Vibration Reduction Characteristics of Hydraulically Interconnected Suspension on Middle and Rear Axles of Three-Axle Vehicle
-
摘要:
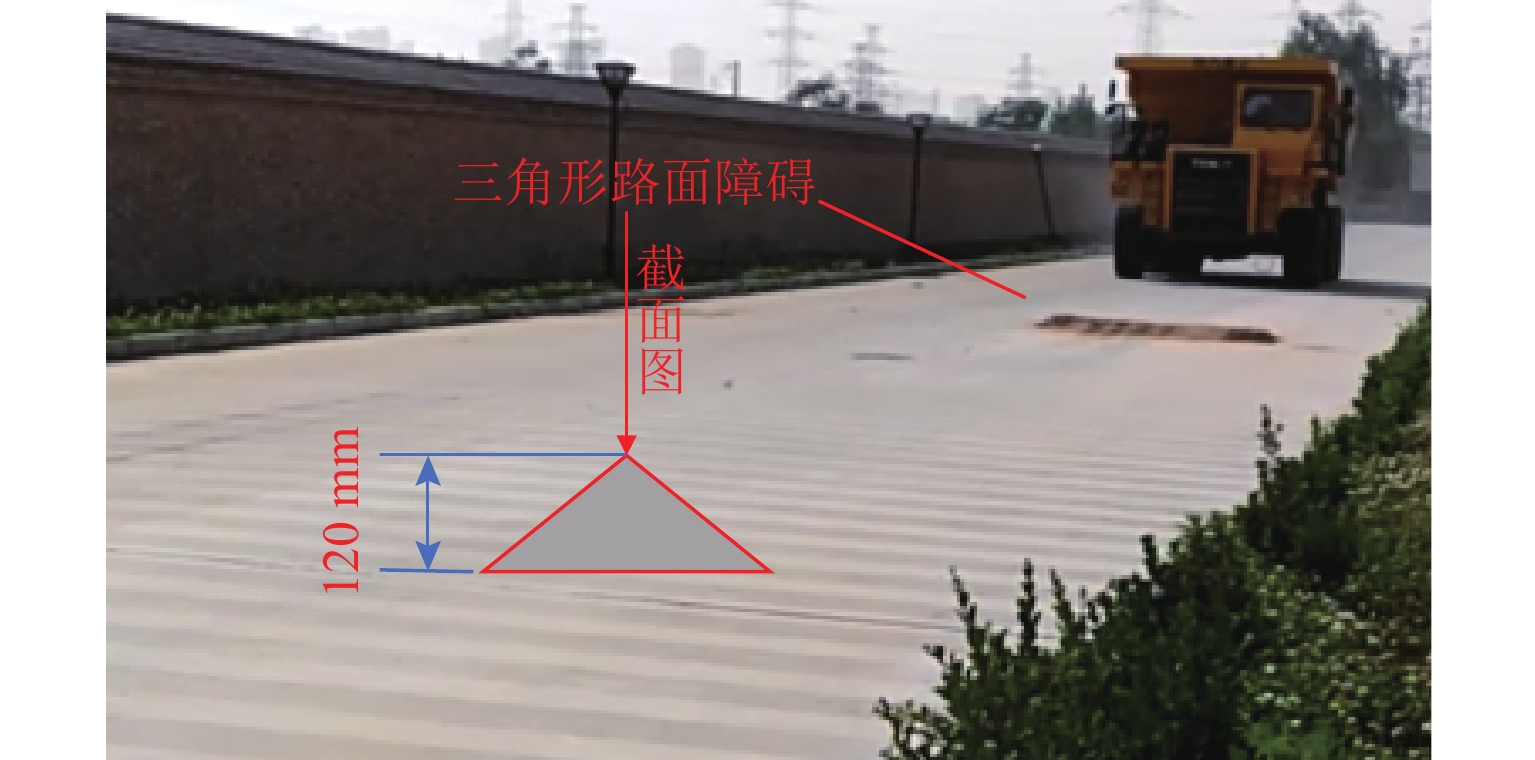
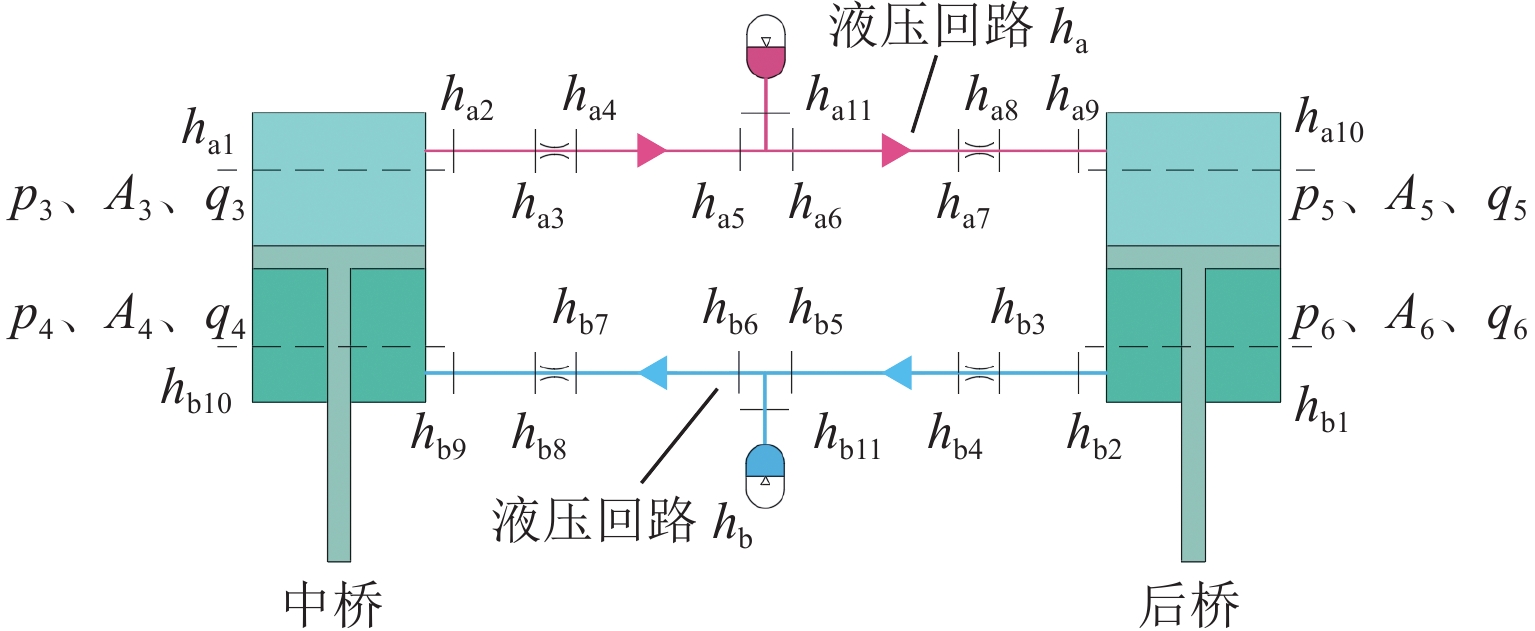
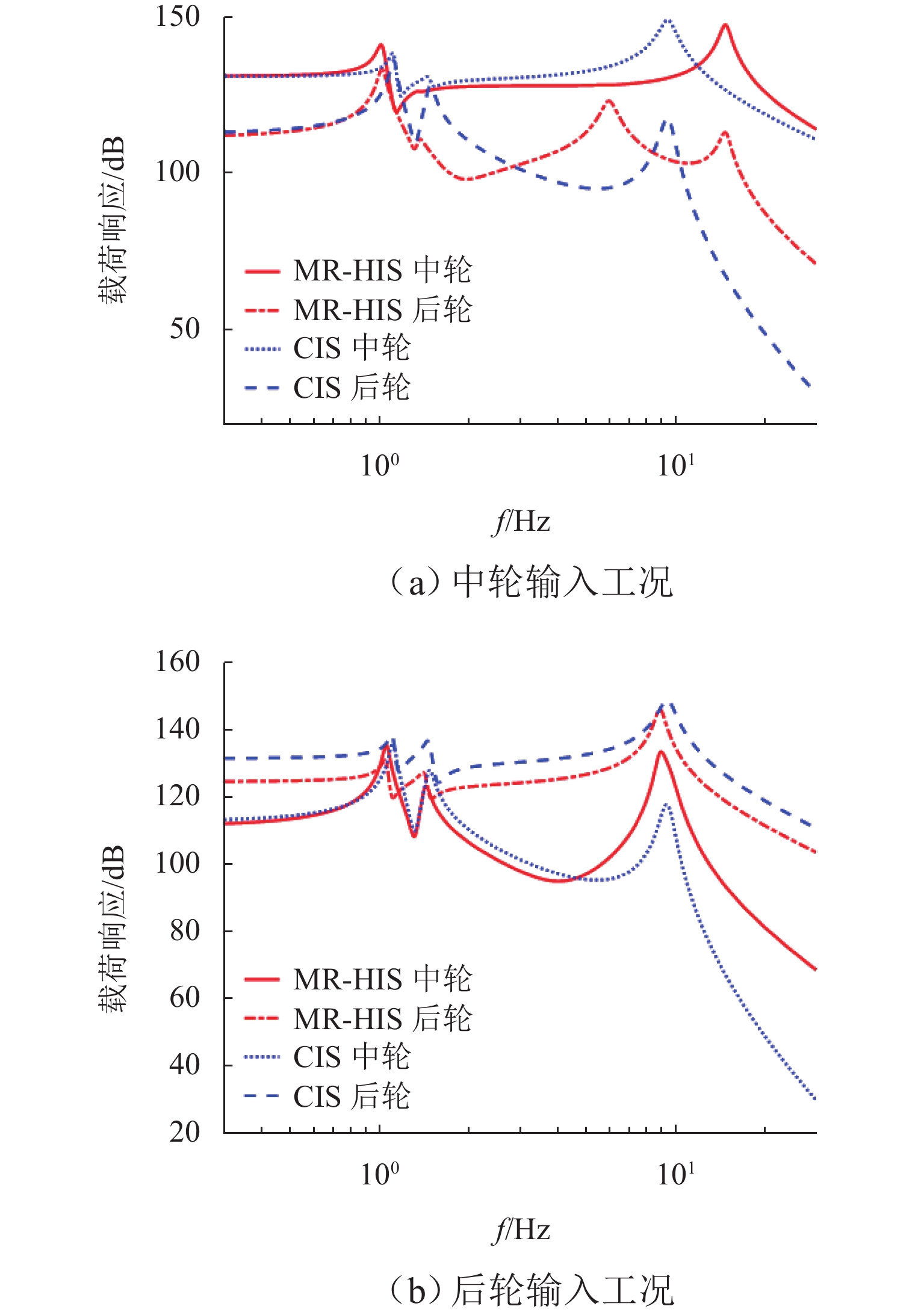
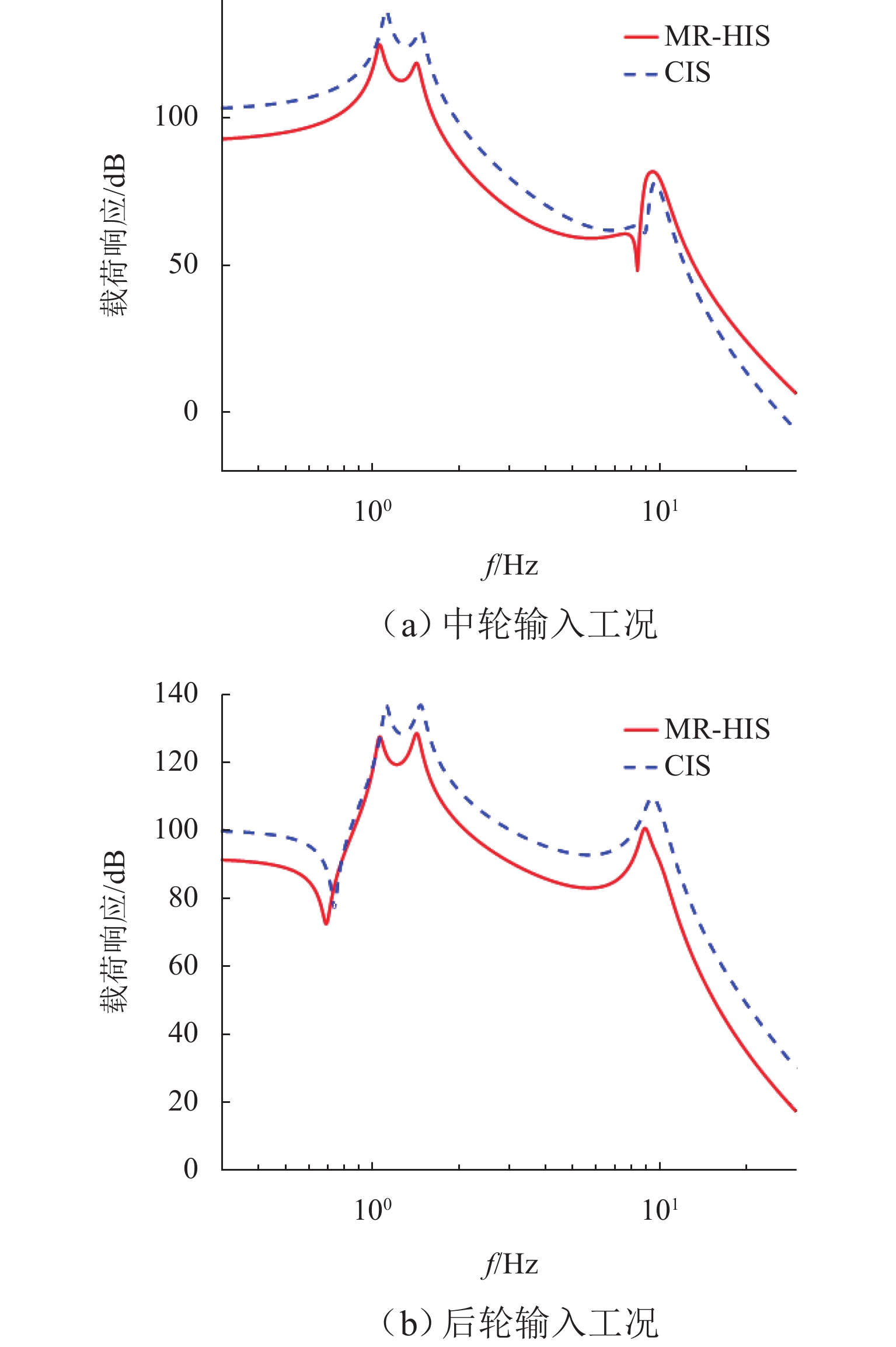
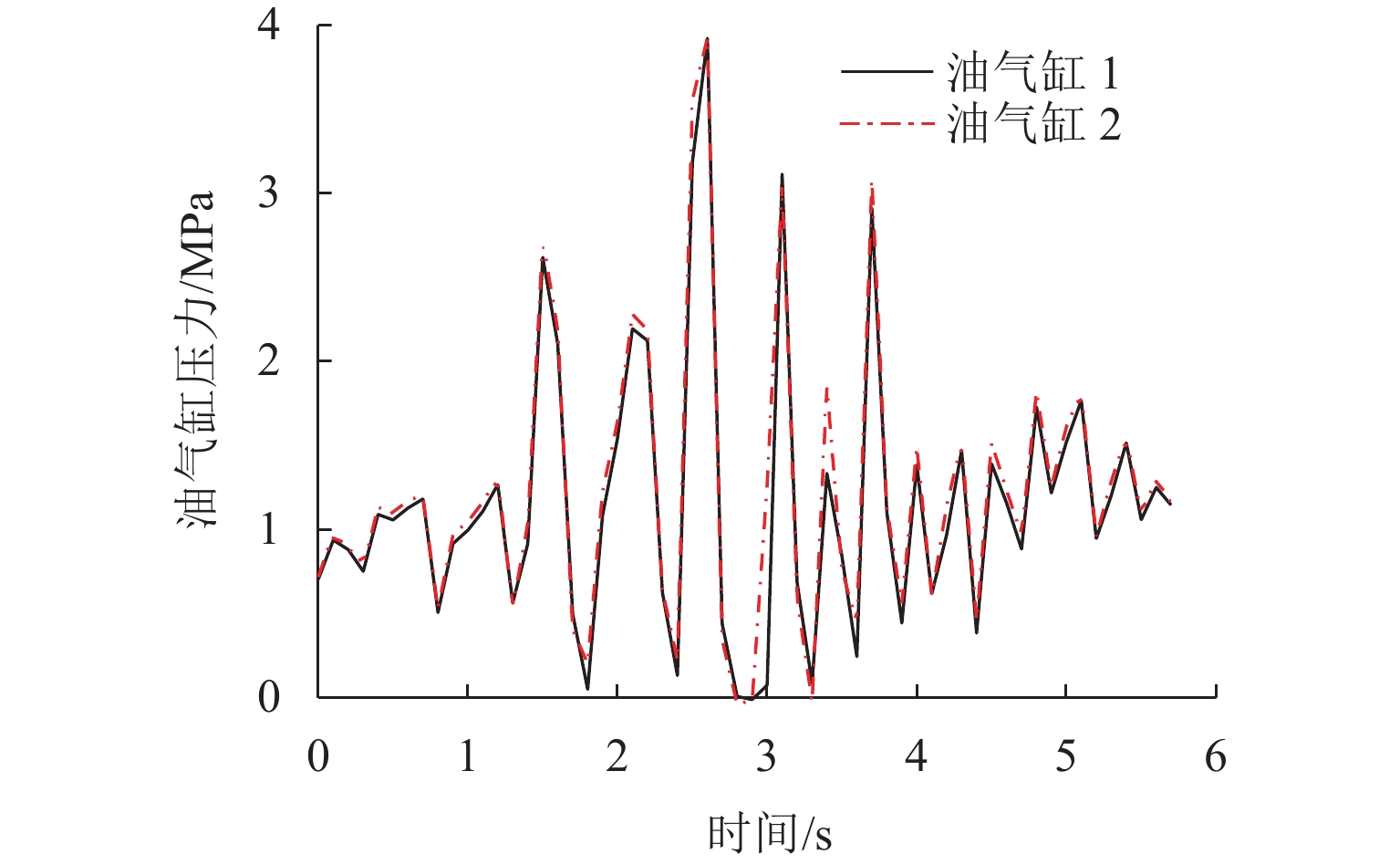
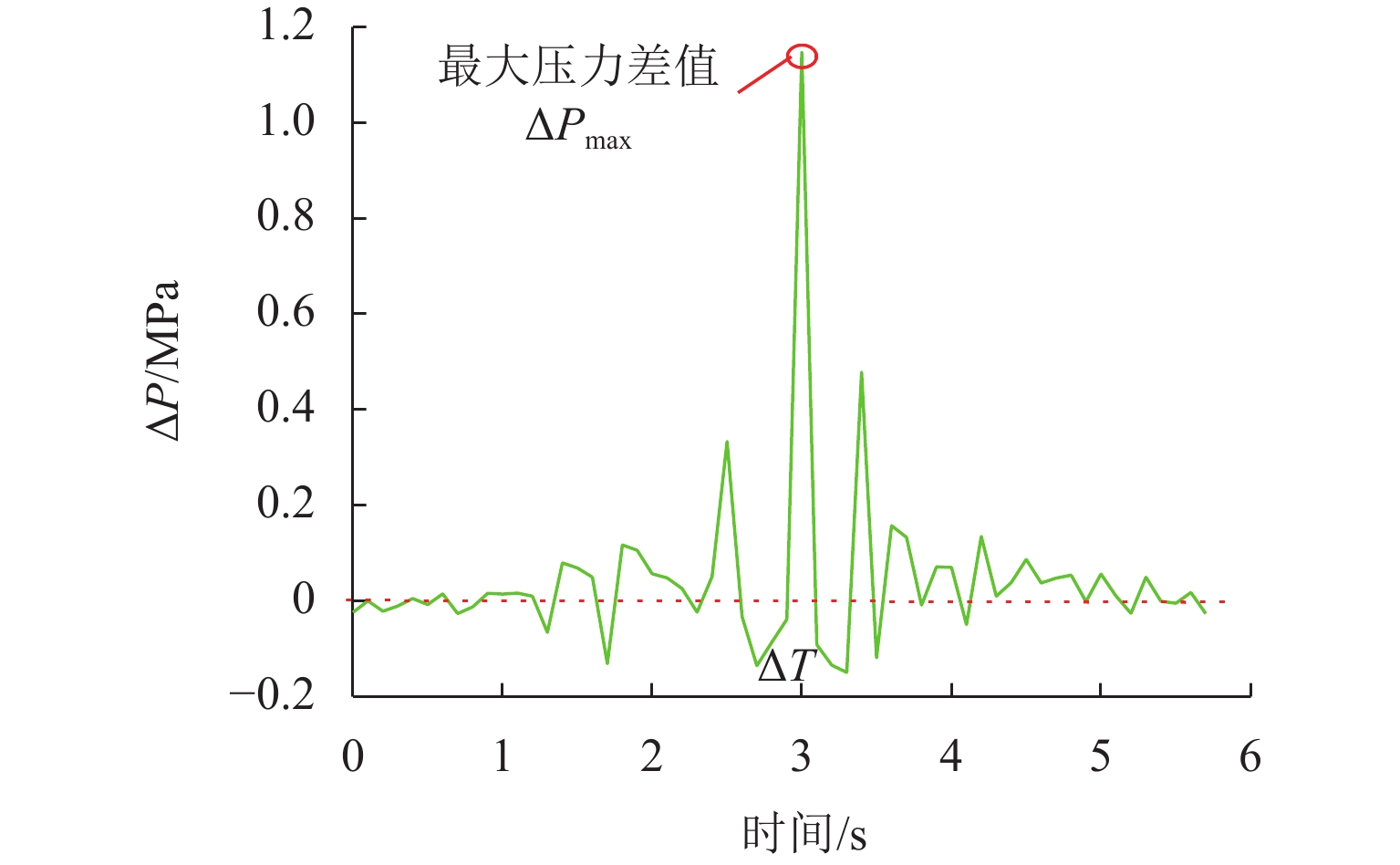
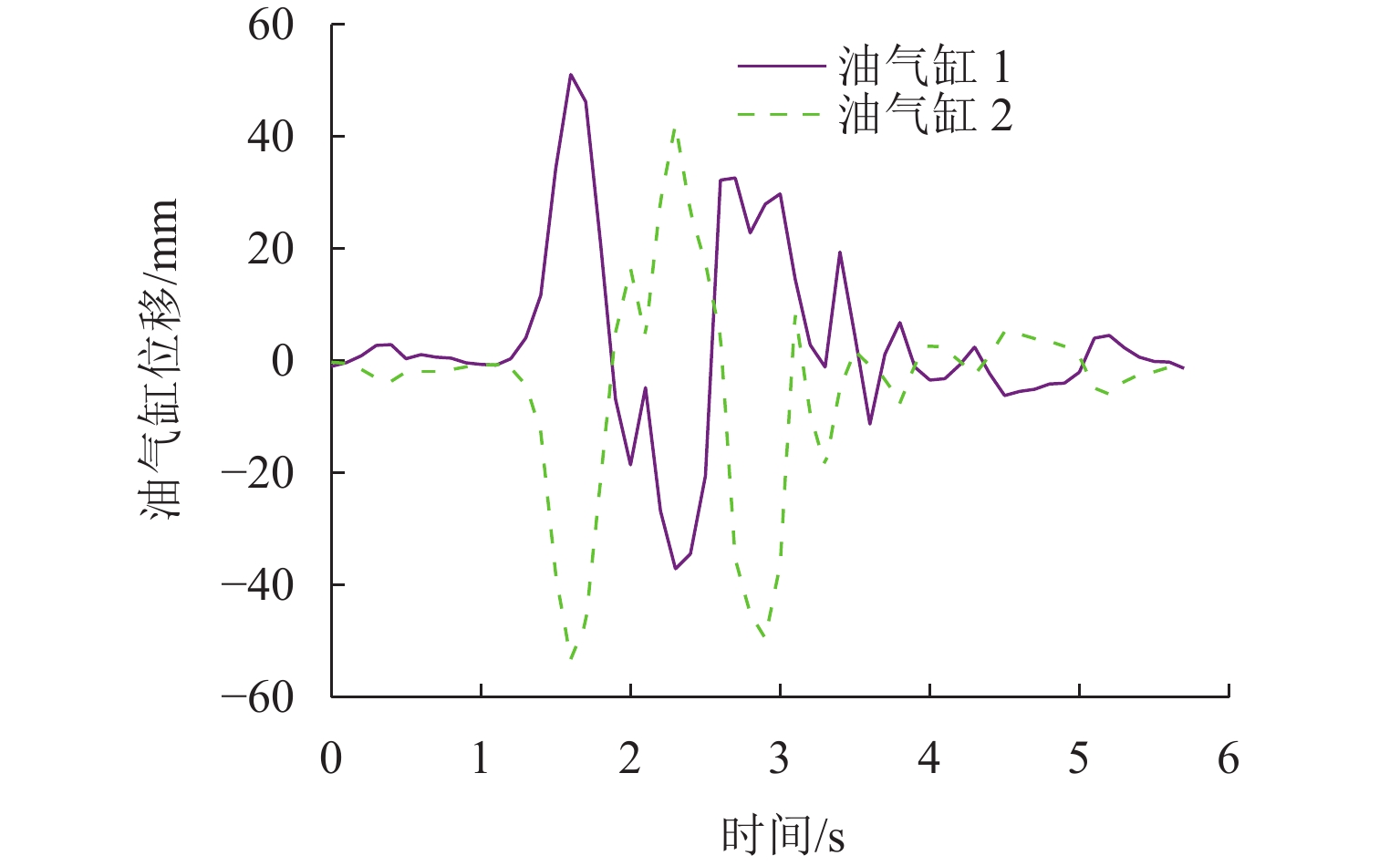
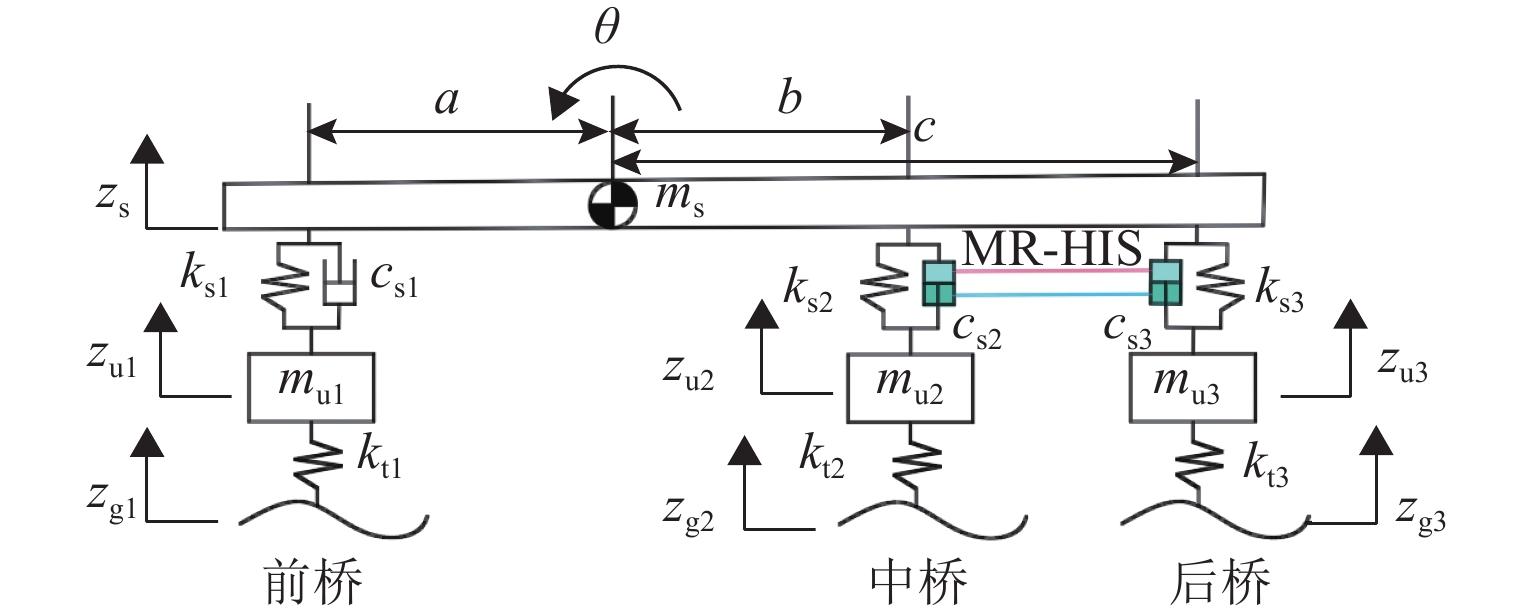
三轴矿用自卸车中、后桥为主要承重桥,其输出特性影响车辆的行驶稳定性. 为解决矿用自卸车的承载问题和提高车辆的行驶稳定性,提出一种液压互联悬架;采用阻抗传递矩阵法推导悬架的压力-流量关系式,得到1/2车辆机械-液压耦合方程;通过求解系统状态矩阵实现对车身-车轮运动模态的完全解耦,并开展路面障碍试验对悬架的工作特性进行研究. 分析结果表明:所提悬架系统能够降低车身垂跳运动的固有频率,增大阻尼比,使车身垂跳振动快速衰减,且改善了中、后轮的动载荷分配情况;当车辆以15 km/h速度驶越120 mm高的三角形障碍物时,其2个油气缸产生的最大压差达1.15 MPa,峰值响应出现在0.3 s内,有效实现负载均匀;2个油气缸位移量近似相等而方向互逆,很好地起到位移补偿作用,有助于维持行驶过程中的车身姿态.
Abstract:The middle and rear axles of three-axle mining dump trucks are the main load-bearing axles, and their output characteristics influence the driving stability of the vehicles. To solve the load-bearing problem of mining dump trucks and improve the driving stability of the vehicles at the same time, a kind of hydraulically interconnected suspension was proposed. The impedance transfer matrix method was adopted to derive the flow-pressure relationship of the suspension, and the 1/2 vehicle mechanical-hydraulic coupling equation was obtained. The complete decoupling of body-wheel motion modes was realized by solving the system state matrix. Finally, the road obstacle experiment was carried out to investigate the operational characteristics of the suspension. The analysis results show that the suspension system reduces the natural frequency of body bounce motion, increases the damping ratio, attenuates the body bounce vibration quickly, and improves the dynamic load distribution of the middle and rear wheels. When the vehicle passes a 120 mm high triangular road obstacle at the speed of 15 km/h, the maximum pressure difference between the two oil cylinders of the hydraulically interconnected suspension is 1.15 MPa, and the maximum response time is 0.3 s. These are good to achieve uniform load. At the same time, the displacement of the two oil cylinders is basically equal, but the direction is opposite, which plays a good role of displacement compensation and helps to maintain the attitude of the body during travel.
-
表 1 悬架系统参数
Table 1. Parameters of suspension system
符号 数值 单位 a, b, c 2.55, 0.75, 1.75 m ms 56000 kg Iyy 105000 kg·m2 mu1, mu2, mu3 1050 ,1550 ,1550 kg ks1, ks2, ks3 1230 ,1230 ,1230 kN/m cs1, cs2, cs3 12.5, 10.0, 10.0 kN·s/m kt1, kt2, kt3 3015 ,4200 ,4200 kN/m 表 2 液压系统参数
Table 2. Parameters of hydraulic system
符号 描述 取值 ρ 油液密度/(kg·m−3) 850 Bm 油液体积模量/MPa 1700 Pi 管道内径/m 0.022 Pw 管壁厚度/m 0.01 E 管道材料杨氏模量/MPa 206000 Pd 活塞直径/m 0.22 Pr 活塞杆直径/m 0.16 Ap 蓄能器预充气压/MPa 5 Av 蓄能器预充体积/m3 0.005 ke 耦连悬架等效刚度/(N·m−1) 1015000 pe 系统平均压力/MPa 8.2 表 3 VCIS和VMR-HIS模态对比表
Table 3. Modal comparison of VCIS and VMR-HIS
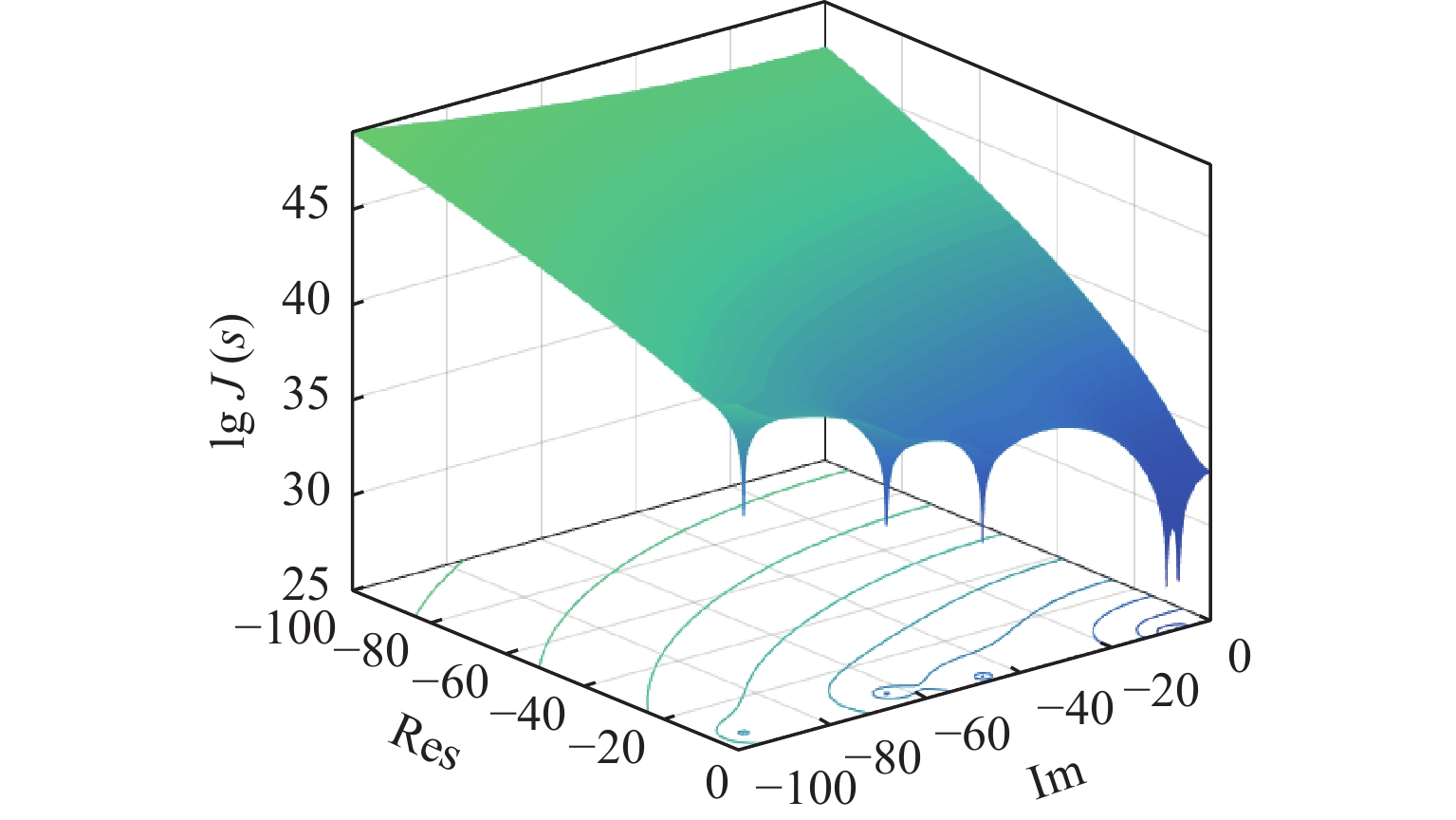
模态 VCIS VMR-HIS λ f/Hz ζ λ f/Hz ζ 第一阶 −0.176 + 5.938i 0.945 0.030 −0.262-4.934i 0.786 0.053 第二阶 −0.691 + 12.739i 2.030 0.054 −1.201-10.967i 1.756 0.109 第三阶 −5.236 + 47.618i 7.624 0.109 −5.227-47.619i 7.624 0.109 第四阶 −5.205 + 57.215i 9.144 0.091 −20.668-44.855i 7.860 0.419 第五阶 −5.718 + 57.506i 9.197 0.099 −2.433-61.206i 9.750 0.040 表 4 试验设备清单
Table 4. List of test equipment
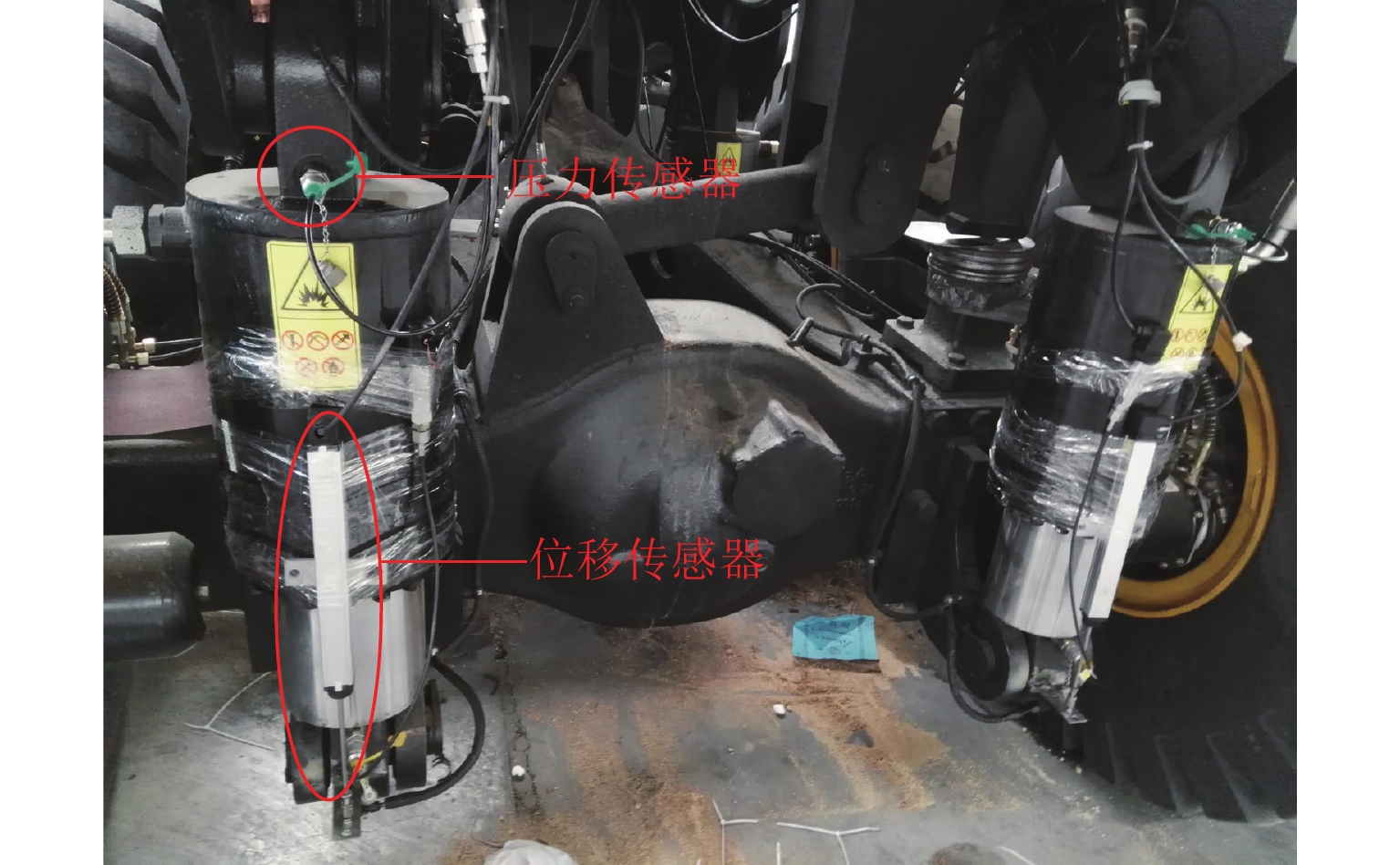
名称 型号 数量 三轴矿用自卸车 TLD110 1 辆 多通道数据采集仪 DEWE-2600 1 台 压力传感器 NS-P-I7 6 个 位移传感器 NS-WY03 6 个 -
[1] 寇发荣, 武大鹏, 许家楠, 等. 电磁混合主动悬架多模式协调切换控制[J]. 振动. 测试与诊断, 2023, 43(3): 467-475, 617-618.KOU Farong, WU Dapeng, XU Jianan, et al. Multi-mode coordinated switching control of electromagnetic hybrid active suspension[J]. Journal of Vibration, Measurement & Diagnosis, 2023, 43(3): 467-475, 617-618. [2] 周庭荣, 王良模, 王陶, 等. 轻型客车悬架系统垂向动力学优化研究[J]. 振动与冲击, 2023, 42(14): 131-137, 188.ZHOU Tingrong, WANG Liangmo, WANG Tao, et al. Vertical dynamics optimization of a light bus suspension system[J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2023, 42(14): 131-137, 188. [3] DING Fei, ZHANG Nong, HAN Xu. Dynamic characteristics of a tri-axle heavy truck fitted hydraulically anti-pith interconnected suspension[J]. Chinese Journal of Automotive Engineering, 2011, 1(4): 415-423. [4] 王玉龙, 张邦基, 郑敏毅. 装有抗侧翻液压互联悬架校车的动态特性分析[J]. 机械科学与技术, 2015, 34(4): 607-612.WANG Yulong, ZHANG Bangji, ZHENG Minyi. Dynamic analysis of school bus fitted with roll resistant specific hydraulically interconnected suspension system[J]. Mechanical Science and Technology for Aerospace Engineering, 2015, 34(4): 607-612. [5] SMITH M C, WALKER G W. Interconnected vehicle suspension[J]. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part D: Journal of Automobile Engineering, 2005, 219: 295-307. [6] ZHANG N, SMITH W A, JEYAKUMARAN J. Hydraulically interconnected vehicle suspension: background and modelling[J]. Vehicle System Dynamics, 2010, 48(1): 17-40. doi: 10.1080/00423110903243182 [7] SMITH W A, ZHANG N, JEYAKUMARAN J. Hydraulically interconnected vehicle suspension: theoretical and experimental ride analysis[J]. Vehicle System Dynamics, 2010, 48(1): 41-64. doi: 10.1080/00423110903243190 [8] QI H M, ZHANG N, CHEN Y C, et al. A comprehensive tune of coupled roll and lateral dynamics and parameter sensitivity study for a vehicle fitted with hydraulically interconnected suspension system[J]. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part D: Journal of Automobile Engineering, 2021, 235(1): 143-161. doi: 10.1177/0954407020944287 [9] WANG M, ZHANG B J, CHEN Y C, et al. Frequency-based modeling of a vehicle fitted with roll-plane hydraulically interconnected suspension for ride comfort and experimental validation[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 1091-1104. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2935260 [10] ZHANG J, DENG Y W, ZHANG N, et al. Vibration performance analysis of a mining vehicle with bounce and pitch tuned hydraulically interconnected suspension[J]. Chinese Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2019, 32(1): 195-211. [11] DING F, HAN X, LUO Z, et al. Modelling and characteristic analysis of tri-axle trucks with hydraulically interconnected suspensions[J]. Vehicle System Dynamics, 2012, 50(12): 1877-1904. doi: 10.1080/00423114.2012.699074 [12] DING F, HAN X, MO X H, et al. Design of hydraulically interconnected suspension systems for tri-axle straight trucks with rear tandem axle bogie suspensions[J]. SAE International Journal of Commercial Vehicles, 2013, 6(1): 200-208. doi: 10.4271/2013-01-1237 [13] DING F, ZHANG N, LIU J, et al. Dynamics analysis and design methodology of roll-resistant hydraulically interconnected suspensions for tri-axle straight trucks[J]. Journal of the Franklin Institute, 2016, 353(17): 4620-4651. doi: 10.1016/j.jfranklin.2016.08.016 [14] 张邦基, 易金花, 张农, 等. 装有动力调节悬架系统车辆的频域建模与仿真[J]. 湖南大学学报(自然科学版), 2016, 43(10): 8-15.ZHANG Bangji, YI Jinhua, ZHANG Nong, et al. Frequency-domain modelling and simulation of a vehicle fitted with kinetic dynamic suspension system[J]. Journal of Hunan University (Natural Sciences), 2016, 43(10): 8-15. [15] 吴晓建, 周兵, 文桂林. 考虑作动器动力学的半车主动互联悬架抗侧倾控制研究[J]. 振动与冲击, 2017, 36(12): 150-154.WU Xiaojian, ZHOU Bing, WEN Guilin. A study on anti-roll control of half-car model active interconnected suspension with consideration of actuator dynamics[J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2017, 36(12): 150-154. [16] 刘启航, 冯汉队, 刘申, 等. 基于AMESim的矿用自卸车悬架系统平顺性分析[J]. 西南交通大学学报, 2025, 60(2): 395-402.LIU Qihang, FENG Handui, LIU Shen, et al. Ride comfort analysis of suspension system of mining dump truck based on AMESim[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2025, 60(2): 395-402. [17] 任杰, 刘洋佐, 马大为. 发射车多轴连通式油气悬架的连通耦合效应[J]. 国防科技大学学报, 2023, 45(4): 153-161.REN Jie, LIU Yangzuo, MA Dawei. Coupling effects of multi-axles interconnected hydropneumatic suspension of launch vehicle[J]. Journal of National University of Defense Technology, 2023, 45(4): 153-161. [18] 刘秀梅, 李永涛. 车辆油气悬架技术研究综述[J]. 西南交通大学学报, 2025, 60(2): 374-394.LIU Xiumei, LI Yongtao. Review of research on vehicle hydro-pneumatic suspension technology[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2025, 60(2): 374-394. [19] 刘启航, 冯汉队, 刘申, 等. 基于AMESim的矿用自卸车悬架系统平顺性分析[J]. 西南交通大学学报, 2025, 60(2): 395-402.LIU Qihang, FENG Handui, LIU Shen, et al. Ride comfort analysis of suspension system of mining dump truck based on amesim[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2025, 60(2): 395-402. [20] DAI L , LIU Y , WANG L , et al. Study on the stiffness and damping characteristics of a single-chamber hydro-pneumatic suspension without hydro-pneumatic separation[J]. Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 2025, 2951(1): 012049. [21] YANG F, DU Y F, WEN C K, et al. Optimization design of the hydro-pneumatic suspension system for high clearance self-propelled sprayer using improved MOPSO algorithm[J]. International Journal of Agricultural and Biological Engineering , 2024, 17(2): 109-122. [22] WANG G F, WANG W T, SUO X F, et al. Multi-objective parameter optimization of a novel hydraulically interconnected suspension for tri-axle mining dump trucks[J]. Journal of Vibration and Control, 2024, 31(17/18): 3585-3598. [23] LI Z L, HOU H T, ZHANG Z, et al. Analysis of vehicle ride comfort and parameter optimization of hydro-pneumatic suspension for heavy duty mining vehicle[J]. Engineering Letters, 2024, 32(11): 2145-2152. [24] SUN A X, YU C C, XIE F W, et al. Ride comfort improvement by back propagation-active disturbance rejection control in semi-active hydro-pneumatic suspension of mining dump truck[J]. Journal of Vibration and Control, 2025, 35(11-12): 2378-2394. [25] 王刚锋, 王万汀, 索雪峰, 等. 矿用自卸车液压互联悬架参数灵敏度分析与优化[J]. 振动与冲击, 2024, 43(19): 232-241.WANG Gangfeng, WANG Wanting, SUO Xuefeng, et al. Sensitivity analysis and optimization of hydraulically interconnected suspensionparameters of mining dump trucks[J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2024, 43(19): 232-241. [26] 曹鸿立, 郭勇, 李洪周. 带有液压互联悬架的履带车行驶平顺性研究[J]. 振动与冲击, 2025, 44(17): 272-280.CAO Hongli, GUO Yong, LI Hongzhou. Ride comfort of tracked vehicles with hydraulic interconnected suspension[J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2025, 44(17): 272-280. -




 下载:
下载: