Improvement Method of Interfacial Cohesiveness of Foam Asphalt Cold Recycled Binder
-
摘要:
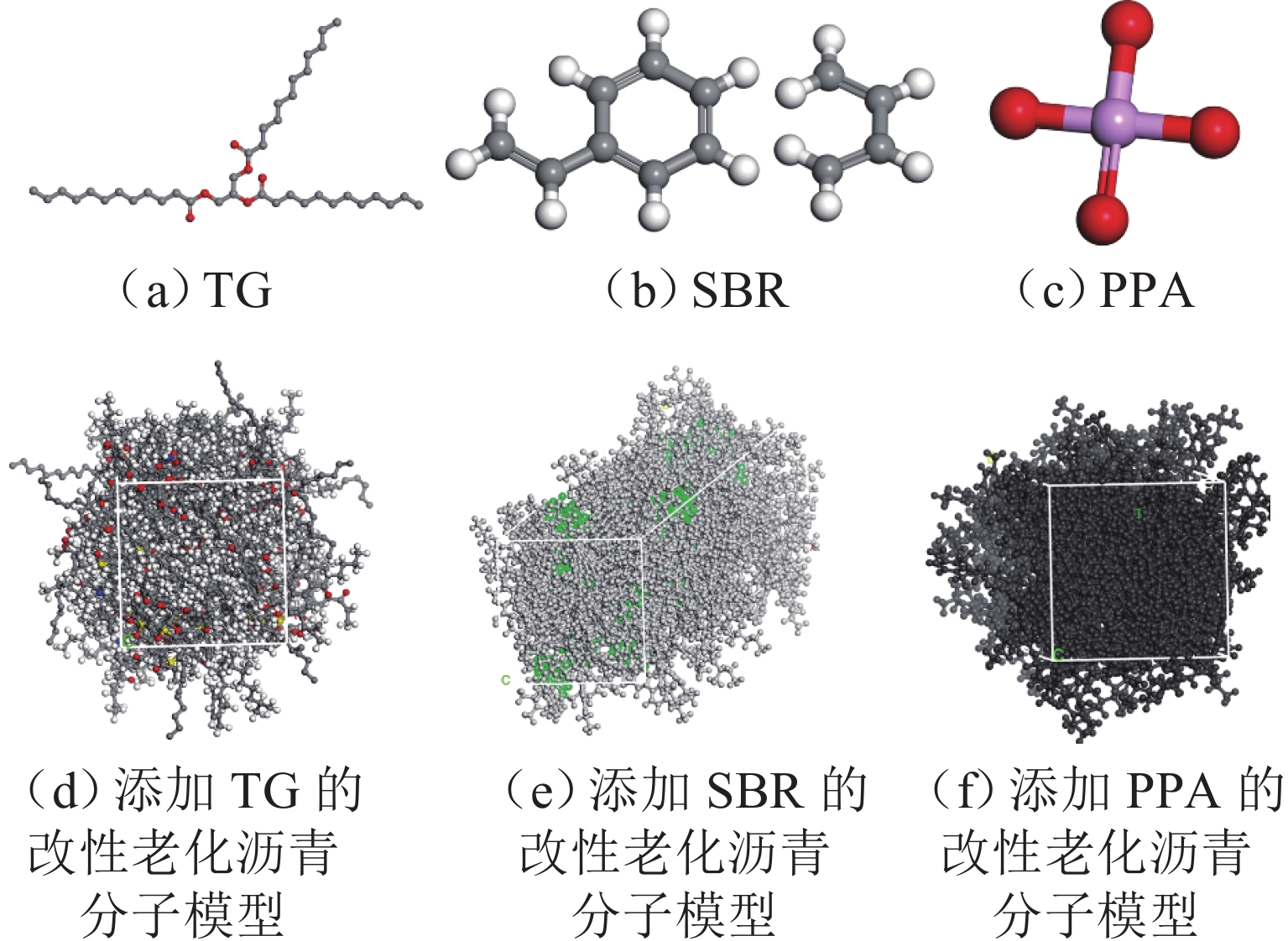
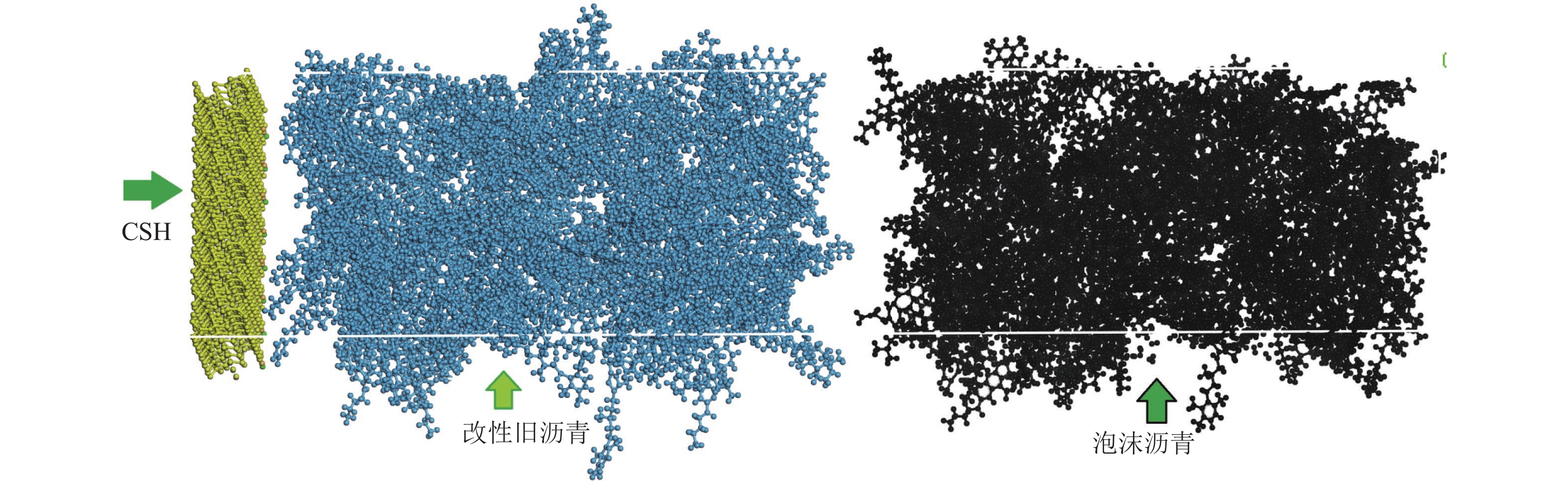
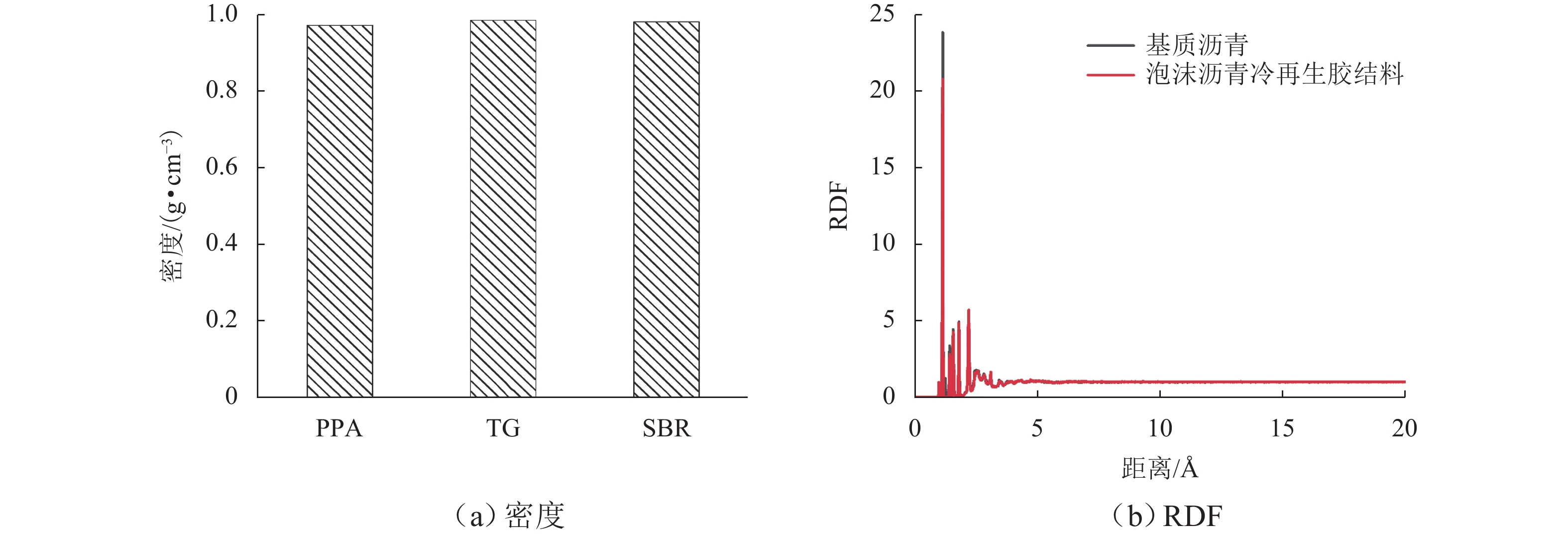
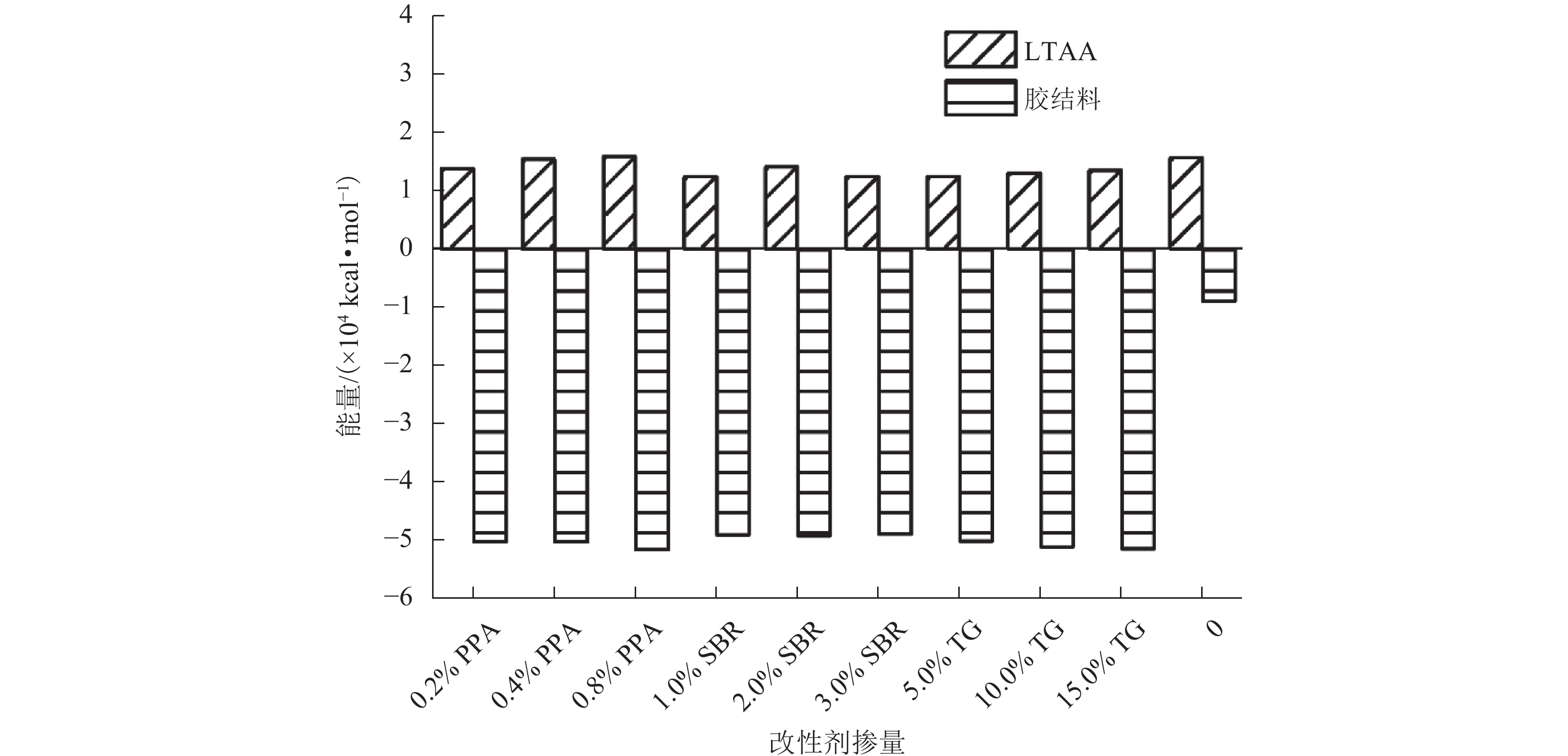
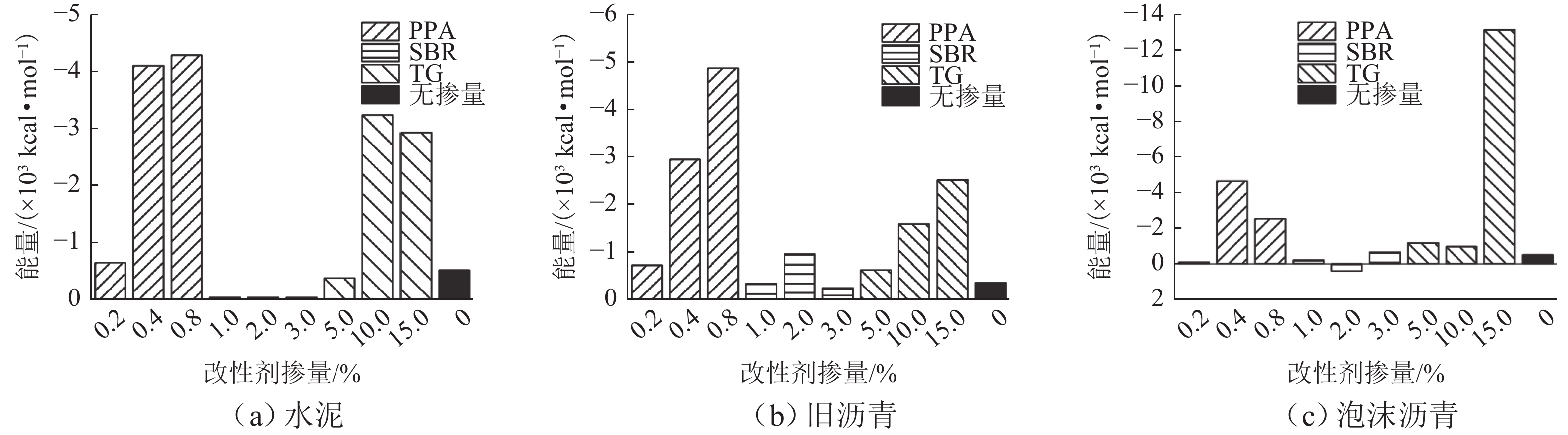
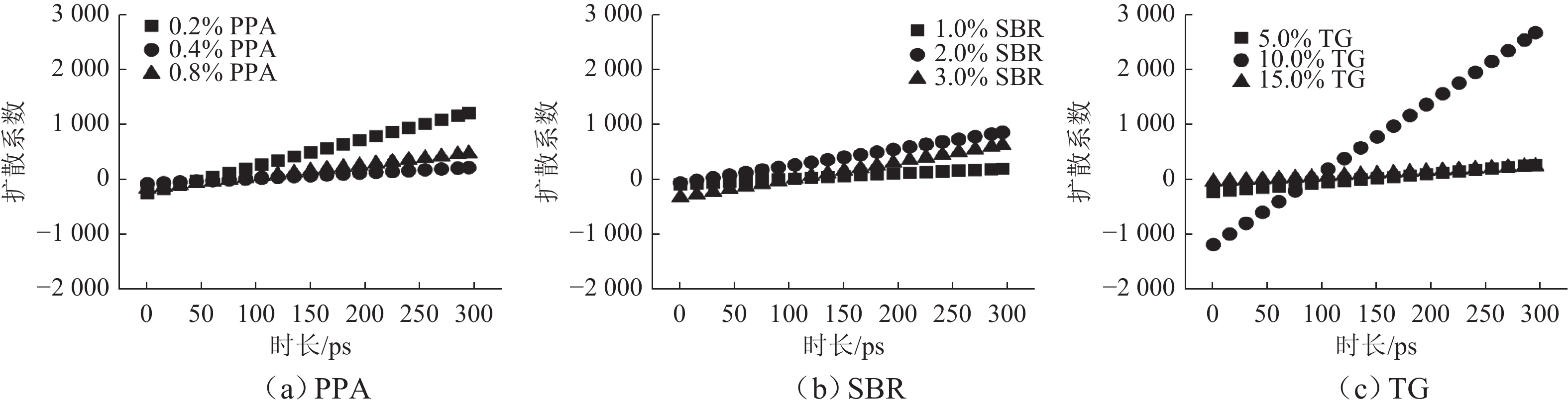
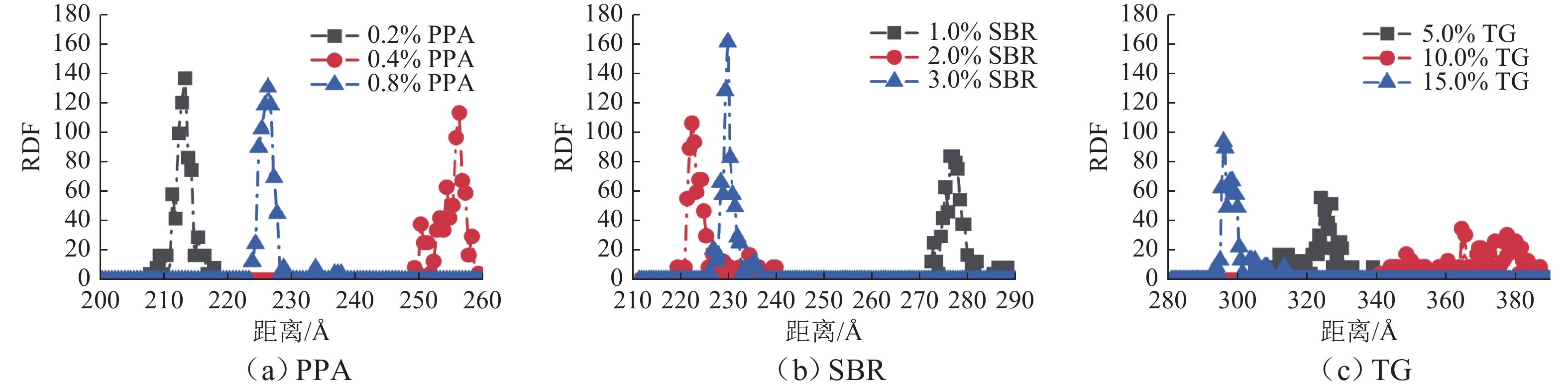
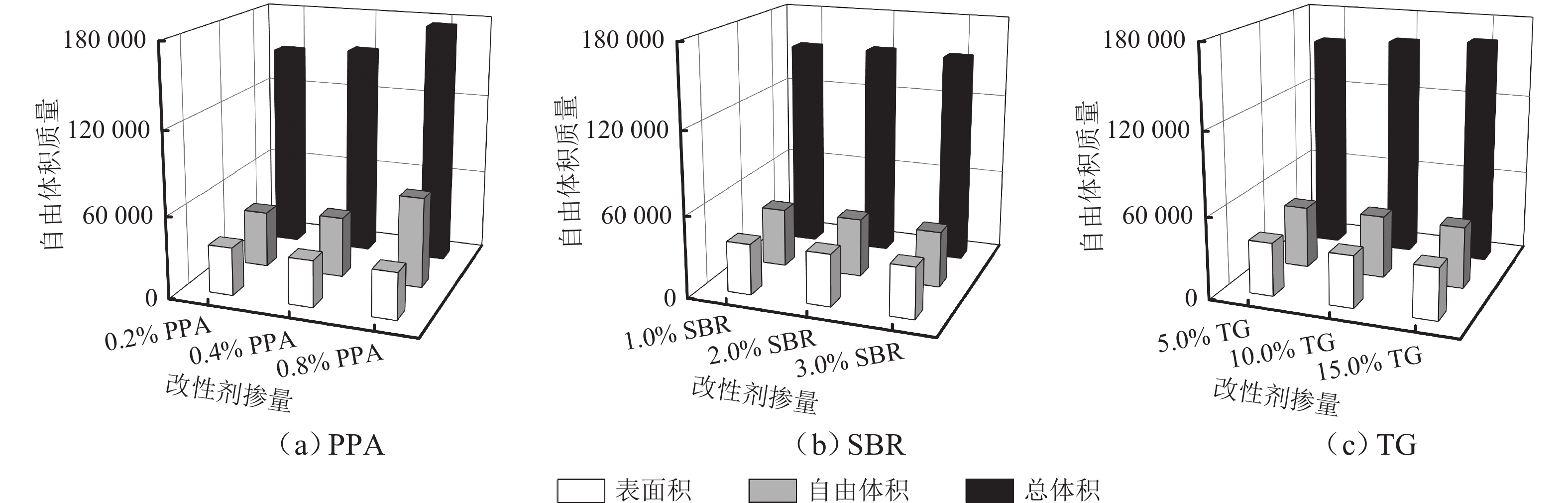
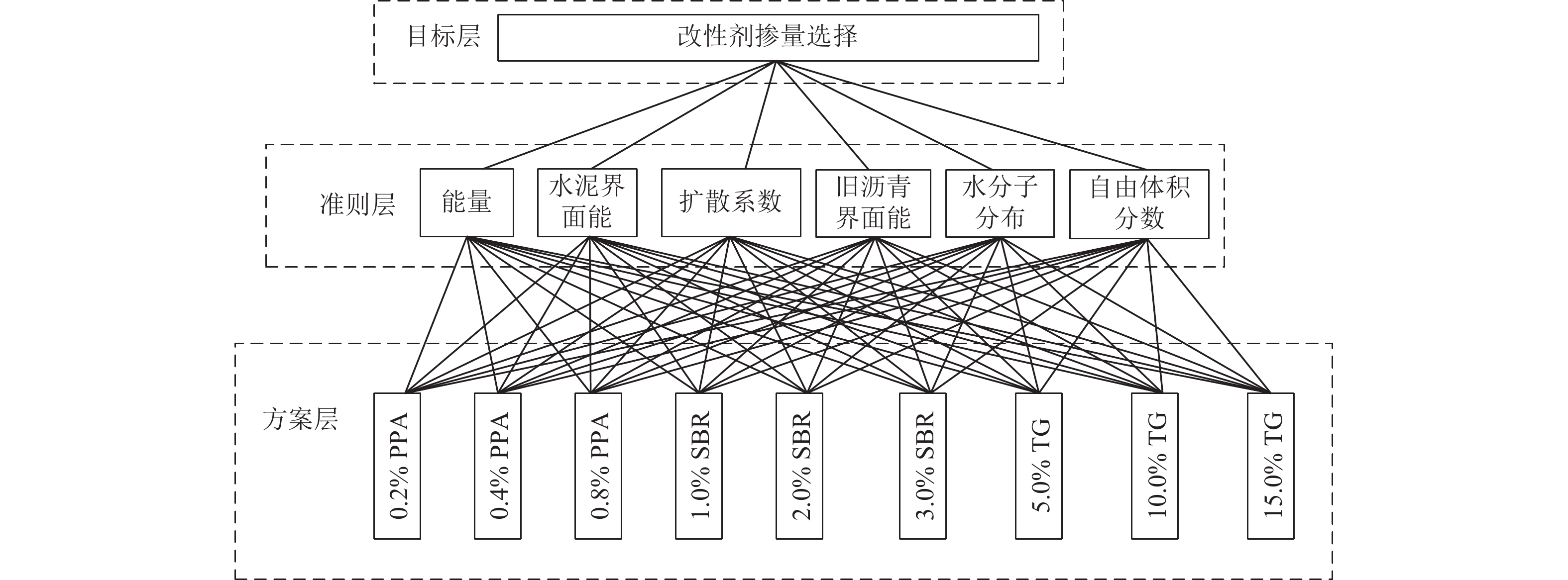
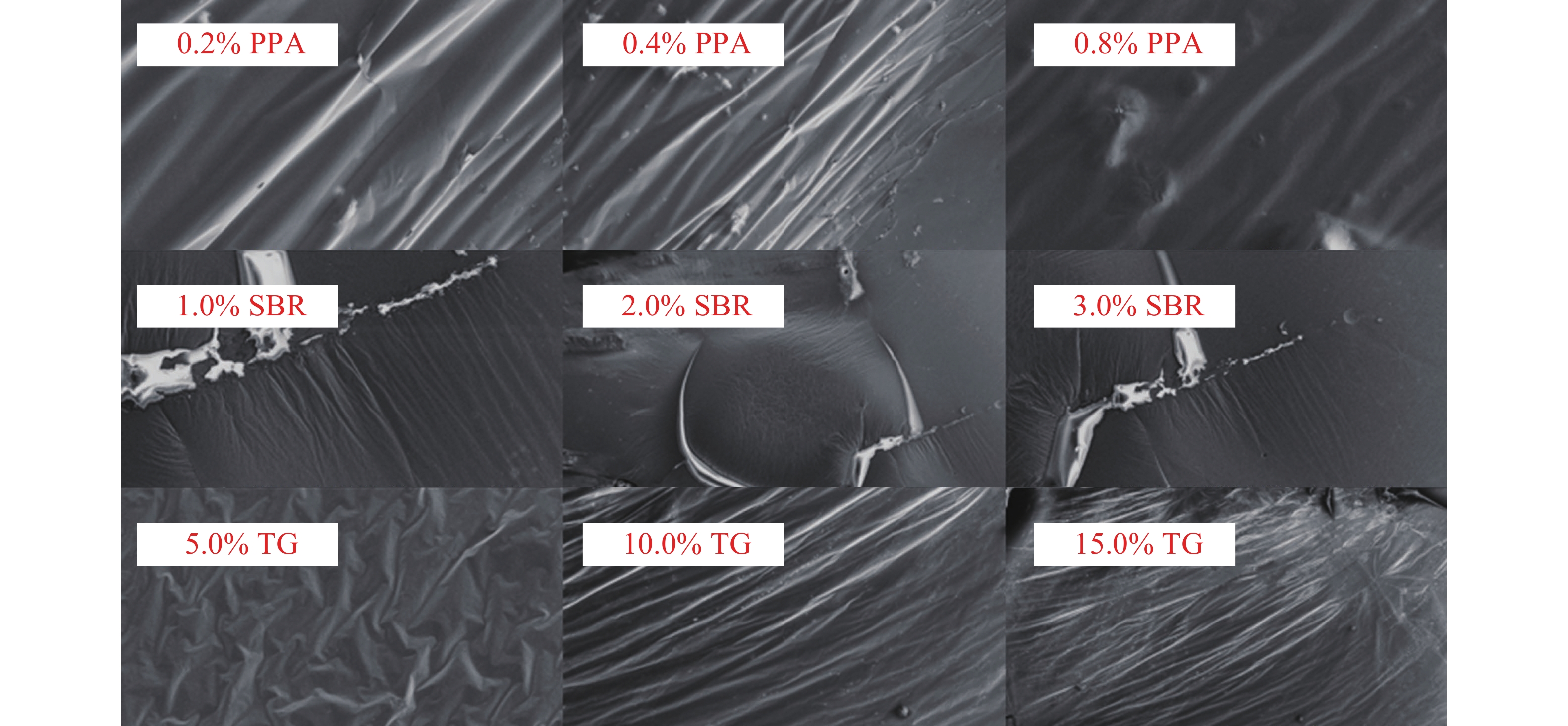
为提升泡沫沥青冷再生胶结料(由水泥、旧沥青和泡沫沥青组成)的黏聚性,选取多聚磷酸(PPA)、丁苯橡胶(SBR)、甘油三酯(TG) 3种泡沫沥青冷再生胶结料改性剂,利用分子动力学模拟方法建立不同改性剂及其掺量的泡沫沥青冷再生胶结料分子模型;基于界面能、相互作用能、扩散系数和水分子径向分布函数(RDF)等指标,研究不同改性剂及其掺量对泡沫沥青冷再生胶结料界面特性改善效果的影响规律,并通过显著性检验和层次分析法分别探讨各指标间显著性差异和改性方案的权重. 结果表明:添加0.8% 的PPA对泡沫沥青冷再生胶结料黏聚性提升效果最为显著,可以有效改善泡沫沥青冷再生胶结料的界面能、自由体积和水损害的影响,亦使泡沫沥青冷再生胶结料具有较好的扩散能力;添加15.0%的TG对泡沫沥青冷再生胶结料的相互作用改善效果较好,但扩散性能较差;添加2.0%的SBR对泡沫沥青冷再生胶结料的抗水损害能力改善效果最好,但SBR总体改性效果一般; 不同剂掺量之间不存在显著性影响,各改性剂掺配方案相互独立且各有优势.
Abstract:To improve the cohesiveness of foam asphalt cold recycled binder (composed of cement, old asphalt, and foam asphalt), three modifiers of foam asphalt cold recycled binder, including polyphosphoric acid (PPA), polymerized styrene butadiene rubber (SBR), and triglyceride (TG) were selected, and molecular models of foam asphalt cold recycled binder with different modifiers and their dosage were established by molecular dynamics simulation method. The effect of different modifiers and their dosage on the improvement of the interface properties of foam asphalt cold recycled binder was studied based on interface energy, interaction energy, diffusion coefficient, and radial distribution function (RDF) of water molecules. The significance difference of each index and the weight of the modification scheme were discussed by significance tests and the analytic hierarchy process. The results have shown that the addition of 0.8% PPA has the most significant effect on the cohesiveness of the foam asphalt cold recycled binder, which can effectively improve the interfacial energy, free volume, and water damage of the foam asphalt cold recycled binder, and also make the foam asphalt cold recycled binder have better diffusion ability. The addition of 15.0% TG can improve the interaction effect of the foam asphalt cold recycled binder, but the diffusion ability is poor. The addition of 2.0% SBR has the best effect on the water damage resistance of foam asphalt cold recycled binder, but the overall modification effect of SBR is not so good. There is no significant influence among different dosages of modifiers, and each modification scheme is independent and has its own advantages. After comprehensive comparisons, 0.8% PPA has the best effect on improving the interfacial cohesiveness of foam asphalt cold recycled binder.
-
Key words:
- aged asphalt /
- cold recycle /
- cohesiveness /
- molecular dynamics /
- modified asphalt
-
表 1 沥青分子模型分子信息
Table 1. Information on asphalt molecule models
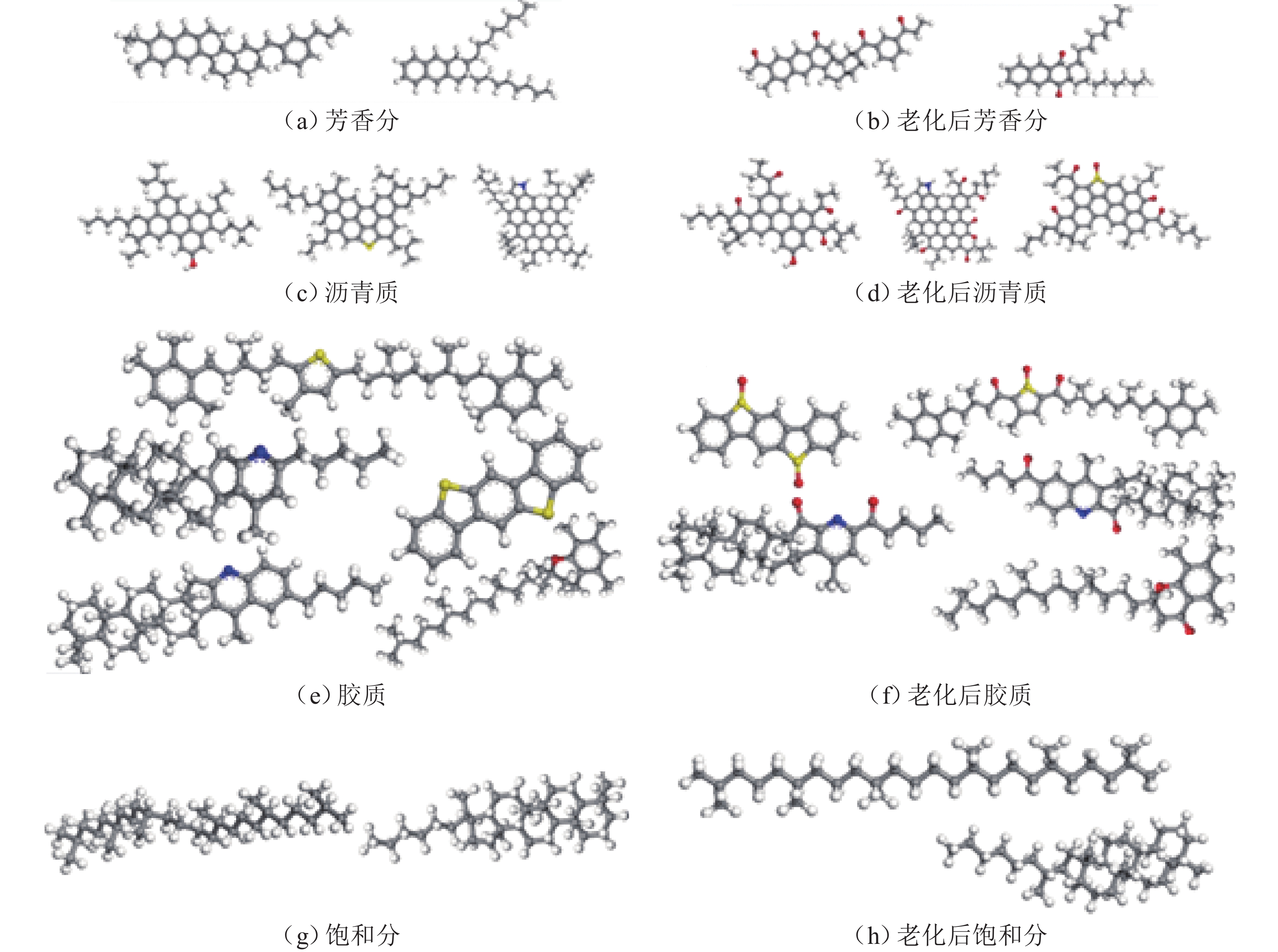
组分 基质沥青模型 LTAA 模型 化学式 个数/个 化学式 个数/个 沥青质 C42H54O 3 C42H46O5 2 C66H81N 2 C66H67NO7 2 C51H62S 3 C51H54O5S 3 饱和分 C30H62 4 C30H62 6 C35H62 4 C35H62 8 芳香分 C35H44 11 C35H36O4 11 C30H46 13 C30H42O2 9 胶质 C40H59N 4 C40H55NO2 2 C40H60S 4 C40H56O3S 8 C18H10S2 15 C18H10O2S2 15 C36H57N 4 C36H53NO2 2 C29H50O 5 C29H48O2 2 表 2 方差齐性检验
Table 2. Test for homogeneity of variance
数据处理方法 莱文统计 自由度 1 自由度 2 显著性 基于平均值 0.001 8 36.00 1 基于中位数 0.009 8 36.00 1 基于中位数且具有
调整后自由度0.009 8 35.91 1 基于剪除后平均值 0.001 8 36.00 1 表 3 层次分析结果
Table 3. Hierarchy analysis results
方案 权重 方案 权重 方案 权重 0.2% PPA 0.08 1.0% SBR 0.05 5.0% TG 0.07 0.4% PPA 0.12 2.0% SBR 0.07 10.0% TG 0.15 0.8% PPA 0.24 3.0% SBR 0.07 15.0% TG 0.11 -
[1] GU F, MA W Y, WEST R C, et al. Structural performance and sustainability assessment of cold central-plant and in-place recycled asphalt pavements: a case study[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2019, 208: 1513-1523. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.10.222 [2] 董文红, 刘金艳, 石津金, 等. 泡沫沥青温拌混合料的环境和经济效益分析[J]. 市政技术, 2022, 40(5): 203-207.DONG Wenhong, LIU Jinyan, SHI Jinjin, et al. Analysis of environmental and economic benefits of warm mix of foamed asphalt[J]. Journal of Municipal Technology, 2022, 40(5): 203-207. [3] XU G J, WANG H. Molecular dynamics study of oxidative aging effect on asphalt binder properties[J]. Fuel, 2017, 188: 1-10. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2016.10.021 [4] YAO H, DAI Q L, YOU Z P. Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy characterization of aging-related properties of original and nano-modified asphalt binders[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2015, 101: 1078-1087. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2015.10.085 [5] QU X, LIU Q, GUO M, et al. Study on the effect of aging on physical properties of asphalt binder from a microscale perspective[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2018, 187: 718-729. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2018.07.188 [6] 温彦凯, 郭乃胜, 王淋, 等. 考虑胶浆黏附性的泡沫沥青冷再生混合料性能[J]. 建筑材料学报, 2020, 23(6): 1504-1511.WEN Yankai, GUO Naisheng, WANG Lin, et al. Performance of cold recycled mixture with foamed asphalt considering adhesion of mastics[J]. Journal of Building Materials, 2020, 23(6): 1504-1511. [7] 王杰, 秦永春, 徐剑, 等. 水泥乳化沥青-旧沥青界面微尺度力学性质原位表征[J]. 东南大学学报(自然科学版), 2022, 52: 288-298.WANG Jie, QIN Yongchun, XU Jian, et al. In-situ characterization of microscale mechanical properties of interface between cement emulsified asphalt and aged asphalt[J]. Journal of Southeast University (Natural Science Edition), 2022, 52: 288-298. [8] YOU L Y, YOU Z P, DAI Q L, et al. Characteristics of water-foamed asphalt mixture under multiple freeze-thaw cycles: laboratory evaluation[J]. Journal of Materials in Civil Engineering, 2018, 30(11): 04018270. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)MT.1943-5533.0002474 [9] MA T, HUANG X M, ZHAO Y L, et al. Evaluation of the diffusion and distribution of the rejuvenator for hot asphalt recycling[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2015, 98: 530-536. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2015.08.135 [10] CUI S, BLACKMAN B R K, KINLOCH A J, et al. Durability of asphalt mixtures: effect of aggregate type and adhesion promoters[J]. International Journal of Adhesion and Adhesives, 2014, 54: 100-111. doi: 10.1016/j.ijadhadh.2014.05.009 [11] LI Y Y, WU S P, AMIRKH-ANIAN S. Investigation of the graphene oxide and asphalt interaction and its effect on asphalt pavement performance[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2018, 165: 572-584. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2018.01.068 [12] GOLCHIN B, HAMZAH M O, HASAN M R M. Optimization in producing warm mix asphalt with polymer modified binder and surfactant-wax additive[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2017, 141: 578-588. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2017.02.123 [13] 王海蛟, 张庆宇, 王凯. 温拌改性泡沫沥青再生混合料性能研究[J]. 施工技术, 2021, 50(14): 93-97, 133.WANG Haijiao, ZHANG Qingyu, WANG Kai. Research on performance of warm mix modified foam asphalt recycled mixture[J]. Construction Technology, 2021, 50(14): 93-97, 133. [14] 李秀君, 高世柱, 赵麟昊, 等. 水性环氧树脂改性泡沫沥青冷再生混合料性能[J]. 建筑材料学报, 2021, 24(4): 874-880.LI Xiujun, GAO Shizhu, ZHAO Linhao, et al. Performances of cold recycling mixture with foamed bitumen and waterborne epoxy resin[J]. Journal of Building Materials, 2021, 24(4): 874-880. [15] 李秀君, 欧阳欢, 张恒, 等. 基于AFM与分子动力学的改性泡沫沥青性能研究[J]. 公路, 2023, 68(2): 253-259.LI Xiujun, OUYANG Huan, ZHANG Heng, et al. Research on performance of modified foamed asphalt based on AFM and molecular dynamics[J]. Highway, 2023, 68(2): 253-259. [16] 戴文亭, 刘丹丹, 郭威, 等. 冻融循环条件下硅烷偶联剂改性泡沫沥青混合料的损伤特性[J]. 材料导报, 2021, 35(增1): 264-268.DAI Wenting, LIU Dandan, GUO Wei, et al. Damage characteristics of foamed asphalt mixture modified by silane coupling agent under freeze-thaw cycles[J]. Materials Reports, 2021, 35(S1): 264-268. [17] RADZISZEWSKI P, LIPHARDT A, SARNOWSKI M, et al. Ageing evaluation of foamed polymer modified bitumen with bio-flux additive[J]. Materials, 2023, 16(6): 2167. doi: 10.3390/ma16062167 [18] HU J Y, ZHANG L Q, ZHANG X J, et al. Comparative evaluation of moisture susceptibility of modified/foamed asphalt binders combined with different types of aggregates using surface free energy approach[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2020, 256: 119429. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2020.119429 [19] ZHANG Z P, HUANG T, SUN J, et al. Laboratory study and molecular dynamics simulation of high- and low-temperature properties of polyurethane-modified asphalt[J]. Journal of Materials in Civil Engineering, 2023, 35(8): 04023257. doi: 10.1061/JMCEE7.MTENG-15115 [20] WANG Y, QIAO J G. Effect of styrene-butadiene rubber on asphalt binder energy at different temperatures based on molecular dynamics simulation[J]. Journal of Materials in Civil Engineering, 2024, 36(2): 04023539. doi: 10.1061/JMCEE7.MTENG-16461 [21] GAO Y M, ZHANG Y Q, YANG Y, et al. Molecular dynamics investigation of interfacial adhesion between oxidised bitumen and mineral surfaces[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2019, 479: 449-462. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2019.02.121 [22] CHEN Z, YI J Y, ZHAO H, et al. Strength development and deterioration mechanisms of foamed asphalt cold recycled mixture based on MD simulation[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2021, 269: 121324. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2020.121324 [23] GAO Y L, TIAN W W, LI Y L, et al. Study on compatibility mechanism of plasticizer and asphalt based on molecular dynamics[J]. Materials & Design, 2023, 228: 111827. [24] FU Z, TANG Y J, PENG C, et al. Properties of polymer modified asphalt by polyphosphoric acid through molecular dynamics simulation and experimental analysis[J]. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 2023, 382: 121999. doi: 10.1016/j.molliq.2023.121999 [25] LI D D, GREENFIELD M L. Chemical compositions of improved model asphalt systems for molecular simulations[J]. Fuel, 2014, 115: 347-356. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2013.07.012 [26] LIU J Z, YU B, HONG Q Z. Molecular dynamics simulation of distribution and adhesion of asphalt components on steel slag[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2020, 255: 119332. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2020.119332 [27] 徐金枝. 泡沫沥青及泡沫沥青冷再生混合料技术性能研究[D]. 西安: 长安大学, 2007. [28] 姚柒忠. 泡沫沥青再生混合料强度形成结构的微观研究及性能分析[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2018. [29] LUO L, CHU L J, FWA T F. Molecular dynamics analysis of moisture effect on asphalt-aggregate adhesion considering anisotropic mineral surfaces[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2020, 527: 146830. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2020.146830 [30] DU S W, HUANG D F. The effect of cement on performance properties of foam asphalt cold recycled mixture[J]. Applied Mechanics and Materials, 2012 (178/179/180/181): 1379-1382. [31] XIAO J J, JIANG W, YE W L, et al. Effect of cement and emulsified asphalt contents on the performance of cement-emulsified asphalt mixture[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2019, 220: 577-586. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2019.06.051 [32] MERLINO S, BONACCORSI E, ARMBRUSTER T. The real structure of tobermorite 11A: normal and anomalous forms, OD character and polytypic modifications[J]. European Journal of Mineralogy, 2001, 13(3): 577-590. doi: 10.1127/0935-1221/2001/0013-0577 [33] ZAJAC M, IRBE L, BULLERJAHN F, et al. Mechanisms of carbonation hydration hardening in Portland cements[J]. Cement and Concrete Research, 2022, 152: 106687. doi: 10.1016/j.cemconres.2021.106687 [34] BERNAL S A, PROVIS J L, WALKLEY B, et al. Gel nanostructure in alkali-activated binders based on slag and fly ash, and effects of accelerated carbonation[J]. Cement and Concrete Research, 2013, 53: 127-144. doi: 10.1016/j.cemconres.2013.06.007 [35] LI H B, DONG B, WANG W J, et al. Effect of waste engine oil and waste cooking oil on performance improvement of aged asphalt[J]. Applied Sciences, 2019, 9(9): 1767. doi: 10.3390/app9091767 [36] FARROKHZADE F, SABOURI M, TABATABAEE N. Aging characteristics of neat and modified asphalt binders based on rheological evaluations at intermediate temperatures[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2022, 322: 126387. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2022.126387 [37] SUO Z, NIE L, XIANG F R, et al. The effect of waste plant oil on the composition and micro-morphological properties of old asphalt composition[J]. Buildings, 2021, 11(9): 407-423. doi: 10.3390/buildings11090407 [38] WANG S Q, GAO Y, YAN K Z, et al. Effect of long-term aging on waste tire rubber and amorphous poly alpha olefin compound modified asphalt binder and its mixtures[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2021, 272: 121667. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2020.121667 [39] LI D N, LENG Z, WANG H P, et al. Structural and mechanical evolution of the multiphase asphalt rubber during aging based on micromechanical back-calculation and experimental methods[J]. Materials & Design, 2022, 215: 110421. [40] WANG H P, LIU X Y, APOSTOLIDIS P, et al. Effect of laboratory aging on chemistry and rheology of crumb rubber modified bitumen[J]. Materials and Structures, 2020, 53(2): 26. doi: 10.1617/s11527-020-1451-9 [41] LIANG P, LIANG M, FAN W Y, et al. Improving thermo-rheological behavior and compatibility of SBR modified asphalt by addition of polyphosphoric acid (PPA)[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2017, 139: 183-192. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2017.02.065 [42] ALAM S, HOSSAIN Z. Changes in fractional compositions of PPA and SBS modified asphalt binders[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2017, 152: 386-393. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2017.07.021 -




 下载:
下载: