Individualized Optimal Shift Schedule for Single-Shaft Parallel Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicles
-
摘要:
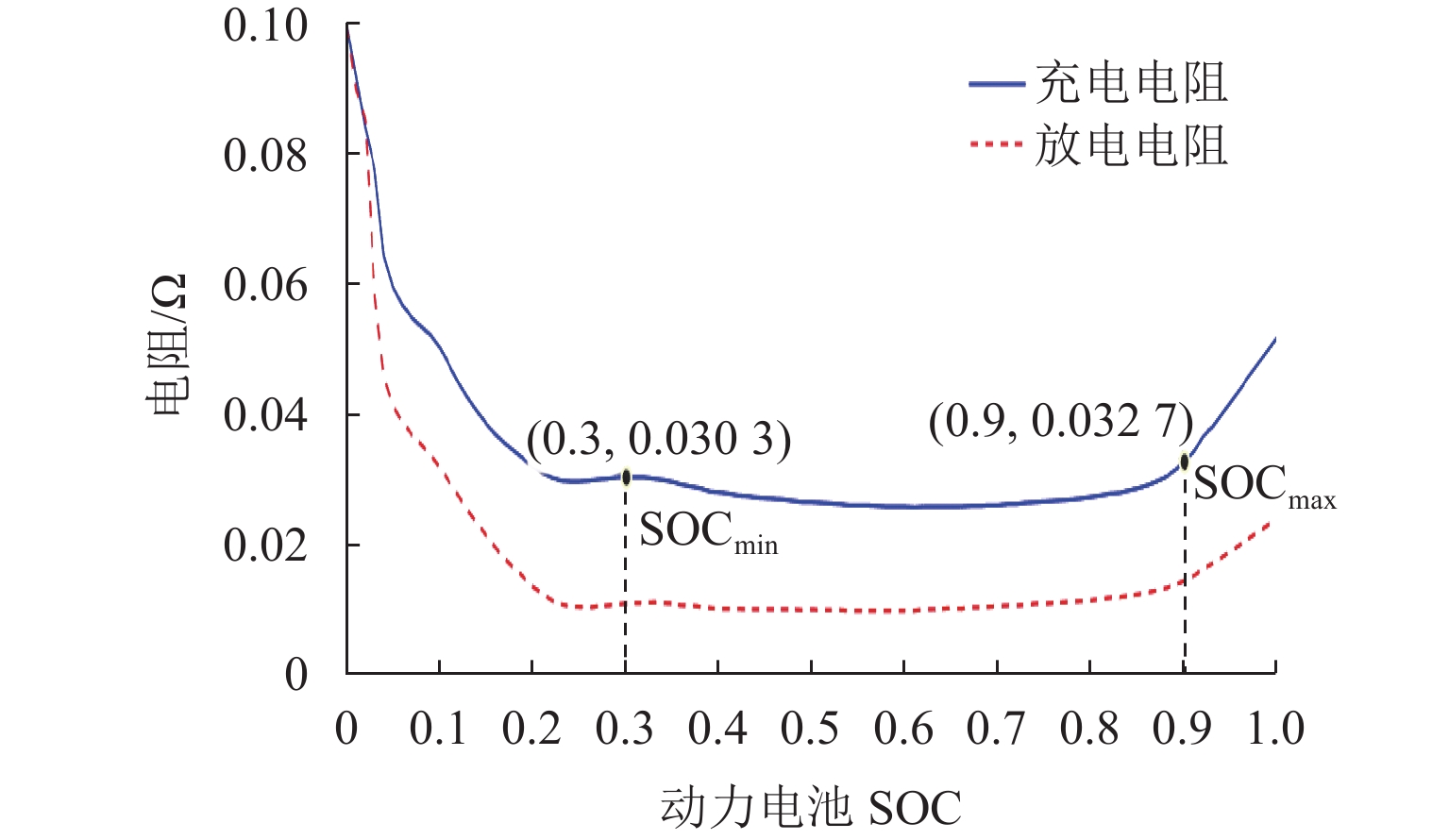
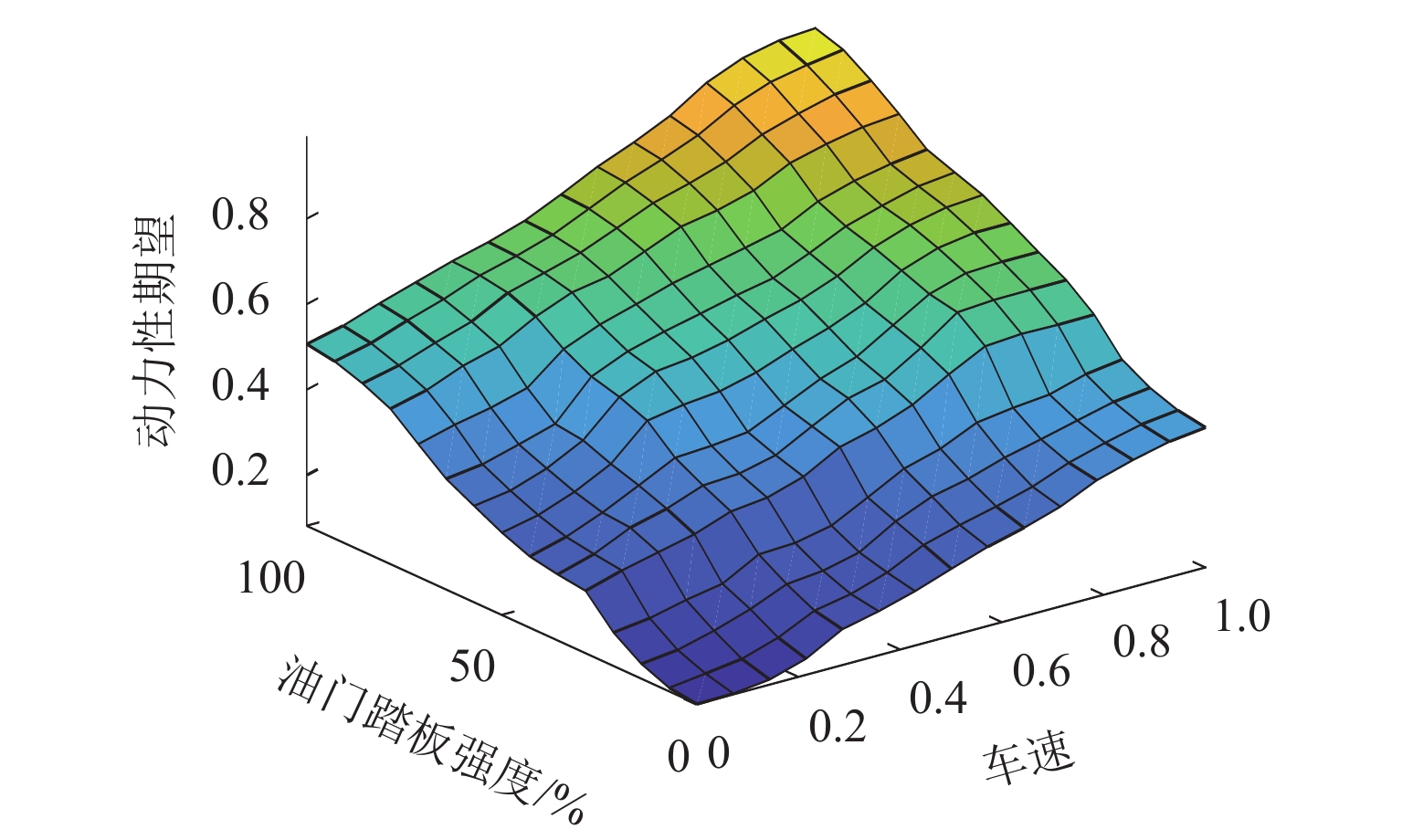
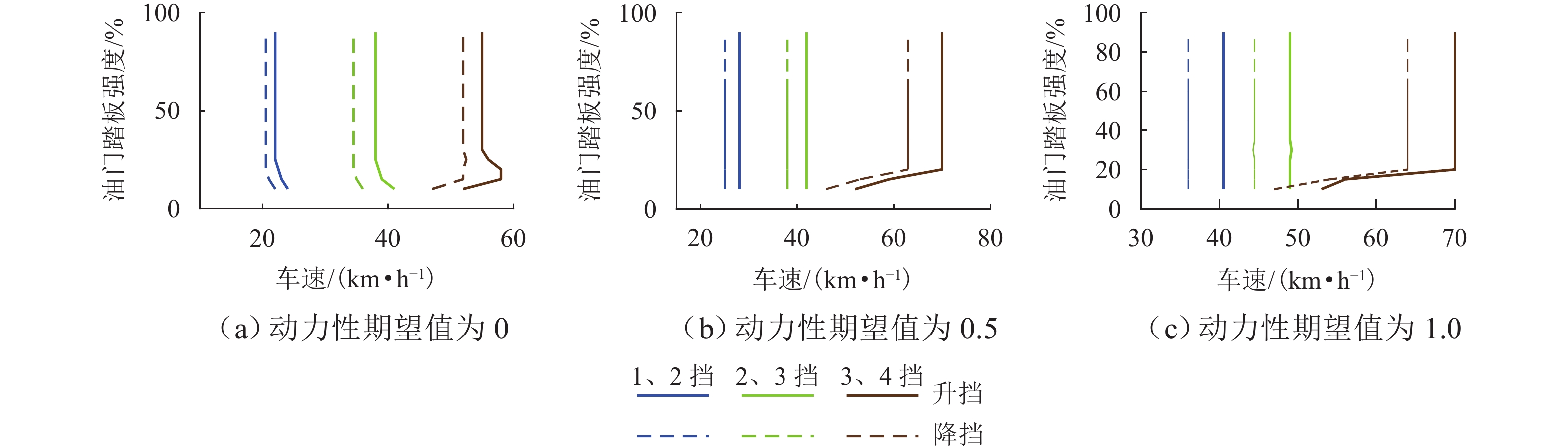
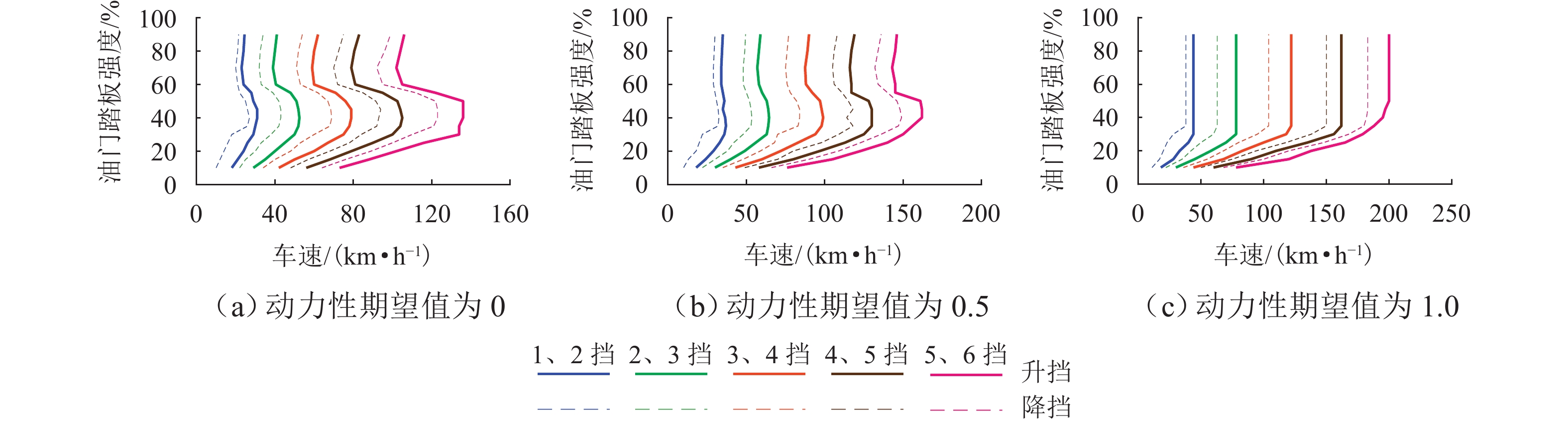
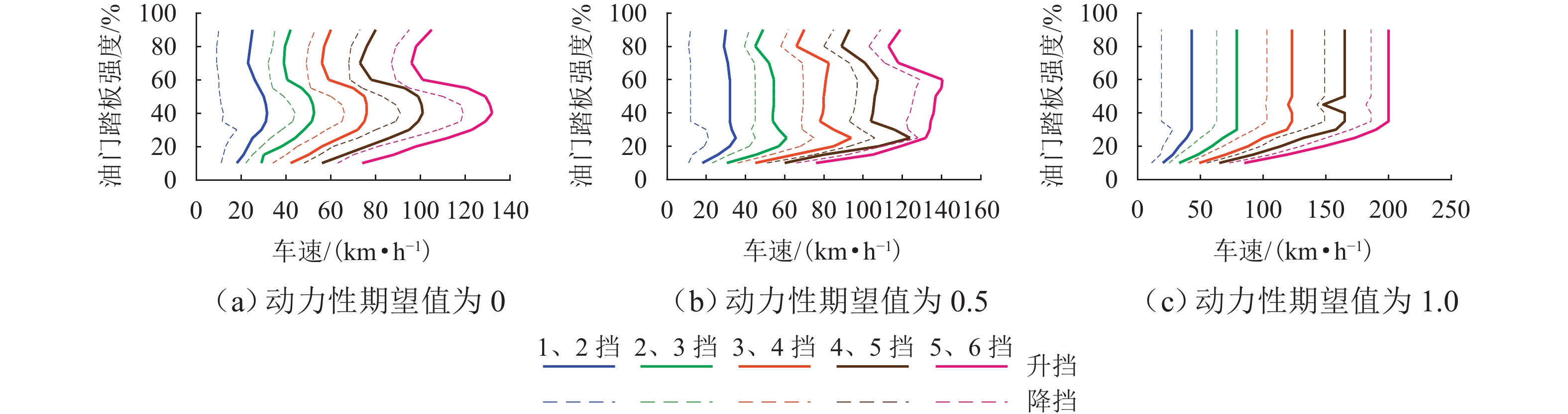
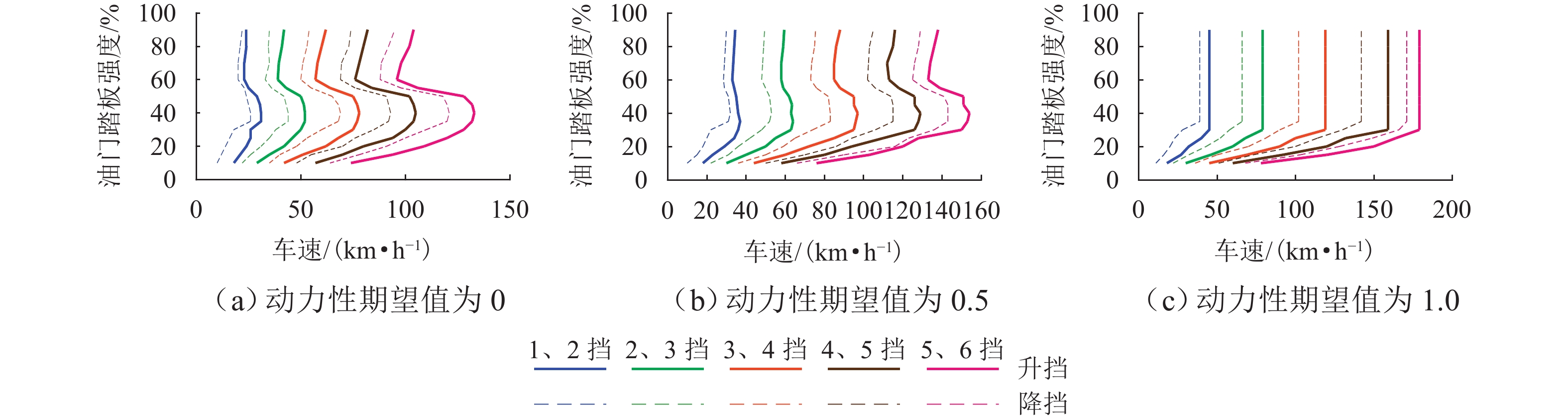
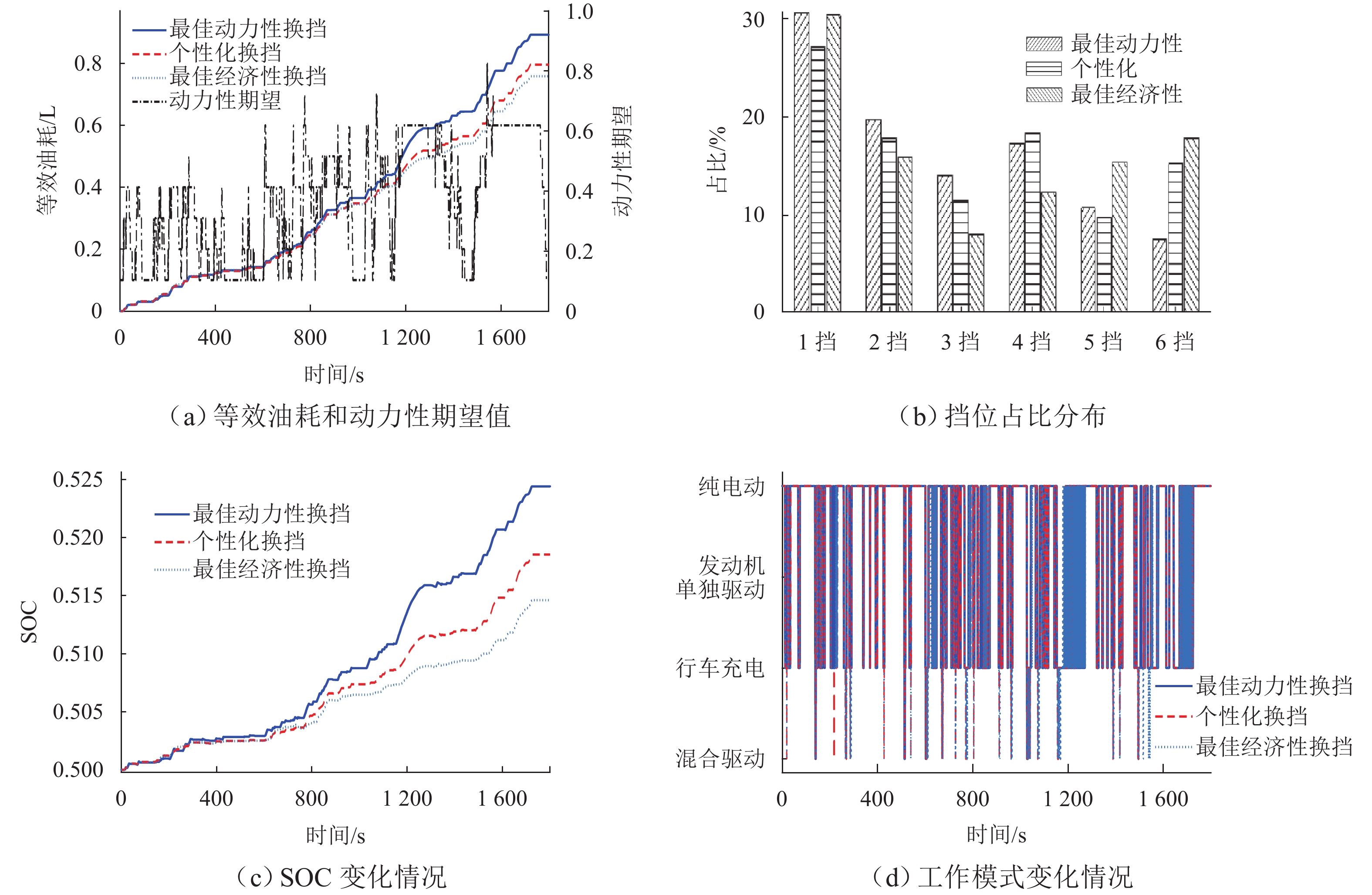
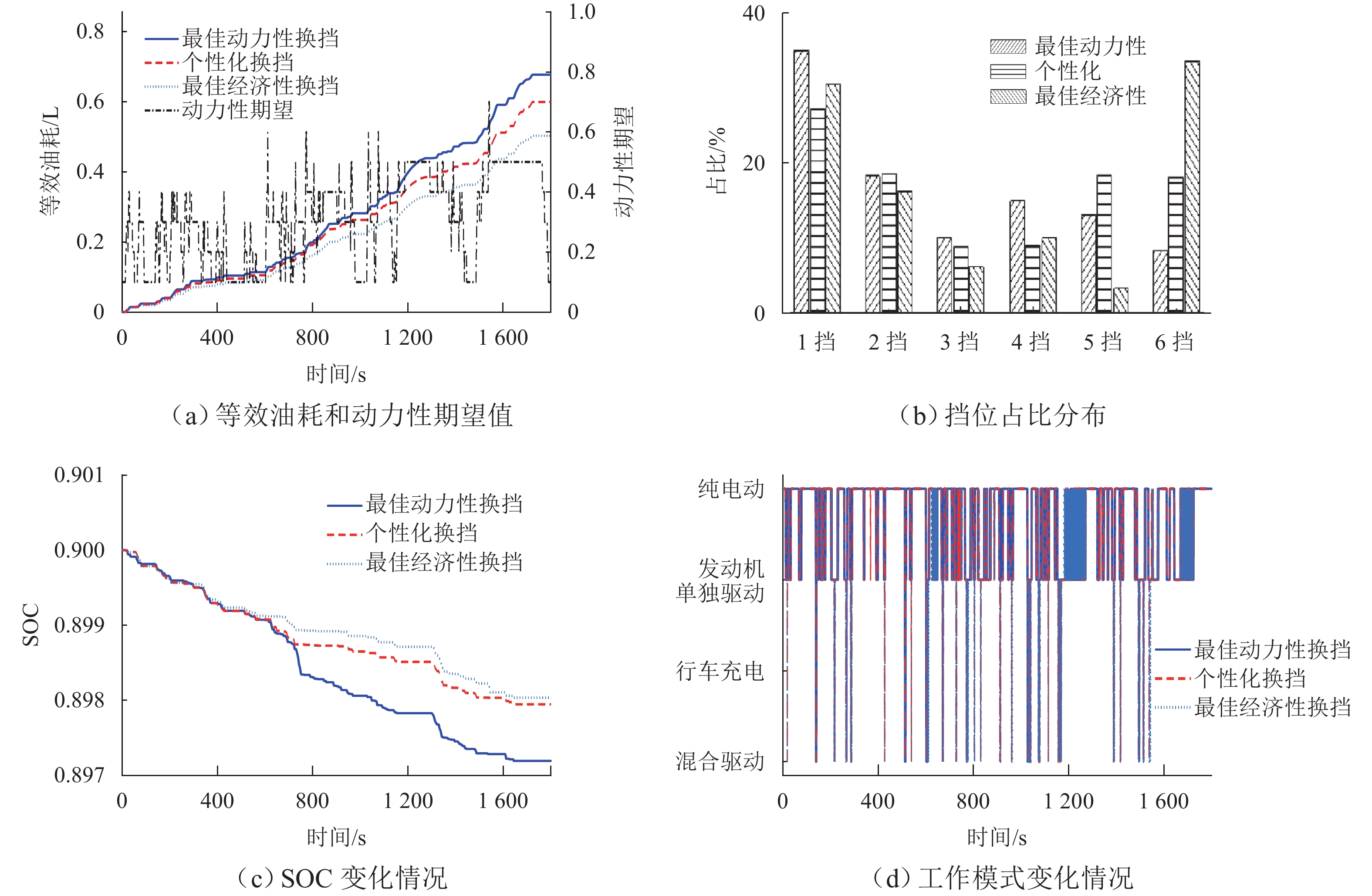
为实现插电式混合动力汽车(PHEV)个性化综合性能最优,针对单轴并联PHEV,提出了一种体现驾驶意图的动力性和经济性综合最优换挡规律优化方法. 首先,根据需求转矩、发动机特性曲线、动力电池荷电状态(SOC)确定不同工作模式之间的切换逻辑,并针对不同模式制定转矩分配策略;其次,采用模糊推理方法建立驾驶意图量化模型,以根据驾驶操作及车辆状态计算驾驶员的动力性和经济性期望值;然后,以不同驾驶意图对应的性能期望值作为动力性和经济性分目标函数的权值,采用线性加权法构造综合评价函数,分别对不同驾驶意图下的换挡规律进行优化;最后,使用MATLAB/Simulink软件搭建仿真模型,分别取SOC初始值为0.5和0.9,使用最佳动力性、最佳经济性和个性化最优换挡规律在世界轻型汽车测试循环工况下进行仿真. 结果表明:2种SOC初始条件下,个性化最优换挡规律在能体现驾驶意图的同时,其等效油耗比最佳动力性换挡规律明显降低,SOC初始值为0.5时,降幅为10.1%,SOC初始值为0.9时,降幅为11.8%;其等效油耗比最佳经济性换挡规律有所增加,SOC初始值为0.5时,增幅为5.3%,SOC初始值为0.9时,增幅为1.7%.
Abstract:To optimize the individualized comprehensive performance of plug-in hybrid electric vehicles (PHEVs), an optimization method for the shift schedule of single-shaft parallel PHEVs considering both dynamic and economic performance while reflecting the driving intention was proposed. Firstly, the switching logic among different operating modes was determined according to the demand torque, the engine characteristic curves, and the state of charge (SOC) of the power battery, and torque distribution strategies under different operating modes were formulated. Subsequently, a fuzzy inference method was used to establish a quantitative model for driving intention, which could calculate the driver’s expectations for dynamic and economic performance based on the driver’s operation and vehicle status. Then, by taking the driver’s expectations for dynamic and economic performance as the weights of corresponding sub-objective functions, a linear weighting method was used to construct a comprehensive performance evaluation function, thereby optimizing the shift schedules under different driving intentions. Finally, a simulation model was developed using MATLAB/Simulink, and simulations under the WLTC test cycle were conducted with initial SOC values of 0.5 and 0.9, respectively, using the optimal dynamic, optimal economic, and individualized optimal shift schedules. Simulation results show that under both SOC initial conditions, while reflecting the driving intention, the equivalent fuel consumption (EFC) of the individualized optimal shift schedules is reduced significantly compared to that of the optimal dynamic shift schedule, with reductions of 10.1% at an SOC of 0.5 and 11.8% at an SOC of 0.9. Meanwhile, the EFC of the individualized optimal shift schedules is increased compared to that of the optimal economic shift schedule, with increases of 5.3% at an SOC of 0.5 and 1.7% at an SOC of 0.9.
-
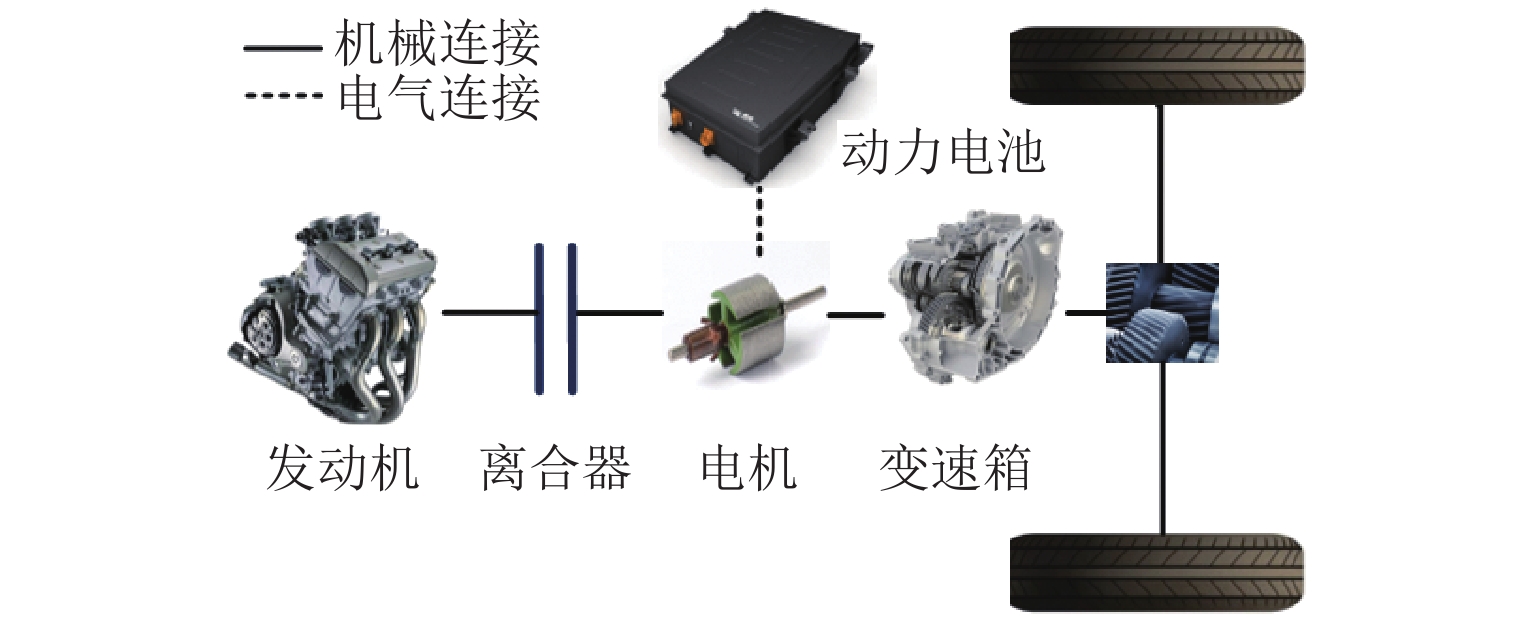
表 1 工作模式
Table 1. Operating modes
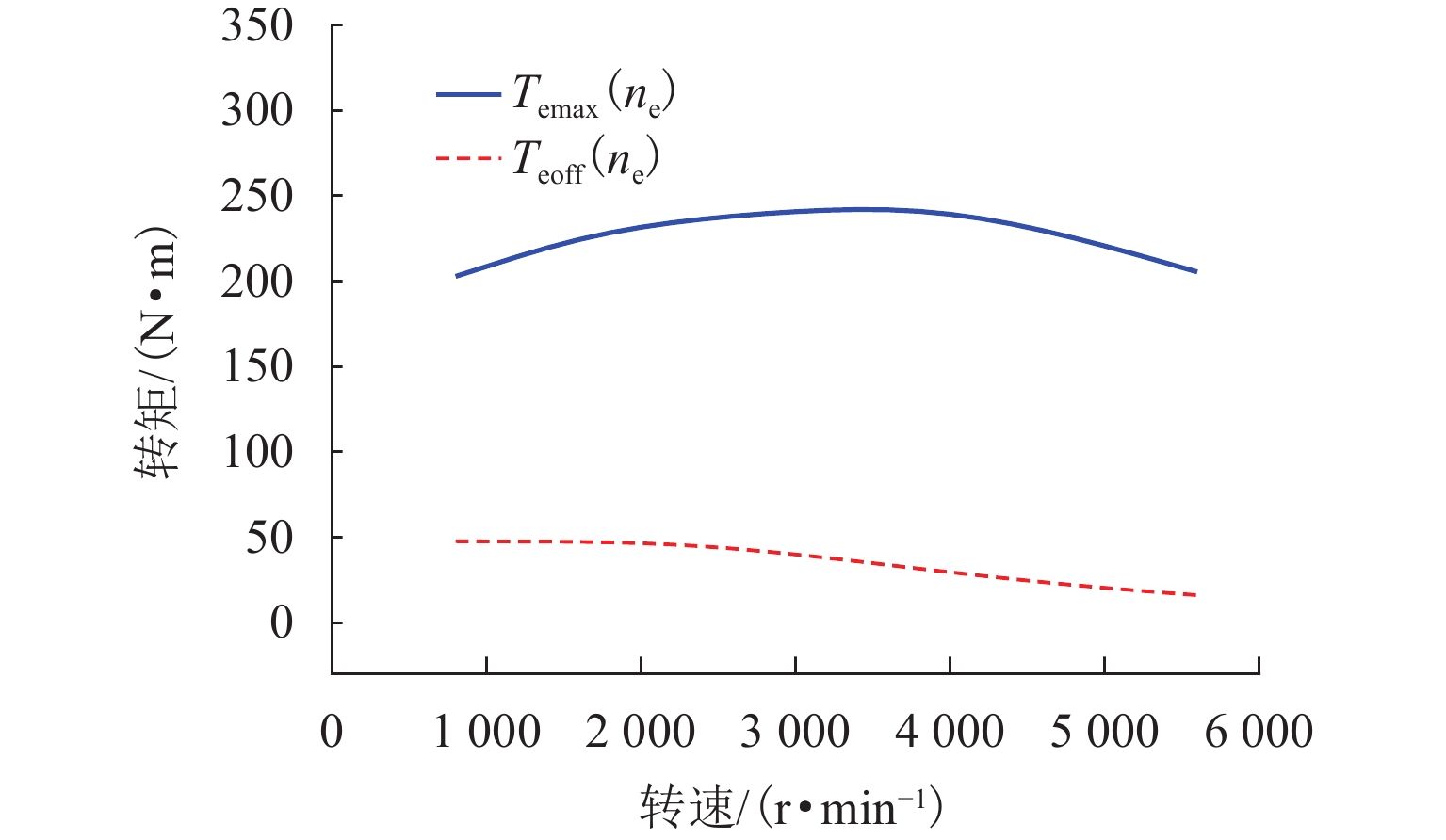
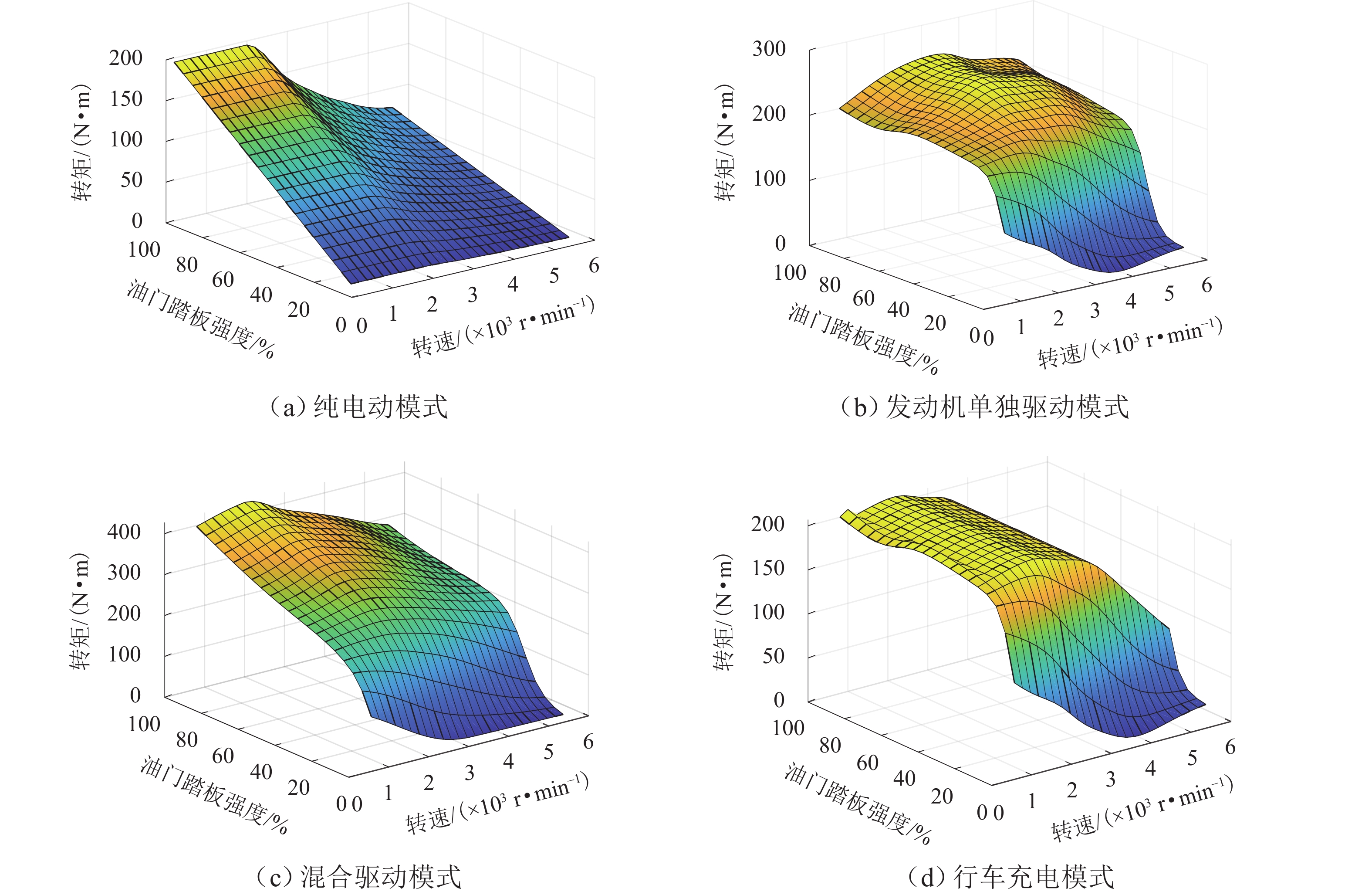
工作模式 离合器 发动机 电机 纯电动模式 分离 停机 驱动 发动机单独驱动 接合 工作 空转 混合驱动模式 接合 工作 驱动 行车充电模式 接合 工作 发电 表 2 PHEV各工作模式转矩分配
Table 2. Torque distribution for PHEVs in each operating mode
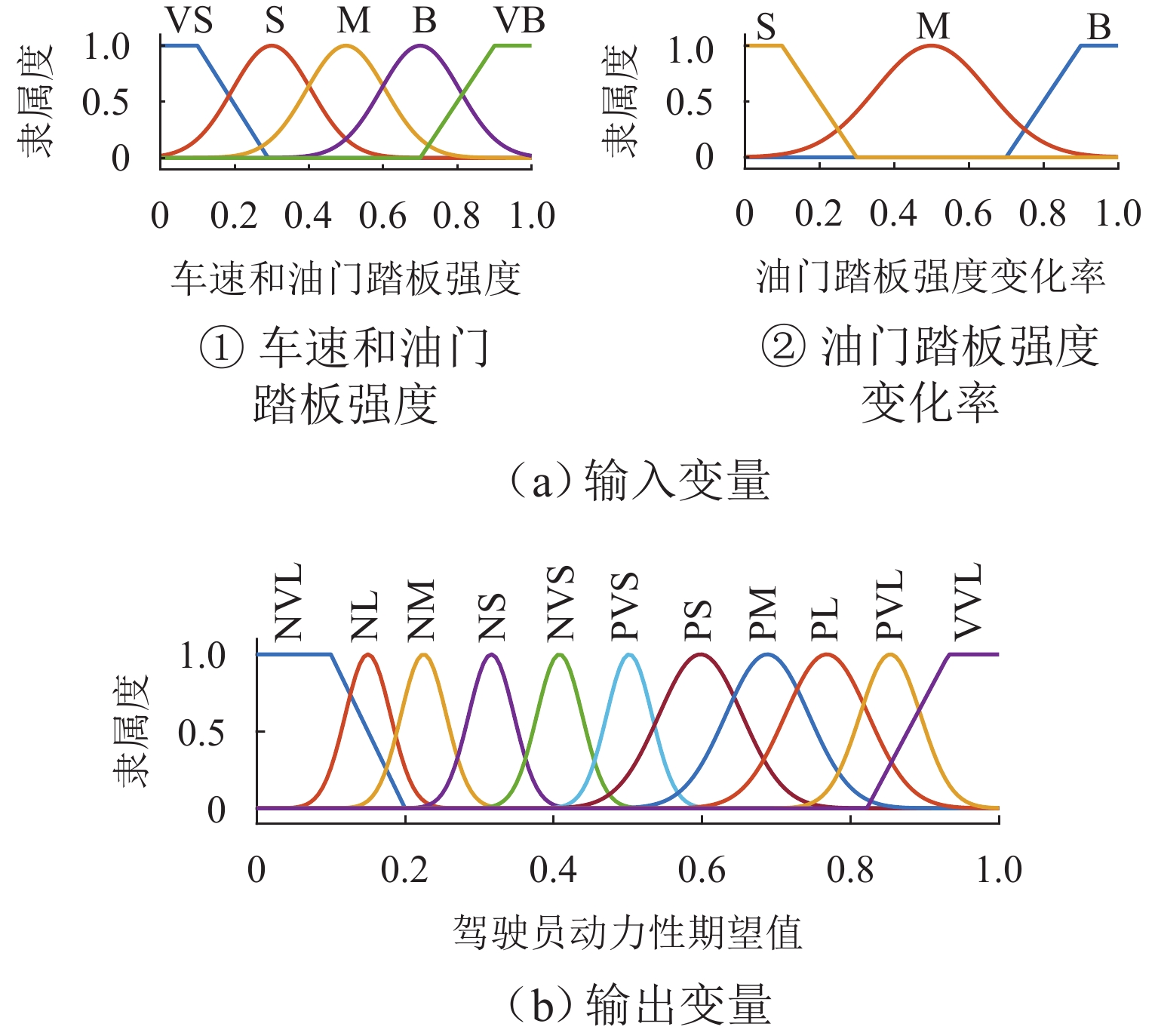
工作模式 转矩分配 纯电动模式 $ {T_{\text{m}}} = {T_{{\text{req}}}},{T_{\text{e}}} = 0 $ 发动机单独驱动 $ {T_{\text{m}}} = 0,{T_{\text{e}}} = {T_{{\text{req}}}} $ 混合驱动模式 $ {T_{\text{m}}} = {T_{{\text{req}}}} - {T_{{\text{emax}}}},{T_{\text{e}}} = {T_{{\text{emax}}}} $ 行车充电模式 $ {T_{\text{m}}} = {T_{{\text{req}}}} - {T_{{\text{emax}}}},{T_{\text{e}}} = {T_{{\text{emax}}}} $ 表 3 模糊规则
Table 3. Fuzzy rules
车速 油门踏板
强度油门踏板强度
变化率动力性
期望VS VS S NVL VS VS M NVL VS VS B NVL VS S S NL $\vdots $ $\vdots $ $\vdots $ $\vdots $ VB VB S PVL VB VB M VVL VB VB B VVL 表 4 整车及动力传动系统参数
Table 4. Vehicle and powertrain parameters
参数 数值 空气阻力系数 0.306 迎风面积/m2 1.937 整车装备质量/kg 2150 电机转动惯量/(kg•m2) 0.34 变速器速比 4.55、2.77、1.85、
1.33、1.02、0.84主减速器速比 2.885 机械传动效率 0.96 车轮转动惯量/(kg•m2) 1.15 -
[1] 解少博, 张康康, 张乾坤, 等. 考虑电池电-热-放电深度的并联PHEV能量管理策略研究[J]. 汽车工程, 2021, 43(6): 791-798, 832.XIE Shaobo, ZHANG Kangkang, ZHANG Qiankun, et al. Study on energy management strategy for parallel plug-in hybrid electric vehicles considering battery electric-thermal-depth-of-discharge[J]. Automotive Engineering, 2021, 43(6): 791-798, 832. [2] 刘阳, 李磊, 阴晓峰. 驾驶意图识别技术研究现状及其在智能网联汽车中的应用展望[C]//2019中国汽车工程学会年会论文集(1). 上海: [出版者不详], 2019: 42-45. [3] 秦大同, 龙海威, 胡明辉, 等. AMT中度混合动力汽车经济性换挡规律研究[J]. 中国机械工程, 2013, 24(20): 2820-2825. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-132X.2013.20.022QIN Datong, LONG Haiwei, HU Minghui, et al. Economic shift rule for medium HEV with AMT[J]. China Mechanical Engineering, 2013, 24(20): 2820-2825. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-132X.2013.20.022 [4] 何仁, 徐益强. 并联混合动力汽车混合驱动模式的换挡规律[J]. 江苏大学学报(自然科学版), 2016, 37(6): 657-662. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-7775.2016.06.007HE Ren, XU Yiqiang. Shift schedule of parallel hybrid electric vehicles under hybrid driving mode[J]. Journal of Jiangsu University (Natural Science Edition), 2016, 37(6): 657-662. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-7775.2016.06.007 [5] 何洪文, 韩陌, 曹剑飞, 等. 双电机两挡驱动系统协同控制策略研究[J]. 重庆理工大学学报(自然科学), 2021, 35(2): 81-89.HE Hongwen, HAN Mo, CAO Jianfei, et al. Research on synergistic control strategy of dual-motor two-speed driving system[J]. Journal of Chongqing University of Technology (Natural Science), 2021, 35(2): 81-89. [6] 吴进军, 颜丙杰, 方继根, 等. 插电式混合动力汽车的次优能量管理策略[J]. 中国机械工程, 2019, 30(11): 1336-1342. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-132X.2019.11.011WU Jinjun, YAN Bingjie, FANG Jigen, et al. Sub-optimal energy management strategy for plug-in hybrid electric vehicles[J]. China Mechanical Engineering, 2019, 30(11): 1336-1342. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-132X.2019.11.011 [7] SHI Y M, CUI N X, DU Y. Energy management strategy based on driving style recognition for plug-in hybrid electric bus[C]//2020 39th Chinese Control Conference (CCC). Shenyang: IEEE, 2020: 5511-5516. [8] LIU S W, ZHENG K, ZHAO L, et al. A driving intention prediction method based on hidden Markov model for autonomous driving[J]. Computer Communications, 2020, 157: 143-149. doi: 10.1016/j.comcom.2020.04.021 [9] MAHAJAN V, KATRAKAZAS C, ANTONIOU C. Prediction of lane-changing maneuvers with automatic labeling and deep learning[J]. Transportation Research Record, 2020, 2674(7): 336-347. doi: 10.1177/0361198120922210 [10] 张利鹏, 贾启康, 刘威, 等. 基于驾驶意图识别的多模耦合驱动系统能量管理[J]. 机械工程学报, 2019, 55(18): 112-124. doi: 10.3901/JME.2019.18.112ZHANG Lipeng, JIA Qikang, LIU Wei, et al. Energy management of multi-mode coupling drive system based on driver intention recognition[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2019, 55(18): 112-124. doi: 10.3901/JME.2019.18.112 [11] LIN X Y, LI K L, WANG L M. A driving-style-oriented adaptive control strategy based PSO-fuzzy expert algorithm for a plug-in hybrid electric vehicle[J]. Expert Systems with Applications, 2022, 201: 117236.1-117236.20. [12] 刘海江, 苏博炜. 基于GM-HMM的DCT车辆驾驶员起步意图辨识研究[J]. 汽车技术, 2020(1): 19-24.LIU Haijiang, SU Bowei. Research on identification of DCT vehicle driver’s starting intention based on GM-HMM[J]. Automobile Technology, 2020(1): 19-24. [13] 张超. 驾驶员起步意图识别方法研究[D]. 银川: 宁夏大学, 2019. [14] YIN X, ZHANG L, CHEN X, et al. Identification of driver's intention for gearshift rules optimization for stepped automatic transmissions[C]//FISITA 2016 World Automotive Congress. Busan: [s.n.], 2016. [15] 刘桓龙. 电液混合动力系统关键技术及能量管理研究综述[J]. 西南交通大学学报, 2024, 59(3): 600-614. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.20211011LIU Huanlong. Summary of research on key technologies and energy management of electro-hydraulic hybrid powertrain[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2024, 59(3): 600-614. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.20211011 [16] 李海波. 插电式混合动力汽车个性化换挡规律研究[D]. 成都: 西华大学, 2021. [17] 罗勇, 褚清国, 隋毅, 等. P0 + P3构型插电式混合动力汽车能量管理策略[J]. 车用发动机, 2023(3): 73-81. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-2222.2023.03.012LUO Yong, CHU Qingguo, SUI Yi, et al. Energy management strategy for P0 + P3 plug-In hybrid electric vehicle[J]. Vehicle Engine, 2023(3): 73-81. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-2222.2023.03.012 [18] 陈维荣, 燕雨, 李奇. 基于状态机的燃料电池混合动力系统控制策略[J]. 西南交通大学学报, 2019, 54(4): 663-670, 660. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.20170279CHEN Weirong, YAN Yu, LI Qi. Control strategy based on state machine for fuel cell hybrid power system[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2019, 54(4): 663-670, 660. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.20170279 [19] 刘阳. 汽车自动变速器个性化换挡规律优化方法研究[D]. 成都: 西华大学, 2020. [20] 谢济铭, 夏玉兰, 秦雅琴, 等. 基于双向长短期记忆网络的城市快速路合流区车速预测[J]. 西南交通大学学报, 2024, 59(5): 1235-1244. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.20220005XIE Jiming, XIA Yulan, QIN Yaqin, et al. Traffic speed prediction in merging zone of urban expressway based on bidirectional long short-term memory network[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2024, 59(5): 1235-1244. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.20220005 [21] 骆光炬, 邓晓亭, 鲁植雄, 等. 发动机管理策略对增程式电动车燃油经济性的影响研究[J]. 内燃机工程, 2020, 41(4): 79-86.LUO Guangju, DENG Xiaoting, LU Zhixiong, et al. Research on influence of engine management strategy on fuel economy of extended-range electric vehicle[J]. Chinese Internal Combustion Engine Engineering, 2020, 41(4): 79-86. [22] 李奇, 孟翔, 陈维荣, 等. 燃料电池混合动力系统参数匹配与多目标优化[J]. 西南交通大学学报, 2019, 54(5): 1079-1086. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.20170117LI Qi, MENG Xiang, CHEN Weirong, et al. Parameter matching and multi-objective optimization of fuel cell hybrid system[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2019, 54(5): 1079-1086. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.20170117 [23] Society of Automotive Engineers. Recommended practice for measuring the exhaust emissions and fuel economy of hybrid electric vehicles: SAE_J1711_JUN2010[S]. Warrendale: Society of Automotive Engineers, 2010. [24] 赵乃刚. 自适应多种群粒子群算法及其应用分析[J]. 山西大同大学学报(自然科学版), 2024, 40(6): 36-40. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-0874.2024.06.008ZHAO Naigang. Analysis of adaptive multi swarm particle swarm optimization algorithm and its applications[J]. Journal of Shanxi Datong University (Natural Science Edition), 2024, 40(6): 36-40. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-0874.2024.06.008 [25] 张金红. 混联式PHEV个性化能量管理及挡位决策联合优化方法研究[D]. 成都: 西华大学, 2023. [26] 杨镇瑜, 韩胜明, 陈桥松, 等. 纯电动汽车PMSM+AMT换挡控制策略[J]. 西华大学学报(自然科学版), 2023, 42(5): 1-10.YANG Zhenyu, HAN Shengming, CHEN Qiaosong, et al. Shift control strategy for PMSM+AMT of pure electric vehicle[J]. Journal of Xihua University (Natural Science Edition), 2023, 42(5): 1-10. -




 下载:
下载: