Mechanical Characteristics of Existing Tunnel Structure Affected by Super Deep Loess Landslide
-
摘要:
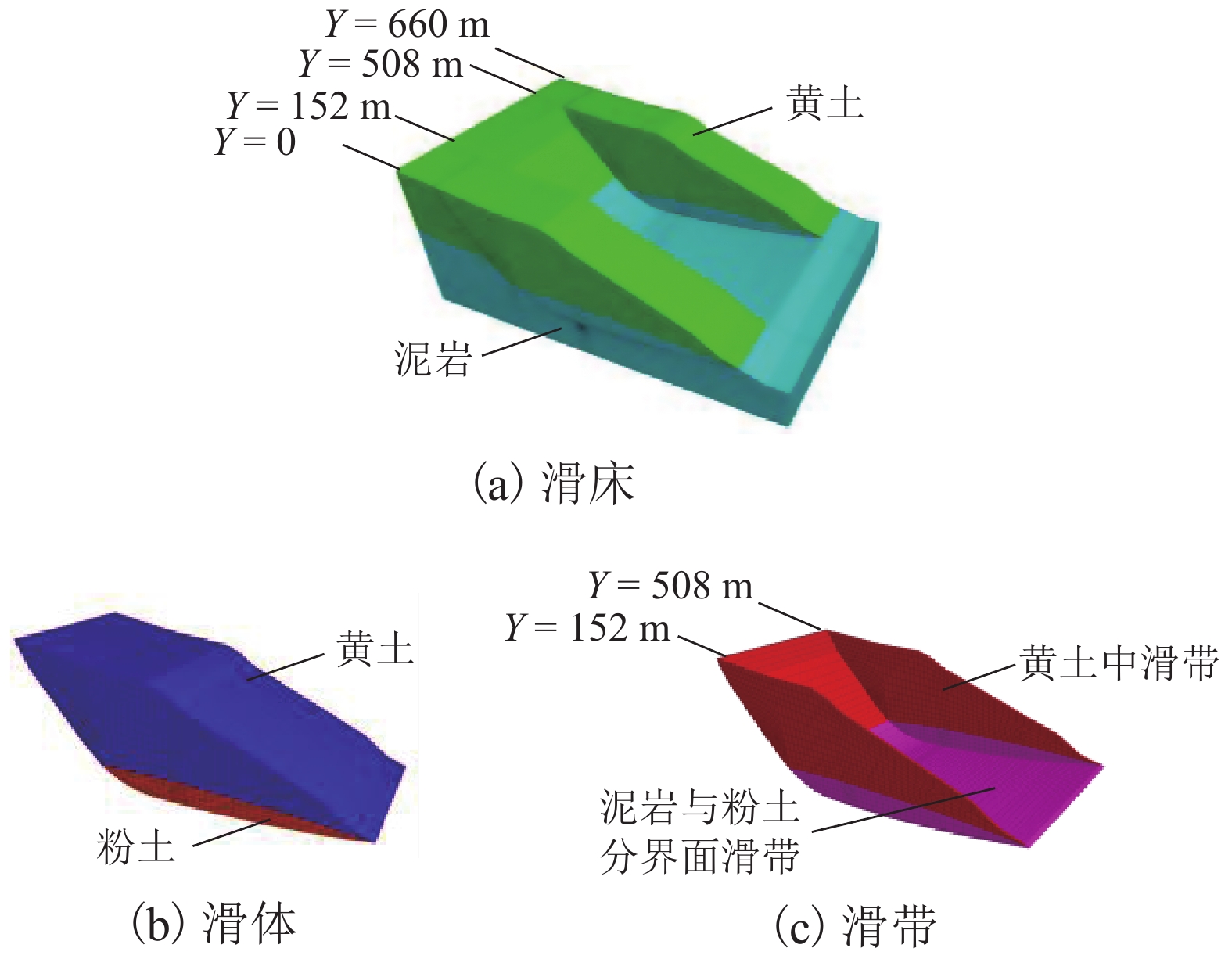
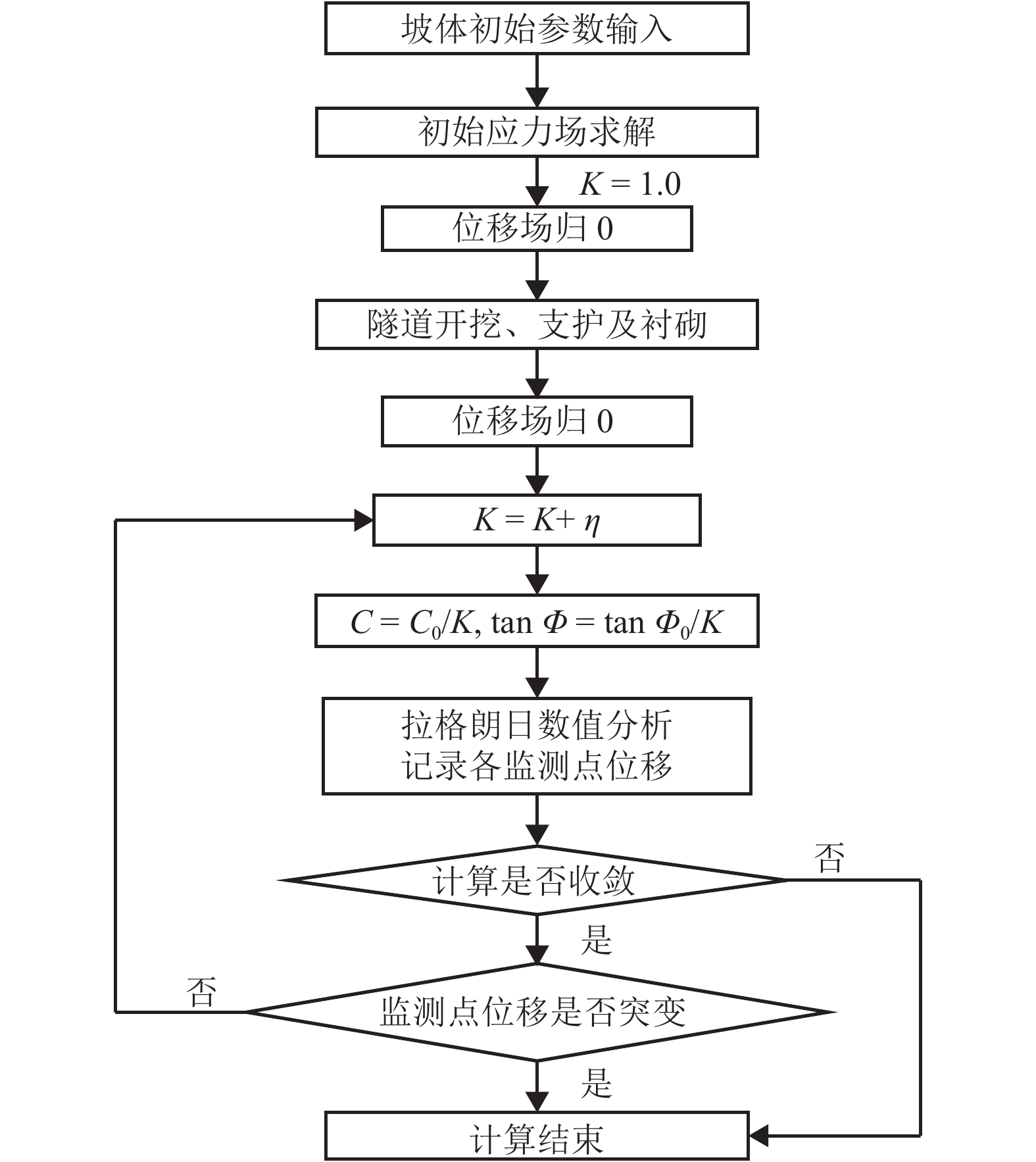
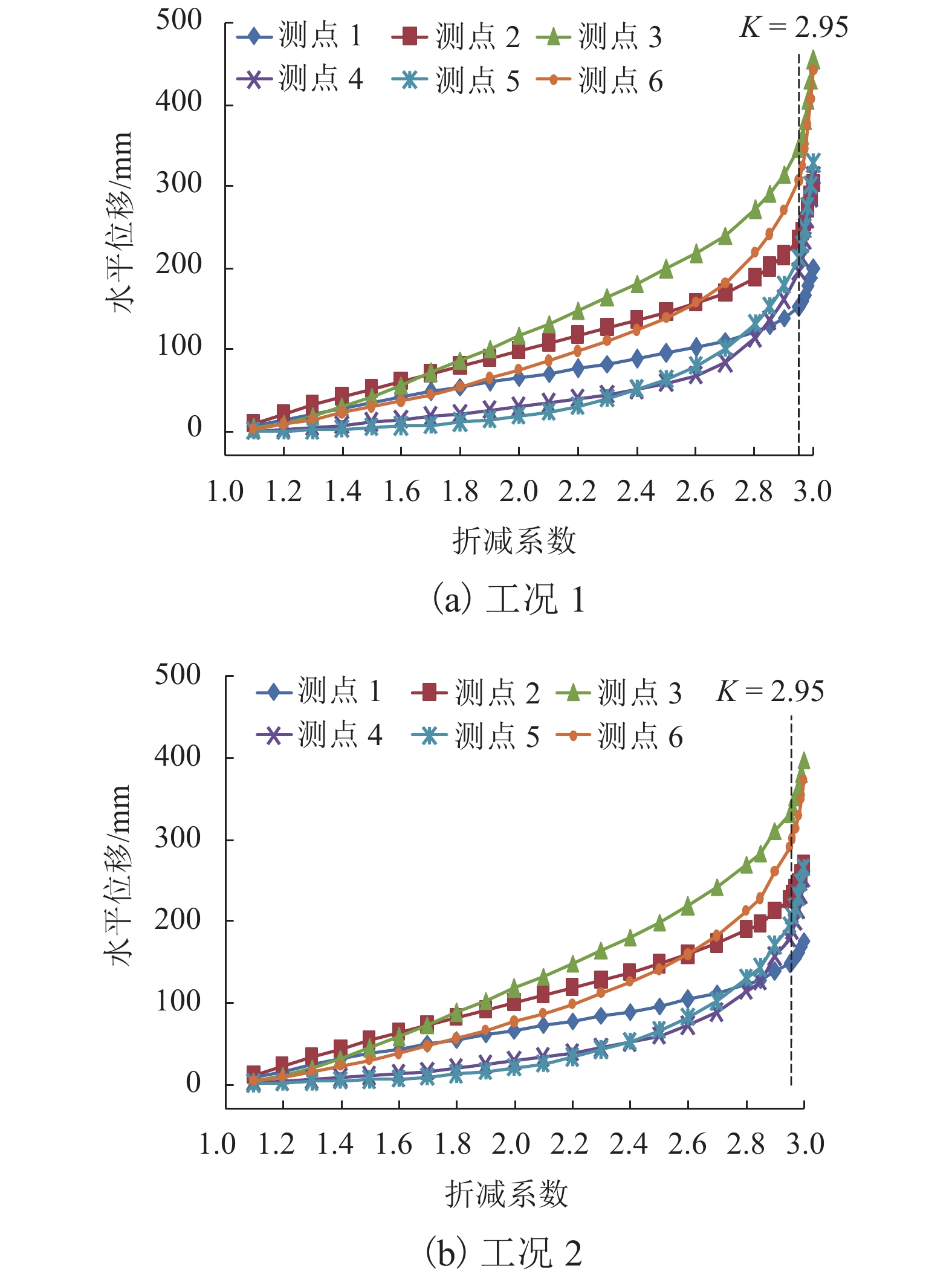
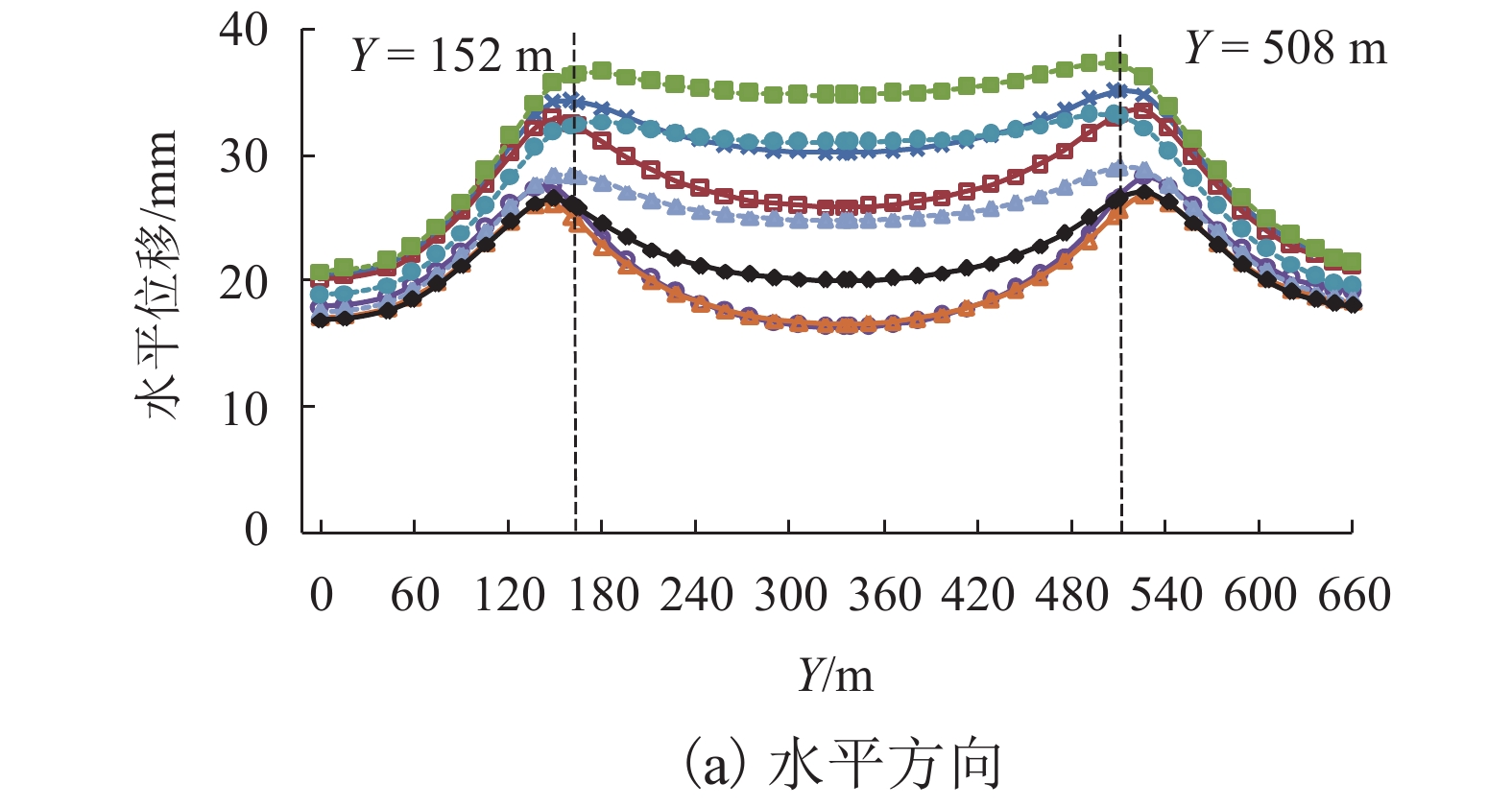
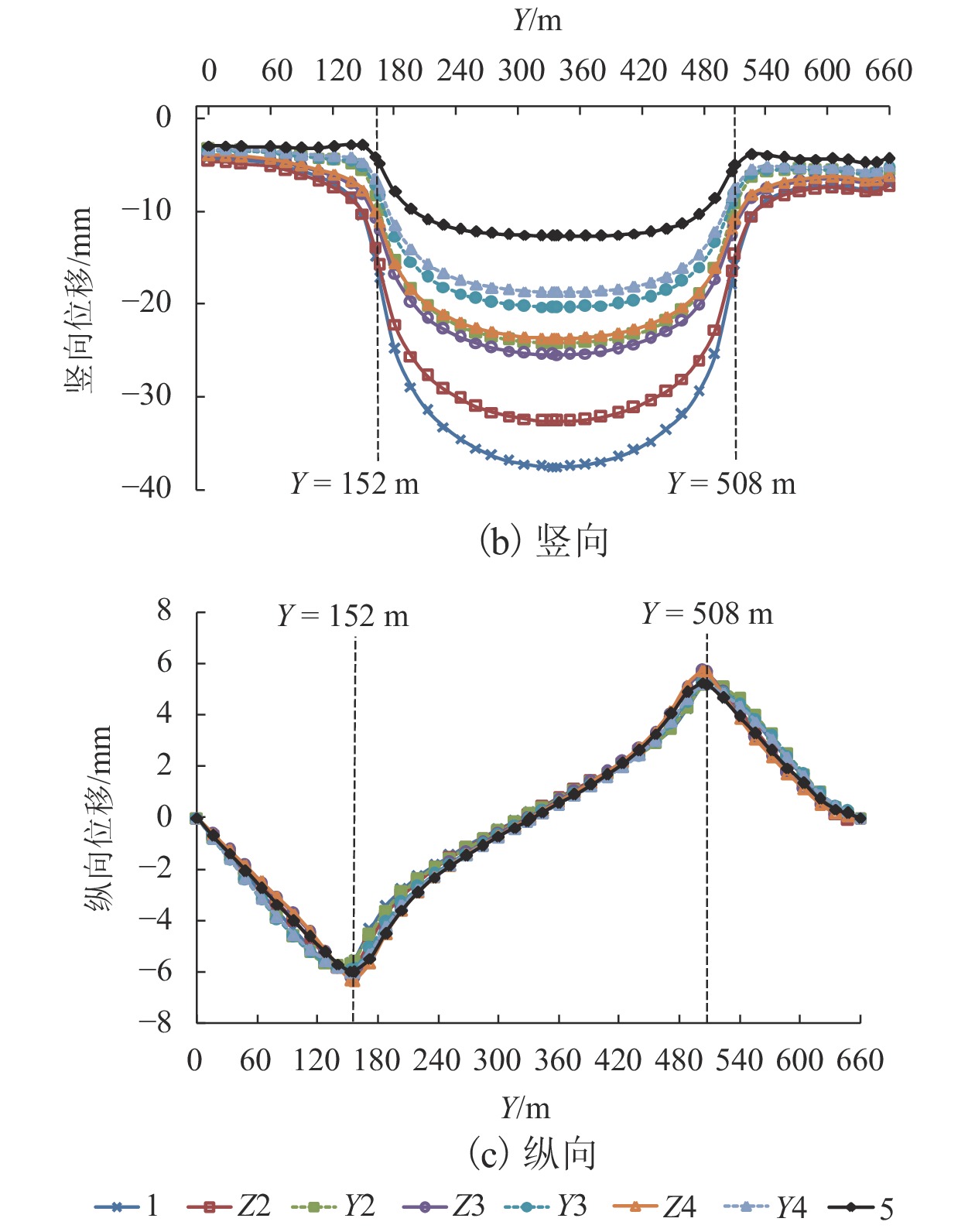
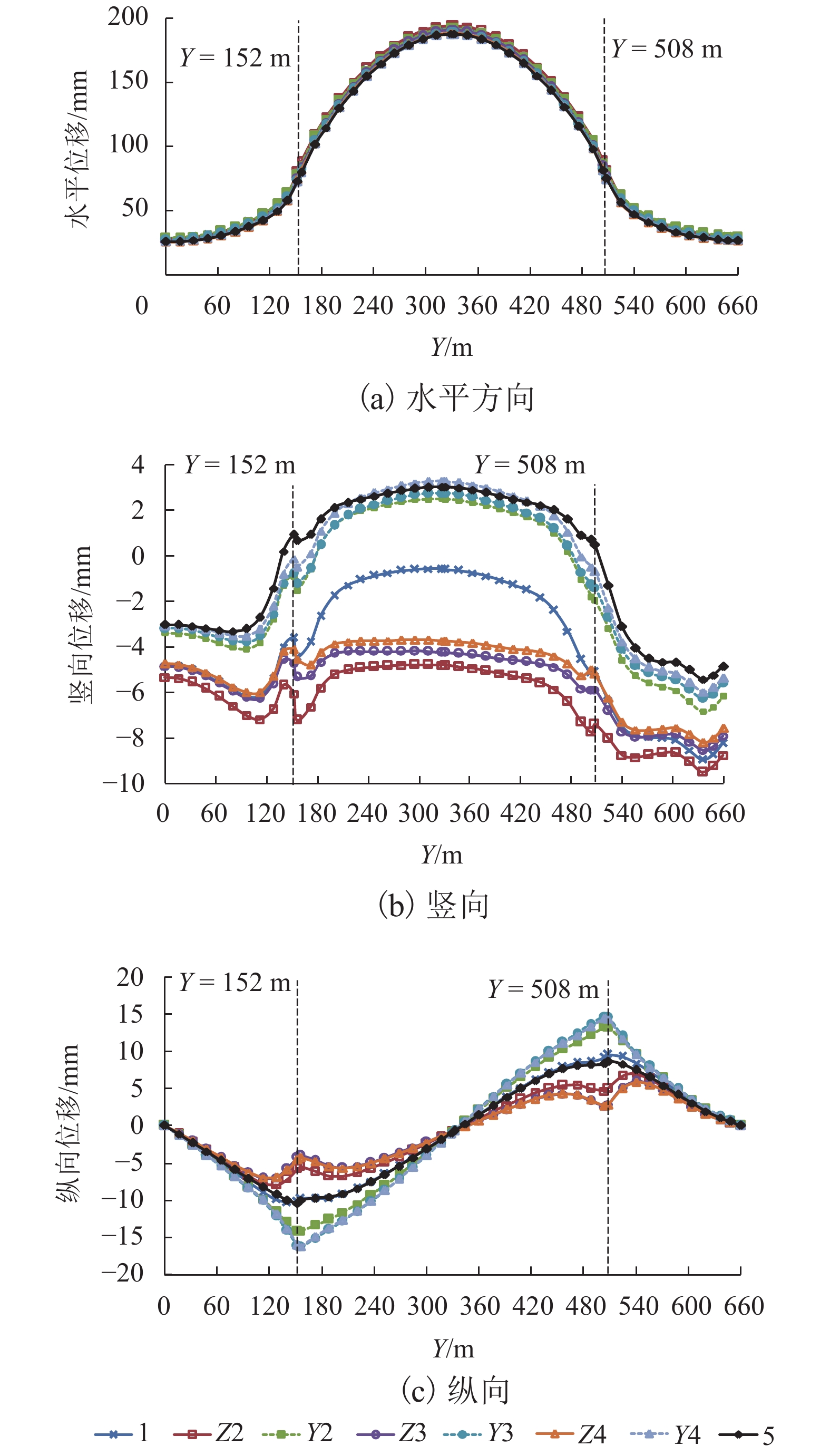
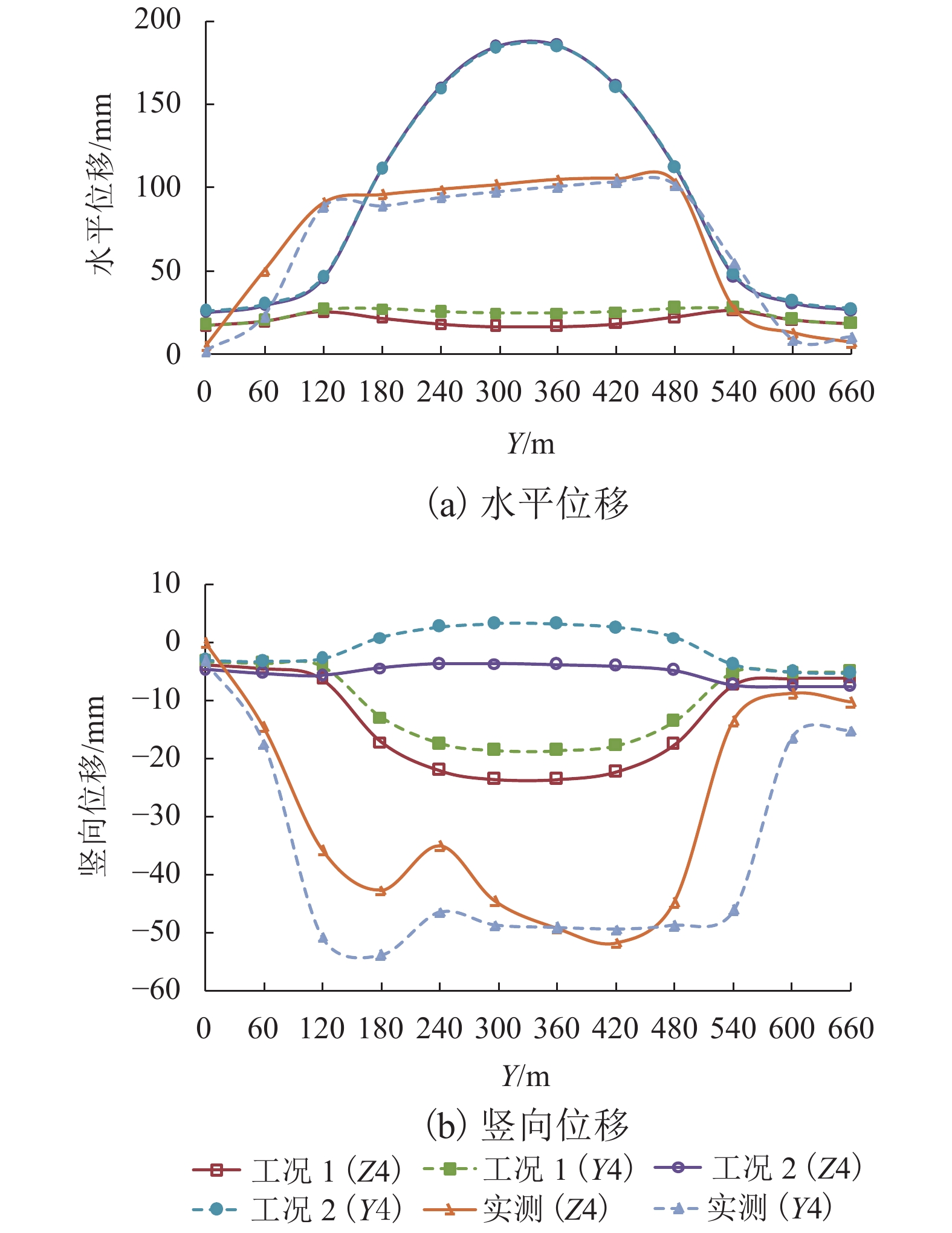
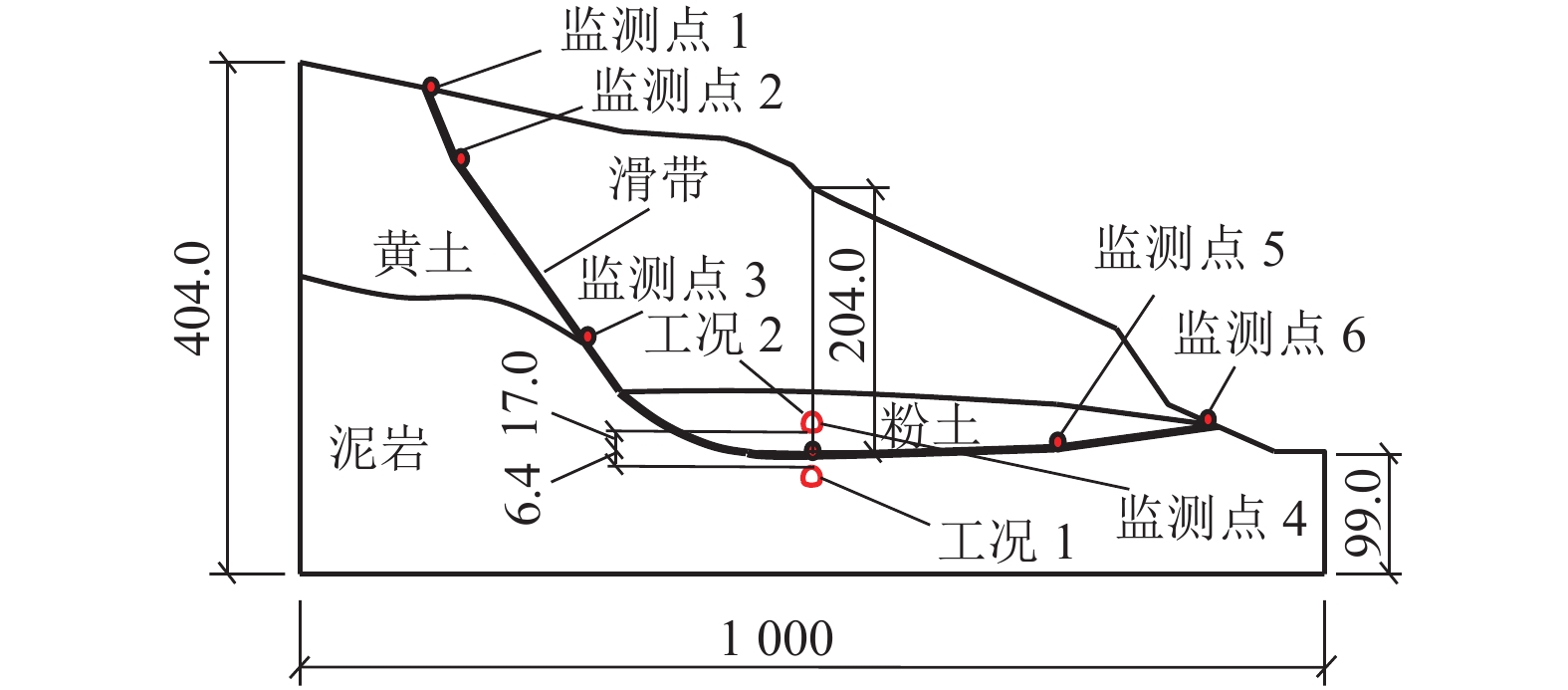
黄土地区滑坡灾害频发,滑坡尤其是超深层滑坡对既有隧道结构受力变形有重要影响,隧道滑坡体系变形特性、力学响应一直是学术界和工程界关注的焦点. 以某超深层滑坡地质灾害中的铁路隧道工程为依托,建立了“超深层黄土边坡-滑带-隧道”FLAC3D三维数值模型;利用基于位移突变的局部强度折减法模拟坡体失稳临界状态;针对不同滑带隧道相对位置,揭示了滑坡诱发条件下既有隧道衬砌结构受力及变形特征变化规律,并结合现场实测数据及结构破损情况初步分析了依托工程事故原因. 数值模拟结果显示:当滑带在隧道上方时,受中间围岩“牵动”作用明显,墙脚水平位移最大值27.83 mm;当滑带在隧道下方时,隧道“坐船”作用显著,墙脚水平位移最大值185.61 mm;当隧道位于滑面上方时危险性更高. 实测结果显示:沿纵向隧道位移呈“坐船”状,墙脚水平位移最大值为105.35 mm,小于滑带在隧道下方时工况;依托工程为黄土(粉土)-基岩滑坡,隧道位于滑体内,且滑坡仍处于蠕动状态,还未达到滑动临界状态.
Abstract:Landslide disasters occur frequently in loess area. Landslides, especially super deep landslides, have a significant impact on the stress and deformation of existing tunnel structures. The deformation characteristics and mechanical responses of tunnel-landslide systems are extremely complex and have been the focus of academic and engineering researchers. Based on a railway tunnel project in a super deep landslide geological disaster, a three-dimensional numerical model of the "super deep loess slope-sliding zone-tunnel" system was established using FLAC3D. The local strength reduction method based on displacement mutation was used to simulate the critical state of slope instability, and variation laws of the mechanical and deformation characteristics of the existing lining structure induced by landslide were analyzed for cases of different relative positions between sliding zones and tunnels. In addition, combined with field measurements and structural damage conditions, the causes of engineering accidents were preliminarily analyzed. Numerical simulations indicate that when the sliding zone is above the tunnel, the surrounding rock exerts a significant pulling effect on the tunnel, and the maximum horizontal displacement of 27.83 mm occurs at the wall foot; when the sliding zone is below the tunnel, the tunnel structure has an obvious overall lateral translation, resulting in a maximum horizontal displacement of 185.61 mm at the wall foot. The most dangerous case is when the tunnel is above the sliding surface. The field measurements indicate that the tunnel has an overall lateral translation perpendicular to the longitudinal axis. The maximum translation (105.35 mm) at the wall foot is smaller than the case when the sliding zone locates below the tunnel. Results also show that the selected tunnel project was built in a loess (silt)-bedrock landslide, which is still in a creeping state and has not yet reached the sliding critical state.
-
Key words:
- Tunnel /
- landslides /
- strength reduction method /
- lining /
- mechanical characteristics /
- deformation
-
表 1 地层及结构物理力学参数
Table 1. Physical parameters of strata and structures
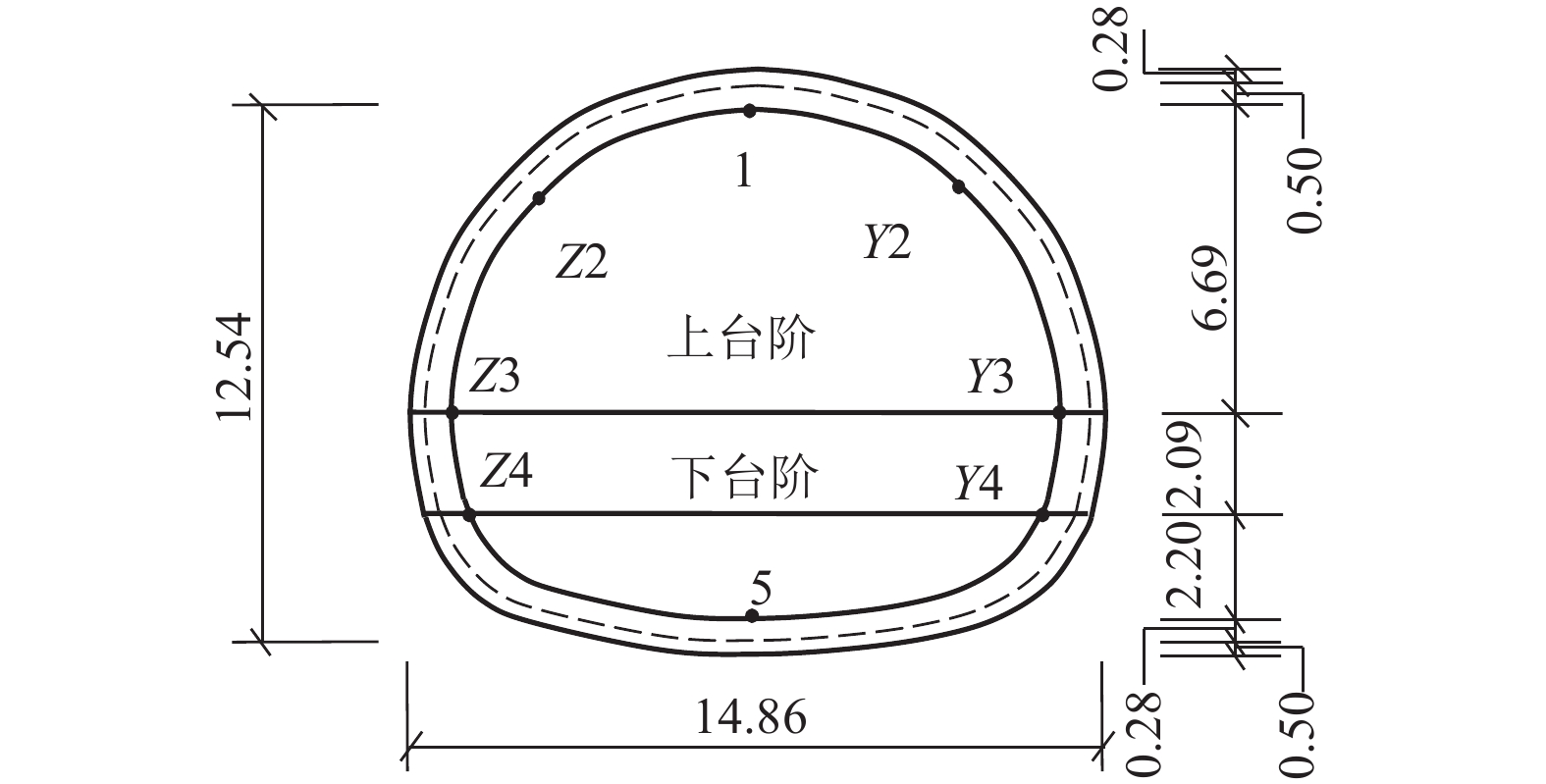
名称 弹性模量 E/MPa 容重 γ/(kN•m−3) 内聚力 C/kPa 内摩擦角 Φ/(°) 抗拉强度/kPa 泊松比 黄土 Q3 500 18.0 23.6 25.3 40 0.35 黄土中滑带初始参数 500 18.0 23.6 25.3 40 0.35 粉土 800 20.2 22.4 30.4 40 0.38 粉土中滑带初始参数 800 20.2 22.4 30.4 40 0.38 泥岩 1 100 20.6 30.4 36.1 110 0.35 初期支护 23 000 23.0 0.20 二次衬砌 C40 32 500 25.0 0.20 表 2 K = 2.96时隧道衬砌位移
Table 2. Displacement of tunnel lining at K = 2.96
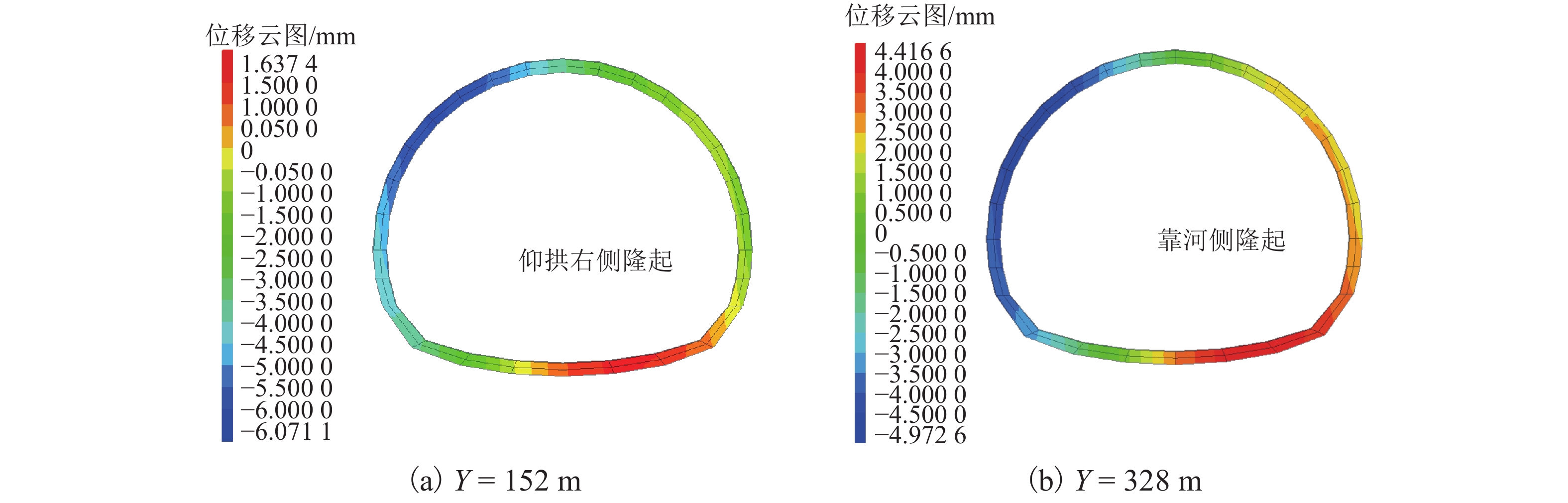
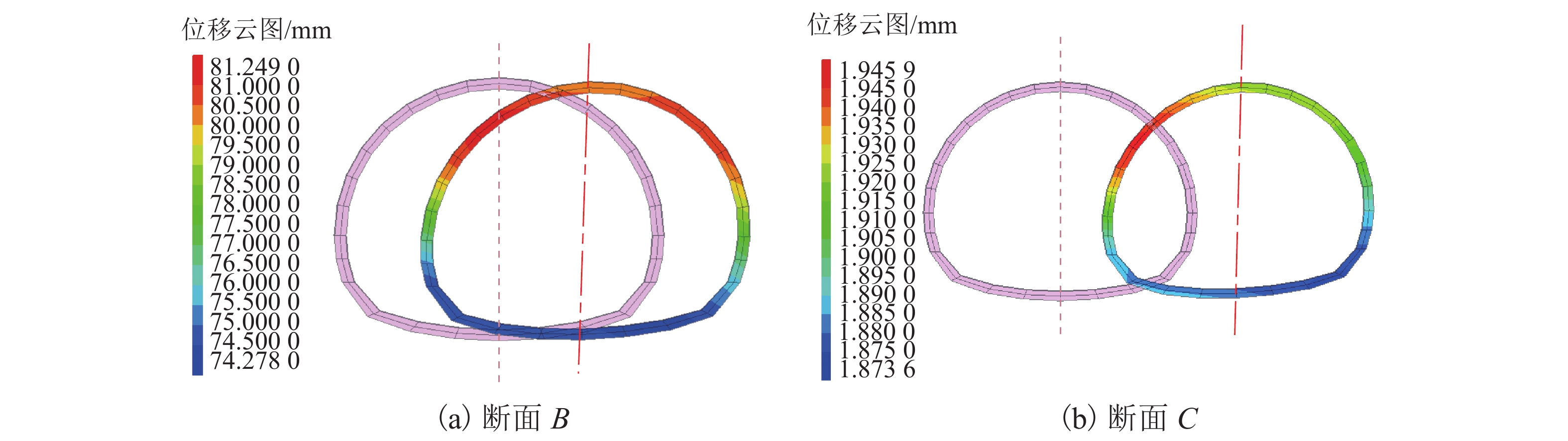
mm 工况 位置 方向 测点编号 1 Y2 Y3 Y4 Z2 Z3 Z4 5 1 B 水平 34.15 36.28 32.29 28.33 32.39 26.11 25.01 25.99 竖向 −14.89 −8.25 −7.17 −6.41 −13.84 −10.66 −9.96 −4.06 竖向或水平 0.44 0.23 0.22 0.23 0.43 0.41 0.40 0.16 C 水平 30.11 34.69 30.93 24.77 25.80 16.28 16.53 20.00 竖向 −37.48 −24.19 −20.31 −18.66 −32.57 −25.42 −23.65 −12.62 竖向或水平 1.24 0.70 0.66 0.75 1.26 1.56 1.43 0.63 2 B 水平 78.80 78.25 74.54 72.54 80.23 76.08 74.07 72.89 竖向 −3.60 −0.89 −0.78 −0.13 −6.07 −4.71 −4.11 0.93 竖向或水平 0.05 0.01 0.01 0.00 0.08 0.06 0.06 −0.01 C 水平 192.63 192.07 189.05 187.86 194.46 190.94 188.67 187.89 竖向 −0.59 2.49 2.75 3.28 −4.81 −4.24 −3.73 3.02 竖向或水平 0.00 −0.01 −0.01 −0.02 0.02 0.02 0.02 −0.02 注:竖向、水平位移分别以z轴正向、x轴正向为正;B、C分别位于Y = 152 m(滑体前端边界)、Y = 328 m(滑体中部). 表 3 K = 2.96时典型断面隧道衬砌主应力汇总
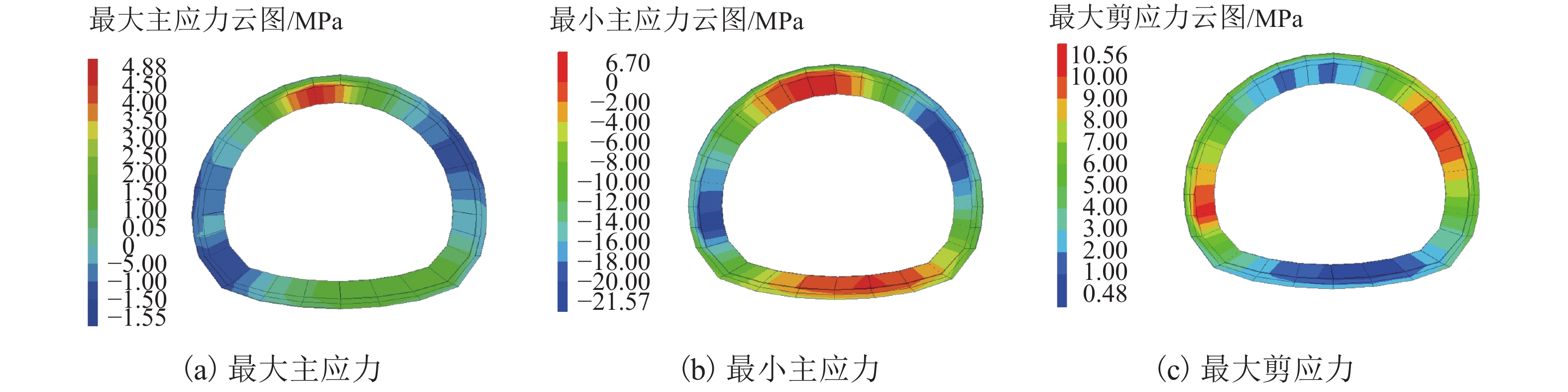
Table 3. Summary of principal stresses of tunnel lining with typical section when K = 2.96
工况 断面
位置埋深/m 最大主应力 最小主应力 最大剪应力 应力值/MPa 增长率/% 应力值 增长率/% 应力值
/MPa增长率/% 1 A 179 2.00 (0.29) 590 −10.45 (−8.48) 23 5.05 (4.15) 22 B 4.32 (0.30) 1340 −14.35 (−8.54) 68 7.14 (4.19) 70 C 4.88 (0.32) 1425 −21.57 (−8.55) 152 10.56 (4.19) 152 2 A 218 1.91 (0.24) 696 −11.07 (−8.08) 37 5.36 (3.95) 36 B 9.15 (0.54) 1594 −20.56 (−8.28) 148 12.83 (4.08) 214 C 1.48 (0.80) 85 −15.86 (−8.38) 89 7.67 (4.19) 83 注:括号中数字为隧道开挖支护后衬砌应力(折减前);断面 A位于 Y =76 m (滑体外). -
[1] 刘文红. 黄土高原滑坡发育背景与成灾模[D]. 西安: 长安大学, 2016. [2] 杨光华,钟志辉,张玉成,等. 滑坡灾害的机制与力学特性分析[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2016,35(增刊2): 4009-4017.YANG Guanghua, ZHONG Zhihui, ZHANG Yucheng, et al. Analysis of mechanism and mechanical characteristics of landslide disaster[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2016, 35(S2): 4009-4017. [3] 马惠民,吴红刚. 山区高速公路高边坡病害防治实践[J]. 铁道工程学报,2011(7): 34-41. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2106.2011.07.007MA Huimin, WU Honggang. Practices on high slope disease control of highways in mountainous area[J]. Chinese Journal of Railway Engineering Society, 2011(7): 34-41. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2106.2011.07.007 [4] 柳墩利. 隧道开挖对边坡稳定性的影响规律[J]. 铁道建筑,2018,58(7): 68-71. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-1995.2018.07.17LIU Dunli. Influence of tunnel excavation on side-slope stability[J]. Railway Engineering, 2018, 58(7): 68-71. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-1995.2018.07.17 [5] 骆晓依,苏永华,廖君橙. 隧道开挖扰动对古滑坡稳定性的影响分析[J]. 铁道科学与工程学报,2019,16(8): 2028-2034.LUO Xiaoyi, SU Yonghua, LIAO Juncheng. Analysis on influence of tunnel excavation disturbance on stability of ancient landslide[J]. Journal of Railway Science and Engineering, 2019, 16(8): 2028-2034. [6] 刘天哲,李红卫,王宇. 坡体病害地段的隧道变形机理分析[J]. 兰州大学学报(自然科学版),2011,47(Proceedings): 36-40.LIU Tianzhe, LI Hongwei, WANG Yu. Deformation mechanism analysis on tunnel in slope disaster section[J]. Journal of Lanzhou University (Natural Sciences), 2011, 47(Proceedings): 36-40. [7] 王雷,沈远,白朝能. 铁路隧道斜穿滑坡体受力变形特征三维分析[J]. 铁道工程学报,2017(1): 16-21. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2106.2017.01.004WANG Lei, SHE Yuan, BAI Chaoneng. Three- dimensional analysis of force and deformation characteristics of oblique crossing of railway tunnel with landslide[J]. Journal of Railway Engineering Society, 2017(1): 16-21. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2106.2017.01.004 [8] NOFERINI L, PIERACCINI M, MECATTI D, et al. Using GB-SAR technique to monitor slow moving landslide[J]. Engineering Geology, 2007, 95(3/4): 88-98. [9] 尹静,邓荣贵,钟志彬,等. 横穿滑坡变形区隧道受力变形规律及影响因素分析[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2016,35(增刊2): 3615-3625.YIN Jing, DENG Ronggui, ZHONG Zhibin, et al. Stress and deformation laws and influence factors analysis of tunnel across the slope deformation zone[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2016, 35(S2): 3615-3625. [10] 周德培,毛坚强,张鲁新,等. 隧道变形与坡体灾害相互关系及其预测模式[J]. 铁道学报,2002,24(1): 81-86. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-8360.2002.01.018ZHOU Peide, MAO Jianqiang, ZHANG Luxin, et al. Relationship between tunnel deformation with slope disasters and its prediction model[J]. Journal of the China Railway Society, 2002, 24(1): 81-86. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-8360.2002.01.018 [11] 赵金,吴红刚,刘德仁,等. 滑坡内隧道变形模式与荷载计算方法[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2019,30(1): 112-118.ZHAO Jin, WU Honggang, LIU Deren, et al. Deformation model of the tunnels within landslides and methods for loading caculation[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2019, 30(1): 112-118. [12] 闫志雄,王磊,刘新荣,等. 黄土隧道变形与坡体灾害相互关系及预测方法[J]. 地下空间与工程学报,2013,9(增刊2): 1840-1844,1881.YAN Zhixiong, WANG Lei, LIU Xinrong, et al. Correlation and prediction methods of loess tunnel deformation and slope disaster[J]. Chinese Journal of Underground Space and Engineering, 2013, 9(S2): 1840-1844,1881. [13] 秦睿,陈小云. 隧道-滑坡体系应力变形机理模型试验研究[J]. 科学技术与工程,2017,17(29): 363-367. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2017.29.054QIN Rui, CHEN Xiaoyun. Experimental research on stress and strain mechanism of tunnel-land system[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2017, 17(29): 363-367. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2017.29.054 [14] 张治国,马兵兵,黄茂松,等. 山区滑坡诱发既有隧道受力变形影响分析[J]. 岩土力学,2018,39(10): 3555-3564,3572.ZHANG Zhiguo, MA Bingbing, HUANG Maosong, et al. Influence analyses on force and deformation of existing tunnels induced by landslide in mountain region[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2018, 39(10): 3555-3564,3572. [15] 潘卫东,张鲁新,朱元林,等. 坡体病害地段利用隧道变形规律预测山体灾害的方法[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2001,20(4): 502-507. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2001.04.016PAN Weidong, ZHANG Luxin, ZHU Yuanlin, et al. Forecast method of mountain disaster using tunnel deformation law in slope field[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2001, 20(4): 502-507. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2001.04.016 [16] 刘天翔,王忠福. 隧道正交穿越深厚滑坡体的相互影响分析与应对措施[J]. 岩土力学,2018,39(1): 265-274.LIU Tianxiang, WANG Zhongfu. Analysis of interaction when tunnel orthogonal crossing deep-seated landslide and the corresponding control measures[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2018, 39(1): 265-274. [17] 中铁第一勘案设计院集团有限公司. 深层黄土地质灾害综合勘测与整治技术成果报告[R]. 西安: 中铁第一勘案设计院集团有限公司, 2017. -




 下载:
下载: