Route Guidance Model of Multi-Layer Network of Regional Highway for Balancing Individual and Social Benefits
-
摘要:
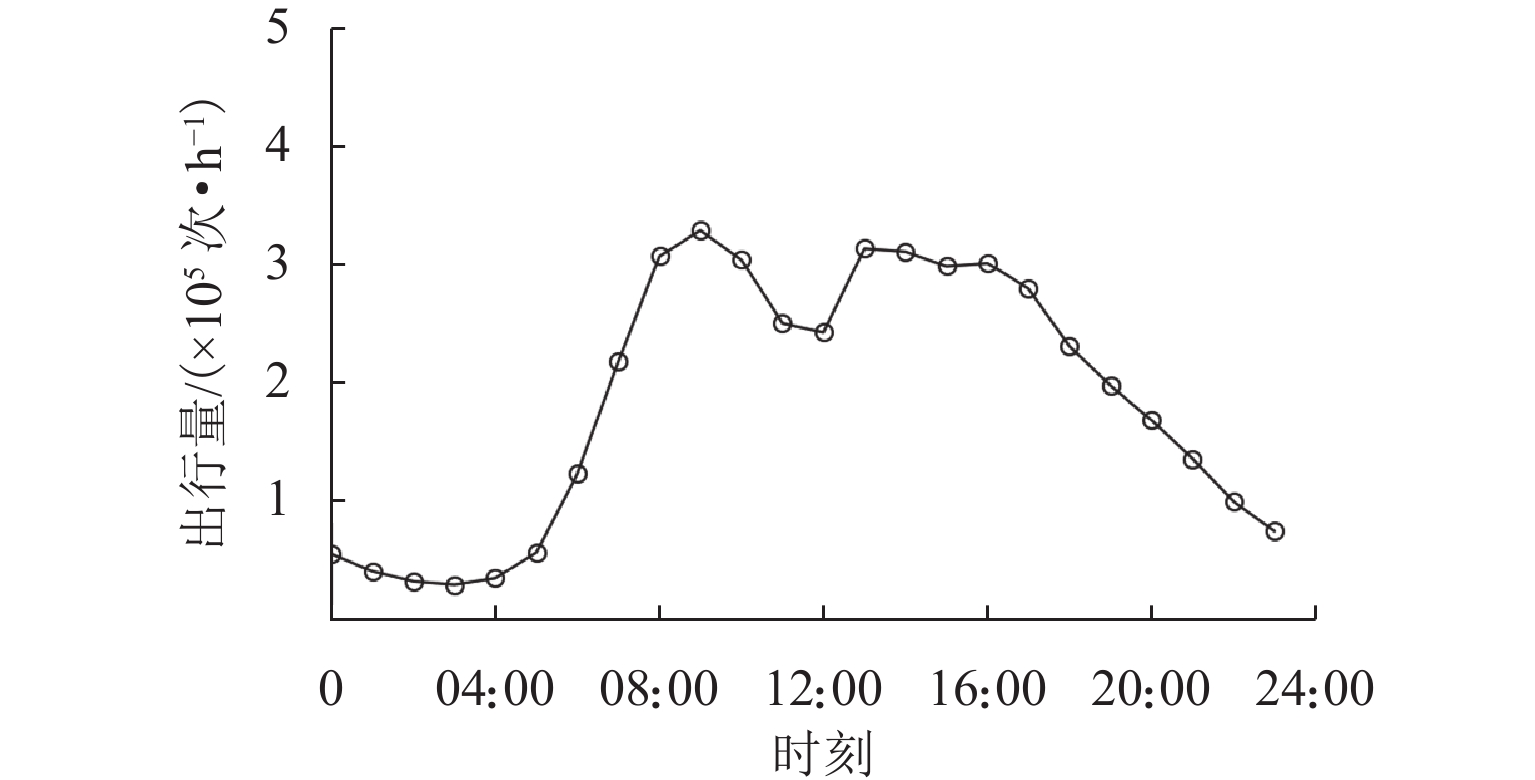
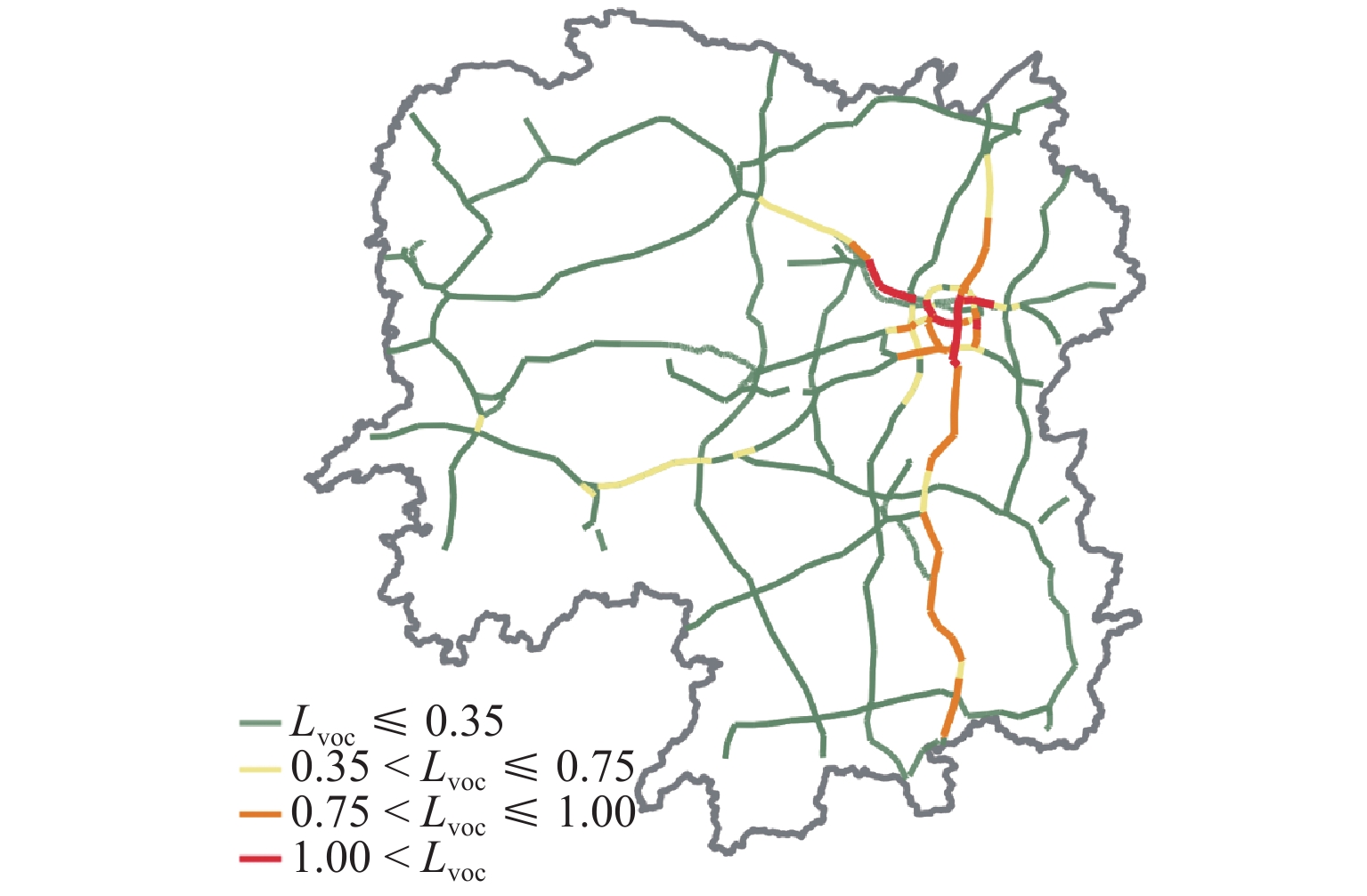
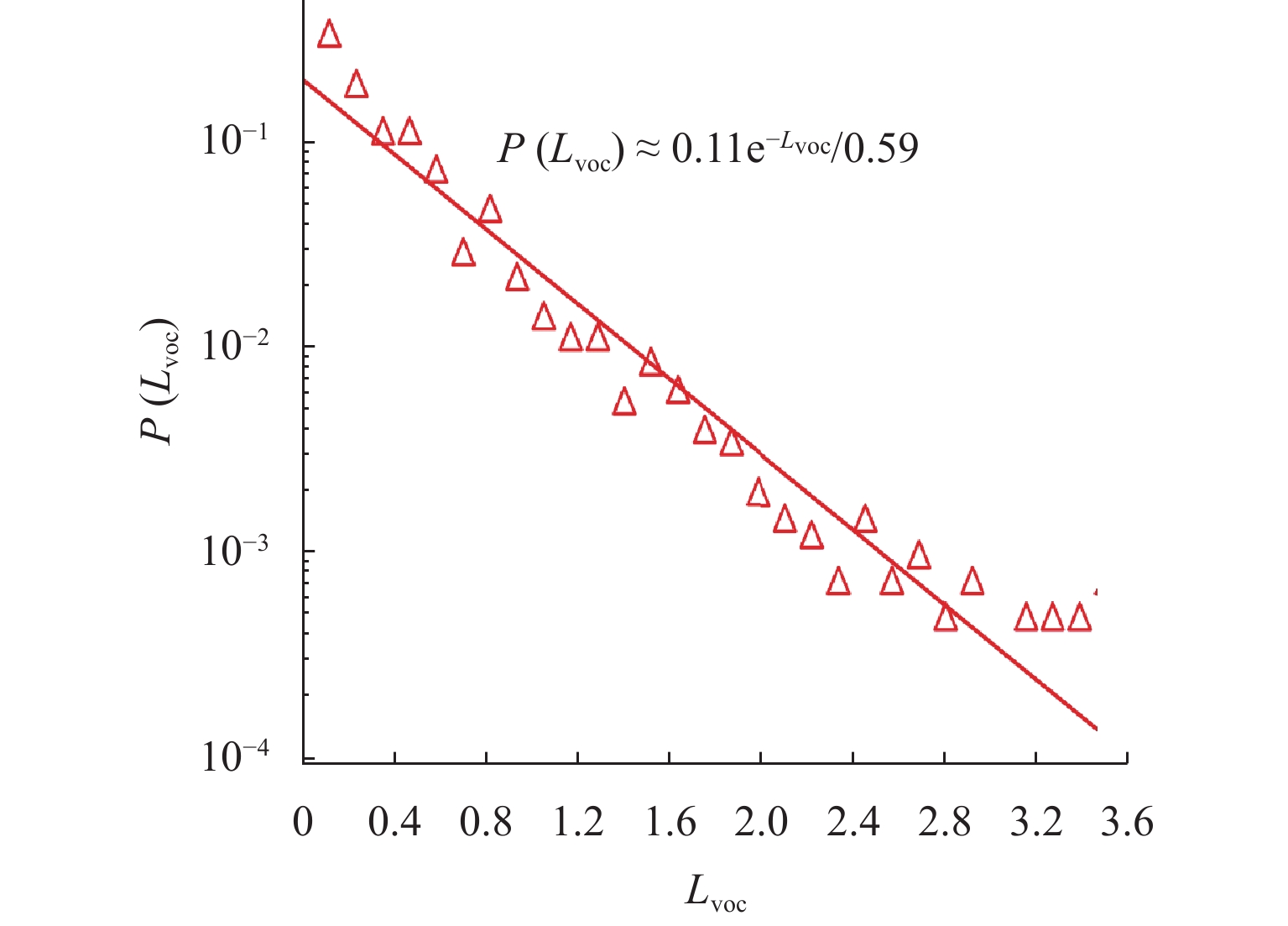
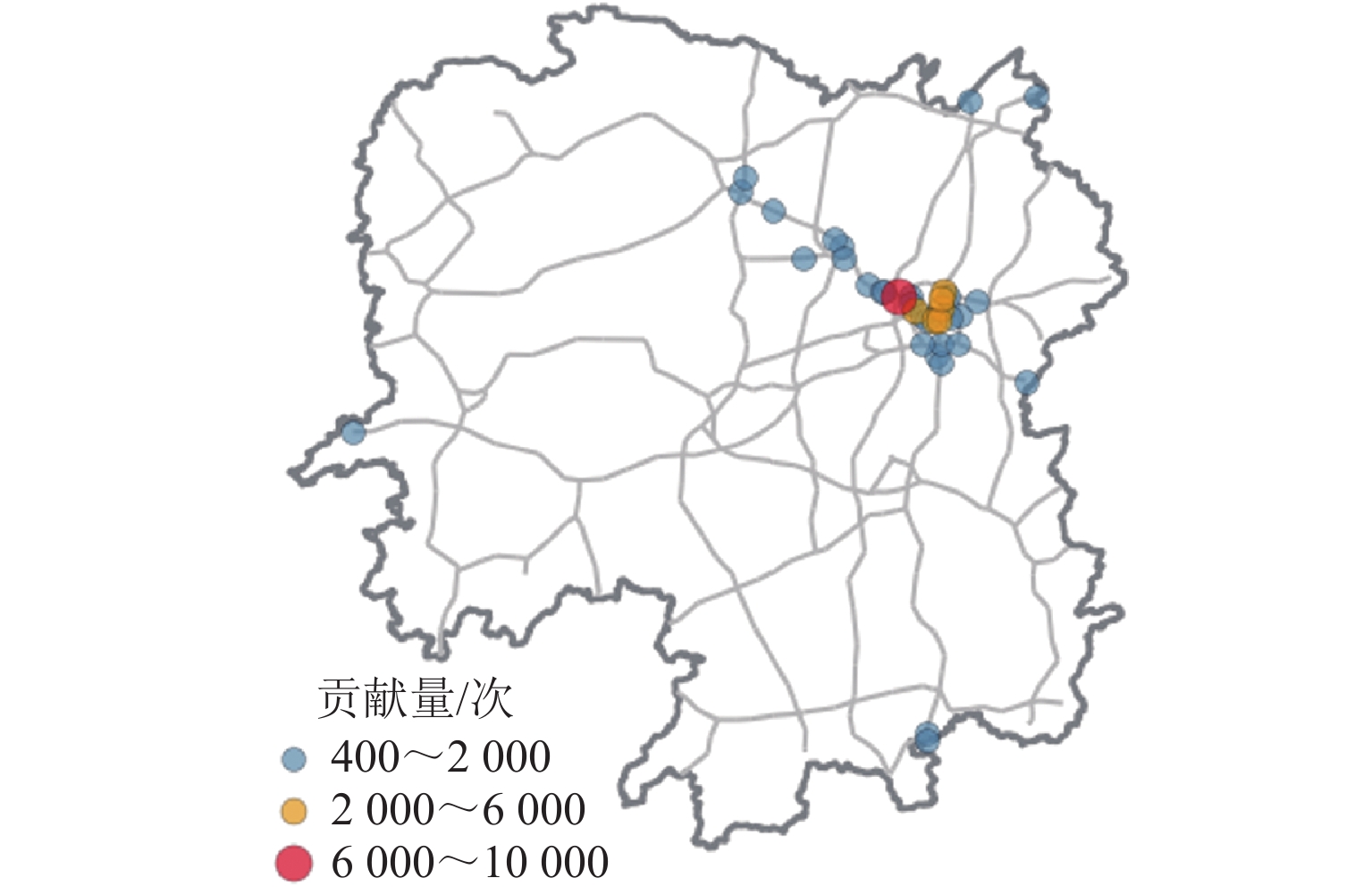
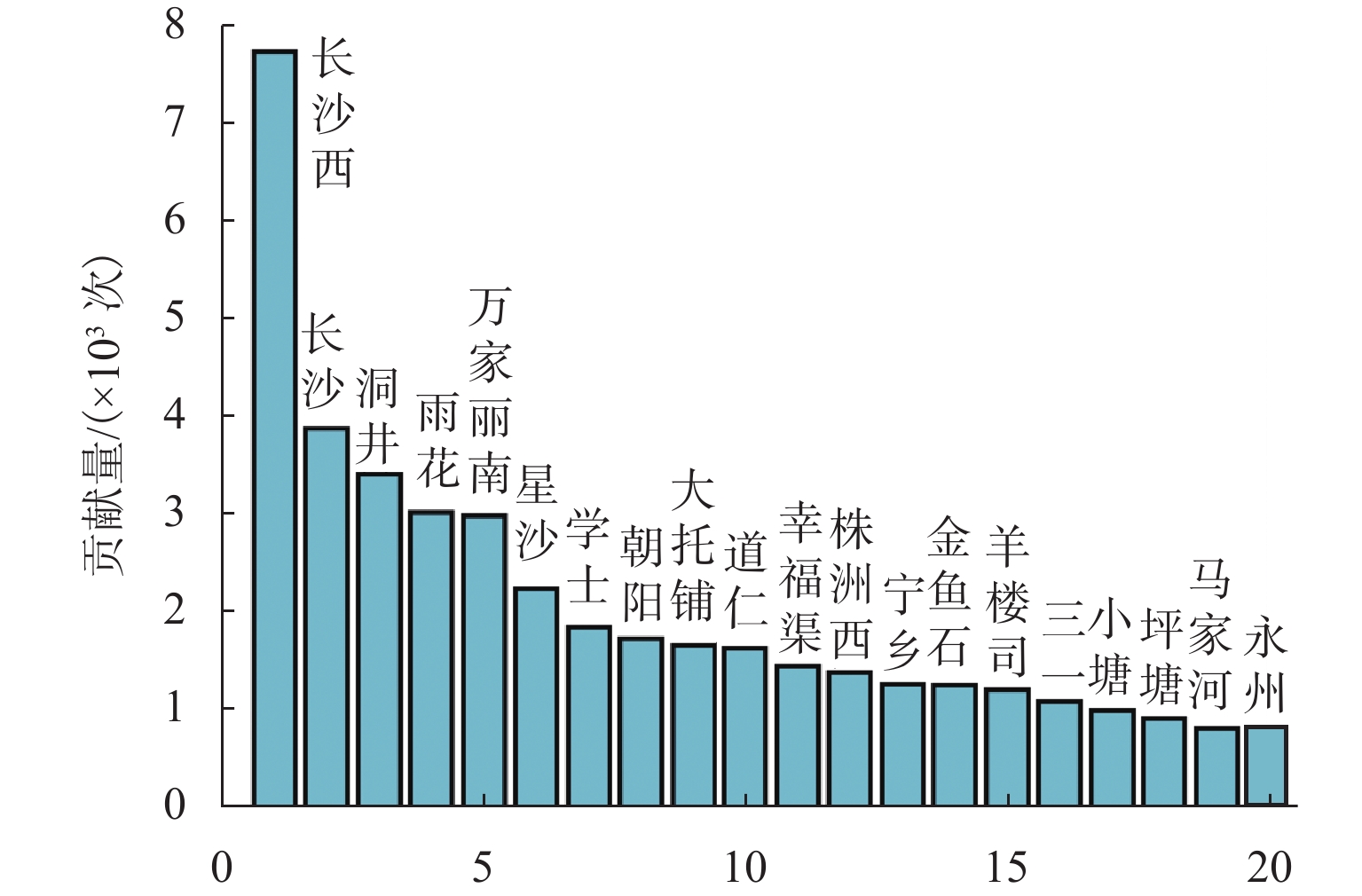
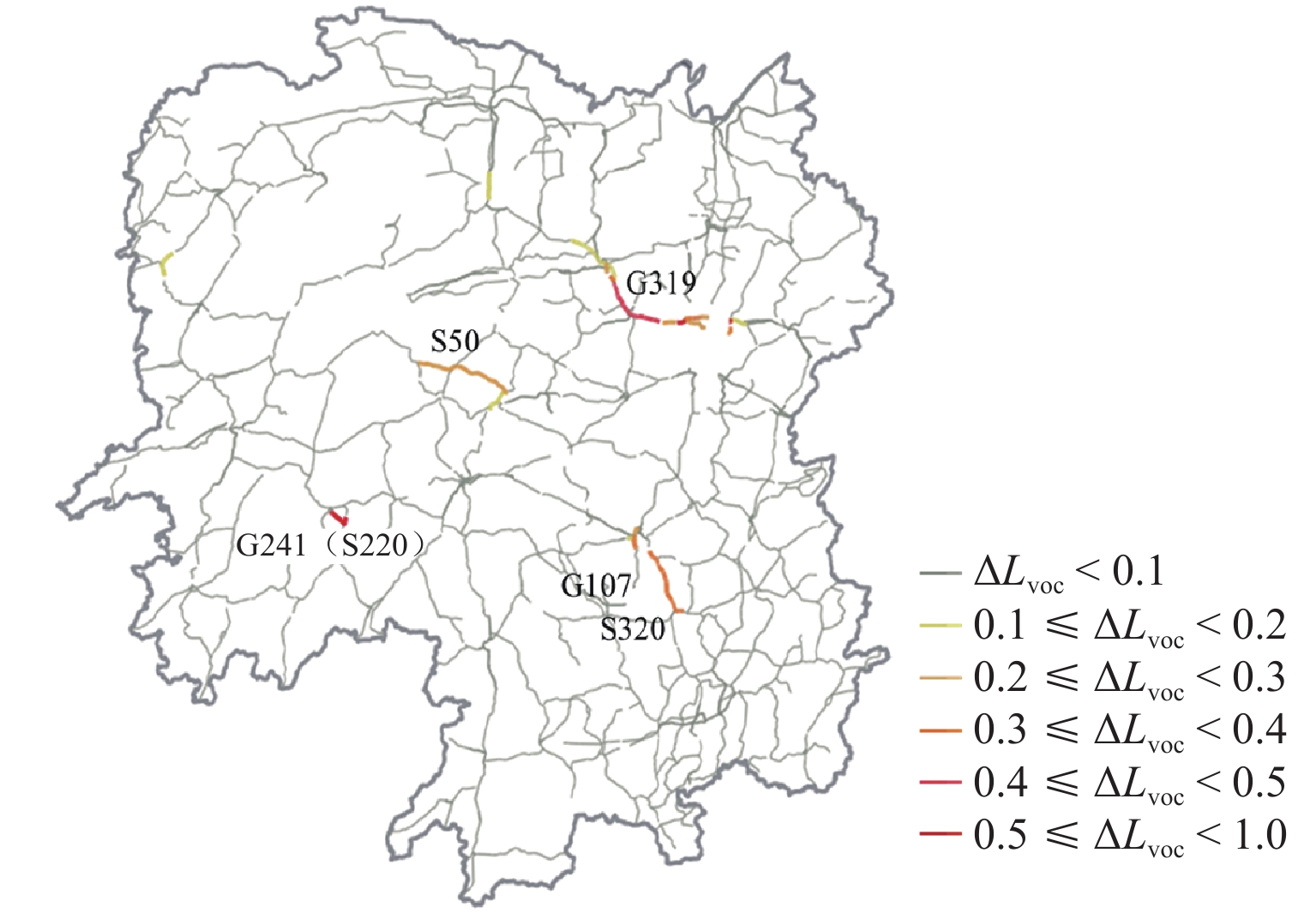
为增强路径诱导策略的针对性,提升路径诱导策略的效率和可实施性,提出一种基于区域高速公路多层网络和道路车源信息的路径诱导模型. 首先,基于复杂网络理论构建区域高速公路多层交通网络,通过识别高速公路网络中的拥堵路段并定位车源,对车源进行聚类以进一步确定发布路径诱导信息的位置;然后,运用社会公益系数控制出行成本函数,建立参数可变的路径诱导模型,以平衡个人和社会利益;最后,构建一个路径诱导信息发布框架,研究实施路径诱导方案时使用诱导路径的出行者占比对系统的影响. 研究结果表明:所提模型针对少部分出行者进行路径诱导,其平均出行时间仅增加2.1 min,而所有出行者的平均出行时间下降9.1 min;生成的路径诱导方案对出行者的不利影响较小,能够在考虑个人公平性的基础上有效减少系统总出行时间,为缓解高速公路交通拥堵提供更高效可行的方案.
Abstract:To make route guidance strategies more targeted for enhancing efficiency and practability, a route guidance model based on a multi-layer network and vehicle-source information of the regional highway was proposed. Firstly, a multi-layer network of the regional highway was constructed based on the complex network theory. The congested segments in the highway network were identified, and their vehicle sources were located and clustered. The locations for distributing route guidance information were further determined. Next, the travel cost function was controlled by applying the social welfare coefficient. A route guidance model with a variable parameter was established for balancing individual and social benefits. Finally, a route guidance information release framework was constructed, and the influence of the proportion of travelers using the guided routes on the system was investigated when the route guidance scheme was implemented. The results have shown that the proposed model guides a few travelers, and their average travel time increases by 2.1 minutes, while the average travel time of all travelers decreases by 9.1 minutes. The generated route guidance scheme poses a small adverse impact on the travelers, effectively decreases the total time spent when considering the fairness, and provides a more efficient and feasible strategy for alleviating highway congestion.
-
表 1 不同社会公益系数下的指标情况
Table 1. Indicators under different social welfare coefficients
$\lambda $ 社会利益指标 个人利益指标 0 最小 最大 (0, 1) 增大 减小 1 最大 最小 表 2 聚类与不聚类结果对比
Table 2. Comparison of clustered and unclustered results
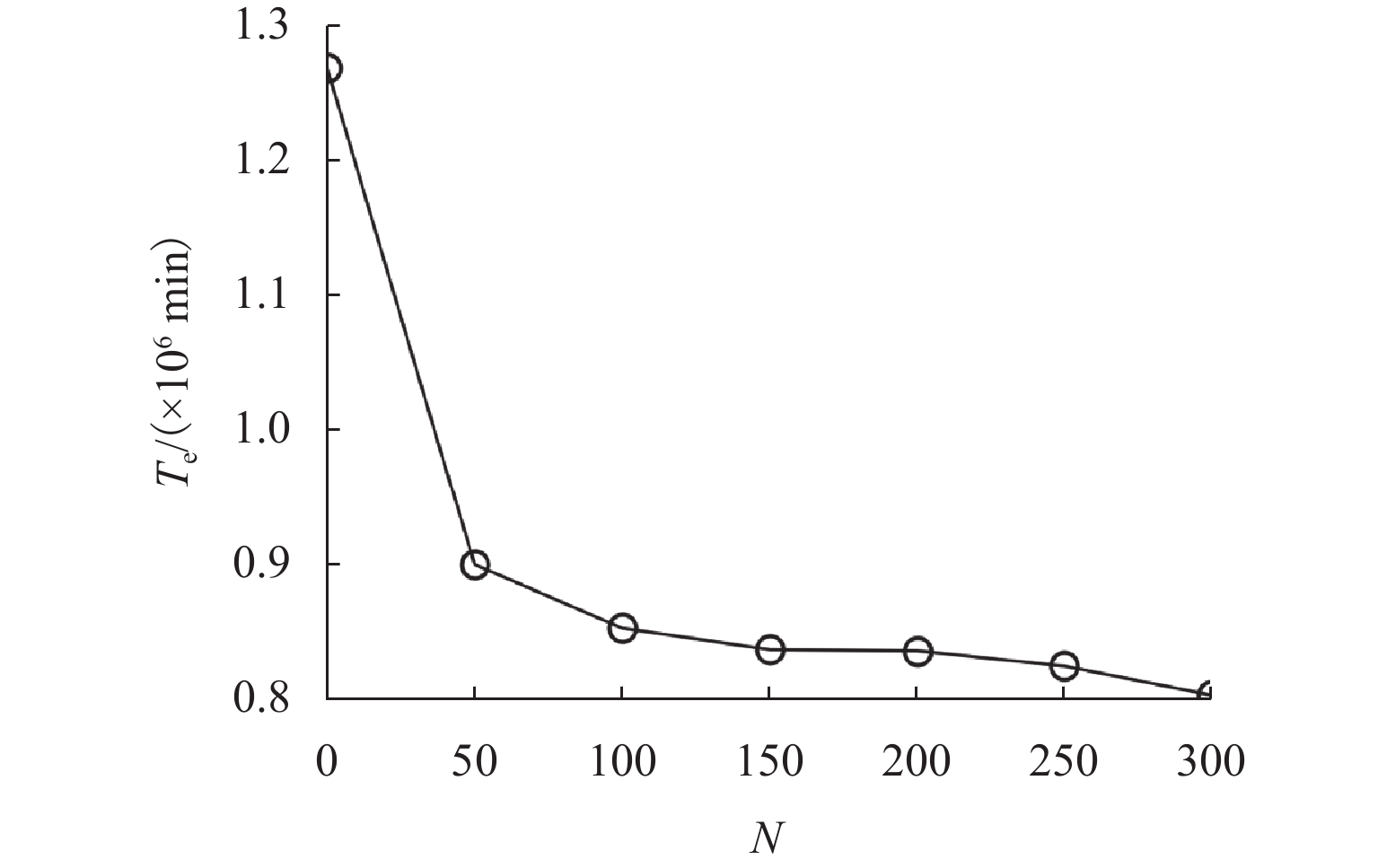
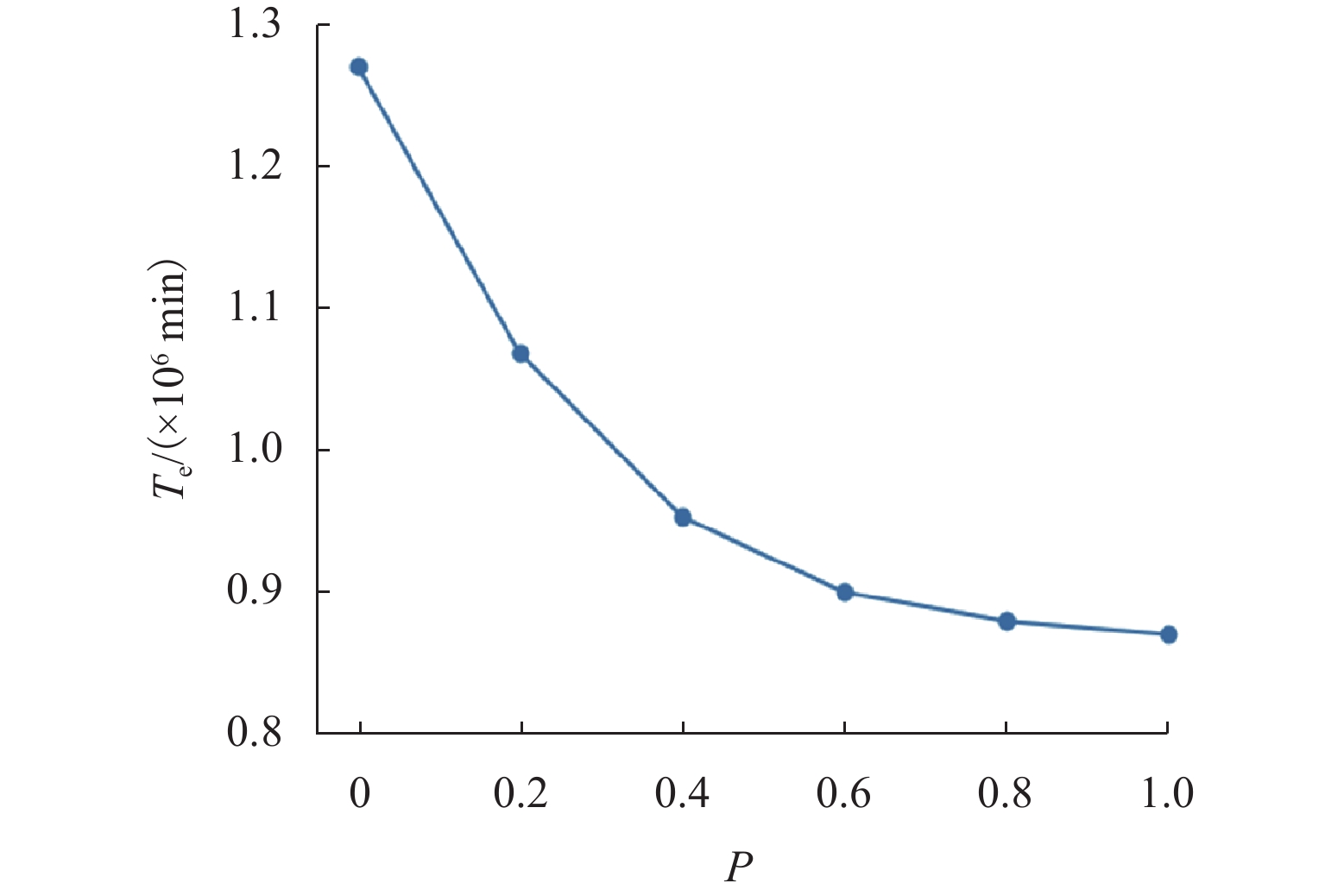
是否
聚类$T_{\mathrm{S}}$ 减少
量/%${T_{\mathrm{e}}}$ 减少
量/%$T_{\mathrm{T}}$ 增加
量/%改变路线的
出行者占比/%否 10.9 32.1 3.2 8.7 是 13.7 38.1 4.8 7.1 表 3 发布路径诱导信息的不同方案
Table 3. Different options to route guidance information
方案 OD 对数/个 出行者占比/% 方案一 677 14.3 方案二 1920 31.3 方案三 3332 42.6 -
[1] CHEN J D, CHEN J T, MIAO Y, et al. Unbalanced development of inter-provincial high-grade highway in China: decomposing the gini coefficient[J]. Transportation Research Part D: Transport and Environment, 2016, 48: 499-510. doi: 10.1016/j.trd.2015.06.008 [2] AÏKOUS M, DUBÉ J, BRUNELLE C, et al. Highway expansion and impacts on land use changes: an event study approach[J]. Transportation Research Part D: Transport and Environment, 2023, 119: 103730. doi: 10.1016/j.trd.2023.103730 [3] CUI H, YUAN G G, LIU N, et al. Convolutional neural network for recognizing highway traffic congestion[J]. Journal of Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2020, 24(3): 279-289. doi: 10.1080/15472450.2020.1742121 [4] LIU W, YANG H, YIN Y F. Efficiency of a highway use reservation system for morning commute[J]. Transportation Research Part C: Emerging Technologies, 2015, 56: 293-308. doi: 10.1016/j.trc.2015.04.015 [5] 赵雪亭, 胡立伟, 寇芳玲. 城市交通拥塞影响范围确定及关键路段识别[J]. 西南交通大学学报, 2024, 59(6): 1389-1397.ZHAO Xueting, HU Liwei, KOU Fangling. Determination of influence range of urban traffic congestion and identification of key road sections[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2024, 59(6): 1389-1397. [6] GUO Y J, LU Q Y, WANG S B, et al. Analysis of air quality spatial spillover effect caused by transportation infrastructure[J]. Transportation Research Part D: Transport and Environment, 2022, 108: 103325. doi: 10.1016/j.trd.2022.103325 [7] ZHENG M, LI T, ZHU R, et al. Traffic accident’s severity prediction: a deep-learning approach-based CNN network[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 39897-39910. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2903319 [8] CORIA J, ZHANG X B. Optimal environmental road pricing and daily commuting patterns[J]. Transportation Research Part B: Methodological, 2017, 105: 297-314. doi: 10.1016/j.trb.2017.09.016 [9] VREESWIJK J D, LANDMAN R L, VAN BERKUM E C, et al. Improving the road network performance with dynamic route guidance by considering the indifference band of road users[J]. IET Intelligent Transport Systems, 2015, 9(10): 897-906. doi: 10.1049/iet-its.2014.0258 [10] 杜牧青, 鞠姿彦, 李大韦. 一种基于交叉口信号延误的超路径规划方法[J]. 西南交通大学学报, 2024, 59(6): 1378-1388.DU Muqing, JU Ziyan, LI Dawei. Hyperpath searching algorithm method based on signal delay at intersections[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2024, 59(6): 1378-1388. [11] ZHANG L, LEVINSON D. Optimal freeway ramp control without origin–destination information[J]. Transportation Research Part B: Methodological, 2004, 38(10): 869-887. doi: 10.1016/j.trb.2003.11.003 [12] GRUMERT E, MA X L, TAPANI A. Analysis of a cooperative variable speed limit system using microscopic traffic simulation[J]. Transportation Research Part C: Emerging Technologies, 2015, 52: 173-186. doi: 10.1016/j.trc.2014.11.004 [13] ZHONG S Q, ZHOU L Z, MA S F, et al. Effects of different factors on drivers’ guidance compliance behaviors under road condition information shown on VMS[J]. Transportation Research Part A: Policy and Practice, 2012, 46(9): 1490-1505. doi: 10.1016/j.tra.2012.05.022 [14] DONG C Y, WANG H, CHEN Q, et al. Simulation-based assessment of multilane separate freeways at toll station area: a case study from Huludao toll station on Shenshan freeway[J]. Sustainability, 2019, 11(11): 3057. doi: 10.3390/su11113057 [15] WEN F, WANG X Q, XU X W. Hierarchical sarsa learning based route guidance algorithm[J]. Journal of Advanced Transportation, 2019, 2019(1): 1019078. [16] YANG H. Evaluating the benefits of a combined route guidance and road pricing system in a traffic network with recurrent congestion[J]. Transportation, 1999, 26(3): 299-322. doi: 10.1023/A:1005129309812 [17] 孙金海. 大数据驱动下的新一代高速公路智慧诱导技术[J]. 河北工业科技, 2019, 36(5): 320-325.SUN Jinhai. New generation intelligence induction technology for expressway driven by big data[J]. Hebei Journal of Industrial Science and Technology, 2019, 36(5): 320-325. [18] ROUGHGARDEN T. How unfair is optimal routing?[C]//Proceedings of the Thirteenth Annual ACM-SIAM Symposium on Discrete Algorithms. Pennsylvania: Society for Industrial and Applied Mathematics, 2002, 203-204. [19] ÇOLAK S, LIMA A, GONZÁLEZ M C. Understanding congested travel in urban areas[J]. Nature Communications, 2016, 7: 10793. doi: 10.1038/ncomms10793 [20] HE K, XU Z Z, WANG P, et al. Congestion avoidance routing based on large-scale social signals[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2016, 17(9): 2613-2626. doi: 10.1109/TITS.2015.2498186 [21] WANG C C, XU Z Z, DU R H, et al. A vehicle routing model based on large-scale radio frequency identification data[J]. Journal of Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2020, 24(2): 142-155. doi: 10.1080/15472450.2019.1598863 [22] WEI D, YANG Z S. Bi-level route guidance method for large-scale urban road networks[J]. EURASIP Journal on Wireless Communications and Networking, 2019, 2019(1): 127-136. doi: 10.1186/s13638-019-1451-z [23] KAVIANI A, THOMPSON R G, RAJABIFARD A. Improving regional road network resilience by optimised traffic guidance[J]. Transportmetrica A: Transport Science, 2017, 13(9): 794-828. doi: 10.1080/23249935.2017.1335807 [24] 李霖. 基于MFD的城市路网双层路径诱导策略研究[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 2017. [25] WANG P, HUNTER T, BAYEN A M, et al. Understanding road usage patterns in urban areas[J]. Scientific Reports, 2012, 2: 1001. doi: 10.1038/srep01001 [26] WANG J J, WEI D, HE K, et al. Encapsulating urban traffic rhythms into road networks[J]. Scientific Reports, 2014, 4: 4141. doi: 10.1038/srep04141 [27] 百度地图开放平台. 百度地图开发者平台[EB/OL]. [2025-08-26]. https: //lbsyun.baidu.com/. [28] Geofabrik. OpenStreetMap China data download [R/OL]. [2025-08-26]. https://download.geofabrik.de/asia/china.html. [29] 杨鹏飞. 取消省界收费站对高速公路车辆运行影响分析研究[D]. 西安: 长安大学, 2021. [30] ENGELSON L. Properties of expected travel cost function with uncertain travel time[J]. Transportation Research Record: Journal of the Transportation Research Board, 2011, 2254(1): 151-159. doi: 10.3141/2254-16 [31] 中华人民共和国交通部. 公路工程技术标准: JTG B01—2003[S]. 北京: 人民交通出版社, 2004. [32] 中华人民共和国住房和城乡建设部. 城市道路工程设计规范: CJJ 37—2012[S]. 北京: 中国建筑工业出版社, 2012. [33] GAO Z Y, SUN H J, SHAN L L. A continuous equilibrium network design model and algorithm for transit systems[J]. Transportation Research Part B: Methodological, 2004, 38(3): 235-250. doi: 10.1016/S0191-2615(03)00011-0 [34] HAMDOUCH Y, SZETO W Y, JIANG Y. A new schedule-based transit assignment model with travel strategies and supply uncertainties[J]. Transportation Research Part B: Methodological, 2014, 67: 35-67. doi: 10.1016/j.trb.2014.05.002 [35] WANG J Y T, EHRGOTT M, CHEN A. A bi-objective user equilibrium model of travel time reliability in a road network[J]. Transportation Research Part B: Methodological, 2014, 66: 4-15. doi: 10.1016/j.trb.2013.10.007 [36] GUO X L, YANG H. User heterogeneity and bi-criteria system optimum[J]. Transportation Research Part B: Methodological, 2009, 43(4): 379-390. doi: 10.1016/j.trb.2008.09.001 [37] FARAHANI H R, RASSAFI A A, Babak M. Forced‐node route guidance system: incorporating both user equilibrium and system optimal benefits[J]. IET Intelligent Transport Systems, 2019, 13(12): 1851-1859. doi: 10.1049/iet-its.2018.5457 [38] CHO H J, CHEN Y K. Finding the ϵ-user equilibrium solution using an augmented frank-Wolfe algorithm[J]. Networks and Spatial Economics, 2010, 10(4): 473-485. doi: 10.1007/s11067-009-9106-y [39] GHADI M Q, TÖRÖK Á. Comparison of different road segmentation methods[J]. Promet-Traffic & Transportation, 2019, 31(2): 163-172. [40] 徐猛, 屈云超, 高自友. Frank-Wolfe算法求解交通分配问题: 比较不同流量更新策略和线搜索技术[J]. 交通运输系统工程与信息, 2008, 8(3): 14-22. doi: 10.1016/S1570-6672(08)60022-7XU Meng, QU Yunchao, GAO Ziyou. Implementing Frank-Wolfe algorithm for traffic assignment problem under different flow update strategies and line search technologies[J]. Journal of Transportation Systems Engineering and Information Technology, 2008, 8(3): 14-22. doi: 10.1016/S1570-6672(08)60022-7 [41] 李美叶. 基于GPS数据的出租车载客路径选择行为研究[D]. 西安: 长安大学, 2019. [42] CANTILLO V, HEYDECKER B, DE DIOS ORTÚZAR J. A discrete choice model incorporating thresholds for perception in attribute values[J]. Transportation Research Part B: Methodological, 2006, 40(9): 807-825. doi: 10.1016/j.trb.2005.11.002 [43] PRAVINVONGVUTH S, CHEN A. Adaptation of the paired combinatorial logit model to the route choice problem[J]. Transportmetrica, 2005, 1(3): 223-240. doi: 10.1080/18128600508685649 [44] 王淞艺. 时间不确定下区域组合出行选择建模方法研究[D]. 北京: 北京交通大学, 2023. -




 下载:
下载: