Evaluation of Acoustic Performance of Porous Asphalt Concrete
-
摘要:
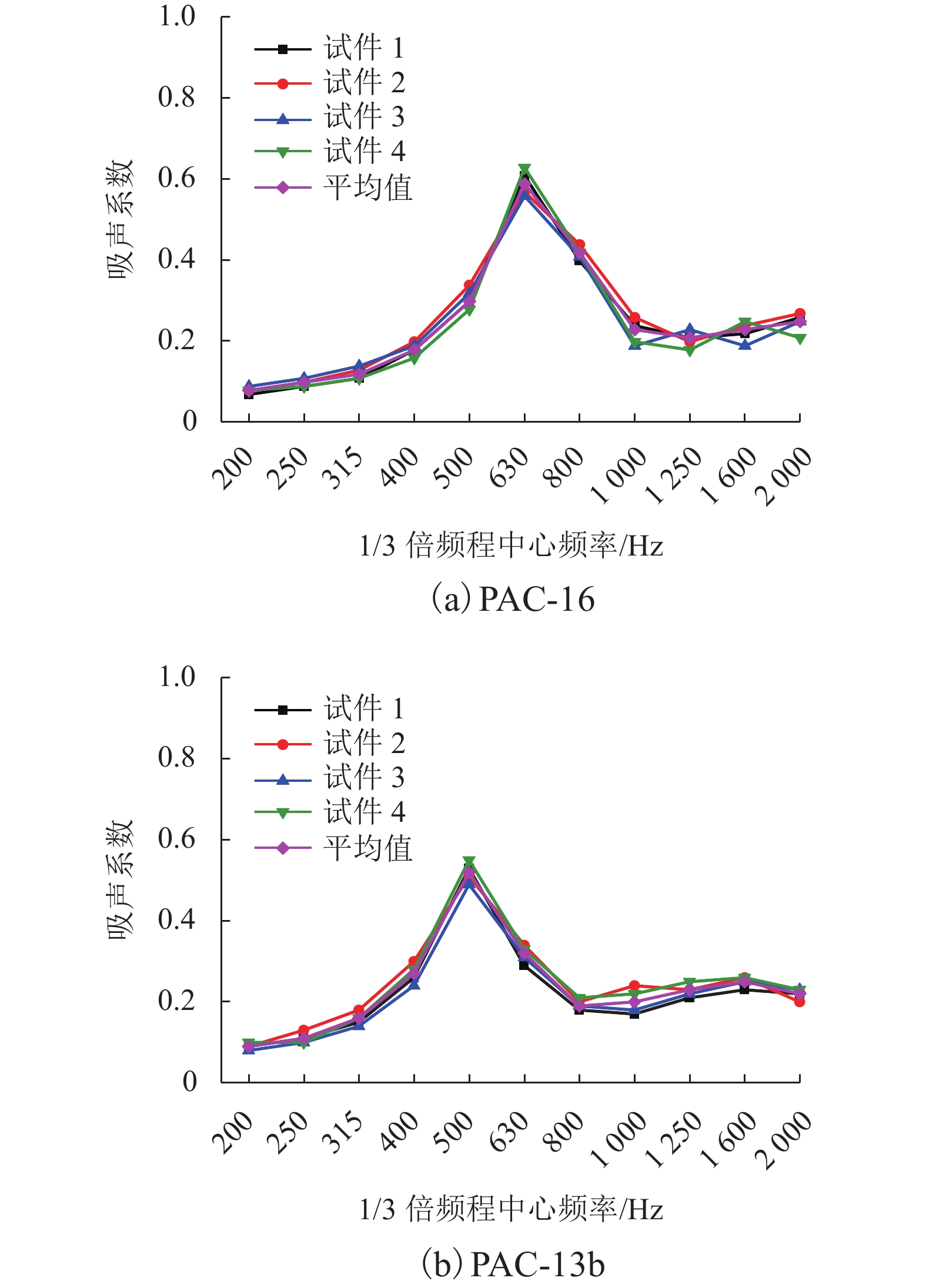
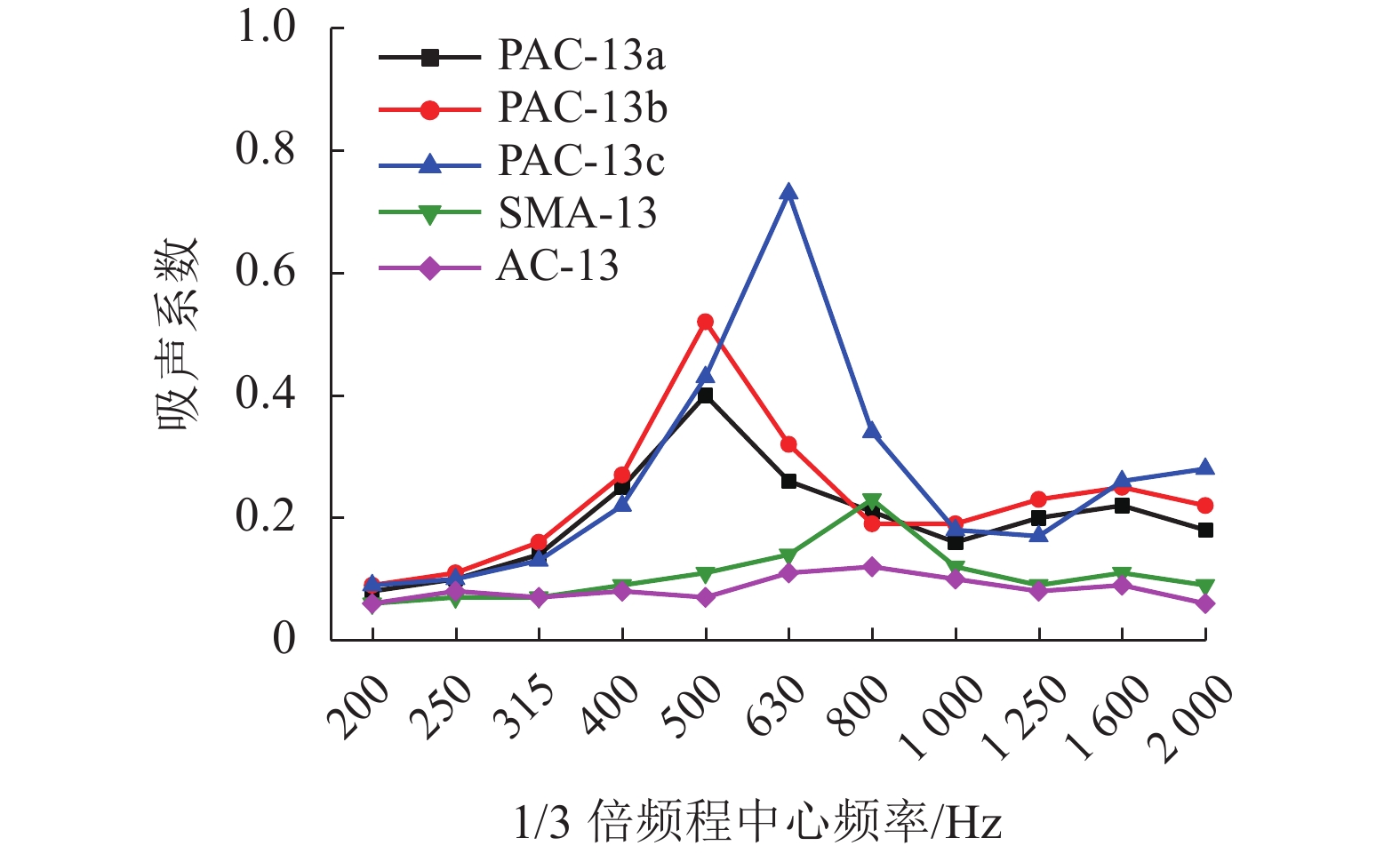
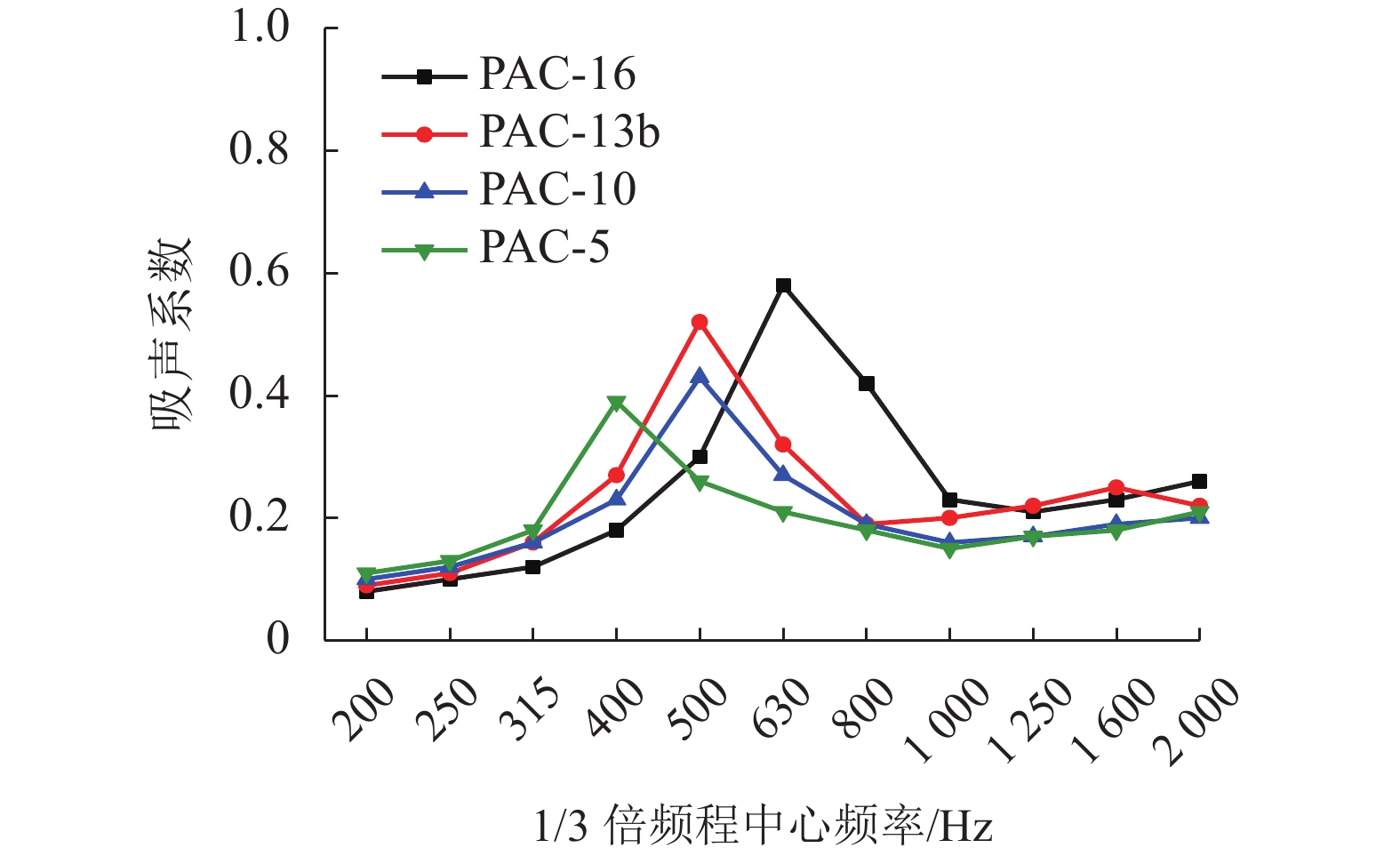
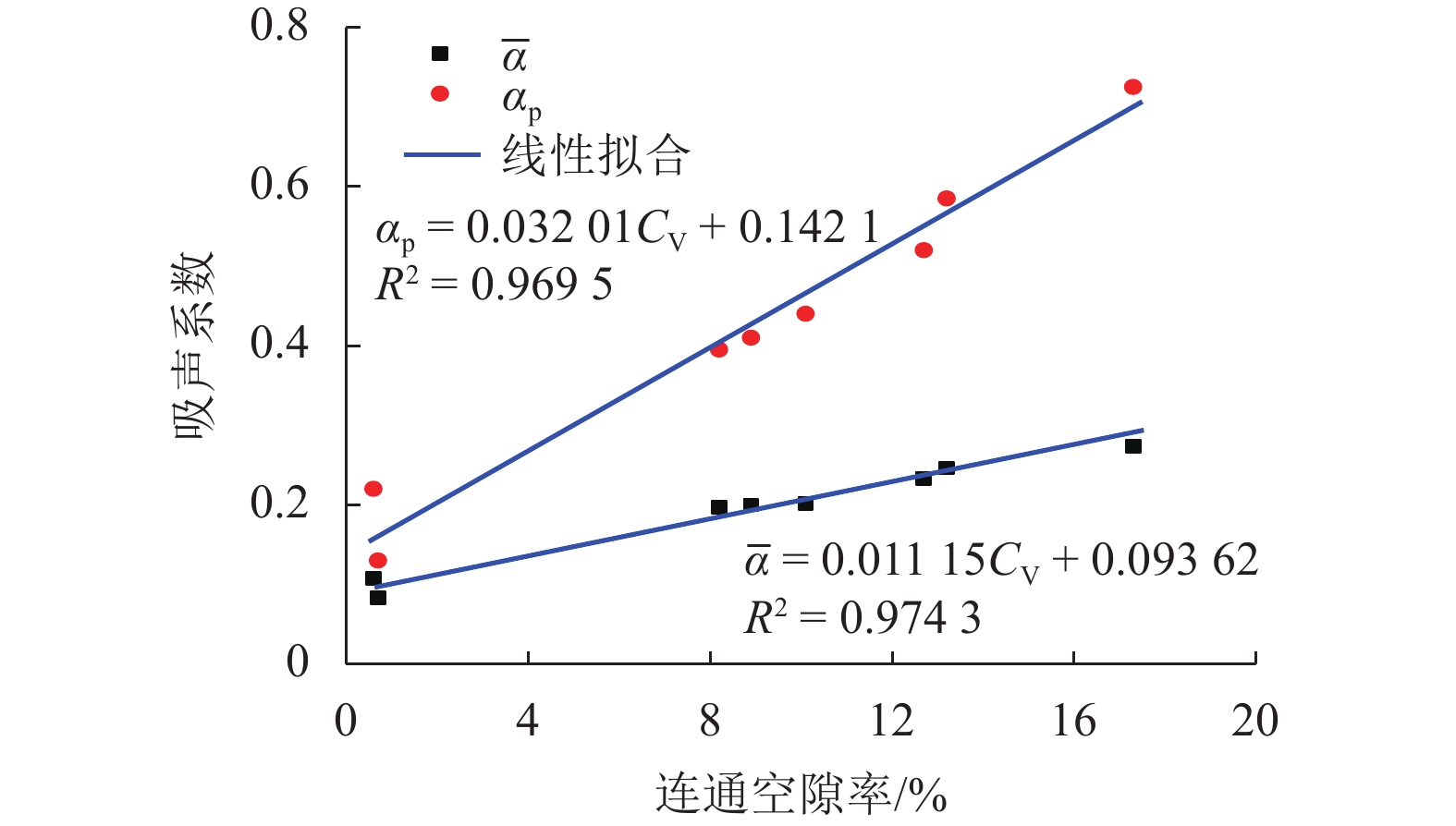
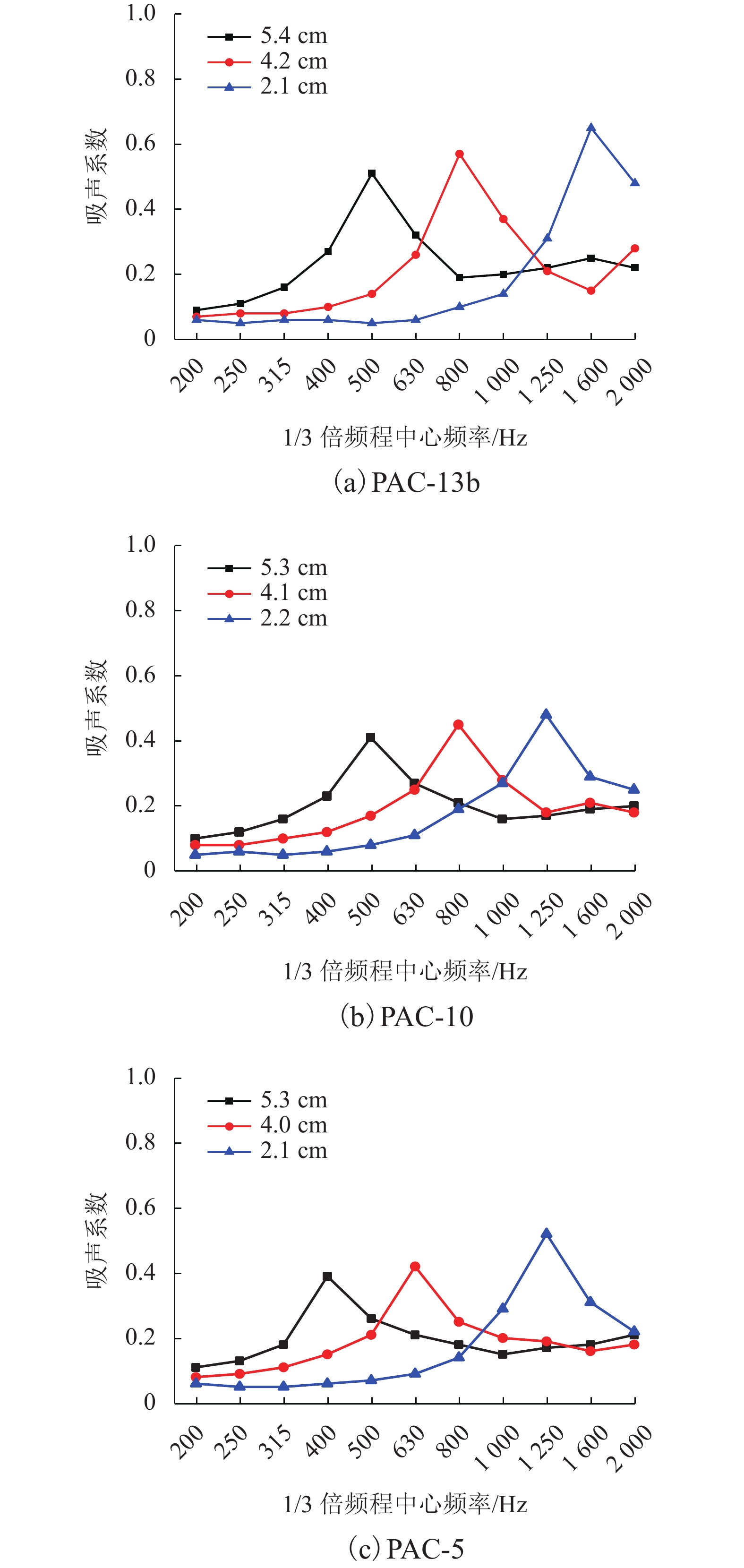
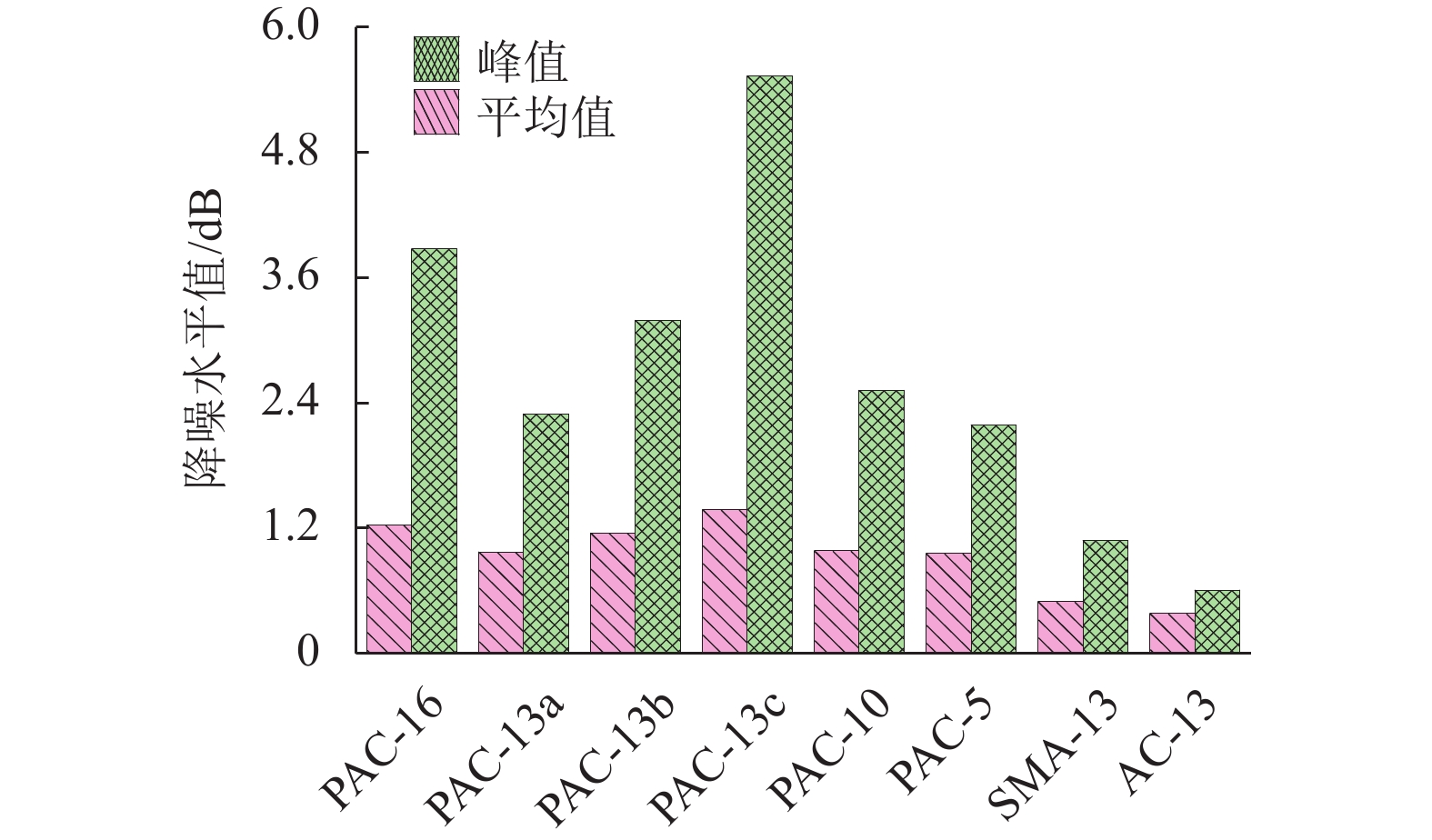
多孔沥青混合料的吸声性能对降低轮胎/路面噪声有重要影响,为此采用驻波管按1/3倍频对多孔沥青混合料(PAC)、沥青玛蹄脂碎石(SMA-13)和密级配沥青混合料(AC-13)的吸声频谱进行了测试,研究分析了级配类型、空隙率、试件厚度及表面纹理构造对混合料吸声性能的影响. 试验结果表明:PAC混合料的空隙率较大,其吸声频谱随频率呈先升后降的变化趋势,吸声性能远好于SMA-13和AC-13,并给出了吸声系数随连通空隙率的线性表达式;PAC的空隙率越高,公称最大粒径越大,平均吸声系数和峰值吸声系数均越大(降噪性能越好),吸声频谱的峰值频率越高;随着试件厚度减小,PAC的峰值吸声系数有所增大,吸声频谱峰值逐渐向高频方向移动,但平均吸声系数逐渐减小;SMA-13相比AC-13的平均吸声系数略大,同一PAC混合料试件的糙面接受声波相比光面接受声波时的平均吸声系数大13.9%,表面纹理构造也是影响PAC混合料吸声性能的重要因素. 空隙率、公称最大粒径和厚度的增加均有利于PAC混合料吸声性能提升,前两者更有益于吸收高频噪声,后者则有益于吸收低频噪声.
Abstract:The sound absorption performance of porous asphalt concrete has an important impact on reducing tire/pavement noise. The sound absorption coefficients of porous asphalt concrete (PAC), stone matrix asphalt (SMA-13) and a dense graded asphalt concrete (AC-13) are tested adopting the standing wave ratio method at one-third octave frequencies. The effects of several concrete properties are investigated; i.e., the grade distribution type, void content of the asphalt mixture, specimen thickness and surface texture. It is found that the sound absorption coefficients of PAC with a higher void content are much larger than those of SMA-13 and AC-13, and the sound absorption spectrum first increases and then decreases with the noise frequency increasing. The linear expressions of the sound absorption coefficient with the connected void content are proposed for asphalt mixture. A higher void content and larger maximum nominal particle size result in a larger peak and average value of the sound absorption coefficient (i.e., better noise reduction performance) for the PAC, with the peak value of the sound absorption spectrum gradually moving to a higher frequency. As the specimen thickness decreases, the average value of the sound absorption coefficient decreases for the PAC, and there is no obvious change in the peak value of the sound absorption coefficient whose corresponding frequency shifts to a high frequency gradually. For SMA-13 and AC-13 with similar void percentages, the peak and average value of the sound absorption coefficient of the former are slightly larger than those of the latter. For the same PAC specimen, the average value of the sound absorption coefficient measured using a rough-surface receiving incident sound wave is about 13.9% larger than that measured using a smooth-surface receiving sound wave, which indicates that the surface texture is an important factor affecting the sound absorption performance of the PAC. In summary, increases in the void content, maximum nominal particle size and thickness contribute to improving the sound absorption performance of the PAC. The two former factors are more beneficial to the absorption of high frequency noise, while the last factor is beneficial for the low frequency.
-
Key words:
- porous asphalt concrete /
- pavement noise /
- impedance tube /
- sound absorption coefficient
-
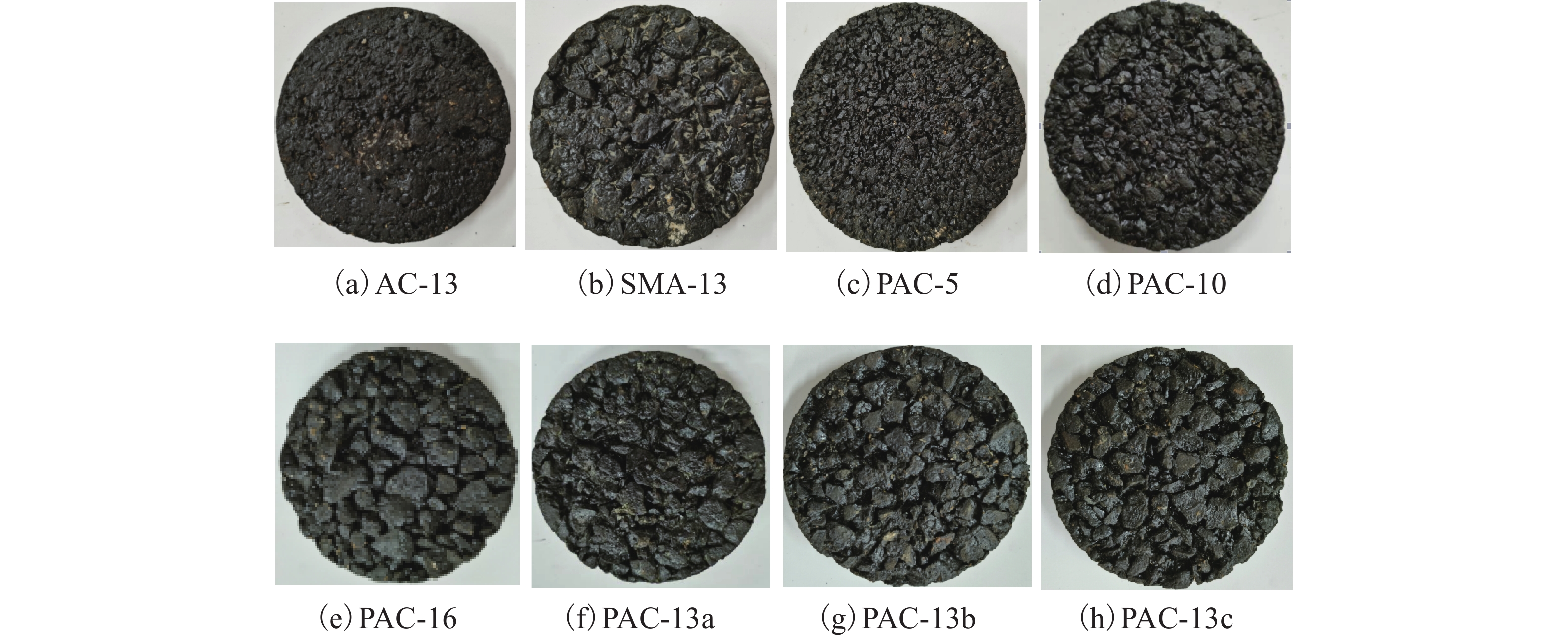
表 1 不同沥青混合料的级配组成
Table 1. Gradation composition of different asphalt concrete
% 试件编号 通过筛孔(mm)的质量百分比 油石比 空隙率 连通空隙率 19.000 16.000 13.200 9.500 4.750 2.360 1.180 0.600 0.300 0.150 0.075 PAC-16 100.0 94.5 82.0 51.0 20.5 16.0 12.5 10.0 7.5 5.5 4.0 4.7 19.5 13.2 PAC-13a 100.0 100.0 95.0 69.0 26.5 20.5 15.5 11.0 8.0 6.0 4.0 4.8 16.7 8.9 PAC-13b 100.0 100.0 90.5 63.0 19.5 14.0 12.5 9.0 7.0 5.5 4.0 4.8 20.0 12.6 PAC-13c 100.0 100.0 86.0 52.0 15.5 13.0 10.5 8.0 6.0 5.0 4.0 4.7 23.1 17.3 PAC-10 100.0 100.0 100.0 90.0 39.0 13.0 9.0 7.0 6.0 5.0 4.0 4.9 19.8 10.1 PAC-5 100.0 100.0 100.0 100.0 88.0 30.0 18.0 12.0 9.0 7.0 5.0 5.1 19.4 8.2 SMA-13 100.0 100.0 95.0 62.5 27.0 20.5 19.0 16.0 13.0 12.0 10.0 6.1 3.9 0.6 AC-13 100.0 100.0 95.0 76.5 53.0 37.0 26.5 19.0 13.5 10.0 6.0 4.6 4.2 0.7 表 2 不同厚度下沥青混合料试样的平均吸声系数
Table 2. Average sound absorption coefficient of asphalt concrete samples with different thicknesses
试样厚度 厚度≈5.3 cm 厚度 ≈4.1 cm 厚度 ≈2.1 cm PAC-13b 0.2309 0.2101 0.1836 PAC-10 0.2018 0.1909 0.1718 PAC-5 0.1973 0.1855 0.1691 -
[1] KIM D R. Burden of disease from environmental noise[R]. Copenhague (Dinamarca): World Health Organization Regional Office for Europe, 2011. [2] DAMIAN C, FOSALAU C. Sources of indoor noise and options to minimize adverse human health effect[J]. Engineering and Management Journal, 2011, 10(3): 393-400. [3] SYGNA K, AASVANG GM, AAMODT G, et al. Road traffic noise,sleep and mental health[J]. Environmental Research, 2014, 131: 17-24. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2014.02.010 [4] FREITAS E F. The effect of time on the contribution of asphalt rubber mixtures to noise abatement[J]. Noise Control Engineering Journal, 2012, 60(1): 1-8. doi: 10.3397/1.3676311 [5] SANDBERG U, EJSMONT J A. Tyre/road noise reference book[M]. Sweden: [s.n.], 2002. [6] WINROTH J, KROPP W, HOEVER G, et al. Investigating generation mechanisms of tyre/road noise by speed exponent analysis[J]. Applied Acoustics, 2017, 115: 101-108. doi: 10.1016/j.apacoust.2016.08.027 [7] LIU M, HUANG X, XUE G. Effects of double layer porous asphalt pavement of urban streets on noise reduction[J]. International Journal of Sustainable Built Environment, 2016, 5: 183-196. doi: 10.1016/j.ijsbe.2016.02.001 [8] GARDZIEJCZYK W, JASKULA P, EJSMONT J A, et al. Investigation of acoustic properties of poroelastic asphalt mixtures in laboratory and field conditions[J]. Materials, 2021, 14: 2649. doi: 10.3390/ma14102649 [9] CHU L, FWA T F, TAN K H. Eveluation of wearing course mix designs on sound absorption improvement of porous asphalt pavement[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2017, 141: 402-409. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2017.03.027 [10] KIM S K, PARK W J, LEE K H. Noise reduction capacity of a composite pavement system[J]. KSCE Journal of Civil Engineering, 2014, 18(6): 1664-1671. doi: 10.1007/s12205-014-0594-z [11] LIAO G, SAKHAEIFAR M S, HEITZMAN M, et al. The effects of pavement surface characteristics on tire/pavement noise[J]. Applied Acoustics, 2014, 76: 14-23. doi: 10.1016/j.apacoust.2013.07.012 [12] KRIVANEK V, PAVKOVA A, TOGEL M, et al. Cleaning low-noise surface as a basic condition for improving pavement’s axoustic absorption capability[J]. Arabian Journal for Science and Engineering, 2016, 41(2): 425-431. doi: 10.1007/s13369-015-1713-y [13] 杜功焕, 朱哲民, 龚秀芬. 声学基础[M]. 3版. 南京: 南京大学出版社, 2015: 131-150. [14] 王辉,董欣雨,邓乔,等. 沥青混合料吸声性能[J]. 建筑材料学报,2018,21(4): 634-638. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-9629.2018.04.017WANG Hui, DONG Xinyu, DENG Qiao, et al. Sound absorption performance of asphalt mixutre[J]. Journal of Building Materials, 2018, 21(4): 634-638. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-9629.2018.04.017 [15] 中国科学院声学研究所, 中国建筑科学院建筑物理研究所. 声学阻抗管中吸声系数和声阻抗的测量: GB/T 18696.1—2004 [S]. 北京: 中国国家标准化管理委员会, 2004. [16] VAITKUS A, RNDRIEJAUSKAS T, VOROBJOVAS V, et al. Asphalt waering course optimization for road traffic noise reduction[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2017, 152: 345-356. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2017.06.130 [17] 王岚,唐宝利,邢永明. 大孔隙胶粉改性沥青混合料吸声特性试验研究[J]. 工程力学,2009,26(增刊1): 181-184.WANG Lan, TANG Baoli, XING Yongming. Experimental study on sound absorption of crumb rubber modified asphalt mixture with large porosity[J]. Engineering Mechnics, 2009, 26(S1): 181-184. [18] GARDZIEJCZYK W. The effect of time on acoustic durability of low noise pavements-the case studies in Poland[J]. Transportation Research Part D: Transport and Environment, 2016, 44: 93-104. doi: 10.1016/j.trd.2016.02.006 [19] 交通运输部公路科学研究院. 公路工程沥青及沥青混合料试验规程: JTG E20-2011 [S]. 北京: 中华人民共和国交通运输部, 2011. [20] 交通运输部公路科学研究院. 公路沥青路面施工技术规范: JTG F40-2004 [S]. 北京: 中华人民共和国交通运输部, 2004. [21] KNABBEN R M, TRICHES G, GERGES S N Y, et al. Evaluation of sound absorption capacity of asphalt mixtures[J]. Applied Acoustics, 2016, 114: 266-274. [22] BURATTI C, MORETTI E. Traffic noise pollution: spectra characteristics and windows sound insulation in laboratory and field measurements[J]. Journal of Environmental Science and Engineering, 2010, 4(12): 28-36. -




 下载:
下载: