Model-Free Adaptive Control for Single-Degree-of-Freedom Magnetically Levitated System
-
摘要:
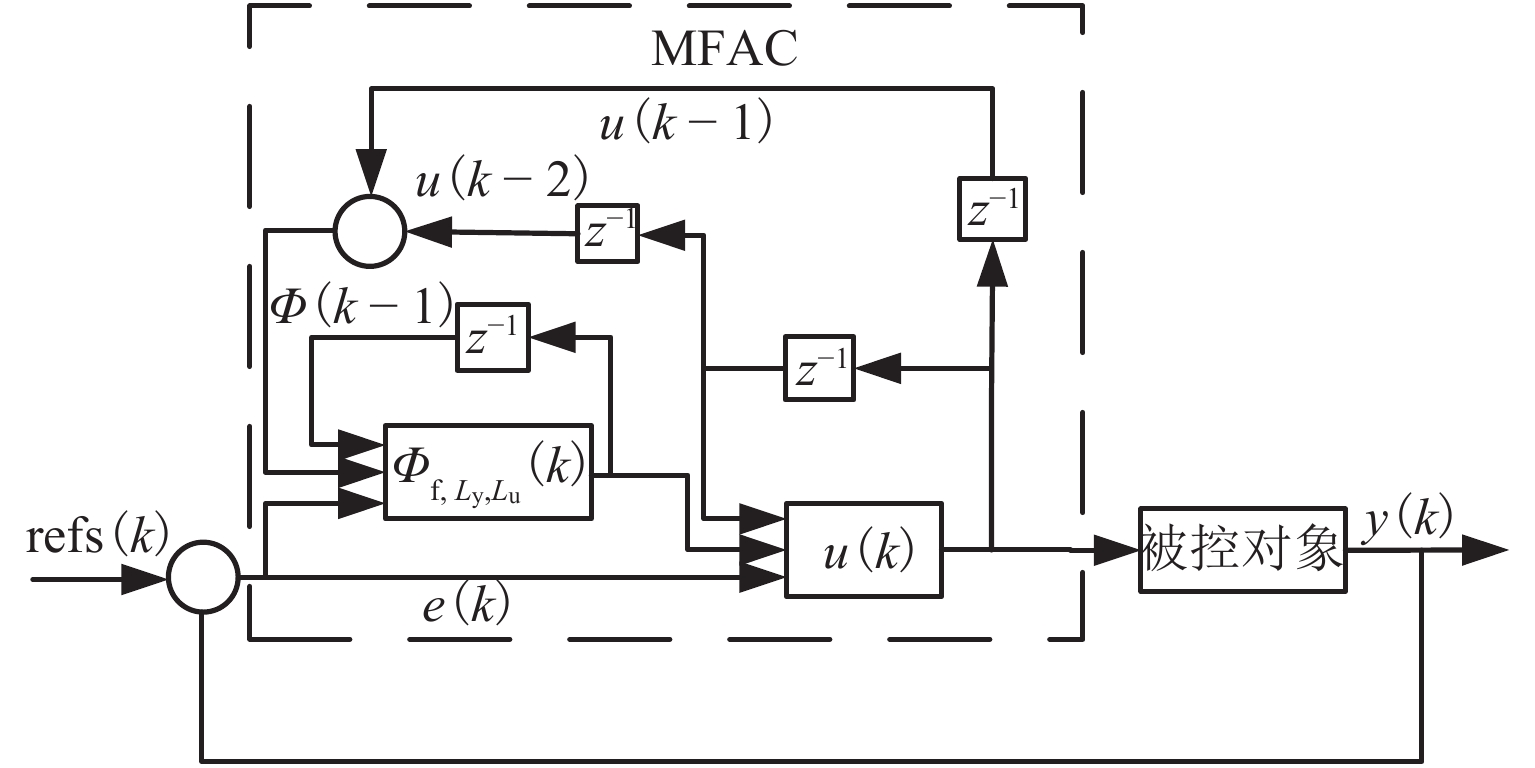
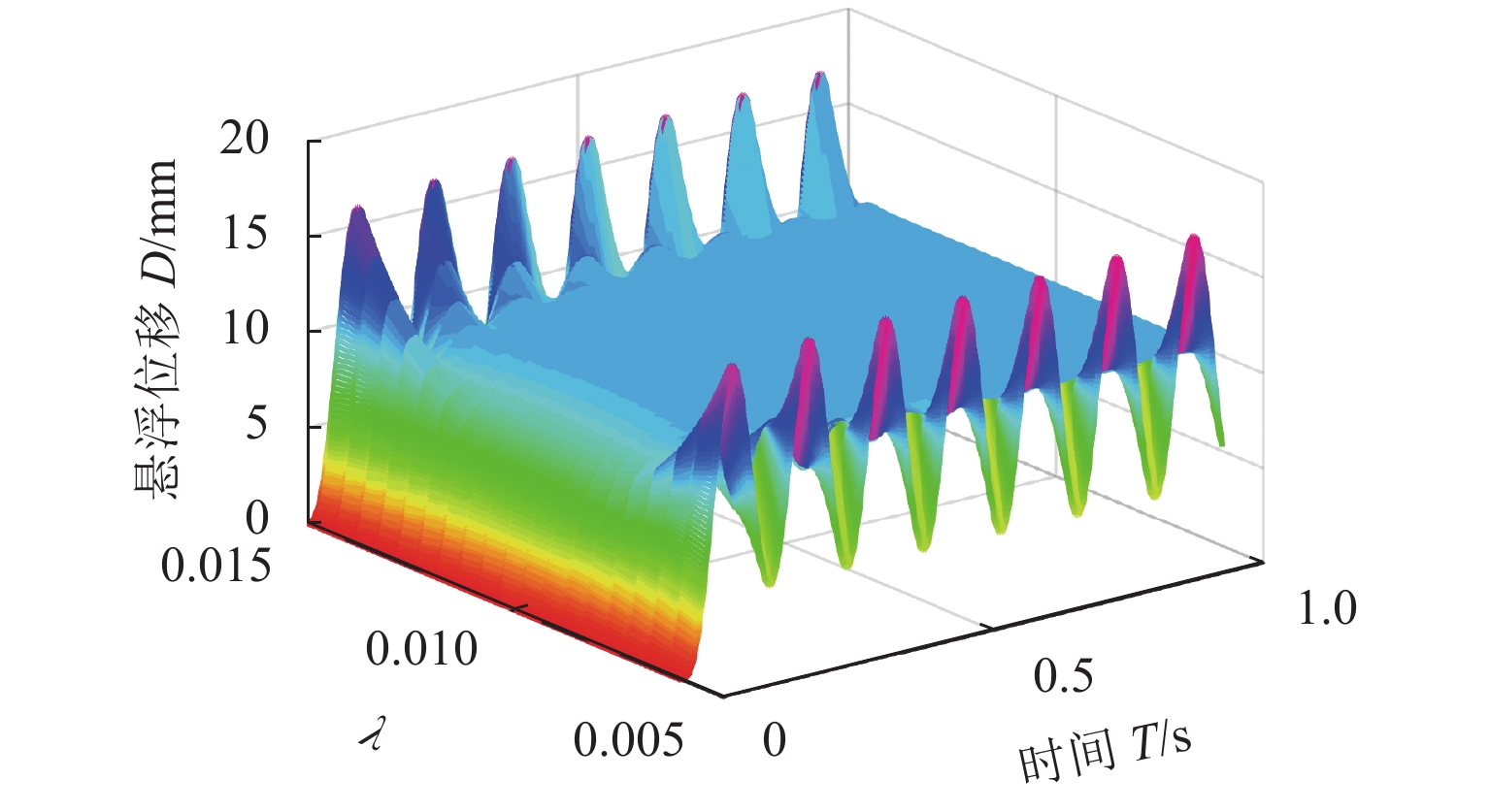
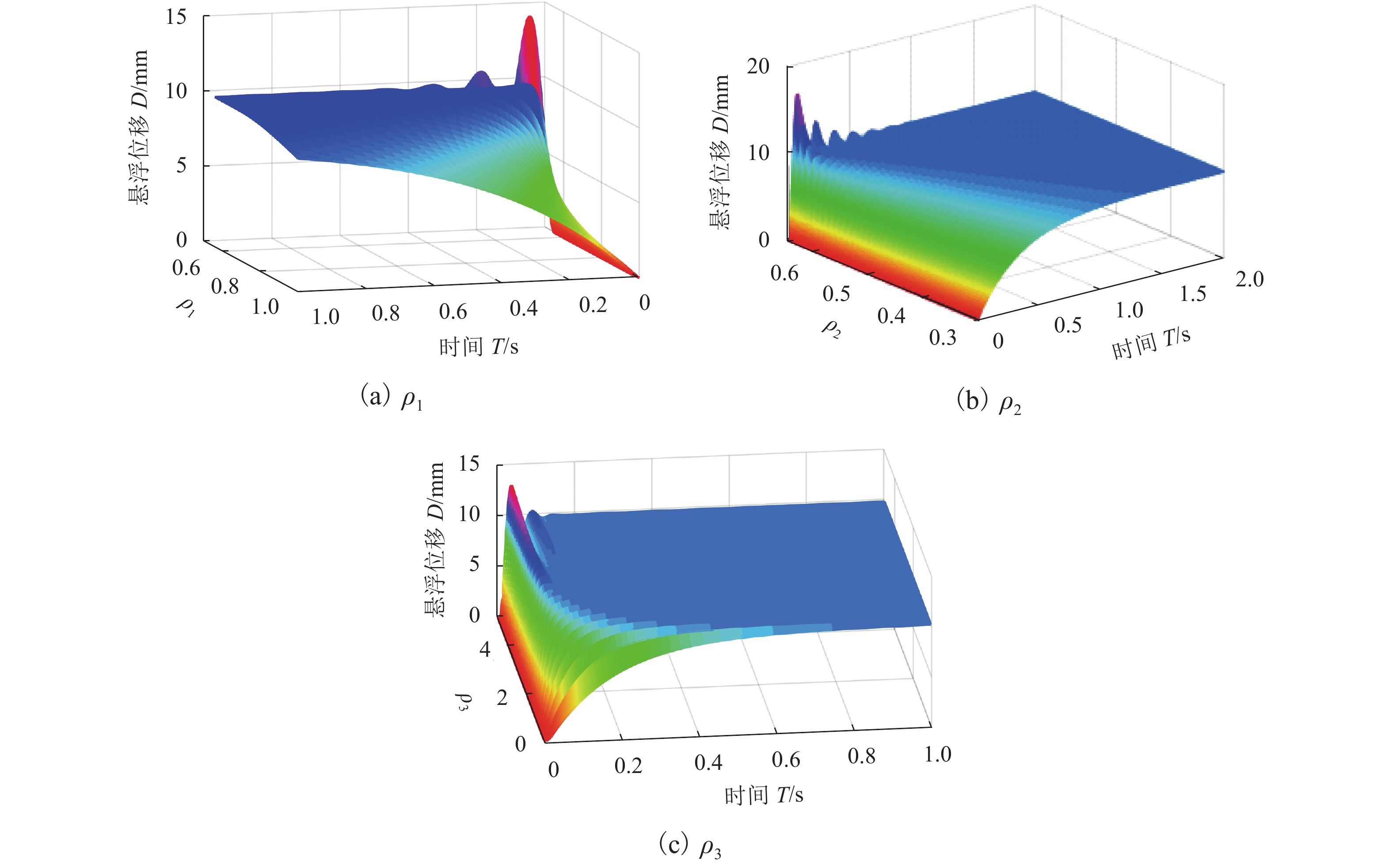
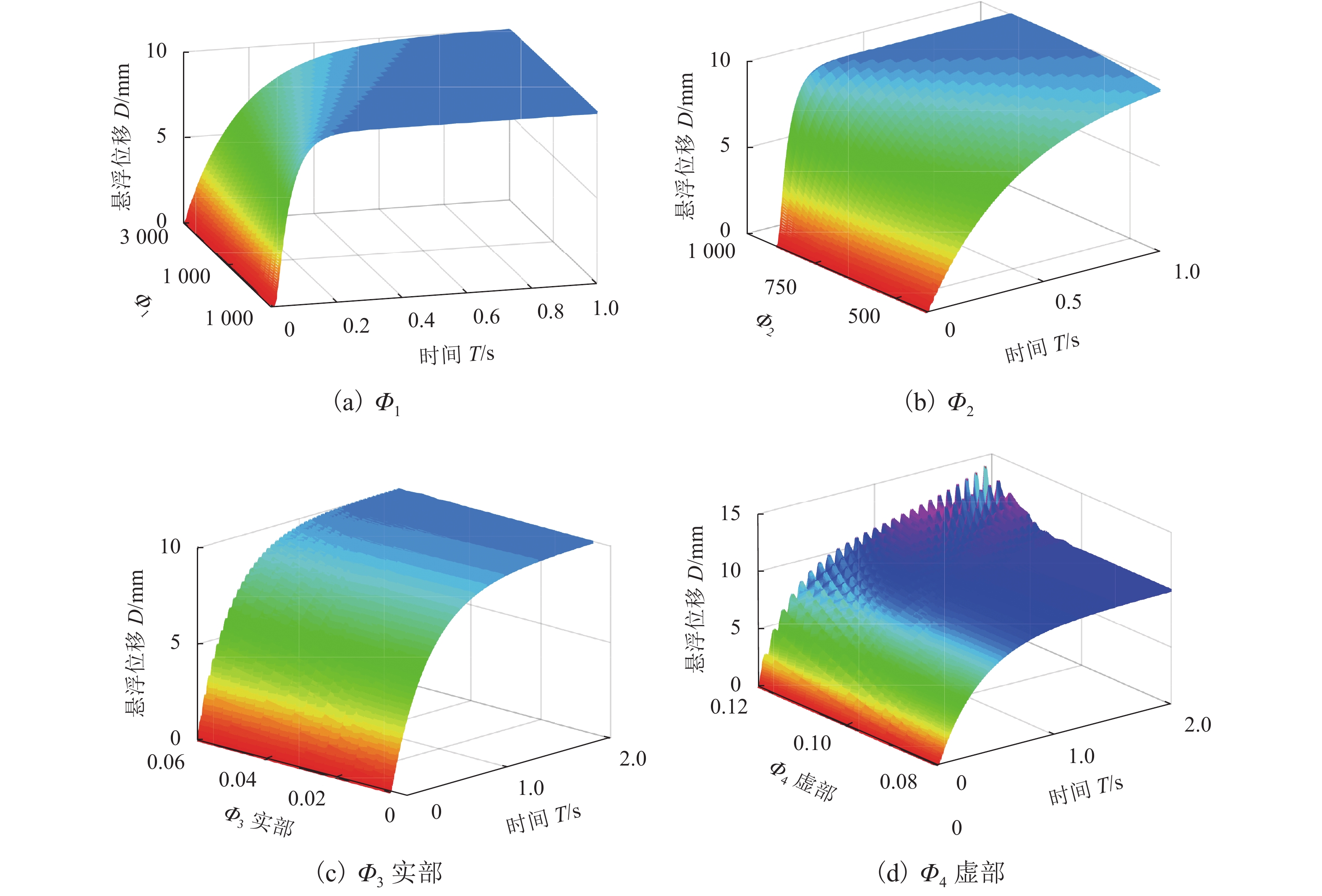
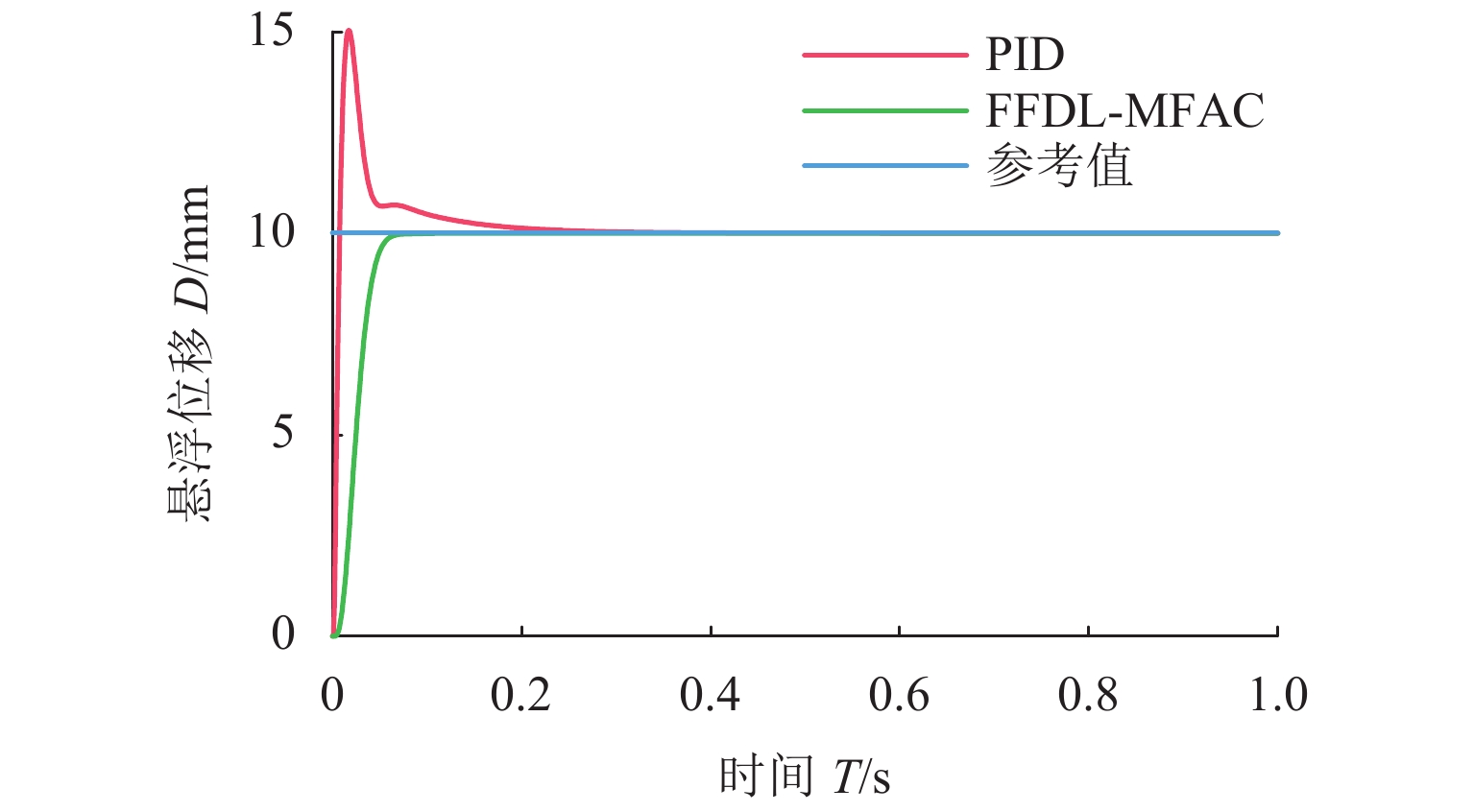
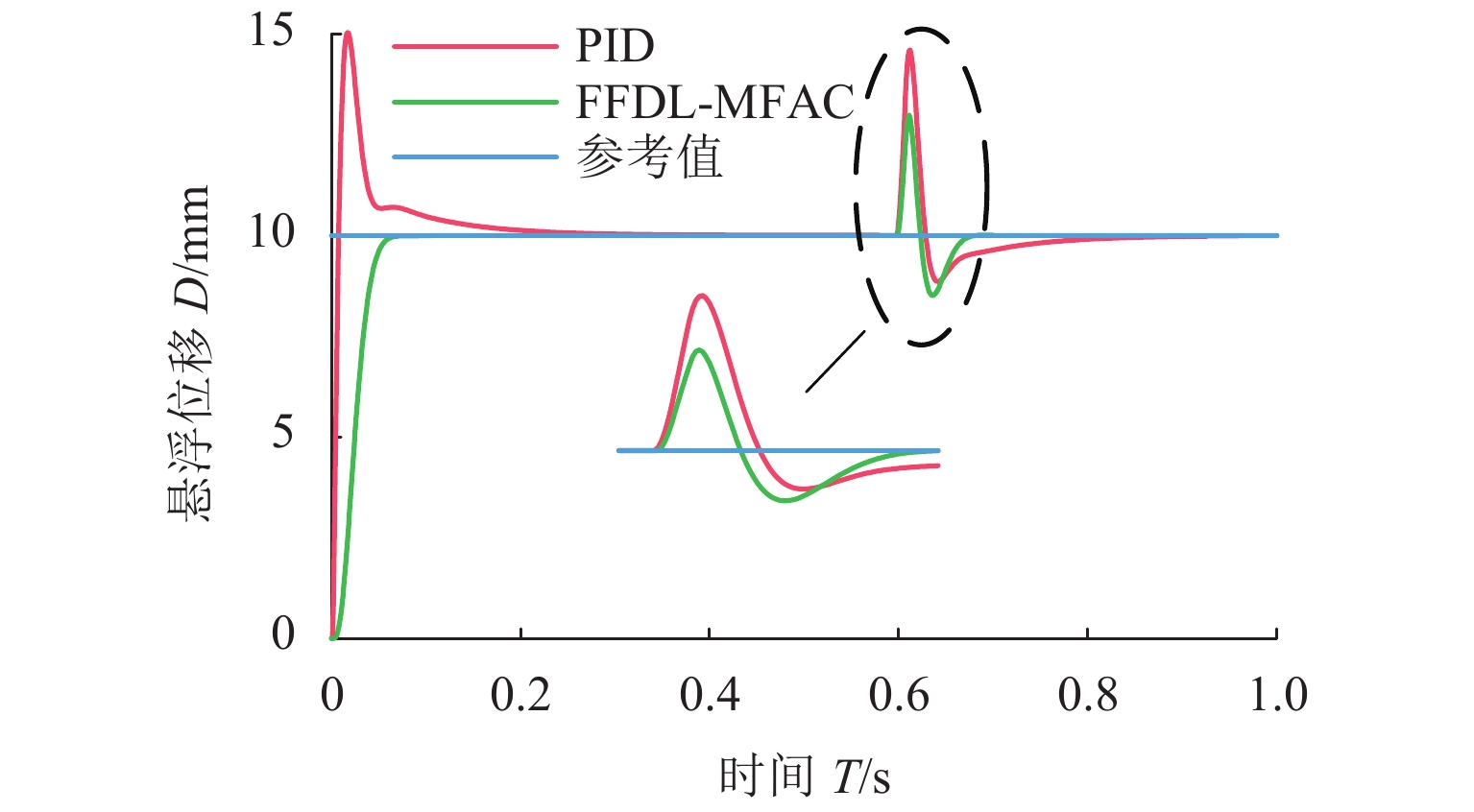
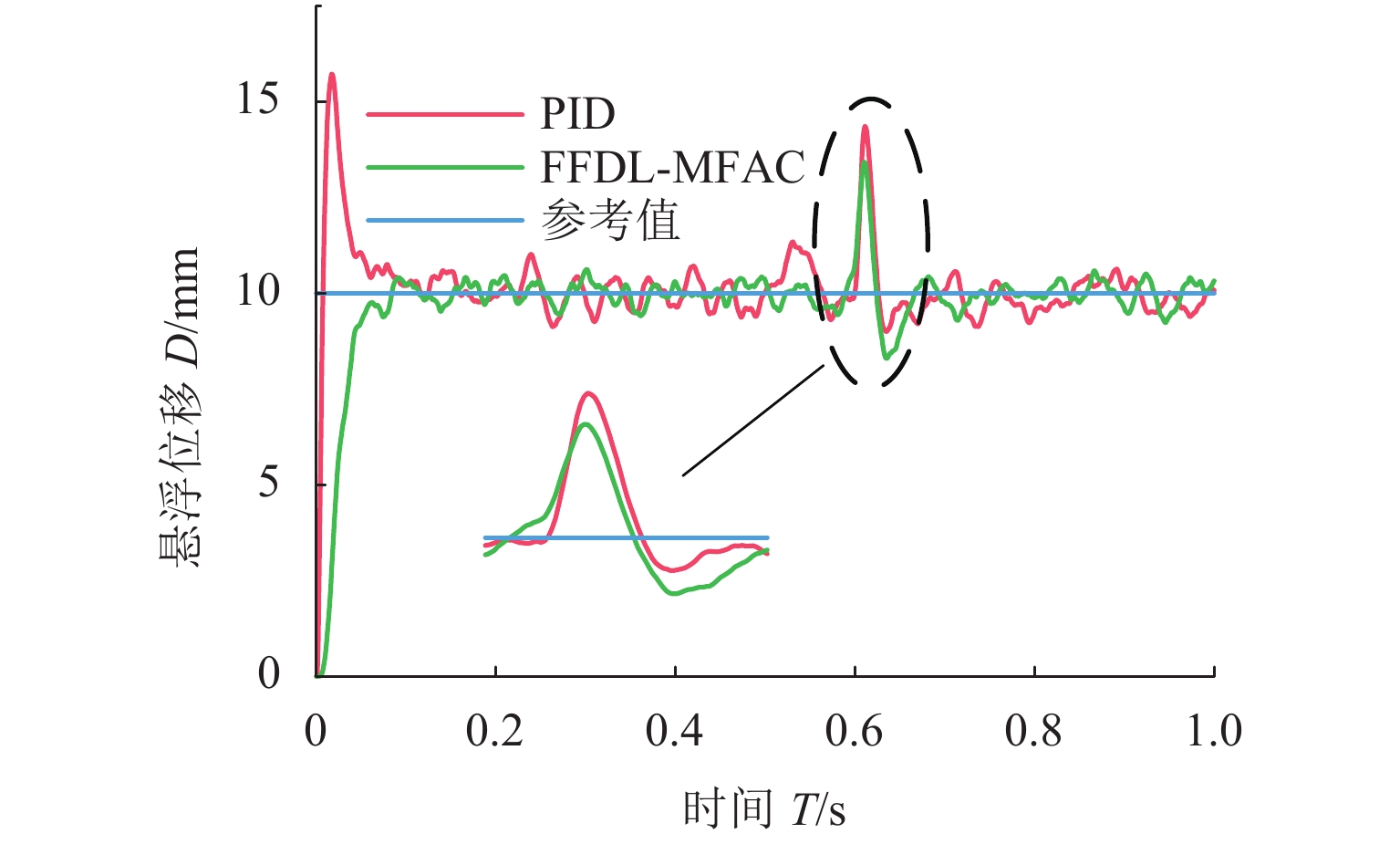
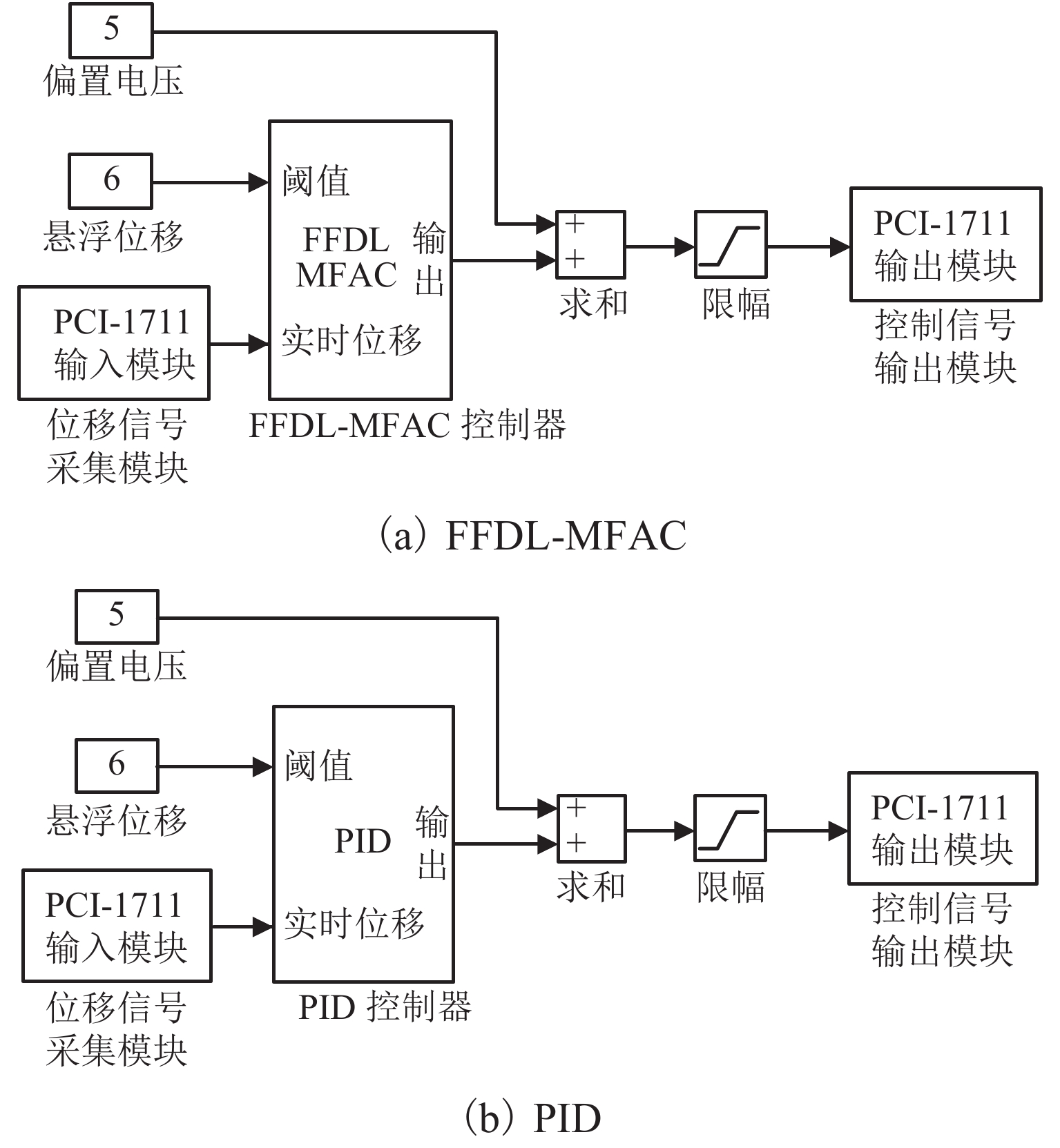
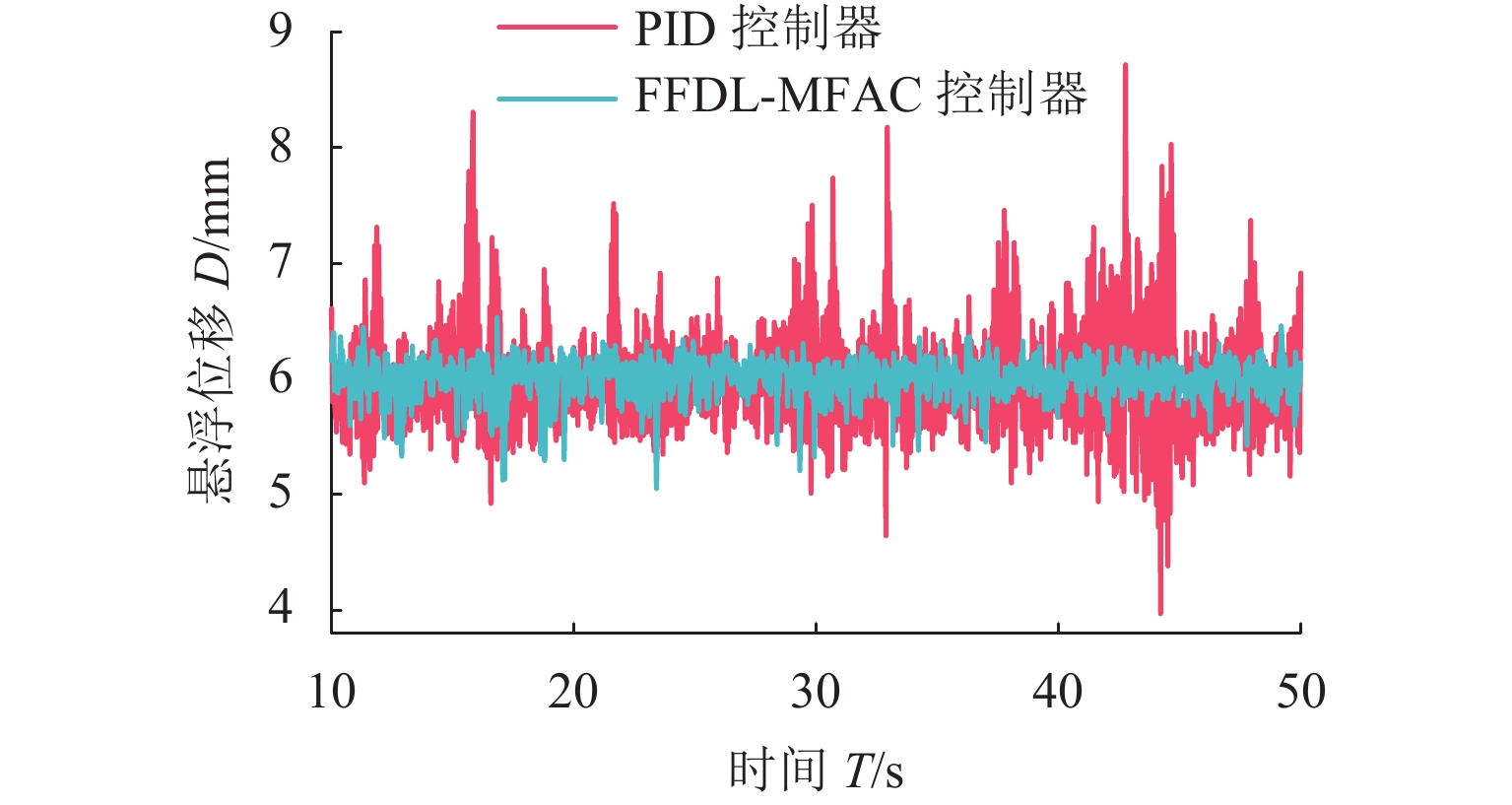
针对单自由度磁悬浮系统的非线性及难以建立精确数学模型的问题,将全格式无模型自适应控制(FFDL-MFAC)方法应用于单自由度磁悬浮系统,首先,采用无模型自适应控制算法、伪梯度估计算法、伪梯度重置算法和单自由度磁悬浮系统的动态化数据模型,设计单自由度磁悬浮系统的控制器;然后,仿真分析MFAC控制参数对单自由度磁悬浮系统控制效果的影响及对阶跃响应信号、干扰信号和噪声信号的响应特性;最后,在磁悬浮球实验装置上进行实验验证. 研究结果表明:全格式无模型自适应控制方法只需采集单自由度磁悬浮系统在工作状态下的I/O数据,无需建立单自由度磁悬浮系统精确数学模型,通过设定全格式无模型自适应控制器参数即可使控制器具备良好的自适应性和鲁棒性,实现高精度稳定悬浮控制;与PID相比,FFDL-MFAC将系统的超调量降低了0.005,稳定悬浮位移的误差均方根减小了0.2607.
Abstract:Aiming at the problem of nonlinear and difficult to establish accurate mathematical model of a single-degree-of-freedom magnetically levitated system, the model-free adaptive control method based on full-format dynamic linearization (FFDL-MFAC) was applied to a single-degree-of-freedom magnetically levitated system. Firstly, model-free adaptive control algorithm, pseudo gradient estimation algorithm, pseudo gradient reset algorithm and dynamic data model of single degree of freedom magnetic levitation system were used to design the controller of single degree of freedom magnetic levitation system. Then the influence of MFAC control parameters on the control effect of the single-degree-of-freedom magnetically levitated system and the response characteristics of step response signal, interference signal and noise signal are analyzed by simulation, and the experimental verification was carried out on the magnetic levitation ball experimental device. Finally, the experimental verification was carried out on the magnetic levitation ball experimental device. The results show that the FFDL-MFAC method only needs to collect the I/O data of the single-degree-of-freedom magnetically levitated system under the working state, and does not need to establish an accurate mathematical model of the single-degree-of-freedom magnetically levitated system. The high precision and stable suspension control can be realized by setting the parameters of the model free adaptive controller, and the controller has good adaptability and robustness. Compared with PID, FFDL-MFAC reduces the overshoot of the system by 0.005, and the root mean square error of stable suspension displacement is reduced by 0.2607.
-
Key words:
- magnetic levitation /
- adaptive algorithms /
- model-free adaptive control /
- pseudo-gradient
-
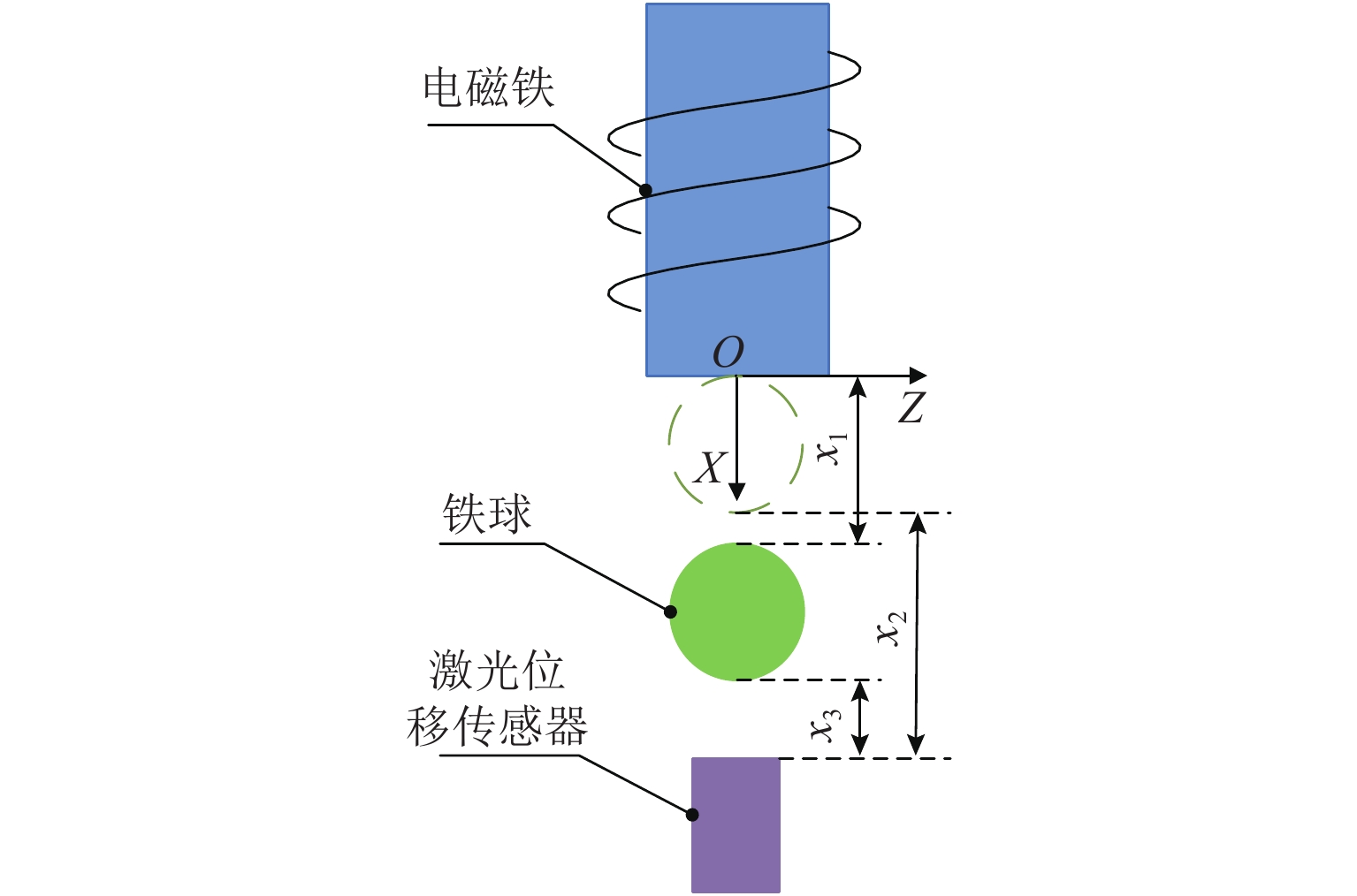
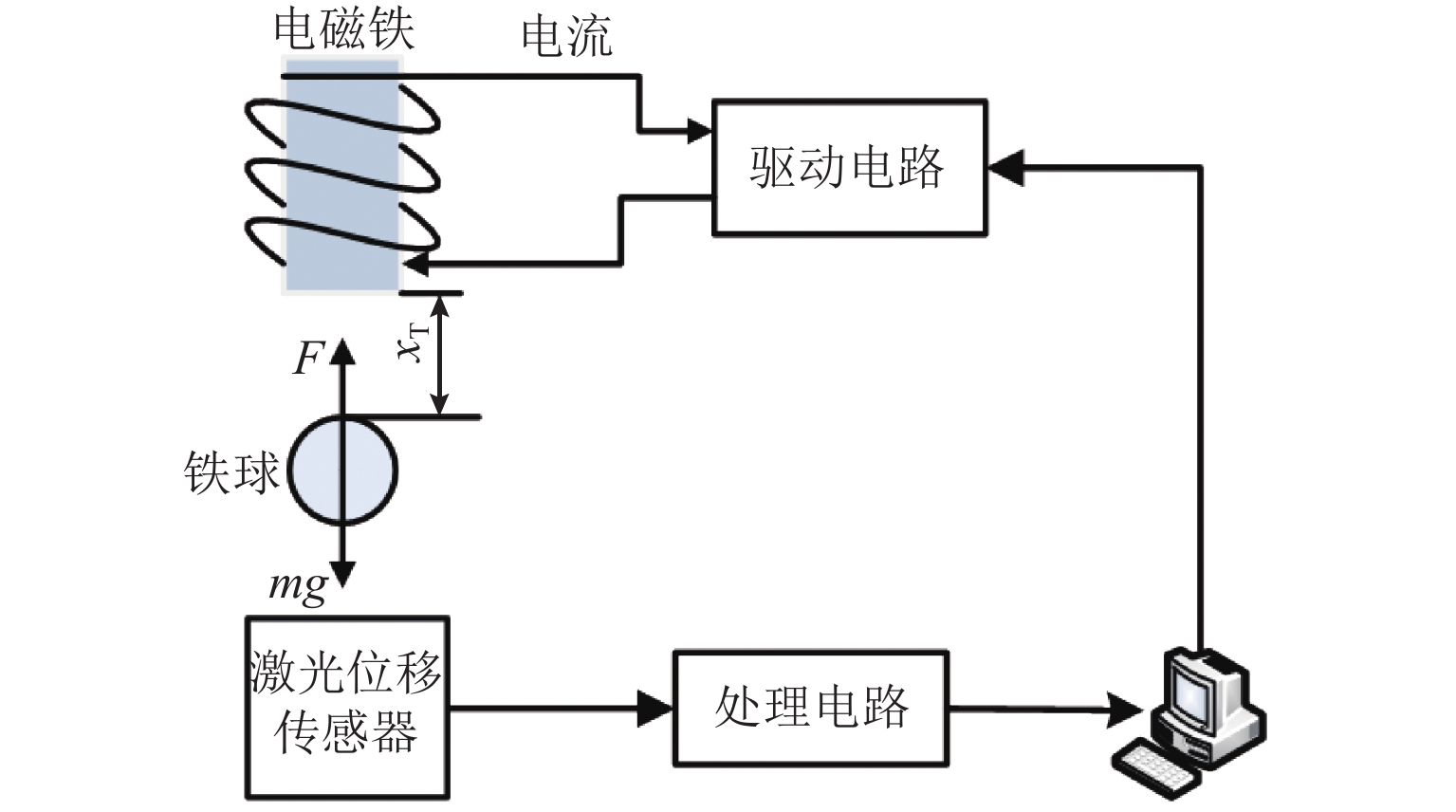
表 1 单自由度磁悬浮系统的物理参数
Table 1. Physical parameters of a single-degree-of-freedom magnetically levitated system
符号 参数 值 m 小球质量/g 94 Ka 放大系数 6.508 A 系数 0.02012 B 系数/(A·m−1) 39.433 表 2 阶跃信号响应下MFAC与PID控制器的性能对比
Table 2. Performances comparison between MFAC and PID controller under step signal response
控制器 超调量 稳定时间/s eRMS PID 0.005 0.205 1.2484 FFDL-MFAC 0 0.070 0.6350 表 3 干扰信号下MFAC与PID控制器的性能对比
Table 3. Performance comparison between MFAC and PID controller under interfering signal response
控制算法 eRMS PID 1.3341 FFDL-MFAC 0.7405 -
[1] 禹春敏,邓智泉,梅磊,等. 基于精确磁路的新型混合型轴向-径向磁悬浮轴承研究[J]. 电工技术学报,2021,36(6): 1219-1228.YU Chunmin, DENG Zhiquan, MEI Lei, et al. Research of new hybrid axial-radial magnetic bearing based on accurate magnetic circuit[J]. Electrical Technology, 2021, 36(6): 1219-1228. [2] 李云钢,常文森. 磁浮列车悬浮系统的串级控制[J]. 自动化学报,1999,25(2): 247-251.LI Yungang, CHANG Wensen. Cascade control of an emsmaglev vehicle slevitatio control system[J]. Acta Automatica Sinica, 1999, 25(2): 247-251. [3] 王东,姜豪,苏振中,等. 船用磁悬浮轴承关键技术与发展综述[J]. 中国电机工程学报,2020,40(20): 6704-6715.WANG Dong, JIANG Hao, SU Zhenzhong, et al. A review on the key technologies and development of marine magnetic bearings[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2020, 40(20): 6704-6715. [4] 张维煜,朱熀秋,袁野. 磁悬浮轴承应用发展及关键技术综述[J]. 电工技术学报,2015,30(12): 12-20.ZHANG Weiyu, ZHU Huangqiu, YUAN Ye. Study on keys and application of magnetic beartings[J]. Transaction of China Electrotechnical Society, 2015, 30(12): 12-20. [5] GERHARD S, MASLEN E H. Magnetic bearings-theory, design, and application to rotating machinery[M]. Berlin: Springer-Verlag, 2009: 1-17. [6] CHEN L L, ZHU C S, ZHONG Z X, et al. Internal model control for the AMB high-speed flywheel rotor system based on modal separation and inverse system method[J]. IET Electric Power Applications, 2019, 13(3): 349-358. doi: 10.1049/iet-epa.2018.5646 [7] CHEN L L, ZHU C S, ZHONG Z X, et al. Radial position control for magnetically suspended high-speed flywheel energy storage system with inverse system method and extended 2-DOF PID controller[J]. IET Electric Power Applications, 2020, 14(1): 71-81. doi: 10.1049/iet-epa.2019.0512 [8] CHEN S Y, SONG M H. Energy-saving dynamic bias current control of active magnetic bearing positioning system using adaptive differential evolution[J]. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems, 2019, 49(5): 942-953. doi: 10.1109/TSMC.2017.2691304 [9] WEI C S, DIRK S. Optimization strategy for PID-controller design of AMB rotor systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Control Systems Technology, 2016, 24(3): 788-803. doi: 10.1109/TCST.2015.2476780 [10] 吕治国,龙志强. 磁悬浮球系统的非线性自适应控制方法[J]. 控制工程,2020,27(1): 127-133.LYU Zhiguo, LONG Zhiqian. Method on nonlinear adaptive controller for maglev levitation ball system[J]. Control Engineering of China, 2020, 27(1): 127-133. [11] 朱坚民,沈正强,李孝茹. 基于神经网络反馈补偿控制的磁悬浮球位置控制[J]. 仪器仪表学报,2014,35(5): 976-986.ZHU Jianmin, SHEN Zhengqiang, LI Xiaoru. Magnetic levitation ball position control based on neural network feedback compensation control[J]. Chinese Journal of Scientific Instrument, 2014, 35(5): 976-986. [12] 张井岗,方线伟,赵志诚. 磁悬浮球系统的分数阶滑模控制[J]. 南京理工大学学报,2014,38(1): 72-77.ZHANG Jinggang, FANG Xianwei, ZHAO Zhicheng. Fractional order sliding mode control of magnetic levitation ball system[J]. Journal of Nanjing University of Science and Technology, 2014, 38(1): 72-77. [13] 宋荣荣,马卫华. 模糊PID控制在单自由度磁悬浮系统中的应用[J]. 重庆理工大学学报(自然科学),2014,28(5): 1-6.SONG Rongrong, MA Weihua. Application of fuzzy PID controller in the a single-degree-of-freedom magnetically levitated system[J]. Journal of Chongqing University of Technology (Natural Science), 2014, 28(5): 1-6. [14] 夏长峰,蔡远文,任元. 磁悬浮控制敏感陀螺转子偏转通道稳定控制方法[J]. 控制理论与应用,2020,37(7): 1535-1543.XIA Changfeng, CAI Yuanwen, REN Yuan. Stable control method for rotor tilt channel in magnetically suspended control and sensing gyro[J]. Control Theory & Applications, 2020, 37(7): 1535-1543. [15] HUO S W, ZHOU Y, LEI J J, et al. Iterative feedback control-based salient object segmentation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Multimedia, 2018, 20(6): 1350-1364. doi: 10.1109/TMM.2018.2831998 [16] ZHENG Y B, LIU X N, ZHAO J J, et al. A novel iterative learning control method and control system design for active magnetic bearing rotor imbalance of primary helium circulator in high-temperature gas-cooled reactor[J]. Measurement and Control, 2020, 53(3): 2029-2039. [17] CHILUKA S K, AMBATI S R, Seepana M M, et al. A novel robust virtual reference feedback tuning approach for minimum and non-minimum phase systems[J]. ISA Transactions, 2021, 115(5): 163-169. [18] 金尚泰,赵汝莉,侯忠生,等. 基于虚拟参考反馈整定的改进无模型自适应控制[J]. 控制与决策,2015,30(12): 66-67.JIN Shangtai, ZHAO Ruli, HOU Zhongsheng, et al. Improved model free adaptive control approach with virtual reference feedback tuning[J]. Control and Decision, 2015, 30(12): 66-67. [19] SCHAAL S, ATKESON C G. Robot juggling: implementation of memory-based learning[J]. IEEE Control Systems, 1994, 14(1): 57-71. doi: 10.1109/37.257895 [20] AHN H, CHEN Y Q, KEVIN L. Iterative learning control: brief survey and categorization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, Part C (Applications and Reviews), 2007, 37(6): 1099-1121. doi: 10.1109/TSMCC.2007.905759 [21] HOU Z S, JIN S T. A novel data-driven control approach for a class of discrete-time nonlinear systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Control Systems Technology, 2011, 19(6): 1549-1558. doi: 10.1109/TCST.2010.2093136 [22] ZHANG X F, MA H B, ZHANG X H, et al. Compact model-free adaptive control algorithm for discrete-time nonlinear systems[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7(2): 141062-141071. [23] WANG Z, CHEN T W. Data and event-driven control of a class of networked non-linear control systems[J]. IET Control Theory and Applications, 2015, 9(7): 1034-1041. doi: 10.1049/iet-cta.2014.0711 [24] HOU Z S, JIN S T. Data-Driven model-free adaptive control for a class of MIMO nonlinear discrete-time systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks, 2011, 22(12): 2173-2183. doi: 10.1109/TNN.2011.2176141 [25] HOU Z S, XIONG S S. On model-free adaptive control and its stability analysis[J]. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2019, 64(11): 4555-4569. doi: 10.1109/TAC.2019.2894586 [26] JIANG Q Q, LIAO Y L, LI Y, et al. Heading control of unmanned surface vehicle with variable output constraint model-free adaptive control algorithm[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7(1): 131008-131018. [27] CHEN C, LU J G. Design of self-tuning SISO partial-form model-free adaptive controller for vapor-compression refrigeration system[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7(1): 125771-125782. [28] LU C, ZHAO Y, MEN K, et al. Wide-area power system stabiliser based on model-free adaptive control[J]. IET Control Theory & Applications, 2015, 9(13): 1996-2007. [29] LIU X, HOU Z S, JIN S T . Model-free adaptive control for magnetic levitation ball system[C]// Chinese Control Conference (CCC). [S.l.]: IEEE, 2012: 401-408. [30] 田涛涛,侯忠生,刘世达,等. 基于无模型自适应控制的无人驾驶汽车横向控制方法[J]. 自动化学报,2017(11): 66-75.TIAN Taotao, HOU Zhongsheng, LIU Shida, et al. Model-free adaptive control based lateral control of self-driving car[J]. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2017(11): 66-75. [31] 杨智,陈志堂,范正平,等. 基于改进粒子群优化算法的PID控制器整定[J]. 控制理论与应用,2010,27(10): 1346-1352.YANG Zhi, CHEN Zhitang, FAN Zhenping, et al. Tuning of PID controller based on improved particle-swarm-optimization[J]. Control Theory and Applications, 2010, 27(10): 1346-1352. -




 下载:
下载: