Measurement Method for Permanent Magnet Guideway Irregularity Based on Self-Adaptive Noise Cancellation
-
摘要:
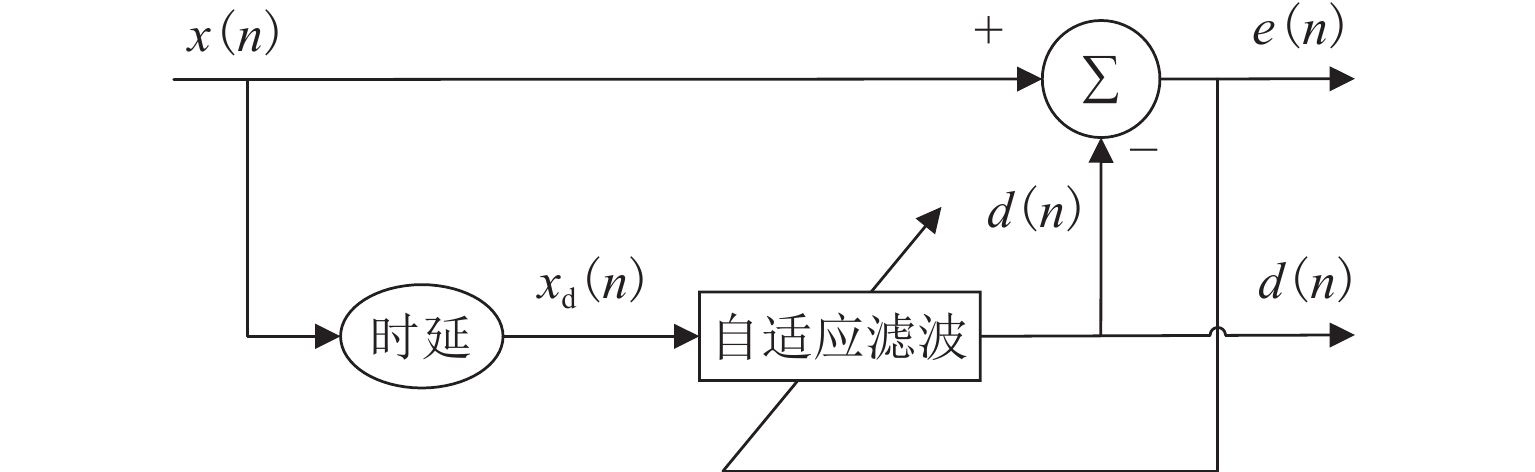
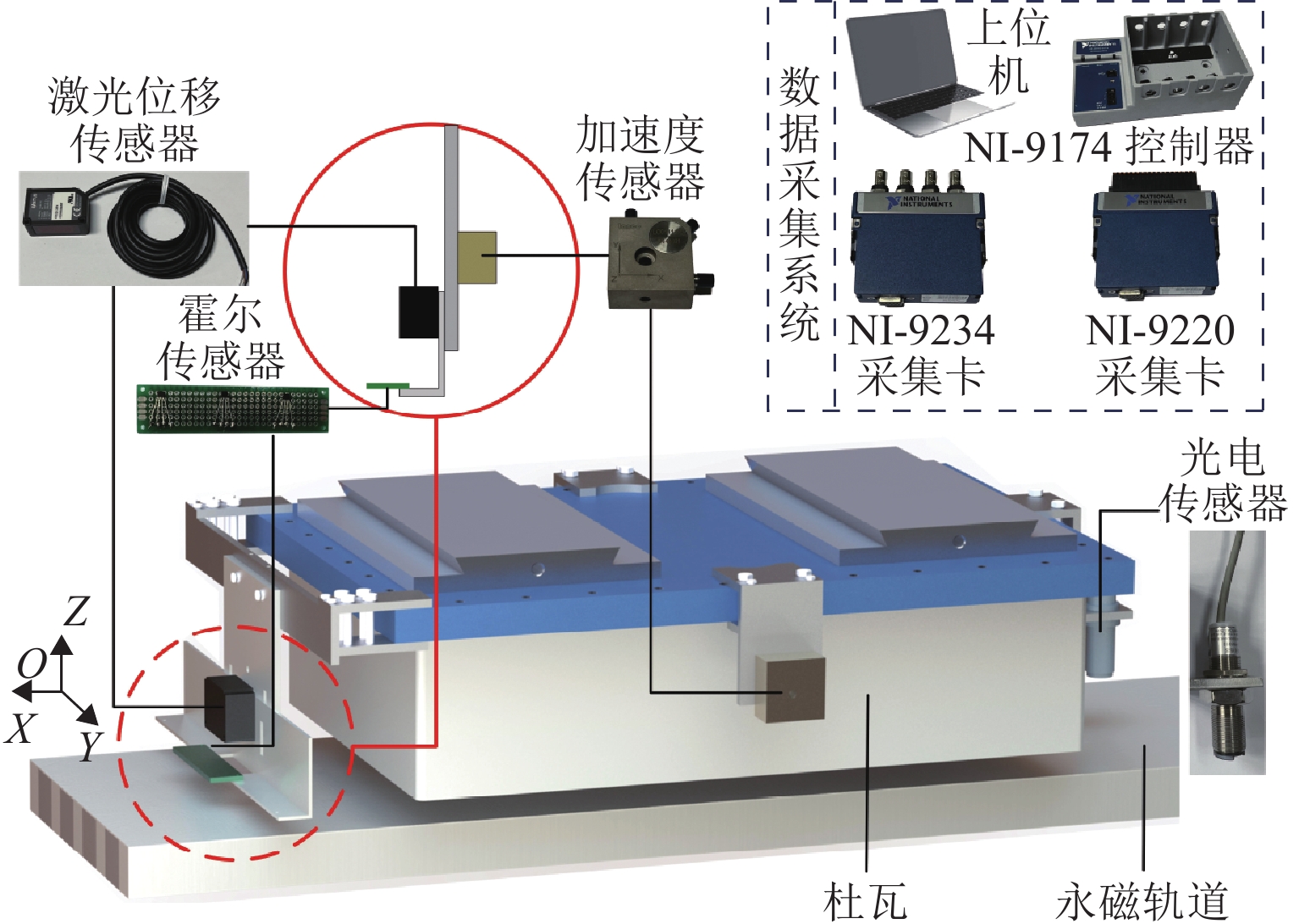
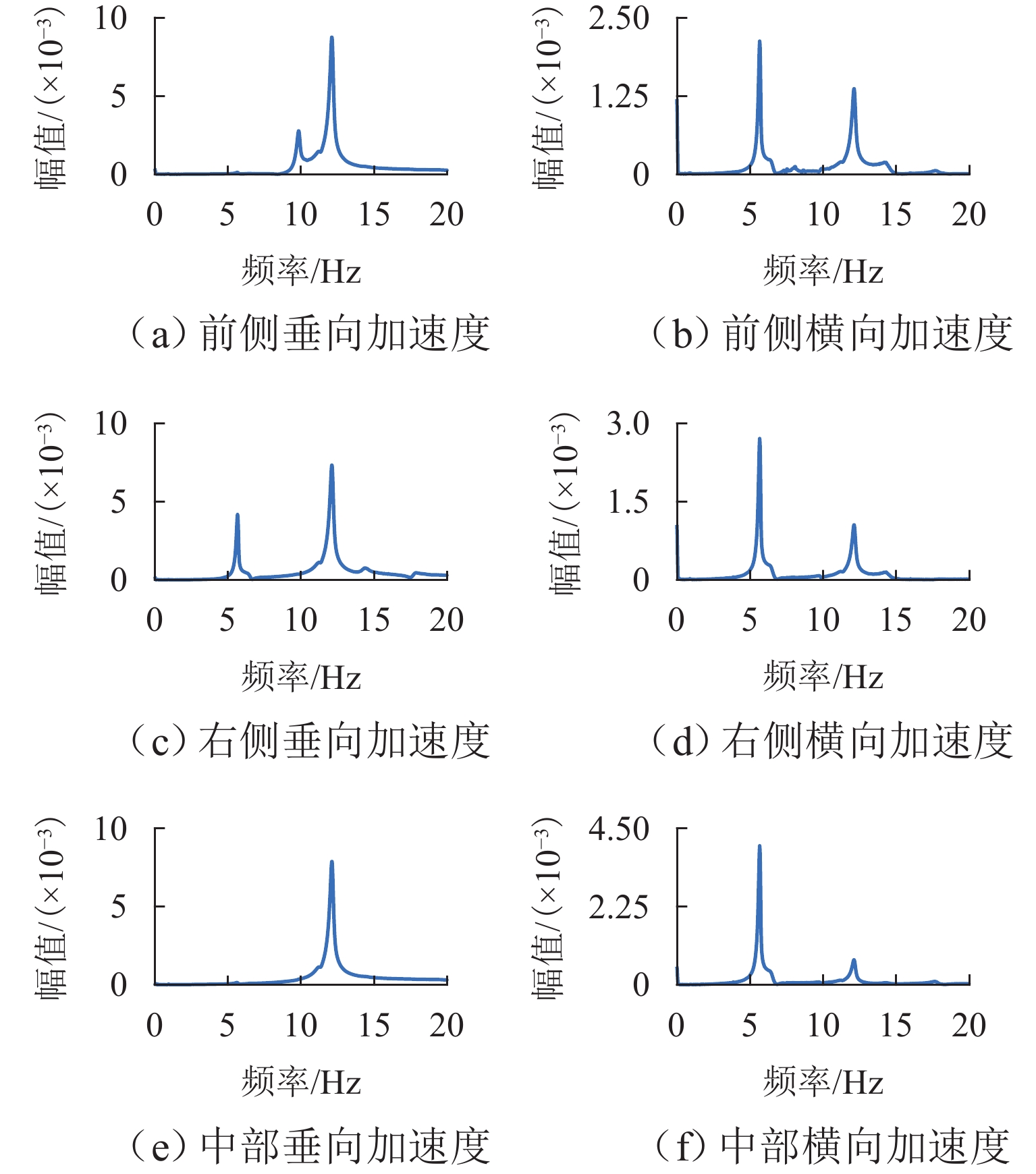
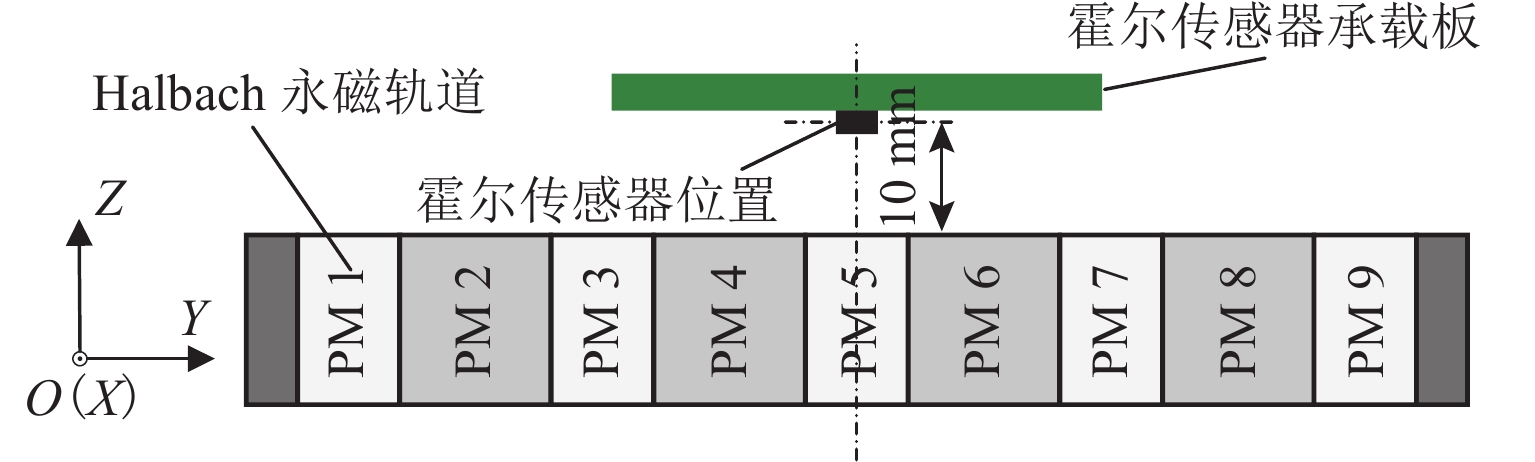
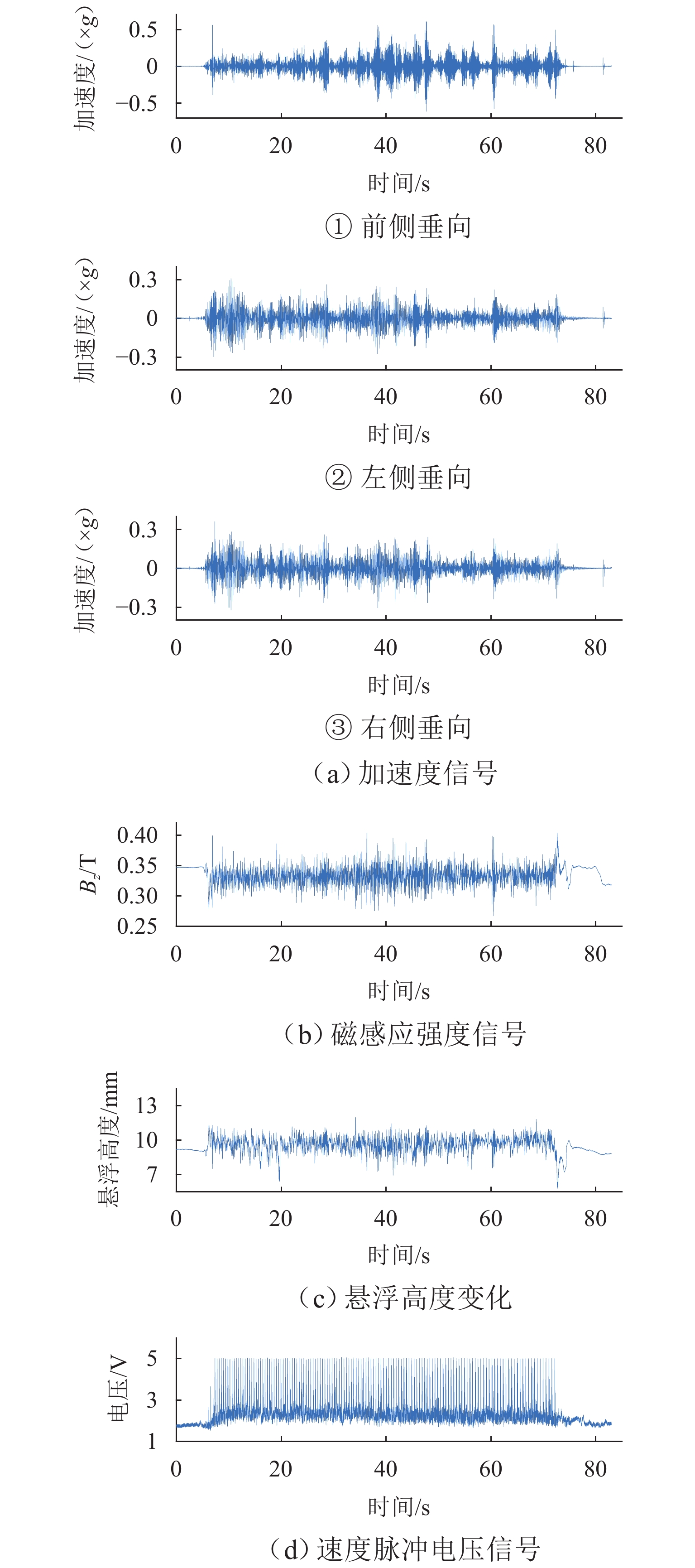
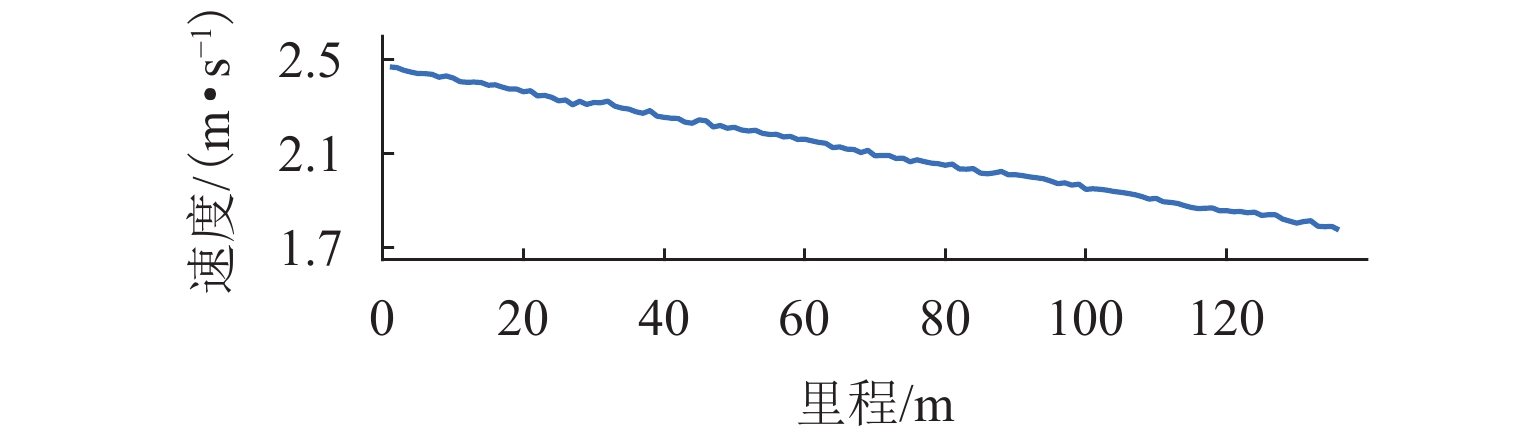
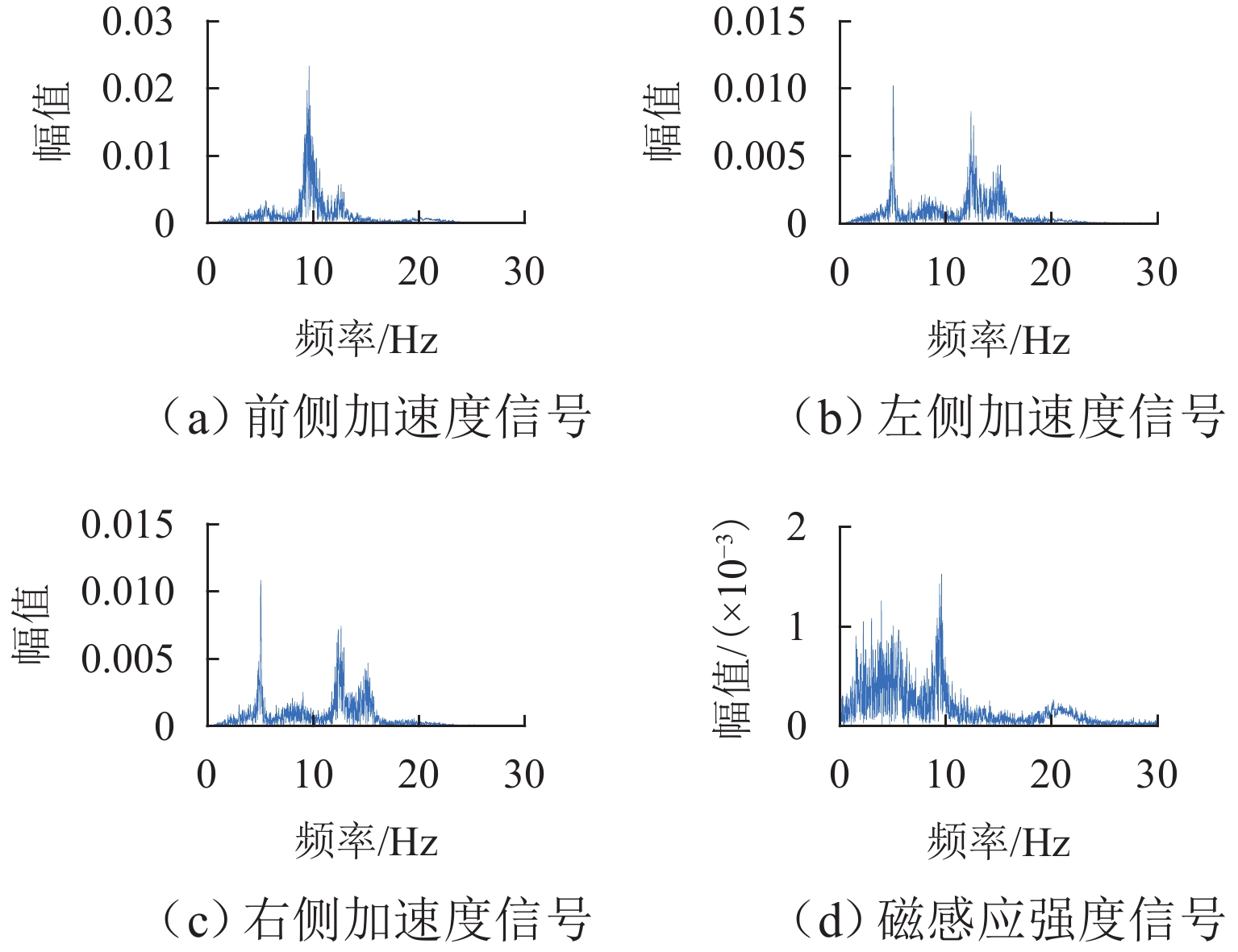
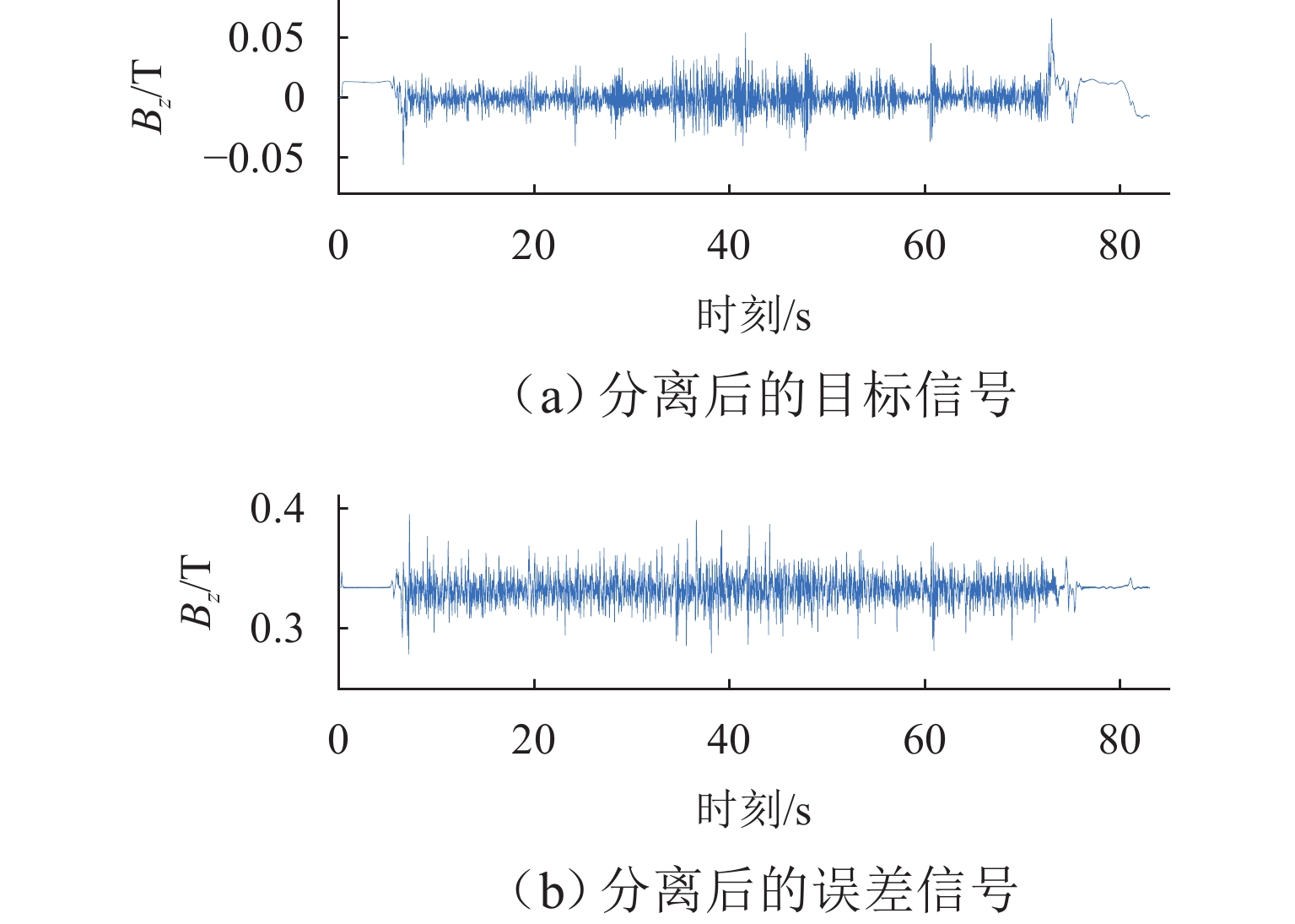
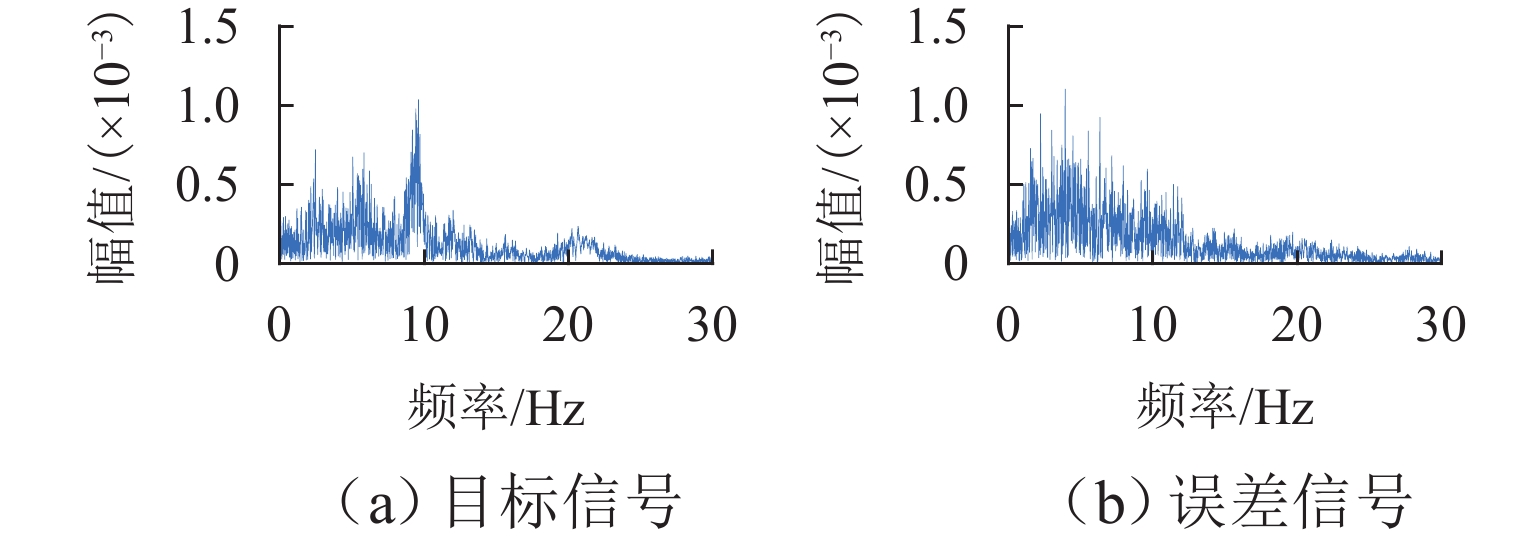
在进行永磁轨道不平顺动态检测时,消除实测信号中由测量载体振动而产生的振动分量,有助于掌握更为准确的轨道实时状态. 将自参考自适应噪声消除方法应用于永磁轨道不平顺检测,使单一信号源实现周期性成分与非周期性成分分离,在进行不平顺管理时有效降低具有周期性特征的振动分量干扰. 对高温超导高速磁浮工程化样车及试验线开展试验研究,将单个杜瓦作为测量载体并配合霍尔传感器进行永磁轨道轨面磁感应强度测量;利用自参考自适应噪声消除方法实现对实测样本的信号分离,分离后所得周期成分为振动分量,随机成分对应实际永磁轨道不平顺;对分离前后的信号进行时域与频域对比分析. 研究表明:时域信号中随机成分相比分离前波动减小,频域信号中测量载体对应的振动分量成分已被分离至周期成分中,证明了本文所提方法的有效性.
-
关键词:
- 高温超导钉扎磁悬浮 /
- 永磁轨道 /
- 轨道不平顺 /
- 自参考自适应噪声消除
Abstract:When the dynamic detection of permanent magnet guideway (PMG) irregularity is conduced, eliminating the vibration components generated by the vibration of the measured carrier in the measured signal is conducive to grasping a more accurate real-time state of the guideway. The self-adaptive noise cancellation (SANC) method was applied to the detection of PMG irregularities, effectively separating the periodic and non-periodic components of a single signal and reducing the interference of vibration components with periodic characteristics when conducting irregularity measurement. Experimental research was carried out on the high-temperature superconducting high-speed maglev engineering prototype and test line. A single Dewar was used as the measurement carrier, and the Hall sensor was employed to measure the magnetic induction intensity on the PMG surface. The SANC method was adopted to separate the measured signal. The periodic components obtained after separation could be defined as vibration components, while the random components represented the actual PMG irregularity. The comparative analysis and research on the signals before and after separation in the time domain and frequency domain show that the random components in the time-domain signal fluctuate less after separation, and the vibration components corresponding to the measurement carrier in the frequency-domain signal have been separated into the periodic components, which proves the effectiveness of the method proposed in this paper.
-
表 1 传感器及数据采集系统参数信息
Table 1. Parameters of sensors and data acquisition system
传感器 量程 信号 采集卡 控制器 加速度 0~20 g IEPE NI-9234 NI-9174 霍尔 电压 NI-9220 NI-9174 激光位移 (35±15) mm 电压 NI-9220 NI-9174 光电效应 0~5 V 电压 NI-9220 NI-9174 表 2 单杜瓦测量系统固有频率
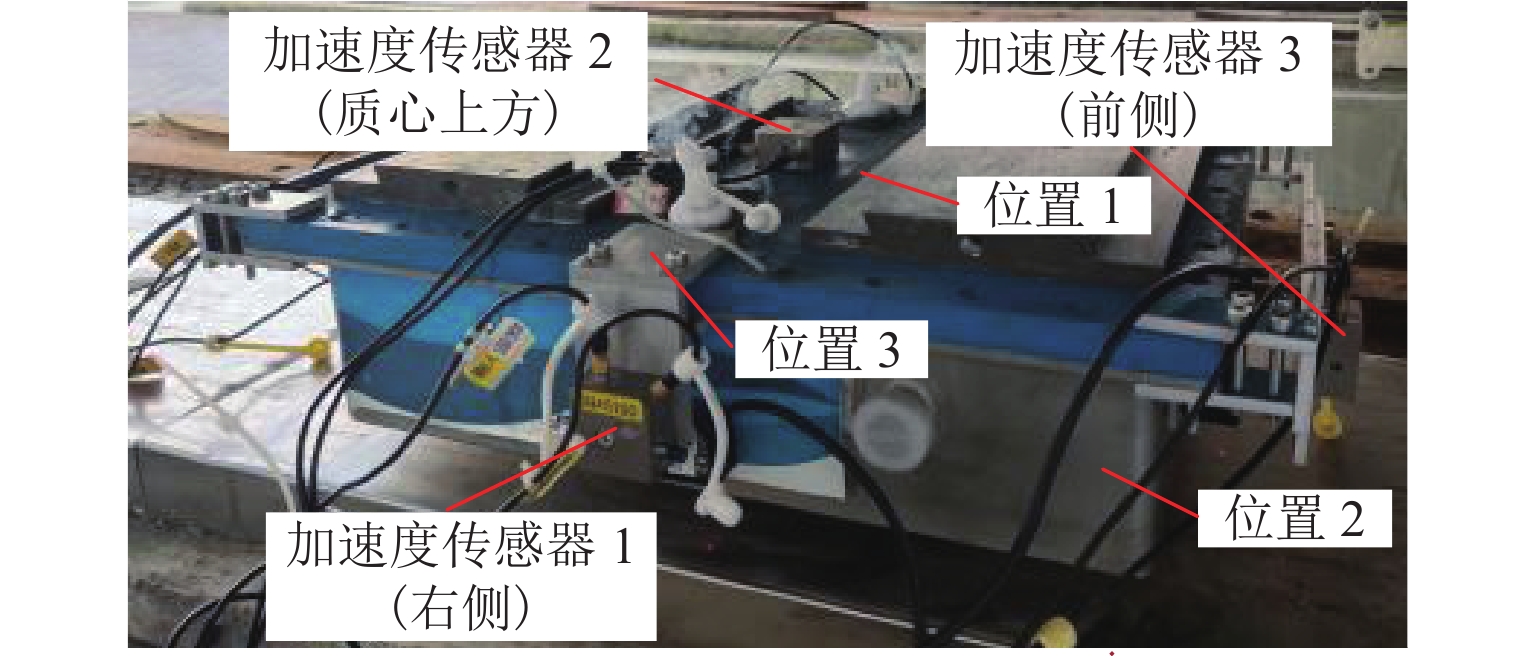
Table 2. Natural frequencies of single-Dewar measurement system
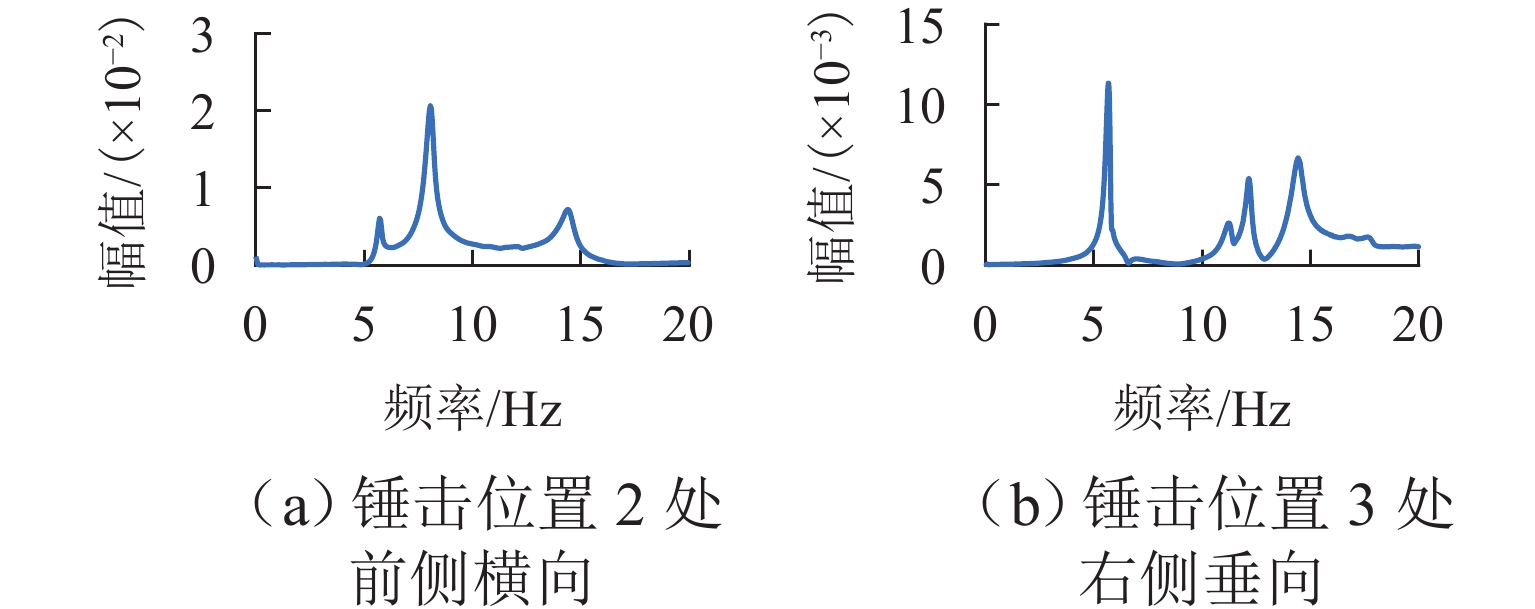
运动姿态 浮沉 横移 点头 侧滚 摇头 频率/Hz 12.16 5.66 9.68 14.43 8.06 -
[1] 邓自刚,刘宗鑫,李海涛,等. 磁悬浮列车发展现状与展望[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2022,57(3): 455-474,530. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.20220001DENG Zigang, LIU Zongxin, LI Haitao, et al. Development status and prospect of maglev train[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2022, 57(3): 455-474,530. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.20220001 [2] 刘晓宁,柯志昊,邓自刚. 高温超导磁悬浮准静态的力弛豫特性[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2023,58(4): 845-852.LIU Xiaoning, KE Zhihao, DENG Zigang. Quasi-static force relaxation characteristics of high temperature superconducting magnetic levitation[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2023, 58(4): 845-852. [3] DENG Z G, ZHOU X C, HUANG H, et al. Measurement and characterization method of permanent magnetic guideway irregularity in HTS maglev system[J]. IEEE Transactions on Applied Superconductivity, 2022, 32(2): 3133332.1-3133332.7. [4] 芦睿泉,练松良. 轨道复合不平顺对提速列车运行影响的研究[J]. 铁道科学与工程学报,2005,2(5): 17-22. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7029.2005.05.004LU Ruiquan, LIAN Songliang. Research of the effect of track complex irregularities on the vehicle dynamic response[J]. Journal of Railway Science and Engineering, 2005, 2(5): 17-22. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7029.2005.05.004 [5] 陈秀方,金守华,曾华亮. 客运专线轨道不平顺功率谱分析[J]. 中国工程科学,2008,10(4): 56-59,83. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-1742.2008.04.007CHEN Xiufang, JIN Shouhua, ZENG Hualiang. PSD analysis on track irregularity of railway line for passenger transport[J]. Strategic Study of CAE, 2008, 10(4): 56-59,83. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-1742.2008.04.007 [6] 张建军. 铁路轨道动态检测与不平顺管理[M]. 北京:中国铁道出版社,2019. [7] OKANO M, IWAMOTO T, SENOKUCHI M, et al. Magnetic rail construction for a low loss superconducting magnetic levitation linear guide[J]. IEEE Transactions on Applied Superconductivity, 2004, 14(2): 944-947. [8] LIN Q X, MA G T, JIANG D H, et al. Study of magnetic field inhomogeneity due to different positional deviations of a permanent magnet guideway[J]. Journal of Superconductivity and Novel Magnetism, 2011, 24(5): 1473-1478. doi: 10.1007/s10948-010-0854-1 [9] SUN R X, ZHENG J, ZHENG B T, et al. Study on the magnetic field inhomogeneity of a halbach permanent-magnet guideway due to different defects[J]. IEEE Transactions on Applied Superconductivity, 2016, 26(1): 1-7. [10] 李海涛. 磁轨不平顺激扰下高温超导钉扎高速磁浮车-轨耦合动力学研究[D]. 成都:西南交通大学,2021. [11] 马家庆,崔宸昱,周大进,等. HTS磁浮系统中永磁轨接头处的运行阻力简化分析方法[J]. 低温物理学报,2017,39(6): 39-44.MA Jiaqing, CUI Chenyu, ZHOU Dajin, et al. A simple method to analysis the drag on the joint of PMG in HTS maglev system[J]. Chinese Journal of Low Temperature Physics, 2017, 39(6): 39-44. [12] 陈起金. 基于A-INS组合导航的铁路轨道几何状态精密测量技术研究[D]. 武汉:武汉大学,2016. [13] 朱洪涛,魏晖,熊瑞文,等. 弦测法检测轨向不平顺的研究[J]. 铁道建筑,2005,45(10): 63-64. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-1995.2005.10.026ZHU Hongtao, WEI Hui, XIONG Ruiwen, et al. Study on detecting track irregularity by chord measurement method[J]. Railway Engineering, 2005, 45(10): 63-64. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-1995.2005.10.026 [14] 杨飞,孙宪夫,谭社会,等. 动静态轨道不平顺评价差异及动态弦测法特性[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2022,57(6): 1239-1249. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.20210732YANG Fei, SUN Xianfu, TAN Shehui, et al. Evaluation difference of dynamic and static track irregularity and characteristics of dynamic chord measurement method[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2022, 57(6): 1239-1249. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.20210732 [15] CHIA L, BHARDWAJ B, LU P, et al. Railroad track condition monitoring using inertial sensors and digital signal processing: a review[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2019, 19(1): 25-33. [16] 朱文发,柴晓冬,郑树彬,等. 基于捷联惯性系统的轨道长波不平顺检测[J]. 城市轨道交通研究,2012,15(11): 87-90. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-869X.2012.11.021ZHU Wenfa, CHAI Xiaodong, ZHENG Shubin, et al. Detection of track long-wave irregularity based on SINS[J]. Urban Mass Transit, 2012, 15(11): 87-90. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-869X.2012.11.021 [17] LUO Y, YUAN Y H, ZENG P Y, et al. Permanent magnet guideway irregularity measurement and characterization by single dewar HTS pinning maglev system[J]. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 2023, 72: 3308222.1-3308222.11. [18] RANDALL R B, LI L. Diagnostics of planetary gear bearings in the presence of gear vibrations[C]//The Second International Conference on Gearbox Vibration and Diagnostics, London: Imeche, 1995: 73-80. [19] ANTONI J, RANDALL R B. Unsupervised noise cancellation for vibration signals: part I: evaluation of adaptive algorithms[J]. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 2004, 18(1): 89-101. doi: 10.1016/S0888-3270(03)00012-8 [20] HO D. Bearing diagnostics and self-adaptive noise cancellation[D]. Sydney: University of South Wales, 1999. [21] 贺东台,郭瑜,伍星,等. 基于自参考自适应消噪的行星轮轴承内圈故障特征提取[J]. 振动与冲击,2018,37(17): 101-106.HE Dongtai, GUO Yu, WU Xing, et al. Fault feature extraction for a planet gear’s bearing inner race based on self-reference adaptive de-noising[J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2018, 37(17): 101-106. [22] 高鹰,谢胜利. 一种变步长LMS自适应滤波算法及分析[J]. 电子学报,2001,29(8): 1094-1097. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0372-2112.2001.08.023GAO Ying, XIE Shengli. A variable step size LMS adaptive filtering algorithm and its analysis[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2001, 29(8): 1094-1097. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0372-2112.2001.08.023 [23] GORRIZ J M, RAMIREZ J, CRUCES-ALVAREZ S, et al. A novel LMS algorithm applied to adaptive noise cancellation[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2009, 16(1): 34-37. [24] BAHRAINI T, NAEIMI SADIGH A. Proposing a robust RLS based subband adaptive filtering for audio noise cancellation[J]. Applied Acoustics, 2024, 216: 109755.1-109755.10 [25] CHATURVEDI G K, THOMAS D W. Bearing fault detection using adaptive noise cancelling[J]. Journal of Mechanical Design, 1982, 104(2): 280-289. doi: 10.1115/1.3256337 [26] LIU X N, KE Z H, CHENG Y X, et al. Strong magnetic field dependence of micro-YBCO superconductor levitated above halbach guideway[J]. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation Measurement, 2022, 71: 3216076.1-3216076.10. -




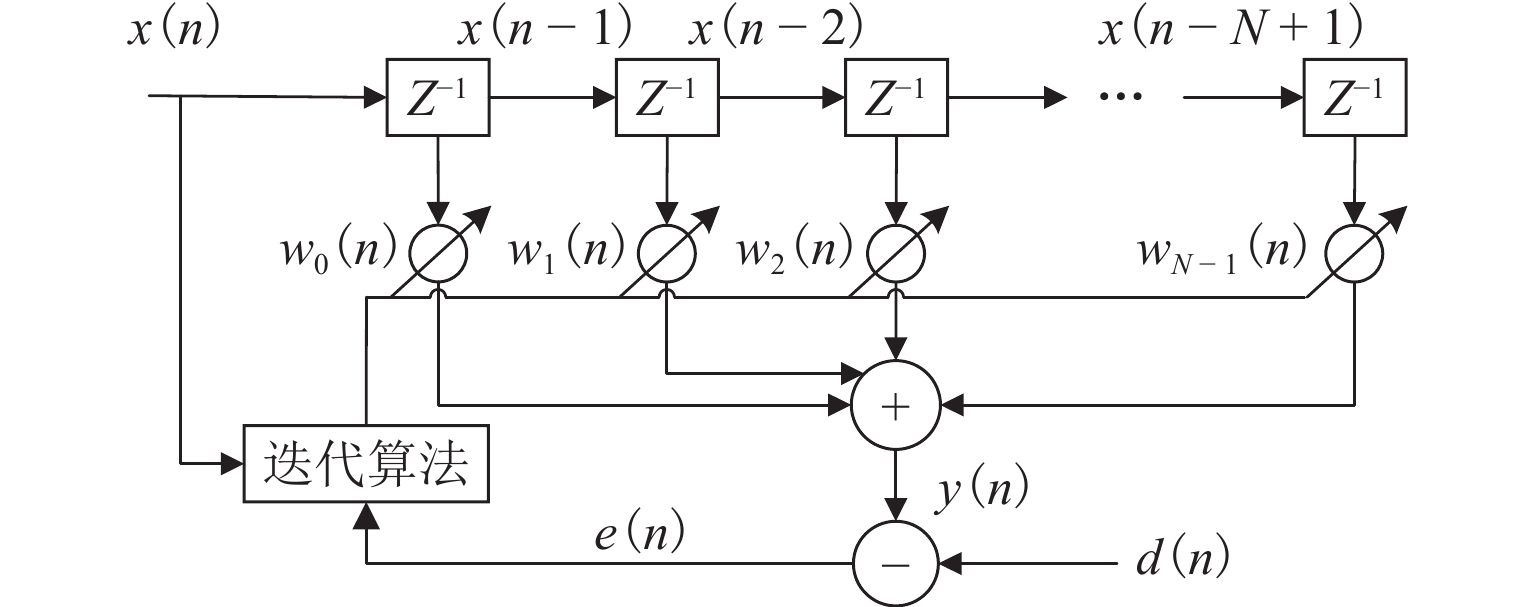
 下载:
下载: