Multi-objective Asymmetric Design for Optimizing Superconducting Electrodynamic Suspension System
-
摘要:
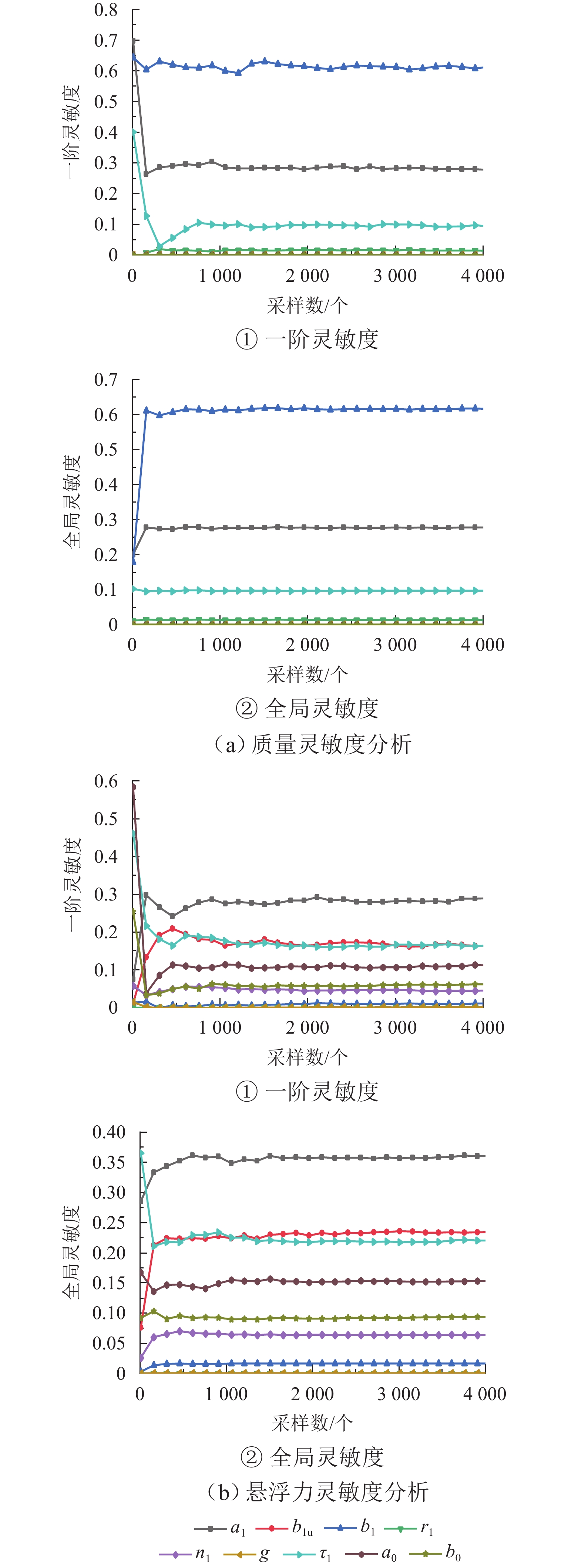
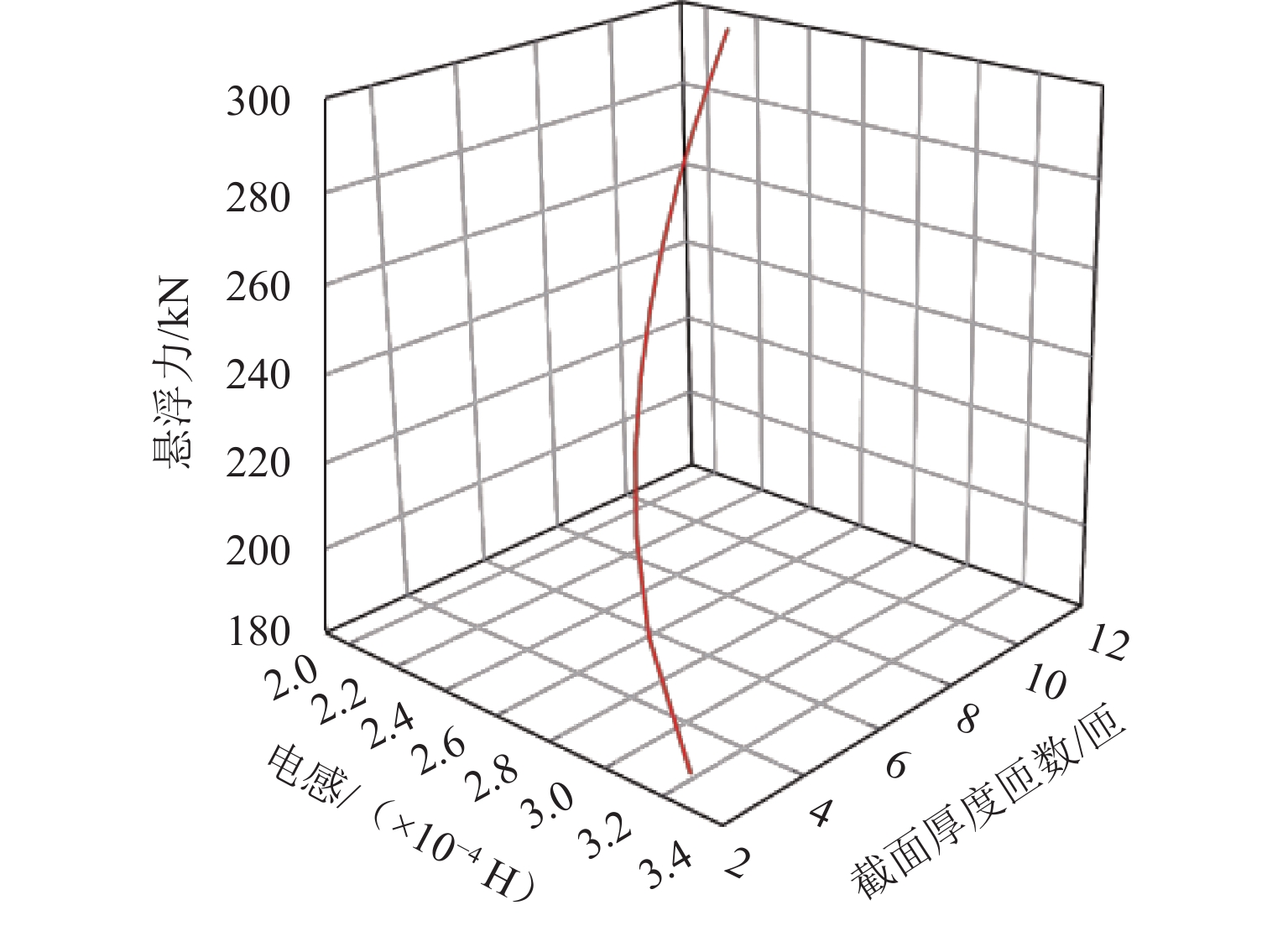
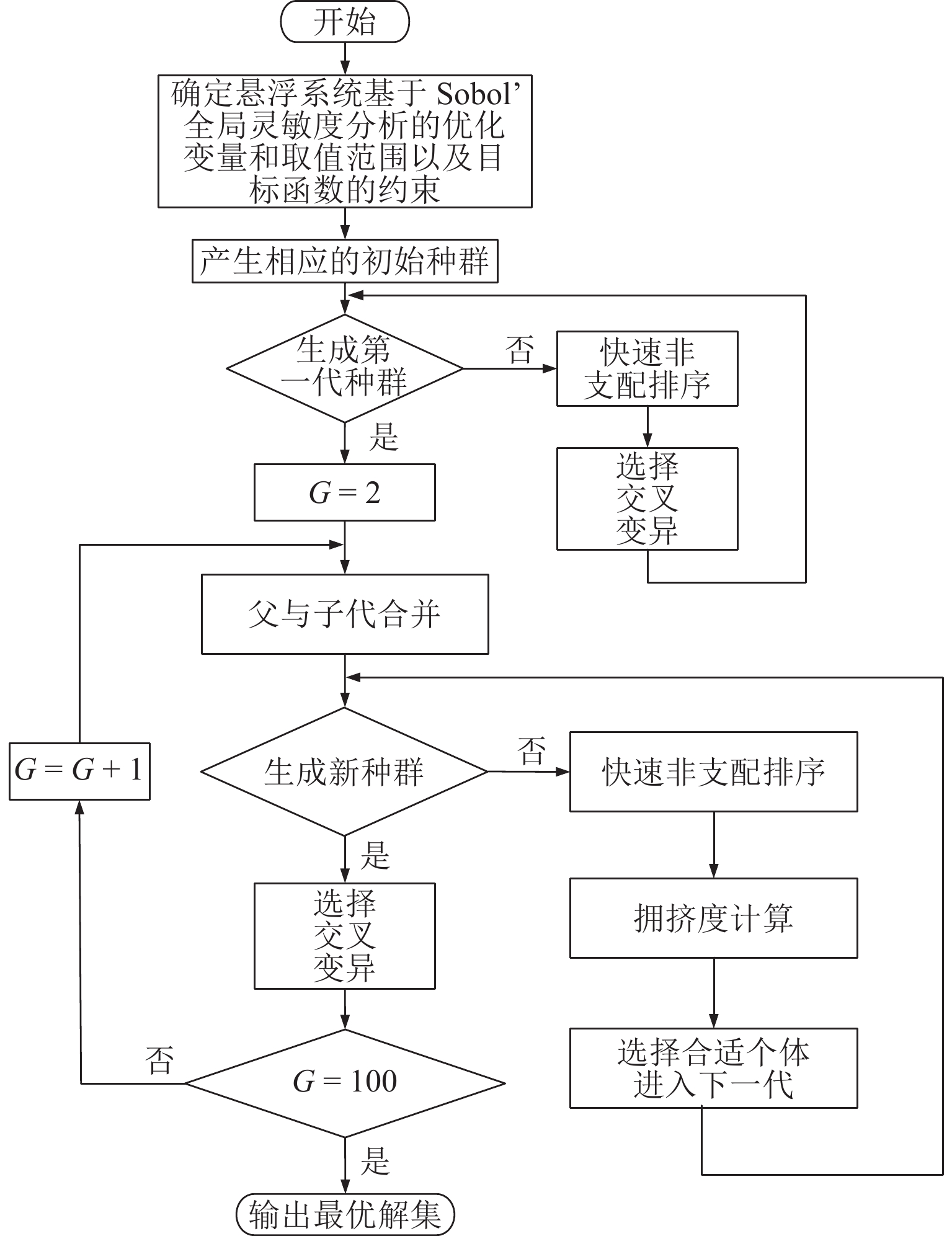
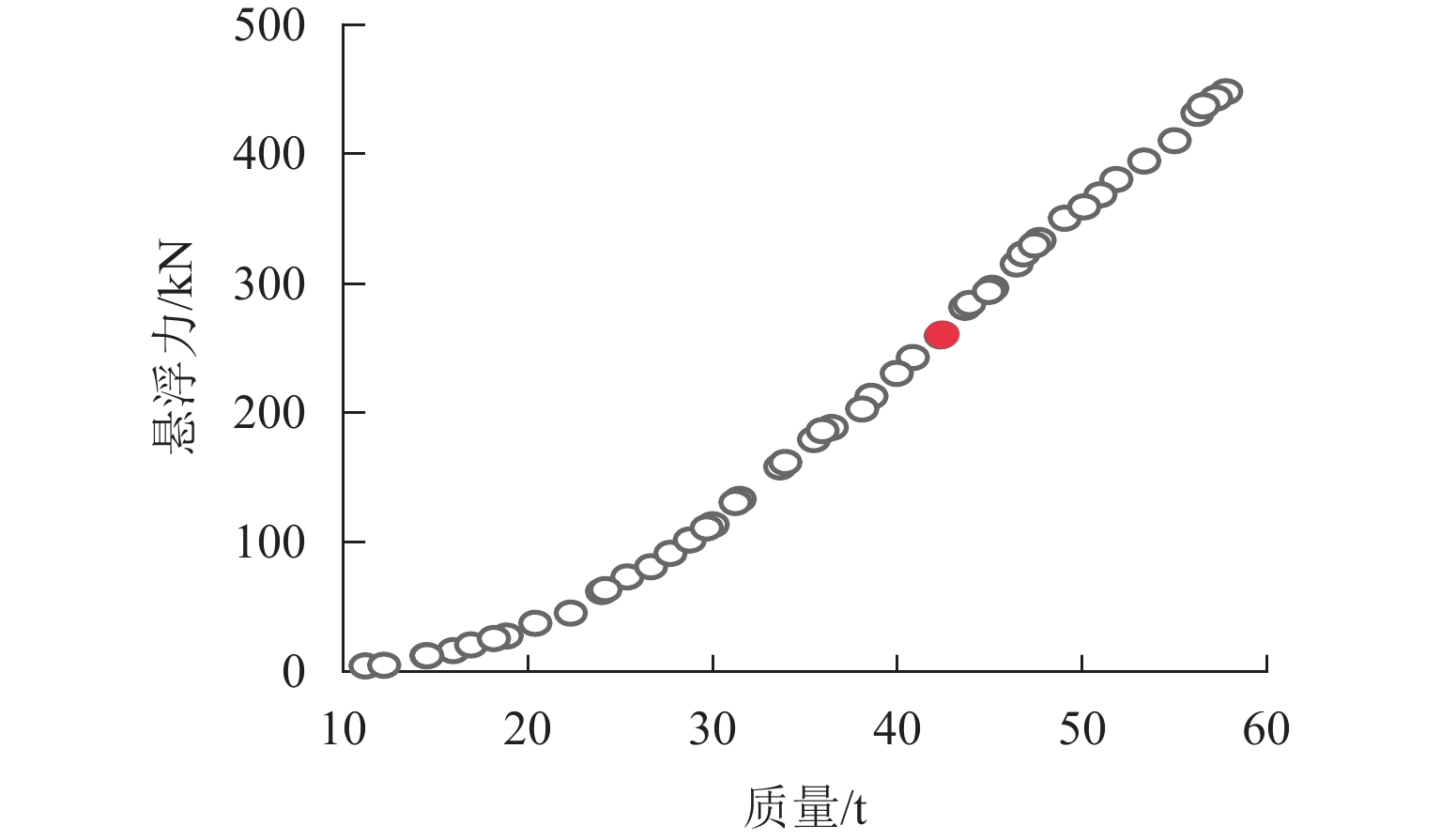
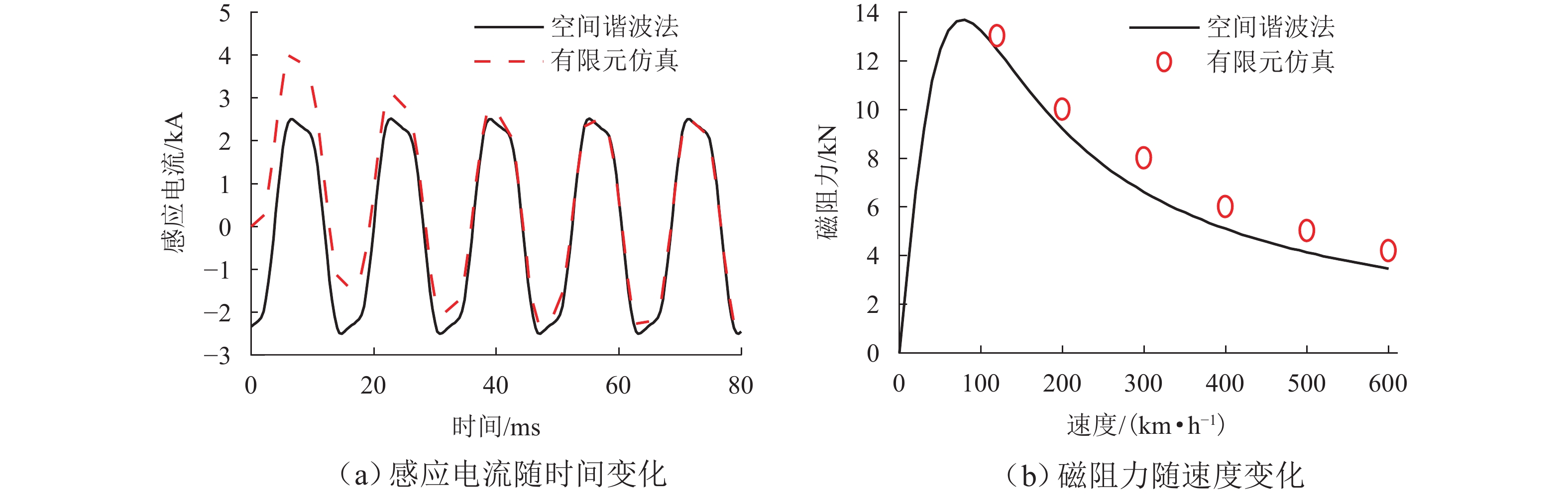
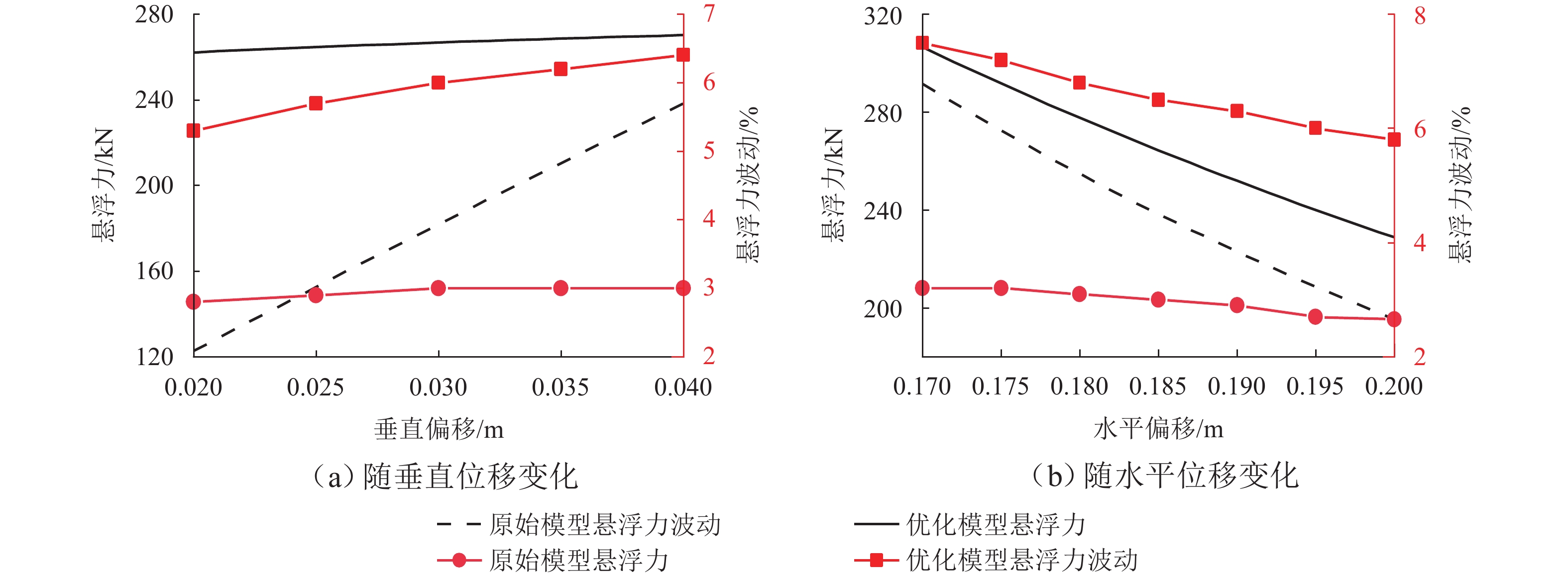
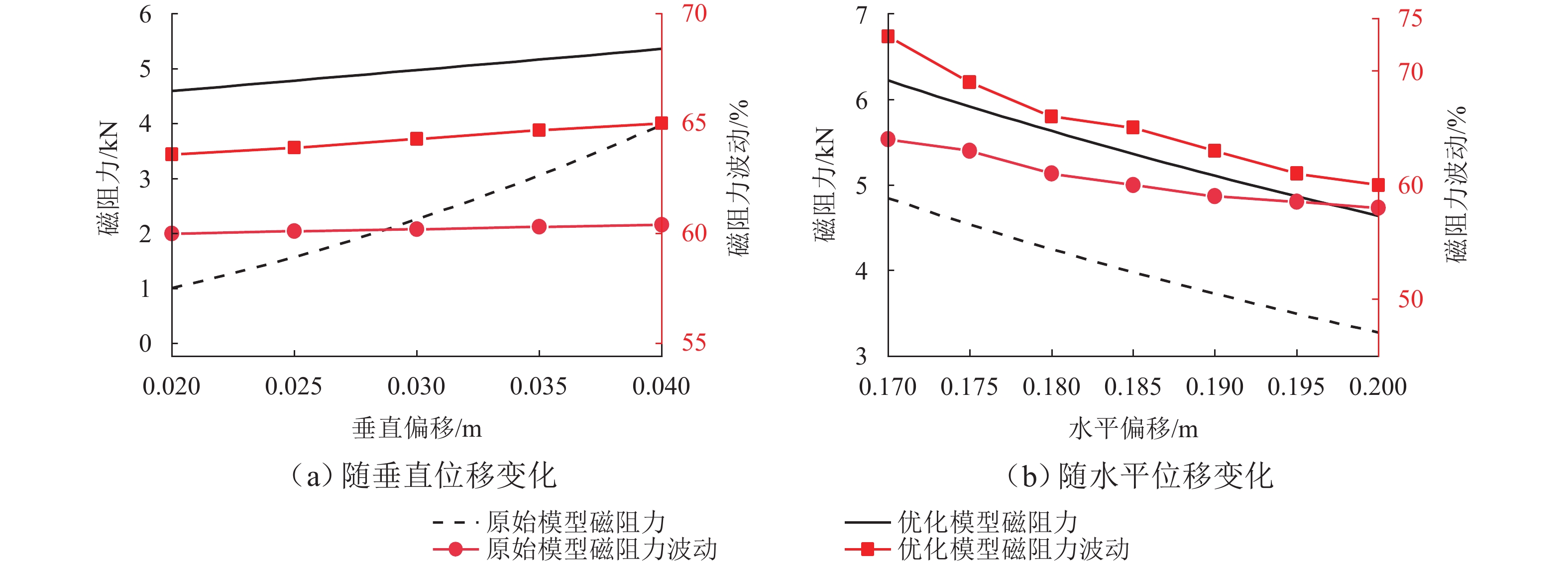
为提高超导电动悬浮系统性能,基于全局灵敏度分析和多目标优化算法,提出一种非对称悬浮线圈优化设计方法. 首先,基于空间谐波法建立超导电动悬浮系统的数学模型,计算超导磁体的磁感应强度以及悬浮线圈的电磁力;其次,对此模型进行非对称优化设计,采用Sobol’ 敏感性分析方法,以悬浮力和每公里悬浮线圈质量为目标,计算各设计参数的灵敏度,并基于灵敏度分析结果进行非支配排序遗传算法Ⅱ (NSGA-Ⅱ)优化设计;最后,通过有限元进行仿真分析,验证空间谐波法解析模型,并对优化前后的模型进行比较. 研究结果表明:空间谐波法建立的悬浮系统模型与有限元模型具有一致性;相比优化前,优化后的非对称悬浮系统悬浮力提高8.3%,每公里铺设线圈质量降低12.9%;垂直位移0.02~0.04 m时,悬浮力由262.2 kN增加到270.2 kN,磁阻力由4.5 kN增加到5.4 kN;水平位移0.17~0.20 m时,悬浮力由306.5 kN减小到228.8 kN,磁阻力由6.2 kN减小到4.6 kN;悬浮力、磁阻力的波动分别约为6%、65%. 研究揭示了悬浮力和磁阻力随着位移方向的变化规律,验证了非对称设计在提升悬浮力和轻量化方面的优势,为超导电动悬浮系统的优化设计提供理论参考.
-
关键词:
- 电动悬浮 /
- 灵敏度分析 /
- 非支配排序遗传算法Ⅱ /
- 有限元仿真 /
- 超导磁体
Abstract:In order to improve the performance of superconducting electrodynamic suspension systems, an optimal design method for asymmetric levitation coils was proposed based on global sensitivity analysis and a multi-objective optimization algorithm. First, a mathematical model of the superconducting electrodynamic suspension system was established using the space harmonic method. The magnetic flux intensity of the superconducting magnets and the electromagnetic forces of the levitation coils were then calculated. Next, the model underwent asymmetric optimization. The Sobol’ method was used to calculate the sensitivity of each design parameter, with the levitation force and the mass of the levitation coils per kilometer as the objectives. Based on the sensitivity analysis results, the non-dominated sorting genetic algorithm Ⅱ (NSGA-Ⅱ) was used for optimization. Finally, finite element simulation was carried out to validate the analytical model based on the space harmonic method. The models before and after optimization were compared. The results indicate that the suspension system model established via the space harmonic method was consistent with the finite element model. Compared with the initial system, the optimized asymmetric suspension system shows an 8.3% improvement in levitation force and a 12.9% reduction in the mass of levitation coils per kilometer. When the vertical displacement is 0.02–0.04 m, the levitation force increases from 262.2 kN to 270.2 kN, and the drag force increases from 4.5 kN to 5.4 kN. When the horizontal displacement is 0.17–0.20 m, the levitation force decreases from 306.5 kN to 228.8 kN, and the drag force decreases from 6.2 kN to 4.6 kN. The fluctuations in levitation force and drag force are approximately 6% and 65%, respectively. The variation patterns of levitation and drag forces with respect to displacement directions were revealed, demonstrating the advantages of asymmetric design in enhancing levitation force and achieving lightweight performance. This provides a theoretical reference for the optimal design of superconducting electrodynamic suspension systems.
-
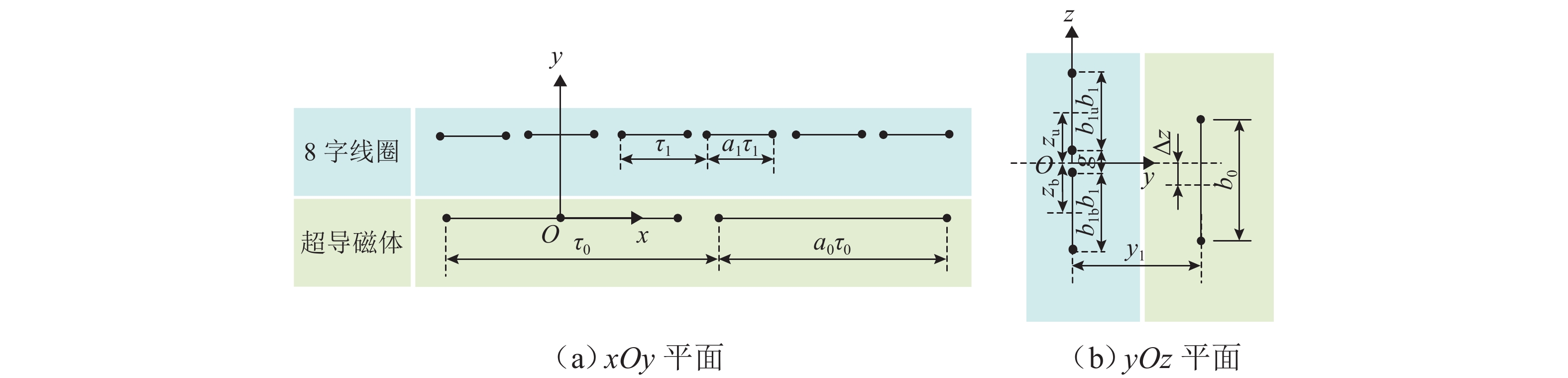
表 1 EDS系统关键参数
Table 1. Main parameters of EDS system
线圈 符号 描述 幅值 8 字
线圈a1 长度与极距比例 0.778 b1u 上线圈高度占比 0.500 b1b 下线圈高度占比 0.500 b1 上下线圈总高度/m 0.680 zu 上线圈中心高度/m 0.380 zb 下线圈中心高度/m 0.380 c1 线圈截面长度/m 0.060 c2 线圈截面宽度/m 0.040 Ng 线圈匝数/匝 24 Sg 截面线圈每匝面积/mm2 100 τ1 极距/m 0.450 g 上下线圈间隙/m 0.080 r1 线圈圆角半径/m 0.115 超导
线圈a0 长度与极距比例 0.793 b0 高度/m 0.500 d1 线圈截面长度/m 0.040 d2 线圈截面宽度/m 0.070 Ns 线圈匝数/匝 1400 超导
线圈Is 额定电流/A 500 τ0 极距/m 1.350 y1 8 字线圈与超导线圈水平距离/m 0.185 Δz 8 字线圈与超导线圈中心垂直位移/m 0 表 2 设计参数及其变量范围
Table 2. Design parameters and their variable ranges
参数 变量范围 参数 变量范围 a1 [0.500,0.900] g/m [0.060,0.100] b1u [0.200,0.400] τ1/m [0.400,0.600] b1/m [0.200,0.800] a0 [0.700,0.800] r1/m [0.100,0.200] b0/m [0.200,0.600] n1/匝数 [2,12] 表 3 优化方案参数
Table 3. Optimized design parameters
参数 目标值 参数 目标值 a1 0.580 τ1/m 0.600 b1u 0.350 a0 0.800 n1/匝 12 b0/m 0.500 -
[1] NASIRI-ZARANDI R, HEKMATI A. A review of suspension and traction technologies in maglev trains[C]//2019 International Power System Conference (PSC). Tehran: IEEE, 2019: 129-135. [2] PHAENKONGNGAM T, CHINNAWONG K, PATUMASUIT N, et al. Reviewing propulsion & levitation system for magnetic levitation train[C]//2021 9th International Electrical Engineering Congress (iEECON). Pattaya: IEEE, 2021: 185-188. [3] 熊嘉阳,邓自刚. 高速磁悬浮轨道交通研究进展[J]. 交通运输工程学报,2021,21(1): 177-198.XIONG Jiayang, DENG Zigang. Research progress of high-speed maglev rail transit[J]. Journal of Traffic and Transportation Engineering, 2021, 21(1): 177-198. [4] 刘士苋,王磊,王路忠,等. 电动悬浮列车及车载超导磁体研究综述[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2023,58(4): 734-753. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.20220621LIU Shixian, WANG Lei, WANG Luzhong, et al. Review on electrodynamic suspension trains and on-board superconducting magnets[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2023, 58(4): 734-753. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.20220621 [5] 张榕欣,蔡小培,汤雪扬,等. 超导电动磁浮道岔线形设计与侧向过岔速度优化[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2025,60(4):893-903.ZHANG Rongxin, CAI Xiaopei, TANG Xueyang, et al. Alignment design of superconducting electrodynamic suspension turnouts and optimization of lateral crossing speed[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2025, 60(4):893-903. [6] 赵春发,李煜寒,彭也也,等. 超导电动悬浮列车明线气动特性及其对悬浮状态的影响[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2025,60(4):793-802.ZHAO Chunfa, LI Yuhan, PENG Yeye, et al. Aerodynamic characteristics of open wire of superconducting maglev train and its influence on levitation state[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2025, 60(4):793-802. [7] MURAI T, IWAMATSU M, YOSHIOKA H. Optimized design of 8-figure null-flux coils in EDS maglev[J]. IEEJ Transactions on Industry Applications, 2003, 123(1): 9-14. doi: 10.1541/ieejias.123.9 [8] MURAI T, FUJIWARA S. Design of coil specifications in EDS maglev using optimization program[J]. IEEJ Transactions on Industry Applications, 1997, 117(7): 905-911. doi: 10.1541/ieejias.117.905 [9] CHEN Y J, FENG J. Optimization of guideway coil dimensions for a magnetic levitation system[J]. IEEE Transactions on Magnetics, 1997, 33(5): 4335-4344. doi: 10.1109/20.620443 [10] CUI L B, LUO J, SU Z H, et al. Fast optimization of null-flux coils for superconducting electrodynamic suspension train with RSM and AMGA[J]. IEEE Transactions on Applied Superconductivity, 2022, 32(5): 3602308.1-3602308.8. [11] 王志涛,蔡尧,龚天勇,等. 基于场–路–运动耦合模型的超导电动悬浮列车特性研究[J]. 中国电机工程学报,2019,39(4): 1162-1171.WANG Zhitao, CAI Yao, GONG Tianyong, et al. Characteristic studies of the superconducting electrodynamic suspension train with a field-circuit-motion coupled model[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2019, 39(4): 1162-1171. [12] GONG X X, LU Q F, LI Y X. Multi-objective optimization for the levitation system of the electrodynamic suspension train with HTS magnets[C]//2021 13th International Symposium on Linear Drives for Industry Applications (LDIA). Wuhan: IEEE, 2021: 1-6. [13] HUANG H, DENG Z G, LI H T, et al. Numerical simulation of dynamic electromagnetic characteristics of superconducting electrodynamic suspension (EDS) train[J]. IEEE Transactions on Applied Superconductivity, 2021, 31(5): 3601105.1-3601105.5. [14] NING X F, ZHAO C F, YU Q S, et al. Suspension and guidance performance of a new superconducting EDS system using the 8-shaped ground coils with nonequal turns[J]. IEEE Transactions on Applied Superconductivity, 2024, 34(4): 3601511.1-3601511.11. [15] 王小农,黄靖宇. 超导电动磁浮列车悬浮和导向特性[J]. 同济大学学报(自然科学版),2022,50(10): 1482-1489.WANG Xiaonong, HUANG Jingyu. Levitation and guidance characteristics of superconducting electrodynamic maglev train[J]. Journal of Tongji University (Natural Science), 2022, 50(10): 1482-1489. [16] YONEZU T, WATANABE K, SUZUKI E, et al. Study on electromagnetic force characteristics acting on levitation/guidance coils of a superconducting maglev vehicle system[J]. IEEE Transactions on Magnetics, 2017, 53(11): 8300605.1-8300605.5. [17] NONAKA S, HIROSAKI T, KAWAKAMI E. Analysis of characteristics of repulsive magnetic levitated train using a space harmonic technique[J]. Electrical Engineering in Japan, 1980, 100(5): 80-88. doi: 10.1002/eej.4391000512 [18] RIBANI P L, URBANO N. Study on figure-eight-shaped coil electrodynamic suspension magnetic levitation systems without cross-connection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Magnetics, 2000, 36(1): 358-365. doi: 10.1109/20.822547 [19] Sobol I M. Global sensitivity indices for nonlinear mathematical models and their Monte Carlo estimates[J]. Mathematics and Computers in Simulation, 2001, 55(1/2/3): 271-280. [20] 宋健,佘湖清,李超,等. 基于Sobol’ 灵敏度分析的火箭弹自力弹射多目标约束优化[J]. 推进技术,2022,43(12): 40-48.SONG Jian, SHE Huqing, LI Chao, et al. Multi-object constraint optimization of rocket self-ejection based on Sobol’ sensitivity analysis[J]. Journal of Propulsion Technology, 2022, 43(12): 40-48. [21] 倪菲,范琳,徐俊起,等. 基于Sobol’ 法的高速磁浮列车单点悬浮系统全局灵敏度分析[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2025,60(4): 812-822.NI Fei, FAN Lin, XU Junqi, et al. Global sensitivity analysis of single-point levitation system for high-speed maglev train based on Sobol’ method[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2025, 60(4): 812-822. [22] 谭富星,李凯,于淼,等. 超导电动悬浮试验线悬浮系统设计及验证[J]. 机车电传动,2024(3): 13-18.TAN Fuxing, LI Kai, YU Miao, et al. Design and verification of levitation system for superconducting electrodynamic suspension test line[J]. Electric Drive for Locomotives, 2024(3): 13-18. [23] OHASHI S, UEDA N. Dependence of the quenched SC coil position on the transient motion of the superconducting magnetically levitated bogie[J]. IEEE Transactions on Applied Superconductivity, 2016, 26(4): 3600604.1-3600604.4. [24] LEE H W, KIM K C, LEE J. Review of maglev train technologies[J]. IEEE Transactions on Magnetics, 2006, 42(7): 1917-1925. doi: 10.1109/TMAG.2006.875842 [25] 邓自刚,刘宗鑫,李海涛,等. 磁悬浮列车发展现状与展望[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2022,57(3): 455-474,530. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.20220001DENG Zigang, LIU Zongxin, LI Haitao, et al. Development status and prospect of maglev train[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2022, 57(3): 455-474,530. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.20220001 [26] 徐杰. 超导磁悬浮列车用直线发电机的设计与特性解析分析[D]. 北京:北京交通大学,2020. -





 下载:
下载: