Acceleration Feedback Control of Bilateral Permanent Magnet and Electromagnetic Hybrid Electrodynamic Suspension
-
摘要:
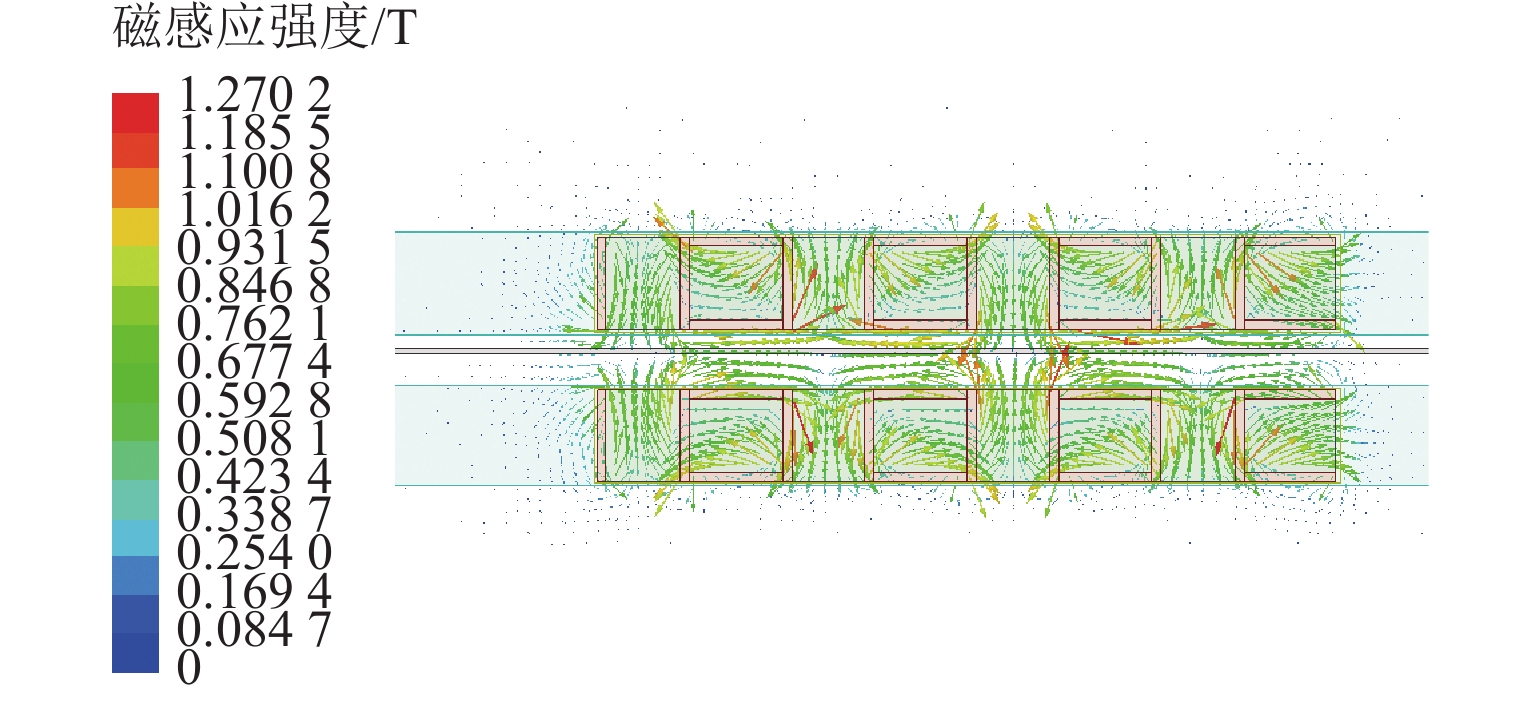
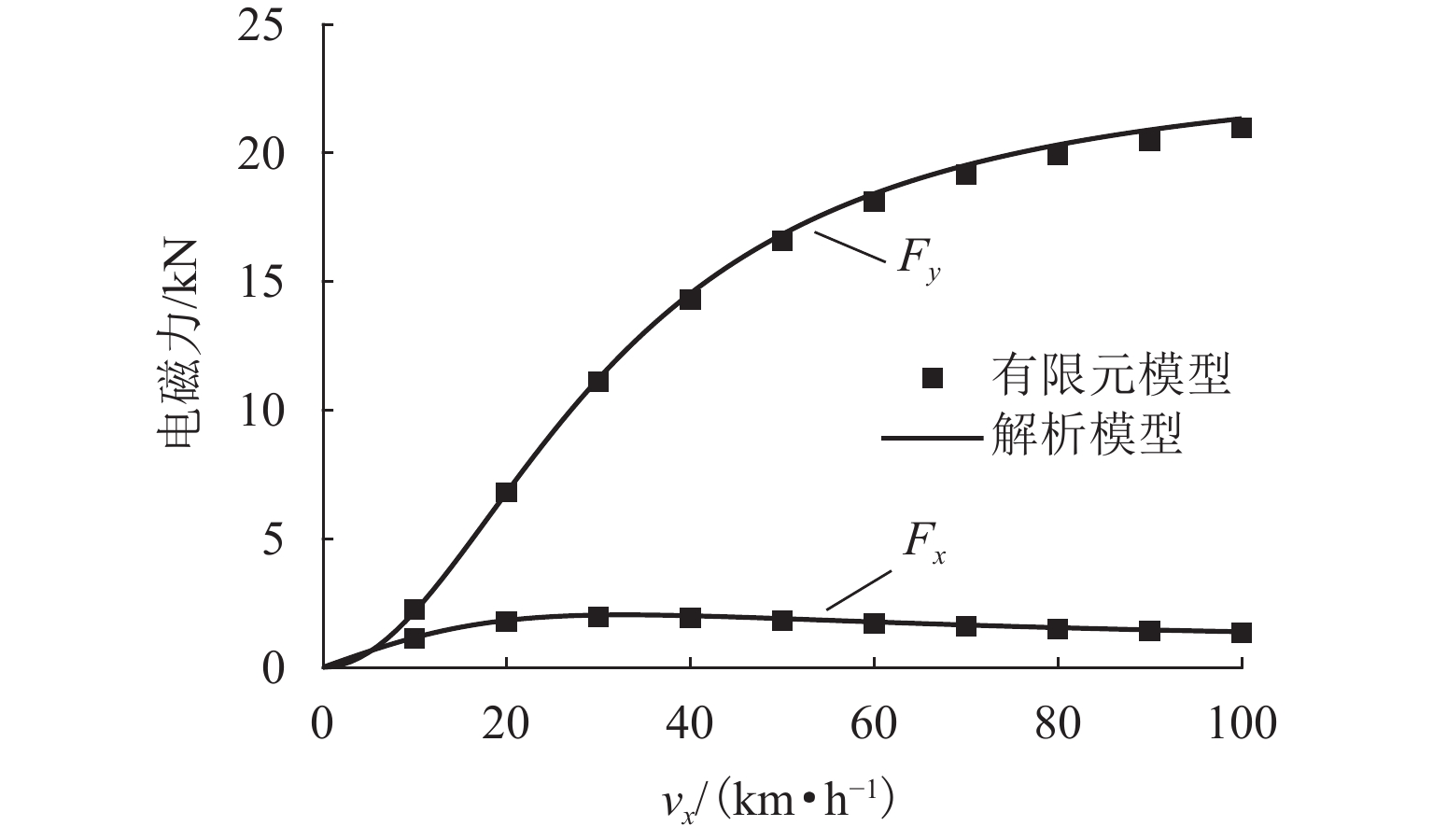
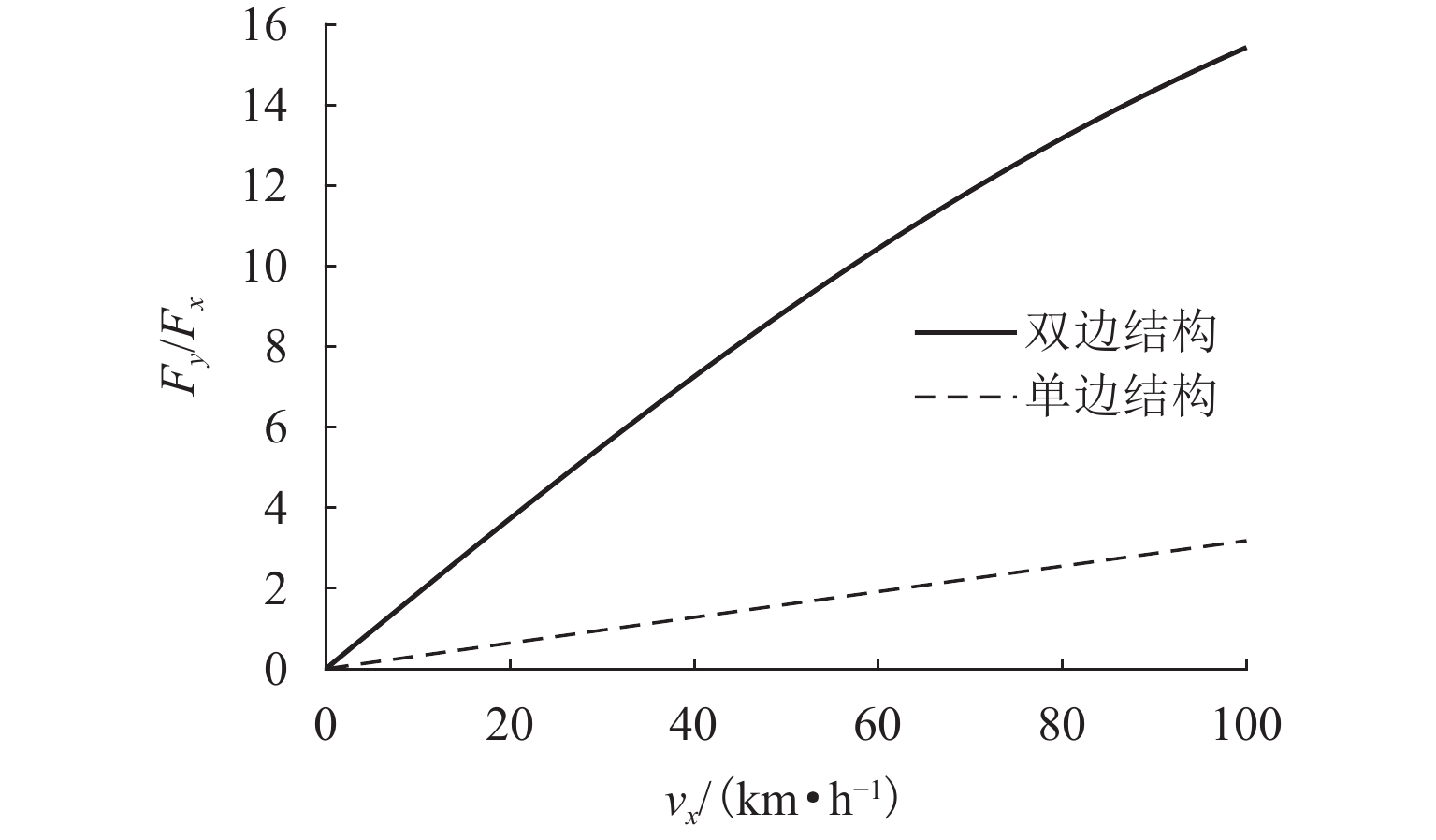
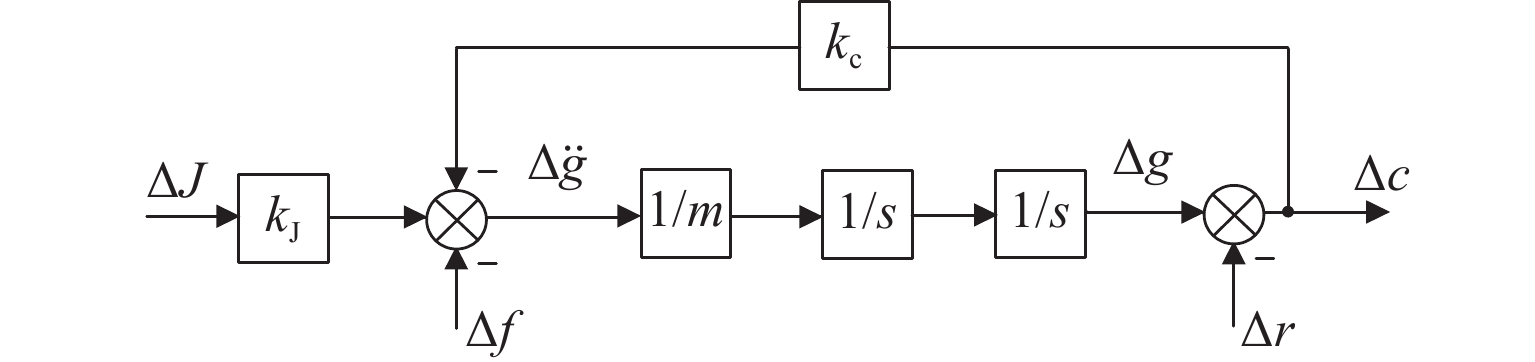
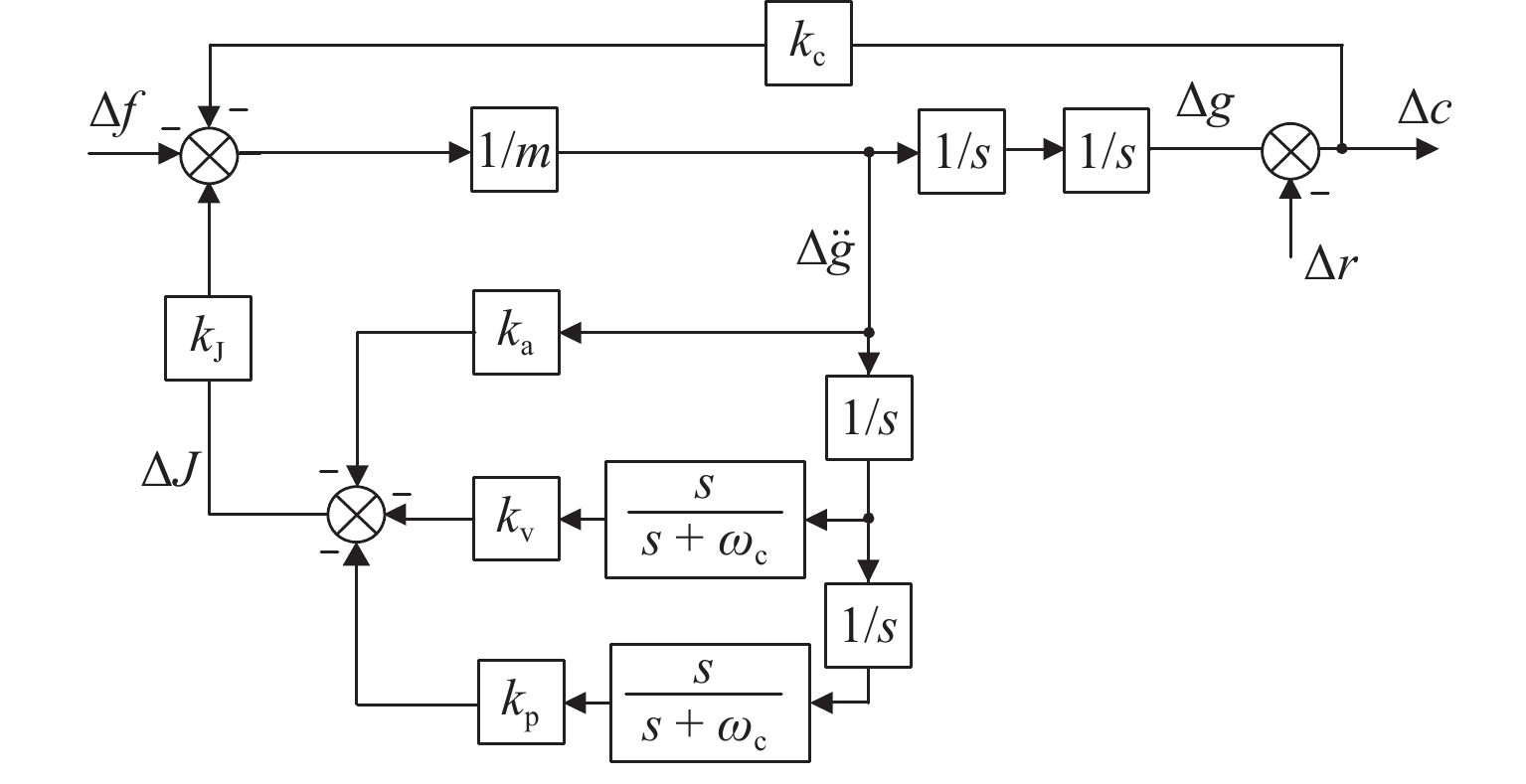
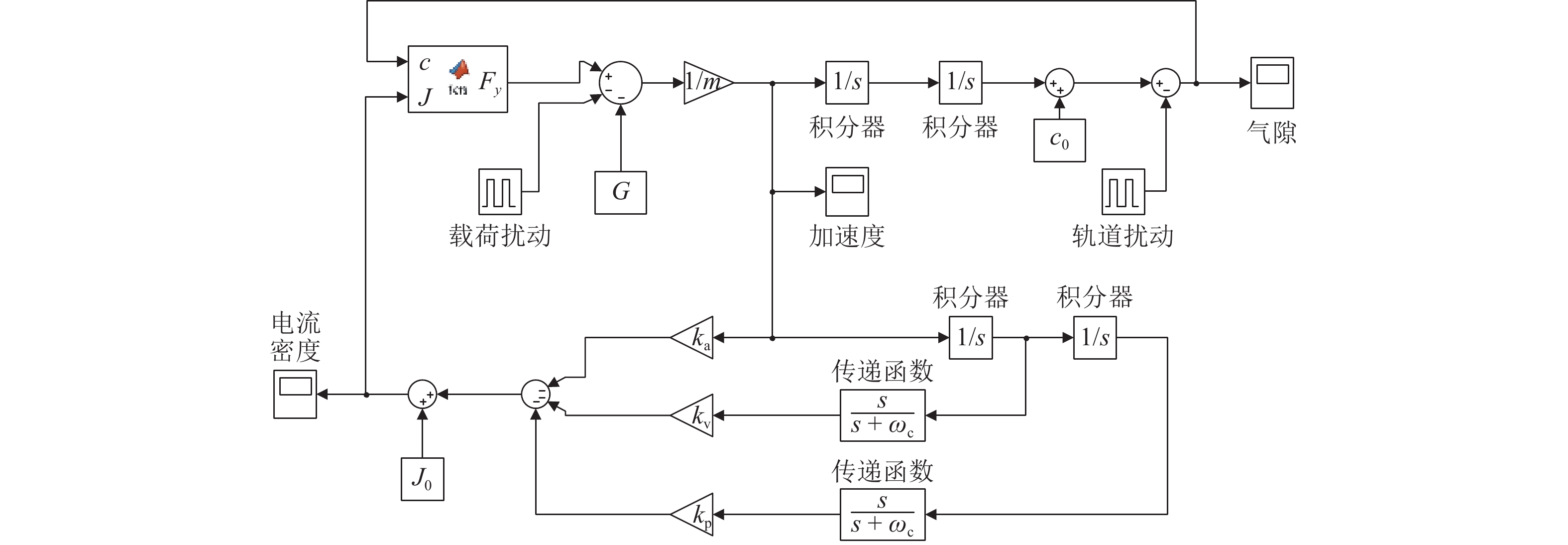
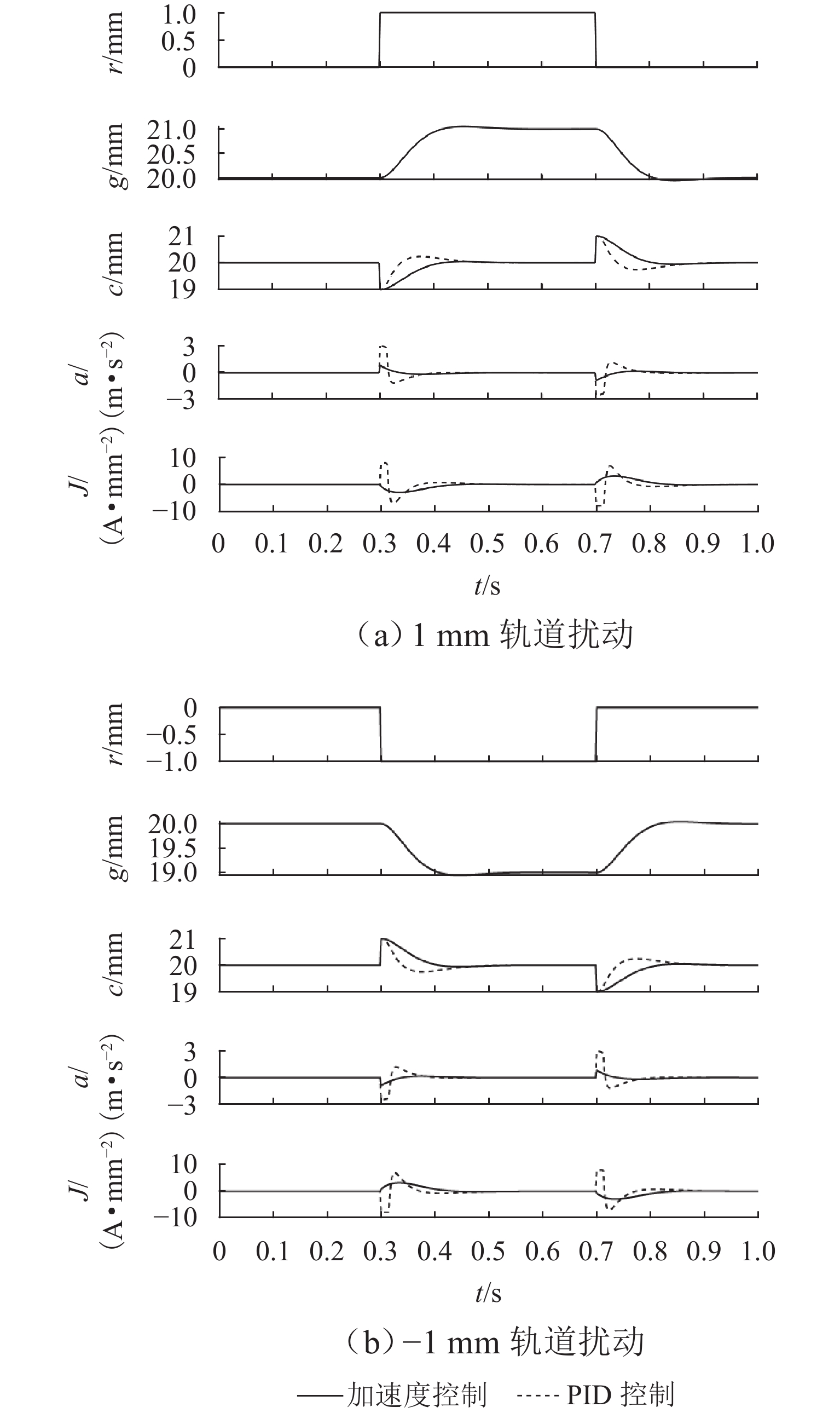
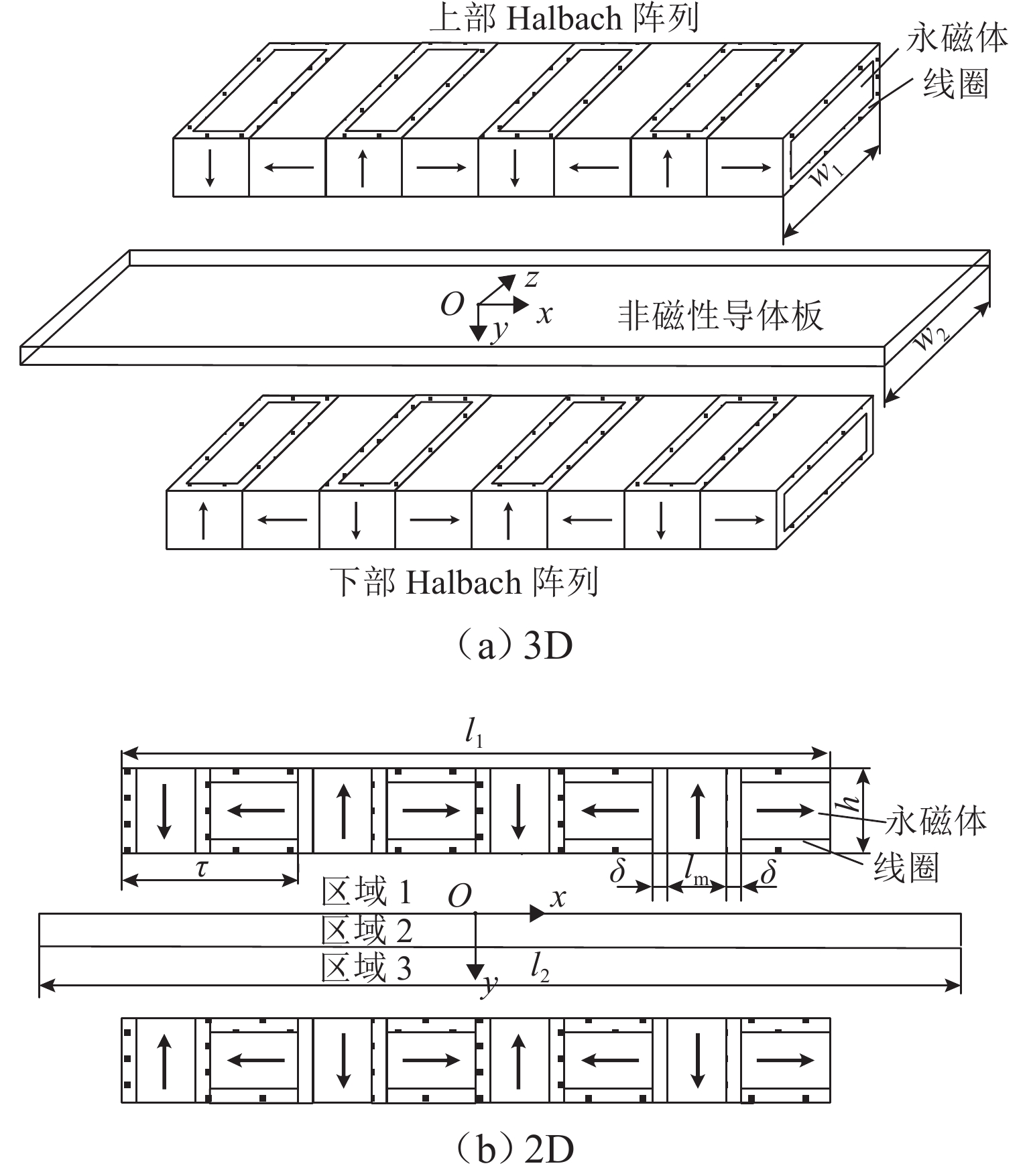
为提升永磁电动悬浮动态稳定性及减小低速运行时的阻力,研究一种双边永磁电磁混合型电动悬浮系统. 首先,基于麦克斯韦方程组推导系统电磁力2D解析式,对解析结果进行有限元数值计算验证,并对比单、双边结构电磁力特性;然后,建立系统悬浮动力学模型,并设计加速度反馈悬浮控制器;最后,利用Simulink仿真,对比分析在加速度反馈悬浮控制和气隙反馈PID控制下,系统受到轨道及载荷扰动时的气隙、加速度及电流波形. 研究结果表明:双边结构可有效增加系统浮阻比,100 km/h运行时单、双边结构浮阻比分别为3.18和15.43;当系统受到 ±1 mm轨道扰动时,控制器能使系统振动加速度及悬浮气隙分别快速稳定于0和20 mm额定位置;当系统受到 ±
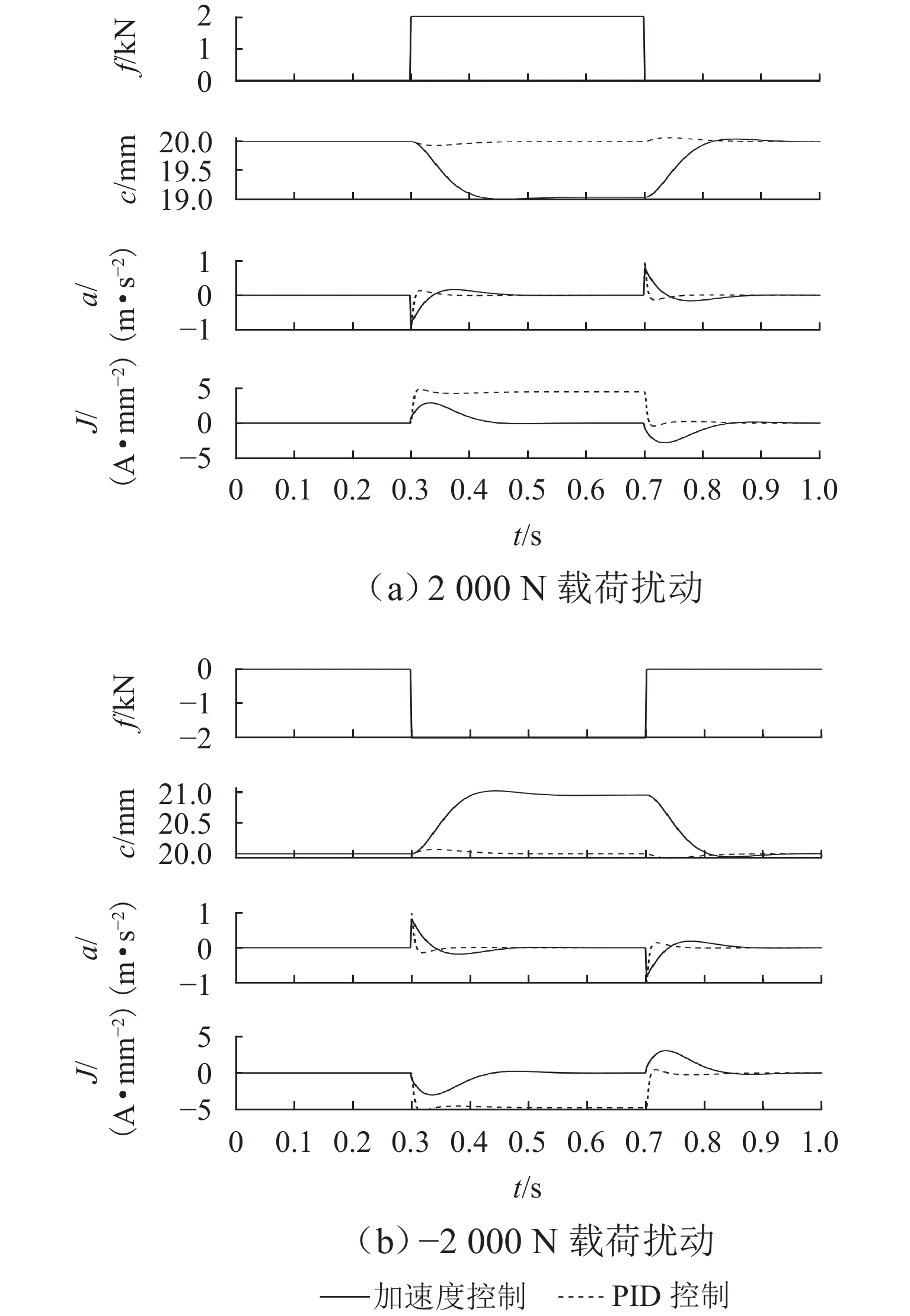
2000 N载荷扰动时,加速度反馈悬浮控制器可使系统悬浮气隙分别快速稳定于19.05 mm和20.96 mm,而PID控制器则使得线圈电流分别稳定于4.43 A/mm2和 −4.66 A/mm2;当系统稳定运行时,加速度反馈悬浮控制下的线圈稳态电流均为0,而PID控制下的稳态悬浮气隙均为0,且当各种扰动消除后,系统均可快速恢复到初始额定运行状态.Abstract:To improve the dynamic stability of the permanent magnet (PM) electrodynamic suspension (EDS) and reduce the drag during low-speed operation, a bilateral PM and electromagnetic hybrid EDS system was studied. Firstly, a 2D analytical expression of the system electromagnetic force was derived based on Maxwell’s equations. The analytical results were verified by finite element numerical calculations, with a comparison of the electromagnetic force characteristics between unilateral and bilateral structures. Secondly, a suspension dynamic model of the system was established, and an acceleration feedback suspension controller was designed. Finally, a comparative analysis of the air gap, acceleration, and current waveforms under acceleration feedback suspension control and air gap feedback PID control was carried out through Simulink simulation when the system was subjected to track and load disturbances. The results show that the bilateral structure effectively increases the system float-to-drag ratio. At an operating speed of 100 km/h, the float-to-drag ratio for the unilateral and bilateral structures are 3.18 and 15.43, respectively. When the system is subjected to ± 1 mm track disturbances, the controller enables the system vibration acceleration and suspension air gap to quickly stabilize at rated positions of 0 and 20 mm, respectively. When the system is subjected to ± 2 000 N load disturbances, the acceleration feedback suspension controller allows the suspension air gap to quickly stabilize at 19.05 mm and 20.96 mm, respectively, while the PID controller stabilizes the coil current at 4.43 A/mm2 and −4.66 A/mm2, respectively. During stable operation, the steady-state coil current under the acceleration feedback suspension control is 0, while the steady-state suspension air gap under the PID control is 0. The system quickly returns to its initial rated operating state after the disturbances are eliminated.
-
表 1 系统参数
Table 1. System parameters
参数 数值 参数 数值 Br/T 1.27 J/( A·mm−2) 3 w1/mm 300 w2/mm 300 lm/mm 80 l2/mm 1800 h/mm 100 d/mm 5 M/块 4 γ2/(S·m−1) 3.77 × 107 N/块 8 c1/mm 20 δ/mm 10 c2/mm 40 -
[1] FLANKL M, WELLERDIECK T, TÜYSÜZ A, et al. Scaling laws for electrodynamic suspension in high-speed transportation[J]. IET Electric Power Applications, 2018, 12(3): 357-364. doi: 10.1049/iet-epa.2017.0480 [2] 刘士苋,王磊,王路忠,等. 电动悬浮列车及车载超导磁体研究综述[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2023,58(4): 734-753. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.20220621LIU Shixian, WANG Lei, WANG Luzhong, et al. Review on electrodynamic suspension trains and on-board superconducting magnets[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2023, 58(4): 734-753. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.20220621 [3] 胡永攀,曾杰伟,王志强,等. 超高速永磁电动悬浮系统性能优化[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2023,58(4): 773-782. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.20230526HU Yongpan, ZENG Jiewei, WANG Zhiqiang, et al. Performance optimization of ultra-high speed permanent magnet electrodynamic suspension system[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2023, 58(4): 773-782. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.20230526 [4] BEAULOYE L, DEHEZ B. Permanent magnet electrodynamic suspensions applied to maglev transportation systems: a review[J]. IEEE Transactions on Transportation Electrification, 2023, 9(1): 748-758. doi: 10.1109/TTE.2022.3193296 [5] 王滢,张昆仑,张慧娴,等. 高速磁浮交通系统制式特征与适应性[J]. 前瞻科技,2023,2(4): 19-30.WANG Ying, ZHANG Kunlun, ZHANG Huixian, et al. Characteristics and adaptability of different types of high-speed maglev transportation systems[J]. Science and Technology Foresight, 2023, 2(4): 19-30. [6] 石洪富,邓自刚,黄欢,等. 零磁通线圈式永磁电动悬浮设计及特性研究[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2023,58(4): 853-862. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.20211062SHI Hongfu, DENG Zigang, HUANG Huan, et al. Design and characteristics of null-flux permanent magnet electrodynamic suspension system[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2023, 58(4): 853-862. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.20211062 [7] CHEN Y, ZHANG W L, BIRD J Z, et al. A 3-D analytic-based model of a null-flux Halbach array electrodynamic suspension device[J]. IEEE Transactions on Magnetics, 2015, 51(11): 8300405.1-8300405.5. [8] 罗成,张昆仑,靖永志. 新型Halbach阵列永磁电动悬浮系统垂向稳定性[J]. 交通运输工程学报,2019,19(2): 101-109. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1637.2019.02.010LUO Cheng, ZHANG Kunlun, JING Yongzhi. Vertical stability of permanent magnet EDS system with novel Halbach array[J]. Journal of Traffic and Transportation Engineering, 2019, 19(2): 101-109. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1637.2019.02.010 [9] KRATZ R, POST R F. A null-current electro-dynamic levitation system[J]. IEEE Transactions on Applied Superconductivity, 2002, 12(1): 930-932. doi: 10.1109/TASC.2002.1018551 [10] 陈殷,张昆仑. 板式双边永磁电动悬浮电磁力计算[J]. 电工技术学报,2016,31(24): 150-156.CHEN Yin, ZHANG Kunlun. Calculation of electromagnetic force of plate type null double side permanent magnet electrodynamic suspension[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2016, 31(24): 150-156. [11] 陈殷. 低速永磁电动悬浮电磁力特性研究[D]. 成都:西南交通大学,2015. [12] POST R F, RYUTOV D. The Inductrack concept: a new approach to magnetic levitation[R]. Livermore: Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory, 1996. [13] POST R F. Inductrack demonstration model[R]. Livermore: Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory, 1998. [14] KO W. Modeling and analysis of the EDS Maglev system with the Halbach magnet array[D]. Orlando: University of Central Florida, 2007. [15] HAN Q H. Analysis and modeling of the EDS Maglev system based on the Halbach permanent magnet array[D]. Orlando: University of Central Florida, 2004. [16] 关炎培. 真空管道磁悬浮列车永磁电动与电磁混合悬浮支承研究[D]. 武汉:武汉理工大学,2018. [17] 熊振宇. EDS与EMS混合磁悬浮支承结构分析与优化设计[D]. 武汉:武汉理工大学,2019. [18] 马于龙,胡业发,陈昌皓,等. 基于Halbach的磁悬浮列车过曲线轨道的控制研究[J]. 武汉理工大学学报(信息与管理工程版),2018,40(1): 113-116. doi: 10.3963/j.issn.2095-3852.2018.01.021MA Yulong, HU Yefa, CHEN Changhao, et al. Research on the control of over levitation trajectory of magnetic levitation vehicle based on Halbach[J]. Journal of Wuhan University of Technology (Information & Management Engineering), 2018, 40(1): 113-116. doi: 10.3963/j.issn.2095-3852.2018.01.021 [19] CHEN S S, ZHU S, CAI Y. On the unsteady-motion theory of magnetic forces for Maglev[R]. Argonne, IL: Argonne National Laboratory, 1996. [20] ZHU S, CAI Y, ROTE D M, et al. Magnetic damping for maglev[J]. Shock and Vibration, 1988, 5(2): 119-128. [21] ZHAO M T, GE Q X, GAO Z, et al. Analysis of electromagnetic and damping characteristics of permanent magnet electrodynamic suspension system[C]//2021 13th International Symposium on Linear Drives for Industry Applications (LDIA). Wuhan: IEEE, 2021: 1-6. [22] 乔冲. 永磁高速电动悬浮系统永磁被动阻尼方案研究[D]. 成都:西南交通大学,2021. [23] 乔冲,单磊,马卫华,等. 基于Halbach阵列的永磁被动阻尼方案研究[J]. 机械,2021,48(5): 29-36.QIAO Chong, SHAN Lei, MA Weihua, et al. Simulation analysis of permanent magnet passive damping method based on Halbach array[J]. Machinery, 2021, 48(5): 29-36. [24] LUO C, ZHANG K L, DUAN J H, et al. Study of permanent magnet electrodynamic suspension system with a novel Halbach array[J]. Journal of Electrical Engineering & Technology, 2020, 15(2): 969-977. [25] 陈殷,张昆仑. Halbach永磁阵列空间磁场的解析计算[J]. 磁性材料及器件,2014,45(1): 1-4,9. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3830.2014.01.001CHEN Yin, ZHANG Kunlun. Analytic calculation of the magnetic field created by Halbach permanent magnets array[J]. Journal of Magnetic Materials and Devices, 2014, 45(1): 1-4,9. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3830.2014.01.001 [26] 雷银照. 时谐电磁场解析方法[M]. 北京:科学出版社,2000. [27] 赵博,张洪亮. Ansoft 12在工程电磁场中的应用[M]. 北京:中国水利水电出版社,2010. [28] 王莉. 混合EMS磁悬浮系统研究[D]. 成都:西南交通大学,2006. [29] 罗成. 永磁电磁混合Halbach阵列电动悬浮特性及稳定控制研究[D]. 成都:西南交通大学,2021. [30] 李云钢,常文森. 磁浮列车悬浮系统的串级控制[J]. 自动化学报,1999,25(2): 247-251.LI Yungang, CHANG Wensen. Cascade control of an EMS maglev vehicle’s levitation control system[J]. Acta Automatica Sinica, 1999, 25(2): 247-251. -




 下载:
下载: