Resistance against Sulfate Erosion of Concrete Partition Under High Temperature and Dry−Wet Cycle
-
摘要:
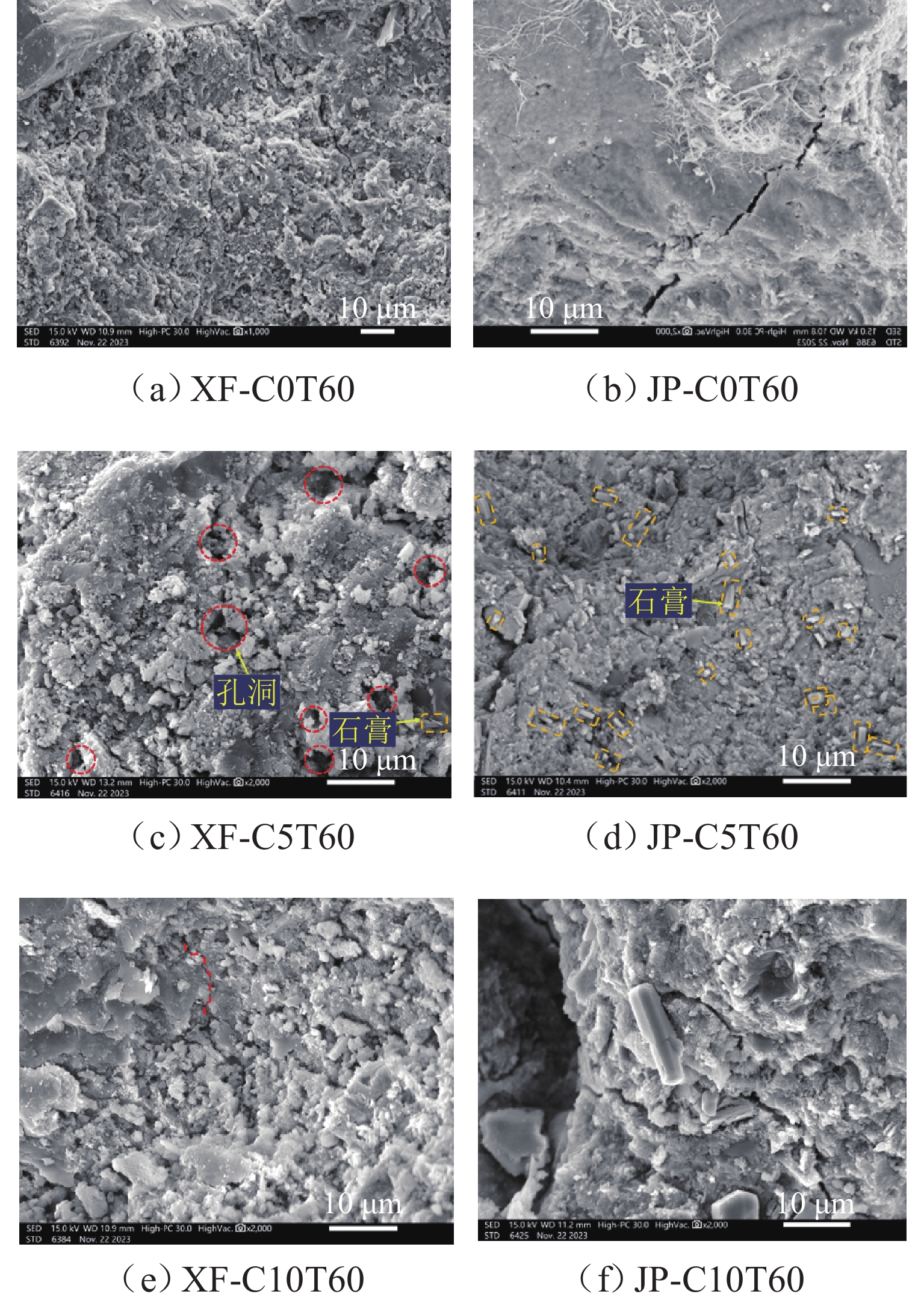
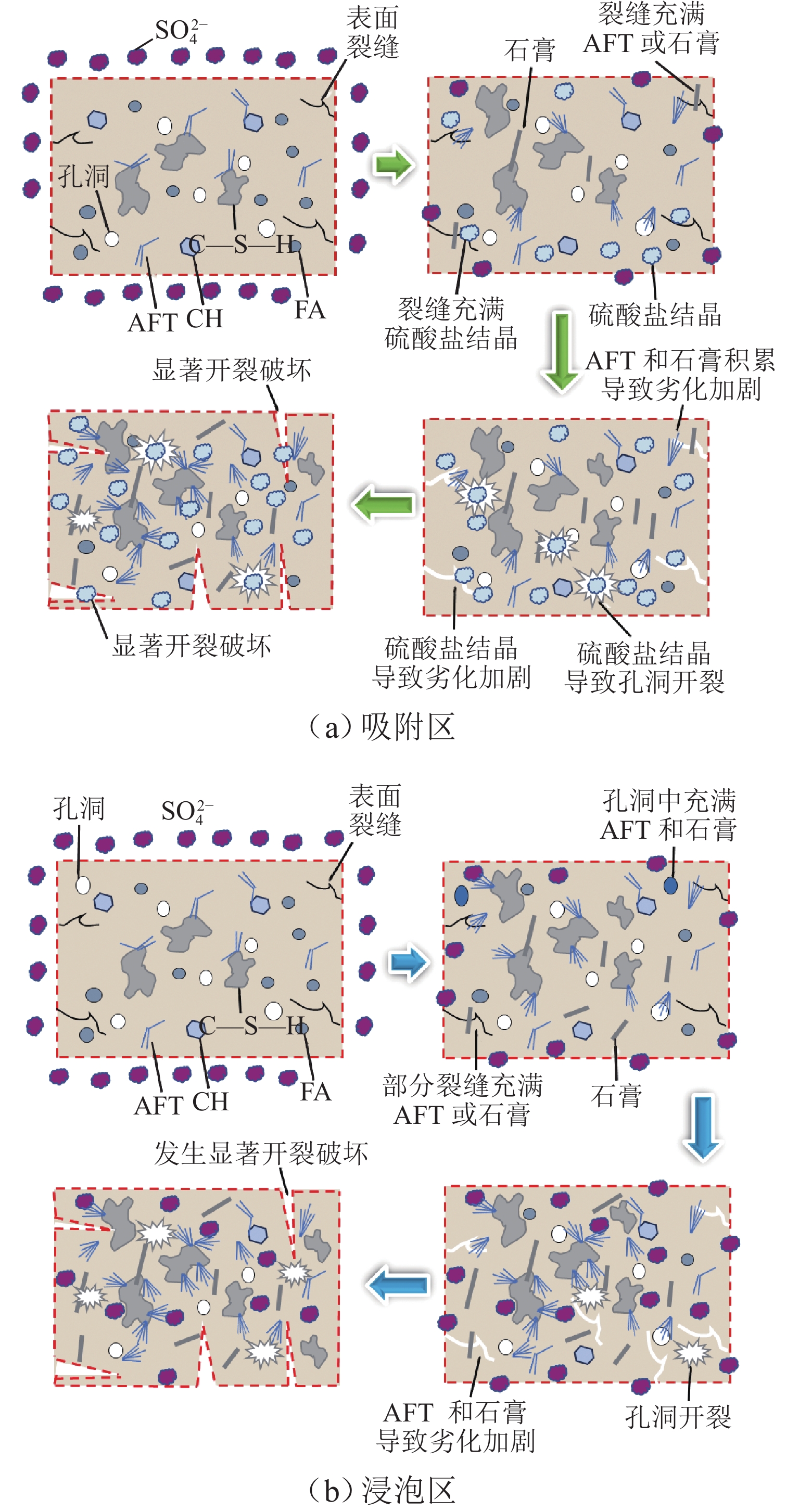
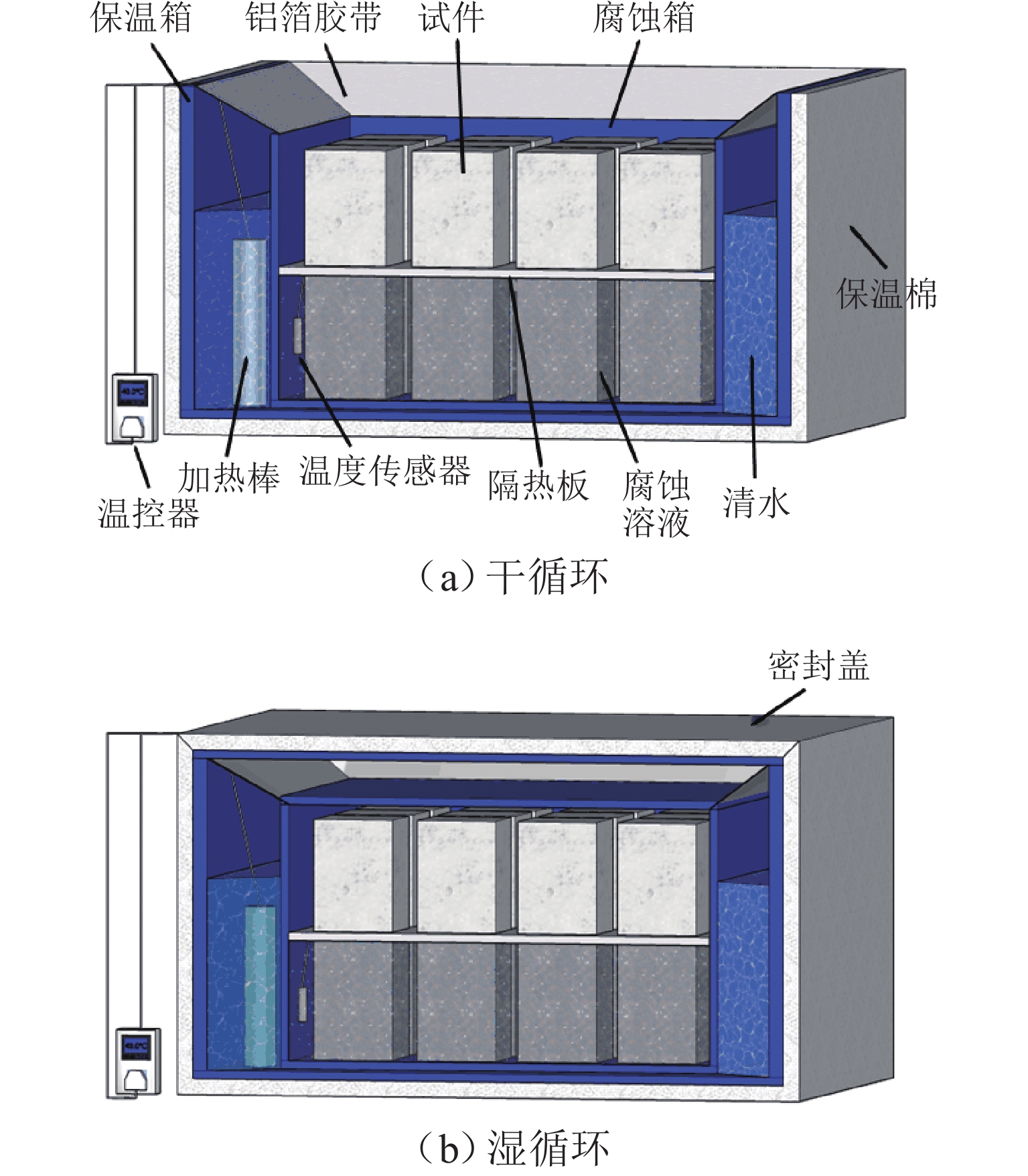
针对海洋工程中混凝土材料在硫酸盐环境中的损伤劣化问题,开展在半浸泡环境中不同浓度的硫酸盐溶液侵蚀和高温作用下混凝土侵蚀试验、微观试验. 通过分析混凝土试件质量变化、动弹性模量、侵蚀产物的成分与含量、硫酸根离子含量,结合微观测试,揭示半浸泡和硫酸盐环境下高温-干湿循环作用下混凝土损伤劣化规律. 结果表明:硫酸盐侵蚀初期,硫酸盐侵入浸泡区混凝土内部,促进水化作用,混凝土内部的AFT、石膏会填充初始缝隙,产物起到填充作用及骨架作用;后期产物量继续增大会对混凝土造成破坏,动弹性模量下降12%~30%;吸附区的混凝土同时受到干湿循环和热循环,2种循环会加剧毛细作用、扩散作用,使盐类在混凝土内部易产生结晶,热循环会加速骨料和水泥基体脱离,形成更多的孔隙,有利于盐类继续侵入;硫酸钠的物理结晶前期填充作用对强度有提升,质量提升0.50%~1.75%,但后期的破坏作用更加严重.
Abstract:To address the damage and deterioration of concrete materials in a sulfate environment in marine engineering, a concrete erosion test and microscopic test under different concentrations of sulfate solution and high temperature in the semi-immersed environment were carried out. By analyzing the mass change, dynamic elastic modulus, composition and content of eroded products, and sulfate ion content of concrete specimens and conducting the microscopic test, the damage and deterioration law of concrete under the high temperature and dry−wet cycle in semi-immersed and sulfate environment was revealed. The results show that in the early stage of sulfate erosion, sulfate invades the interior of concrete in the immersion zone and promotes hydration. The ettringite (AFT) and gypsum inside the concrete fill the initial gap, and the products play a filling and skeleton role. However, the continuous increase of the product amount in the later stage causes damage to the concrete, and the dynamic elastic modulus decreases by 12%–30%. The concrete in the adsorption zone is subjected to both the dry−wet cycle and the thermal cycle. The two cycles aggravate the capillary and diffusion effects so that the salt is easy to crystallize inside the concrete. Additionally, the thermal cycle accelerates the separation of aggregate and cement matrix, forming more pores, which is conducive to the continued intrusion of salt. The filling effect in the early stage of sodium sulfate crystallization improves the strength, and the mass increases by 0.5%–1.75%. However, the damage effect in the later stage is more serious.
-
Key words:
- concrete in marine engineering /
- sulfate erosion /
- semi-immersion /
- thermal cycle /
- dry−wet cycle
-
表 1 混凝土配合比
Table 1. Proportion of concrete mix
kg/m 材料 水 水泥 粉煤灰 砂 小石 中石 用量/(kg·m−3) 157 279 70 736 220 885 表 2 试验工况
Table 2. Test conditions
编号 Na2SO4 溶液
浓度/%温度/℃ 侵蚀
时间/dC0T20 0 20 0、30、60、
90、120、150C0T40 0 40 C0T60 0 60 C5T20 5 20 C5T40 5 40 C5T60 5 60 C10T20 10 20 C10T40 10 40 C10T60 10 60 -
[1] 唐颖玉. 西部艰险地区铁路桥梁工程技术风险管理研究[D]. 长沙: 中南大学, 2022. [2] 陆娅楠. 中国铁路, 丈量大国前行步伐[N]. 人民日报, 2022-11-22. [3] HAKEEM I, HOSEN M A, ALYAMI M, et al. Influence of heat–cool cyclic exposure on the performance of fiber-reinforced high-strength concrete[J]. Sustainability, 2023, 15(2): 1433.1-1433.24. [4] YAO J W, SONG H, CHEN J K. Effect of temperature on damage of mortars with different supplementary cementitious materials (SCMs) under sulfate attack[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2023, 394: 132183.1-132183.19. [5] 王程程. 热害对混凝土硫酸盐腐蚀的影响研究[D]. 成都: 西南交通大学, 2015. [6] SANTHANAM M, COHEN M D, OLEK J. Modeling the effects of solution temperature and concentration during sulfate attack on cement mortars[J]. Cement and Concrete Research, 2002, 32(4): 585-592. doi: 10.1016/S0008-8846(01)00727-X [7] ZOU D J, QIN S S, LIU T J, et al. Experimental and numerical study of the effects of solution concentration and temperature on concrete under external sulfate attack[J]. Cement and Concrete Research, 2021, 139: 106284.1-106284.11. [8] 葛子毅, 逯静洲, 王晨, 等. 轴压荷载对半浸泡混凝土硫酸盐侵蚀的影响[J]. 工业建筑, 2020, 50(1): 130-134, 161.GE Ziyi, LU Jingzhou, WANG Chen, et al. Effect of axial load on sulfate attack of semi-impregnated concrete[J]. Industrial Construction, 2020, 50(1): 130-134, 161. [9] IRASSAR E F, DI MAIO A, BATIC O R. Sulfate attack on concrete with mineral admixtures[J]. Cement and Concrete Research, 1996, 26(1): 113-123. doi: 10.1016/0008-8846(95)00195-6 [10] 李果, 陈建壮, 郭东芹. 盐渍土环境掺粉煤灰、矿粉混凝土的硫酸盐腐蚀[J]. 徐州工程学院学报(自然科学版), 2015, 30(3): 70-75. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-358X.2015.03.012LI Guo, CHEN Jianzhuang, GUO Dongqin. Sulfate corrosion of concrete with fly ash or slag in saline soil environment[J]. Journal of Xuzhou Institute of Technology (Natural Sciences Edition), 2015, 30(3): 70-75. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-358X.2015.03.012 [11] 刘赞群, 裴敏, 张丰燕, 等. 半浸泡在Na2SO4溶液中水泥净浆不同部位化学侵蚀产物对比[J]. 建筑材料学报, 2020, 23(3): 485-492.LIU Zanqun, PEI Min, ZHANG Fengyan, et al. Comparison of chemical attack products in different zones of cement paste partially immersed in Na2SO4 solution[J]. Journal of Building Materials, 2020, 23(3): 485-492. [12] CHEN F, GAO J M, QI B, et al. Deterioration mechanism of plain and blended cement mortars partially exposed to sulfate attack[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2017, 154: 849-856. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2017.08.017 [13] WEN R J, CHEN Y Q, GUO T, et al. Effects of temperature on ion transport in C-A-S-H gel nanopores: insights from molecular dynamics simulations[J]. Journal of Materials Science, 2022, 57(39): 18437-18455. doi: 10.1007/s10853-022-07796-3 [14] WINKLER E M, SINGER P C. Crystallization pressure of salts in stone and concrete[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 1972, 83(11): 3509-3514. doi: 10.1130/0016-7606(1972)83[3509:CPOSIS]2.0.CO;2 [15] THAULOW N, SAHU S. Mechanism of concrete deterioration due to salt crystallization[J]. Materials Characterization, 2004, 53(2/3/4): 123-127. [16] HAYNES H, O’NEILL R, NEFF M, et al. Salt weathering distress on concrete exposed to sodium sulfate environment[J]. ACI Materials Journal, 2008, 105(1): 35-43. [17] VOGLER N, DRABETZKI P, LINDEMANN M, et al. Description of the concrete carbonation process with adjusted depth-resolved thermogravimetric analysis[J]. Journal of Thermal Analysis and Calorimetry, 2022, 147(11): 6167-6180. doi: 10.1007/s10973-021-10966-1 [18] PAVLÍK Z, TRNÍK A, KULOVANÁ T, et al. DSC and TG analysis of a blended binder based on waste ceramic powder and Portland cement[J]. International Journal of Thermophysics, 2016, 37(3): 32.1-32.14. [19] SUN D D, WU K, SHI H S, et al. Effect of interfacial transition zone on the transport of sulfate ions in concrete[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2018, 192: 28-37. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2018.10.140 [20] MIN H G, SUI L L, XING F, et al. An effective transport model of sulfate attack in concrete[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2019, 216: 365-378. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2019.04.218 [21] KOZUBAL J, WYJADŁOWSKI M, STESHENKO D. Probabilistic analysis of a concrete column in an aggressive soil environment[J]. PLoS One, 2019, 14(3): e0212902.1-e0212902.20. [22] KUMAR M, PANDEY S. Correlation of solute diffusion with dynamic viscosity in lithium salt-added (choline chloride + glycerol) deep eutectic solvents[J]. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 2023, 25(48): 33141-33151. doi: 10.1039/D3CP04664H [23] ZHANG X, QIAN C X, CHEN H C, et al. Calculation of expansion stresses and strains in concrete under sulfate crystallization attack in dry–wet cycles environments[J]. Journal of Materials in Civil Engineering, 2021, 33(3): 04020479.1-04020479.8. [24] 吴笑梅, 高强, 丁浩, 等. 低热硅酸盐水泥混凝土疲劳性能研究[J]. 西南交通大学学报, 2019, 54(2): 313-318. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.20160817WU Xiaomei, GAO Qiang, DING Hao, et al. Flexural fatigue performance of concrete prepared with low-heat Portland cement[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2019, 54(2): 313-318. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.20160817 [25] 夏冬桃, 吴晨, 崔凯, 等. 粉煤灰和硅灰取代率对碱矿渣混凝土力学性能影响分析[J]. 西南交通大学学报, 2024, 59(5): 1113-1122. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.20230036XIA Dongtao, WU Chen, CUI Kai, et al. Effect of fly ash and silica fume contents on mechanical properties of alkali-activated slag-based concrete[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2024, 59(5): 1113-1122. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.20230036 -




 下载:
下载: