Online Motion Planning for Inspection Manipulator Based on Adaptive Proximal Policy Optimization Algorithm
-
摘要:
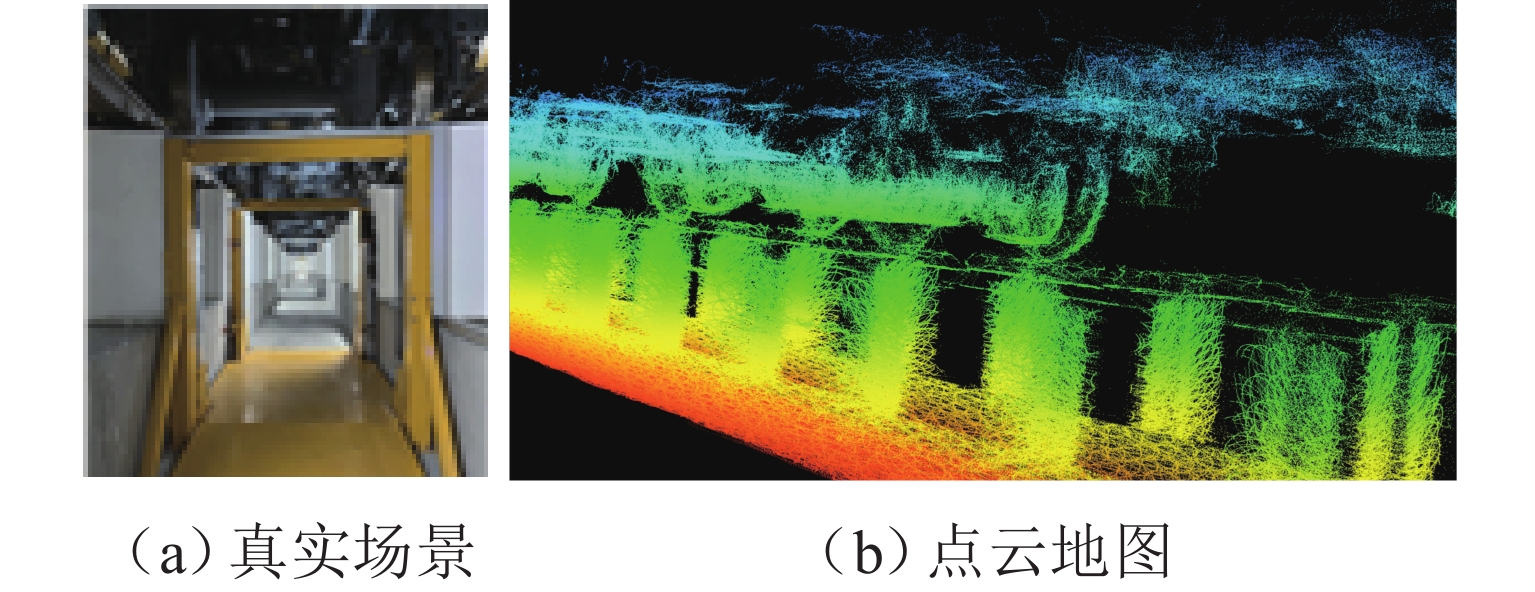
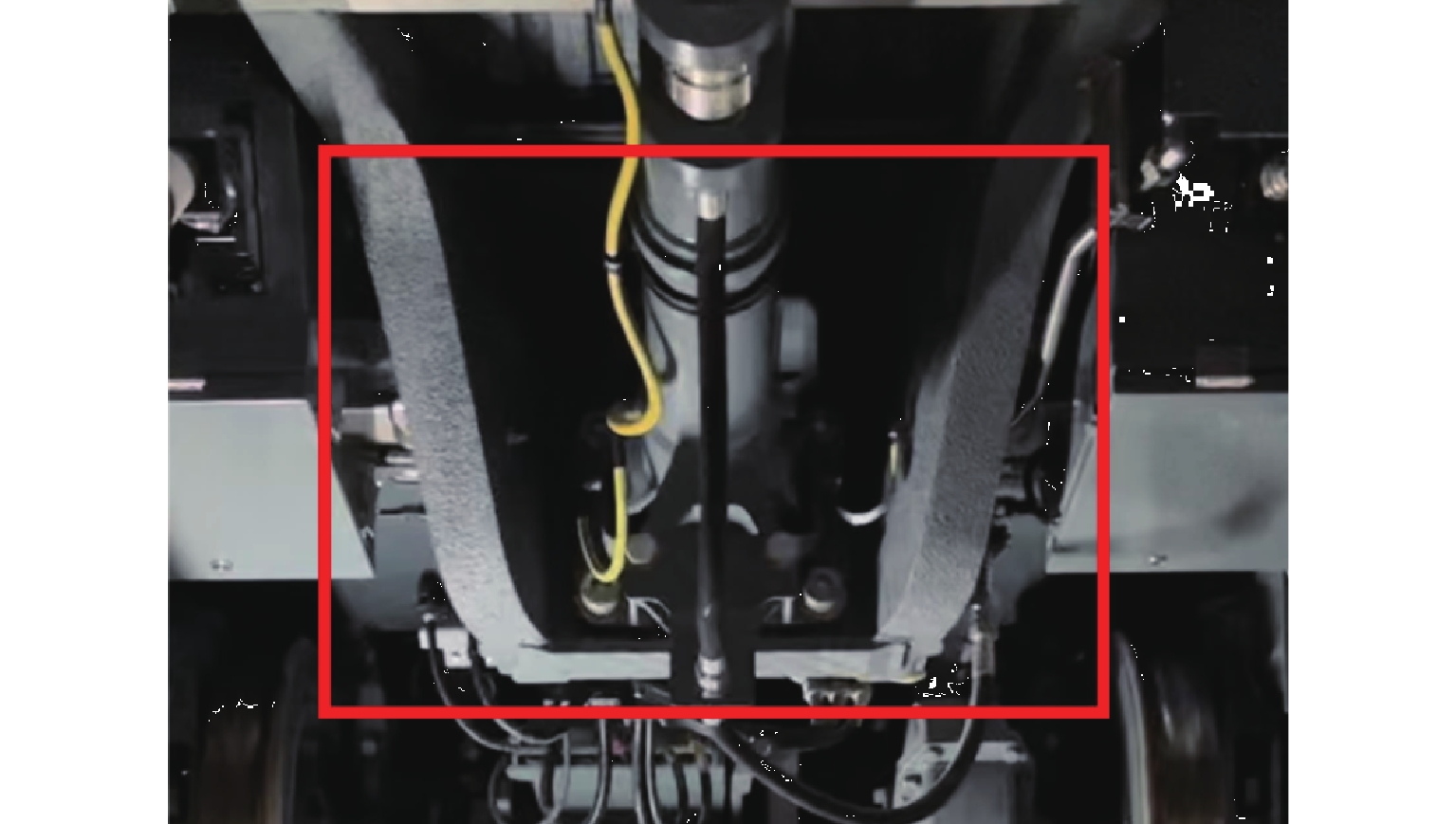
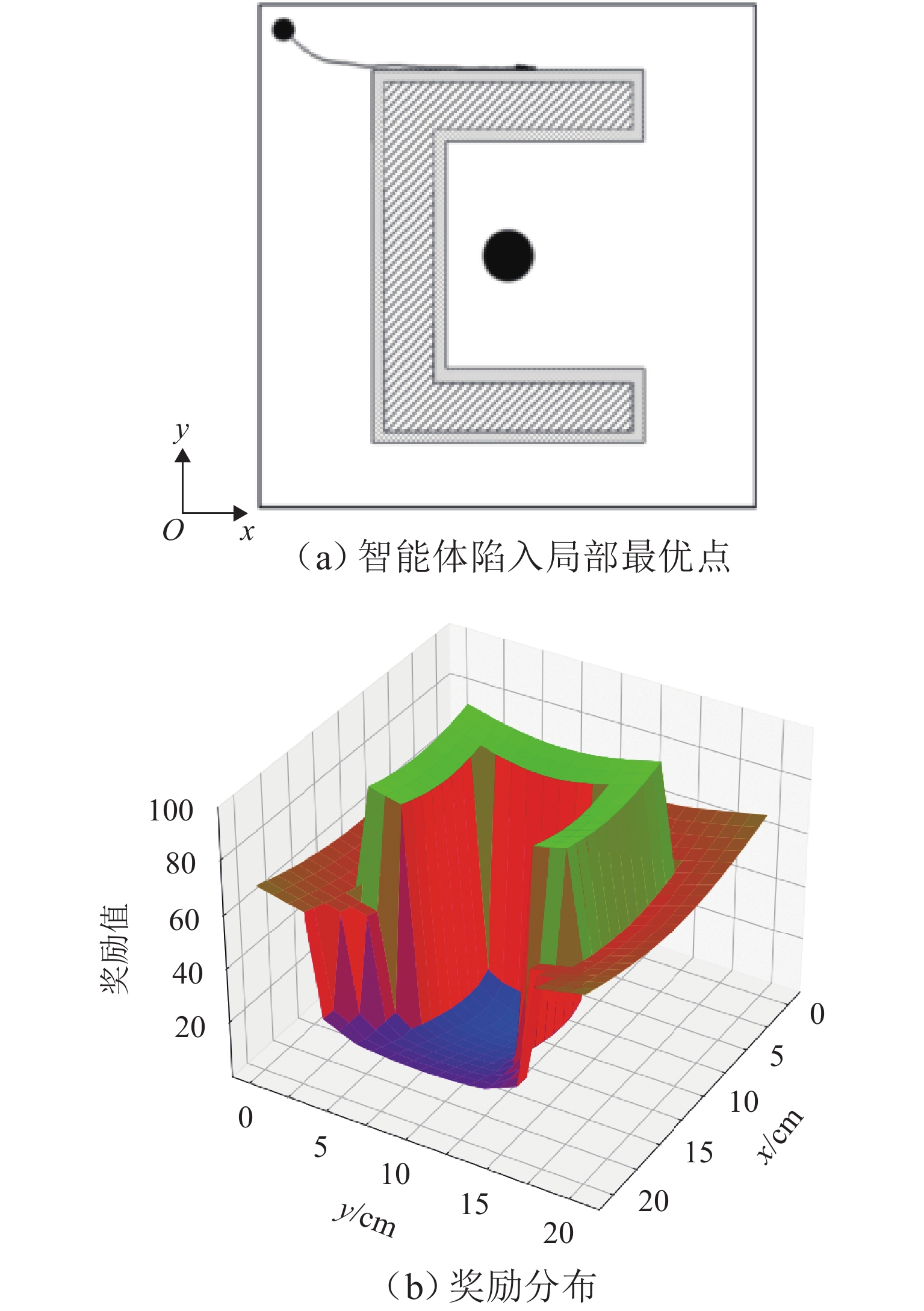
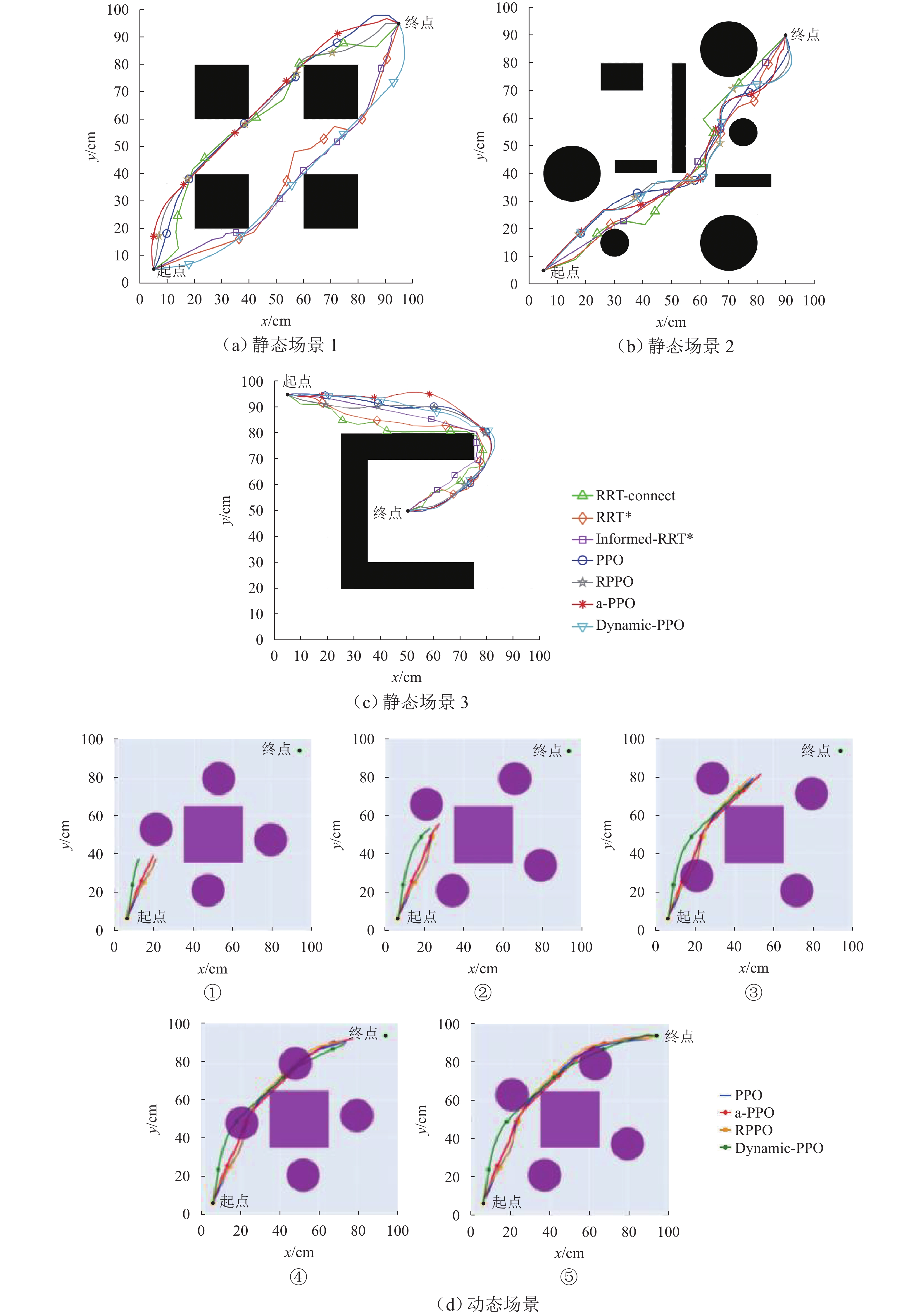
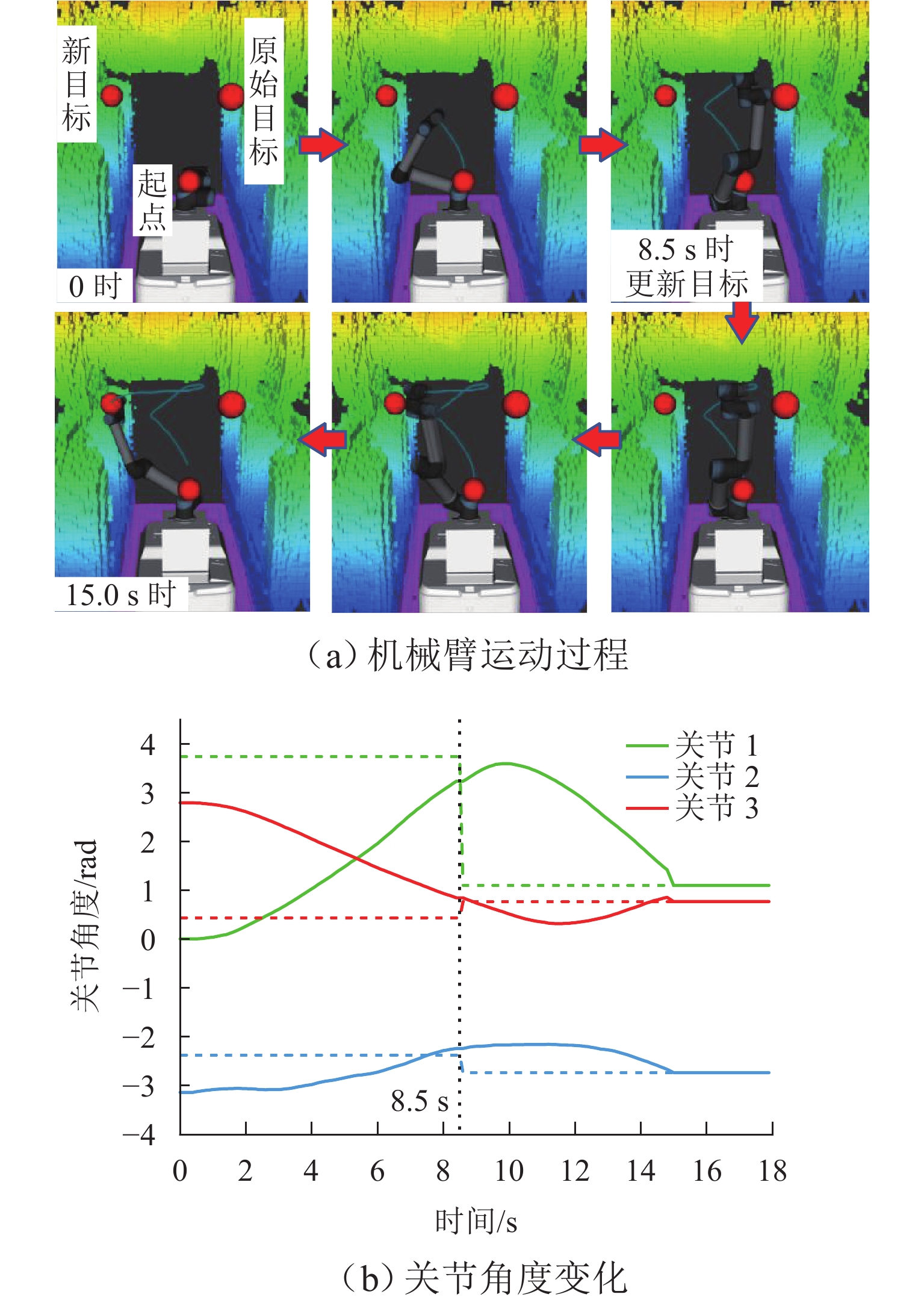
为满足列车底部场景中巡检机械臂主动配合工作人员的人机协作需求,并提高PPO (proximal policy optimization)算法的收敛速度,提出一种自适应PPO (adaptive-PPO, a-PPO)算法,并将其应用于列检机械臂的在线运动规划. 首先,设计系统模型,根据当前环境状态即刻输出策略动作;然后,引入几何强化学习构建奖励函数,通过智能体的探索不断优化奖励值分布;接着,基于策略更新前后的相似度自适应地确定裁剪值,形成a-PPO算法;最后,通过在二维地图上对比分析a-PPO算法的改进效果,并验证其在仿真和真实列车场景中的可行性和有效性. 结果表明:在二维平面仿真中,a-PPO算法在收敛速度上优于其他PPO算法,且路径稳定性显著提高,路径长度标准差平均比PPO算法低16.786%,比Informed-RRT* 算法低66.179%;仿真与真实列车场景的应用实验中,机械臂可实现运动过程中动态更改目标点和主动规避动态障碍物,展现出对动态环境的适应能力.
Abstract:To meet the needs of human-robot collaboration, where an inspection manipulator actively cooperates with a person under the railroad car and to enhance the convergence speed of the proximal policy optimization (PPO) algorithm, an adaptive PPO (a-PPO) algorithm was proposed and innovatively applied in the online motion planning of the inspection manipulator. Firstly, the system model was designed to immediately output policy actions based on the current environmental state. Secondly, geometric reinforcement learning was introduced to construct the reward function, utilizing the agent’s exploration to continuously optimize the distribution of rewards. Thirdly, the clipping value was adaptively determined based on the policy similarity between before and after the update, and the a-PPO algorithm was developed. Finally, the improvement effects of the a-PPO algorithm were compared on two-dimensional maps, and the feasibility and effectiveness of its application were experimentally verified in both simulation and real train scenarios. The results indicate that in the two-dimensional plane simulation, the a-PPO algorithm shows certain advantages in convergence speed compared to other PPO algorithms. Additionally, the stability of paths has been improved, with the average length standard deviation being 16.786% lower than that of the PPO algorithm and 66.179% lower than that of the Informed-RRT* algorithm. In the application experiments in both simulated and real train scenarios, the manipulator demonstrates the capability to dynamically adjust target points and actively avoid dynamic obstacles during motion, reflecting its adaptability to dynamic environments.
-
Key words:
- reinforcement learning /
- deep learning /
- motion planning /
- manipulator /
- railroad car
-
表 1 实验参数设置
Table 1. Experimental parameter settings
参数 值 学习率 $3 \times {10^{ - 4}}$ 折扣因子 0.99 迭代的最大步数/步 $1.5 \times {10^3}$ 小批量数量/批 $4 \times {10^3}$ 每次小批量更新网络的次数/次 80 训练的总轮数/轮 $1.1 \times {10^3}$ 优势函数因子 0.99 策略网络输出的动作分布标准差 0.5 基准截断参数值 0.2 碰撞概率高斯分布标准差 0.5 k1 2 k2 40 k3 0.1 k4 900 c1 0.5 c2 0.01 表 2 二维空间下的实验数据
Table 2. Experimental data in two-dimensional space
cm 场景 算法 最大值 最小值 平均值 标准差 静态场景 1 RRT-connect 218.67 132.09 147.59 13.01 RRT* 199.65 125.47 148.52 16.50 Informed-RRT* 151.99 122.87 126.81 4.32 PPO 147.76 137.79 141.76 2.13 RPPO 144.87 136.28 140.46 1.91 Dynamic-PPO 150.16 137.09 143.16 2.29 a-PPO 149.11 137.52 141.39 1.98 静态场景 2 RRT-connect 202.61 140.51 156.35 11.14 RRT* 179.99 140.22 155.24 9.16 Informed-RRT* 165.98 135.20 138.38 4.36 PPO 142.79 131.77 141.01 2.33 RPPO 145.92 137.04 140.57 1.67 Dynamic-PPO 151.19 138.51 142.75 1.92 a-PPO 141.61 133.16 137.01 1.86 静态场景 3 RRT-connect 255.77 124.29 169.83 29.49 RRT* 241.27 124.05 163.99 33.66 Informed-RRT* 190.79 116.97 126.13 18.89 PPO 140.98 127.75 133.41 2.88 RPPO 141.59 126.52 133.57 2.79 Dynamic-PPO 146.42 128.72 135.69 4.21 a-PPO 140.31 127.71 132.58 2.45 动态场景 PPO 151.32 138.36 141.95 2.28 RPPO 145.74 138.97 141.40 1.52 Dynamic-PPO 148.75 139.21 142.91 1.98 a-PPO 148.48 138.09 141.77 1.71 -
[1] JING G Q, QIN X Y, WANG H Y, et al. Developments, challenges, and perspectives of railway inspection robots[J]. Automation in Construction, 2022, 138: 104242. doi: 10.1016/j.autcon.2022.104242 [2] OLLERO A, TOGNON M, SUAREZ A, et al. Past, present, and future of aerial robotic manipulators[J]. IEEE Transactions on Robotics, 2022, 38(1): 626-645. doi: 10.1109/TRO.2021.3084395 [3] 江海凡, 丁国富, 肖通, 等. 数字孪生演进模型及其在智能制造中的应用[J]. 西南交通大学学报, 2022, 57(6): 1386-1394.JIANG Haifan, DING Guofu, XIAO Tong, et al. Digital twin evolution model and its applications in intelligent manufacturing[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2022, 57(6): 1386-1394. [4] GUALTIERI L, RAUCH E, VIDONI R. Emerging research fields in safety and ergonomics in industrial collaborative robotics: a systematic literature review[J]. Robotics and Computer-Integrated Manufacturing, 2021, 67: 101998.1-101998.30. [5] OMISORE O M, HAN S P, XIONG J, et al. A review on flexible robotic systems for minimally invasive surgery[J]. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems, 2022, 52(1): 631-644. doi: 10.1109/TSMC.2020.3026174 [6] 窦汝桐, 于慎波, 孙凤, 等. 7自由度仿人机械臂工作空间求解的降密蒙特卡洛法[J]. 西南交通大学学报, 2023, 58(6): 1328-1338.DOU Rutong, YU Shenbo, SUN Feng, et al. Density-reducing Monte Carlo method for 7 degrees of freedom humanoid robot arm workspace solution[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2023, 58(6): 1328-1338. [7] BILAL H, YIN B Q, KUMAR A, et al. Jerk-bounded trajectory planning for rotary flexible joint manipulator: an experimental approach[J]. Soft Computing, 2023, 27(7): 4029-4039. doi: 10.1007/s00500-023-07923-5 [8] CHENG X, ZHOU J M, ZHOU Z, et al. An improved RRT-connect path planning algorithm of robotic arm for automatic sampling of exhaust emission detection in Industry 4.0[J]. Journal of Industrial Information Integration, 2023, 33: 100436.1-100436.13. [9] YU X L, DONG M S, YIN W M. Time-optimal trajectory planning of manipulator with simultaneously searching the optimal path[J]. Computer Communications, 2022, 181: 446-453. doi: 10.1016/j.comcom.2021.10.005 [10] 黄文东. 基于ROS的机械臂路径规划算法研究[D]. 成都: 西南交通大学, 2022. [11] XIE G H, ZHAO D, TANG Q C, et al. Path planning for robotic arm based on reinforcement learning under the train[C]//2023 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Biomimetics (ROBIO). Koh Samui: IEEE, 2023: 1-8. [12] WANG M, FU W J, HE X N, et al. A survey on large-scale machine learning[J]. IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering, 2022, 34(6): 2574-2594. [13] WANG J J, MA Y L, ZHANG L B, et al. Deep learning for smart manufacturing: methods and applications[J]. Journal of Manufacturing Systems, 2018, 48: 144-156. doi: 10.1016/j.jmsy.2018.01.003 [14] LE N, RATHOUR V S, YAMAZAKI K, et al. Deep reinforcement learning in computer vision: a comprehensive survey[J]. Artificial Intelligence Review, 2022, 55(4): 2733-2819. doi: 10.1007/s10462-021-10061-9 [15] JAMES S, MA Z C, ARROJO D R, et al. RLBench: the robot learning benchmark & learning environment[J]. IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters, 2020, 5(2): 3019-3026. doi: 10.1109/LRA.2020.2974707 [16] TALAEI KHOEI T, OULD SLIMANE H, KAABOUCH N. Deep learning: systematic review, models, challenges, and research directions[J]. Neural Computing and Applications, 2023, 35(31): 23103-23124. doi: 10.1007/s00521-023-08957-4 [17] SHAKYA A K, PILLAI G, CHAKRABARTY S. Reinforcement learning algorithms: a brief survey[J]. Expert Systems with Applications, 2023, 231: 120495. doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2023.120495 [18] LI Y K, HAO X L, SHE Y C, et al. Constrained motion planning of free-float dual-arm space manipulator via deep reinforcement learning[J]. Aerospace Science and Technology, 2021, 109: 106446.1-106446.13. [19] KIRAN B R, SOBH I, TALPAERT V, et al. Deep reinforcement learning for autonomous driving: a survey[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2022, 23(6): 4909-4926. doi: 10.1109/TITS.2021.3054625 [20] SCHULMAN J, WOLSKI F, DHARIWAL P, et al. Proximal policy optimization algorithms[DB/OL]. [2017-8-28]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1707.06347. [21] SCHULMAN J, LEVINE S, MORITZ P, et al. Trust region policy optimization[C]//Proceedings of the 31st International Conference on Machine Learning. Lille: PMLR, 2015: 1889-1897. [22] WEN S H, WEN Z T, ZHANG D, et al. A multi-robot path-planning algorithm for autonomous navigation using meta-reinforcement learning based on transfer learning[J]. Applied Soft Computing, 2021, 110: 107605. doi: 10.1016/j.asoc.2021.107605 [23] ZHANG B C, MAO Z L, LIU W Q, et al. Geometric reinforcement learning for path planning of UAVs[J]. Journal of Intelligent & Robotic Systems, 2015, 77(2): 391-409. [24] MNIH V, BADIA A P, MIRZA M, et al. Asynchronous methods for deep reinforcement learning[C]// Proceedings of the 33rd International conference on machine learning. New York: PMLR, 2016: 1928-1937. [25] FUJINMOTO S, VAN HOOF H, MEGER, D. Addressing function approximation error in actor-critic methods[C]//Proceedings of the 35th International Conference on Machine Learning. Stockholm: PMLR, 2018: 1587-1596. -





 下载:
下载: