Sensorless Control Method of High-Frequency Injection for Long-Stator Synchronous Motor of Maglev Trains Considering Phase Shift Compensation
-
摘要:
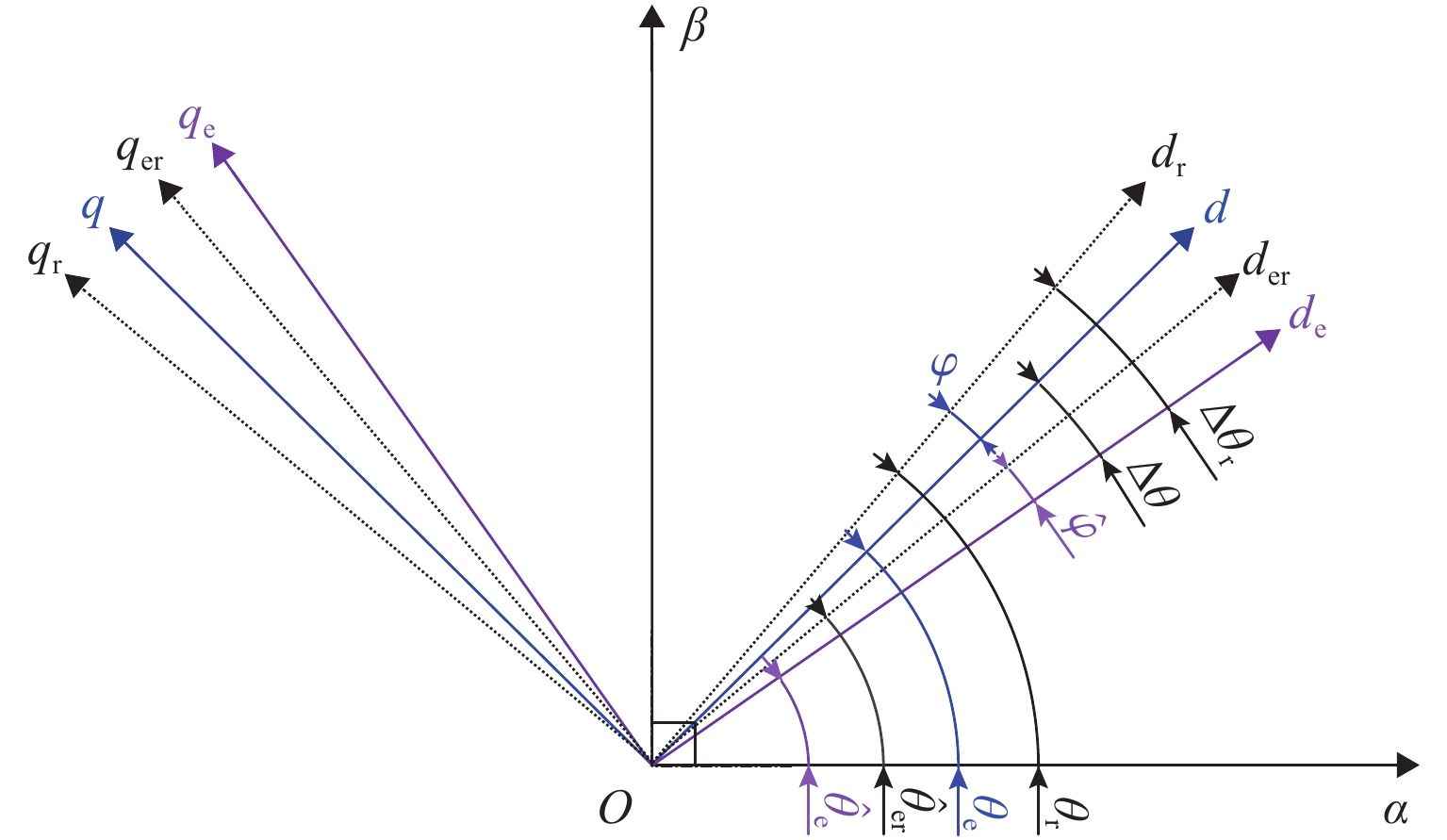
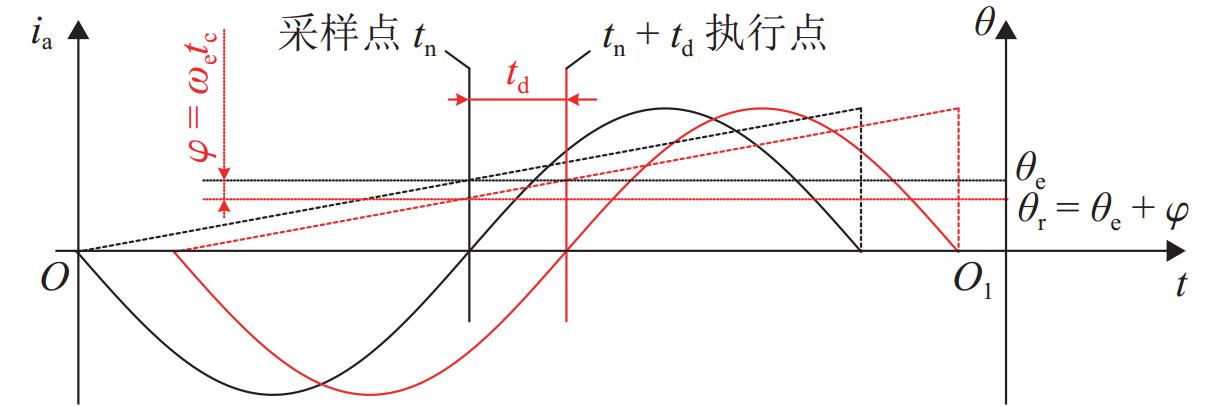
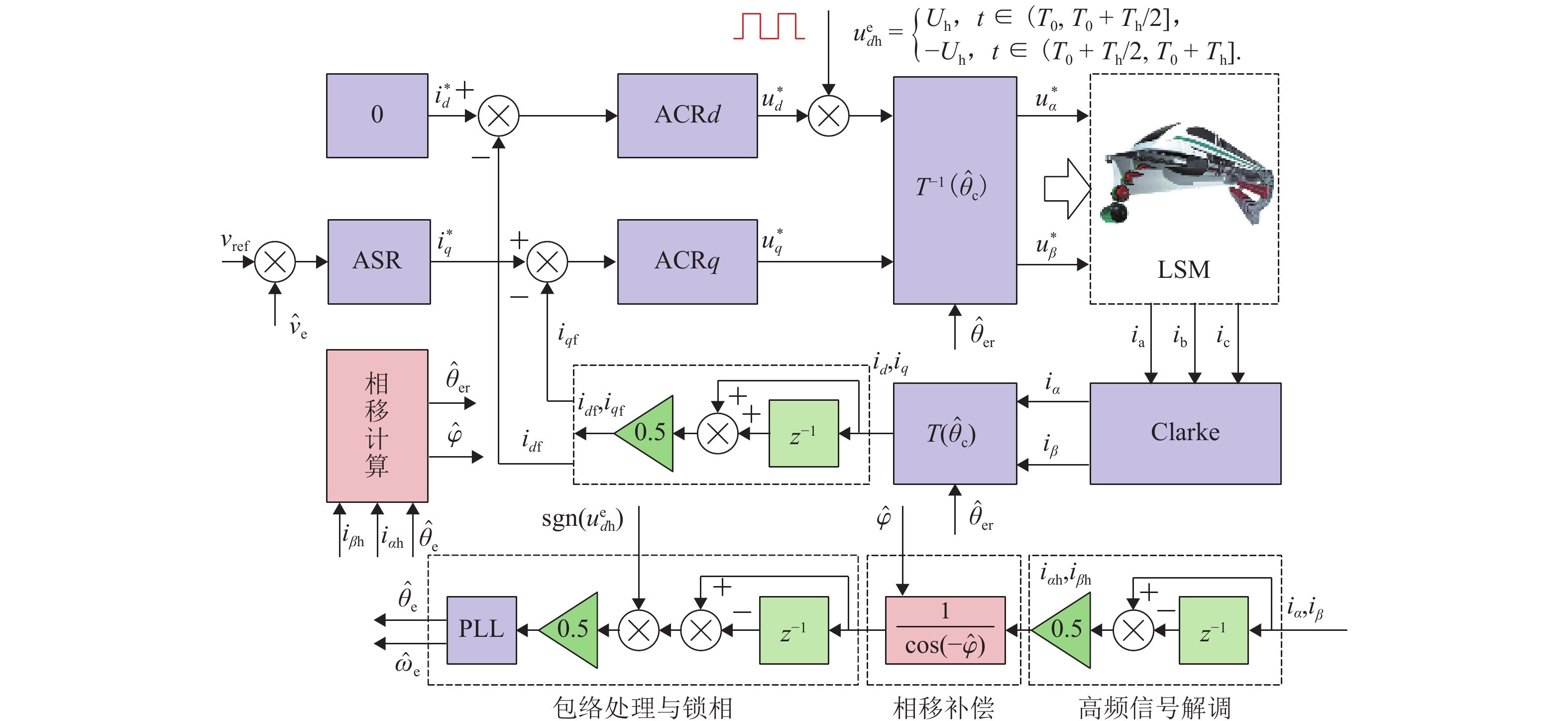
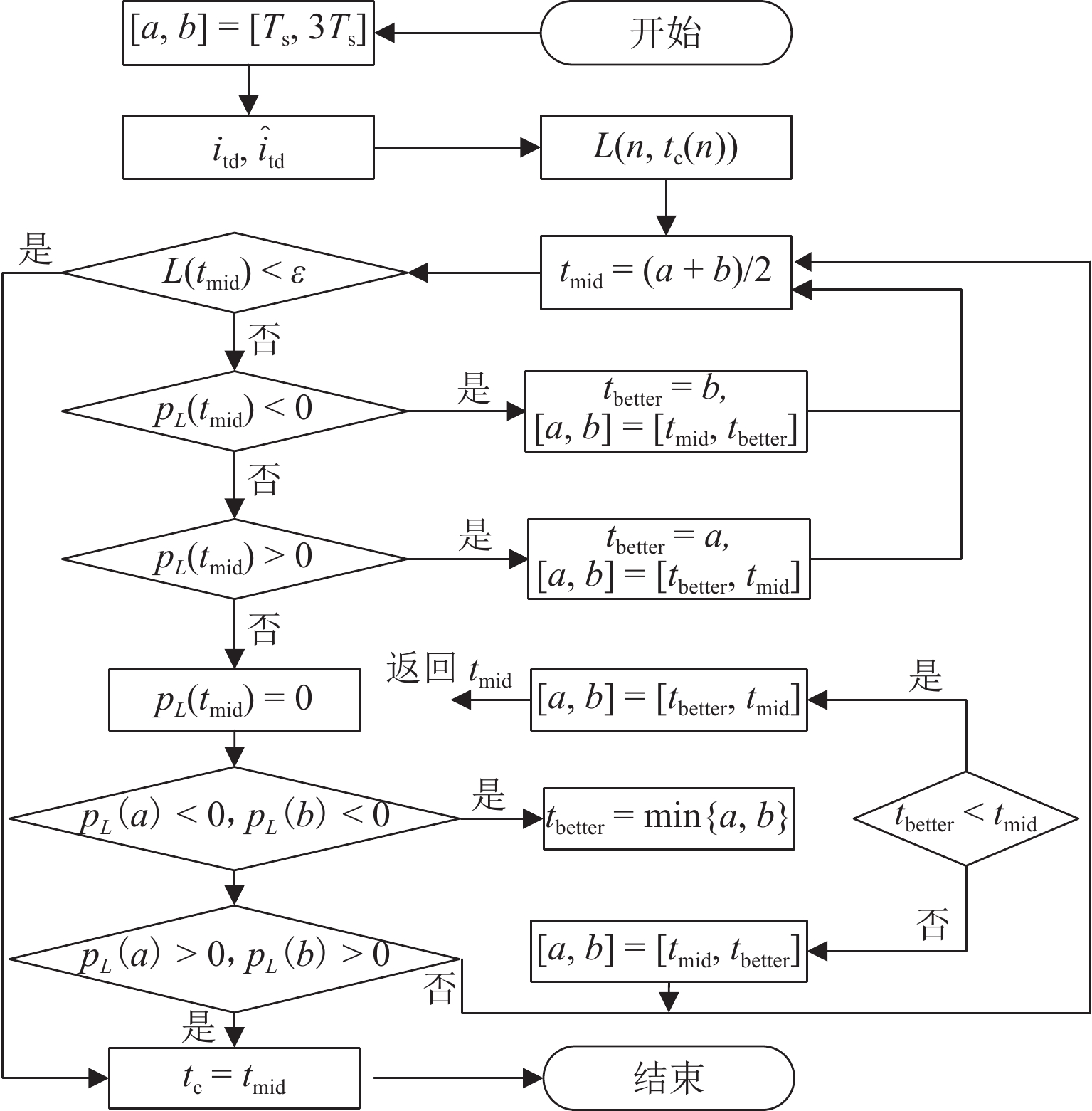
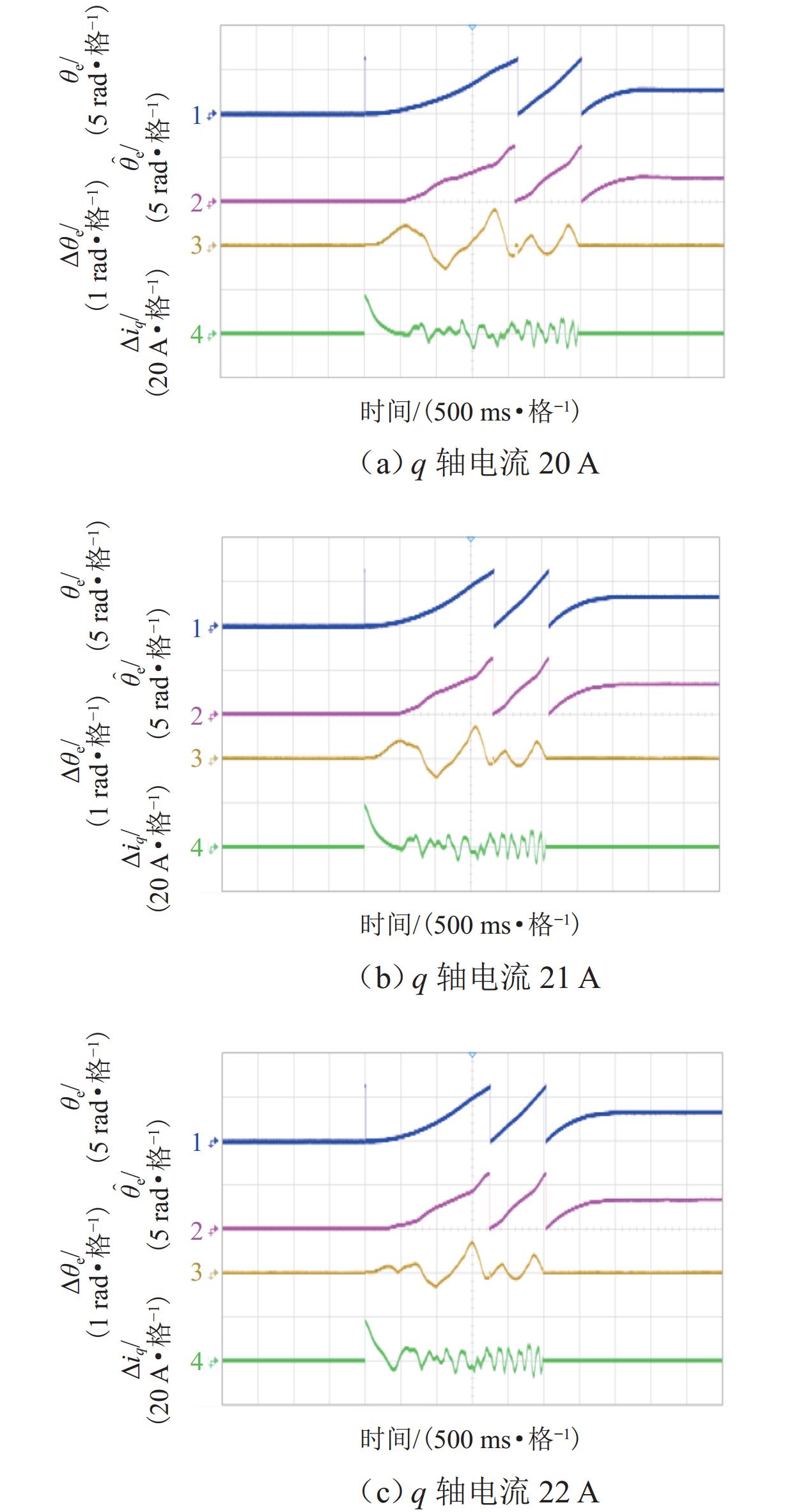
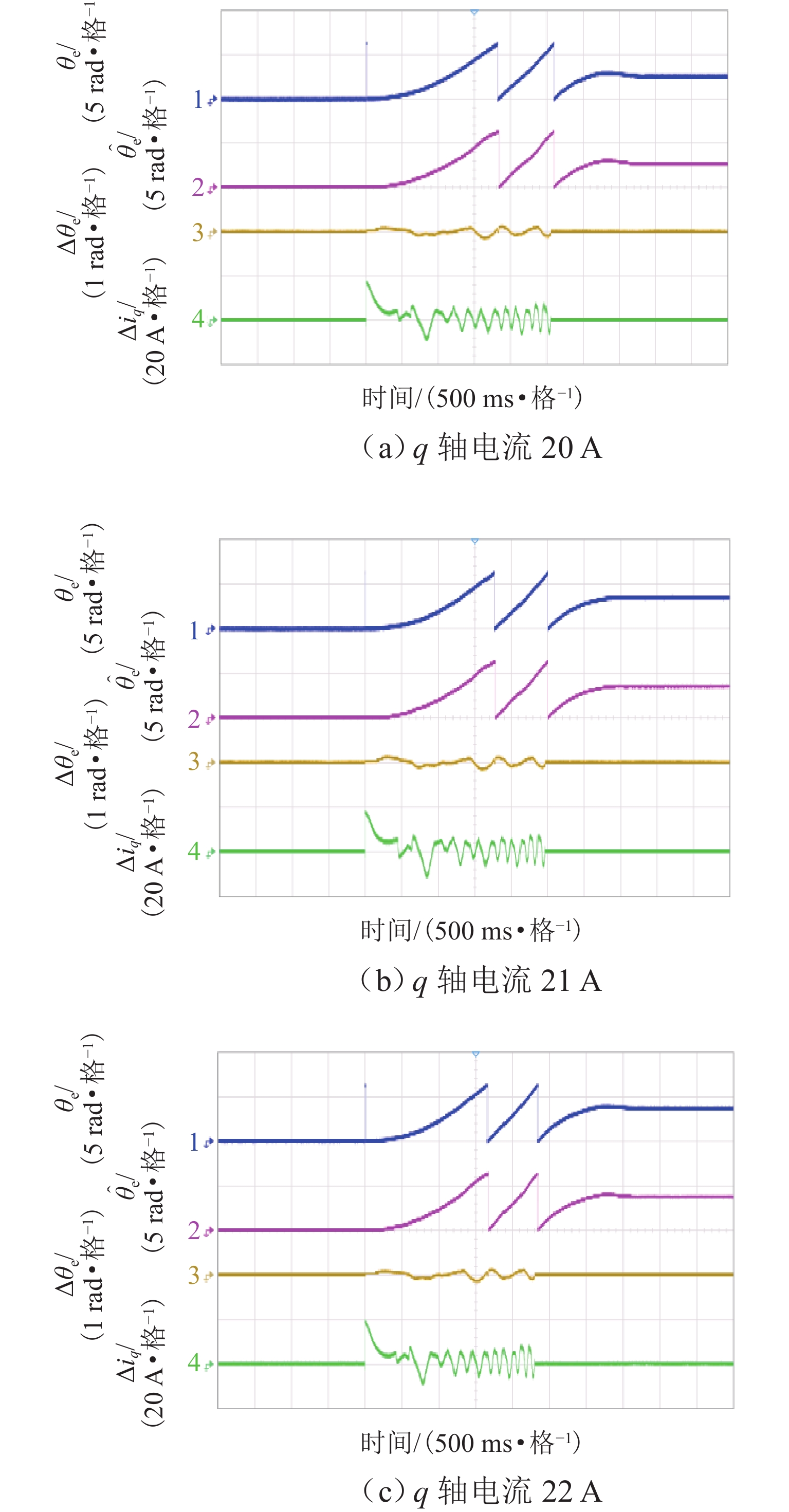
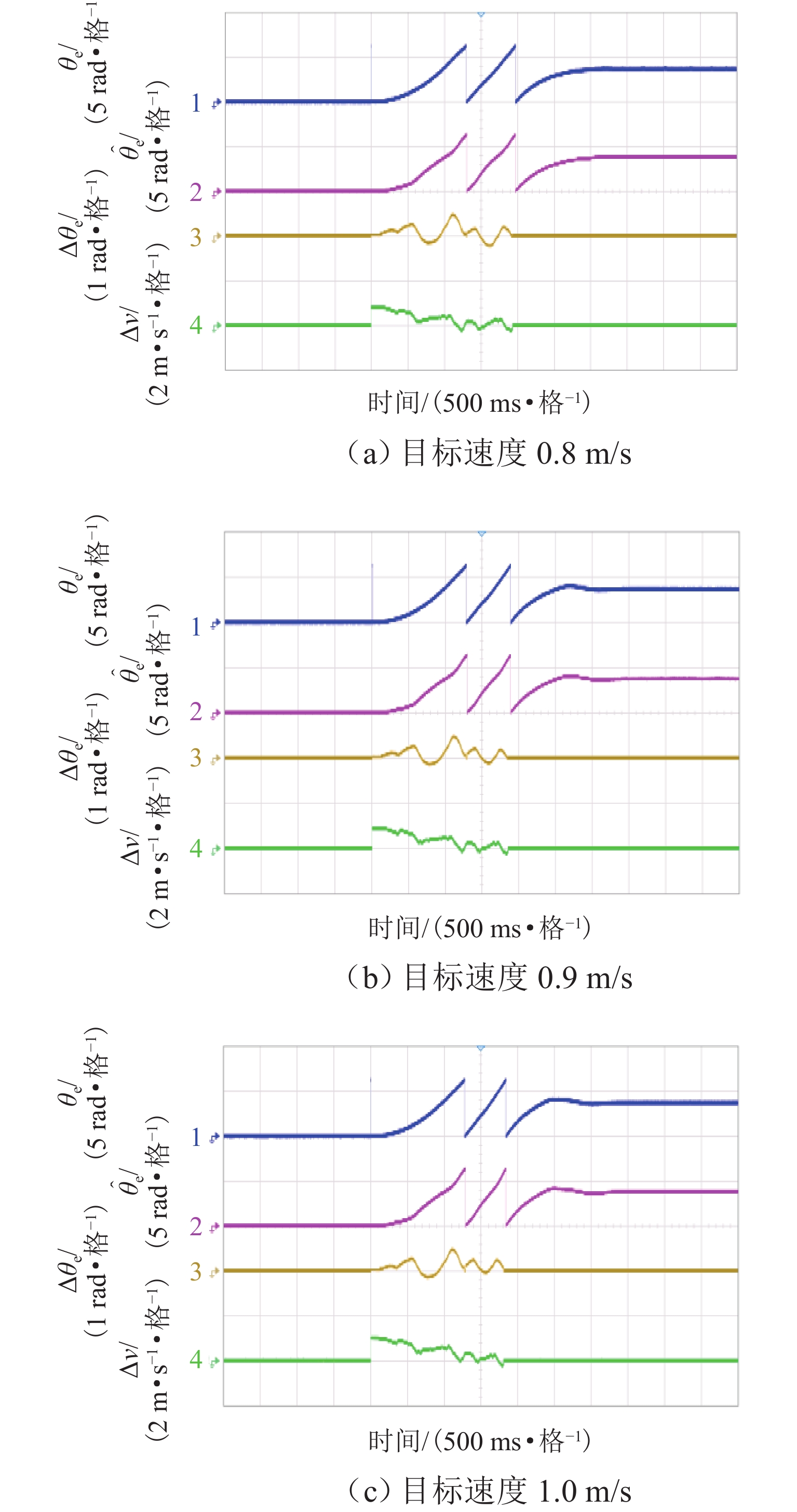
为研究高频注入响应电角度相移对磁浮列车低速控制精度的影响,考虑控制延时与采样延时对角度偏差滞后的约束关系,提出一种无传感估计角度偏差最小化寻优的补偿方法. 首先,建立高速磁浮长定子同步电机零低速高频方波信号注入模型,利用估计-实际-延时坐标系变换理论,构建高频响应电流模型;其次,通过分析大功率电传动系统中系统延时对角度偏差的影响,重构含估计角度相移偏差的高频响应电流模型;然后,设计离散化的估计角度偏差目标函数,提出采用考虑梯度变化的二分法在线计算系统延时与角度偏差;最后,通过磁浮电机低速试验平台验证算法. 试验结果表明:本文提出的考虑相移滞后补偿方法与未经补偿的无传感控制相比,当给定电流为20、21、22 A时,估计角度误差分别减小73.3%,70.4%和72.1%;当速度环给定速度为0.8、0.9、1.0 m/s时,估计角度误差分别减小67.9%、70.5%、75.5%,速度跟踪误差平均减小50%.
Abstract:In order to study the influence of high-frequency signal injection (HFSI) response to electrical angle phase shift on the low-speed control accuracy of maglev trains, the constraint relationship between the control delay and the sampling delay on the angular error lag was considered, and a compensation method for minimizing the angle error of sensorless estimation was proposed. Firstly, a zero-low-speed HFSI model for long-stator synchronous motor (LSM) of high-speed maglev trains was established, and a high-frequency response current model was constructed by using the estimation-real-delay coordinate transformation theory. Secondly, by analyzing the influence of system delay on angular error in a high-power electric drive system, the high-frequency response current model with estimated angular phase shift error was reconstructed. Then, the objective function for the discrete estimation of the angular error was designed, and the bisection method considering the gradient change was proposed to calculate system delay and angular error online. Finally, the algorithm was verified by the low-speed test platform of maglev motors. The experimental results show that compared with the uncompensated sensorless control, when the set current is 20, 21 A, and 22 A, the estimated angular error is decreased by 73.3%, 70.4%, and 72.1% by the proposed compensation method considering phase shift lag compensation. When the set speed is 0.8 m/s, 0.9 m/s, and 1.0 m/s, the estimated angular error is decreased by 67.9%, 70.5%, and 75.5%, and the speed tracking error is decreased by 50% on average.
-
表 1 磁浮电机试验平台主要参数
Table 1. Main parameters of maglev motor test platform
参数 数值 直流侧电压/V 220 定子相电阻/Ω 0.12 d 轴电感/mH 1.8 q 轴电感/mH 1.4 定子极距/mm 258 动子极距/mm 266.5 励磁电流/A 20~23 动子励磁磁链/Wb 0.324 7 表 2 不同电流下补偿前、后误差最大波动
Table 2. Maximum fluctuation of error before and after compensation under different currents
电流/A 电角误差/rad 电流误差/A 电角波动变化/% 电流波动变化/% 补偿前 补偿后 补偿前 补偿后 20 0.86 0.23 7.5 7.5 73.3 0 21 0.71 0.21 7.5 7.5 70.4 0 22 0.68 0.19 7.5 7.5 72.1 0 表 3 不同速度下补偿前、后误差最大波动
Table 3. Maximum fluctuation of error before and after compensation under different speeds
速度/(m·s−1) 电角误差/rad 速度误差/(m·s−1) 电角波动变化/% 电流波动变化/% 补偿前 补偿后 补偿前 补偿后 0.8 0.53 0.17 0.36 0.21 67.9 50 0.9 0.51 0.15 0.36 0.21 70.5 50 1.0 0.49 0.12 0.36 0.21 75.5 50 -
[1] 丁叁叁. 时速600公里高速磁浮交通系统[M]. 上海:上海科学技术出版社,2021. [2] 林国斌,刘万明,徐俊起,等. 中国高速磁浮交通的发展机遇与挑战[J]. 前瞻科技,2023,2(4): 7-18.LING Guobin, LIU Wanming, XU Junqi, et al. Opportunities and challenges for the development of high-speed maglev transportation in China[J]. Science and Technology Foresight, 2023, 2(4): 7-18. [3] 朱进权,葛琼璇,张波,等. 考虑悬浮系统影响的高速磁悬浮列车牵引控制策略[J]. 电工技术学报,2022,37(12): 3087-3096.ZHU Jinquan, GE Qiongxuan, ZHANG Bo, et al. Traction control strategy of high-speed maglev considering the influence of suspension system[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2022, 37(12): 3087-3096. [4] 康劲松,丁浩,倪菲,等. 计及悬浮系统影响的高速磁浮直线同步电机建模方法[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2024,59(4): 729-736. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.20230431KANG Jinsong, DING Hao, NI Fei, et al. Modeling of high-speed maglev linear synchronous motors considering influence of suspension system[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2024, 59(4): 729-736. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.20230431 [5] ZHU J Q, GE Q X, SUN P K. Extended state observer-based sensorless control for high-speed maglev application in single-feeding mode and double-feeding mode[J]. IEEE Transactions on Transportation Electrification, 2022, 8(1): 1350-1361. doi: 10.1109/TTE.2021.3093342 [6] WANG G L, VALLA M, SOLSONA J. Position sensorless permanent magnet synchronous machine drives—a review[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2020, 67(7): 5830-5842. doi: 10.1109/TIE.2019.2955409 [7] KIM H, JUNG H S, SUL S K. Stator winding temperature and magnet temperature estimation of IPMSM based on high-frequency voltage signal injection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2023, 70(3): 2296-2306. doi: 10.1109/TIE.2022.3174285 [8] ORTOMBINA L, BERTO M, ALBERTI L. Sensorless drive for salient synchronous motors based on direct fitting of elliptical-shape high-frequency currents[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2023, 70(4): 3394-3403. doi: 10.1109/TIE.2022.3177753 [9] 吴婷. 永磁同步电机全速范围无位置传感器控制策略研究[D]. 长沙:湖南大学,2022. [10] 王涛,黄景春,杨天昊. 基于改进的Super-Twisting滑模观测器的永磁同步电机无传感器控制[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2025,60(3):445-453.WANG Tao, HUANG Jinchun, YANG Tianhao. Sensorless control of permanent magnet synchronous motor based on improved super-twisting sliding mode observer[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2025, 60(3):445-453. [11] 沈泽微,蒋栋,陈嘉楠. 一种通用的PWM变流器开关脉冲延时补偿策略[J]. 中国电机工程学报,2021,41(9): 2990-2998.SHEN Zewei, JIANG Dong, CHEN Jianan. A general switch pulse delay compensation strategy for PWM converter[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2021, 41(9): 2990-2998. [12] 鄢永,黄文新. 基于闭环电流预测的永磁同步电机电流环延时补偿策略研究[J]. 中国电机工程学报,2022,42(10): 3786-3795.YAN Yong, HUANG Wenxin. Research on delay compensation strategy of permanent magnet synchronous motor based on closed-loop current prediction[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2022, 42(10): 3786-3795. [13] 王志强,郭伟鹏,桑孜良,等. 高速磁浮列车导向系统优化控制方法研究[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2025,60(4):833-841,864.WANG Zhiqiang, GUO Weipeng, SANG Ziliang, et al. Optimization control for the guidance system of high-speed maglev train [J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2025, 60(4):833-841,864. [14] WANG Y R, XU Y X, ZOU J B. Sliding-mode sensorless control of PMSM with inverter nonlinearity compensation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics, 2019, 34(10): 10206-10220. doi: 10.1109/TPEL.2018.2890564 [15] WU X, LI C, ZHANG Y Y, et al. Sensorless control of IPMSM equipped with LC sinusoidal filter based on full-order sliding mode observer and feedforward QPLL[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics, 2024, 39(7): 8072-8085. doi: 10.1109/TPEL.2024.3390050 [16] LIU Z H, NIE J, WEI H L, et al. A newly designed VSC-based current regulator for sensorless control of PMSM considering VSI nonlinearity[J]. IEEE Journal of Emerging and Selected Topics in Power Electronics, 2021, 9(4): 4420-4431. doi: 10.1109/JESTPE.2020.3033037 [17] WU S H, HU C X, ZHAO Z Y, et al. High-accuracy sensorless control of permanent magnet linear synchronous motors for variable speed trajectories[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2024, 71(5): 4396-4406. doi: 10.1109/TIE.2023.3288145 [18] ZHANG H, LIANG W R, GAO L Y, et al. Switching angle fitting-based delay compensation with IPLL for IPMSM sensorless drives under SHEPWM[J]. IEEE Transactions on Transportation Electrification, 2024, 10(1): 660-669. doi: 10.1109/TTE.2023.3276878 [19] CAO X Q, GE Q X, ZHU J Q, et al. Periodic traction force fluctuations suppression strategy of maglev train based on flux linkage observation and harmonic current injection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Transportation Electrification, 2023, 9(2): 3434-3451. doi: 10.1109/TTE.2022.3221193 [20] ZHANG H, LIU W G, CHEN Z, et al. An overall system delay compensation method for IPMSM sensorless drives in rail transit applications[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics, 2021, 36(2): 1316-1329. doi: 10.1109/TPEL.2020.3015742 [21] KANG J S, DING H, ZOU P R, et al. Model predictive thrust force control for 3L-NPC fed linear synchronous motor of maglev train[J]. IEEE Transactions on Transportation Electrification, 2024, 1: 3368071.1-3368071.9. [22] KANG J S, MU S Y, NI F. Improved EL model of long stator linear synchronous motor via analytical magnetic coenergy reconstruction method[J]. IEEE Transactions on Magnetics, 2020, 56(8): 3002964.1-3002964.13. [23] 张昕,翟凌露,王舰深,等. 基于加权融合的常导高速磁浮列车UKF定位算法[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2024,59(4): 832-838. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.20230501ZHANG Xin, ZHAI Linglu, WANG Jianshen, et al. Weighted fusion-based unscented Kalman filter positioning algorithm for normal-conducting high-speed maglev trains[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2024, 59(4): 832-838. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.20230501 [24] WU T, LUO D R, WU X, et al. Square-wave voltage injection based PMSM sensorless control considering time delay at low switching frequency[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2022, 69(6): 5525-5535. doi: 10.1109/TIE.2021.3094444 -





 下载:
下载: