Influence of Number of Pebble Fracture Surfaces on Direct Shear Properties of Aggregates
-
摘要:
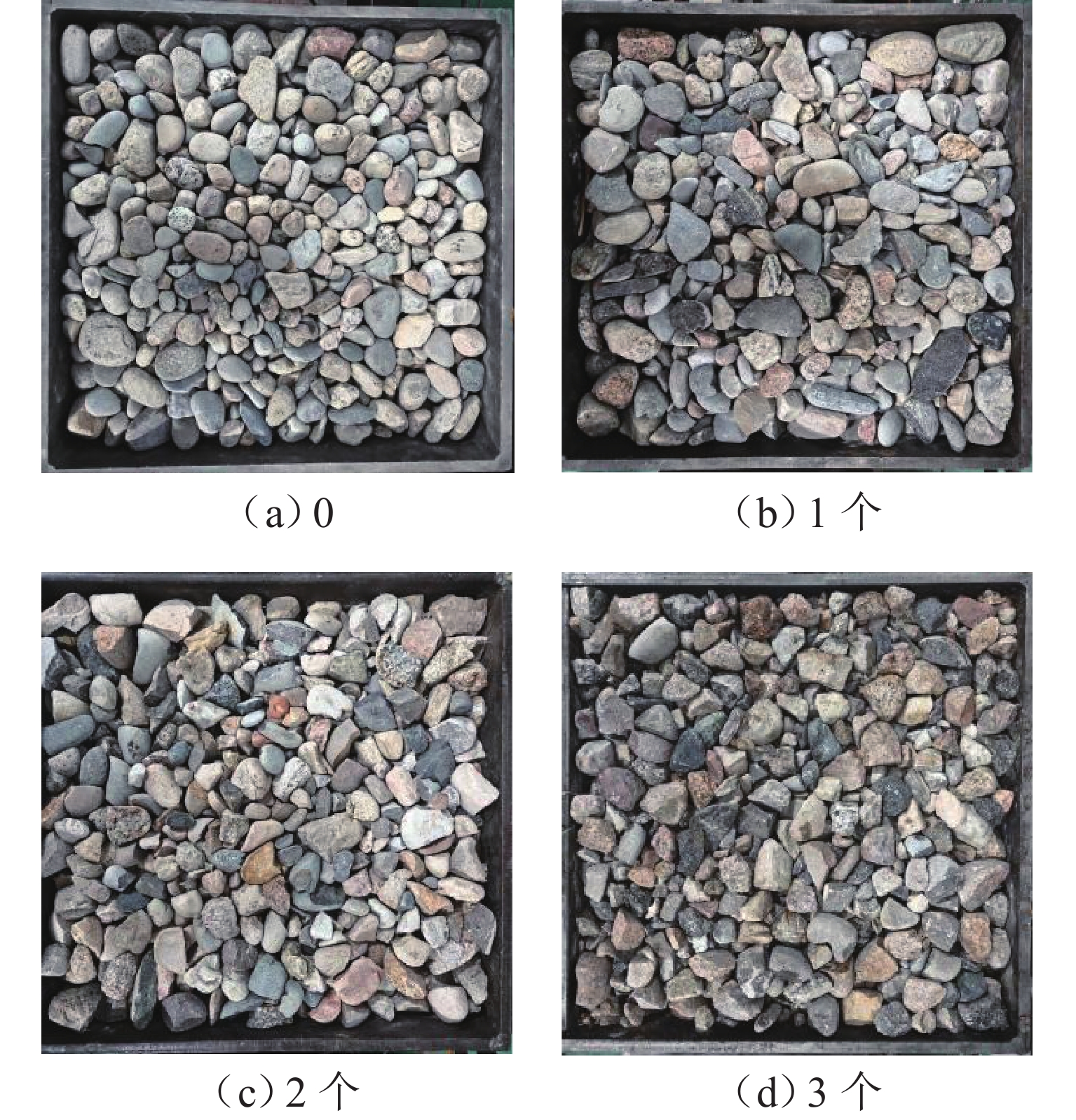
为了研究道砟颗粒的破碎面数目对道床直剪性能的影响规律,首先,对光滑的河卵石进行破碎,得到拥有不同破碎面数目的道砟集料;其次,针对以上工况在不同垂向应力下开展直剪试验,得到剪切过程中道砟集料的应力应变关系和变形特性;最后,通过公式计算,得出道砟集料的峰值抗剪强度和内摩擦角随垂向应力的变化规律. 研究结果表明:在强度特性方面,道砟破碎面数目为0、1、2、3个时,同一垂向应力下道砟集料的剪切强度和内摩擦角在一定范围内会随着道砟破碎面数目的增加而增加,剪切强度依次提高了14.7%~25.6%、12.2%~27.4%、6.0%~10.1%;对于变形特性,道砟集料的剪缩特性会随着破碎面数目的增加而增加,最大增加了76.4%,而剪胀特性会随着破碎面数目的增加而减少,最大减少20.8%.
Abstract:In order to investigate the influence of the number of ballast particle fracture surfaces on the direct shear performance of the ballast bed, pebbles were crushed to obtain ballast aggregates with different numbers of fracture surfaces. Direct shear tests were carried out under different vertical stresses to obtain the stress–strain relationship and deformation characteristics of ballast aggregates. Based on formula calculation, the variation laws of peak shear strength and internal friction angle of ballast aggregates with vertical stress were obtained. The results show that, in terms of strength characteristics, when the number of fracture surfaces is 0, 1, 2, and 3, the shear strength and internal friction angle of ballast aggregates under the same vertical stress increase with the number of fracture surfaces. The shear strength increases by 14.7%–25.6%, 12.2%–27.4%, and 6.0%–10.1%, respectively. In terms of deformation characteristics, the shear shrinkage of ballast aggregates increases with fracture surface number, with a maximum increase of 76.4%, while the shear dilation decreases with a maximum decrease of 20.8%.
-
Key words:
- ballast /
- fracture surface /
- direct shear test /
- shear characteristic
-
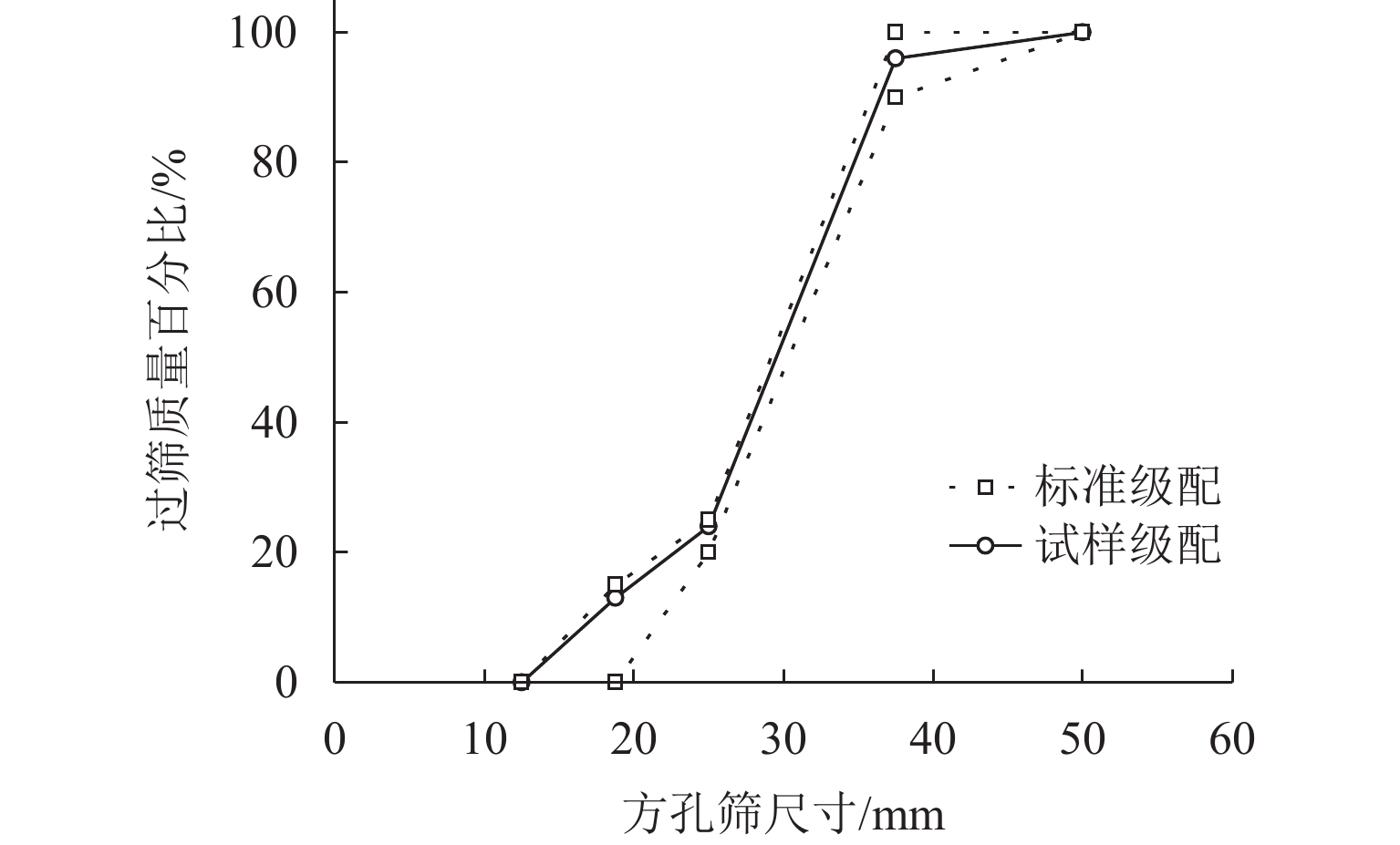
表 1 AREA4道砟级配推荐
Table 1. Recommended ballast gradation of AREA4
尺寸/mm 50.00 37.50 25.00 18.75 过筛率/% 100 90~100 20~25 0~15 表 2 直剪试验不同工况下的最大剪缩剪、胀量
Table 2. Maximum shear shrinkage and dilation under different conditions in direct shear tests
mm 垂向压力/kPa 最大剪缩量 最大剪胀量 0 1 个破碎面 2 个破碎面 3 个破碎面 0 1 个破碎面 2 个破碎面 3 个破碎面 50 0.058 0.082 0.130 0.158 14.310 14.235 13.160 12.350 100 0.086 0.120 0.200 0.266 13.310 12.810 10.145 9.155 200 0.180 0.212 0.374 0.478 9.870 9.680 9.440 8.520 -
[1] 井国庆. 铁路有砟道床[M]. 北京: 中国铁道出版社, 2012: 196-199. [2] 曾树谷. 铁路散粒体道床[M]. 北京: 中国铁道出版社, 1997: 41. [3] GUO Y L, XIE J L, FAN Z, et al. Railway ballast material selection and evaluation: a review[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2022, 344: 128218. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2022.128218 [4] TOLOMEO M, MCDOWELL G R. Modelling real particle shape in DEM: a comparison of two methods with application to railway ballast[J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences, 2022, 159: 105-221. [5] DISSANAYAKE D, KURUKULASURIYA L C, DISSANAYAKE P. Evaluation of shear strength parameters of rail track ballast in Sri Lanka[J]. Journal of the National Science Foundation of Sri Lanka, 2016, 44(1): 61-67. doi: 10.4038/jnsfsr.v44i1.7982 [6] 崔旭浩, 肖宏, 令行. 脏污对散体道床动态行为影响的宏细观分析[J]. 铁道学报, 2022, 44(9): 120-127. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8360.2022.09.016CUI Xuhao, XIAO Hong, LING Xing. Macro and micro analysis of effect of ballast fouling on dynamic characteristics of ballast bed[J]. Journal of the China Railway Society, 2022, 44(9): 120-127. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8360.2022.09.016 [7] 陈宪麦, 陈楠, 王日吉, 等. 粗、细粒径煤质对道砟颗粒剪切性能的影响[J]. 中南大学学报(自然科学版), 2022, 53(7): 2789-2797. doi: 10.11817/j.issn.1672-7207.2022.07.035CHEN Xianmai, CHEN Nan, WANG Riji, et al. Influence of coarse and fine coal quality on shear performance of ballast particles[J]. Journal of Central South University (Science and Technology), 2022, 53(7): 2789-2797. doi: 10.11817/j.issn.1672-7207.2022.07.035 [8] 周陶勇, 夏建军, 许平. 道砟颗粒二维廓形对破碎的影响研究[J]. 公路交通科技, 2022, 39(11): 56-61. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-0268.2022.11.008ZHOU Taoyong, XIA Jianjun, XU Ping. Study on influence of railway ballast 2D profile on crushing[J]. Journal of Highway and Transportation Research and Development, 2022, 39(11): 56-61. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-0268.2022.11.008 [9] MISHRA D, NAZIUR MAHMUD S M. Effect of particle size and shape characteristics on ballast shear strength: a numerical study using the direct shear test[C]//2017 Joint Rail Conference. Philadelphia: [s. n.], 2017. [10] JING G Q, JI Y M, QIANG W L, et al. Experimental and numerical study on ballast flakiness and elongation index by direct shear test[J]. International Journal of Geomechanics, 2020, 20(10): 04020169. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)GM.1943-5622.0001791 [11] ZHENG S F, LIU Y, ZHANG N, et al. Experimental studies on shape and size effects on particle breakage of railway ballast[J]. Transportation Geotechnics, 2022, 37: 100883. doi: 10.1016/j.trgeo.2022.100883 [12] JENSEN R P, EDIL T B, BOSSCHER P J, et al. Effect of particle shape on interface behavior of DEM-simulated granular materials[J]. International Journal of Geomechanics, 2001, 1(1): 1-19. [13] RAO C. Development of three-dimensional image analysis techniques to determine shape and size properties of coarse aggregate[M]. Champaign: University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, 2001. [14] SHI C, FAN Z, CONNOLLY D P, et al. Railway ballast performance: recent advances in the understanding of geometry, distribution and degradation[J]. Transportation Geotechnics, 2023, 41: 101042. [15] 高睿, 石知政, 刘洋泽鹏, 等. 土工格栅对受污道砟直剪特性影响的试验研究[J]. 西南交通大学学报, 2021, 56(6): 1185-1191.GAO Rui, SHI Zhizheng, LIU Yangzepeng, et al. Experimental study on effect of geogrid on direct shear behavior of contaminated ballast[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2021, 56(6): 1185-1191. [16] INDRARATNA B, WIJEWARDENA L S S, BALASUBRAMANIAM A S. Large-scale triaxial testing of grey wacke rockfill[J]. Géotechnique, 1993, 43(1): 37-51. [17] RAYMOND G P. Track and support rehabilitation for a mine company railroad[J]. Canadian Geotechnical Journal, 2000, 37(2): 318-332. doi: 10.1139/t99-108 [18] American Railway Engineering and Maintenance-of-Way Association AREMA. Manual for Railway Engineering[S]. AREMA: Lutherville, 2023. [19] 中华人民共和国铁道部. 铁路碎石道砟: TB/T 2140—2008[S]. 北京: 中国铁道出版社, 2008. [20] 井国庆, 强伟乐, 常锦秀, 等. 针片状指数对道砟直剪力学特性的影响[J]. 西南交通大学学报, 2020, 55(4): 688-694. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.20180677JING Guoqing, QIANG Weile, CHANG Jinxiu, et al. Effect of flakiness-elongation index on shear behavior of railway ballast[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2020, 55(4): 688-694. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.20180677 [21] ASADZADEH M, SOROUSH A. Direct shear testing on a rockfill material[J]. Arabian Journal for Science and Engineering, 2009, 34(2): 379-396. [22] 井国庆, 黄红梅, 常锦秀, 等. 清洗后的劣化道砟直剪力学特性分析[J]. 西南交通大学学报, 2017, 52(6): 1055-1060.JING Guoqing, HUANG Hongmei, CHANG Jinxiu, et al. Analysis of mechanical characteristics of degradation railway ballast by direct shear test[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2017, 52(6): 1055-1060. [23] INDRARATNA B, IONESCU D, CHRISTIE H D. Shear behavior of railway ballast based on large-scale triaxial tests[J]. Journal of Geotechnical and Geoenvironmental Engineering, 1998, 124(5): 439-449. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)1090-0241(1998)124:5(439) [24] SUSSMANN T R, RUEL M, CHRISMER S M. Source of ballast fouling and influence considerations for condition assessment criteria[J]. Transportation Research Record: Journal of the Transportation Research Board, 2012, 2289(1): 87-94. doi: 10.3141/2289-12 -





 下载:
下载: