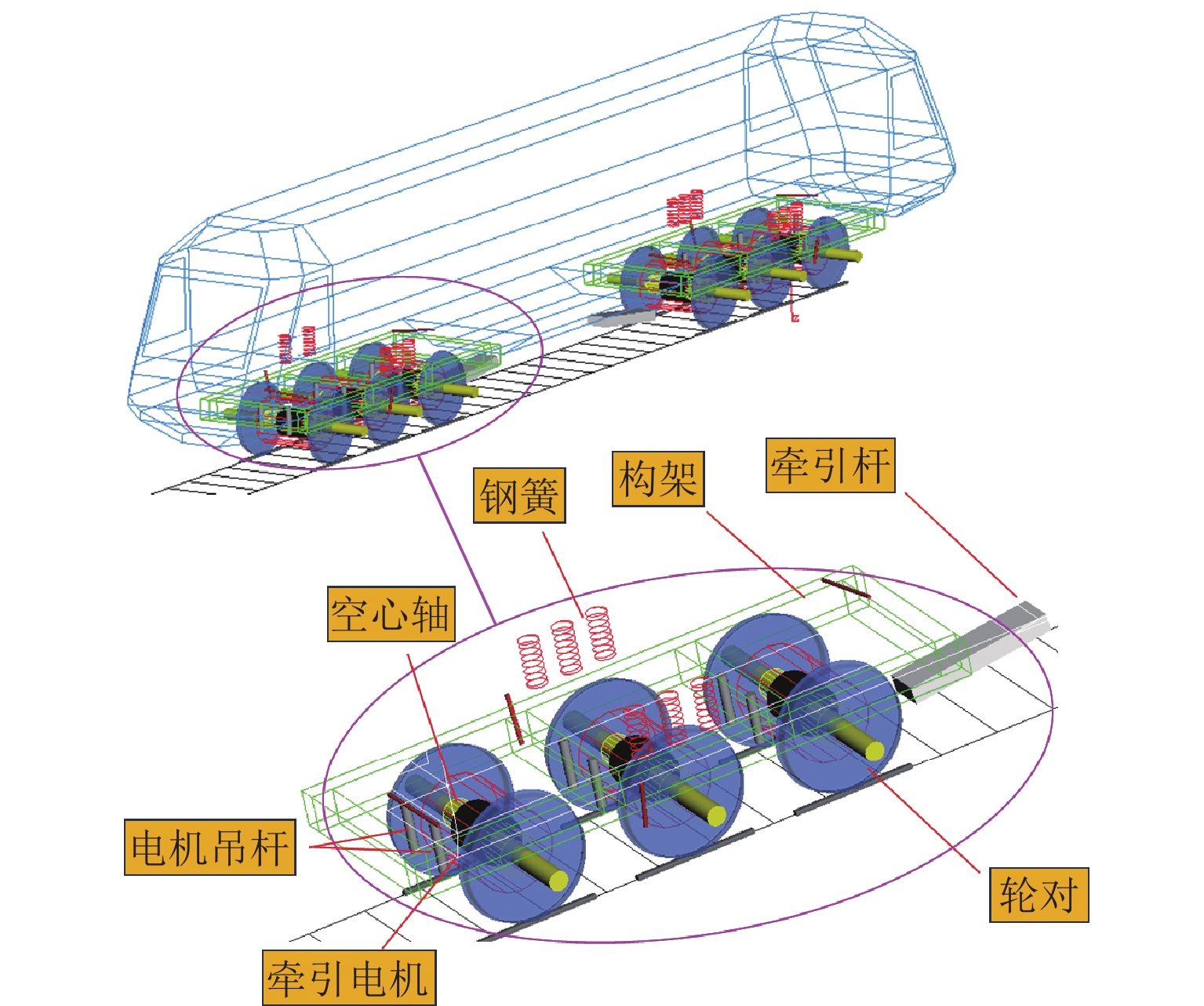
Re-adhesion Performance of High-Power Permanent-Magnet Direct-Drive Bogie-Suspended Locomotives
-
摘要:
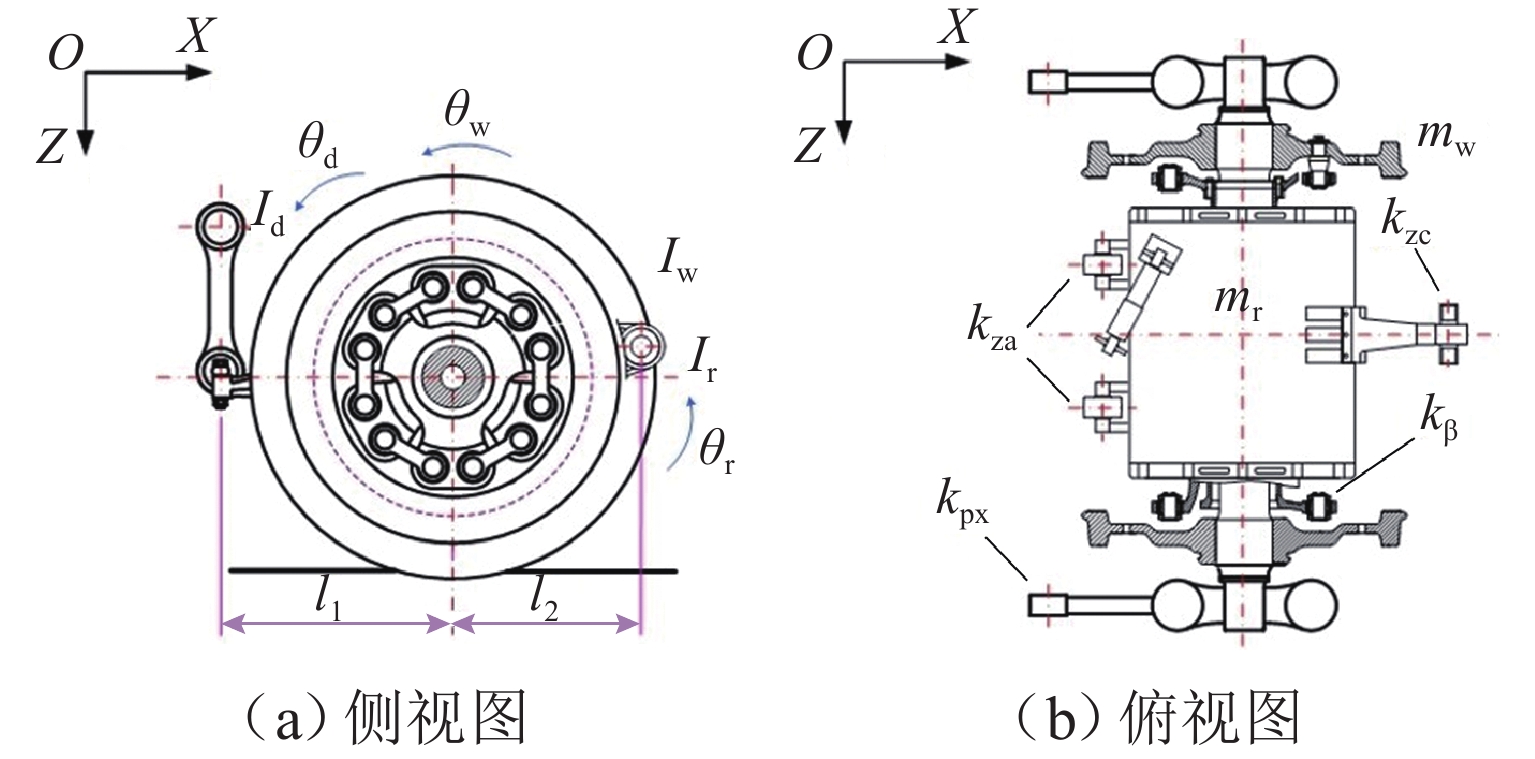
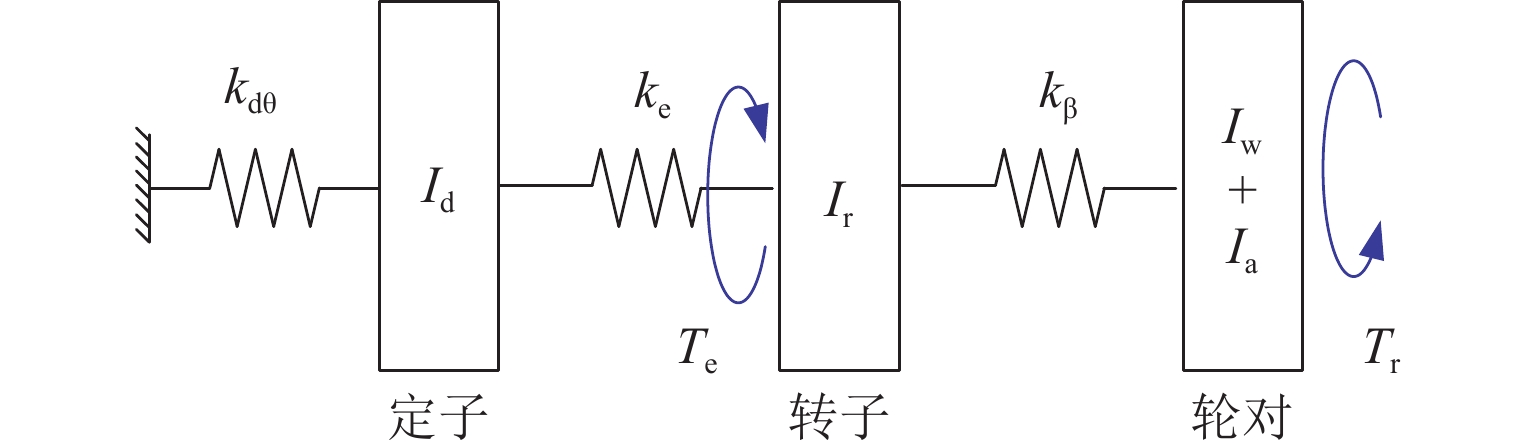
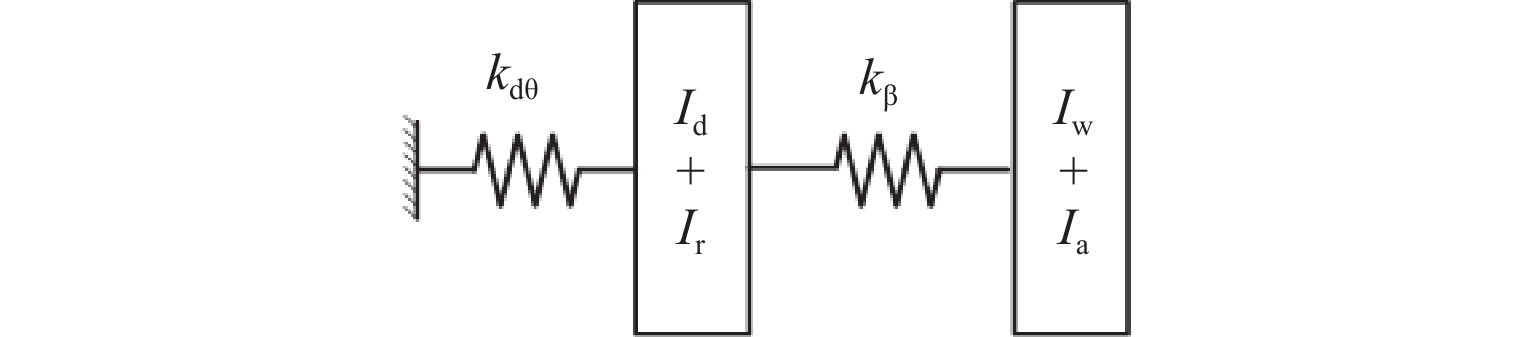
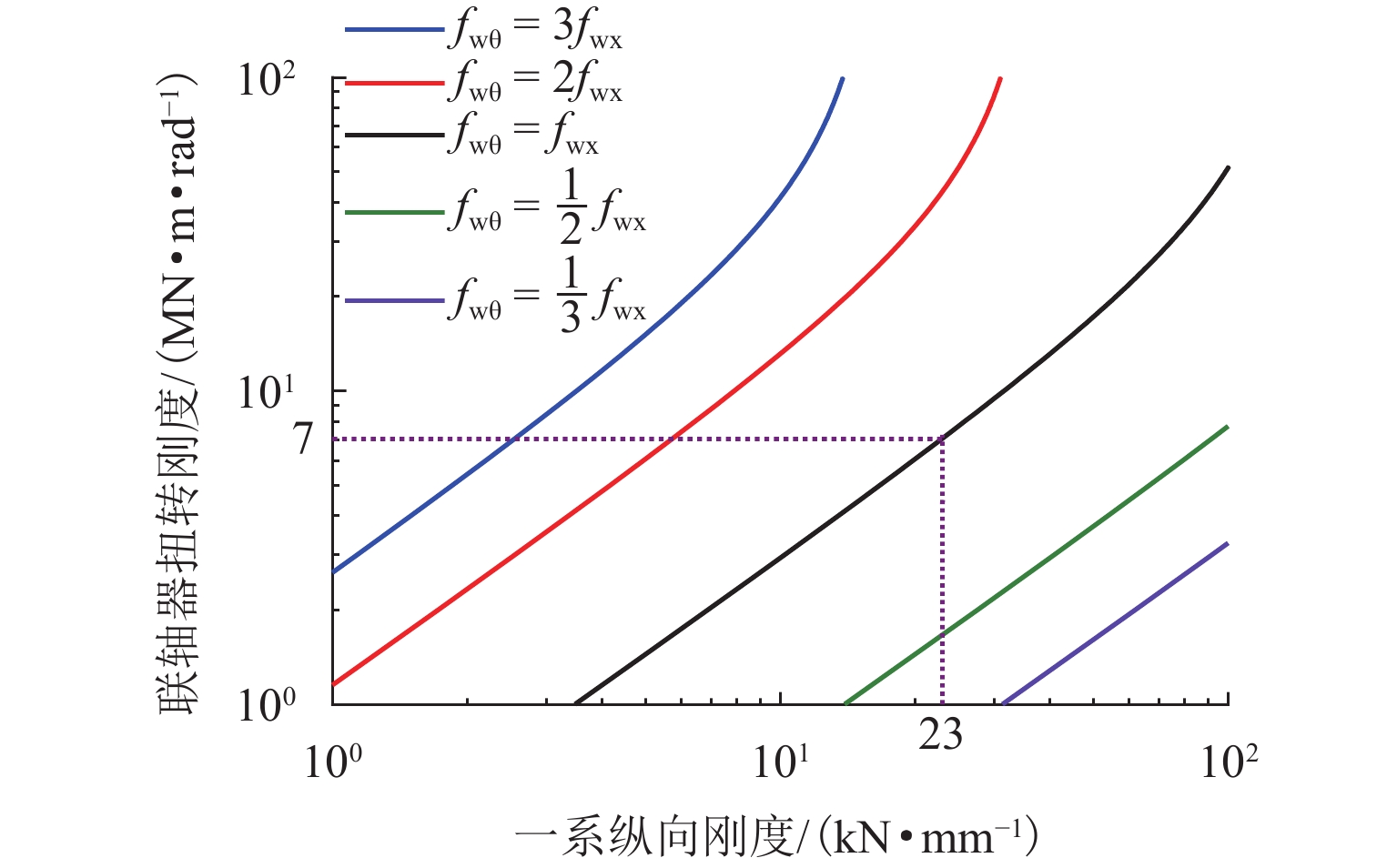
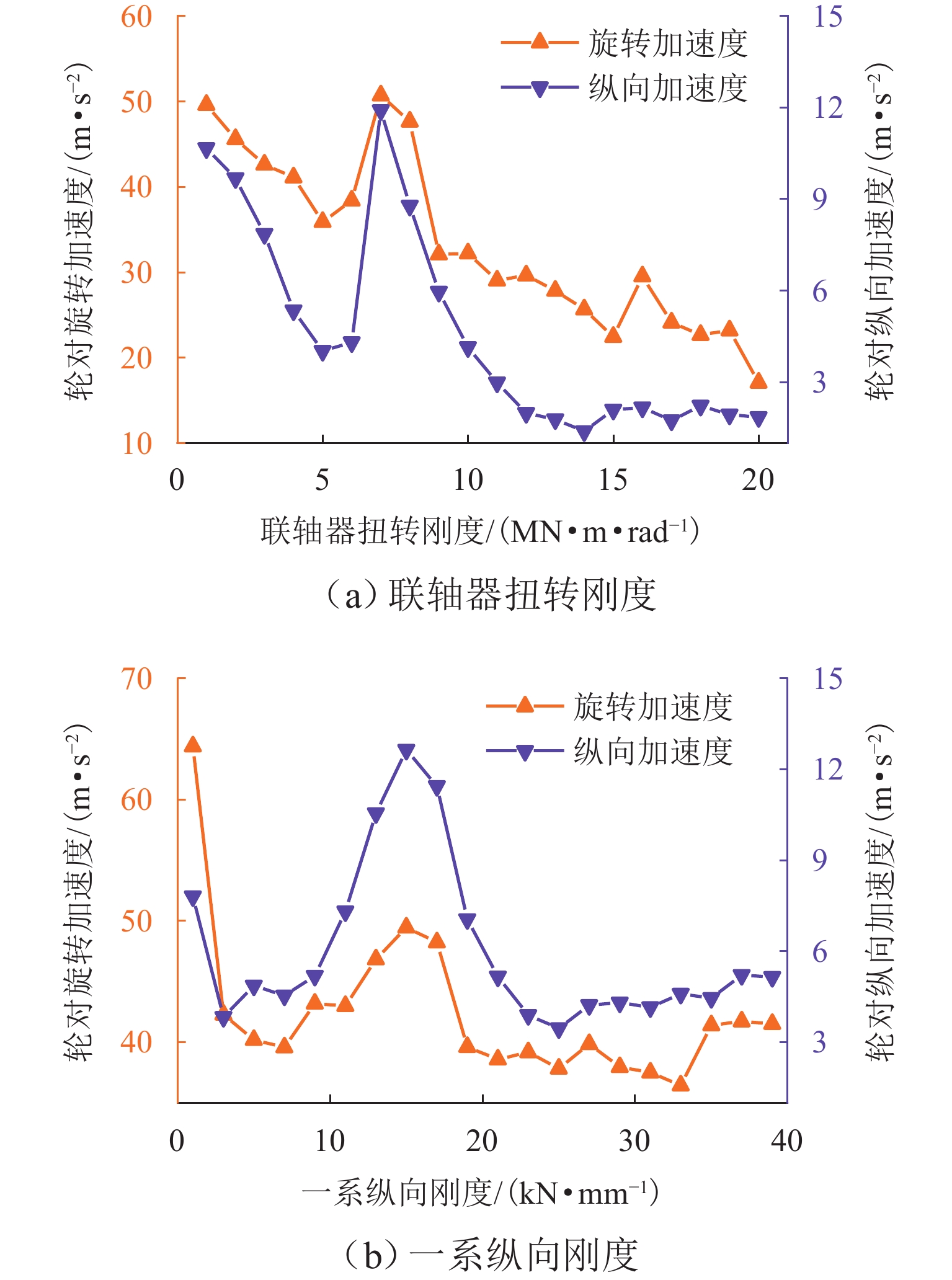
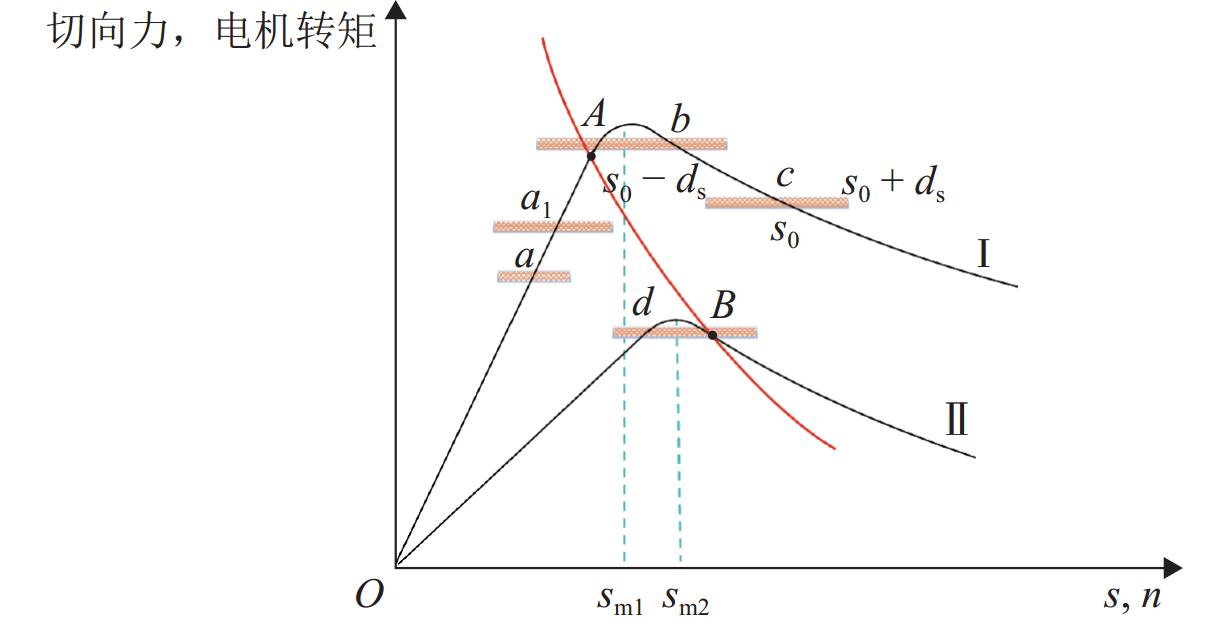
针对大功率架悬式永磁直驱驱动系统,研究轮对驱动系统悬挂参数对机车重建黏着性能的影响. 基于平均滑移率和动态滑移率,分析机车黏滑振动机理,并建立轮对驱动系统扭转振动的简化模型,明确悬挂参数匹配原则;搭建某机车多体动力学仿真模型,以启动工况为例,探讨轮对驱动系统悬挂参数对机车重建黏着性能的影响. 仿真结果表明,较小的轮对驱动系统悬挂刚度增大了机车发生黏滑振动的风险,提高膜片式联轴器扭转刚度和一系纵向刚度能有效增强机车的重建黏着性能,将联轴器扭转刚度从1 MN·m/rad增加到5 MN·m/rad时,机车重建黏着性能提升了约12%;不合理的悬挂参数匹配可能将导致轮对纵向-旋转振动共振,不仅加剧了轮对驱动系统结构振动,而且极大削弱机车重建黏着性能. 因此,合理匹配轮对驱动系统悬挂参数对于提高机车重建黏着性能至关重要.
Abstract:To address the high-power permanent-magnet direct-drive bogie-suspended traction systems, the impact of suspension parameters of the wheelset drive system on the re-adhesion performance of locomotives was investigated. Based on the average slip rate and dynamic slip rate, the mechanism of locomotive stick-slip vibration was analyzed, and a simplified torsional vibration model of the wheelset drive system was established to clarify the suspension parameter matching principles. A multi-body dynamics simulation model of a specific locomotive was constructed, and the starting condition was taken as an example to explore the impact of suspension parameters of the wheelset drive system on the locomotive’s re-adhesion performance. Simulation results show that lower suspension stiffness of the wheelset drive system increases the risk of stick-slip vibration in the locomotive. Increasing the torsional stiffness of the diaphragm coupling and the primary longitudinal stiffness can effectively enhance the locomotive’s re-adhesion performance. When the torsional stiffness of the coupling was increased from 1 MN·m/rad to 5 MN·m/rad, the locomotive’s re-adhesion performance is improved by approximately 12%. However, improper matching of suspension parameters may lead to the longitudinal-rotational resonance of the wheelset, which not only exacerbates the vibration of the wheelset drive system but also significantly weakens the locomotive’s re-adhesion performance. Therefore, proper matching of the suspension parameters of the wheelset drive system is crucial for improving the locomotive’s re-adhesion performance.
-
表 1 不同轮轨黏着状态参数
Table 1. Parameters of different wheel-rail adhesion states
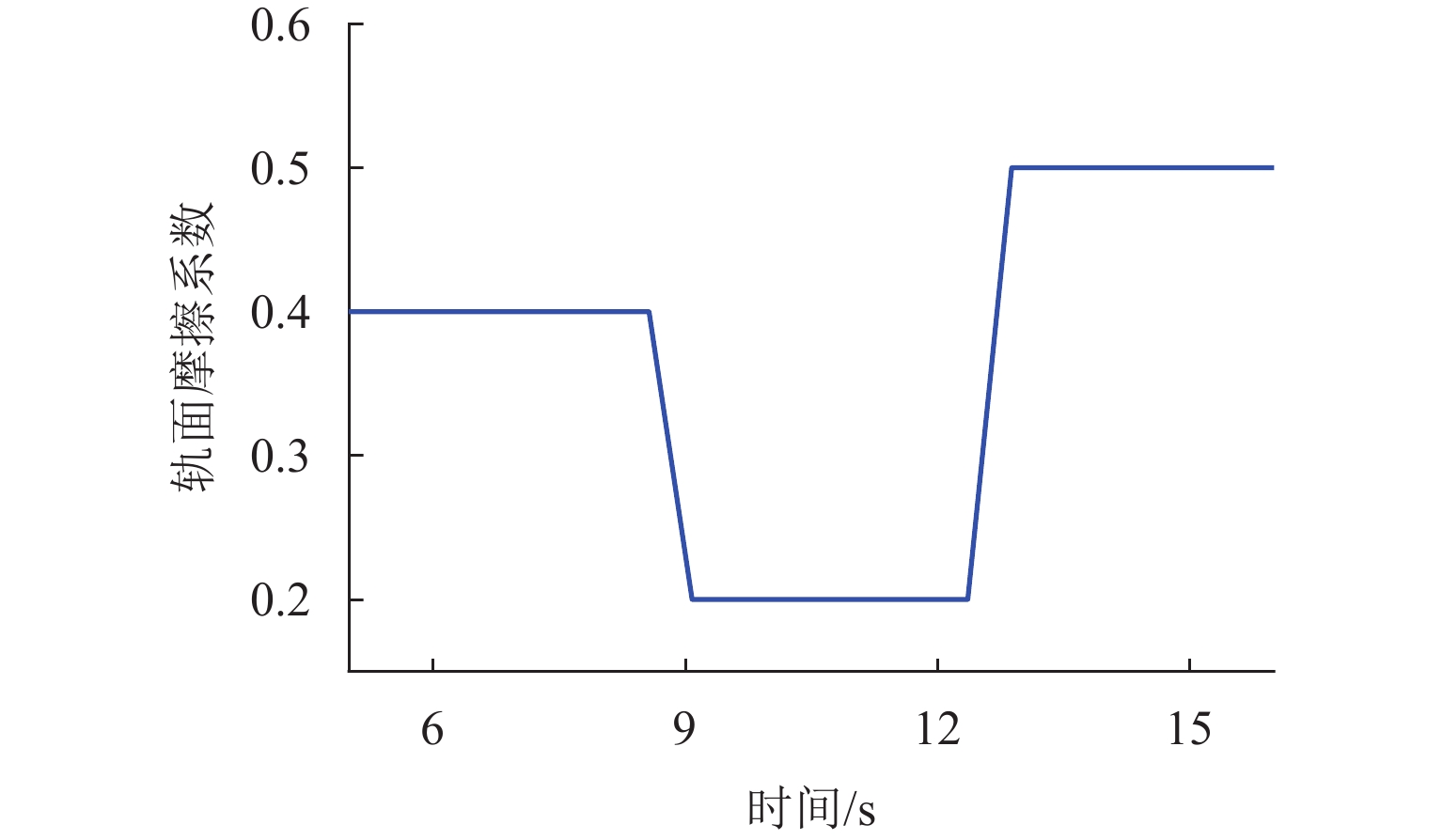
黏着状态 μ0 A B 干燥 0.55 0.40 0.60 湿润 0.30 0.40 0.20 油态 0.30 0.50 0.10 -
[1] 李华祥,张志和,刘鹏,等. 大功率永磁直驱技术优势及技术难点的深入研究[J]. 铁道机车车辆,2020,40(4): 50-53,93. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-7842.2020.04.10LI Huaxiang, ZHANG Zhihe, LIU Peng, et al. In-depth study on technical advantages and technical difficulties of high power permanent magnet direct drive[J]. Railway Locomotive & Car, 2020, 40(4): 50-53,93. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-7842.2020.04.10 [2] 马光同,孙振耀,徐帅,等. 轨道车辆永磁直驱技术综述[J]. 交通运输工程学报,2021,21(1): 217-232.MA Guangtong, SUN Zhenyao, XU Shuai, et al. Review on permanent magnet direct drive technology of railway vehicles[J]. Journal of Traffic and Transportation Engineering, 2021, 21(1): 217-232. [3] 黄志辉,许峻峰. 直驱转向架结构特点与应用展望[J]. 机车电传动,2013(4): 67-69. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-128X.2013.04.020HUANG Zhihui, XU Junfeng. Structure feature and forecast of bogie driven directly[J]. Electric Drive for Locomotives, 2013(4): 67-69. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-128X.2013.04.020 [4] 罗湘萍,张文超,吴凯桦. 永磁同步直驱电机悬挂模式研究[J]. 城市轨道交通研究,2018,21(4): 5-7,13.LUO Xiangping, ZHANG Wenchao, WU Kaihua. On the suspension type of permanent magnet synchronous motor[J]. Urban Mass Transit, 2018, 21(4): 5-7,13. [5] 马晓光,杨陈,肖遥,等. 架悬式永磁直驱转向架的动力学性能研究[J]. 铁道机车车辆,2023,43(5): 143-150. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-7842.2023.05.23MA Xiaoguang, YANG Chen, XIAO Yao, et al. Study on dynamic performance of frame-mounted permanent magnet direct-drive bogie[J]. Railway Locomotive & Car, 2023, 43(5): 143-150. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-7842.2023.05.23 [6] 徐艳晖. 车轮多边形对永磁直驱机车动态特性的影响研究[J]. 铁道车辆,2024,62(4): 54-60. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-7602.2024.04.010XU Yanhui. Study on the impact of the wheel polygon on the dynamic characteristics of the locomotive directly driven by permanent magnet[J]. Rolling Stock, 2024, 62(4): 54-60. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-7602.2024.04.010 [7] OLOFSSON U, SUNDVALL K. Influence of leaf, humidity and applied lubrication on friction in the wheel-rail contact: pin-on-disc experiments[J]. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part F: Journal of Rail and Rapid Transit, 2004, 218(3): 235-242. doi: 10.1243/0954409042389364 [8] WANG W J, SHEN P, SONG J H, et al. Experimental study on adhesion behavior of wheel/rail under dry and water conditions[J]. Wear, 2011, 271(9/10): 2699-2705. [9] 姚远,张红军,罗赟,等. 黏滑振动理论及其在铁路机车中的应用[J]. 机械工程学报,2010,46(24): 75-82. doi: 10.3901/JME.2010.24.075YAO Yuan, ZHANG Hongjun, LUO Yun, et al. Theory of stick-slip vibration and its application in locomotive[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2010, 46(24): 75-82. doi: 10.3901/JME.2010.24.075 [10] 崔晓璐,唐传平,包鹏羽,等. 高速列车制动区段钢轨波磨抑制方法[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2023,58(3): 656-664. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.20220256CUI Xiaolu, TANG Chuanping, BAO Pengyu, et al. Rail corrugation suppressing method on braking sections of high-speed trains[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2023, 58(3): 656-664. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.20220256 [11] 董雅宏,曹树谦. 车轮高阶多边形磨耗发生与演化特征分析[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2023,58(3): 665-676. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.20210989DONG Yahong, CAO Shuqian. Analysis of generation and evolution characteristics of wheel high-order polygonal wear[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2023, 58(3): 665-676. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.20210989 [12] 张波,杨云帆,凌亮,等. 车轮多边形对重载机车轮轨相互作用及接触损伤的影响分析[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2023,58(6): 1339-1346. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.20210448ZHANG Bo, YANG Yunfan, LING Liang, et al. Wheel-rail interaction and rolling fatigue damage of heavy-haul locomotive subjected to wheel polygonal wear[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2023, 58(6): 1339-1346. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.20210448 [13] 张斌,付秀琴. 铁路车轮、轮箍踏面剥离的类型及形成机理[J]. 中国铁道科学,2001,22(2): 73-78. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-4632.2001.02.011ZHANG Bin, FU Xiuqin. Type and formation mechanism of railway wheel and tire tread spall[J]. China Railway Science, 2001, 22(2): 73-78. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-4632.2001.02.011 [14] POLACH O. Creep forces in simulations of traction vehicles running on adhesion limit[J]. Wear, 2005, 258(7/8): 992-1000. [15] SPIRYAGIN M, WOLFS P, SZANTO F, et al. Simplified and advanced modelling of traction control systems of heavy-haul locomotives[J]. Vehicle System Dynamics, 2015, 53(5): 672-691. doi: 10.1080/00423114.2015.1008016 [16] SPIRYAGIN M, WOLFS P, COLE C, et al. Influence of AC system design on the realisation of tractive efforts by high adhesion locomotives[J]. Vehicle System Dynamics, 2017, 55(8): 1241-1264. doi: 10.1080/00423114.2017.1308522 [17] LATA M, VOLTR P. Identification of transient phenomena occurring at the initiation and termination of wheelset sliding[J]. Transport, 2012, 27(1): 86-91. [18] COLLINA A, PRONE L, RUSPINI E, et al. Study of torsional vibrations in the powertrain of diesel locomotive during manoeuvring by means of a multi-body model[J]. International Journal of Heavy Vehicle Systems, 2013, 20(2): 120-143. doi: 10.1504/IJHVS.2013.053008 [19] FRÖHLING R, SPANGENBERG U, REITMANN E. Root cause analysis of locomotive wheel tread polygonisation[J]. Wear, 2019, 432/433: 102911.1-102911.12. [20] 孙翔. 高粘着利用机车的系统设计[J]. 西南交通大学学报,1994,29(3): 235-248.SUN Xiang. System design for locomotives with high adhesion[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 1994, 29(3): 235-248. [21] 孙翔. 机车的传动、驱动、控制与粘着[J]. 铁道学报,1994,16(增1): 8-16. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-8360.1994.z1.002SUN Xiang. Relation of adhesion to power transmission, driving and system control for locomotives[J]. Journal of the China Railway Society, 1994, 16(S1): 8-16. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-8360.1994.z1.002 [22] 吴永芳. 架悬式驱动系统振动稳定性分析[J]. 铁道学报,1992,14(2): 1-8. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-8360.1992.02.001WU Yongfang. Stability analysis of the vibration of the frame-mounted motor driving system[J]. Journal of the China Railway Society, 1992, 14(2): 1-8. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-8360.1992.02.001 [23] YAO Y, ZHANG H J, LI Y M, et al. The dynamic study of locomotives under saturated adhesion[J]. Vehicle System Dynamics, 2011, 49(8): 1321-1338. doi: 10.1080/00423111003668195 [24] YAO Y, ZHANG H J, LUO S H. An analysis of resonance effects in locomotive drive systems experiencing wheel/rail saturation adhesion[J]. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part F: Journal of Rail and Rapid Transit, 2014, 228(1): 4-15. doi: 10.1177/0954409712457519 [25] YAO Y, ZHAO S Y, XIAO F X, et al. The effects of wheelset driving system suspension parameters on the re-adhesion performance of locomotives[J]. Vehicle System Dynamics, 2015, 53(12): 935-1951. [26] 姚远,张红军,罗世辉. 机车黏着极限态驱动装置结构共振研究[J]. 铁道学报,2011,33(11): 16-22. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8360.2011.11.003YAO Yuan, ZHANG Hongjun, LUO Shihui. Analysis on resonance of locomotive drive system under wheel-rail saturated adhesion[J]. Journal of the China Railway Society, 2011, 33(11): 16-22. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8360.2011.11.003 [27] 于蓬,章桐,孙玲,等. 集中驱动式纯电动车动力传动系统扭转振动研究[J]. 振动与冲击,2015,34(10): 121-127.YU Peng, ZHANG Tong, SUN Ling, et al. Powertrain torsional vibration of a central-driven pure EV[J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2015, 34(10): 121-127. [28] 陈星. 车用机电复合传动系统机电耦合非线性振动研究[D]. 北京:北京理工大学,2015. [29] KUMAR S,钱立新. 轮轨接触参数的实验室模拟及轮轨冲角、蛇行运动、油水污染、真实接触面积对粘着—蠕滑性能的影响[J]. 中国铁道科学,1984,5(1): 12-35.KUMAR S, QIAN Lixin. Laboratory simulation of wheel and rail contact related parameters and influence of contact area, angles of attack, kinematic oscillation and water, oil contamination on wheel rail adhesion[J]. China Railway Science, 1984, 5(1): 12-35. [30] 师陆冰,李群,郭俊,等. 不同工况下轮轨黏着-蠕滑曲线特性[J]. 机械工程学报,2019,55(10): 151-157. doi: 10.3901/JME.2019.10.151SHI Lubing, LI Qun, GUO Jun, et al. Adhesion-creep curve characteristics of wheel/rail under various conditions[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2019, 55(10): 151-157. doi: 10.3901/JME.2019.10.151 [31] 常崇义,陈波,蔡园武,等. 基于全尺寸试验台的水介质条件下高速轮轨黏着特性试验研究[J]. 中国铁道科学,2019,40(2): 25-32. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4632.2019.02.04CHANG Chongyi, CHEN Bo, CAI Yuanwu, et al. Experimental study on adhesion property of high speed wheel and rail in wet condition by full scale roller rig[J]. China Railway Science, 2019, 40(2): 25-32. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4632.2019.02.04 [32] 王文健,岳子恒,向鹏程,等. 列车轮轨增黏撒砂过程试验模拟与撒砂效果研究[J]. 机械工程学报,2023,59(22): 424-432. doi: 10.3901/JME.2023.22.424WANG Wenjian, YUE Ziheng, XIANG Pengcheng, et al. Study on experimental simulation of sanding process for train wheel-rail improving adhesion and sanding effect[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2023, 59(22): 424-432. doi: 10.3901/JME.2023.22.424 [33] 申鹏,王文健,张鸿斐,等. 撒砂对轮轨粘着特性的影响[J]. 机械工程学报,2010,46(16): 74-78. doi: 10.3901/JME.2010.16.074SHEN Peng, WANG Wenjian, ZHANG Hongfei, et al. Effect of spraying sand on adhesion characteristic of wheel/rail[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2010, 46(16): 74-78. doi: 10.3901/JME.2010.16.074 -




 下载:
下载: