Development and Experimental Research on Spherical Bearings for Vertical Vibration Isolation of Bridges
-
摘要:
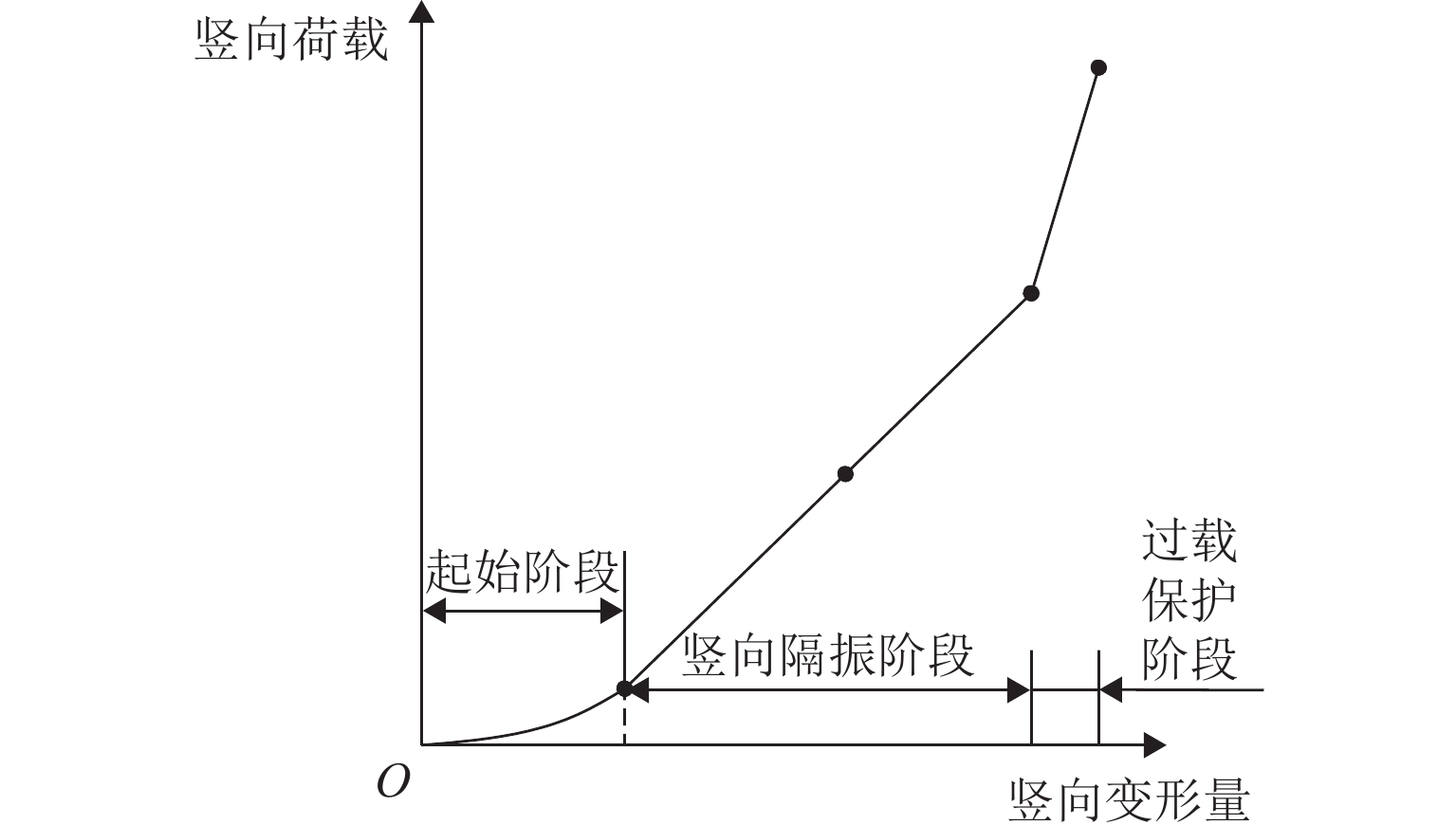
为降低高铁桥梁车致振动对周围环境的影响,首先,提出一种内置金属盘式隔振器的桥梁竖向隔振球型支座,给出支座力学本构模型和整体竖向刚度计算方法;结合仿真和试验对比研究金属盘式隔振器竖向刚度的设计符合性,并仿真分析不同摩擦支承面对金属盘式隔振器竖向刚度和应力的影响;然后,通过竖向隔振球型支座的系列试验,研究了支座的常规性能、竖向刚度、隔振荷载、动静刚度比和刚度稳定性;最后,以高速铁路32 m跨混凝土简支箱梁为背景,探究了列车作用下的支座隔振效果. 结果表明:3种不同竖向承载力设计的金属盘式隔振器的竖向刚度仿真与实测值偏差均在±10%以内;金属盘式隔振器的底部支承面摩擦系数在0.01~0.10内时,竖向刚度增加2.1%,应力减小0.9%;竖向隔振球型支座样件的常规性能满足设计要求,竖向刚度和隔振荷载的试验值与设计值偏差均在±10%以内;支座在过载卸载后竖向刚度保持稳定,对金属盘式隔振器起到保护作用;激励频率1~17 Hz时,支座动静刚度比的范围为1.00~1.15;支座
1000 万次疲劳后刚度增加量小于10%,各部件完好;竖向隔振球型支座支承下的桥梁满足列车安全性和乘坐舒适性指标要求,竖向隔振球型支座较普通球型支座的土体振动响应衰减量达4 dB左右.Abstract:In order to reduce the impact of vehicle-induced vibration on the surrounding environment of high-speed railway bridges, firstly, a spherical bearing with built-in metal disc isolators for vertical vibration isolation of bridges was proposed, and the mechanical constitutive model and overall vertical stiffness calculation method of the bearings were given. The design compliance of the vertical stiffness of the metal disc isolator was studied by combining simulation and experimental comparison. Simulation was also used to analyze the influence of different friction support surfaces on the vertical stiffness and stress of the metal disc isolator. Secondly, through a series of tests on spherical bearings for vertical vibration isolation, the conventional performance, vertical stiffness, isolation load, dynamic and static stiffness ratio, and stiffness stability of the bearings were studied. Finally, taking the 32-meter-span concrete simply supported box girder of high-speed railway as the background, the vibration isolation effect of the bearings under the action of trains was explored. The results show that the deviation between the simulated and measured vertical stiffness values of the metal disc isolator with three different vertical bearing capacity designs is within ±10%. The friction coefficient of the bottom support surface of the metal disc isolator ranges from 0.01 to 0.10, with a 2.1% increase in vertical stiffness and a 0.9% decrease in stress. The conventional performance of the spherical bearing for vertical vibration isolation meets the design requirements, and the deviation between the test values and the design values of vertical stiffness and isolation load is less than ±10%. The vertical stiffness of the bearing remains stable after overload and unloading, providing protection for the metal disc isolator. At an excitation frequency of 1–17 Hz, the range of the dynamic to static stiffness ratio of the bearings is 1.00–1.15. The stiffness increase of the bearings after 10 million fatigue cycles is less than 10%, and all components are intact. The bridge supported by spherical bearings for vertical vibration isolation meets the requirements of train safety and riding comfort indicators. The soil vibration response attenuation of the former bridge is about 4 dB higher than that of the bridge supported by ordinary spherical bearings.
-
表 1 不同规格盘式隔振器竖向刚度仿真与实测结果比较
Table 1. Comparison between simulation and measurement results of vertical stiffness of disc isolators with different specifications
竖向承载力/kN 仿真竖向刚度/
(kN·mm−1)实测竖向刚度/
(kN·mm−1)偏差/% 1 000 250.2 230.3 −7.9 2 500 726.5 719.0 −1.0 5 000 2 077.2 1 938.5 −7.6 表 2 不同摩擦工况下的盘式隔振器性能
Table 2. Performance of disc isolators under different friction conditions
摩擦工况 摩擦系数 仿真计算刚度/
(kN·mm−1)最大应力/
MPa1 0.01 1 543 646 2 0.03 1 550 645 3 0.05 1 557 644 4 0.07 1 564 643 5 0.10 1 576 640 6 0.20 2 155 589 表 3 不同基频下的支座仿真计算刚度与设计值比较
Table 3. Comparison of calculated stiffness by simulation and design values of bearings under different fundamental frequencies
基频/Hz K/(kN·mm−1) 仿真竖向刚度/
(kN·mm−1)刚度偏差/% 10 1 180 1 174 −0.5 11 1 440 1 424 −1.1 12 1 700 1 743 2.5 13 2 000 2 046 2.3 14 2320 2329 0.4 表 4 成品支座
5000 kN型式检测结果Table 4. 5 000 kN-type inspection results of finished bearings
项目 竖向承载力 水平静摩擦系数 转动力矩/
(kN·mm)竖向刚度/
(kN·mm−1)隔振荷载/kN 设计值 外观
良好≤0.03 ≤ 94500 1440 5000 试验值 外观
良好0.015 48667 1545.4 5439.7 偏差/% + 7.31 + 8.79 表 5 不同激励频率下的支座动、静刚度比测试结果
Table 5. Test results of dynamic and static stiffness ratios of bearings under different excitation frequencies
频率/Hz 动刚度/(kN·mm−1) 动、静刚度比 1 187 1.15 3 188 1.15 5 187 1.14 7 186 1.14 9 185 1.13 11 182 1.12 13 174 1.07 15 171 1.05 17 166 1.02 表 6 不同疲劳次数下的刚度测试
Table 6. Stiffness testing under different fatigue cycles
疲劳次数/
万次刚度/
(kN·mm−1)疲劳次数/
万次刚度/
(kN·mm−1)100 612.2 600 638.3 200 620.7 700 647.5 300 621.8 800 647.5 400 638.3 900 647.5 500 647.5 1000 652.2 表 7 列车运行安全性及乘坐舒适性评价
Table 7. Evaluation of train operation safety and riding comfort
评价指标 计算结果 效果 脱轨系数≤0.8 0.111~0.115 满足 轮重减载率≤0.6 0.32~0.43 满足 车辆竖向舒适性 sperling 值 1.798~1.804 优良 车辆横向舒适性 sperling 值 2.400~2.427 优良 表 8 2种地质下支座隔振效果
Table 8. Vibration isolation effect of bearings under two different geological conditions
地质 与桥墩距离/m 10 20 30 砂卵石 4.10 3.90 3.90 基岩 3.65 3.92 3.90 -
[1] 杨飞, 吴细水, 孙宪夫, 等. 钢轨轧制不平顺激扰下的动车组动力响应特性[J]. 西南交通大学学报, 2022, 57(2): 267-276.YANG Fei, WU Xishui, SUN Xianfu, et al. Dynamic response characteristics of EMU under excitation of rail straightening irregularity[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2022, 57(2): 267-276. [2] 李小珍, 刘全民, 张迅, 等. 铁路高铁车站车致振动实测与理论分析[J]. 西南交通大学学报, 2014, 49(4): 612-618. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2014.04.008LI Xiaozhen, LIU Quanmin, ZHANG Xun, et al. Measurement and theoretical analysis of vehicle-induced vibration on elevated railway station[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2014, 49(4): 612-618 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2014.04.008 [3] 李小珍, 张志俊, 冉汶民, 等. 桥上列车高速运行引起的地面振动试验研究[J]. 西南交通大学学报, 2016, 51(5): 815-823. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2016.05.001LI Xiaozhen, ZHANG Zhijun, RAN Wenmin, et al. Field test of ground vibration induced by high-speed train on elevated bridge[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2016, 51(5): 815-823. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2016.05.001 [4] 雷晓燕, 翁凌霄, 刘庆杰, 等. 高速铁路桥梁结构振动、噪声与环境振动现场试验[J]. 铁道学报, 2022, 44(11): 121-128. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8360.2022.11.015LEI Xiaoyan, WENG Lingxiao, LIU Qingjie, et al. Field test of structural vibration, noise and environmental vibration of high-speed railway bridges[J]. Journal of the China Railway Society, 2022, 44(11): 121-128. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8360.2022.11.015 [5] 花雨萌, 谢伟平, 陈斌. 地铁振动对建筑物竖向楼层响应的影响研究[J]. 建筑结构学报, 2023, 44(3): 122-129.HUA Yumeng, XIE Weiping, CHEN Bin. Research on influence of metro vibration on vertical floor response of buildings[J]. Journal of Building Structures, 2023, 44(3): 122-129. [6] 陈兆玮, 徐鸿, 尹镪, 等. 地铁运行引发临近建筑群低频微振动及传递规律研究[J]. 振动工程学报, 2023, 36(6): 1623-1632.CHEN Zhaowei, XU Hong, YIN Qiang, et al. Low-frequency microvibration and its transfer law of nearby building group caused by running metro train[J]. Journal of Vibration Engineering, 2023, 36(6): 1623-1632. [7] 汪振国. 轨道交通简支梁桥振动特性与控制研究[D]. 南昌: 华东交通大学, 2018. [8] 雷晓燕, 汪振国, 罗琨. 城市轨道交通简支箱梁桥结构振动特性分析[J]. 铁道工程学报, 2017, 34(9): 96-102. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2106.2017.09.017LEI Xiaoyan, WANG Zhenguo, LUO Kun. Analysis of structural vibration characteristics of simply supported box girder bridge in urban rail transit[J]. Journal of Railway Engineering Society, 2017, 34(9): 96-102. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2106.2017.09.017 [9] 詹志雄. 弹性支承条件下轨道梁的车致振动响应分析[D]. 荆州: 长江大学, 2021. [10] 胡叙洪, 等. 高速铁路减振降噪技术研究与应用[M]. 北京: 中国铁道出版社, 2018: 151-158. [11] 宋晓东, 邱晓为, 李小珍, 等. 莫-喀高速铁路简支箱梁竖向下限基频研究[J]. 西南交通大学学报, 2019, 54(4): 709-714. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.20170306SONG Xiaodong, QIU Xiaowei, LI Xiaozhen, et al. Lower vertical frequency limit for simply supported box-girder on Moscow-Kazan high-speed railway line[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2019, 54(4): 709-714. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.20170306 [12] 张志俊, 李小珍, 张迅, 等. 弹性支座对桥梁车致振动的隔振效果研究[J]. 工程力学, 2015, 32(4): 103-111.ZHANG Zhijun, LI Xiaozhen, ZHANG Xun, et al. Study on the vibration-isolation effects of elastic bearings on train-induced vibration of railway bridge[J]. Engineering Mechanics, 2015, 32(4): 103-111. [13] 孙亮明, 赵寒冰, 谢伟平. 橡胶减振支座对竖向车致振动减振效果实测研究[J]. 建筑结构, 2019, 49(14): 96-101.SUN Liangming, ZHAO Hanbing, XIE Weiping. Field measurement on damping effects of elastic bearing pad for vertical train-induced vibrations[J]. Building Structure, 2019, 49(14): 96-101. [14] 孙亮明, 胡振, 杜友福, 等. 高架轨道桥梁新型橡胶减振支座的减振效果分析[J]. 振动与冲击, 2020, 39(8): 64-71.SUN Liangming, HU Zhen, DU Youfu, et al. Vibration reduction effect of a novel rubber anti-vibration bearing for rail transit viaduct[J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2020, 39(8): 64-71. [15] 张迅, 李小珍, 王党雄, 等. 典型铁路简支箱梁的中高频振动试验研究[J]. 铁道学报, 2017, 39(8): 137-147.ZHAN Xun, LI Xiaozhen, WANG Dangxiong, et al. Experimental study on medium and high frequency vibrations of typical railway simply-supported box-girders[J]. Journal of The China Railway Society, 2017, 39(8): 137-147. [16] MARIONI, 陈列, 胡京涛. 橡胶减振支座在台湾高速铁路上的应用[J]. 工程抗震与加固改造, 2011, 33(2): 63-66.MARIONI, CHEN Lie, HU Jingtao. Application of EBP on Taiwan high-speed railway[J]. Earthquake Resistant Engineering and Retrofitting, 2011, 33(2): 63-66. [17] KAWATANI M, KOBAYASHI Y, KAWAKI H. Influence of elastomeric bearings on traffic-induced vibration of highway bridges[J]. Transportation Research Record: Journal of the Transportation Research Board, 2000, 1696(1): 76-82. doi: 10.3141/1696-47 [18] KIM C W, KAWATANI M, HWANG W S. Reduction of traffic-induced vibration of two-girder steel bridge seated on elastomeric bearings[J]. Engineering Structures, 2004, 26(14): 2185-2195. doi: 10.1016/j.engstruct.2004.08.002 [19] YAU J D, WU Y S, YANG Y B. Impact response of bridges with elastic bearings to moving loads[J]. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 2001, 248(1): 9-30. doi: 10.1006/jsvi.2001.3688 [20] YANG Y B, LIN C L, YAU J D, et al. Mechanism of resonance and cancellation for train-induced vibration on bridges with elastic bearings[J]. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 2004, 269(1): 345-360. [21] 张锐, 高芳清, 范晨光. 一种合金减振与隔振支座减振特性研究[J]. 四川建筑, 2017, 37(2): 209-211. [22] 罗登发, 姜文英, 张晓武. 桥梁支座摩擦材料发展与展望[J]. 材料开发与应用, 2017, 32(5): 95-97.LUO Dengfa, JIANG Wenying, ZHANG Xiaowu. Development and prospect of friction materials for bridge bearings[J]. Development and Application of Materials, 2017, 32(5): 95-97. [23] 中国国家铁路集团有限公司. 铁路桥梁支座 第二部分: 球型支座: Q/CR 756.2—2020[S]. 北京: 中国铁道出版社有限公司, 2020. [24] International Organization for Standardization. Mechanical vibration and shock-Evaluation of human exposure to whole-body vibration—Part I: General requirements: ISO 2631-1: 1997(E)[S]. Geneve, Switzerland: International Organization for Standardization, 1997. [25] 张志俊. 高速铁路桥梁段车致地面振动的半解析分析与试验研究[D]. 成都: 西南交通大学, 2016. -





 下载:
下载: