Analysis of Polygonal Wear Characteristics of Chinese High-Speed Train Wheels
-
摘要:
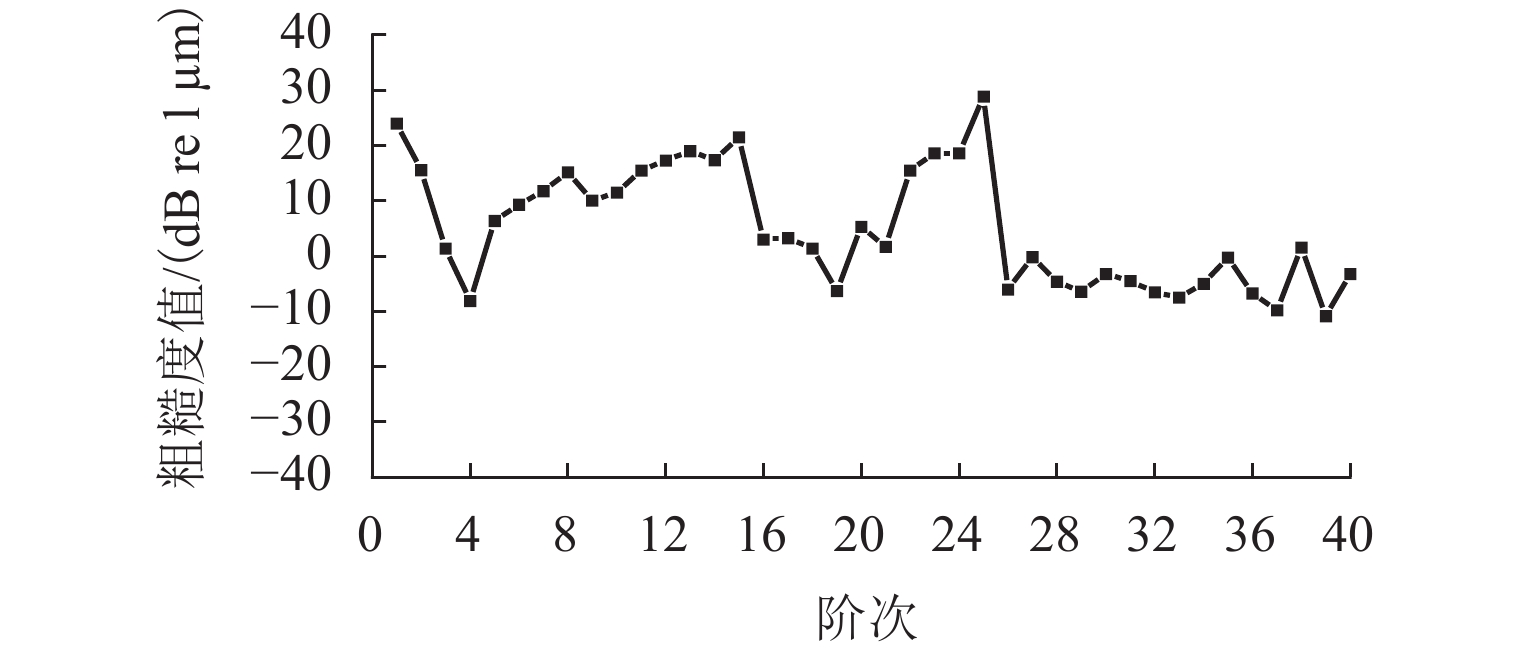
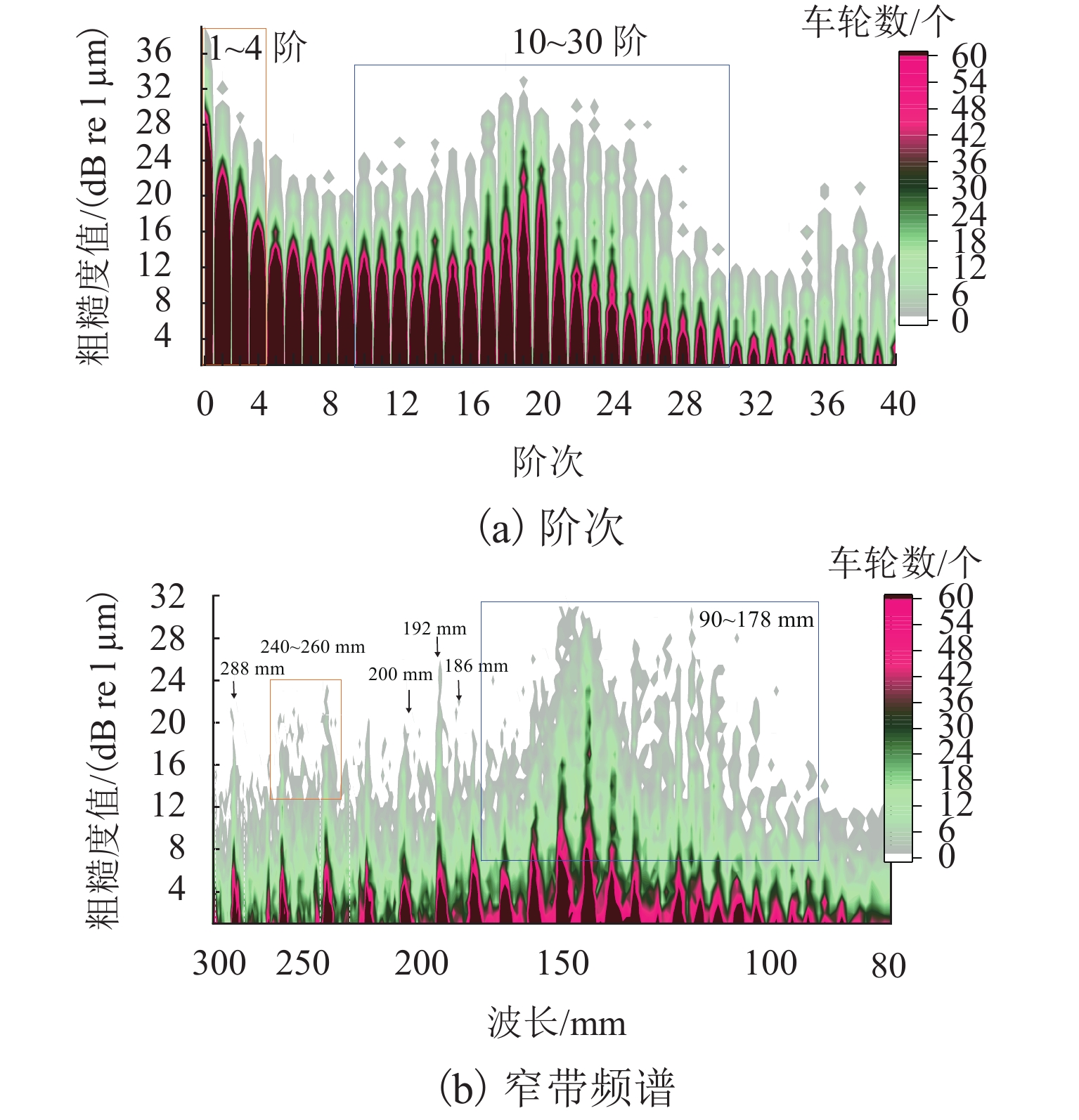
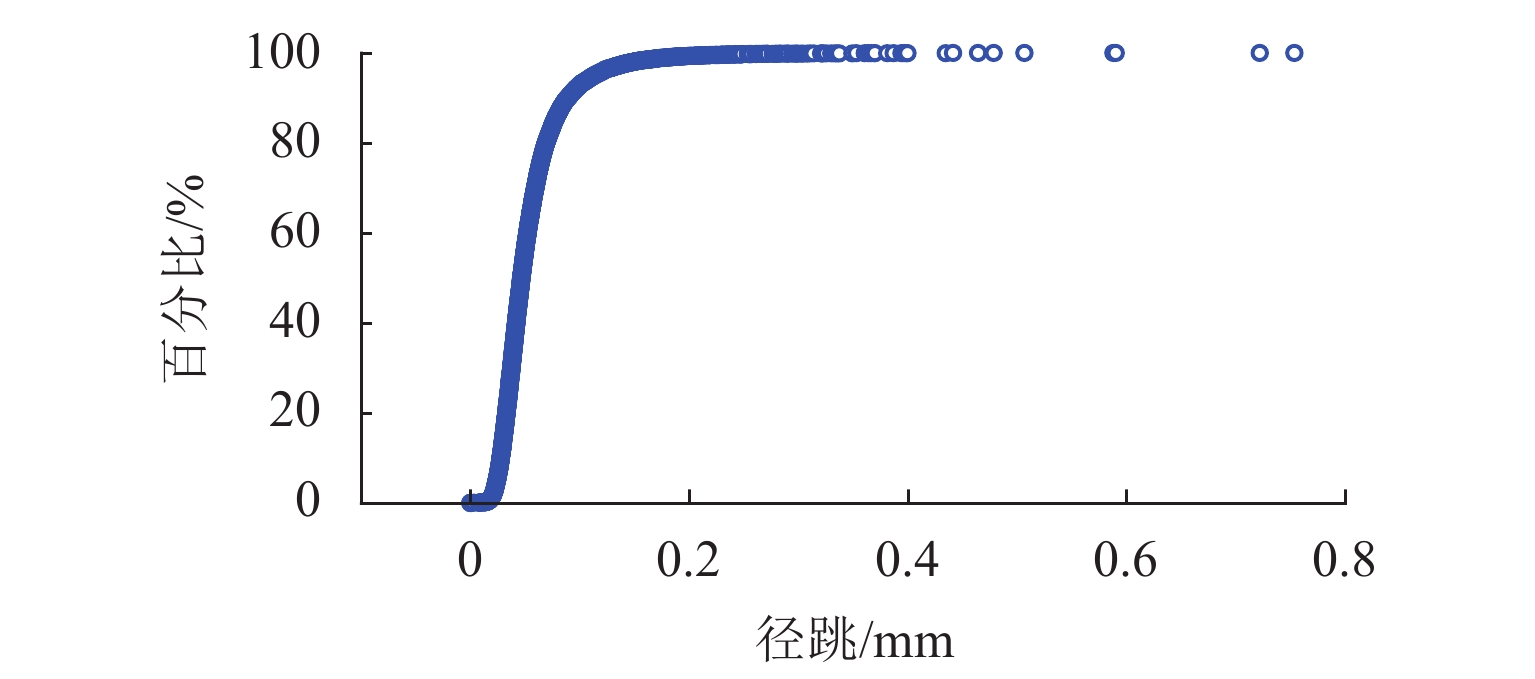
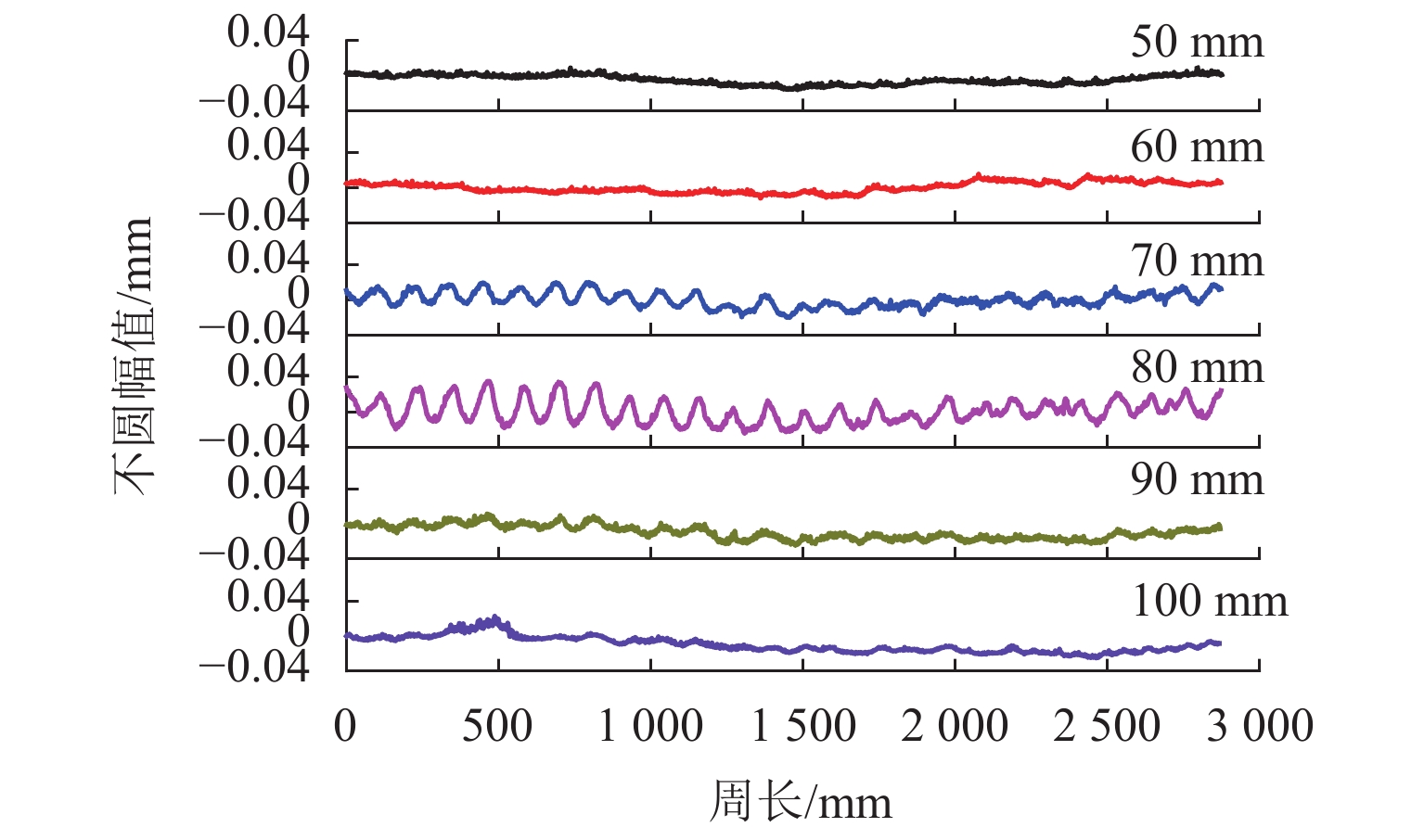
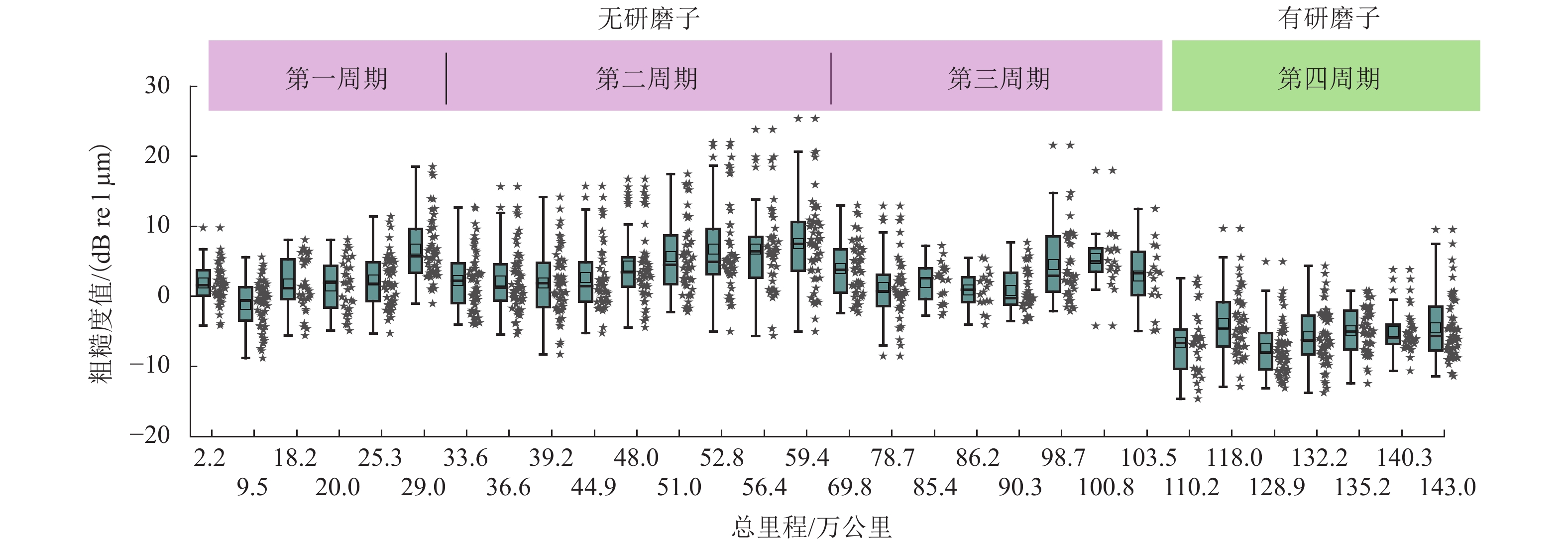
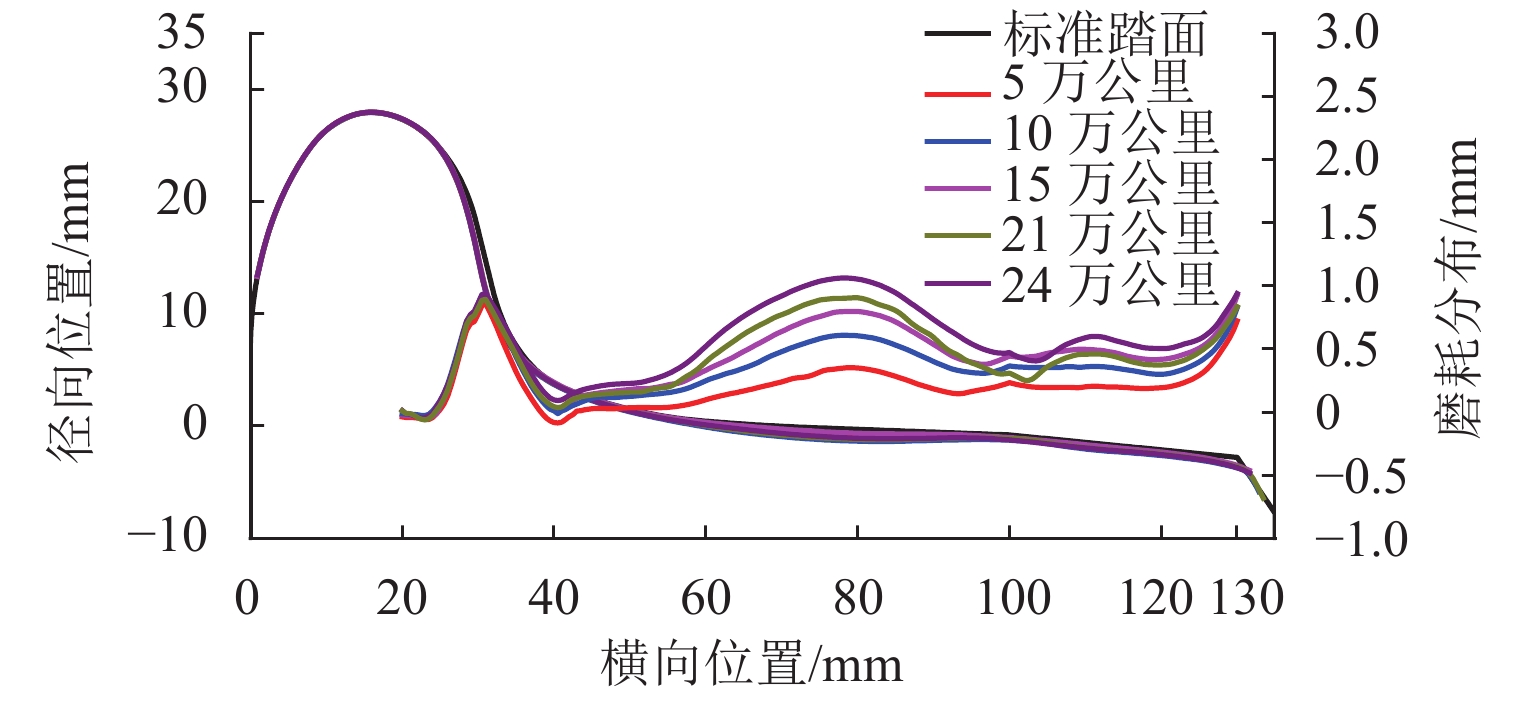
车轮失圆问题广泛存在于我国高速列车,对列车乘坐舒适性和运行安全性有显著影响. 从2011年至2020年,测试了12条高铁线路中9种型号高速动车组的车轮不圆度,包括200、250、300、350 km/h 4种运营速度,共3.05万个车轮;对车轮不圆度测试数据进行特征分析,掌握我国高速动车组车轮多边形磨耗的发展规律;分析影响车轮多边形发展的关键因素,包括车辆轴距、轨道结构和研磨子修形. 结果表明:高速动车组车轮存在10~30阶多边形磨耗,多边形波长为90~288 mm,且在100~178 mm波长范围的多边形磨耗最为严重;车辆轴距、扣件类型和环境温度与车轮多边形磨耗形成密切相关,通过改善研磨子和车轮踏面匹配关系,保证踏面横向和圆周处于良好的磨耗状态,使高阶车轮多边形粗糙度水平最大下降60%.
Abstract:Wheel out-of-roundness (OOR), which is commonly observed on the wheels of Chinese high-speed trains, has a significant influence on the vehicle ride comfort and operation safety. From 2011 to 2020, 30500 wheels of nine types of high-speed trains were selected for tests and the wheel OOR was measured. The tested high-speed trains operated on 12 high-speed railway lines with different operating speeds, including operating speeds of 200, 250, 300, and 350 km/h. The characteristics of the wheel OOR were analyzed to determine the development rules for wheel polygonal wear of high-speed EMUs in China. The key factors that affect the wheel polygon wear were analyzed, including the wheelbase, track structure, and abrasive block. The test results show that the dominant harmonic orders of the wheel polygonal wear range from 10th to 30th order. The corresponding wavelengths of the 10th–30th-order polygonization are 90–288 mm, with a wheel polygonal wear of 100‒178 mm being the most severe. The analysis of the key factors that affect the wheel polygonal wear shows that the wheelbase, fastening stiffness, and ambient temperature are closely related to the formation of wheel polygonal wear. By improving the matching relationship between the abrasive block and the wheel tread, the transverse and circumferential wear is minimized and the roughness level of the high-order polygonal wear is reduced by 60% at most.
-
Key words:
- high-speed train /
- wheels /
- wear /
- polygon /
- abrasive block /
- wheelbase /
- fastening stiffness
-
表 1 高速动车组车轮不圆测试信息
Table 1. Measurement information of wheel OOR of high-speed EMUs
厂家 车型 设计速度/
(km·h−1)车轮初始
直径/mm运行线路 列次/列 测试车轮数/个 A A1 200 860 兰州—乌鲁木齐 16 4122 A2 250 860 大同—西安、贵阳—广州、
南宁—广州、南昌—福州130 4080 A3 250 920 成都—贵阳 2 1608 A4 300 860 大同—西安、北京—广州 53 6088 B B1 200 890 兰州—乌鲁木齐 40 1800 B2 250 860 大同—西安、上海—昆明 2 440 B3 300 920 武汉—广州、北京—广州、
北京—上海502 8456 B4 300 920 哈尔滨—大连 78 1902 B5 350 920 大同—西安 、郑州—徐州、
北京—广州、北京—上海、
北京—天津12 2004 表 2 A厂列车车轮多边形磨耗波长
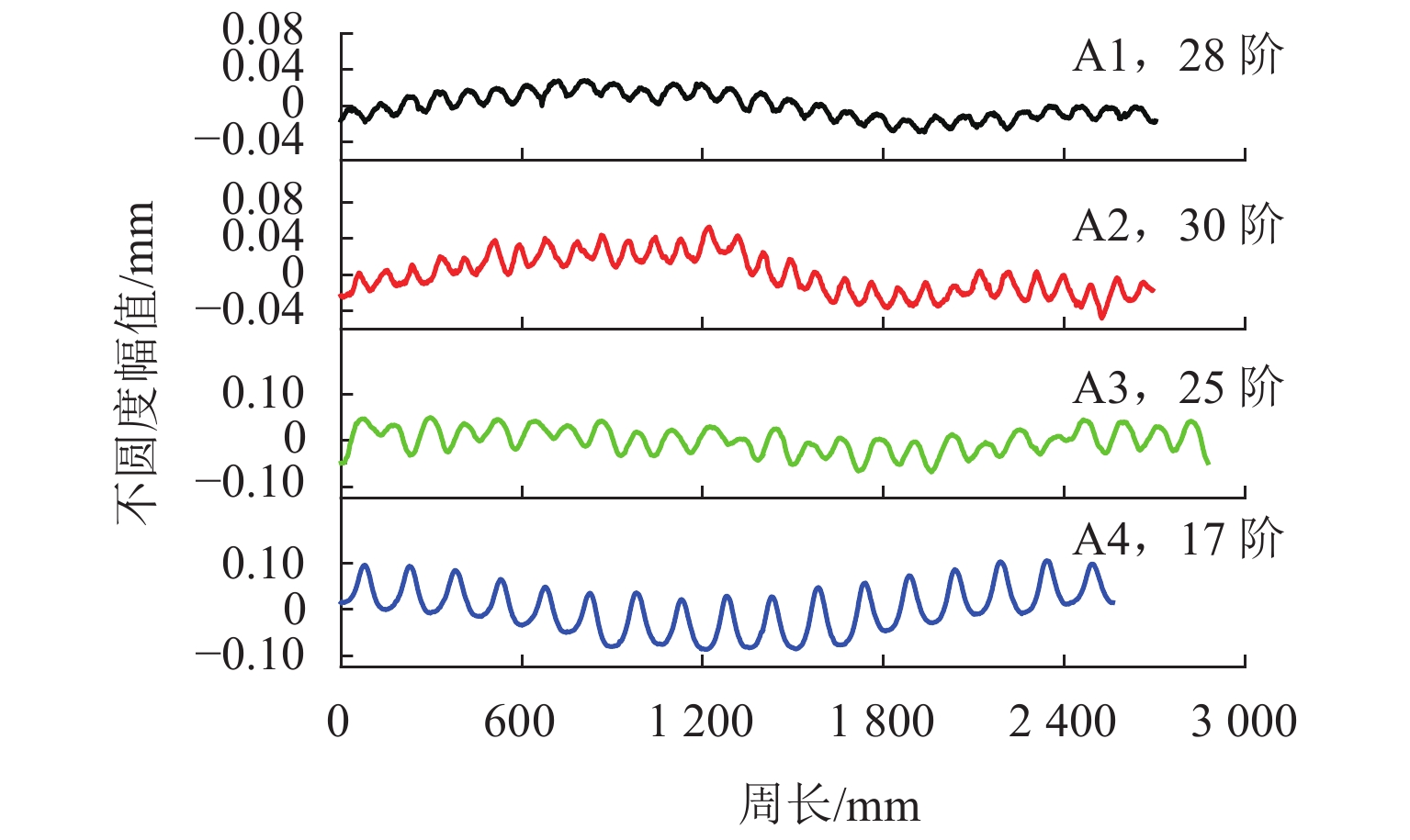
Table 2. Wavelengths of wheel polygonal wear for manufacturer A
车型 直径/mm 主要阶次/阶 波长/mm A1 860 26~28 96~102 A2 860 14
22~24
29~30192
112~122
90~92A3 920 15
22~26192
111~131A4 860 10
17250
150表 3 B厂列车车轮多边形磨耗波长
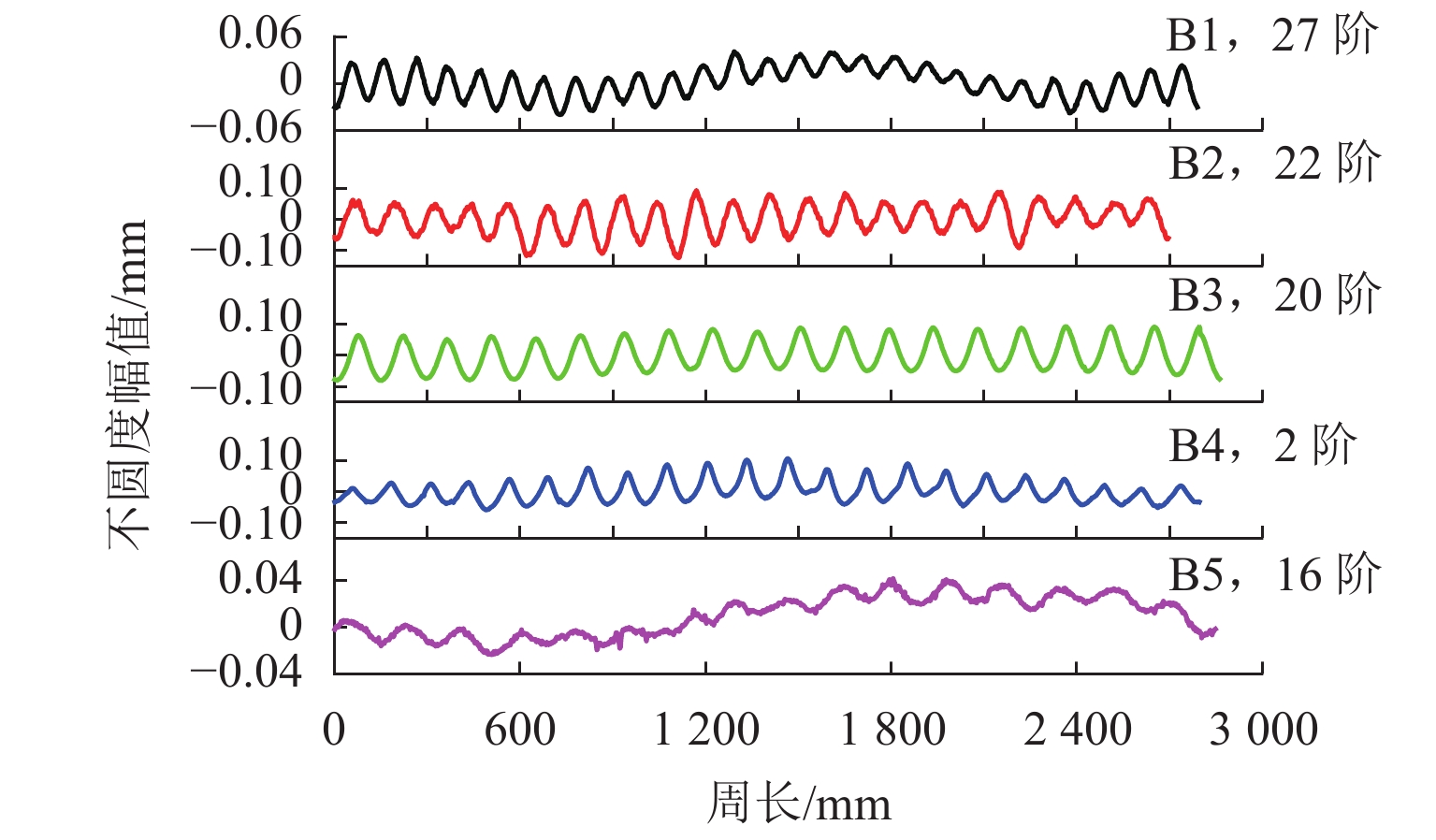
Table 3. Wavelengths of wheel polygonal wear for manufacturer B
车型 直径/mm 主要阶次 波长/mm B1 890 14~16
22~28174~200
100~126B2 860 14
22~24192
112~122B3 920 12
18~20240
143~160B4 920 21~23 124~136 B5 920 10
16~17288
167~178表 4 2种轴距下多边形磨耗对比
Table 4. Comparison of wheel polygonal wear under two wheelbases
轴距/m 车型 阶次 波长/mm 频率/Hz 2.5 A1~A4、
B2~B510~15 192、
240~288330~354 16~30 90~178 520~613 21~23 124~136 613~672 2.7 B1 14~16 174~200 266~306 21~28 100~126 423~533 表 5 高铁线路调查结果
Table 5. Investigation results for high-speed railway lines
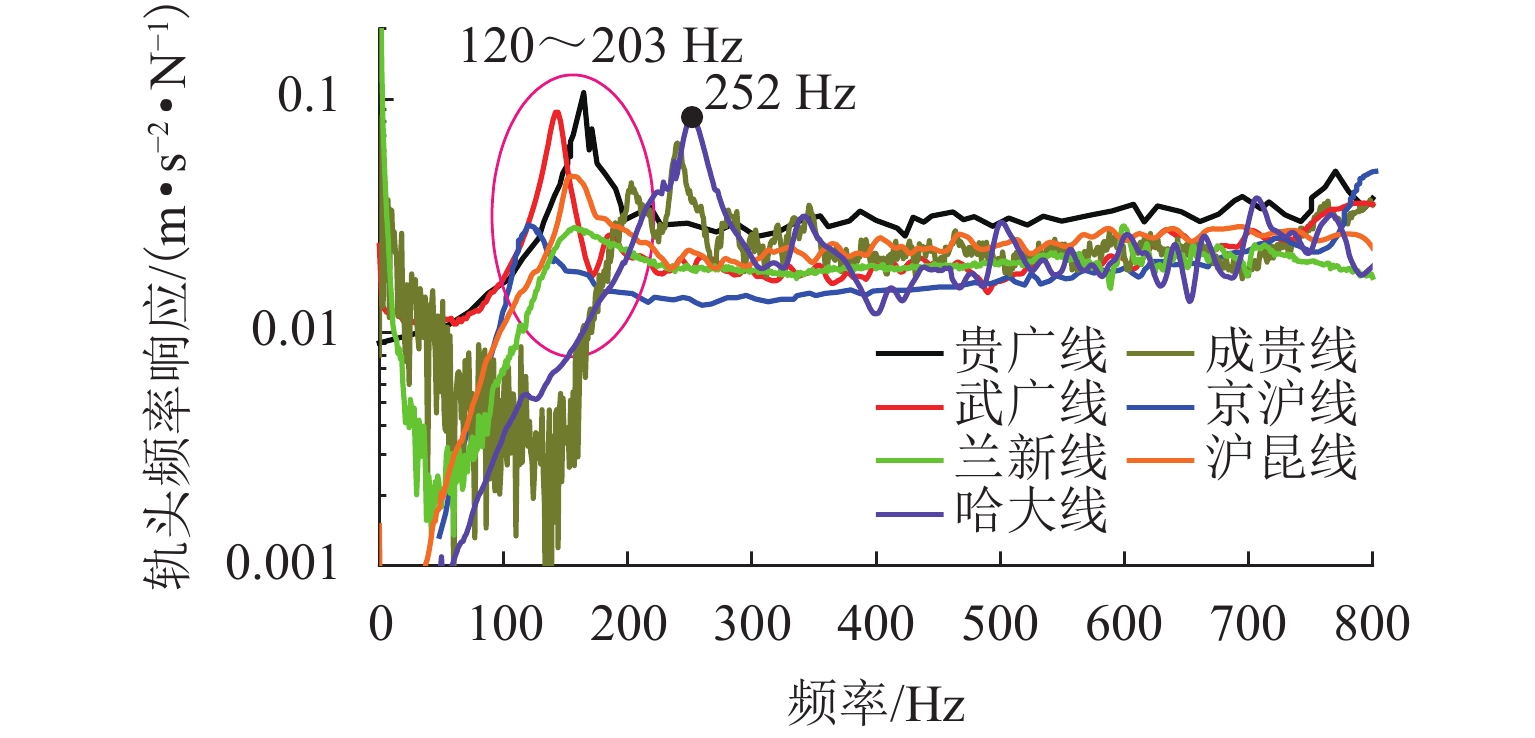
线路 主要运行车型 轨道板类型 扣件类型 扣件间距/mm 扣件刚度/(kN·mm−1) 频响主要频率/Hz 大西线 A2、A4、B2、B5 CRTS Ⅰ WJ-8 629 20~40 贵广线 A2 CRTS Ⅰ WJ-8 629 20~40 165 成贵线 A3 CRTS Ⅰ/CRTS Ⅲ WJ-8 629 20~40 203 京广线 A4、B3、B5 CRTS Ⅰ WJ-8/Vossloh 300 650 20~40 142 京沪线 B3、B5 CRTS Ⅱ WJ-8/Vossloh 300 650 20~40 120 兰新线 A1、B1 CRTS Ⅰ Vossloh 650 20~40 160 沪昆线 B2 CRTS Ⅰ WJ-8 650 20~40 155 哈大线 B4 CRTS Ⅰ WJ-7 629 30~40 252 -
[1] 陶功权,周小江,周业明,等. B型地铁车轮失圆问题分析[J]. 机械工程学报,2020,56(14): 152-160. doi: 10.3901/JME.2020.14.152TAO Gongquan, ZHOU Xiaojiang, ZHOU Yeming, et al. Analysis of the wheel out-of-roundness of type B metro train[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2020, 56(14): 152-160. doi: 10.3901/JME.2020.14.152 [2] TAO G Q, WANG L F, WEN Z F, et al. Measurement and assessment of out-of-round electric locomotive wheels[J]. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part F: Journal of Rail and Rapid Transit, 2018, 232(1): 275-287. doi: 10.1177/0954409716668210 [3] 金学松,吴越,梁树林,等. 车轮非圆化磨耗问题研究进展[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2018,53(1): 1-14. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2018.01.001JIN Xuesong, WU Yue, LIANG Shulin, et al. Mechanisms and countermeasures of out-of-roundness wear on railway vehicle wheels[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2018, 53(1): 1-14. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2018.01.001 [4] TAO G Q, WEN Z F, JIN X S, et al. Polygonisation of railway wheels: a critical review[J]. Railway Engineering Science, 2020, 28(4): 317-345. doi: 10.1007/s40534-020-00222-x [5] 刘佳,韩健,肖新标,等. 高速车轮非圆化磨耗对轴箱端盖异常振动影响初探[J]. 机械工程学报,2017,53(20): 98-105. doi: 10.3901/JME.2017.20.098LIU Jia, HAN Jian, XIAO Xinbiao, et al. Influence of wheel non-circular wear on axle box cover abnormal vibration in high-speed train[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2017, 53(20): 98-105. doi: 10.3901/JME.2017.20.098 [6] ZHANG J, HAN G X, XIAO X B, et al. Influence of wheel polygonal wear on interior noise of high-speed trains[J]. Journal of Zhejiang University—Science A (Applied Physics & Engineering), 2014, 15(12): 1002-1018. [7] HU W G, LIU Z M, LIU D K, et al. Fatigue failure analysis of high speed train gearbox housings[J]. Engineering Failure Analysis, 2017, 73: 57-71. doi: 10.1016/j.engfailanal.2016.12.008 [8] 彭来先,韩健,初东博,等. 高速动车组垂向止挡异常振动特性及成因分析[J]. 机械工程学报,2019,55(12): 121-127. doi: 10.3901/JME.2019.12.121PENG Laixian, HAN Jian, CHU Dongbo, et al. Analysis of abnormal vibration characteristics and causes of vertical block in high-speed EMU[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2019, 55(12): 121-127. doi: 10.3901/JME.2019.12.121 [9] 肖俊恒,闫子权,涂英辉,等. 轮轨振动对高铁扣件伤损的影响分析[J]. 中国铁路,2017(11): 10-14. doi: 10.19549/j.issn.1001-683x.2017.11.010XIAO Junheng, YAN Ziquan, TU Yinghui, et al. On impact of wheel-rail vibration on HSR fastener damage[J]. China Railway, 2017(11): 10-14. doi: 10.19549/j.issn.1001-683x.2017.11.010 [10] PALLGEN G. Unrunde rader an eisenbahnfahraeugen[J]. Der Eisenbahningenieur, 1998, 49(1): 56-60. [11] JOHANSSON A. Out-of-round railway wheels—assessment of wheel tread irregularities in train traffic[J]. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 2006, 293(3/4/5): 795-806. [12] QU S, ZHU B, ZENG J, et al. Experimental investigation for wheel polygonisation of high-speed trains[J]. Vehicle System Dynamics, 2021, 59(10): 1573-1586. doi: 10.1080/00423114.2020.1772984 [13] WU Y, DU X, ZHANG H J, et al. Experimental analysis of the mechanism of high-order polygonal wear of wheels of a high-speed train[J]. Journal of Zhejiang University—Science A (Applied Physics & Engineering), 2017, 18(8): 579-592. doi: 10.1631/jzus.A1600741 [14] CAI W B, CHI M R, WU X W, et al. Experimental and numerical analysis of the polygonal wear of high-speed trains[J]. Wear, 2019, 440/441: 1-12. [15] 金学松,吴越,梁树林,等. 高速列车车轮多边形磨耗、机理、影响和对策分析[J]. 机械工程学报,2020,56(16): 118-136. doi: 10.3901/JME.2020.16.118JIN Xuesong, WU Yue, LIANG Shulin, et al. Characteristics, mechanism, influences and countermeasures of polygonal wear of high-speed train wheels[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2020, 56(16): 118-136. doi: 10.3901/JME.2020.16.118 [16] European Committee for Standardization. Railway applications-acoustics-rail and wheel roughness measurement related to noise generation: EN 15610[S]. Brussels: CEN-CENELEC Management Centre, 2019. [17] 翟志浩,和振兴. 极寒环境下铁路扣件新型网孔式弹性垫板动力性能及影响研究[J]. 中国科学:技术科学,2020,50(2): 235-244.ZHAI Zhihao, HE Zhenxing. Research on dynamic performance and influence of new mesh-hole elastic pads for railway fasteners in an extremely cold environment[J]. Scientia Sinica (Technologica), 2020, 50(2): 235-244. [18] 乔青峰,李明星,赵晓男,等. 研磨子抑制高速列车车轮多边形磨耗的机理研究[J]. 摩擦学学报,2020,40(2): 234-239. doi: 10.16078/j.tribology.2019037QIAO Qingfeng, LI Mingxing, ZHAO Xiaonan, et al. Mechanism of suppression of polygonal wear of wheel on high-speed trains by abrasive block[J]. Tribology, 2020, 40(2): 234-239. doi: 10.16078/j.tribology.2019037 -





 下载:
下载: