Response Analysis and Load Optimization of High Temperature Reactor-Pebblebed Modules Main Helium Blower Rotor System
-
摘要:
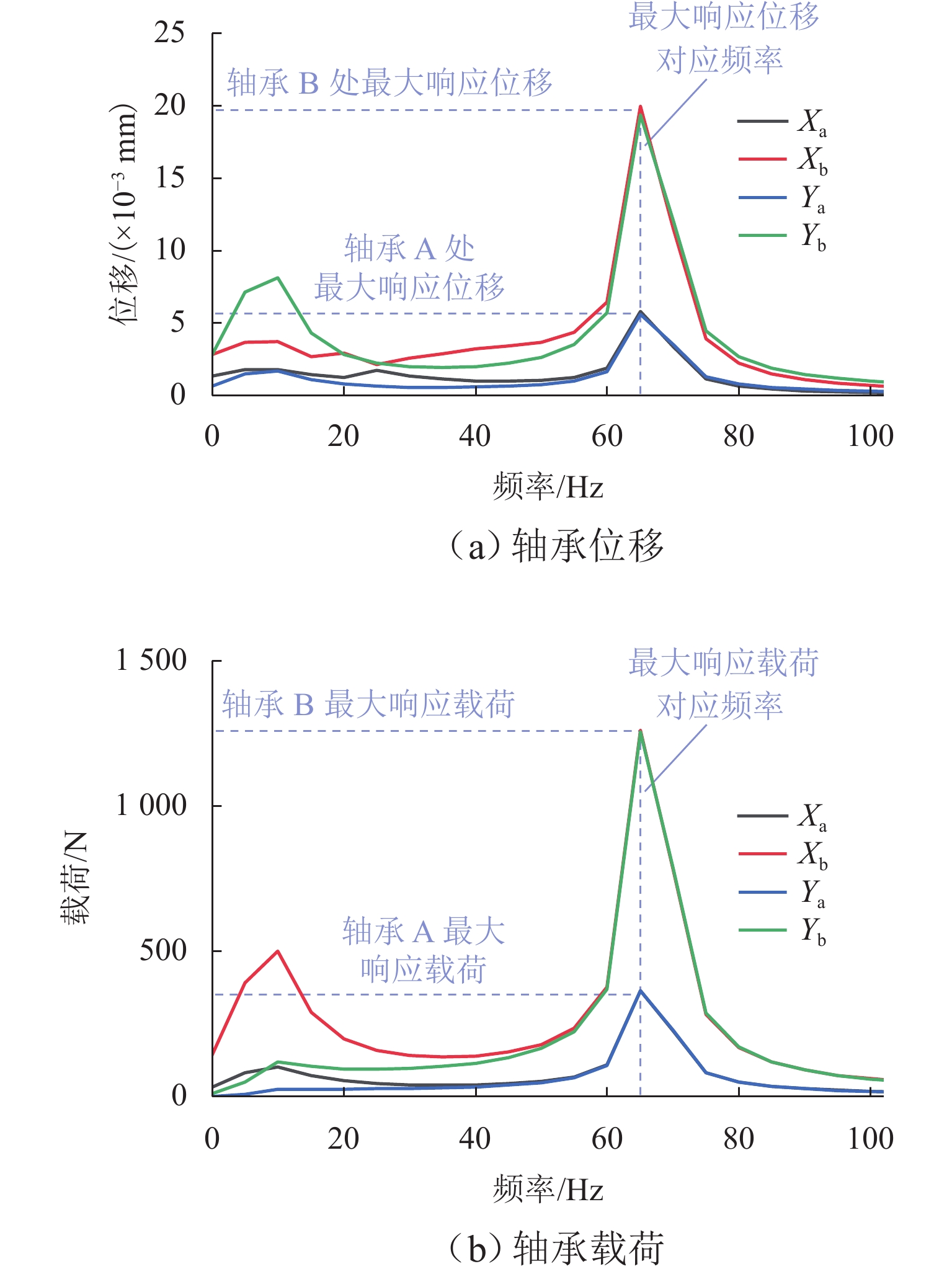
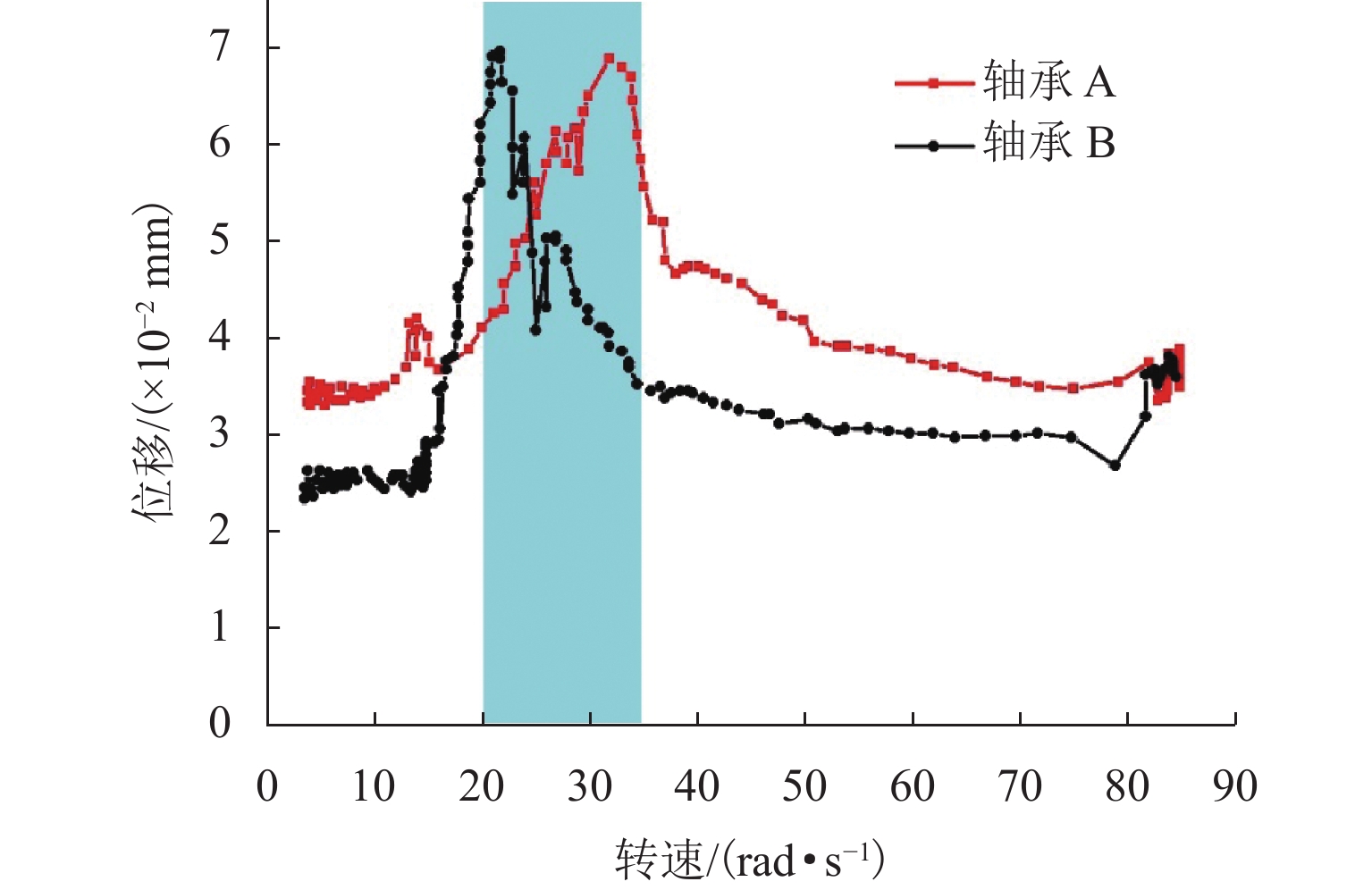
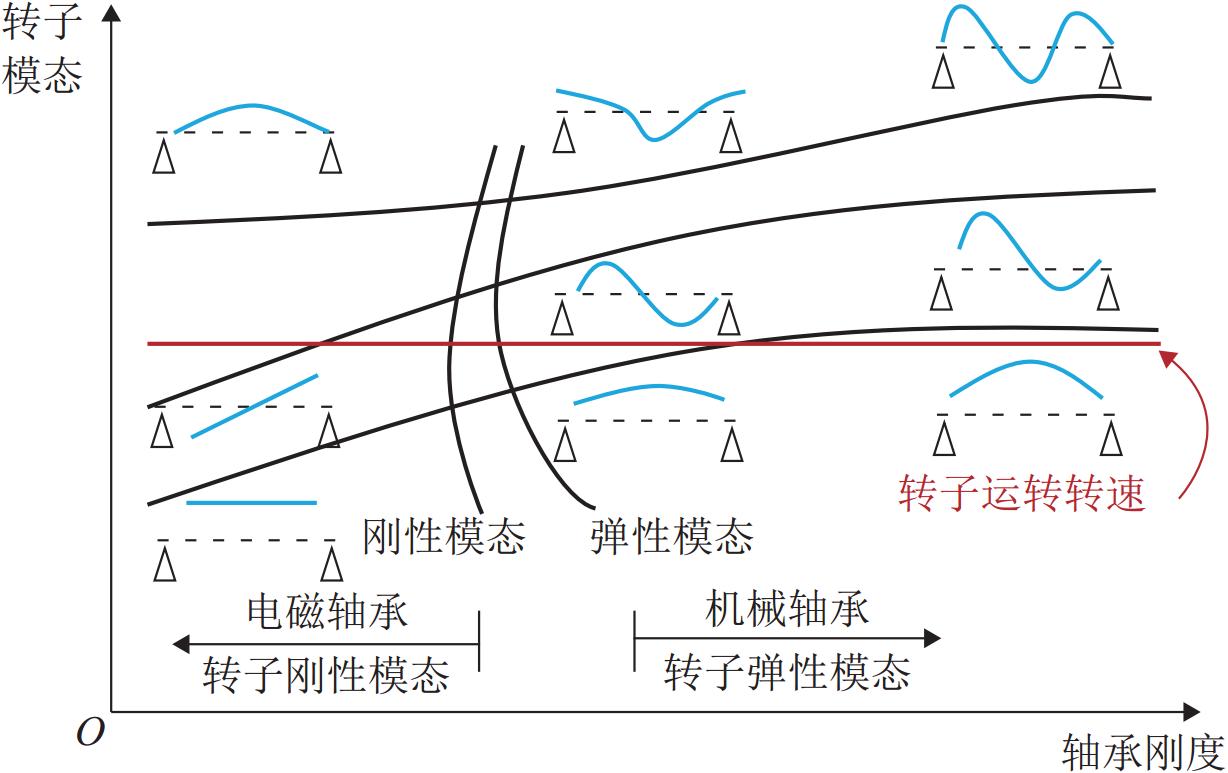
针对HTR-PM (high temperature reactor-pebblebed modules)主氦风机磁轴承-转子系统中径向主动磁轴承的参数设计与性能优化问题,首先,通过将期望特性应用于动力学分析对系统边界条件进行梳理;其次,采用瞬态分析法模拟轴承控制参数对系统响应和载荷的影响,得到转子系统满足设计期望的理想控制参数范围;进一步根据该参数范围内转子在不同的转速、等效不平衡、轴承刚度和轴承阻尼下的动力响应结果,分析控制参数与转子响应间的影响,根据其规律求解磁轴承-转子系统在工作频率范围内各频段的最优控制参数;最后,研究归纳磁轴承-转子系统在不同工作条件和性能需求下,响应位移、轴承载荷与磁轴承等效刚度和阻尼比间的变化规律,据此设计并验证根据转子的即时工作频率选取合适控制参数的控制方案. 结果表明:参数选择符合优化条件时,该方法能在满足转子系统工作需求的同时抑制不平衡响应的总体幅值,消除谐振峰,并且轴承处的最大载荷也得到了优化.
Abstract:In response to the parameter design and performance optimization of radial active magnetic bearings in the magnetic bearing rotor system of the high temperature reactor-pebblebed modules (HTR-PM) main helium blower, the system boundary conditions were sorted out by applying the expected characteristics to dynamic analysis. Meanwhile, the transient analysis method was used to simulate the influence of bearing control parameters on the system’s response and loads, and the ideal control parameter range that satisfied the design expectations for the rotor system was obtained. Subsequently, based on the dynamic response results of the rotor under different rotational speeds, equivalent unbalance, bearing stiffness, and bearing damping within the parameter range, the influence between the control parameters and rotor response was analyzed. According to the obtained patterns, the optimal control parameters for the magnetic bearing–rotor system at each frequency band within the operating frequency range were determined. Finally, the variation laws between the response displacement, bearing load, equivalent stiffness, and damping ratio of magnetic bearing–rotor system under different working conditions and performance requirements were summarized. A control scheme for selecting appropriate control parameters based on the real-time operating frequency of the rotor was designed and verified. The results show that when the control parameter selection meets the optimization conditions, this method is able to suppress the overall amplitude of the unbalanced response, eliminate the resonance peaks, and optimize the maximum load at the bearings while achieving the working requirements of the rotor system.
-
Key words:
- electromagnetic bearing /
- finite element analysis /
- rotor dynamics /
- unbalance analysis
-
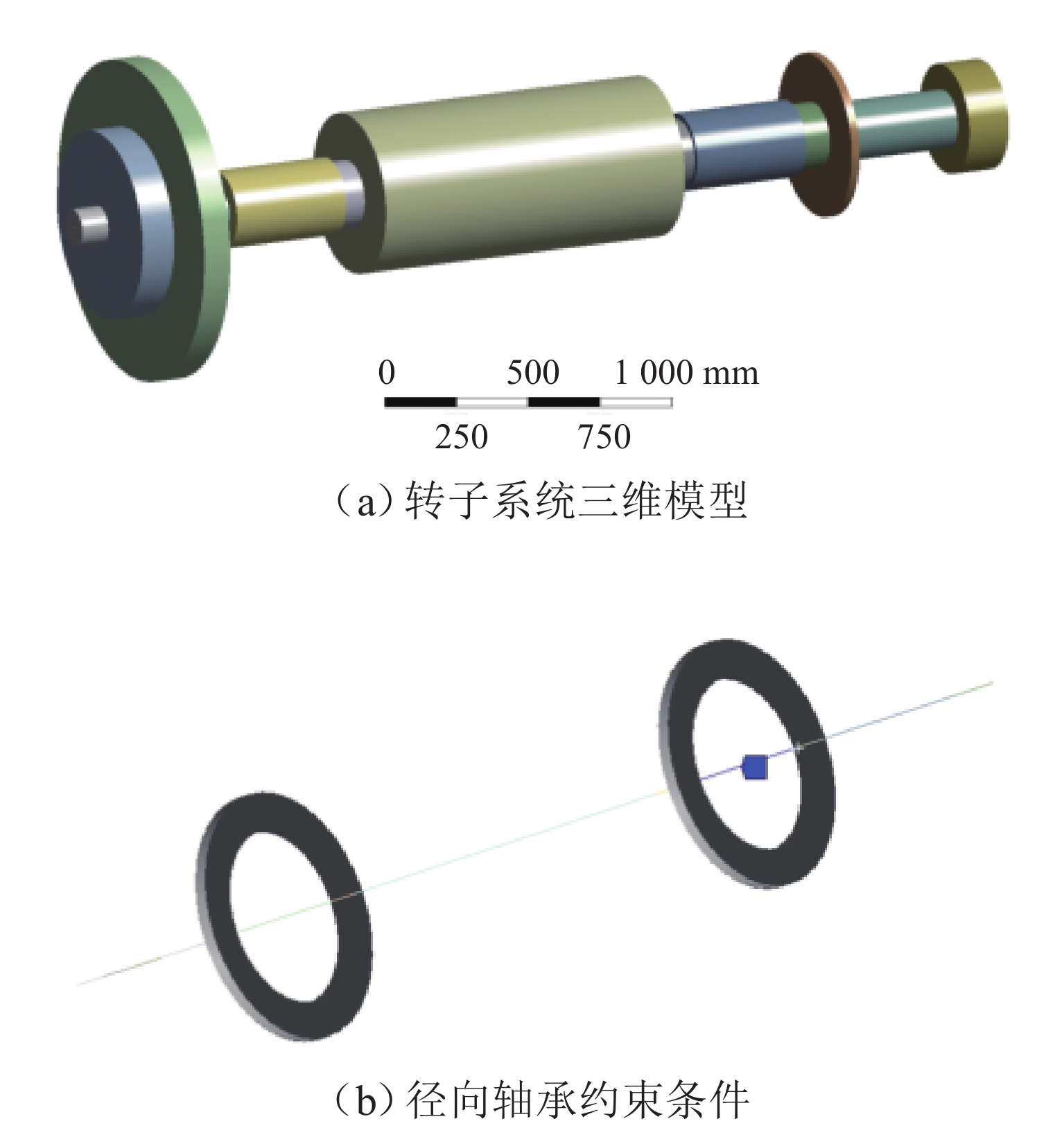
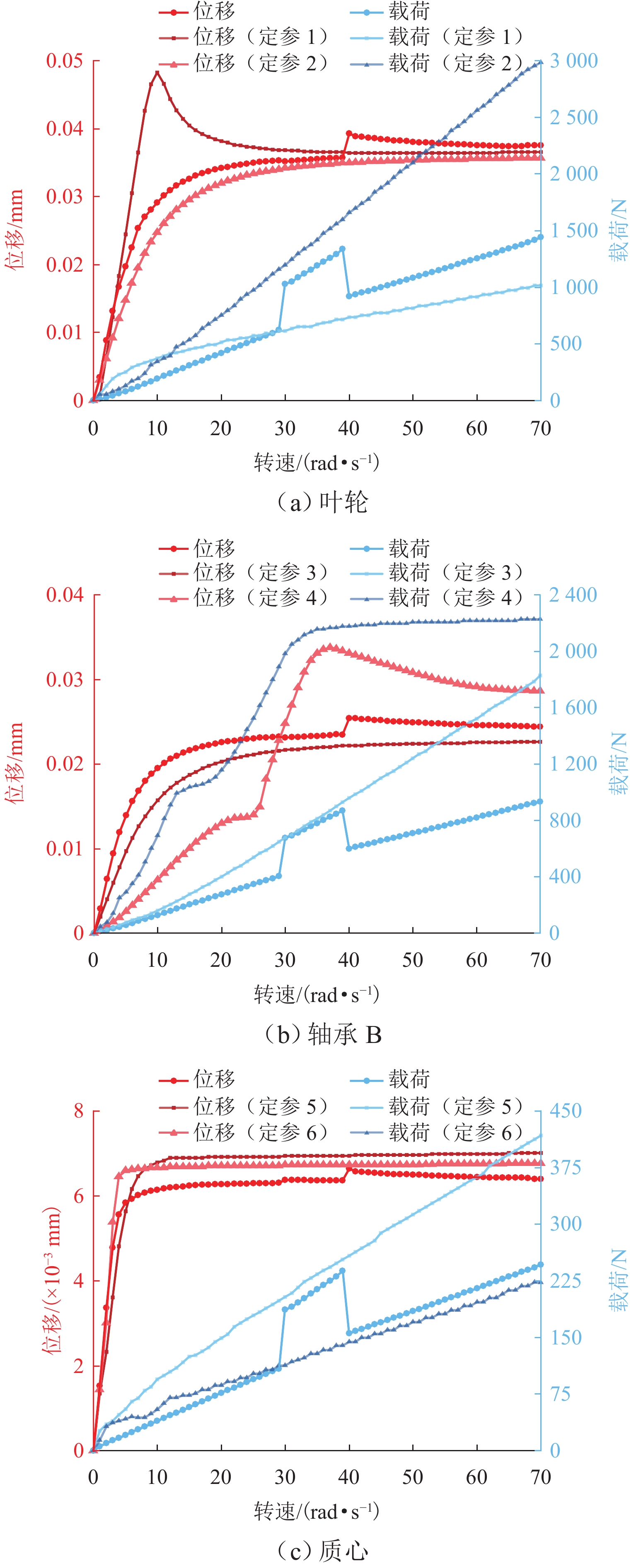
表 1 HTR-PW主氦风机转子主要性能指标
Table 1. Main performance parameters of HTR-PM main helium blower rotor
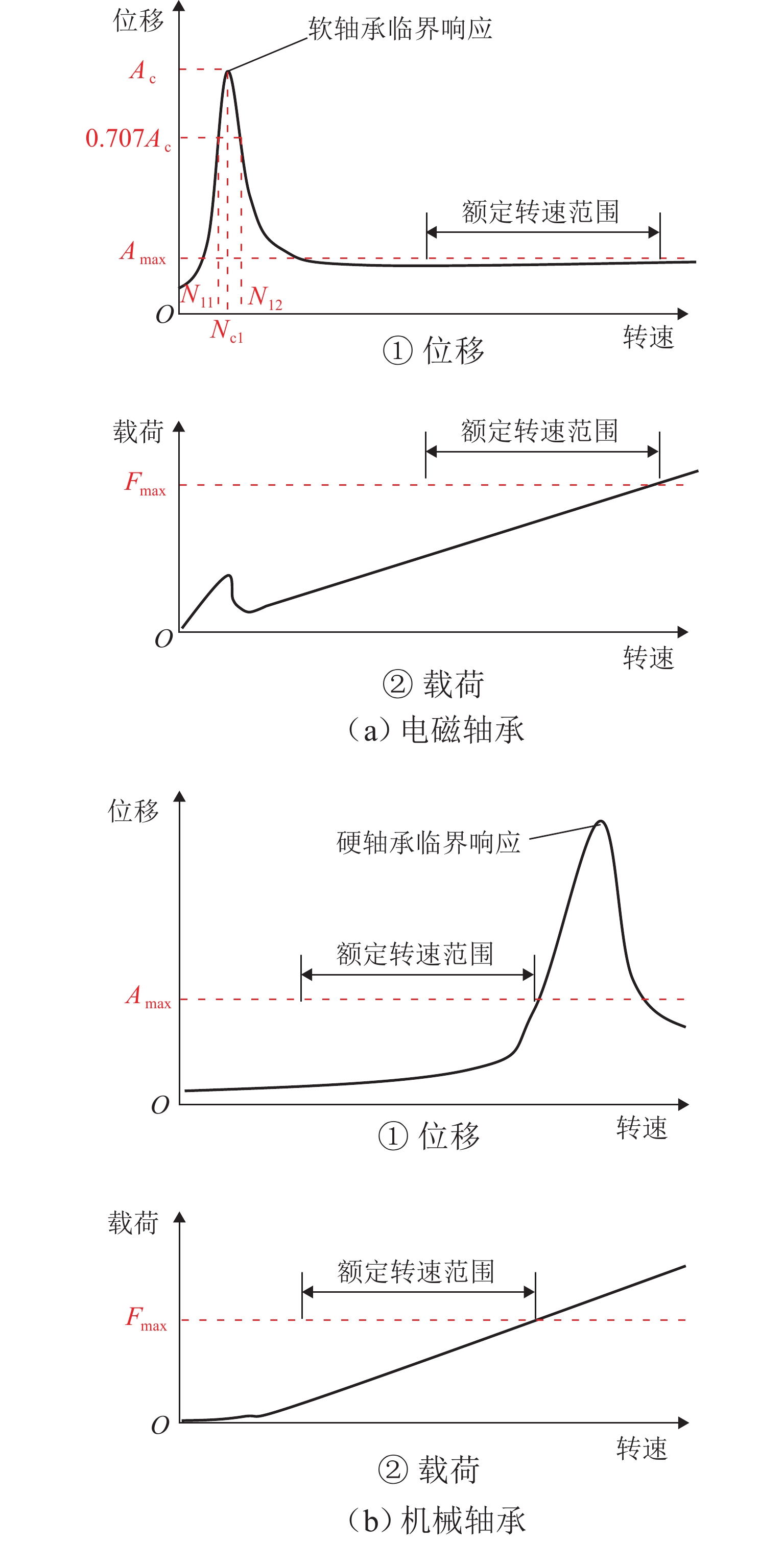
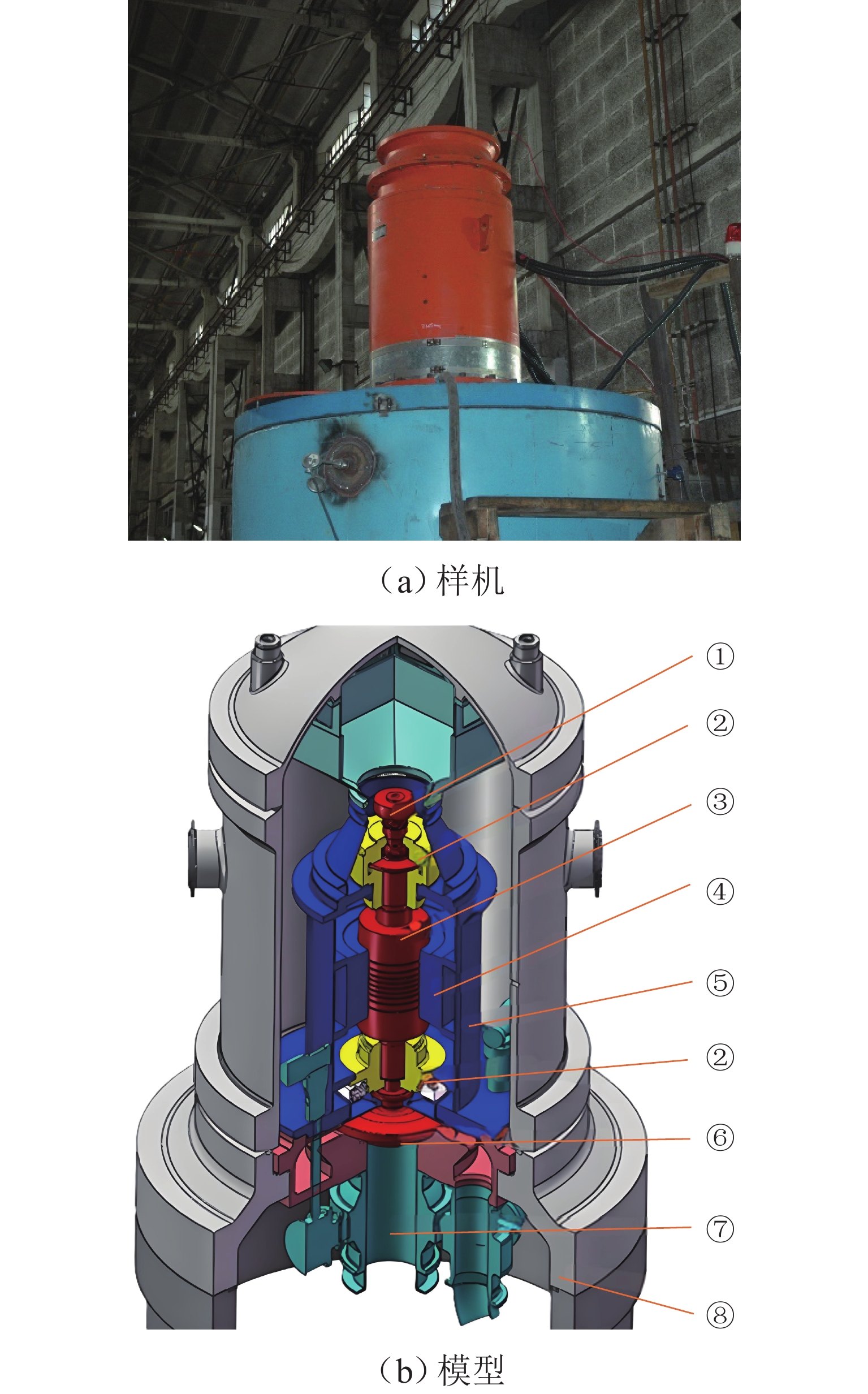
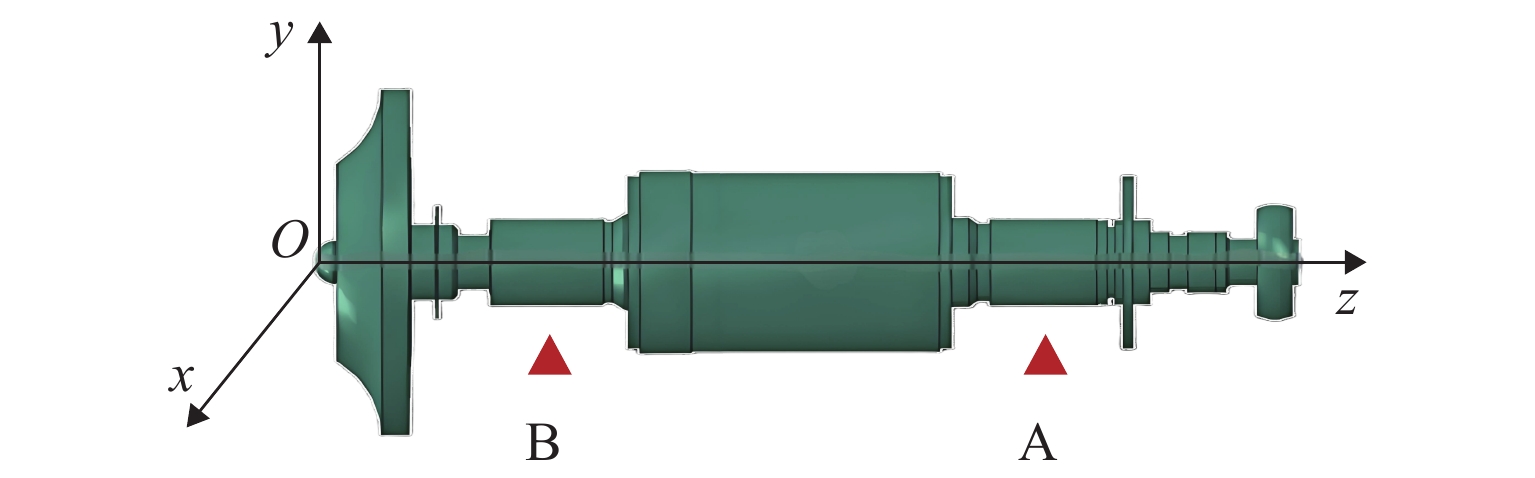
项目 参数 转子质量m/kg 4000 质心位置/mm 1500 径向转动惯量/(kg·mm2) 2.7 × 109 轴向转动惯量/(kg·mm2) 2.2 × 108 转子长度/mm 3500 工作转速范围/(rad·s−1) 14~70 分离裕度/(rad·s−1) 14 转子一阶弯曲频率/(rad·s−1) > 84 × (70 + 14) 表 2 径向轴承设计参数
Table 2. Design parameters of radial bearings
轴承参数 数值 电磁轴承 A 位置ZA/mm 2600 电磁轴承 B 位置ZB/mm 800 轴承 A 力臂$ {{l}}_{\mathrm{A}} $/mm 1100 轴承 B 力臂$ {{l}}_{\mathrm{B}} $/mm 700 磁导率$ {\mathrm{\mu }}_{0} $/(H·m−1) 4π × 10−7 线圈匝数N/匝 30 轴承轴向厚度/mm 300 轴承单磁极宽度/mm 60 轴承处转子直径/mm 300 电磁铁偏置电流/A 20 轴承与转子间隙/mm 1 磁极投影面积/mm2 1.7 × 104 表 3 3种预设不平衡的力臂
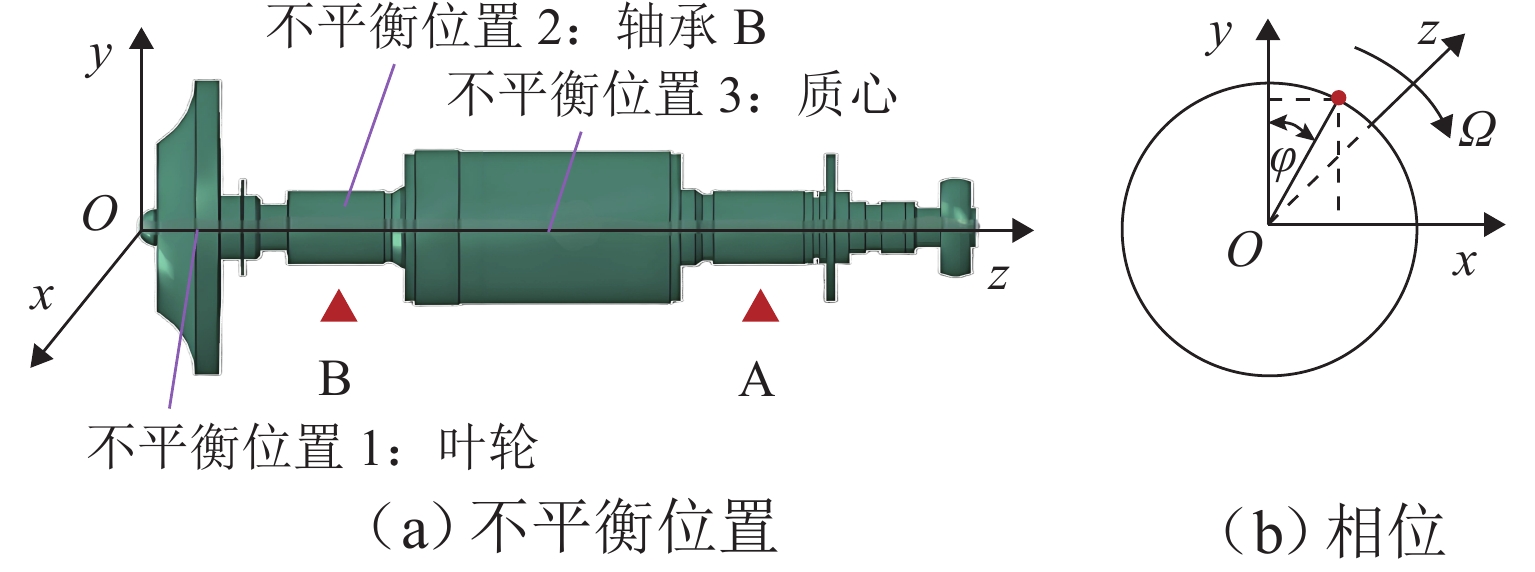
Table 3. Moment arms of three preset unbalances
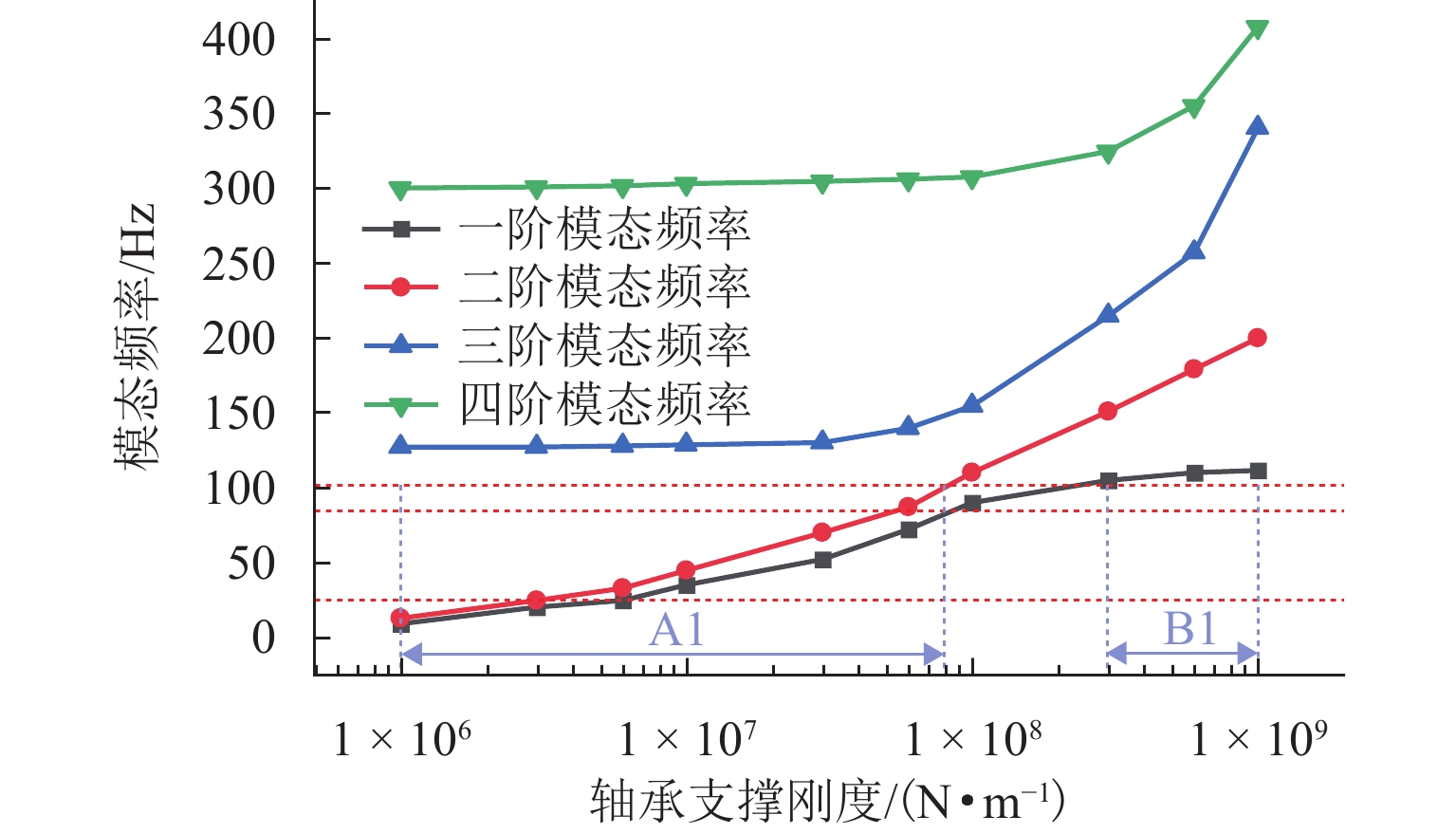
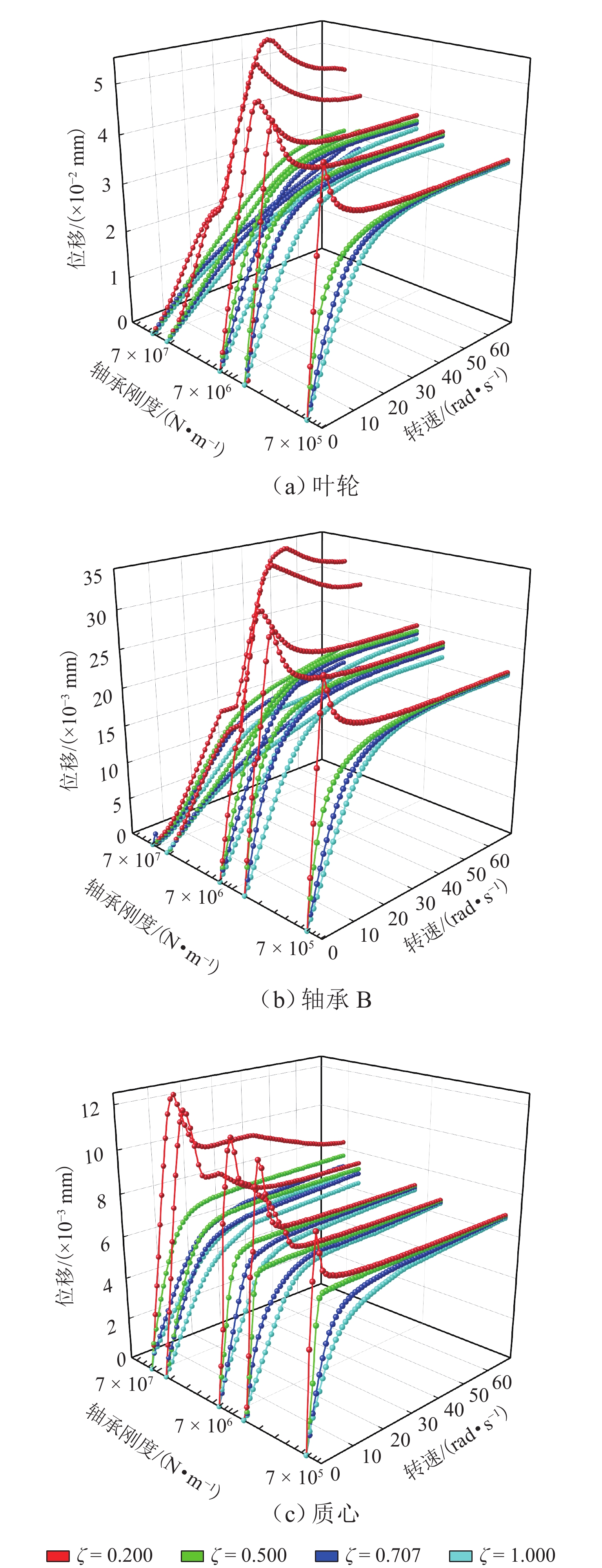
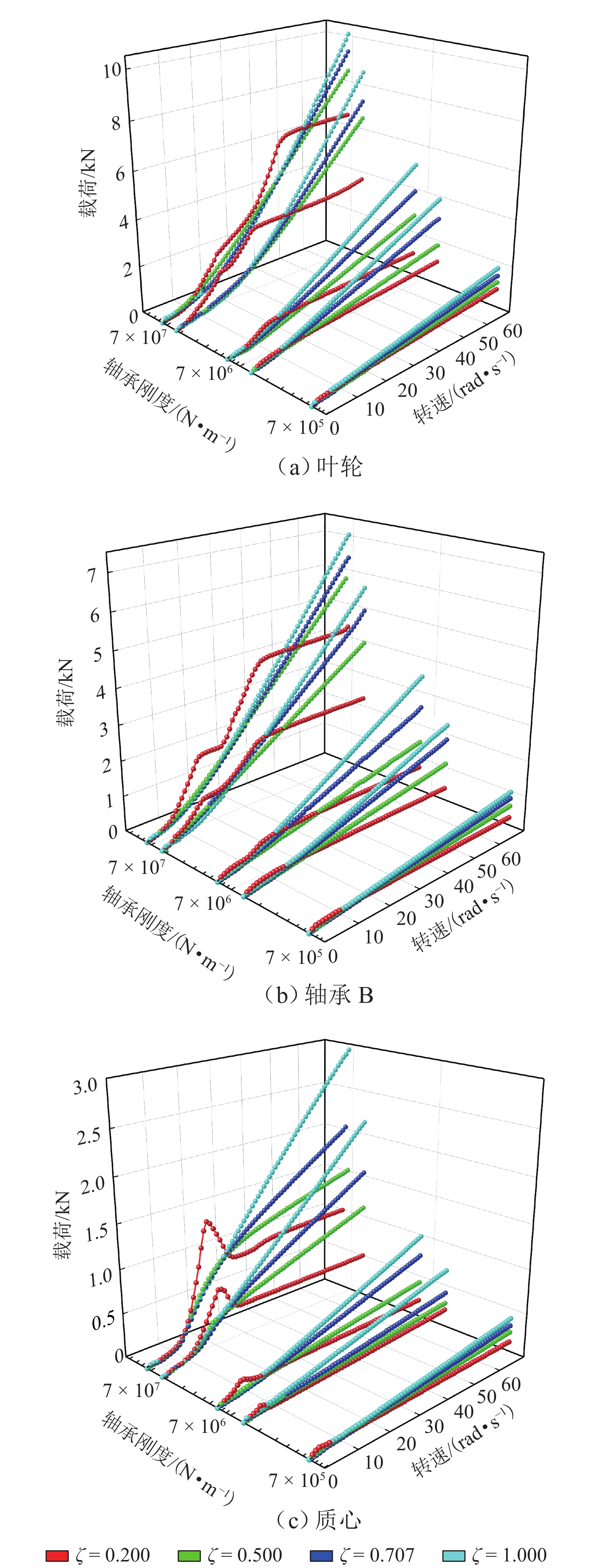
不平衡位置 叶轮处 轴承 B 处 质心处 力臂/mm − 1200 −700 0 注:力臂值为负表示径向平面向外的方向. 表 4 各转速阶段下轴承刚度和阻尼比
Table 4. Bearing stiffnesses and damping ratios at different rotational rates
转速/(rad·s−1) ke/(N·m−1) ζ 0~30 1 × 106 0.707 30~40 5 × 106 0.500 40~70 1 × 107 0.200 -
[1] ZHANG Z Y, SUN Y L. Economic potential of modular reactor nuclear power plants based on the Chinese HTR-PM project[J]. Nuclear Engineering and Design, 2007, 237(23): 2265-2274. doi: 10.1016/j.nucengdes.2007.04.001 [2] ZHANG Z Y, WU Z X, WANG D Z, et al. Current status and technical description of Chinese 2 × 250 MWth HTR-PM demonstration plant[J]. Nuclear Engineering and Design, 2009, 239(7): 1212-1219. doi: 10.1016/j.nucengdes.2009.02.023 [3] 赵钢,马艳秀,符晓铭,等. 高温堆磁悬浮轴承备用氦风机热工实验研究[J]. 原子能科学技术,2009,43(增2): 252-255.ZHAO Gang, MA Yanxiu, FU Xiaoming, et al. Thermal experimental study on standby helium fan for magnetic bearing of high temperature reactor[J]. Atomic Energy Science and Technology, 2009, 43(S2): 252-255. [4] 李红伟,赵雷,石磊,等. HTR-10氦气气轮机电磁轴承系统控制器研究[J]. 核动力工程,2008,29(4): 100-103,116.LI Hongwei, ZHAO Lei, SHI Lei, et al. Study on active magnetic bearing controller for HTR-10 helium turbine rotor[J]. Nuclear Power Engineering, 2008, 29(4): 100-103,116. [5] 赵泾雄,杨国军,李悦,等. HTR-10氦风机磁悬浮转子跌落在辅助轴承上的数值分析[J]. 核动力工程,2012,33(3): 61-64,88. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-0926.2012.03.013ZHAO Jingxiong, YANG Guojun, LI Yue, et al. Numerical analysis of magnetically suspended rotor in HTR-10 helium circulator being dropped into auxiliary bearings[J]. Nuclear Power Engineering, 2012, 33(3): 61-64,88. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-0926.2012.03.013 [6] 杜国伟. 高温气冷堆主氦风机电磁轴承-转子动力学特性研究[D]. 北京:清华大学,2019. [7] 金超武,辛宇,周扬,等. 高温磁悬浮轴承-转子系统建模与动力学分析[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2024,59(4): 746-754,822. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.20230667JIN Chaowu, XIN Yu, ZHOU Yang, et al. Modeling and dynamics analysis of high-temperature magnetic bearing-rotor system[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2024, 59(4): 746-754,822. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.20230667 [8] BELSKII G V, RASTORGUEV A P, LYAMKIN A A. Active magnetic bearing system research[C]//2019 Ⅲ International Conference on Control in Technical Systems (CTS). Petersburg: IEEE, 2019: 132-135. [9] SAMANTA P, HIRANI H. On the evolution of passive magnetic bearings[J]. Journal of Tribology, 2022, 144(4): 040801.1-040801.19. [10] SLININGER T S, CHAN W Y, SEVERSON E L, et al. An overview on passive magnetic bearings[C]//2021 IEEE International Electric Machines & Drives Conference (IEMDC). Hartford: IEEE, 2021: 1-8. [11] 金俊杰,王岩峰,徐程程,等. 人工肾脏泵用磁悬浮轴承设计与磁力特性分析[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2024,59(4): 795-803. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.20230090JIN Junjie, WANG Yanfeng, XU Chengcheng, et al. Design and magnetic force characteristic analysis of magnetic levitation bearing for artificial kidney pumps[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2024, 59(4): 795-803. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.20230090 [12] 周扬,周瑾,王艺宇,等. 考虑界面接触的磁悬浮轴承-转子系统建模及鲁棒控制[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2024,59(4): 755-765. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.20230510ZHOU Yang, ZHOU Jin, WANG Yiyu, et al. Modeling and robust control of magnetic bearing-rotor system considering interface contact[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2024, 59(4): 755-765. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.20230510 [13] 宋春生,尹睿,魏子航,王鹏. 磁悬浮柔性转子系统解耦控制仿真[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2023,58(4): 761-772. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.20220773SONG Chunsheng, YIN Rui, WEI Zihang, WANG Peng. Simulation on decoupling control of maglev flexible rotor system[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2023, 58(4): 761-772. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.20220773 [14] ZHOU J, WU H C, WANG W Y, et al. Online unbalance compensation of a maglev rotor with two active magnetic bearings based on the LMS algorithm and the influence coefficient method[J]. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 2022, 166: 108460.1-108460.22. [15] TANG J Q, XIANG B, ZHANG Y B. Dynamic characteristics of the rotor in a magnetically suspended control moment gyroscope with active magnetic bearing and passive magnetic bearing[J]. ISA Transactions, 2014, 53(4): 1357-1365. doi: 10.1016/j.isatra.2014.03.009 [16] SAEED N A, KANDIL A. Two different control strategies for 16-pole rotor active magnetic bearings system with constant stiffness coefficients[J]. Applied Mathematical Modelling, 2021, 92: 1-22. doi: 10.1016/j.apm.2020.11.005 [17] XU X P, HAN Q K. A general electromagnetic model and vibration control for shape deviations in PMSM supported by three-pole active magnetic bearings[J]. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 2021, 158: 107710.1-107710.17. [18] XU Y P, SHEN Q, ZHANG Y, et al. Dynamic modeling of the active magnetic bearing system operating in base motion condition[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 166003-166013. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3022996 [19] 巩磊,何派,石勇,等. 主动磁悬浮轴承非奇异快速终端滑模转子位置控制[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2025,60(4): 976-985.GONG Lei, HE Pai, SHI Yong, et al. Non-singular fast terminal sliding mode rotor position control of active magnetic bearings[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University , 2025, 60(4): 976-985. [20] NAYEK B, DAS A S, DUTT J K. Model based estimation of inertial parameters of a rigid rotor having dynamic unbalance on active magnetic bearings in presence of noise[J]. Applied Mathematical Modelling, 2021, 97: 701-720. doi: 10.1016/j.apm.2021.04.015 [21] 翟明达,张博,李晓龙,等. 基于模糊PID控制的准零刚度磁悬浮隔振平台的设计与实现[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2023,58(4): 886-895. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.20220880ZHAI Mingda, ZHANG Bo, LI Xiaolong, et al. Design and implementation of magnetic suspension vibration isolation platform with quasi-zero stiffness based on fuzzy PID control[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2023, 58(4): 886-895. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.20220880 [22] LIU X B, HE T, YAN Y, et al. Effects of axial offset and deflection on load-bearing characteristics of the permanent magnet bearing[J]. Engineering Failure Analysis, 2023, 146: 107123.1-107123.12. [23] BIAO X, SHUAI W, TAO W, et al. Design, modeling, and validation of a 0.5 kWh flywheel energy storage system using magnetic levitation system[J]. Energy, 2024, 308: 132867.1-132867.16. [24] DORF R C, BISHOP R H. Modern control systems[M]. [s.l.]: Prentice Hall, 2022. [25] JIA X Y, XU Y, BAI Y J, et al. Rotor passing through critical speed with assistance of electromagnetic damper[C]//Nuclear Power Plants: Innovative Technologies for Instrumentation and Control Systems. Singapore: Springer, 2022: 301-315. [26] International Organization for Standardization. Mechanical vibration-balance quality requirements of rigid rotors—part 1: determination of permissible residual unbalance, including marine applications: ISO 1940-1: 2003[S]. Geneva:ISO Publications, 2003. -




 下载:
下载: