Study on Driver’s Sight Line Under Vertical Vortex-Induced Vibration of Long Span Suspension Bridges
-
摘要:
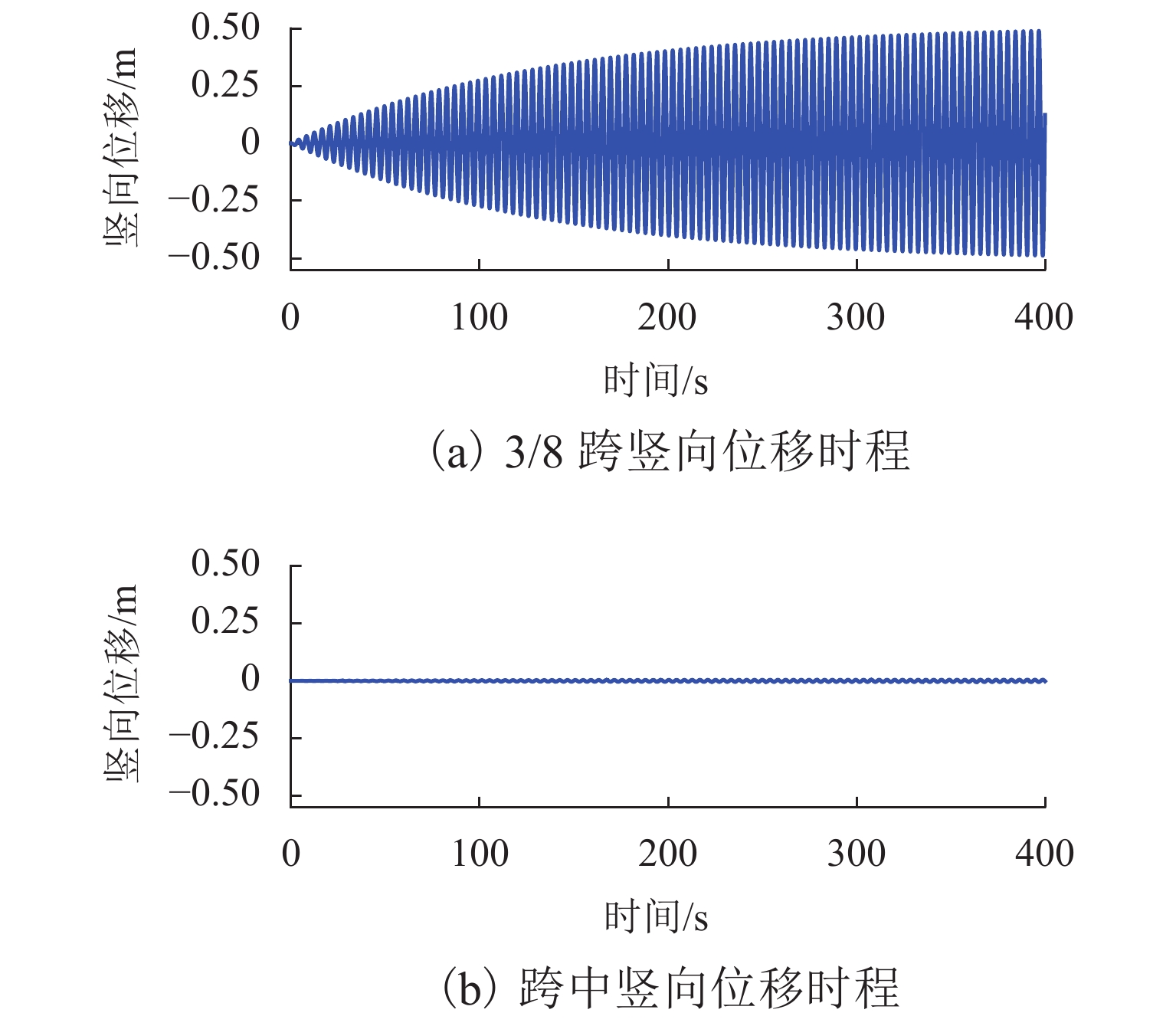
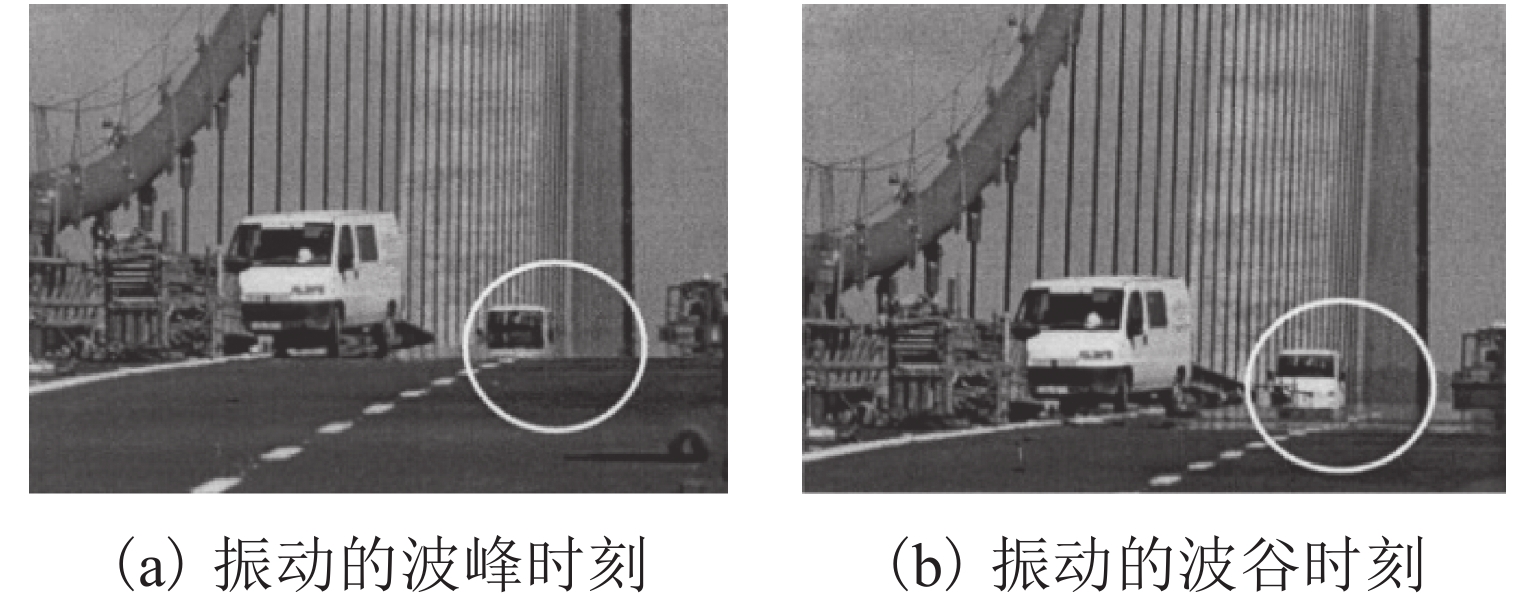
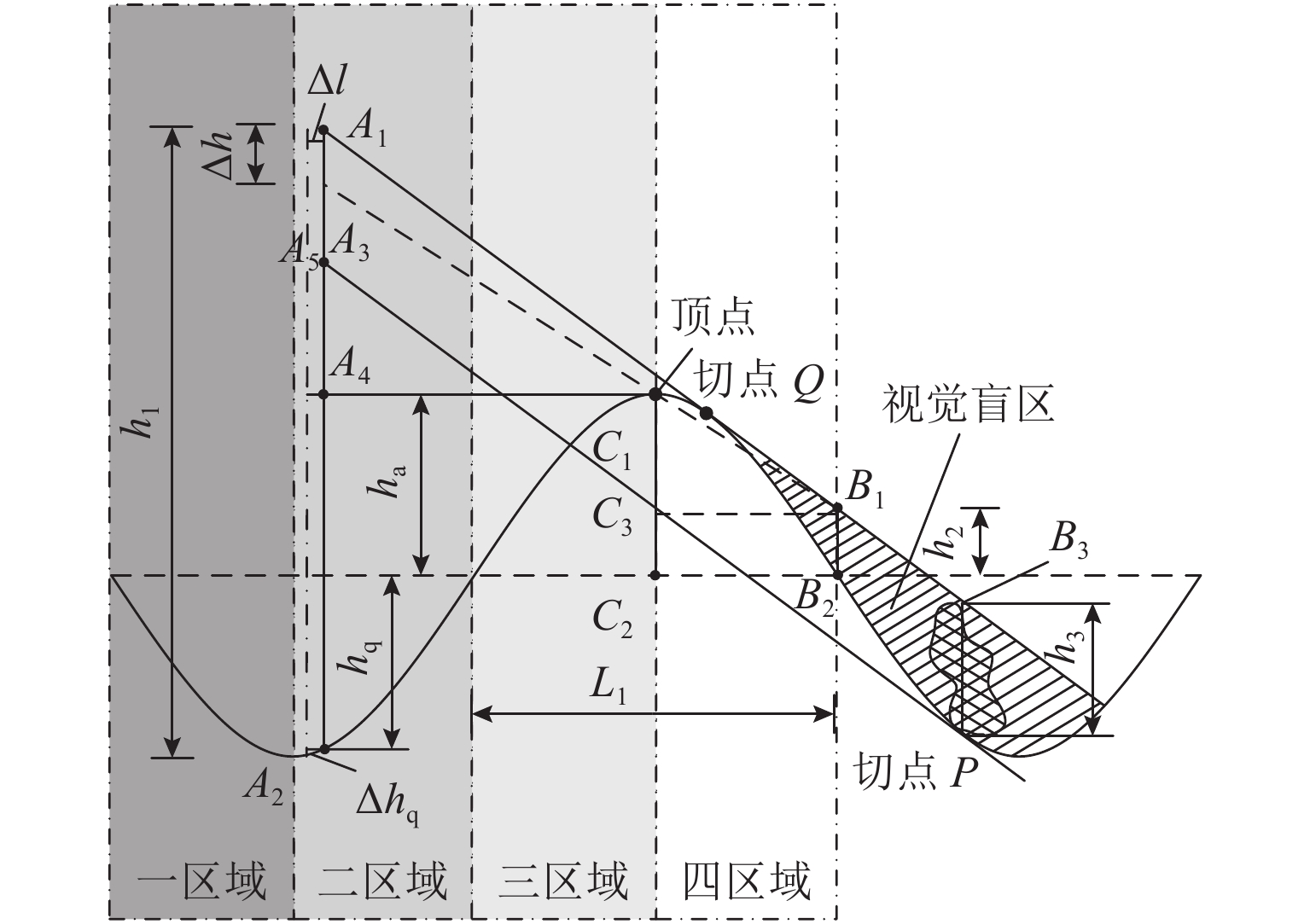
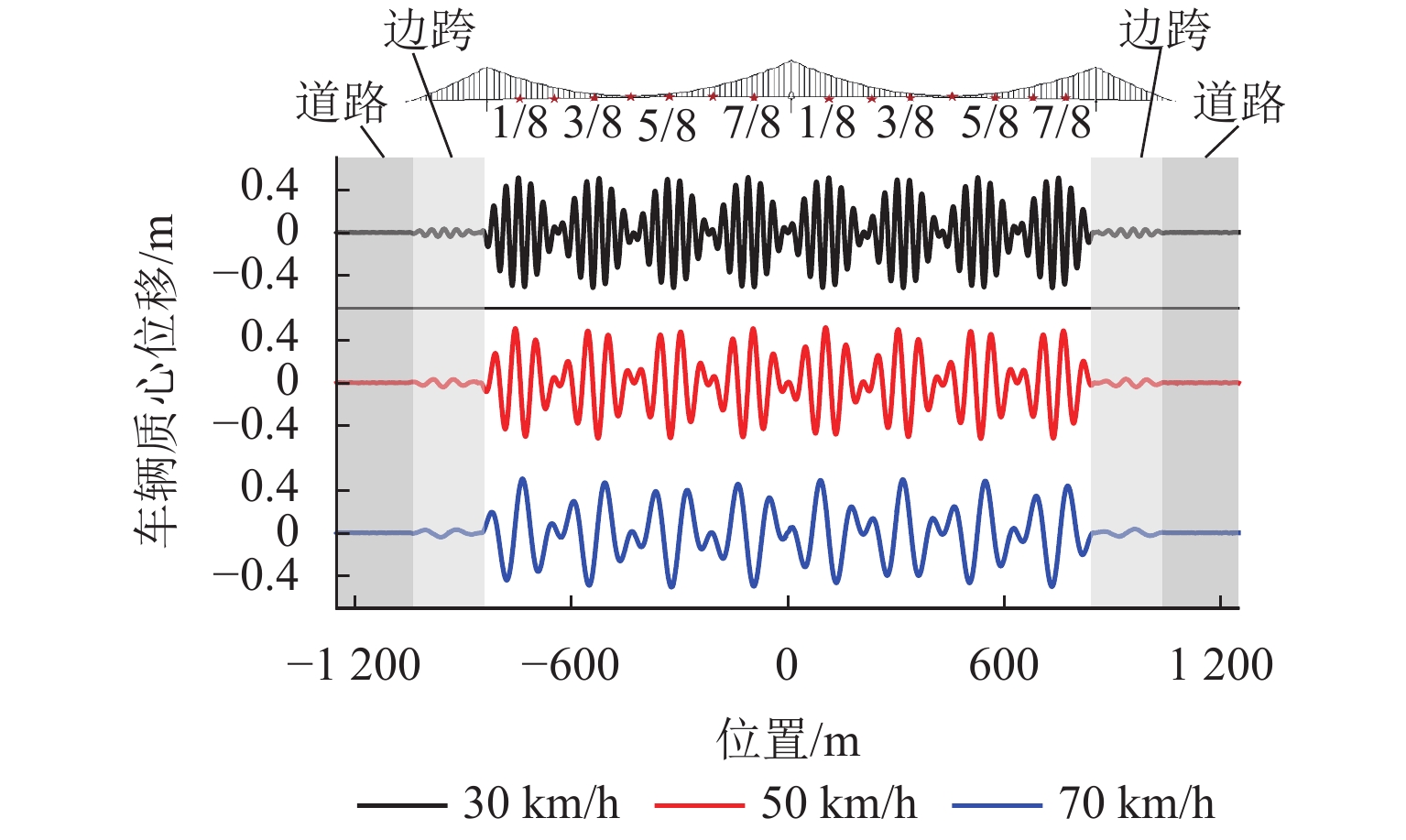
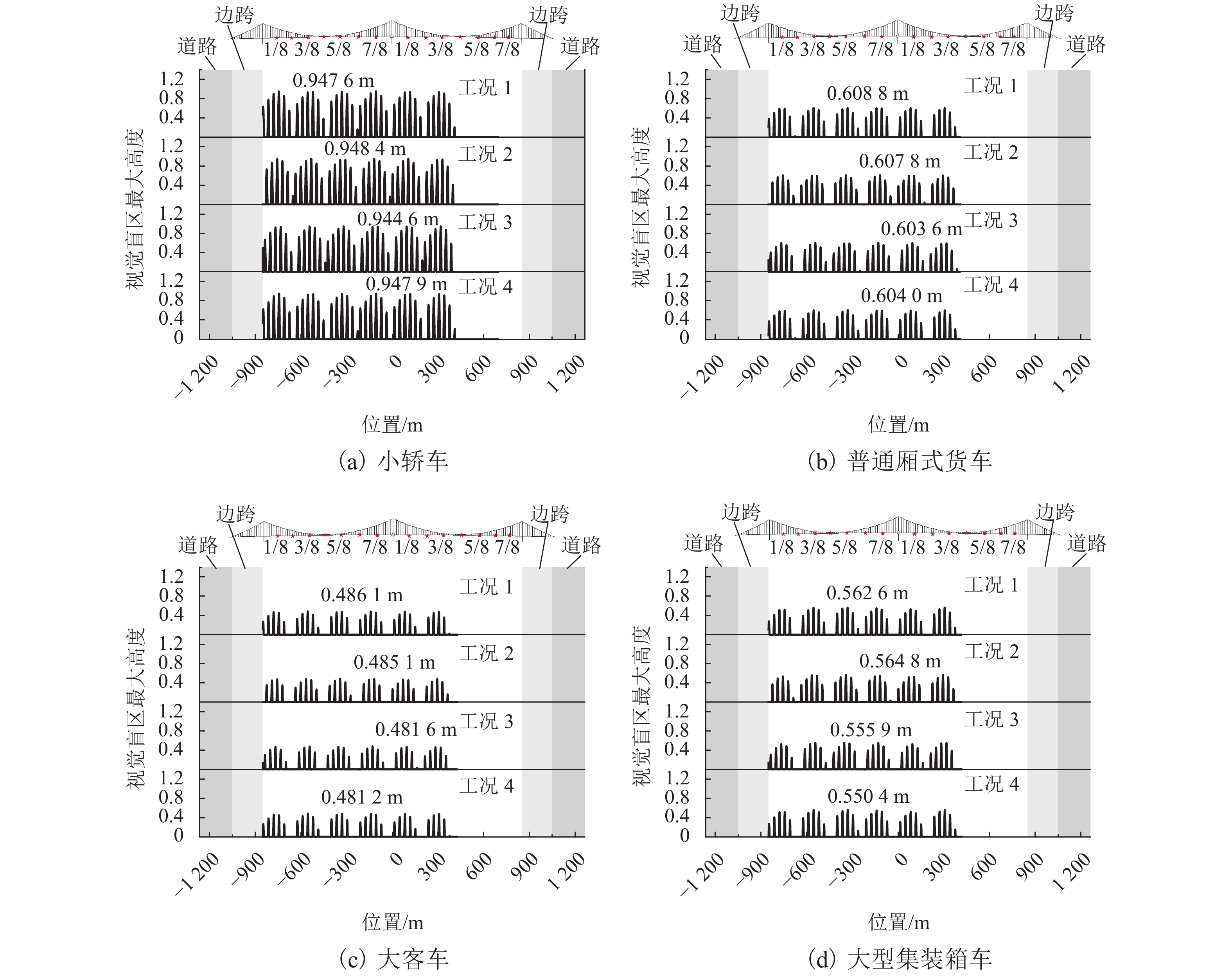
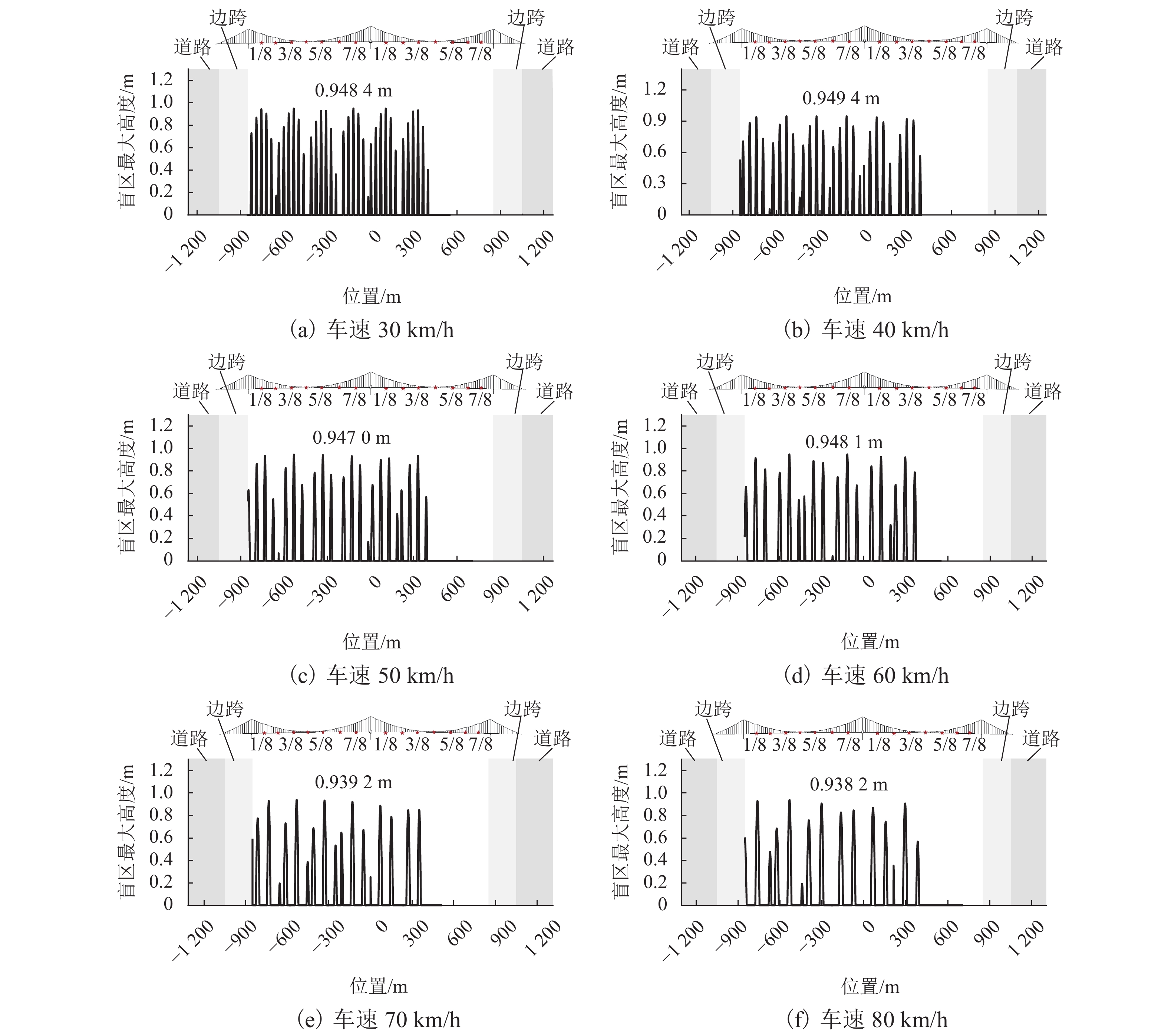
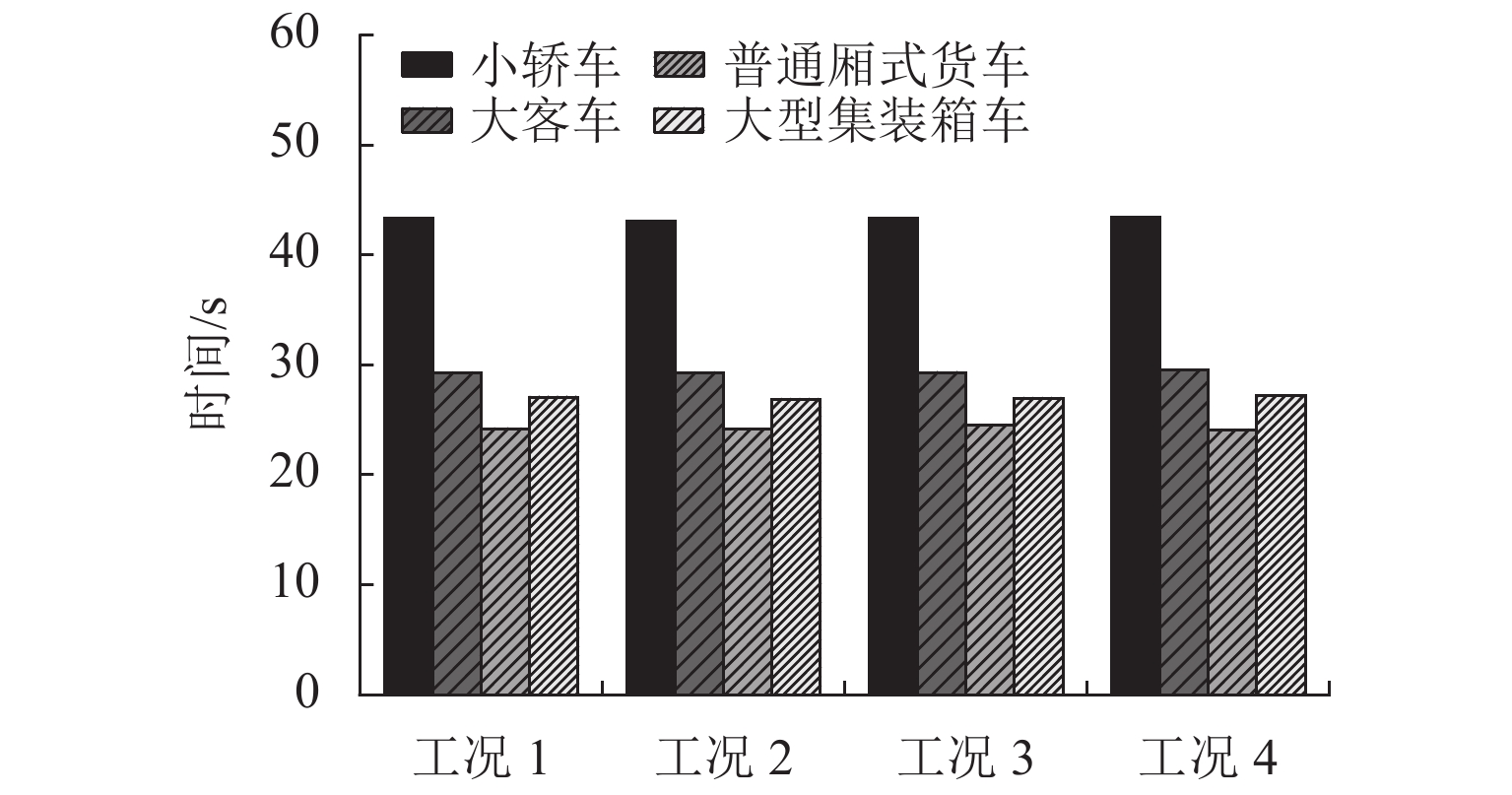
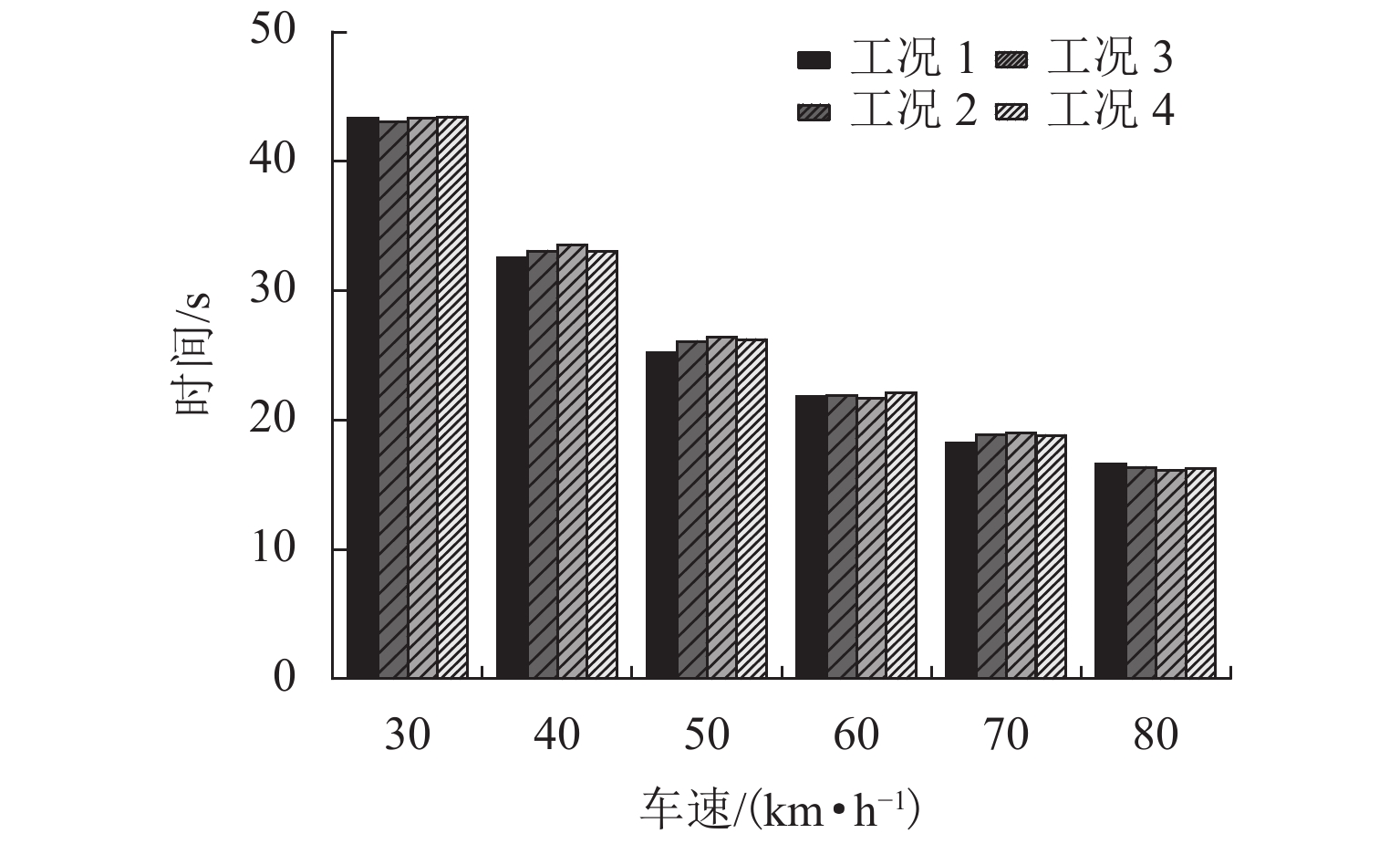
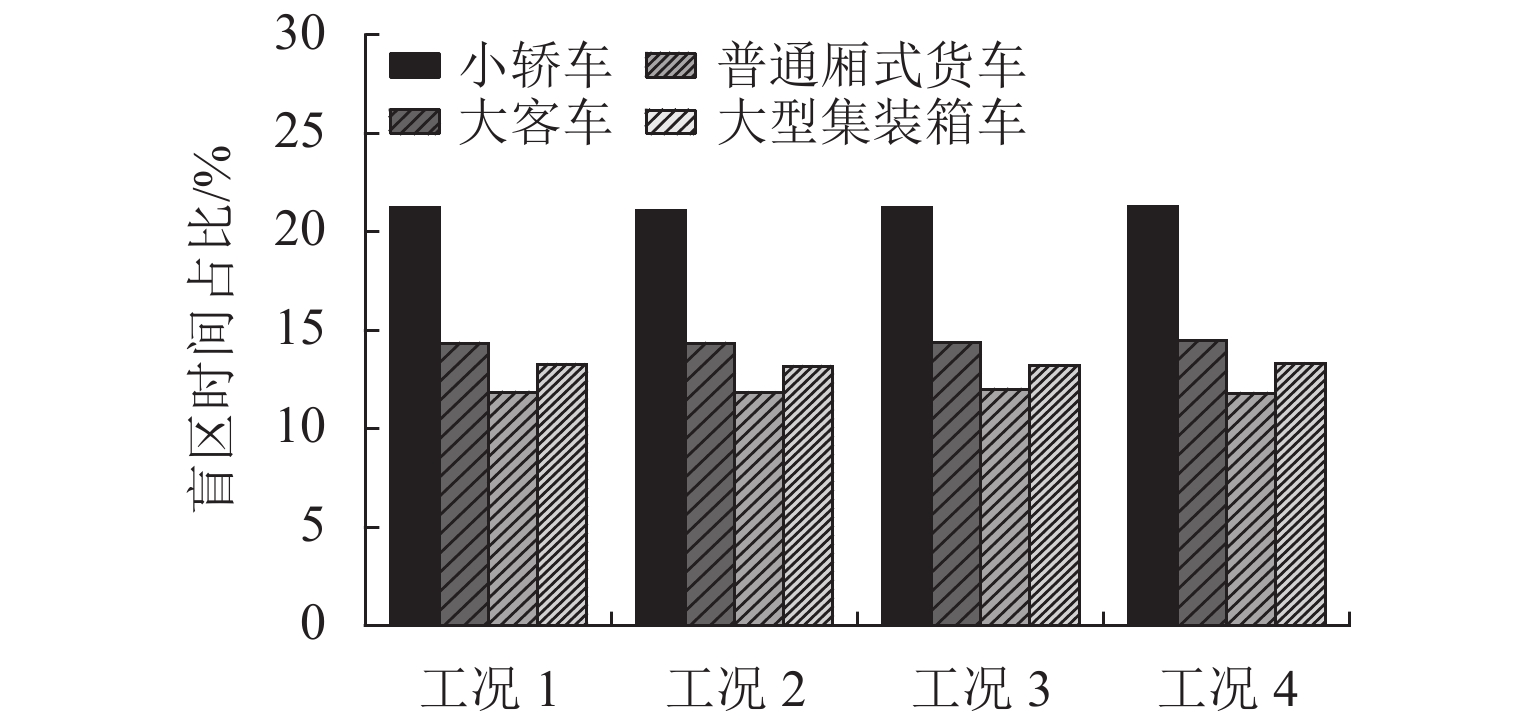
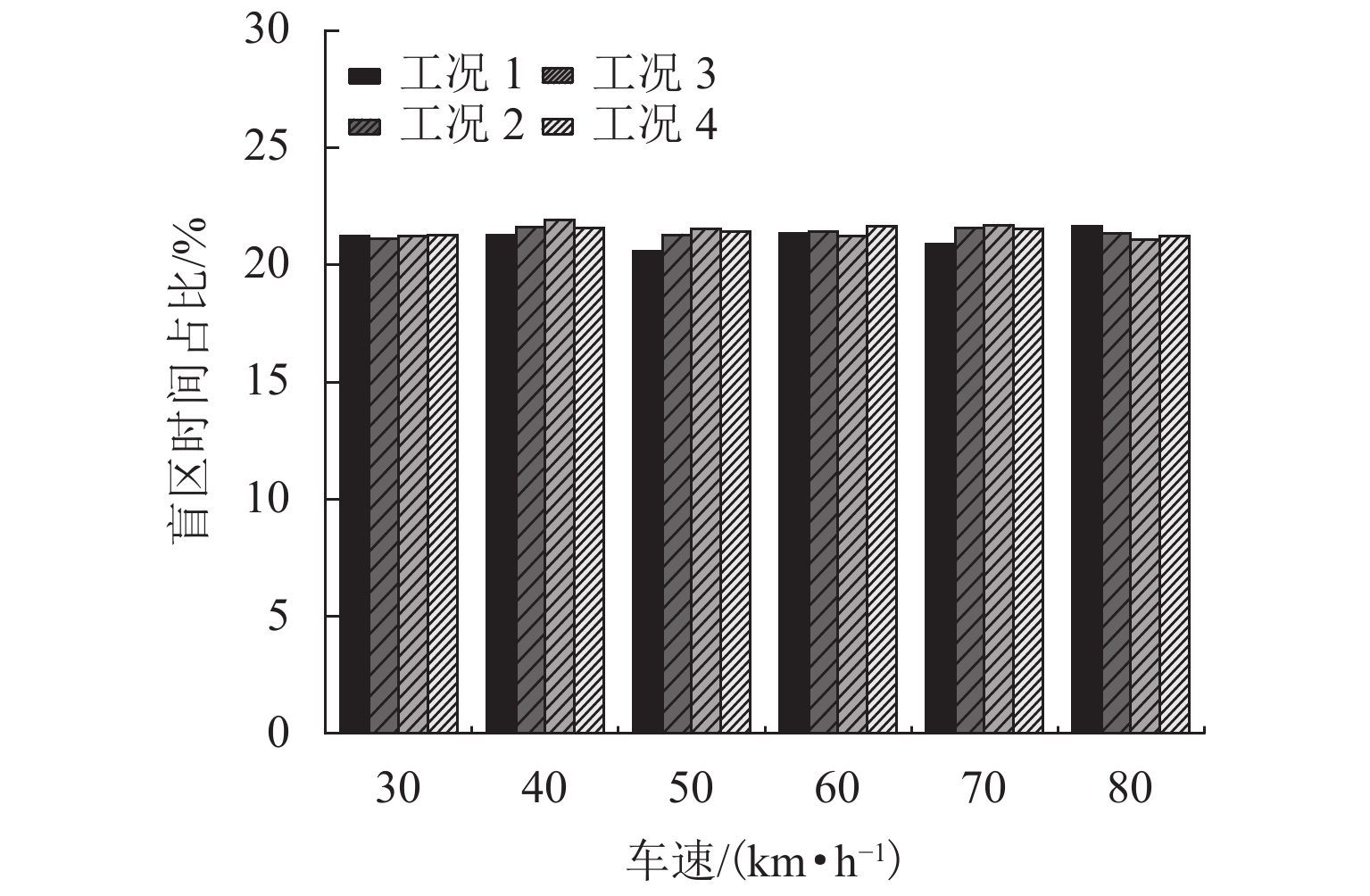
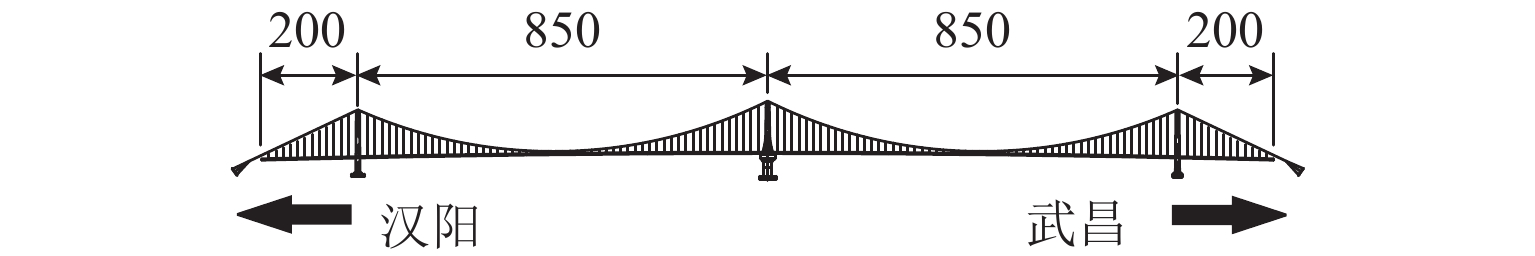
为研究大跨度悬索桥竖弯涡振条件下桥上驾驶员的行车视线,首先,基于传统的风-车-桥耦合振动分析理论,引入桥梁涡激力数值模型,自主编制了涡振条件下风-车-桥耦合振动分析程序;其次,以有3个半波的涡振振型为例,借助几何作图法推导了桥面发生涡振时车内驾驶员视线盲区的计算公式;最后,基于已建立的涡振条件下风-车-桥耦合振动分析程序和驾驶员视线盲区的计算公式,以一座发生竖弯涡激共振的大跨度悬索桥为工程背景,分析了车型、车速和入桥时刻对车内驾驶员视觉盲区最大高度、盲区总持时和盲区占比的影响规律. 研究结果表明:驾驶员盲区最大高度呈现周期性变化,其周期约为车辆前进一个涡振半波长度所需要的时间;车速变化不会影响驾驶员盲区的最大高度,但车辆类型不同则驾驶员目高不同,车内驾驶员目高越低,驾驶员前方视觉盲区最大高度也就越高;车重会进一步增加驾驶员前方视觉盲区的最大高度;车辆入桥时刻对驾驶员盲区总持时的影响很小,但驾驶员盲区总持时随着车速的提高而降低;车辆入桥时刻或车速对驾驶员盲区占比的影响小,而车型则对驾驶员盲区占比的影响显著,其中小轿车驾驶员的盲区占比最高(21%左右),大客车驾驶员的盲区占比最小(12%左右).
Abstract:In order to study the driver’s sight line under vertical vortex-induced vibration (VVIV) of long span suspension bridges, a numerical framework of coupled wind-vehicle-bridge system considering VVIV (termed as WVB-VIWW) is proposed by introducing a vortex aerodynamic model into the traditional coupled WVB theory. Based on the proposed framework and with the aid of geometric construction method, the equation of driver’s blind region under VIVV is derived based on a vortex vibration mode with three half-sine-waves. Subsequently, the proposed WVB-VIVV framework and equation of driver’s blind region are applied to a long span suspension bridge which has experienced VVIV. The influence of several key factors, i.e., vehicle type, vehicle speed, and the time instant where vehicle enters the bridge, on the maximum height of driver’s blind region, the total time duration of the driver’s blind region, and the ratio of driver’s blind region is investigated. The results indicate that the maximum height of the driver’s blind region varies periodically, and the period is approximately equal to the time required by the vehicle to travel through a half-sine-wave. The vehicle speed has an insignificant effect on the maximum height of driver’s blind region. Because the driver’s sight line height varies with the vehicle type, the lower the driver’s sight line height, the higher the maximum height of the driver’s blind region. Additionally, the vehicle weight could increase the maximum height of the driver’s blind region by increasing the overall deflection of the bridge span. It is also found that the total time duration of driver’s blind region is insensitive to the time instant where vehicle enters the bridge, but the total time duration of driver’s blind region decreases with the increase of the vehicle speed. Furthermore, the time instant where the vehicle enters or the vehicle speed has barely no effect on the ratio of driver’s blind region. However, the vehicle type has remarkable influence on the ratio of driver’s blind region, e.g., the ratio of driver’s blind region for sedan car and megabus is approximately 21% and 12%, respectively.
-
表 1 与驾驶员视线相关的参数取值
Table 1. Parameters related to driver’s line of sight
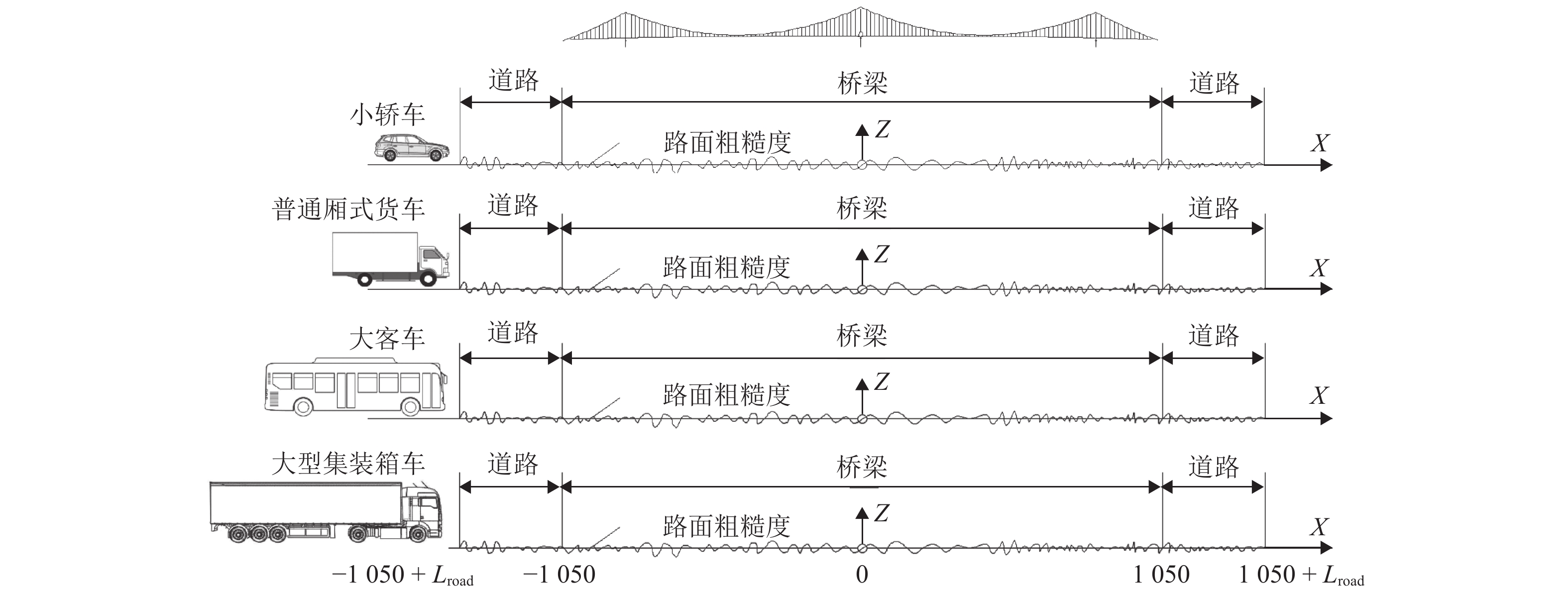
m 车型 hv hc hs h1 小轿车 0.72 0.3 0.65 1.07 普通厢式货车 1.50 0.7 0.65 1.45 大客车 1.35 0.4 0.65 1.6 大型集装箱车 1.35 0.4 0.65 1.6 表 2 行车视线工况设置
Table 2. Case settings on studying diver’s sight line
车速/(km·h−1) 工况 1 工况 2 工况 3 工况 4 Lroad /m t /s Lroad /m t/s Lroad /m t/s Lroad /m t /s 30 213.34 62.44 224.34 89.32 203.66 112.04 214.32 138.88 40 203.22 45.92 243.12 68.68 193.56 83.12 233.00 105.84 50 216.34 37.68 204.46 52.16 195.00 66.60 240.34 85.20 60 251.68 33.52 211.34 43.88 242.66 58.36 201.66 68.68 70 264.66 29.40 252.34 39.72 243.78 50.08 231.44 60.40 80 254.78 25.28 271.12 35.60 198.88 41.80 215.22 52.12 -
[1] HOSOMI M, KOBAYASHI H, NITTA Y. Fatigue strength design for vortex-induced oscillation and buffeting of a bridge[J]. Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, 1997, 67(4): 227-237. [2] LARSEN A, ESDAHL S, ANDERSEN J E, et al. Storebælt suspension bridge-vortex shedding excitation and mitigation by guide vanes[J]. Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, 2000, 88(2/3): 283-296. doi: 10.1016/S0167-6105(00)00054-4 [3] FRANDSEN J B. Simultaneous pressures and accelerations measured full-scale on the Great Belt East suspension bridge[J]. Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, 2001, 89(1): 95-129. doi: 10.1016/S0167-6105(00)00059-3 [4] FUJINO Y, YOSHIDA Y. Wind-induced vibration and control of trans-Tokyo bay crossing bridge[J]. Journal of Structural Engineering, 2002, 128(8): 1012-1025. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9445(2002)128:8(1012) [5] 陈政清,黄智文. 大跨度桥梁竖弯涡振限值的主要影响因素分析[J]. 中国公路学报,2015,28(9): 30-37. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7372.2015.09.005CHEN Zhengqing, HUANG Zhiwen. Analysis of main factors influencing allowable magnitude of vertical vortex-induced vibration of long-span bridges[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2015, 28(9): 30-37. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7372.2015.09.005 [6] 祝自强. 桥梁构件扭转涡激共振的疲劳研究[D]. 长沙: 湖南大学, 2011. [7] XU K, BI K M, HAN Q, et al. Using tuned mass damper inerter to mitigate vortex-induced vibration of long-span bridges: analytical study[J]. Engineering Structures, 2019(182): 101-111. [8] CAO S G, ZHANG Y, TIAN H, et al. Drive comfort and safety evaluation for vortex-induced vibration of a suspension bridge based on monitoring data[J]. Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, 2020(204): 104266.1-104266.12. [9] 陈尚烽. 考虑行车安全性的桥梁竖向涡振限值计算[J]. 中外公路,2019,39(6): 114-117. doi: 10.14048/j.issn.1671-2579.2019.06.024CHEN Shangfeng. Computation of threshold vertical vortex-induced vibration of bridges accounting for traffic safety[J]. Journal of China and Foreign Highway, 2019, 39(6): 114-117. doi: 10.14048/j.issn.1671-2579.2019.06.024 [10] 中华人民共和国交通运输部. 公路工程技术标准: JTG B01—2003[S]. 北京: 人民交通出版社, 2004. [11] 刘焕举,韩万水,丁晓婷,等. 斜风作用下风-车-桥非线性分析系统建立[J]. 中国公路学报,2018,31(7): 110-118. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7372.2018.07.009LIU Huanju, HAN Wanshui, DING Xiaoting, et al. A nonlinear analysis system for wind-vehicle-bridge under skew wind[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2018, 31(7): 110-118. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7372.2018.07.009 [12] 李永乐,赵凯,陈宁,等. 风-汽车-桥梁系统耦合振动及行车安全性分析[J]. 工程力学,2012,29(5): 206-212.LI Yongle, ZHAO Kai, CHEN Ning, et al. Wind-vehicle-bridge system coupling vibration and traffic safety analysis[J]. Engineering Mechanics, 2012, 29(5): 206-212. [13] 陈宁. 侧风作用下桥上汽车行车安全性及防风措施研究[D]. 成都: 西南交通大学, 2015. [14] 邓露,何维,俞扬,等. 公路车-桥耦合振动的理论和应用研究进展[J]. 中国公路学报,2018,31(7): 38-54. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7372.2018.07.003DENG Lu, HE Wei, YU Yang, et al. Research progress in theory and applications of highway vehicle-bridge coupling vibration[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2018, 31(7): 38-54. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7372.2018.07.003 [15] ZHOU Y F, CHEN S R. Vehicle ride comfort analysis with whole-body vibration on long-span bridges subjected to crosswind[J]. Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, 2016(155): 126-140. [16] 华旭刚,黄智文,陈政清. 大跨度悬索桥的多阶模态竖向涡振与控制[J]. 中国公路学报,2019,32(10): 115-124. doi: 10.19721/j.cnki.1001-7372.2019.10.011HUA Xugang, HUANG Zhiwen, CHEN Zhengqing. Multi-mode vertical vortex-induced vibration of suspension bridges and control strategy[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2019, 32(10): 115-124. doi: 10.19721/j.cnki.1001-7372.2019.10.011 [17] K S Association. Mechanical vibration-road surface profiles-reporting of measured data: ISO 8608[S]. Geneva: [s.n.], 1995. -




 下载:
下载: