Investigation on In-Plane Stability of Double-Limb Cold-Formed C-Shaped Steel Rigid Frame of Yurt
-
摘要:
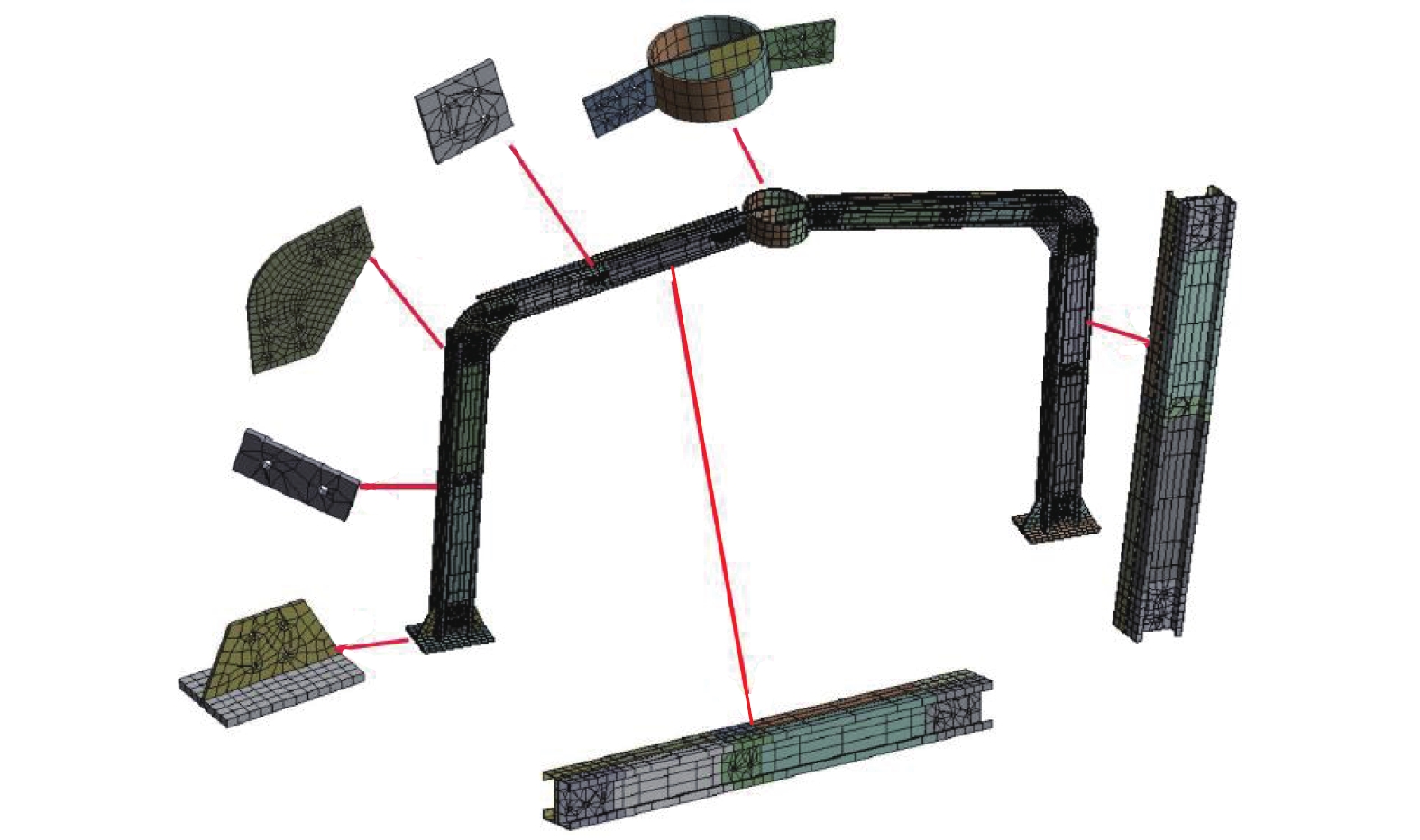
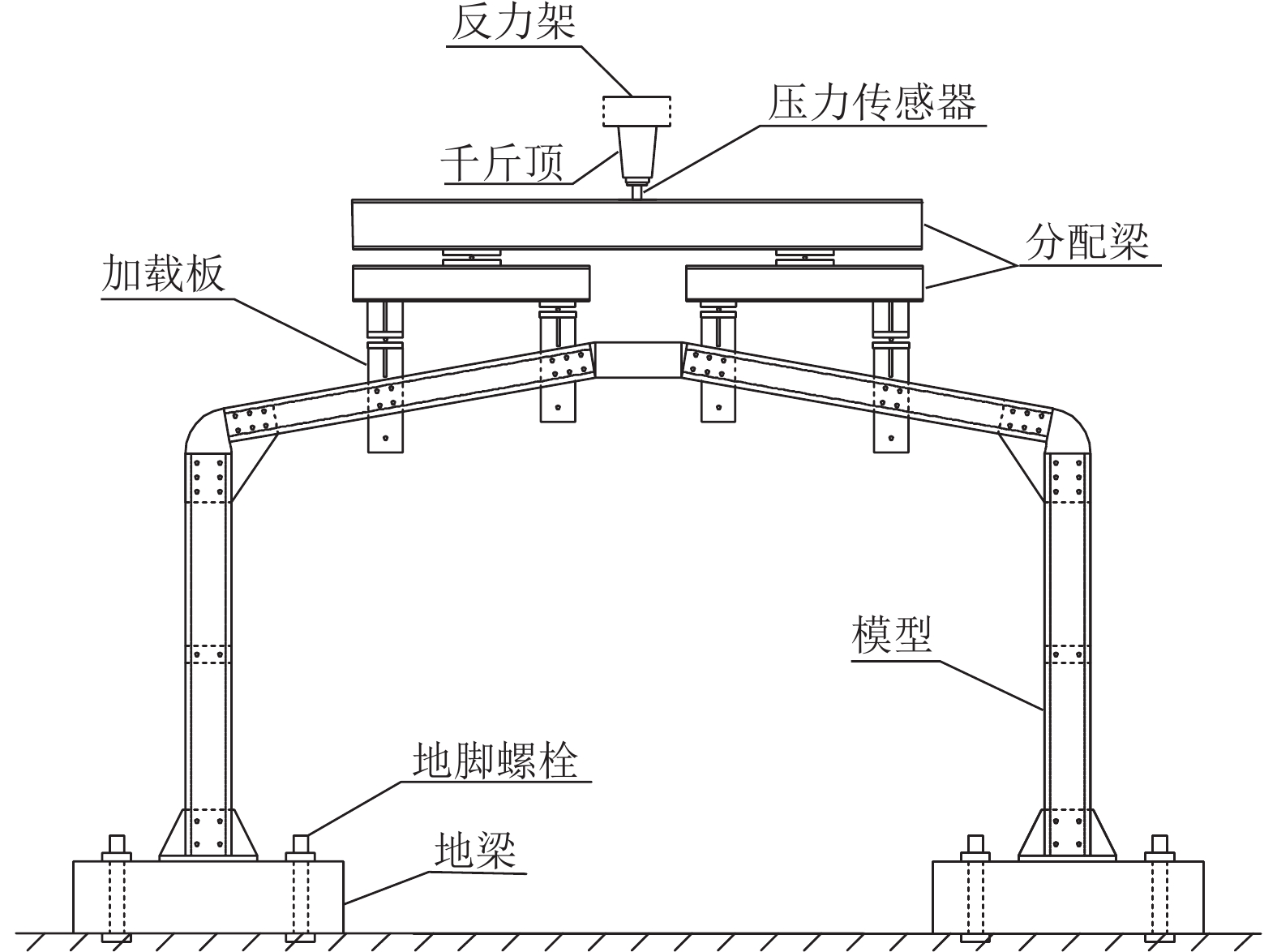
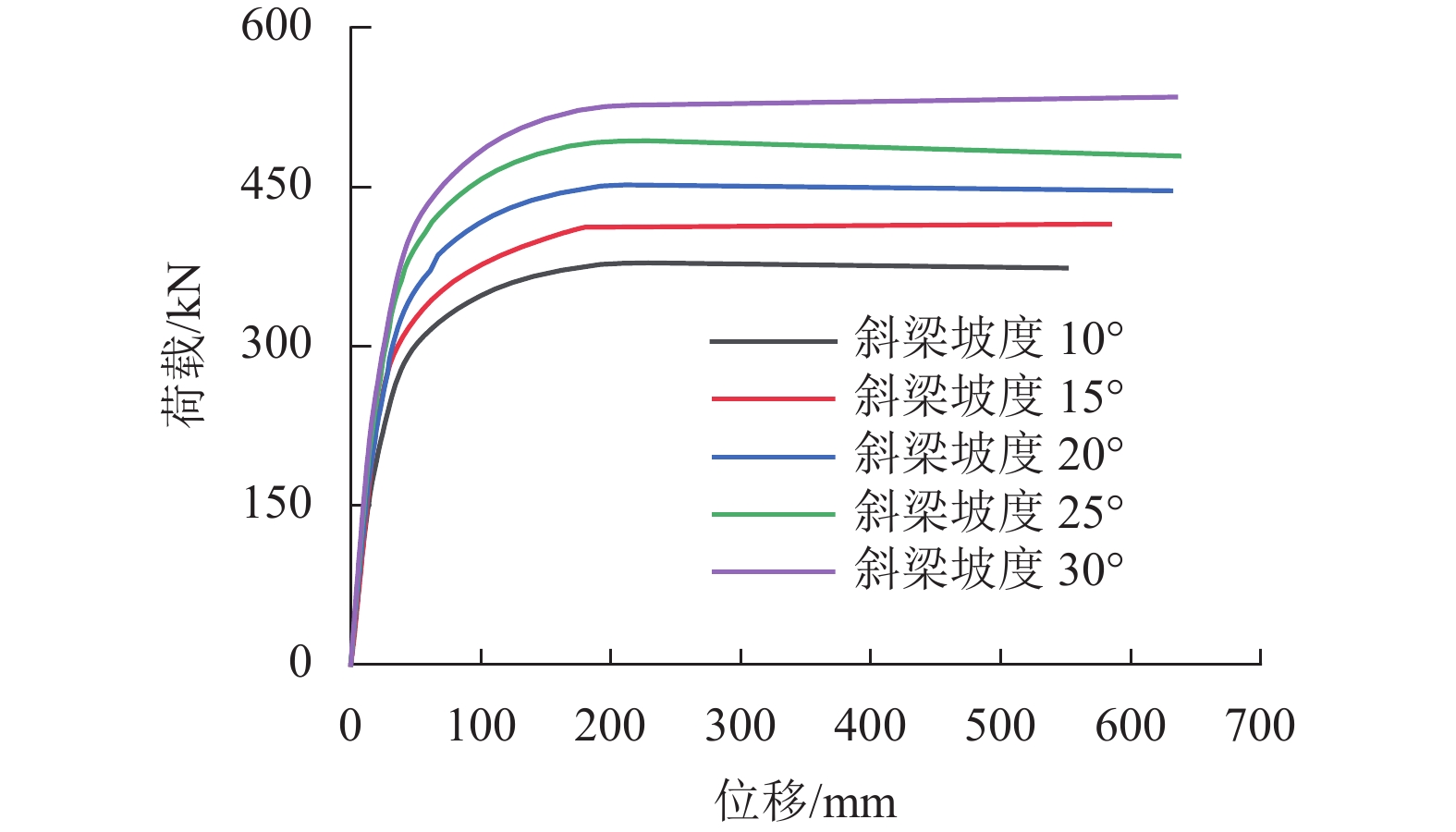
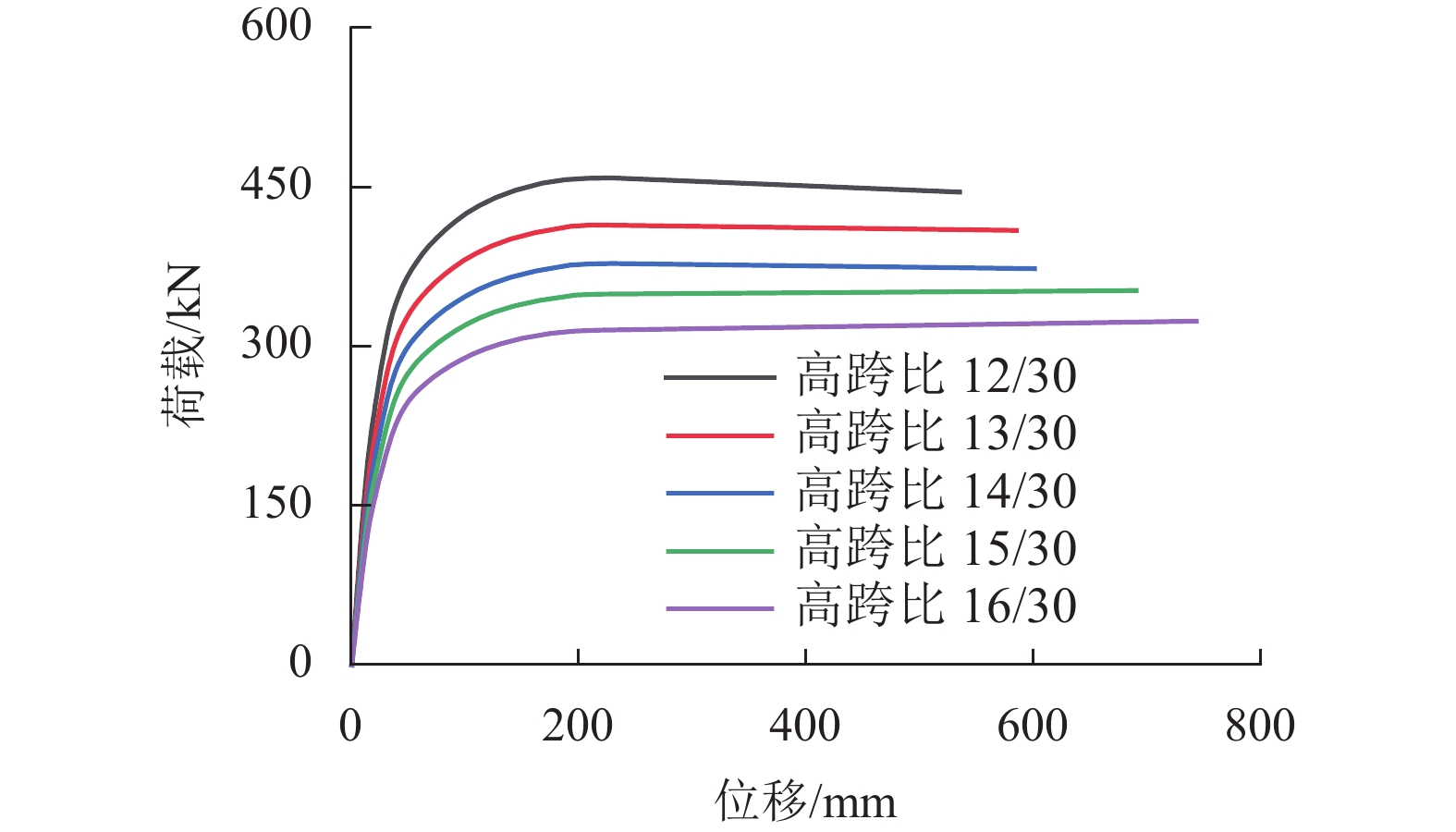
为了解决新型双肢冷弯C型钢蒙古包结构在冰雪等竖向荷载工况下可能出现的失稳问题,对带陶脑的双肢冷弯C型钢门式刚架平面内的稳定性展开研究,通过改变斜梁坡度、刚架高跨比、陶脑直径3种参数下的刚架试验与数值模拟,对该类门式刚架的破坏形态和承载力等方面进行了分析和探讨. 研究结果表明:斜梁坡度和陶脑直径的增加会使刚架承载力增加,刚架高跨比的增加会使刚架承载力降低;综合考虑斜梁坡度对刚架稳定承载力和柱顶侧移的影响,建议刚架的斜梁坡度设计为20° 以内,此时《门式刚架轻型房屋钢结构技术规范》对柱计算长度系数的计算偏于安全,满足工程设计要求.
Abstract:To solve the instability problem of newly designed double-limb cold-formed C-shaped steel yurts under vertical loads such as ice and snow, the stability performance of a double-limb cold-formed C-shaped steel portal frame with an in-plane toono was investigated. The failure modes and bearing capacity of this type of portal frame were analyzed through testing and numerical simulations using three parameters: the slope of the inclined beam, the height-to-span ratio, and the toono diameter. The results show that increases in the inclined beam slope and the toono diameter can increase the load bearing capacity of the rigid frame, and an increase in the high span ratio of the rigid frame then reduces the rigid frame’s load bearing capacity. Following consideration of the influence of the inclined beam slope and the lateral displacement of the column top, the work in this paper indicates that the inclined beam slope should be designed to be within 20°, where the column effective length coefficient is calculated to be safe according to
The Technical Code for Steel Structure of Light-Weight Building with Gabled Frames ; this also meets the engineering design requirements. -
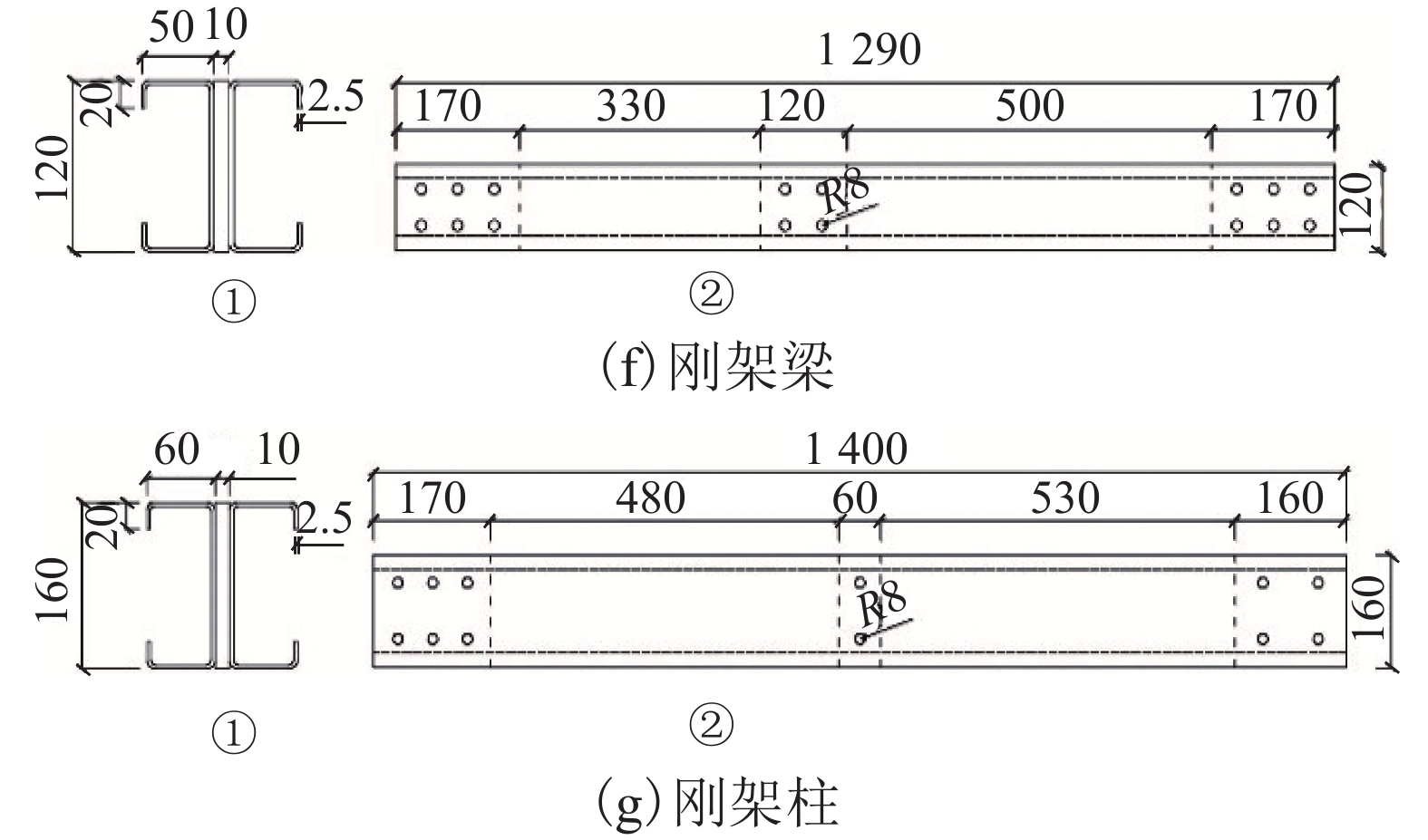
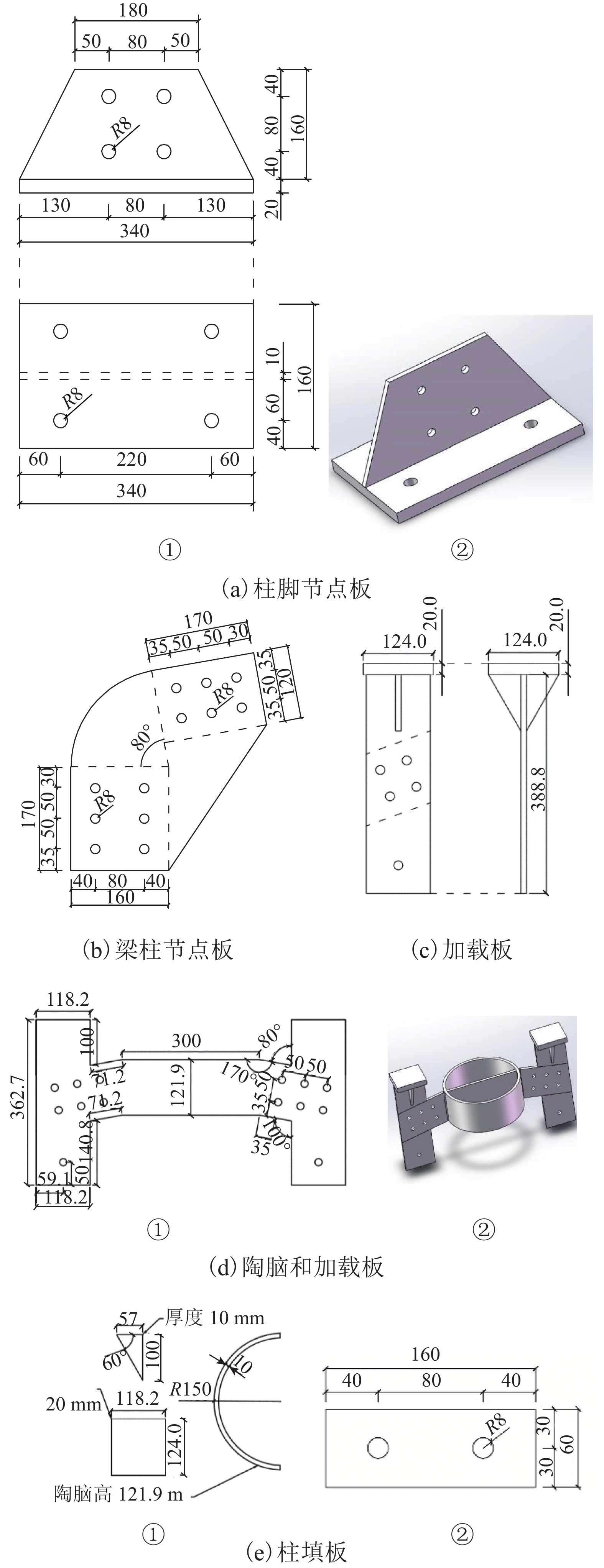
表 1 刚架试件设计参数
Table 1. Design parameters of rigid frames
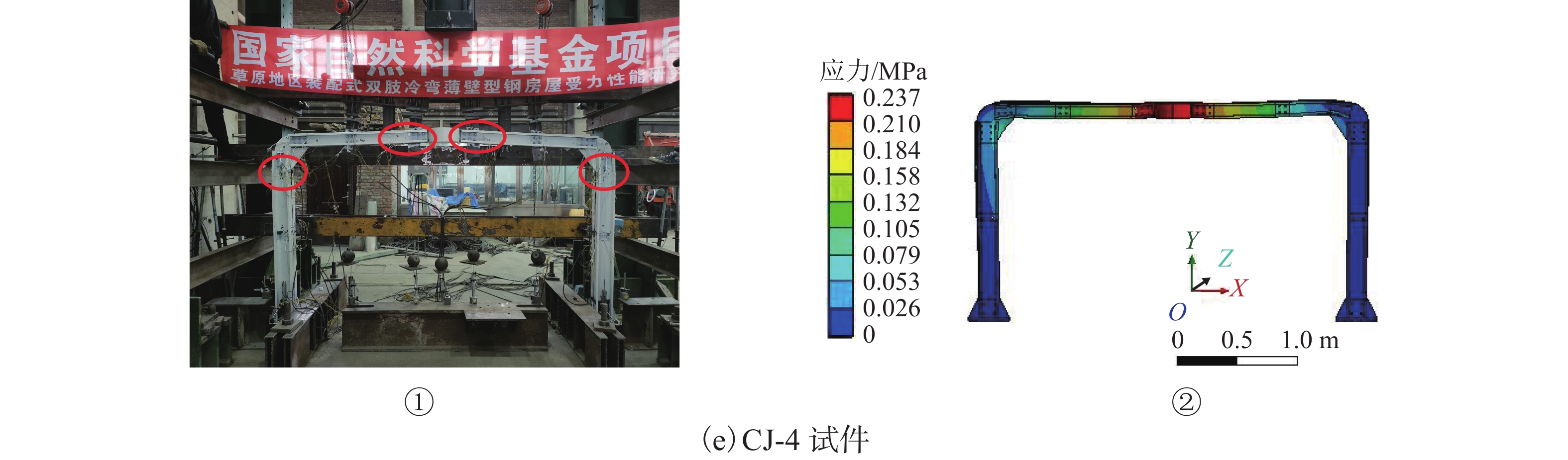
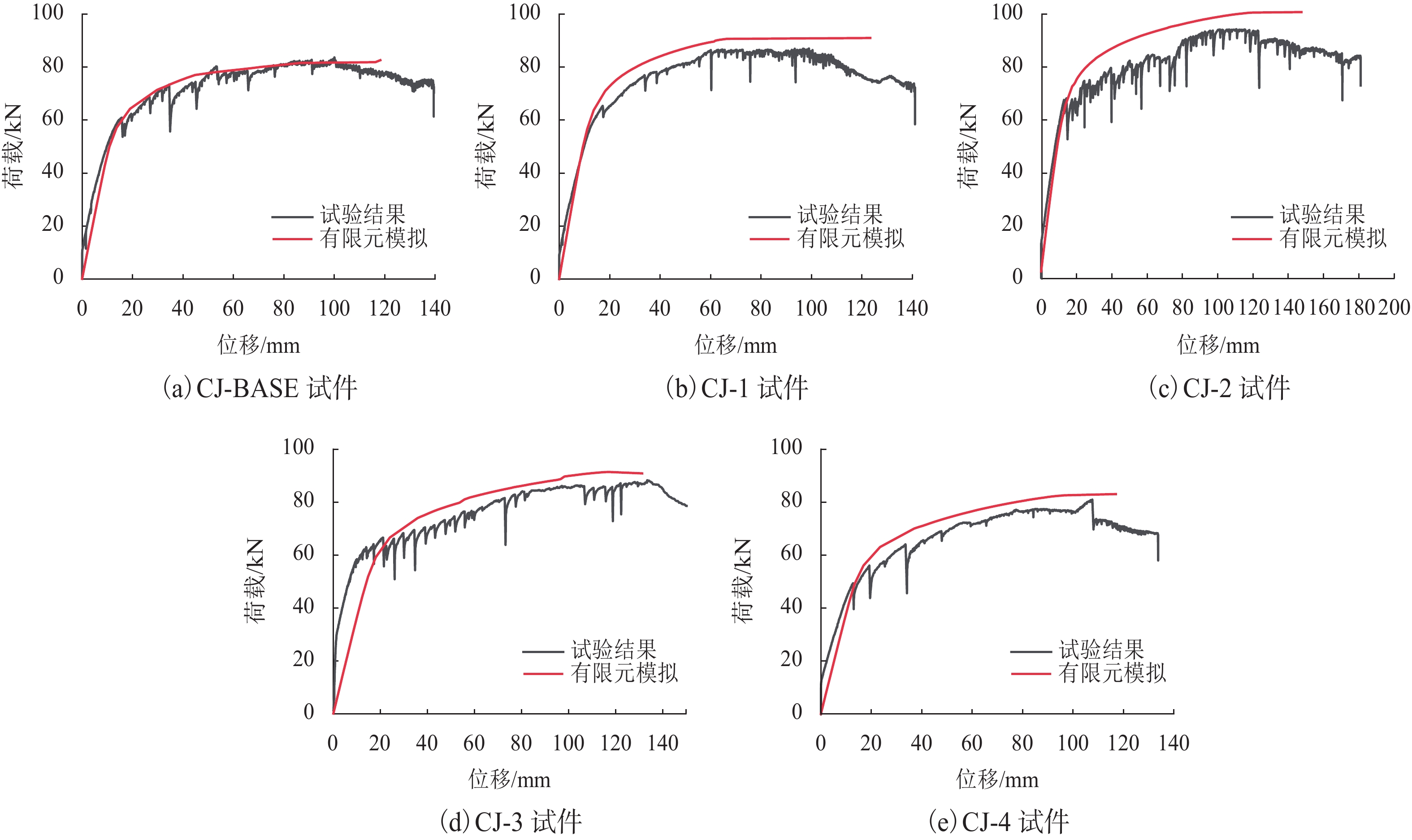
试件编号 斜梁坡度/(°) 檐口高度/mm 刚架高跨比 CJ-BASE 10 1400 7/15 CJ-1 15 1400 7/15 CJ-2 20 1400 7/15 CJ-3 10 1200 6/15 CJ-4 10 1600 8/15 表 2 钢材的材料性能参数
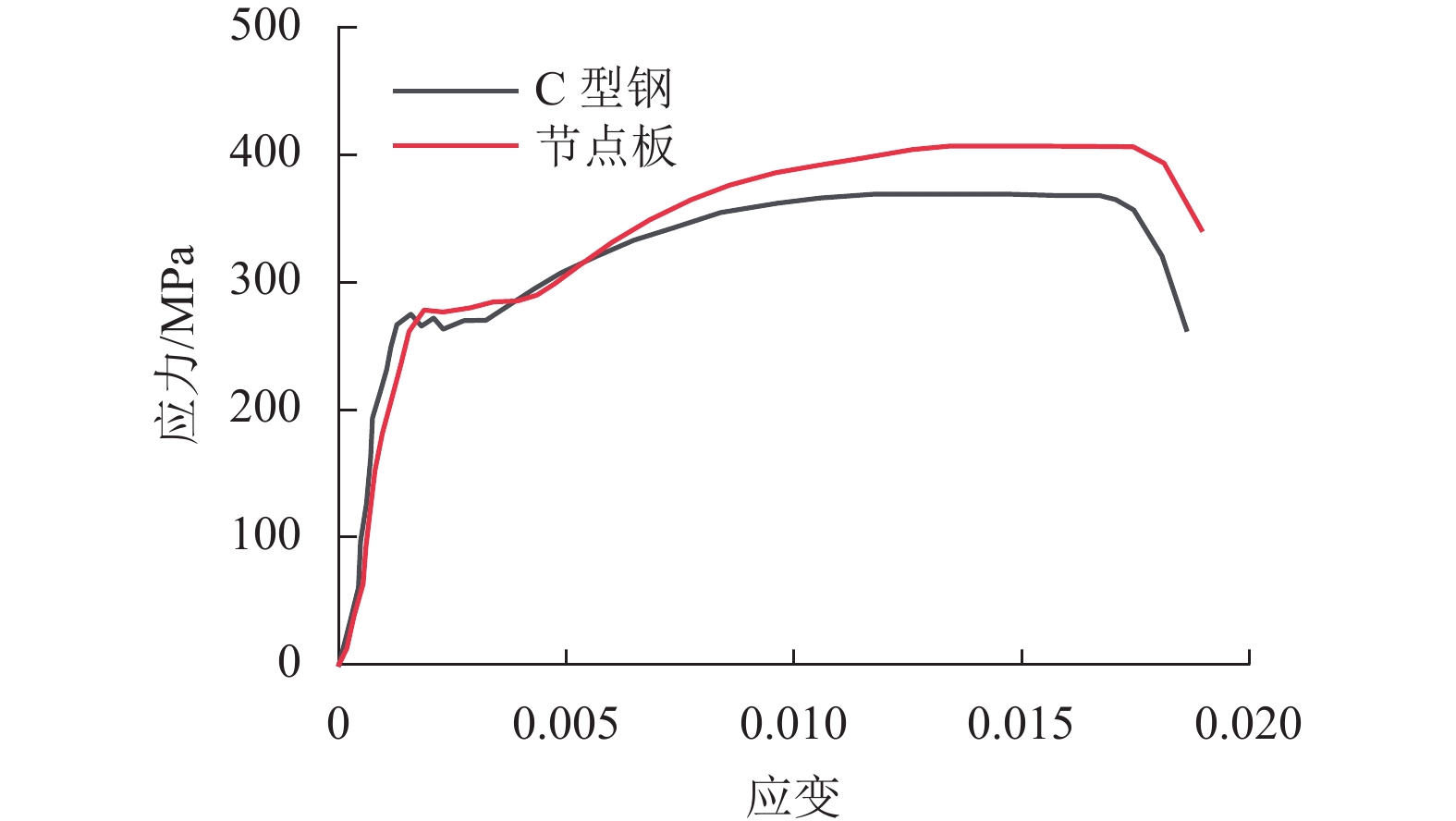
Table 2. Material behavior of steel
材料 屈服
强度/MPa极限
强度/MPa弹性
模量/GPa泊松比 C 型钢 263.20 369.12 2.01 0.30 节点板 276.50 406.71 1.97 0.31 高强螺栓 645.00 860.00 2.06 0.30 表 3 刚架试件柱顶最大侧移值
Table 3. Maximum lateral displacement of column top of rigid frames
试件编号 斜梁
坡度
/(°)柱高
/mm柱顶最大侧移值
/mm柱顶侧移规范值
/mm稳定
承载力
/kNCJ-BASE 10 1400 2.49 7.78 82.007 CJ-1 15 1400 7.45 7.78 86.269 CJ-2 20 1400 16.99 7.78 91.180 CJ-3 10 1200 1.99 6.67 87.328 CJ-4 10 1600 2.23 8.89 79.900 表 4 不同斜梁坡度下模型有限元分析结果
Table 4. Finite element analysis results of models with different inclined beam slopes
模型编号 斜梁
坡度/(°)刚架
高跨比陶脑
直径/mm稳定承
载力/kNPF-BASE 10 14/30 1200 302.501 PF-HSR-15 15 14/30 1200 331.757 PF-HSR-20 20 14/30 1200 361.367 PF-HSR-25 25 14/30 1200 394.585 PF-HSR-30 30 14/30 1200 427.534 表 5 不同高跨比下模型有限元分析结果
Table 5. Finite element analysis results of models with different height-span ratios
模型编号 斜梁
坡度/(°)刚架
高跨比陶脑
直径/mm稳定承
载力/kNPF-BASE 10 14/30 1200 302.501 PF-RS-12 10 12/30 1200 367.056 PF-RS-13 10 13/30 1200 331.529 PF-RS-15 10 15/30 1200 282.127 PF-RS-16 10 16/30 1200 259.111 表 6 不同陶脑直径下模型有限元分析结果
Table 6. Finite element analysis results of models with different toono diameters
模型编号 斜梁
坡度/(°)刚架
高跨比陶脑
直径/mm稳定承
载力/kNCJ-BASE 10 14/30 1200 302.501 PF-TN-14 10 14/30 1400 311.668 PF-TN-16 10 14/30 1600 323.075 PF-TN-18 10 14/30 1800 331.990 PF-TN-20 10 14/30 2000 338.939 表 7 柱计算长度系数模拟值与规范值对比
Table 7. Comparison between simulated values and standard values of column calculated length coefficient
模型编号 模拟值 规范值 差值/% PF-BASE 2.940 2.940 0 PF-HSR-15 2.789 2.957 6.67 PF-HSR-20 2.689 2.973 10.56 PF-HSR-25 2.596 2.995 15.37 PF-HSR-30 2.457 3.047 24.01 PF-RS-12 3.040 3.063 0.70 PF-RS-13 2.922 2.984 2.12 PF-RS-15 2.823 2.896 2.59 PF-RS-16 2.762 2.852 3.26 PF-TN-14 2.896 2.928 1.10 PF-TN-16 2.827 2.916 3.14 PF-TN-18 2.789 2.903 4.09 PF-TN-20 2.761 2.890 4.67 -
[1] DAVIES J M. Inplane stability in portal frame[J]. Journal of Engineering, 1990, 68(1): 1-17. [2] BAIGENT H, HANCOCK G J. The behavior of portal frames composed of cold-formed members[J]. Thin-Walled Structures, 1978: 209-222. [3] ZHANG X, RASMUSSEN K, ZHANG H. Experimental investigation of locally and distortionally buckled portal frames[J]. Journal of Constructional Steel Research, 2016, 122: 517-583. [4] RINCHEN R, RASMUSSEN K. Experiments on long-span cold-formed steel single C-section portal frames[J]. Journal of Structural Engineering, 2019, 146(1): 04019187.1-04019187.18. [5] RINCHEN R, RASMUSSEN K, ZHANG H. Design of cod-formed steel single C-section portal frames[J]. Journal of Constructional Steel Research, 2019, 162: 105722.1-10572.14. [6] 刘朝宏,李天. 轻型门式刚架的平面内稳定系数计算[J]. 郑州工业大学学报,2001,22(2): 73-76.LIU Chaohong, LI Tian. In-plane stability factors calculating of light-weight portal frame[J]. Journal of Zhengzhou University of Technology, 2001, 22(2): 73-76. [7] 李天,张哲,刘朝宏. 门式刚架轻钢结构平面内整体稳定分析中的几个问题[J]. 郑州大学学报(工学版),2003,24(1): 16-19. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6833.2003.01.004LI Tian, ZHANG Zhe, LIU Chaohong. Discussion on the calculation of in-plane stability of light-weight portal frame[J]. Journal of Zhengzhou University (Engineering Science), 2003, 24(1): 16-19. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6833.2003.01.004 [8] 卢林枫,董刘方,周绪红. 冷弯薄壁型钢门式刚架极限承载力影响因素[J]. 重庆建筑大学学报,2008,30(3): 27-31.LU Linfeng, DONG Liufang, ZHOU Xuhong. Factors affecting the ultimate bearing capacity of cold-formed steel portal frames[J]. Journal of Chongqin Jianzhu University, 2008, 30(3): 27-31. [9] 王万祯,郭金池,孙玉萍,等. 偏心支撑半刚接钢框架柱计算长度系数研究[J]. 建筑结构,2010,40(4): 16-18.WANG Wanzhen, GUO Jinchi, SUN Yuping, et al. Effective length factor of column in eccentrically braced steel frames with semi rigid connections[J]. Building Structure, 2010, 40(4): 16-18. [10] 陈明,黄骥辉,赵根田. 组合截面冷弯薄壁型钢结构研究进展[J]. 工程力学,2016,33(12): 1-11. doi: 10.6052/j.issn.1000-4750.2016.05.ST03CHEN Ming, HUANG Jihui, ZHAO Gentian. Research progress of compound section cold-formed thin-wall steel strutures[J]. Engineering Mechanics, 2016, 33(12): 1-11. doi: 10.6052/j.issn.1000-4750.2016.05.ST03 [11] 贾文腾. 装配式冷弯C型钢蒙古包设计与受力性能研究[D]. 包头: 内蒙古科技大学, 2019. [12] 中华人民共和国住房和城乡建设部. 门式刚架轻型房屋钢结构技术规范: GB 51022—2015 [S]. 北京: 中国建筑工业出版社, 2015. [13] 中华人民共和国住房和城乡建设部. 冷弯薄壁型钢结构技术规范: GB 50018—2016 [S]. 北京: 中国计划出版社, 2016. -




 下载:
下载: