Sliding Mode Active Disturbance Rejection Control Method for Heavy-Haul Trains During Operation
-
摘要:
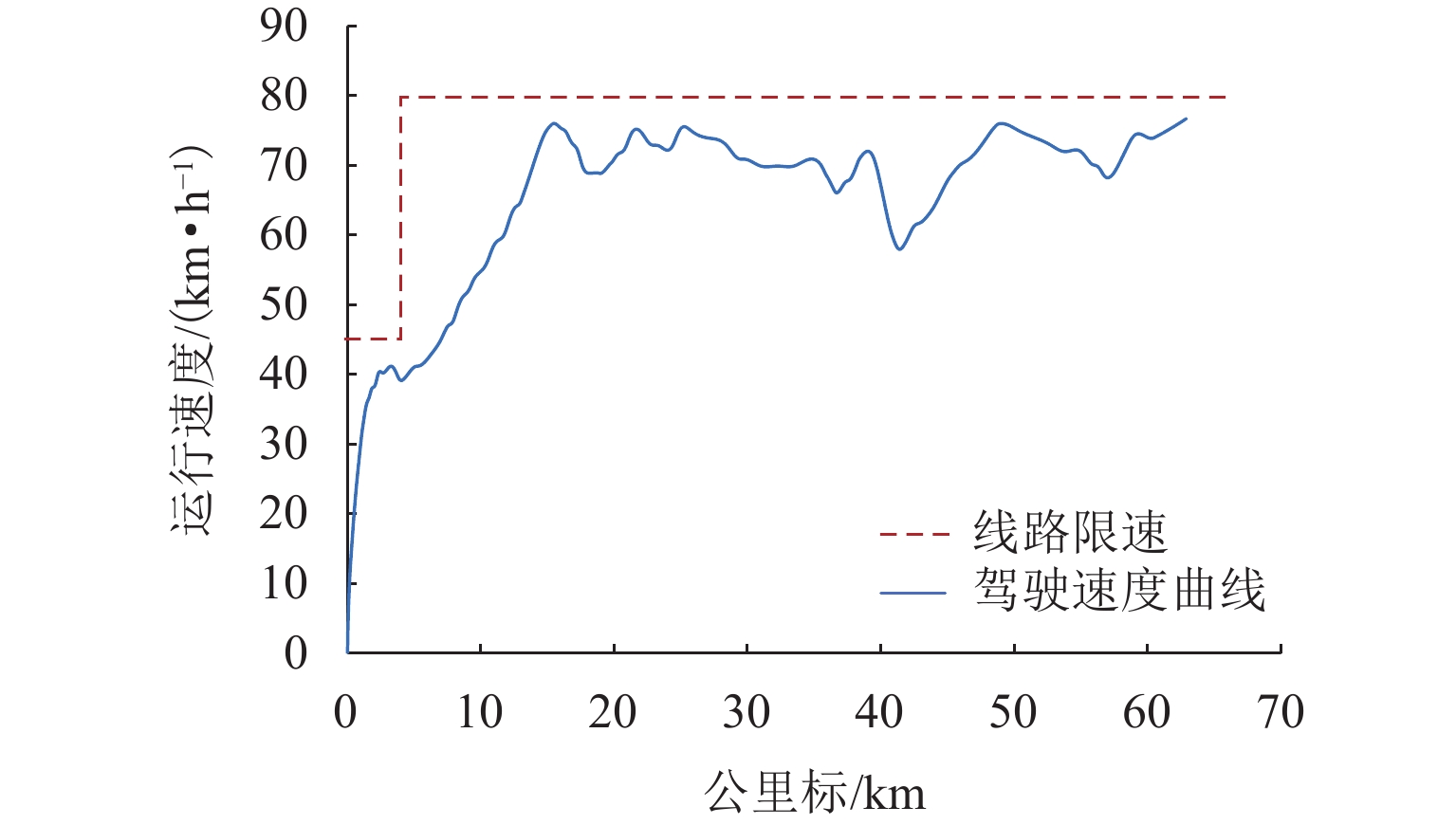
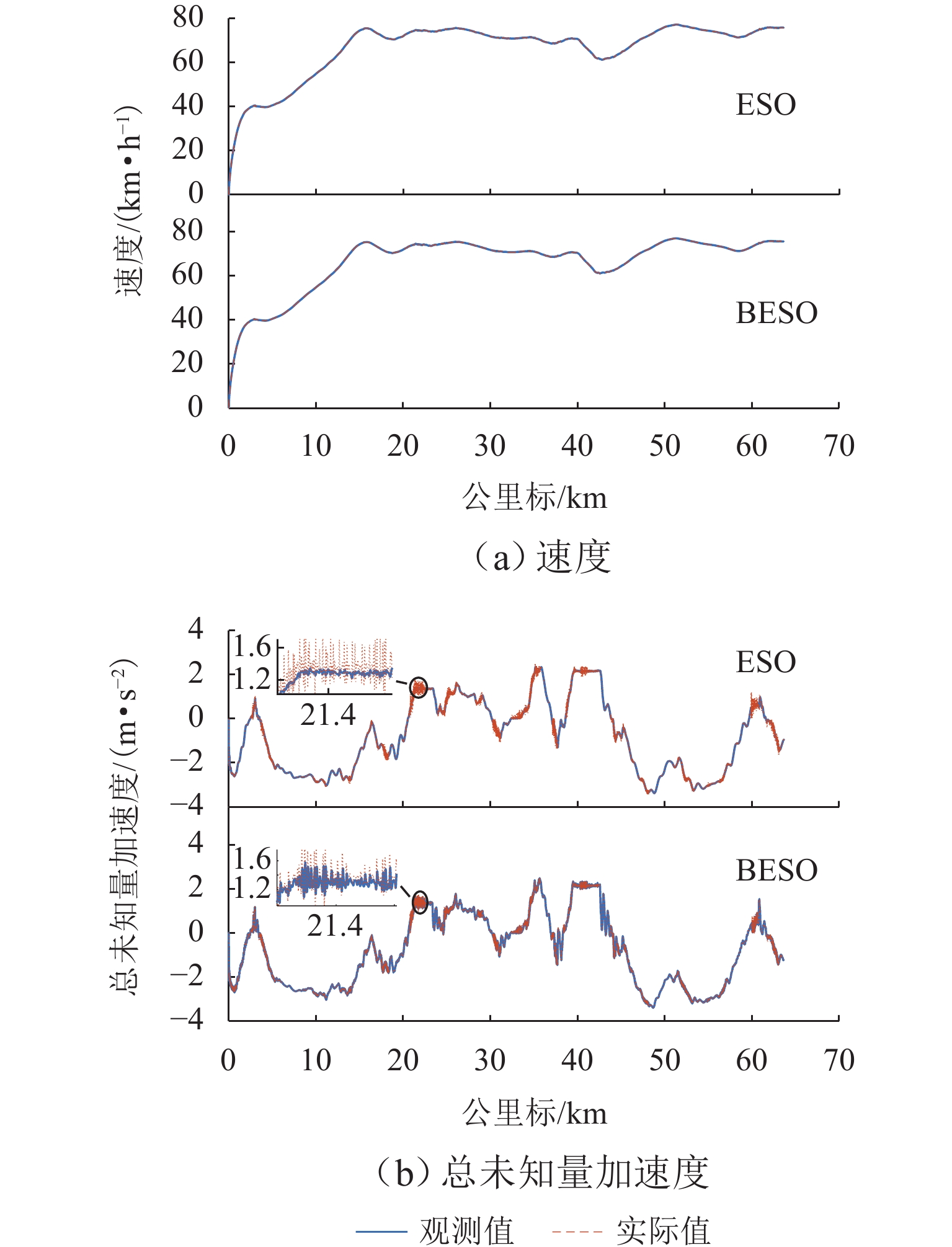
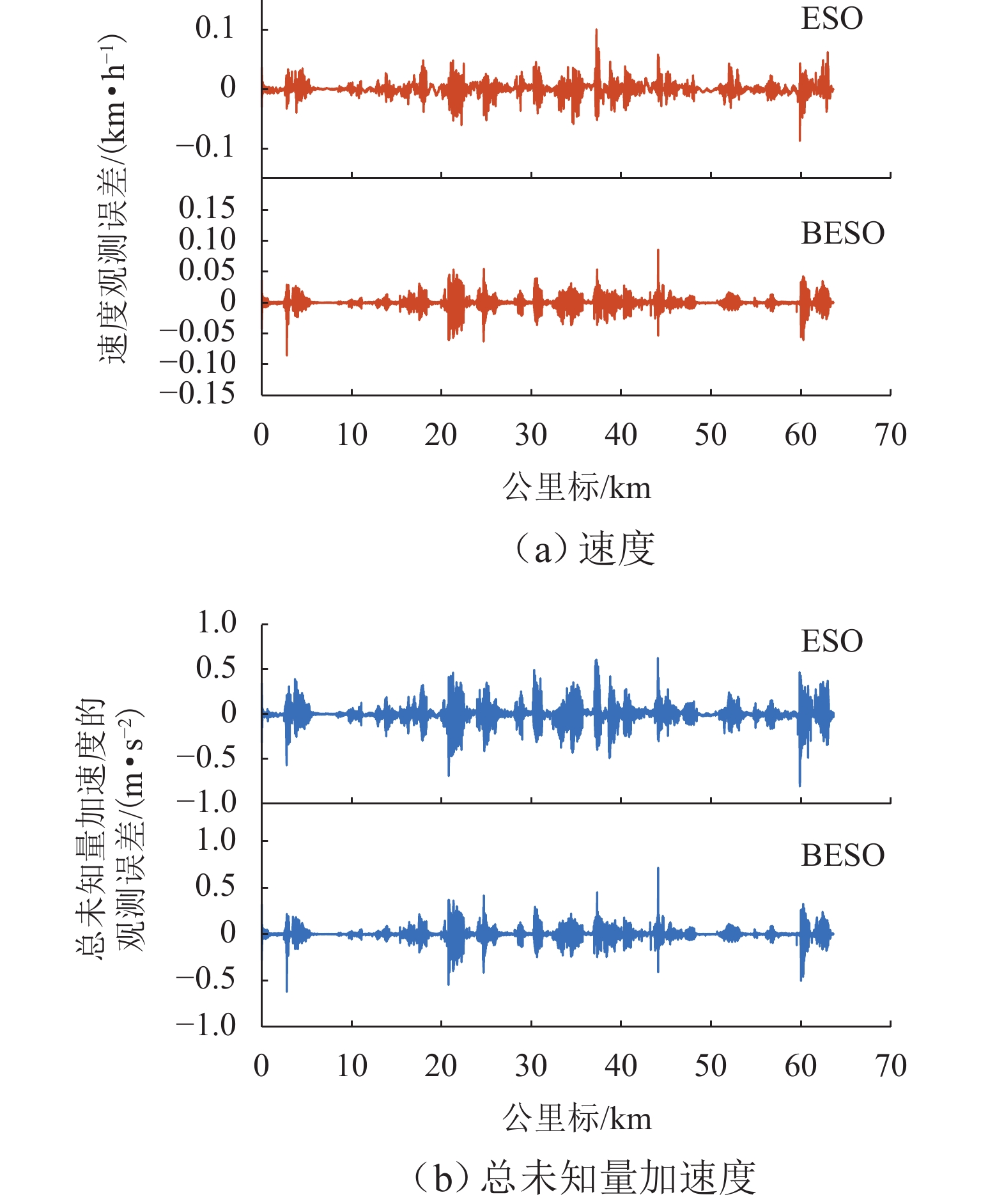
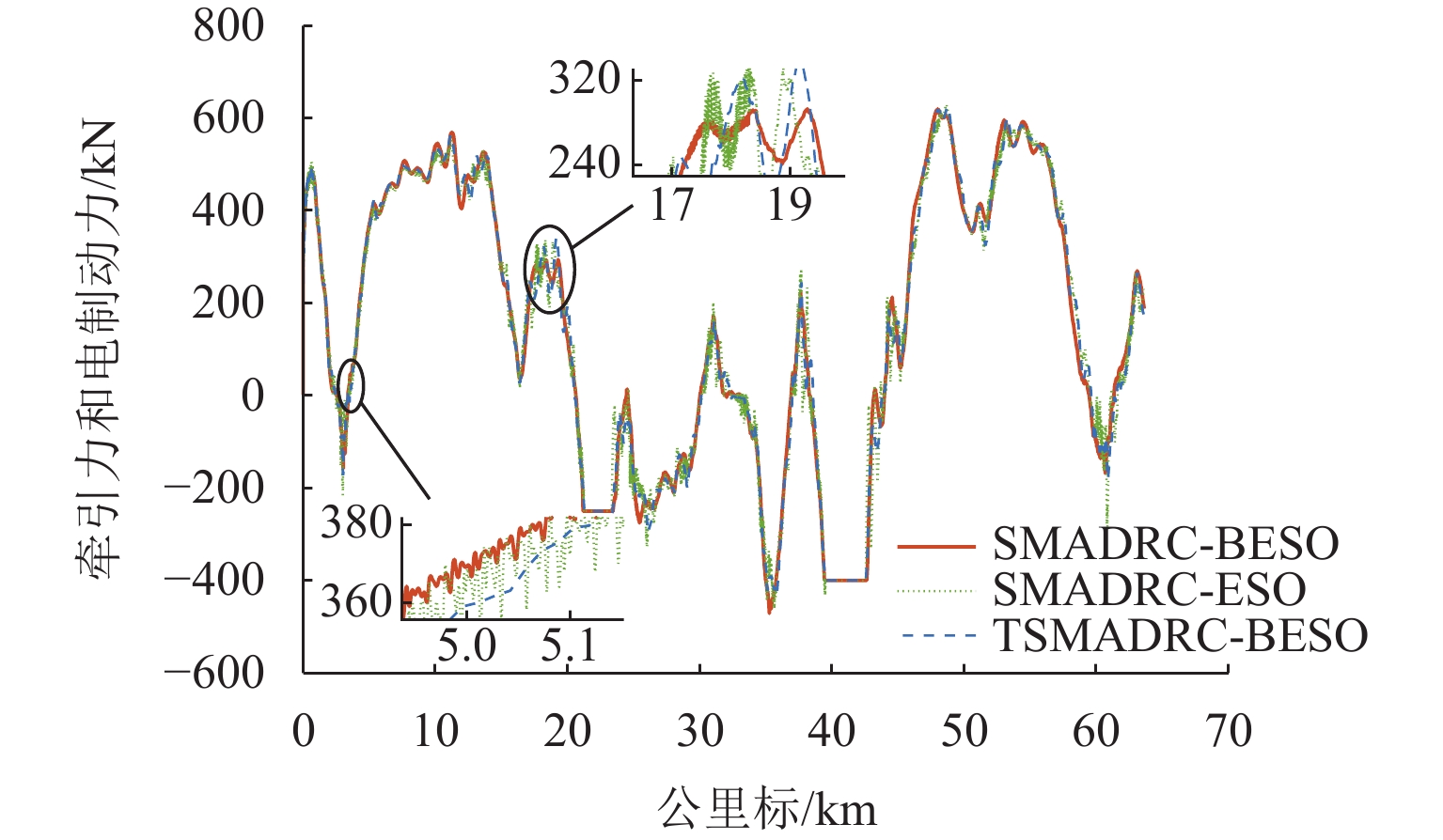
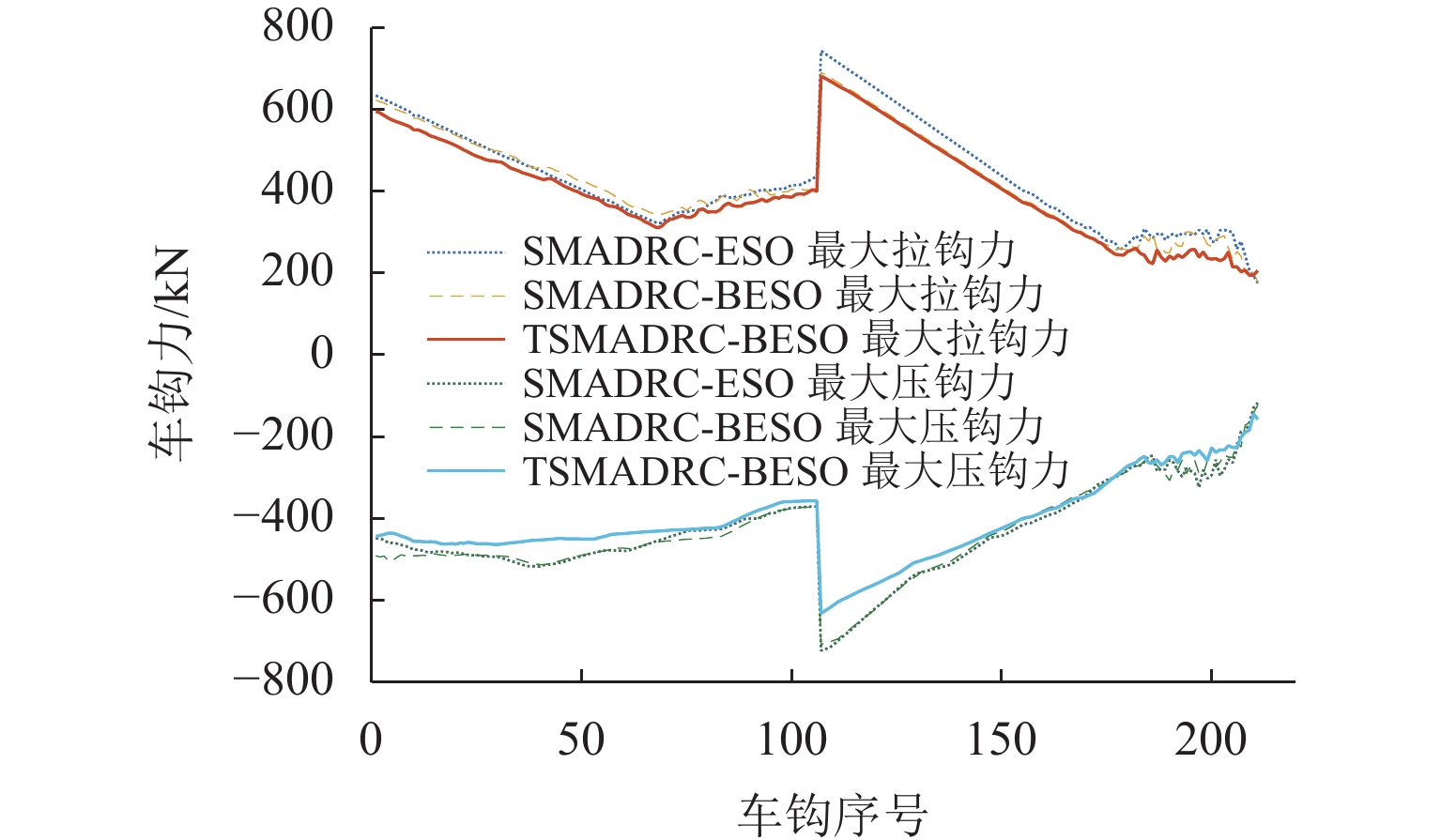
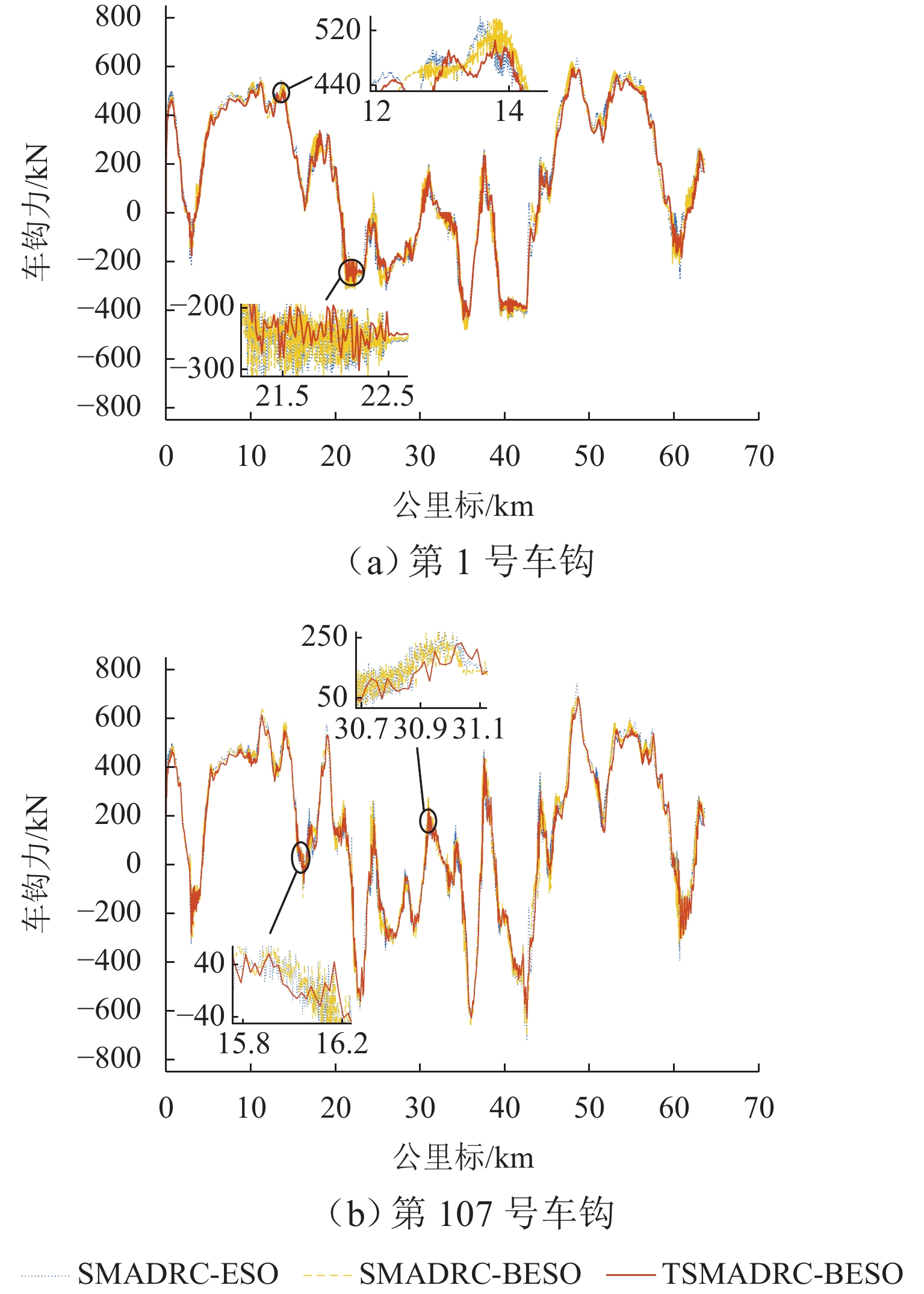
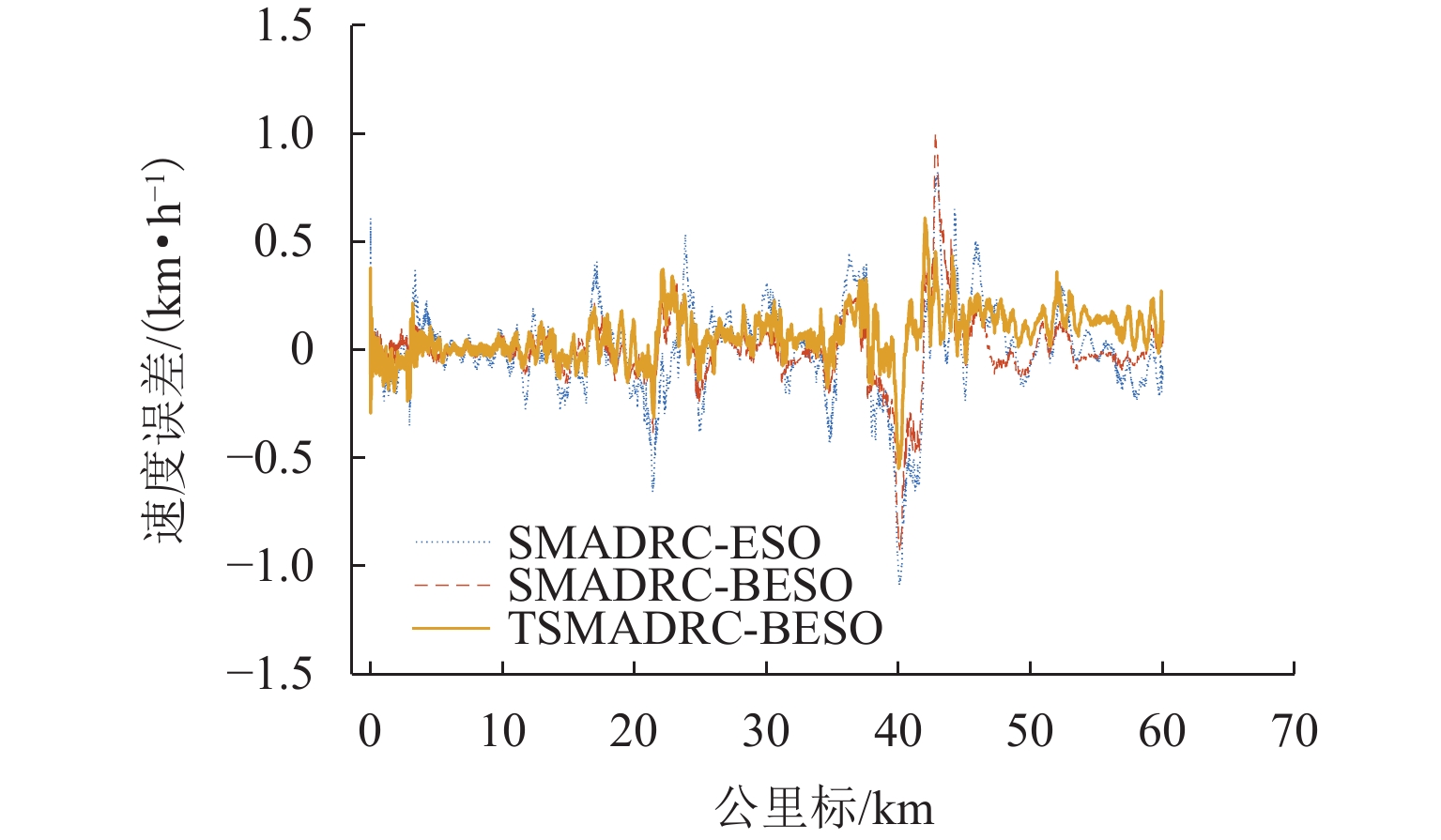
为解决重载列车在复杂环境中运行时易因司机经验不足而导致控车难的问题,基于大秦线Locotrol同步控制原理,建立多机牵引的重载列车多质点动力学模型;针对主控机车设计控制器,将主控机车受到的车钩力、运行阻力及外界干扰等时变量的总和视为总未知量,同时,将总未知量的加速度作为扩张状态设计扩张状态观测器,对其进行实时估计与补偿;引入快速终端滑模控制对自抗扰控制中的非线性误差反馈控制率进行改进,并利用改进的自适应趋近率调节滑模趋近运动的动态品质;以编组形式为“1 + 105 + 1 + 105 + 可控列尾”的重载列车为例,结合大秦线的实际线路数据和金牌司机的驾驶经验进行仿真分析,并与传统方法进行比较. 仿真结果表明:与传统滑模自抗扰控制方法相比,所提控制方法主从控机车的控制力抖振现象降低23.7%,跟踪精度提升19%,跟踪误差可被限定在(−0.7,0.7) km/h.
-
关键词:
- 快速终端滑模自抗扰控制 /
- 重载列车 /
- 速度跟踪 /
- 自适应趋近率 /
- 大秦线
Abstract:To resolve the difficulty in controlling heavy-haul trains operating in complex environments caused by insufficient driver experience, a multi-mass dynamic model for multi-locomotive traction was established based on the Locotrol synchronous control principle of the Datong–Qinhuangdao Railway. A controller was designed for the main locomotive, where the total time-varying unknowns, including coupler forces, running resistance, and external disturbances, were regarded as aggregated uncertainties. The acceleration of these uncertainties was further treated as an extended state, enabling real-time estimation and compensation via an extended state observer. Moreover, the fast terminal sliding mode control was introduced to improve the nonlinear error feedback control law in active disturbance rejection control, and an improved adaptive reaching law was employed to refine the dynamic quality of the sliding mode reaching motion. Simulations were conducted on a heavy-haul train with the formation of “1 + 105 + 1 + 105 + controllable end” by incorporating actual line data from Datong–Qinhuangdao Railway and expert driver experience, and compared with traditional methods. The simulation results demonstrate that, compared to conventional sliding mode active disturbance rejection control, the proposed method reduces control force chattering in master-slave locomotives by 23.7%, improves tracking accuracy by 19%, and confines tracking errors within ±0.7 km/h.
-
表 1 整列货运列车基本参数
Table 1. Basic parameters of whole freight train
参数名称 数值 列车车厢数量/节 210 单节机车质量/t 184 敞车满载质量/t 100 机车长度/m 35.222 货车长度/m 12.0 机车启动牵引力/kN 760 机车最大电制动力/kN 461 表 2 制动参数
Table 2. Braking parameters
参数名称 HXD1 C80 制动缸直径/mm 225 254 制动缸压力/kPa 450 430 制动传动效率 0.95 0.9 制动缸个数/个 16 1 闸片/瓦个数/个 32 8 机车车轮半径/mm 1250 制动盘半径/mm 448 表 3 性能指标对比
Table 3. Performance index comparison
控制方法 MSE/×10−3 IAFV SMADRC-ESO 3.36 12.65 SMADRC-BESO 3.21 10.42 TSMADRC-BESO 2.72 9.65 -
[1] PHIL H. Optimal strategies for the control of a train[J]. Automatica, 1996, 32(4): 519-532. doi: 10.1016/0005-1098(95)00184-0 [2] LIU R, GOLOVITCHER I M. Energy-efficient operation of rail vehicles[J]. Transportation Research Part A: Policy and Practice, 2003, 37(10): 917-932. [3] 杨辉, 王禹, 李中奇, 等. 专家监督的SAC强化学习重载列车运行优化控制[J]. 控制理论与应用, 2022, 39(5): 799-808. doi: 10.7641/CTA.2021.10132YANG Hui, WANG Yu, LI Zhongqi, et al. Supervised SAC reinforcement learning method for heavy haul train optimization control[J]. Control Theory & Applications, 2022, 39(5): 799-808. doi: 10.7641/CTA.2021.10132 [4] 何闻. 考虑纵向冲动的重载列车自动驾驶操纵研究[D]. 北京: 中国铁道科学研究院, 2023. [5] 李紫宜, 周艳丽, 杨辉, 等. 面向节能的重载列车辅助驾驶模型预测控制研究[J]. 铁道科学与工程学报, 2024, 21(8): 3107-3118.LI Ziyi, ZHOU Yanli, YANG Hui, et al. Study on model predictive control of energy saving assisted driving for heavy-haul trains[J]. Journal of Railway Science and Engineering, 2024, 21(8): 3107-3118. [6] 俞花珍, 黄友能, 王明主, 等. 基于遗传算法的重载列车驾驶策略研究[J]. 铁道学报, 2020, 42(7): 110-116.YU Huazhen, HUANG Youneng, WANG Mingzhu, et al. Research on operating strategies of heavy haul train based on genetic algorithm[J]. Journal of the China Railway Society, 2020, 42(7): 110-116. [7] SUN X B, NIU L P, YAN S S. MPC-PI cascade control method for heavy-haul train[C]//2019 IEEE Intelligent Transportation Systems Conference (ITSC). Auckland: IEEE, 2019: 2527-2532. [8] 孙鹏飞, 张传鑫, 蒋春宏, 等. 结合迭代学习和模型预测的重载列车运行控制[J]. 中国铁道科学, 2023, 44(2): 111-119.SUN Pengfei, ZHANG Chuanxin, JIANG Chunhong, et al. Operation control of heavy-haul train based on combination of iterative learning and model prediction[J]. China Railway Science, 2023, 44(2): 111-119. [9] 李中奇, 孙鹏昕, 杨辉, 等. 重载列车离散积分终端滑模预测控制[J]. 控制理论与应用, 2025, 42(2): 235-244.LI Zhongqi, SUN Pengxin, YANG Hui, et al. Discrete integral terminal sliding mode predictive control for heavy haul train[J]. Control Theory & Applications, 2025, 42(2): 235-244. [10] 陆小红, 郑木火, 林宏泉. 重载列车智能化操控算法研究与实现[J]. 铁道学报, 2017, 39(1): 11-18. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8360.2017.01.002LU Xiaohong, ZHENG Muhuo, LIN Hongquan. Research on and implementation of intelligent control algorithm for heavy haul train[J]. Journal of the China Railway Society, 2017, 39(1): 11-18. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8360.2017.01.002 [11] 韩京清. 自抗扰控制技术[J]. 前沿科学, 2007, 1(1): 24-31. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-8128.2007.01.004HAN Jingqing. Auto disturbances rejection control technique[J]. Frontier Science, 2007, 1(1): 24-31. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-8128.2007.01.004 [12] HUANG Y, XUE W C. Active disturbance rejection control: Methodology and theoretical analysis[J]. ISA Transactions, 2014, 53(4): 963-976. doi: 10.1016/j.isatra.2014.03.003 [13] 魏远明, 罗亚中, 朱海洋. 液体运载火箭线性自抗扰容错姿态控制方法[J]. 载人航天, 2022, 28(3): 330-337. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-5825.2022.03.007WEI Yuanming, LUO Yazhong, ZHU Haiyang. Linear active disturbance rejection fault tolerant attitude control method for liquid launch vehicle[J]. Manned Spaceflight, 2022, 28(3): 330-337. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-5825.2022.03.007 [14] DONG L, CHEN Z Q, SUN M W, et al. Phase compensation active disturbance rejection control for shimmy vibration with magnetorheological damper of aircraft[J]. Expert Systems with Applications, 2023, 213: 119126.1-119126.9. [15] ZUO Y F, MEI J, JIANG C Q, et al. Linear active disturbance rejection controllers for PMSM speed regulation system considering the speed filter[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics, 2021, 36(12): 14579-14592. doi: 10.1109/TPEL.2021.3098723 [16] FENG L Y, SUN X D, YANG Z B, et al. Optimal torque sharing function control for switched reluctance motors based on active disturbance rejection controller[J]. IEEE/ASME Transactions on Mechatronics, 2023, 28(5): 2600-2608. doi: 10.1109/TMECH.2023.3240986 [17] 李伟, 宁君, 李悦琪. 基于自抗扰的反步非奇异终端滑模船舶航向控制器设计[J]. 船舶工程, 2019, 41(11): 83-88.LI Wei, NING Jun, LI Yueqi. Backstepping nonsingular terminal sliding mode ship course controller design based on the active disturbance rejection[J]. Ship Engineering, 2019, 41(11): 83-88. [18] WANG B, YANG J, JIAO H N, et al. Design of auto disturbance rejection controller for train traction control system based on artificial bee colony algorithm[J]. Measurement, 2020, 160: 107812.1-107812.9. [19] 李自康, 戴春辉, 黄翠翠, 等. 基于多种群遗传算法的磁浮列车自抗扰速度控制[J]. 西南交通大学学报, 2025, 60(4): 912-920.LI Zikang, DAI Chunhui, HUANG Cuicui, et al. Active disturbance rejection speed control for maglev trains based on multiple population genetic algorithm[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2025, 60(4): 912-920. [20] 孙友刚, 张丹丹, 吉文, 等. 基于模糊补偿的磁浮列车悬浮系统非奇异终端滑模控制[J]. 西南交通大学学报, 2025, 60(4): 803-811.SUN Yougang, ZHANG Dandan, JI Wen, et al. Fuzzy compensation-based non-singular terminal sliding mode control of maglev vehicle levitation system[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2025, 60(4): 803-811. [21] 付雅婷, 原俊荣, 李中奇, 等. 基于钩缓约束的重载列车驾驶过程优化[J]. 自动化学报, 2019, 45(12): 2355-2365.FU Yating, YUAN Junrong, LI Zhongqi, et al. Optimization of heavy haul train operation process based on coupler constraints[J]. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2019, 45(12): 2355-2365. [22] 杨辉, 马红萍, 付雅婷, 等. 基于多质点模型的重载列车制动策略[J]. 北京工业大学学报, 2020, 46(2): 169-179. doi: 10.11936/bjutxb2018110010YANG Hui, MA Hongping, FU Yating, et al. Brake strategy for heavy-haul train based on multi-particle model[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Technology, 2020, 46(2): 169-179. doi: 10.11936/bjutxb2018110010 [23] 罗建涛. 基于多质点模型的重载列车动力学仿真与分析[J]. 机车电传动, 2019(4): 61-66.LUO Jiantao. Dynamic simulation and analysis of heavy haul train based on multi-particle model[J]. Electric Drive for Locomotives, 2019(4): 61-66. [24] 徐明龙, 李谷, 李蔚, 等. 重载组合列车纵向力劣化分析与运行安全研究[J]. 铁道科学与工程学报, 2023, 20(1): 321-332.XU Minglong, LI Gu, LI Wei, et al. Analysis of longitudinal force degradation and running safety of heavy-haul combined trains[J]. Journal of Railway Science and Engineering, 2023, 20(1): 321-332. [25] YANG L Y, LIU L L, ZHANG J. A bi-bandwidth extended state observer for a system with measurement noise and its application to aircraft with abrupt structural damage[J]. Aerospace Science and Technology, 2021, 114: 106742.1-106742.12. -





 下载:
下载: