Numerical Analysis of Influence of Aircraft Taxiing Load on Pile-Net Composite Foundation in Runway
-
摘要:
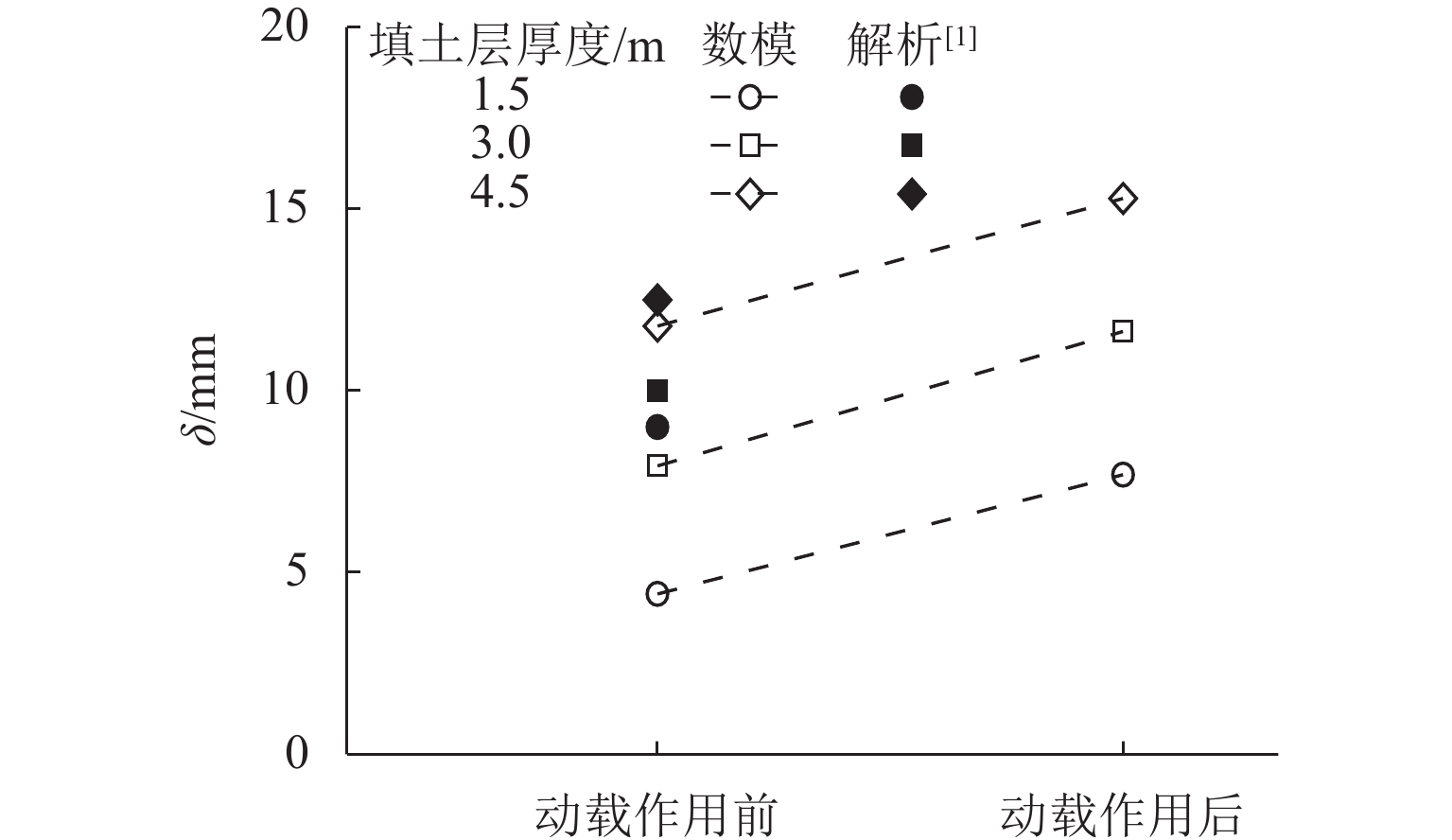
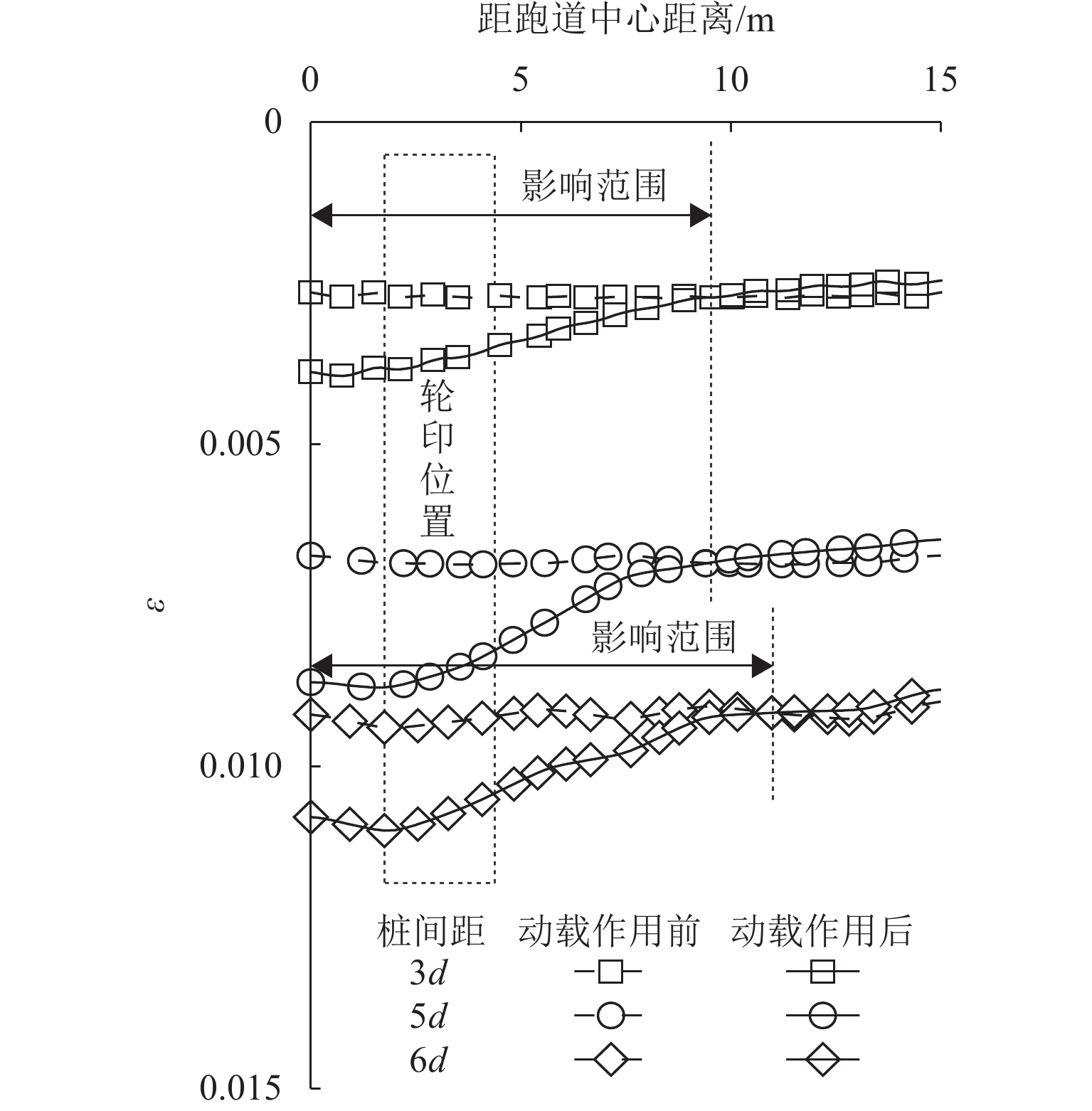
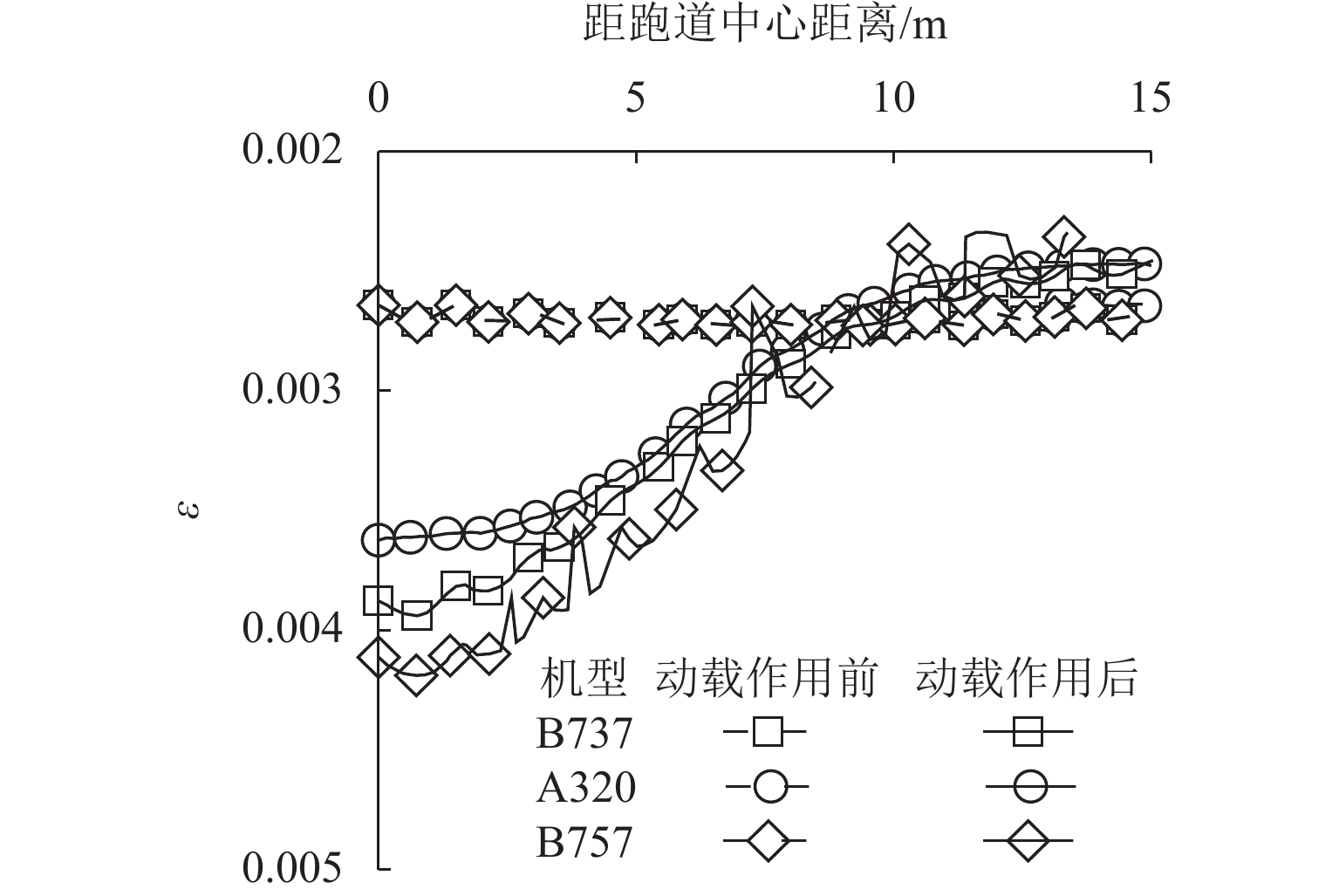
桩网复合地基可以有效降低道路工程工后沉降,近年来常用于对我国沿海机场飞行区的跑道和机坪系统进行地基处理. 然而,目前关于桩网复合地基的研究多集中于工前静承载特性,缺乏跑道下地基工前沉降完成后,飞机滑行荷载作用对跑道桩网复合地基影响的定量评价研究. 本文通过改变填土层厚度、桩间距、飞机机型等参数,基于动载影响系数、工后差异沉降比和土拱度退化系数等指标,利用有限元软件ABAQUS对飞机滑行荷载作用下跑道桩网复合地基的受力变形特性进行数值分析,量化飞机滑行荷载对跑道桩网复合地基承载和沉降特性的影响. 研究表明:当填土层厚度由4.5 m减小至1.5 m时,土拱退化参数由3.3%升至15.1%;当桩间距由6
d 减小至3d (d 为桩直径)时,土拱退化参数由7.8%升至12.0%,软土层位置处的工后差异沉降比可能超过规范建议值;填土层厚度越小、桩间距和飞机重量越大、起落架荷载越集中,飞机滑行荷载作用后的土拱弱化越明显.Abstract:The pile-net composite foundation can effectively reduce the post-construction settlement in road engineering, and has often been used for ground improvement for runway and apron systems in the airfield of coastal airports in China recently. However, the available research on the pile-net composite foundation is mostly focused on the bearing characteristics before construction, lacking research to quantitatively evaluate the influence of aircraft taxiing loads on the bearing characteristics of the pile-net composite foundation in the runway. Therefore, the parameters such as the thickness of the fill layer, the spacing between piles, and the type of aircraft were changed. In addition, based on the dynamic load influence coefficient, the differential settlement ratio after construction, and the degradation coefficient of soil arch, the finite element software ABAQUS was used, and a numerical analysis of the mechanical deformation characteristics of the pile-net composite foundation in the runway under the influence of aircraft taxiing load was conducted. The influence of aircraft taxiing load on the bearing and settlement characteristics of the pile-net composite foundation in the runway was quantified. The results show that when the thickness of the fill layer decreases from 4.5 m to 1.5 m, the soil arching effect is weakened by about 3.3% to 15.1%. When the spacing between piles decreases from 6
d to 3d , the soil arching effect is weakened by about 7.8% to 12.0%. The differential settlement ratio after construction at the location of the soft soil layer may exceed the recommended value of the code. As the fill layer becomes thinner, the pile spacing and aircraft weight are greater; the main gear load is more concentrated, and the soil arching effect becomes weaker.-
Key words:
- runway /
- pile-net composite foundation /
- taxiing load /
- soil arching effect /
- settlement ratio
-
表 1 亚塑性模型参数
Table 1. Hypoplastic model parameters
参数 数值 临界状态摩擦角 Φc/(°) 33 颗粒硬度 h1/GPa 1 无量纲参数 n 0.28 最小孔隙比 ed0 0.55 临界孔隙比 ec0 0.95 最大孔隙比 ei0 1.05 无量纲参数 α 0.25 无量纲参数 β 1.5 控制初始加载及应变路径 180° 反转时的
初始刚度的参数 mR5 控制应变路径 90° 反转时的初始刚度的参数 mT 2 应变空间中弹性范围 R 0.000 1 控制刚度随应变变化的减少率参数 βr 0.5 控制刚度随应变变化的减少速率参数 χ 6 表 2 加载前数值模拟与理论计算结果对比
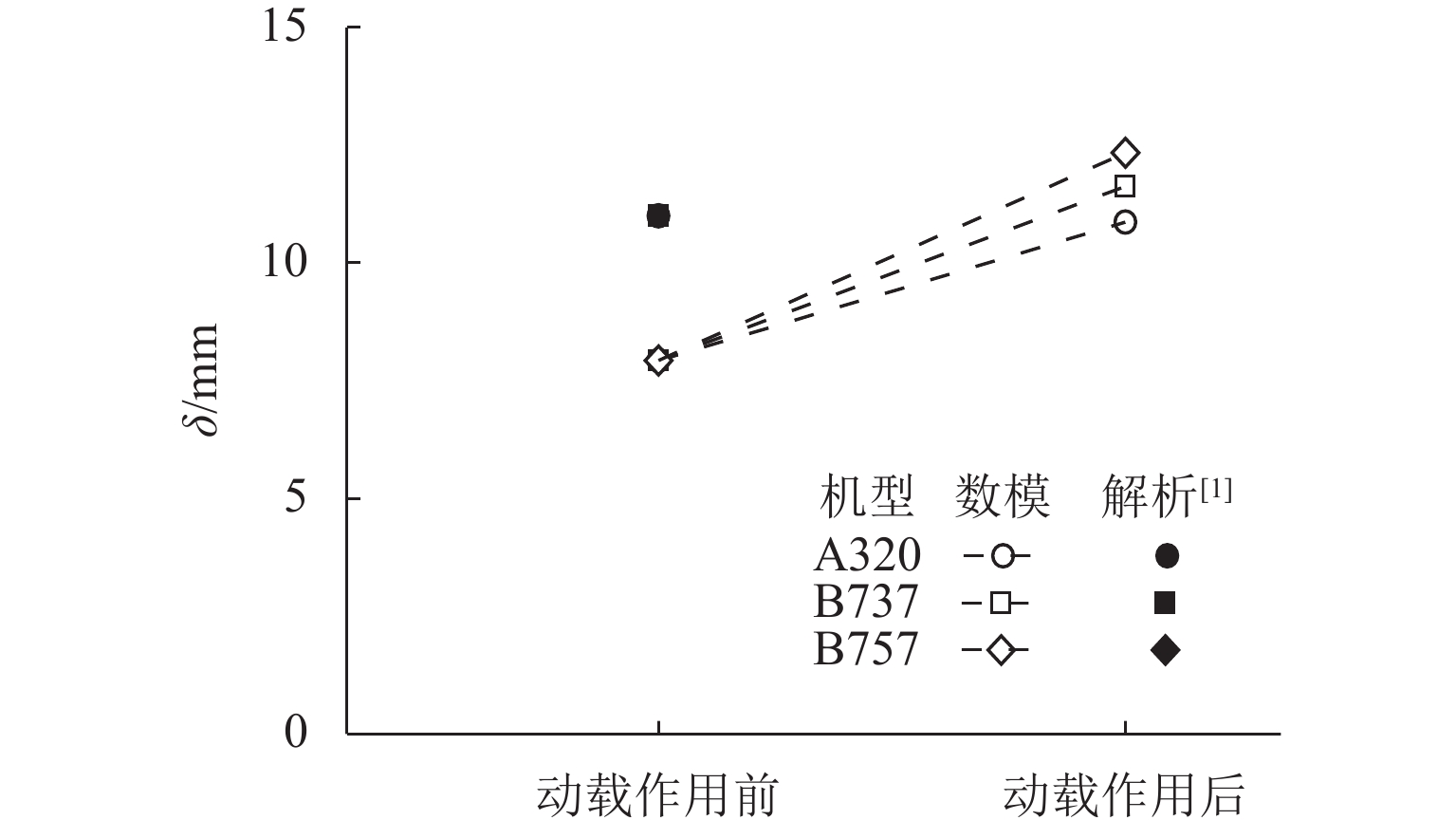
Table 2. Comparison of numerical simulation and theoretical calculation results before loading
类别 $ \rho $ $ \delta $/m 数值模拟 0.34 0.005 理论计算 0.36 0.008 表 3 不同模拟工况
Table 3. Different simulation conditions
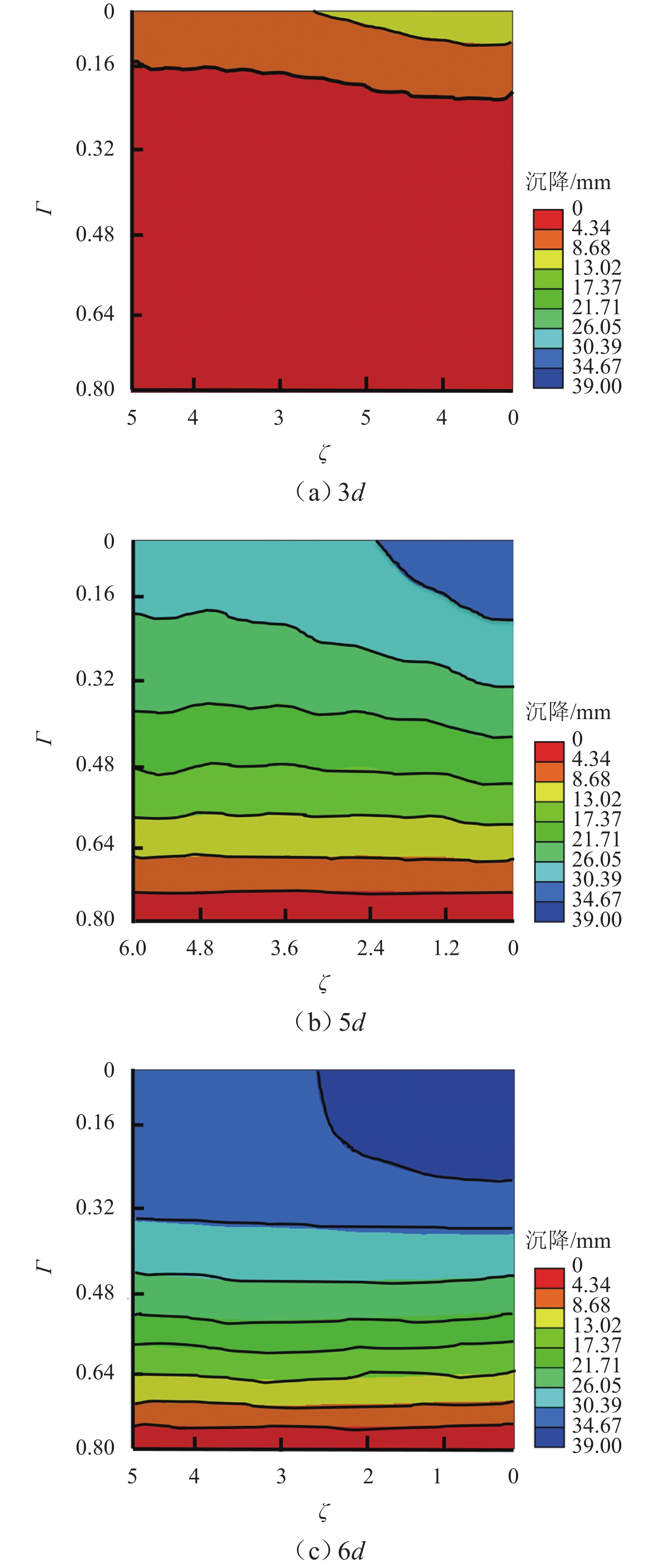
工况 hs/m s 机型 1 1.5 3d B737-800 2 4.5 3d B737-800 3 3.0 5d B737-800 4 3.0 6d B737-800 5 3.0 3d A320 6 3.0 3d B757-200 表 4 加载前后土拱度及退化参数
Table 4. Soil arch ratio and degradation parameters before and after loading
填土层厚度/m $ {\rho _{{\text{ini}}}} $ $ {\rho _{{\mathrm{load}}}} $ $ {\alpha _3} $/% 1.5 0.27 0.38 15.1 3.0 0.34 0.42 12.0 4.5 0.40 0.42 3.3 表 5 加载前、后土拱度及退化参数
Table 5. Soil arch ratio and degradation parameters before and after loading
桩间距 $ {\rho _{{\text{ini}}}} $ $ {\rho _{{\mathrm{load}}}} $ $ {\alpha _3} $/% 3d 0.34 0.42 12.0 5d 0.32 0.37 7.4 6d 0.36 0.41 7.8 表 6 各机型参数
Table 6. Parameters for each type of aircraft
机型 飞机重
力/kN分配系数 起落架
个数/个主起落架
间距/m起落架
形式B737-800 663.8 0.95 2 5.72 单轴
双轮A320 645.0 0.95 2 7.60 双轴
双轮B757-200 952.5 0.95 2 7.32 双轴
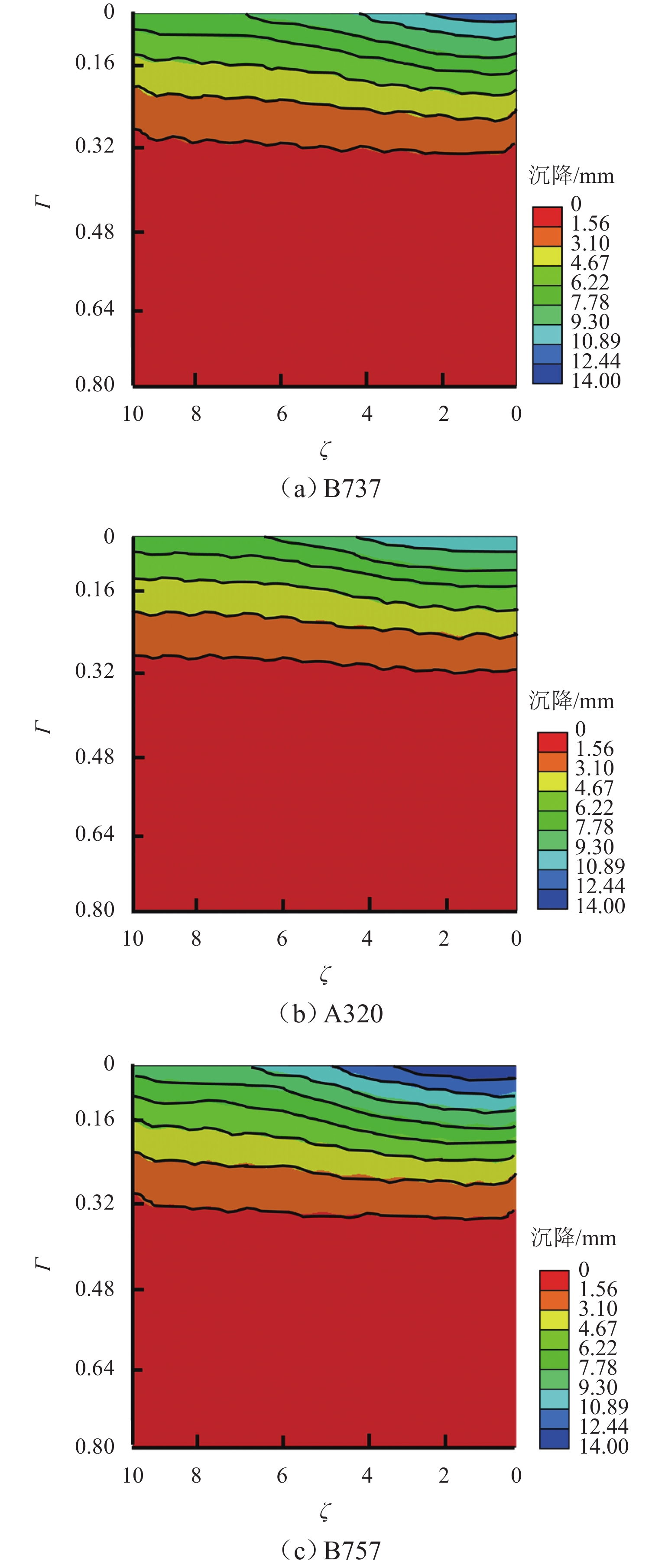
双轮表 7 不同机型加载前、后土拱度及退化参数
Table 7. Soil arch and degradation parameters before and after loading of different types of aircrafts
机型 $ {\rho _{{\text{ini}}}} $ $ {\rho _{{\mathrm{load}}}} $ $ {\alpha _3} $/% B737-800 0.34 0.42 12.00 A320 0.43 0.46 5.30 B757-200 0.43 0.49 0.53 -
[1] HAN G X, GONG Q M, ZHOU S H. An experimental investigation of soil arching under dynamic loads[C]//ICCTP 2011. Nanjing: American Society of Civil Engineers, 2011: 3030-3037. [2] DONG J, WU Z H, LI X, et al. Dynamic response and pile-soil interaction of a heavy-haul railway embank-ment slope reinforced by micro-piles[J]. Computers and Geotechnics, 2018, 100: 144-157. doi: 10.1016/j.compgeo.2018.04.005 [3] EEKELEN S J M, BEZUIJEN A, DUIJNEN P, et al. Piled embankment using geosynthetic reinforcement in the Netherlands: design, monitoring & evaluatio[C]//Proceedings of the 17th International Conference on Soil Mechanics and Geotechnical Engineering. Netherland: IOS Press, 2009: 1690-1693. [4] 张述涛, 陈丽娟. 海南博鳌机场跑道道槽区的软土地基处理研究[J]. 路基工程, 2017(3): 73-77.ZHANG Shutao, CHEN Lijuan. Study on the soft soil foundation treatment of channel slot of Hainan bo’ao airport runway[J]. Subgrade Engineering, 2017(3): 73-77. [5] 吴军. 桩网复合地基在深圳机场南停机坪中的应用[J]. 铁道建筑, 2014, 54(7): 113-115.WU Jun. Application of pile-net composite foundation in south apron of Shenzhen airport[J]. Railway Engineering, 2014, 54(7): 113-115. [6] PHAM T. A. Load-deformation of piled embankments considering geosynthetic membrane effect and interface friction[J]. Geosynthetics International, 2020, 27(3): 275-300. doi: 10.1680/jgein.19.00030 [7] VAN EEKELEN S J M, BEZUIJEN A, VAN TOL A F. An analytical model for arching in piled embankments[J]. Geotextiles and Geomembranes, 2013, 39: 78-102. doi: 10.1016/j.geotexmem.2013.07.005 [8] ABUSHARAR S W, ZHENG J J, CHEN B G, et al. A simplified method for analysis of a piled embankment reinforced with geosynthetics[J]. Geotextiles and Geomembranes, 2009, 27(1): 39-52. doi: 10.1016/j.geotexmem.2008.05.002 [9] ZHUANG Y, WANG K Y, LIU H L. A simplified model to analyze the reinforced piled embankments[J]. Geotextiles and Geomembranes, 2014, 42(2): 154-165. doi: 10.1016/j.geotexmem.2014.01.002 [10] HEWLETT W J, RANDOLH M F. Analysis of piled embankments[J]. Ground Engineering, 1988, 21(3): 12-18. [11] LIU W, QU S, ZHANG H, et al. An integrated method for analyzing load transfer in geosynthetic-reinforced and pile-supported embankment[J]. KSCE Journal of Civil Engineering, 2016, 21: 687-702. [12] German Geotechnical Society. Recommendations for design and analysis of earth structures using geosynthetic reinforcements-EBGEO[M]. Berlin: [s.n.], 2012. [13] 杨以国, 刘开富, 谢新宇. 循环荷载下长短桩桩网复合地基变形试验研究[J]. 浙江大学学报(工学版), 2021, 55(6): 1027-1035.YANG Yiguo, LIU Kaifu, XIE Xinyu. Experimental research on deformation of pile-net composite foundation with long-short piles under cyclic load[J]. Journal of Zhejiang University (Engineering Science), 2021, 55(6): 1027-1035. [14] 尹锋, 周航, 刘汉龙, 等. 车辆载重与动荷载对X形桩桩-网复合地基动力特性影响的试验研究[J]. 岩土力学, 2019, 40(4): 1324-1330, 1340.YIN Feng, ZHOU Hang, LIU Hanlong, et al. Experimental investigation on dynamic characteristics of XCC pile-geogrid composite foundation under static and dynamic loads of vehicles[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2019, 40(4): 1324-1330, 1340. [15] 牛婷婷, 孙广超. 高速铁路X形桩桩网复合地基动态响应分析[J]. 岩土力学, 2021, 42(5): 1266-1280.NIU Tingting, SUN Guangchao. Dynamic response analysis of X-pile-net composite embankment in high-speed railway[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2021, 42(5): 1266-1280. [16] 中国民用航空局. 民用机场飞行区技术标准: MH 5001—2021[S]. 北京: 中国民航出版社, 2021. [17] 中国民用航空局. 民用机场水泥混凝土道面设计规范: MH/T 5004—2010[S]. 北京: 中国民航出版社, 2010. [18] THO K K, LEUNG C F, CHOW Y K, et al. Eulerian finite-element technique for analysis of jack-up spudcan penetration[J]. International Journal of Geomechanics, 2012, 12(1): 64-73. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)GM.1943-5622.0000111 [19] PHAM H. V, DIAS D, DUDCHENKO A. 3D modeling of geosynthetic-reinforced pile-supported embankment under cyclic loading[J]. Geosynthetics International, 2018, 27(2): 157-169. [20] 刁红国, 王新泉, 魏纲, 等. 亚塑性模型对土-结构相互作用问题的预测能力分析[J]. 自然灾害学报, 2022, 31(4): 210-218.DIAO Hongguo, WANG Xinquan, WEI Gang, et al. Analysis of prediction ability of hypoplastic model for soil-structure interaction problem[J]. Journal of Natural Disasters, 2022, 31(4): 210-218. [21] GUDEHUS G, AMOROSI A, GENS A, et al. The soilmodels.info project[J]. International Journal for Numerical and Analytical Methods in Geomechanics, 2008(32): 1571-1572. [22] THO K K, LEUNG C F, CHOW Y K, et al. Eulerian finite element simulation of spudcan–pile interaction[J]. Canadian Geotechnical Journal, 2013, 50(6): 595-608. doi: 10.1139/cgj-2012-0288 [23] HAN J, GABR M A. Numerical analysis of geosynthetic-reinforced and pile-supported earth platforms over soft soil[J]. Journal of Geotechnical and Geoenvironmental Engineering, 2002, 128(1): 44-53. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)1090-0241(2002)128:1(44) [24] 薛华鑫. 飞机滑行状态下振动频率响应分析[D]. 天津: 中国民航大学, 2014. [25] 中国国家质量监督检验检疫总局. 机械振动道路路面谱测量数据报告: GB/T 7031—2005[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2005. [26] 周苏杰. 飞机荷载作用下机场道基动力响应及沉降分析[D]. 南京: 南京航空航天大学, 2018. [27] 中国民用航空局. 民用机场岩土工程设计规范: MH/T5027—2013[S]. 北京: 中共民航出版社, 2013. [28] 李格烨, 徐超, 沈盼盼, 等. 局部动荷载作用下土拱效应的离散元分析[J]. 长江科学院院报, 2022, 39(3): 98-103.LI Geye, XU Chao, SHEN Panpan, et al. Discrete element analysis of soil arching under localized cyclic loading[J]. Journal of Yangtze River Scientific Research Institute, 2022, 39(3): 98-103. -





 下载:
下载: