Fast Quantitative Diagnosis Method for Early-Stage Internal Short Circuit in Lithium Battery Pack Under Floating Charge Conditions
-
摘要:
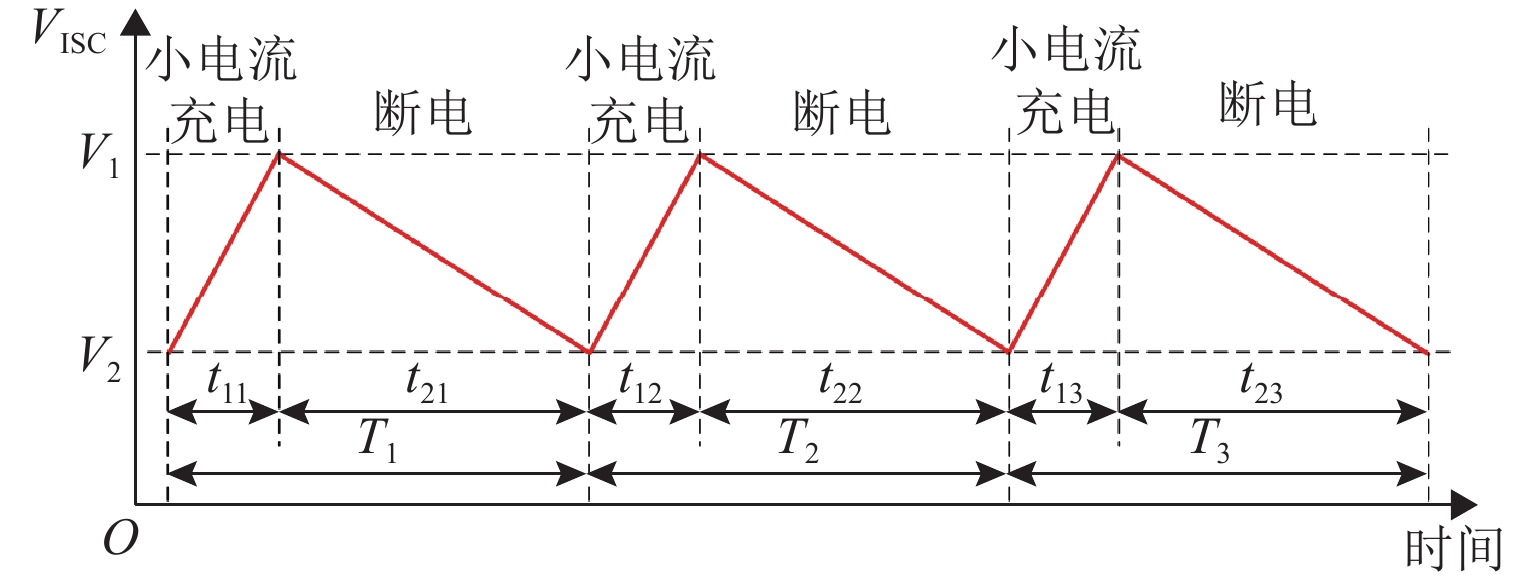
锂离子电池的浮充工况广泛存在于备用电源、通讯基站等场景,是一种状态趋于稳定的特殊工况,这种稳定性却对该工况下电池内短路定量诊断带来挑战. 本文提出一种基于间歇式充电的锂离子电池组早期内短路定量诊断方法,该方法利用重复的“充电—断电”过程,根据充电电量与漏电量的关系计算出等效漏电流,实现内短路的快速定量诊断. 仿真与实验结果表明:对于500 Ω级别的电池微短路,所提方法的诊断误差小于2%,检测时间约为33 min,实现对浮充电工况下电池内短路的早期高精度定量诊断;在诊断100 Ω级别中,所提方法相较于常规恒压源方法内短路的精度提高超16倍,且计算负担低,对提高电池组安全性具有重要意义.
Abstract:The floating charge condition of lithium-ion batteries widely exists in scenarios such as backup power sources and communication base stations, and is a special condition that tends to stabilize. This stability poses a challenge to the quantitative diagnosis of internal short circuit (ISC) in batteries under this condition. In this study, a quantitative diagnosis method for early ISC in lithium-ion battery packs based on intermittent charging was proposed. This method utilized a repeated “charging-rest” process to calculate the equivalent leakage current according to the relationship between charging capacity and leakage, thereby achieving rapid quantitative diagnosis of ISC. The simulation and experimental results show that the proposed method has a diagnostic accuracy of less than 2% and a detection time of about 33 minutes for a micro-ISC battery with an ISC resistance of 500 Ω. It achieves early-stage and high-precision quantitative diagnosis of battery ISC under floating charge conditions. In addition, compared with conventional constant voltage source methods, the proposed method improves the accuracy of diagnosing short circuits within 100 Ω by at least 16 times. The proposed ISC method has a very low computational burden and is of great significance for improving the safety of battery packs.
-
表 1 不同内短路程度下漏电流与内短路阻值估计结果
Table 1. Estimation results of leakage current and ISC resistance under different degrees of ISC
外接阻
值/ΩIleak1/
mAIleak2/
mAIleak3/
mA$\bar{I}_{\mathrm{leak}} $/
mA阻值估计
结果/Ω误差/% 55 60.3 60.3 62.5 61.0 57.1 3.86 100 34.6 34.2 33.5 34.1 102.1 2.10 200 17.3 16.4 17.4 17.0 204.5 2.24 300 11.3 11.6 11.5 11.5 303.8 1.28 500 7.0 7.3 7.0 7.1 491.0 1.79 表 2 内短路阻值与诊断时间的关系
Table 2. Relationship between ISC resistance and diagnostic time
外接阻
值/Ωt11/s t21/s 最小检测
时间/s占空比 55 32.2 225.5 257.7 0.137 100 30.2 408.4 438.6 0.075 200 29.3 811.2 833.2 0.036 300 28.3 1203.4 1231.7 0.023 500 28.8 1950.3 1979.1 0.014 表 3 恒压源法诊断电池内短路结果
Table 3. Results of ISC diagnosis in battery by constant voltage source method
短路阻
值/Ω电流滤波结果 漏电流/A 阻值诊断
结果/Ω诊断误
差/%I1/A I2/A 10 1.58759 1.89699 0.30940 11.150 11.5 20 1.58337 1.74219 0.15882 21.720 8.6 50 1.58456 1.66968 0.08512 40.531 18.9 100 1.58577 1.63719 0.05142 67.095 32.9 -
[1] 邹大中, 陈浩舟, 李勋, 等. 基于云端充电数据的锂电池组一致性评价方法[J]. 电网技术, 2022, 46(3): 1049-1064.ZOU Dazhong, CHEN Haozhou, LI Xun, et al. Cell-to-cell variation evaluation for lithium-ion battery packs in electric vehicles with cloud charging data[J]. Power System Technology, 2022, 46(3): 1049-1064. [2] 来鑫, 李云飞, 郑岳久, 等. 基于SOC-OCV优化曲线与EKF的锂离子电池荷电状态全局估计[J]. 汽车工程, 2021, 43(1): 19-26.LAI Xin, LI Yunfei, ZHENG Yuejiu, et al. An overall estimation of state-of-charge based on SOC-OCV optimization curve and EKF for lithium-ion battery[J]. Automotive Engineering, 2021, 43(1): 19-26. [3] LI H G, ZHOU D, ZHANG M H, et al. Multi-field interpretation of internal short circuit and thermal runaway behavior for lithium-ion batteries under mechanical abuse[J]. Energy, 2023, 263: 126027. doi: 10.1016/j.energy.2022.126027 [4] 张健豪, 高兴奇, 张莉. 基于容量增量曲线与充电容量差的电池组微短路诊断方法[J]. 汽车工程, 2023, 45(2): 191-198, 230.ZHANG Jianhao, GAO Xingqi, ZHANG Li. Micro short circuit diagnosis method of battery pack based on capacity increment curve and charge capacity difference[J]. Automotive Engineering, 2023, 45(2): 191-198, 230. [5] 熊瑞, 孙万洲, 杨瑞鑫, 等. 储能电池外部短路的损伤与失效边界及其预测[J]. 机械工程学报, 2023, 59(4): 113-124. doi: 10.3901/JME.2023.04.113XIONG Rui, SUN Wanzhou, YANG Ruixin, et al. Damage and failure boundaries and prediction of external short circuit in lithium-ion battery[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2023, 59(4): 113-124. doi: 10.3901/JME.2023.04.113 [6] LAI X, JIN C Y, YI W, et al. Mechanism, modeling, detection, and prevention of the internal short circuit in lithium-ion batteries: recent advances and perspectives[J]. Energy Storage Materials, 2021, 35: 470-499. doi: 10.1016/j.ensm.2020.11.026 [7] DUAN X D, LI J N, JIA Y K, et al. Understanding of stress-driven internal short circuit mechanisms in lithium-ion batteries with high SOCs[J]. Advanced Science, 2023, 10(29): 2302496. doi: 10.1002/advs.202302496 [8] WANG L B, LI J P, CHEN J Y, et al. Revealing the internal short circuit mechanisms in lithium-ion batteries upon dynamic loading based on multiphysics simulation[J]. Applied Energy, 2023, 351: 121790. doi: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2023.121790 [9] 余抒阳, 罗文雷, 解晶莹, 等. 锂离子电池释热机理与模型及安全改性技术研究综述[J]. 化学进展, 2023, 35(4): 620-642.YU Shuyang, LUO Wenlei, XIE Jingying, et al. Review on mechanism and model of heat release and safety modification technology of lithium-ion batteries[J]. Progress in Chemistry, 2023, 35(4): 620-642. [10] FENG X N, OUYANG M G, LIU X, et al. Thermal runaway mechanism of lithium ion battery for electric vehicles: a review[J]. Energy Storage Materials, 2018, 10: 246-267. doi: 10.1016/j.ensm.2017.05.013 [11] 陈素华, 白莹. 锂离子动力电池热失控机理及热管理技术研究进展[J]. 中国科学基金, 2023, 37(2): 187-198.CHEN Suhua, BAI Ying. Thermal runway mechanism and research progress on thermal management of lithium-ion power batteries[J]. Bulletin of National Natural Science Foundation of China, 2023, 37(2): 187-198. [12] QIAO D D, WANG X Y, LAI X, et al. Online quantitative diagnosis of internal short circuit for lithium-ion batteries using incremental capacity method[J]. Energy, 2022, 243: 123082. doi: 10.1016/j.energy.2021.123082 [13] FENG X N, WENG C H, OUYANG M G, et al. Online internal short circuit detection for a large format lithium ion battery[J]. Applied Energy, 2016, 161: 168-180. doi: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2015.10.019 [14] WANG H, NIE J H, HE Z W, et al. A reconstruction-based model with transformer and long short-term memory for internal short circuit detection in battery packs[J]. Energy Reports, 2023, 9: 2420-2430. doi: 10.1016/j.egyr.2023.01.092 [15] MA R F, DENG Y L, WANG X X. Simplified electrochemical model assisted detection of the early-stage internal short circuit through battery aging[J]. Journal of Energy Storage, 2023, 66: 107478. doi: 10.1016/j.est.2023.107478 [16] YUAN H T, CUI N X, LI C L, et al. Early stage internal short circuit fault diagnosis for lithium-ion batteries based on local-outlier detection[J]. Journal of Energy Storage, 2023, 57: 106196. doi: 10.1016/j.est.2022.106196 [17] QIAO D D, WEI X Z, FAN W J, et al. Toward safe carbon–neutral transportation: Battery internal short circuit diagnosis based on cloud data for electric vehicles[J]. Applied Energy, 2022, 317: 119168. doi: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2022.119168 [18] KONG X D, ZHENG Y J, OUYANG M G, et al. Fault diagnosis and quantitative analysis of micro-short circuits for lithium-ion batteries in battery packs[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2018, 395: 358-368. doi: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2018.05.097 [19] WU Q, YANG L, LI N, et al. In-situ thermography revealing the evolution of internal short circuit of lithium-ion batteries[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2022, 540: 231602. doi: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2022.231602 [20] SAZHIN S V, DUFEK E J, GERING K L. Enhancing Li-ion battery safety by early detection of nascent internal shorts[J]. Journal of The Electrochemical Society, 2016, 164(1): 6281-6287. [21] JIA Y K, XU J. Data-driven short circuit resistance estimation in battery safety issues[J]. Journal of Energy Chemistry, 2023, 79: 37-44. doi: 10.1016/j.jechem.2022.12.035 [22] CHANG C K. Factors affecting capacity design of lithium-ion stationary batteries[J]. Batteries, 2019, 5(3): 58-71. doi: 10.3390/batteries5030058 [23] MATSUSHIMA T. Deterioration estimation of lithium-ion cells in direct current power supply systems and characteristics of 400-Ah lithium-ion cells[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2009, 189(1): 847-854. doi: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2008.08.023 [24] 尹涛. 浮充工况下储能锂离子电池性能研究[D]. 青岛: 青岛大学, 2022. [25] 李晓枫, 常益, 杨章, 等. 应用阻抗谱的锂电池模组早期内短路故障诊断[J]. 西安交通大学学报, 2024, 58(1): 1-13.LI Xiaofeng, CHANG Yi, YANG Zhang, et al. Early diagnosis of internal short circuit faults in lithium battery modules using impedance spectroscopy[J]. Journal of Xi’an Jiaotong University, 2024, 58(1): 1-13. [26] 徐俊, 郭喆晨, 谢延敏, 等. 储能锂电池系统综合管理研究进展[J]. 西安交通大学学报, 2024, 58(10): 1-23. doi: 10.7652/xjtuxb202410001.XU Jun, GUO Zhechen, XIE Yanmin, et al. Review of research progress in integrated management for energy storage lithium battery systems[J]. Journal of Xi’an Jiaotong University, 2024, 58(10): 1-23. doi: 10.7652/xjtuxb202410001. [27] 万广伟, 张强. 锂离子电池SOC评估方法研究进展[J]. 电源技术, 2023, 47(9): 1122-1125.WAN Guangwei, ZHANG Qiang. Research progress of SOC evaluation methods for lithium ion batteries[J]. Chinese Journal of Power Sources, 2023, 47(9): 1122-1125. [28] LI K, GAO X, LIU C X, et al. A novel co-estimation framework of state-of-charge, state-of-power and capacity for lithium-ion batteries using multi-parameters fusion method[J]. Energy, 2023, 269: 126820. doi: 10.1016/j.energy.2023.126820 [29] LAI X, YI W, KONG X D, et al. Online detection of early stage internal short circuits in series-connected lithium-ion battery packs based on state-of-charge correlation[J]. Journal of Energy Storage, 2020, 30: 101514. doi: 10.1016/j.est.2020.101514 [30] JUN A, TAKUYA N, TOSHIYUKI N, et al. Battery internal short-circuit detecting device and method, battery pack, and electronic device system: America, 2010201321-A1 [P/OL]. (2010-08-12)[2023-04-32]. https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/patent/US-2010201321-A1. -





 下载:
下载: