Dynamic Simulation of Load Process for Urban Rail Power Supply System Driven by Operation Diagram
-
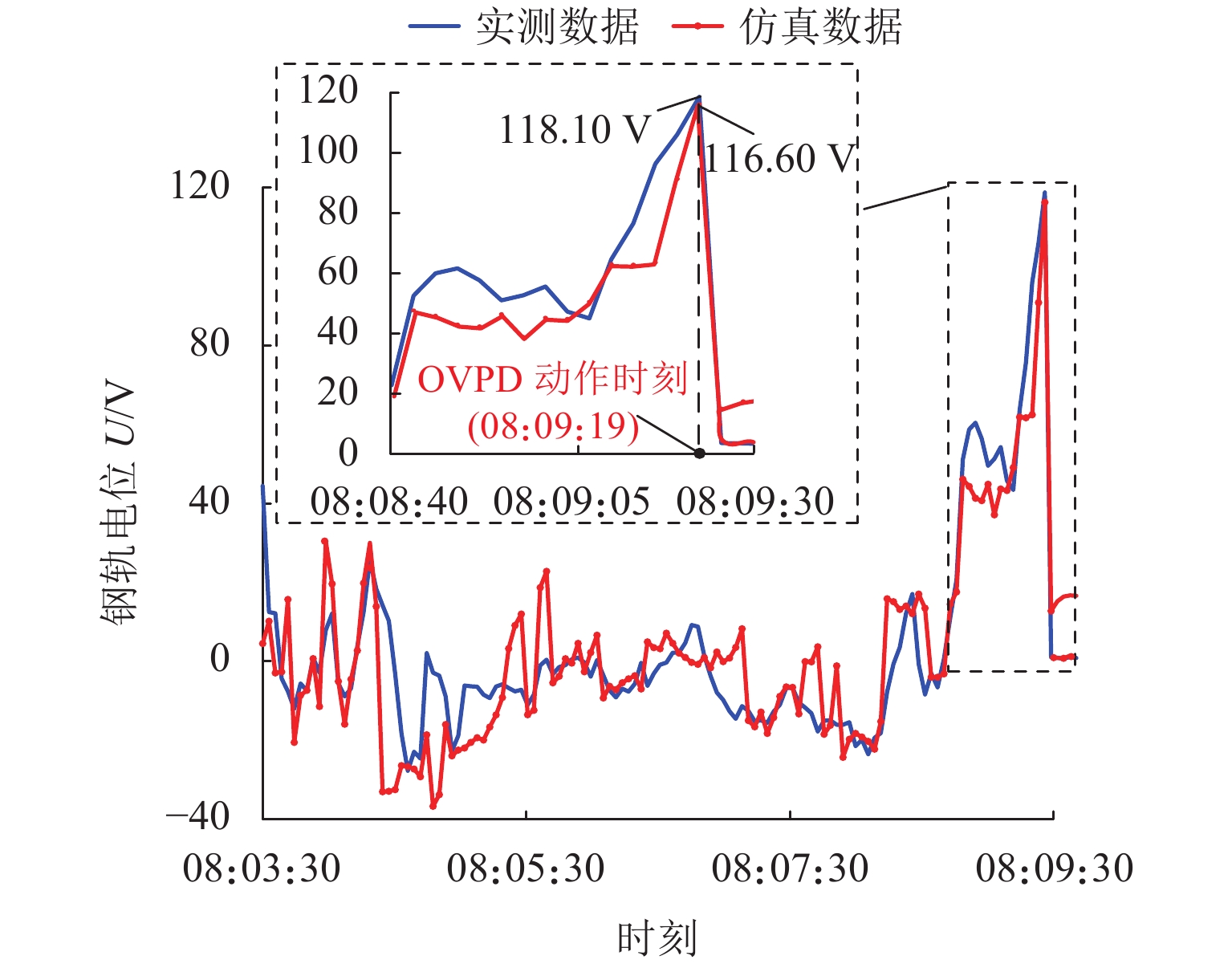
摘要:
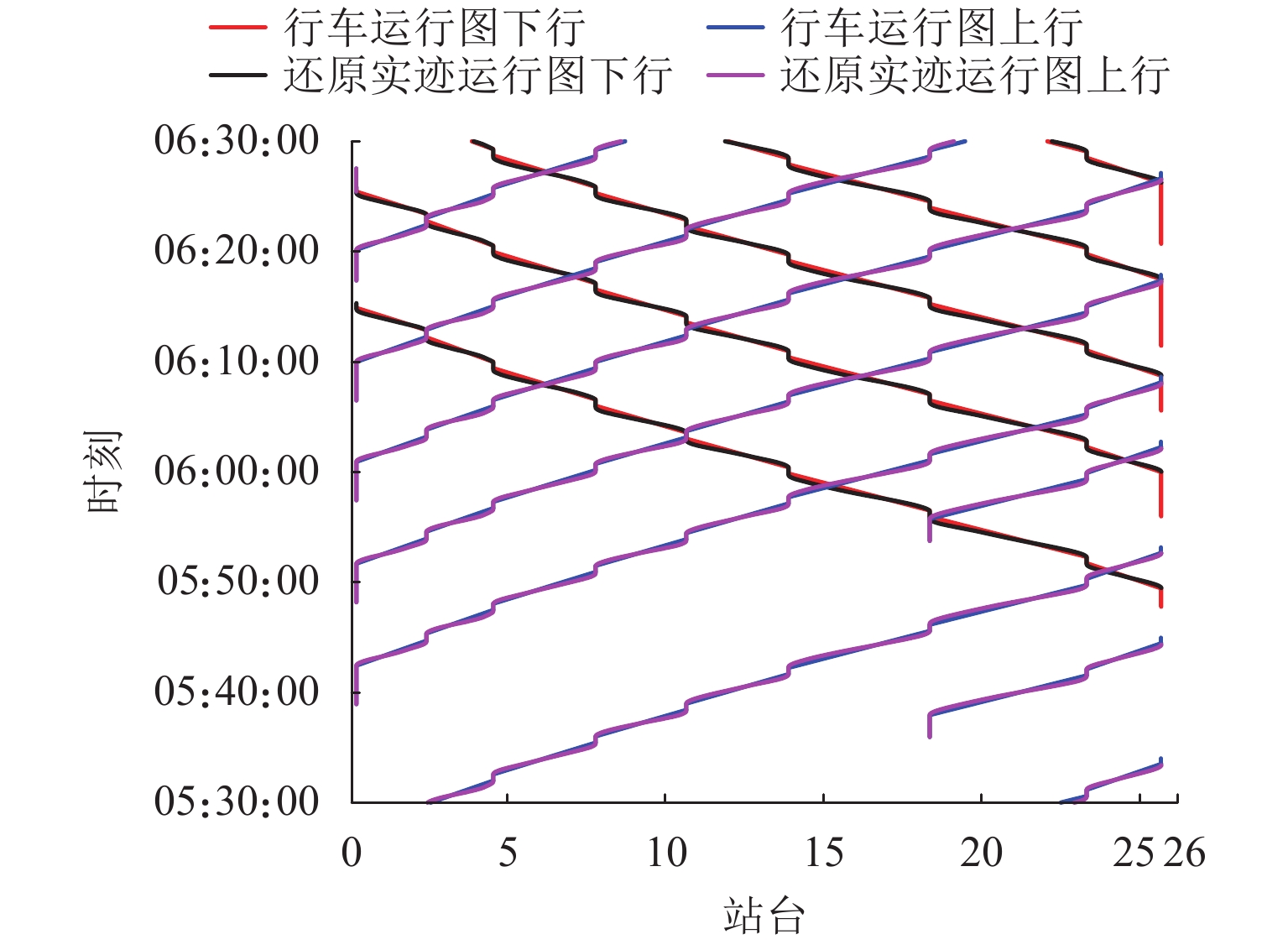
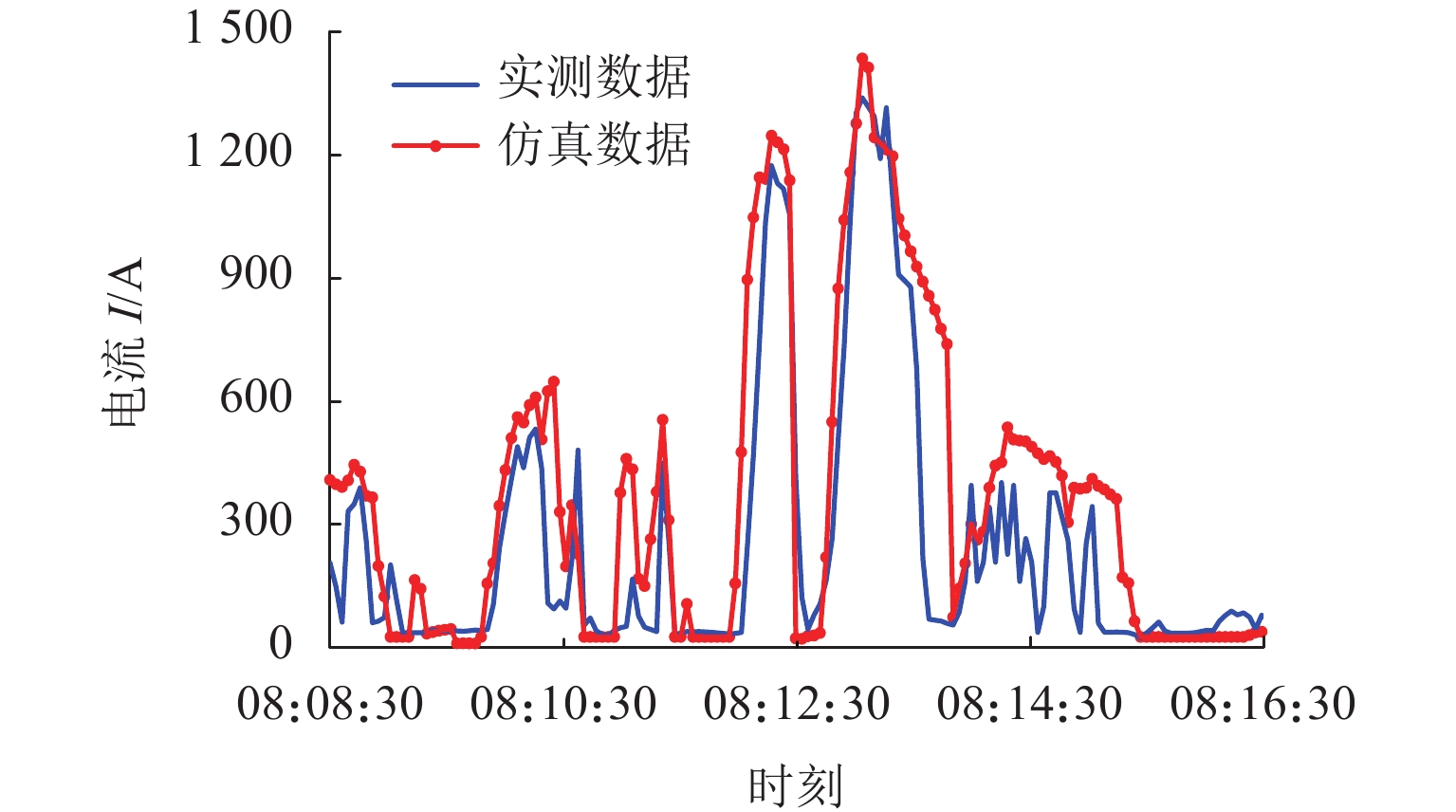
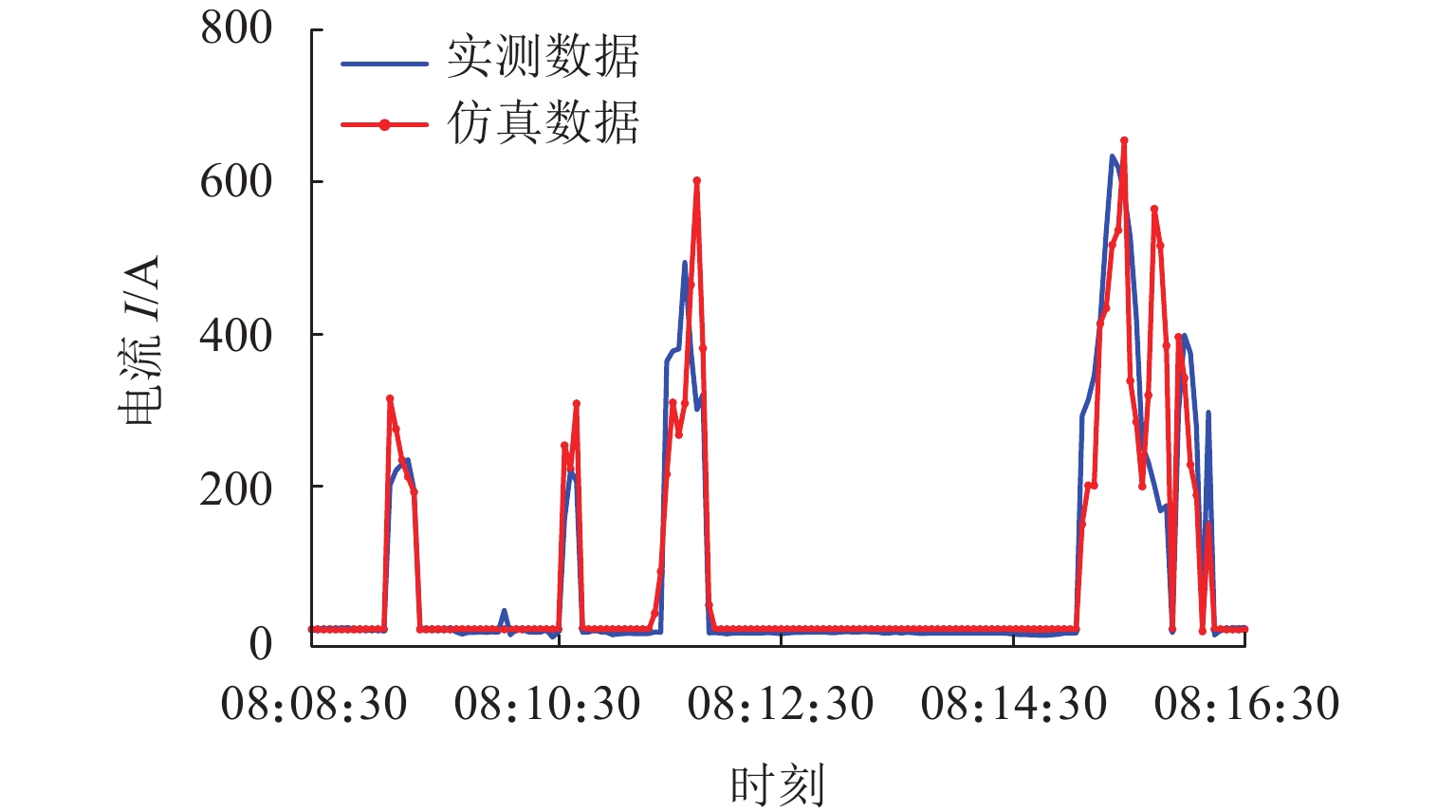
针对城轨供电系统采用平铺运行图进行负荷过程仿真分析与实际负荷过程差别大,不能准确反应供电系统运营阶段的诸多问题,将运行图中各列车运行时分作为约束条件,建立列车定时节能运行的指标函数,以提高仿真模型准确性;基于固定阶梯级目标速度搜索算法优化列车操纵序列,还原多列车具有电气信息的运行轨迹;以实迹运行图为驱动,实现了供电系统正常运行与异常情形下的负荷过程仿真分析. 算例分析结果表明:基于实迹运行图的仿真结果与实测牵引变电所负荷过程曲线的Pearson相关系数在0.89以上,负荷过程特征值仿真与实测的最大误差不超过6.85%,较平铺运行图仿真结果准确度最高可提升12.91%.
Abstract:Load process simulation analysis based on the paving operation diagram for urban rail power supply system is significantly different from the actual load process, which cannot accurately reveal many issues in the operation stage of the power supply system. To improve the accuracy of the simulation model, with the train running time in operation diagram as constraints, the objective function with respect to the scheduled energy-saving train operation is established. The target velocity search algorithm with a fixed step is used to optimize the train control sequence and restore the electrical information of the operation diagram with multiple trains. Driven by the actual operation diagram, the load process simulation analysis of the power supply system is performed under normal and abnormal operations. The case study shows that the Pearson correlation coefficient between the simulation results from the actual-track operation diagram and the measured load process curve from traction substations is above 0.89, and the maximum error between the simulated and measured characteristic values in load process is not more than 6.85%, which can improve the accuracy of the simulation results by 12.91% in comparison to the tiled operation diagram.
-
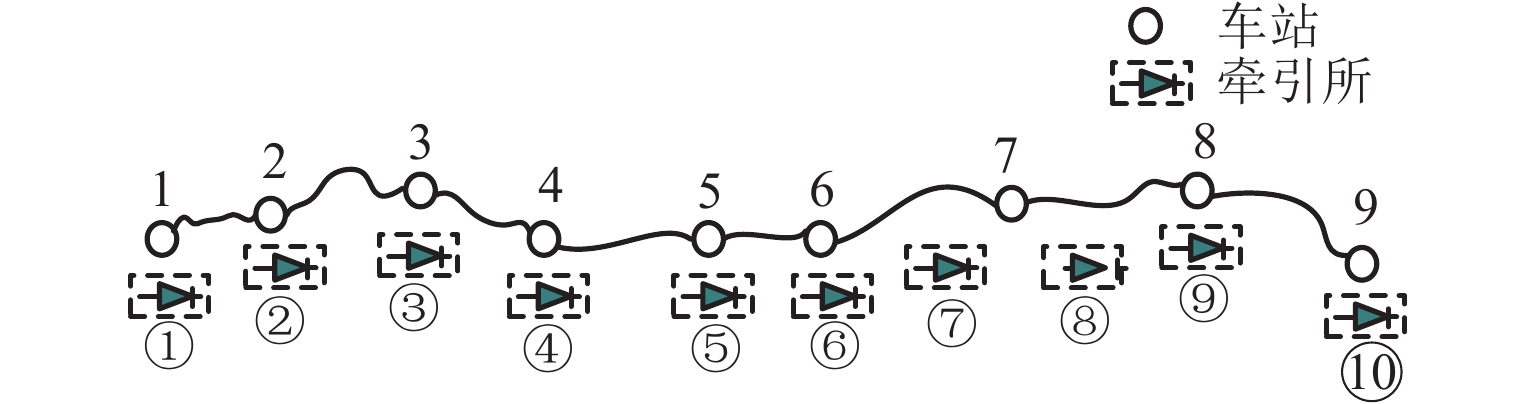
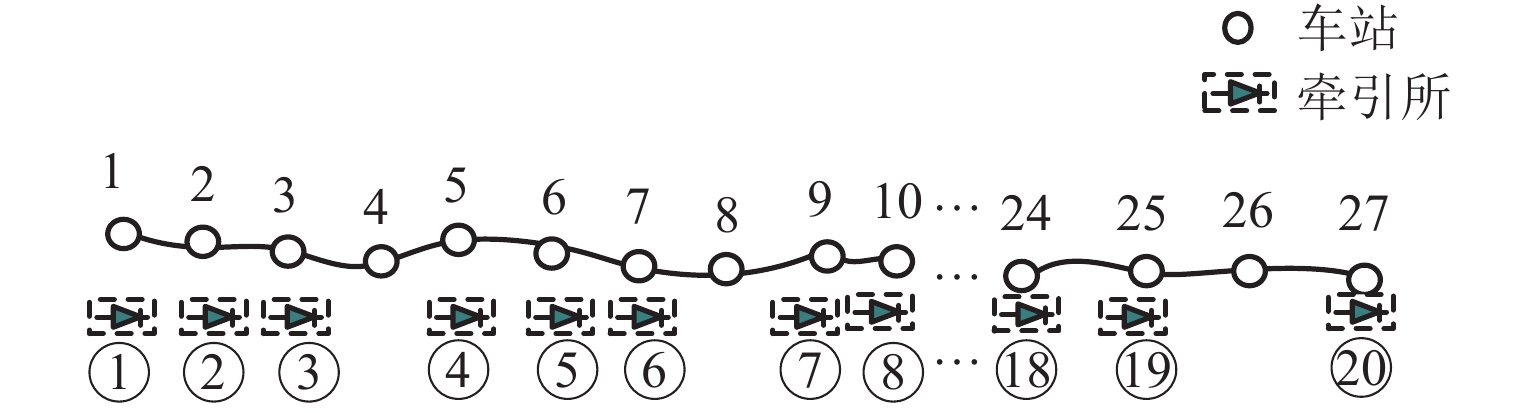
表 1 车站位置信息
Table 1. Information of station locations
车站编号 位置/km 车站编号 位置/km 1 0.243 6 13.900 2 2.456 7 18.461 3 4.568 8 23.322 4 7.804 9 25.650 5 10.670 表 2 车公里能耗与吨公里能耗实测与仿真对比
Table 2. Comparison of measured and simulated energy consumption of trains per km and per ton-km
kW•h 工况 车公里能耗 吨公里能耗 CaseA1 2.179 0.045 CaseA2 2.298 0.047 CaseA3 2.171 0.045 表 3 高峰小时负荷过程统计表
Table 3. Statistics of load process at peak hour
工况 整流机组
电流/A逆变装置
电流/A牵引
能耗/
(kW•h)反馈
能量/
(kW•h)装置节
能率/%均值 峰值 均值 峰值 CaseB1 262.4 1508.5 36.2 708.6 514.450 77.570 15.0 CaseB2 294.1 1471.2 39.7 597.6 580.830 90.810 16.5 CaseB3 280.4 1488.3 38.3 698.2 547.900 82.610 15.0 -
[1] 彭其渊,朱松年,王培. 网络列车运行图的数学模型及算法研究[J]. 铁道学报,2001,23(1): 1-8. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-8360.2001.01.001PENG Qiyuan, ZHU Songnian, WANG Pei. Study on a general optimization model and its solution for railway network train diagram[J]. Journal of the China Railway Society, 2001, 23(1): 1-8. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-8360.2001.01.001 [2] 彭其渊,王超宇,鲁工圆. 基于到发线运用方案的列车到达追踪间隔时间压缩方法及仿真研究[J]. 中国铁道科学,2020,41(2): 131-138. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4632.2020.02.16PENG Qiyuan, WANG Chaoyu, LU Gongyuan. Compression method and simulation of train arrival interval based on utilization of arrival-departure track[J]. China Railway Science, 2020, 41(2): 131-138. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4632.2020.02.16 [3] ALBRECHT T, OETTICH S. A new integrated approach to dynamic-schedule synchronization and energy-saving train control[J]. Computers in Railways Ⅷ, 2002, 13: 847-856. [4] SU S, LI X, TANG T, et al. A subway train timetable optimization approach based on energy-efficient operation strategy[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2013, 14(2): 883-893. doi: 10.1109/TITS.2013.2244885 [5] 高豪,张亚东,郭进,等. 基于动态规划的列车节能运行两阶段优化方法[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2020,55(5): 946-954. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.20191208GAO Hao, ZHANG Yadong, GUO Jin, et al. Two-stage optimization method of train energy-efficient operation based on dynamic programming[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2020, 55(5): 946-954. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.20191208 [6] GONZÁLEZ-GIL A, PALACIN R, BATTY P, et al. A systems approach to reduce urban rail energy consumption[J]. Energy Conversion and Management, 2014, 80: 509-524. doi: 10.1016/j.enconman.2014.01.060 [7] FAN B, ROBERTS C, WESTON P. A comparison of algorithms for minimising delay costs in disturbed railway traffic scenarios[J]. Journal of Rail Transport Planning & Management, 2012, 2(1/2): 23-33. [8] 柏赟,周雨鹤,邱宇,等. 长大下坡道区间地铁列车节能操纵方法[J]. 中国铁道科学,2018,39(1): 108-115. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4632.2018.01.15BAI Yun, ZHOU Yuhe, QIU Yu, et al. Energy-efficient control method for subway train in section with long heavy down grade[J]. China Railway Science, 2018, 39(1): 108-115. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4632.2018.01.15 [9] 王青元,冯晓云. 列车准点节能运行的控制工况最优切换研究[J]. 中国铁道科学,2016,37(2): 91-98. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4632.2016.02.13WANG Qingyuan, FENG Xiaoyun. Optimal switching for control conditions of punctual and energy efficient operation of train[J]. China Railway Science, 2016, 37(2): 91-98. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4632.2016.02.13 [10] 王青元,冯晓云,朱金陵,等. 考虑再生制动能量利用的高速列车节能最优控制仿真研究[J]. 中国铁道科学,2015,36(1): 96-103. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4632.2015.01.14WANG Qingyuan, FENG Xiaoyun, ZHU Jinling, et al. Simulation study on optimal energy-efficient control of high speed train considering regenerative brake energy[J]. China Railway Science, 2015, 36(1): 96-103. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4632.2015.01.14 [11] 刘炜,吴拓剑,禹皓元,等. 直流牵引供电系统地面储能装置建模与仿真分析[J]. 电工技术学报,2020,35(19): 4207-4215.LIU Wei, WU Tuojian, YU Haoyuan, et al. Modeling and simulation of way-side energy storage devices in DC traction power supply system[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2020, 35(19): 4207-4215. [12] 刘炜,张扬鑫,张戬,等. 考虑牵引所多运行状态的城轨交直流供电计算[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2020,55(6): 1163-1170. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.20190854LIU Wei, ZHANG Yangxin, ZHANG Jian, et al. Calculation of urban rail AC/DC power supply with traction substation in multi-operation modes[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2020, 55(6): 1163-1170. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.20190854 [13] 盛昭,蔡伯根,上官伟,等. 一种结合时刻表调整的列车节能驾驶优化方法[J]. 铁道学报,2019,41(10): 68-75. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8360.2019.10.010SHENG Zhao, CAI Baigen, SHANGGUAN Wei, et al. Energy-efficient optimization method for train operation combining driving strategy and timetabling[J]. Journal of the China Railway Society, 2019, 41(10): 68-75. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8360.2019.10.010 [14] 李正洋,赵军,彭其渊. 考虑多交路多编组的城市轨道线路列车交路计划优化[J]. 铁道学报,2020,42(6): 1-11. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8360.2020.06.001LI Zhengyang, ZHAO Jun, PENG Qiyuan. Optimizing the train service route plan in an urban rail transit line with multiple service routes and multiple train sizes[J]. Journal of the China Railway Society, 2020, 42(6): 1-11. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8360.2020.06.001 [15] 魏润斌,杜鹏,杨雍彬,等. 地铁列车再生制动能量利用分析与时刻表优化方法研究[J]. 铁道学报,2020,42(8): 1-9. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8360.2020.08.001WEI Runbin, DU Peng, YANG Yongbin, et al. Analysis on utilization of regenerative braking energy for metro trains and research on timetable optimization method[J]. Journal of the China Railway Society, 2020, 42(8): 1-9. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8360.2020.08.001 [16] 丁勇,刘海东,栢赟,等. 地铁列车节能运行的两阶段优化模型算法研究[J]. 交通运输系统工程与信息,2011,11(1): 96-101. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6744.2011.01.016DING Yong, LIU Haidong, BAI Yun, et al. A two-level optimization model and algorithm for energy-efficient urban train operation[J]. Journal of Transportation Systems Engineering and Information Technology, 2011, 11(1): 96-101. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6744.2011.01.016 [17] 曹佳峰,刘斌. 基于2阶段优化的高速列车节能运行仿真研究[J]. 铁道科学与工程学报,2018,15(4): 821-828. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7029.2018.04.001CAO Jiafeng, LIU Bin. Research on simulation for energy-saving operation of high-speed trains based on two-stage optimization[J]. Journal of Railway Science and Engineering, 2018, 15(4): 821-828. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7029.2018.04.001 [18] 曲健伟,冯晓云,王青元,等. 考虑冲击限制和响应下列车参考速度仿真模型[J]. 哈尔滨工业大学学报,2019,51(9): 125-129. doi: 10.11918/j.issn.0367-6234.201808069QU Jianwei, FENG Xiaoyun, WANG Qingyuan, et al. Simulation model of train reference speed considering jerk limitation and response process[J]. Journal of Harbin Institute of Technology, 2019, 51(9): 125-129. doi: 10.11918/j.issn.0367-6234.201808069 -





 下载:
下载: