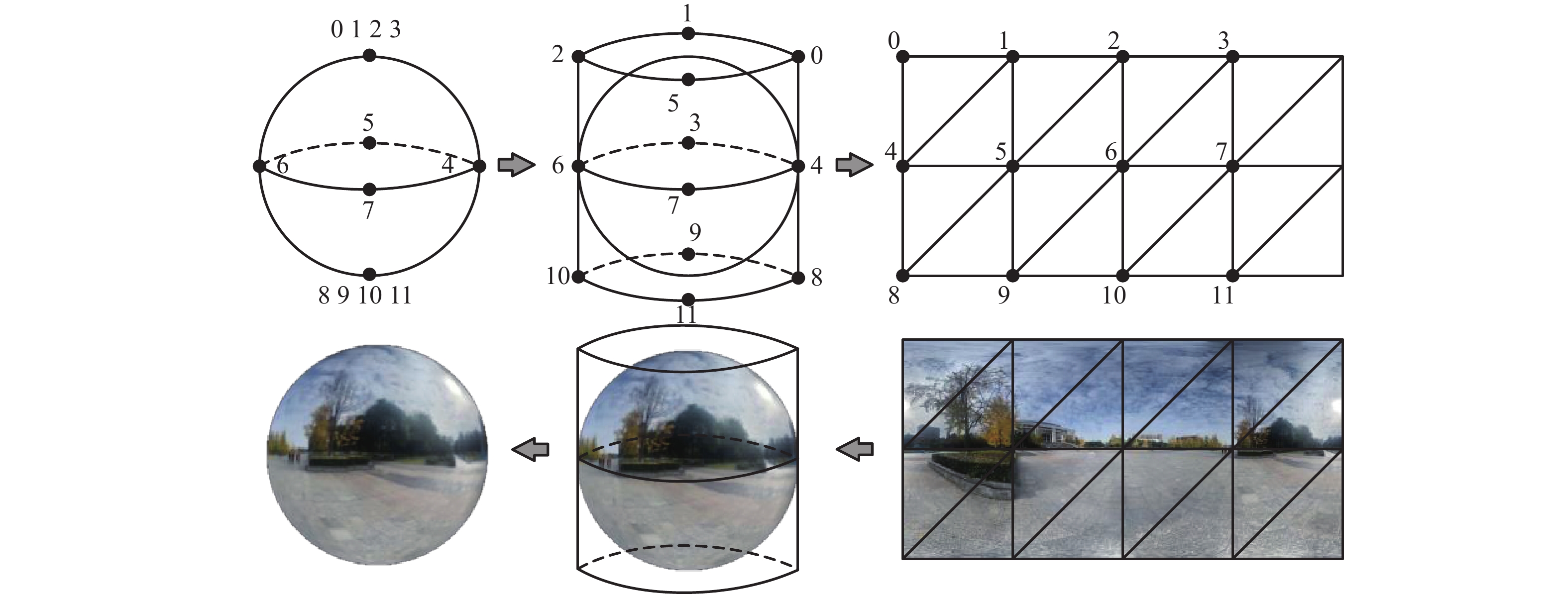
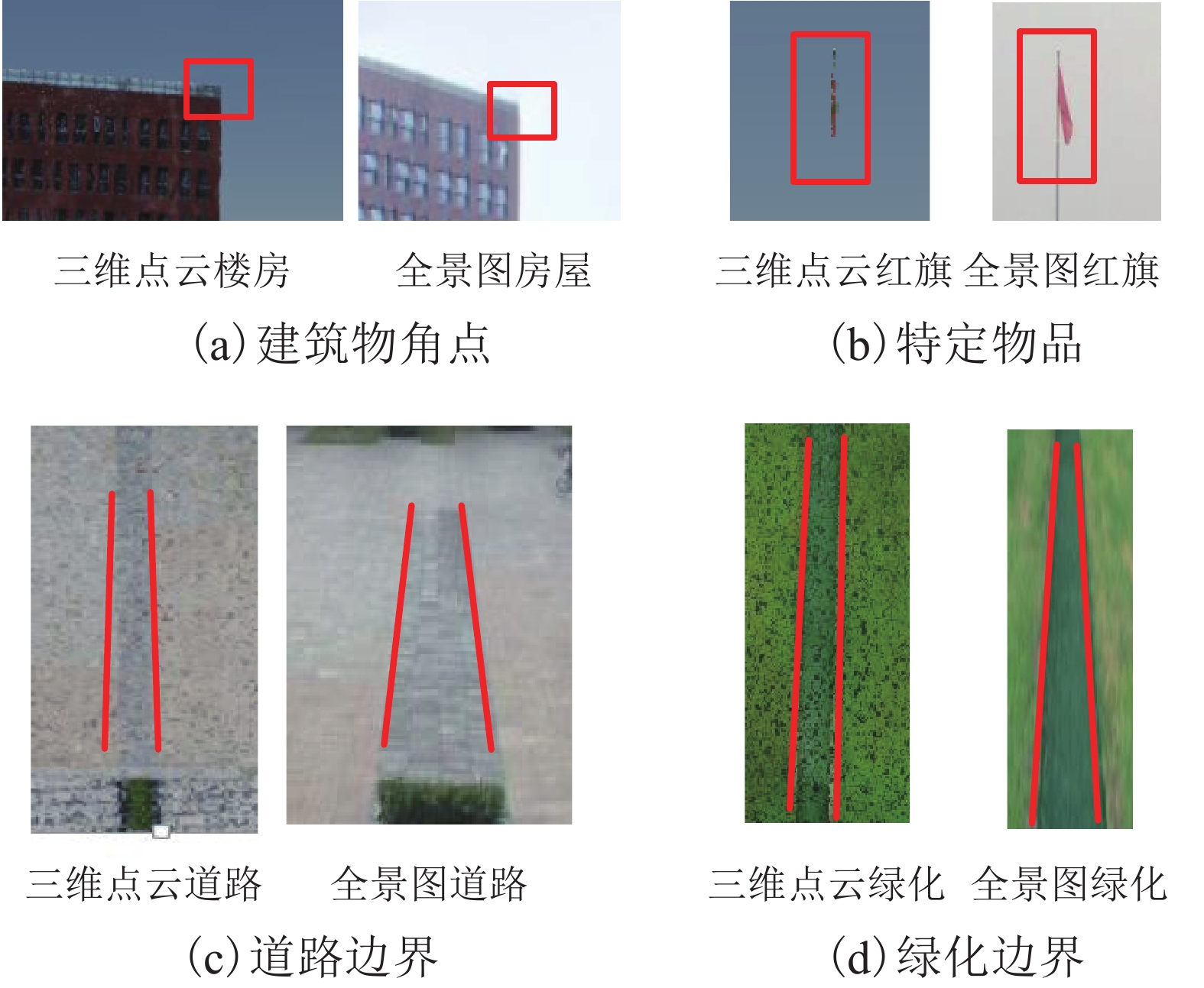
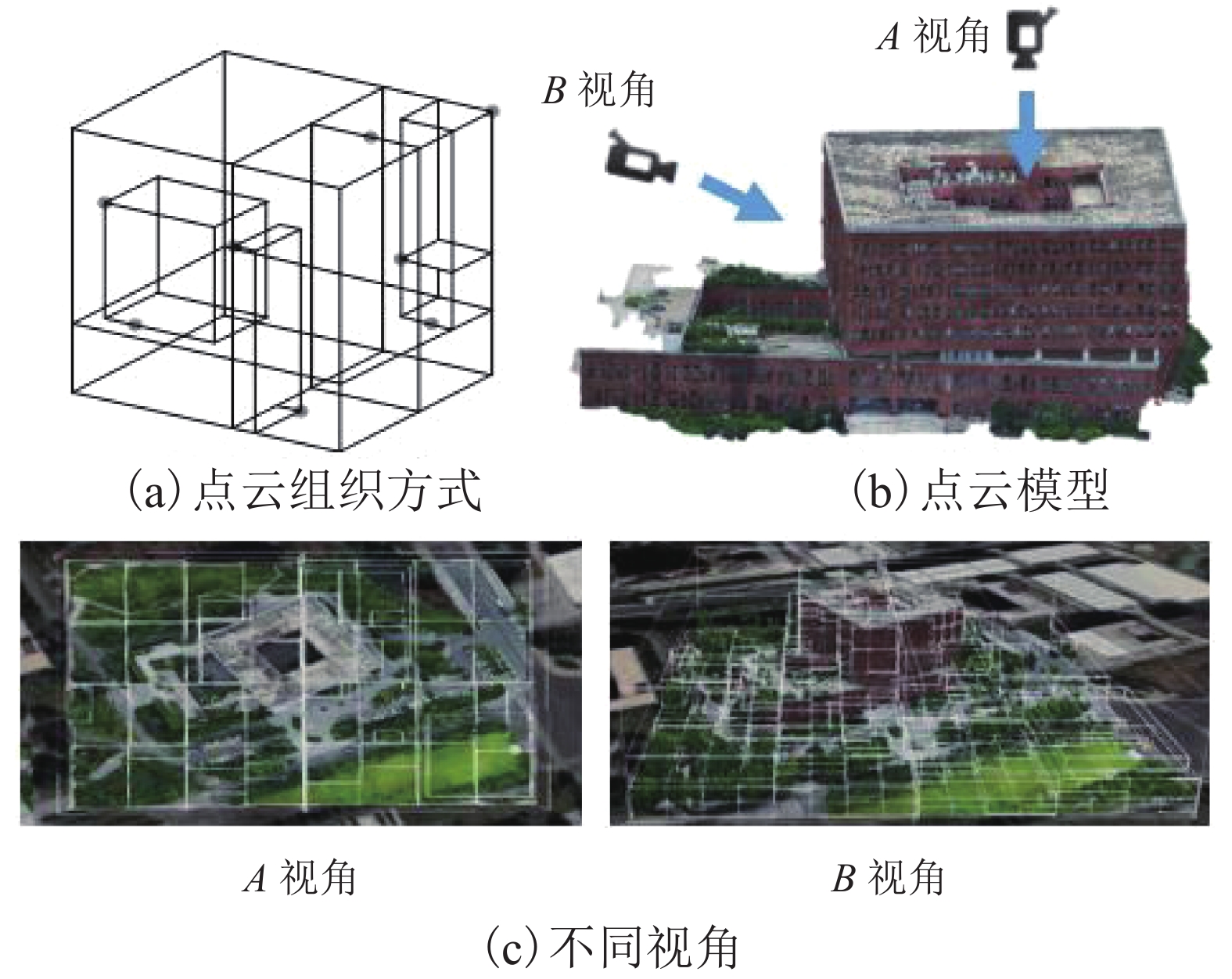
Visualization Method for Fast Fusion of Panorama and Point Cloud Data in Network Environment
-
摘要:
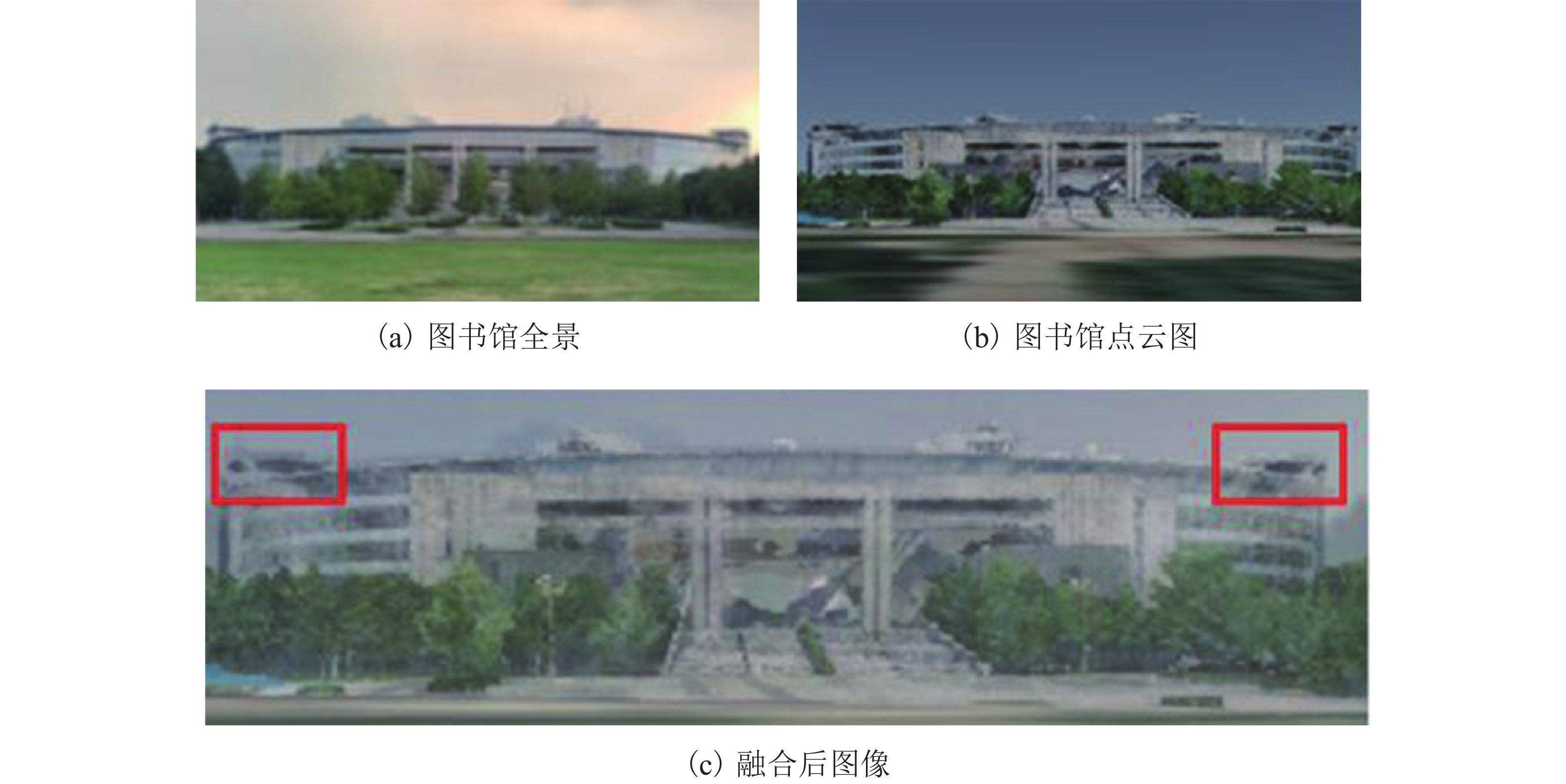
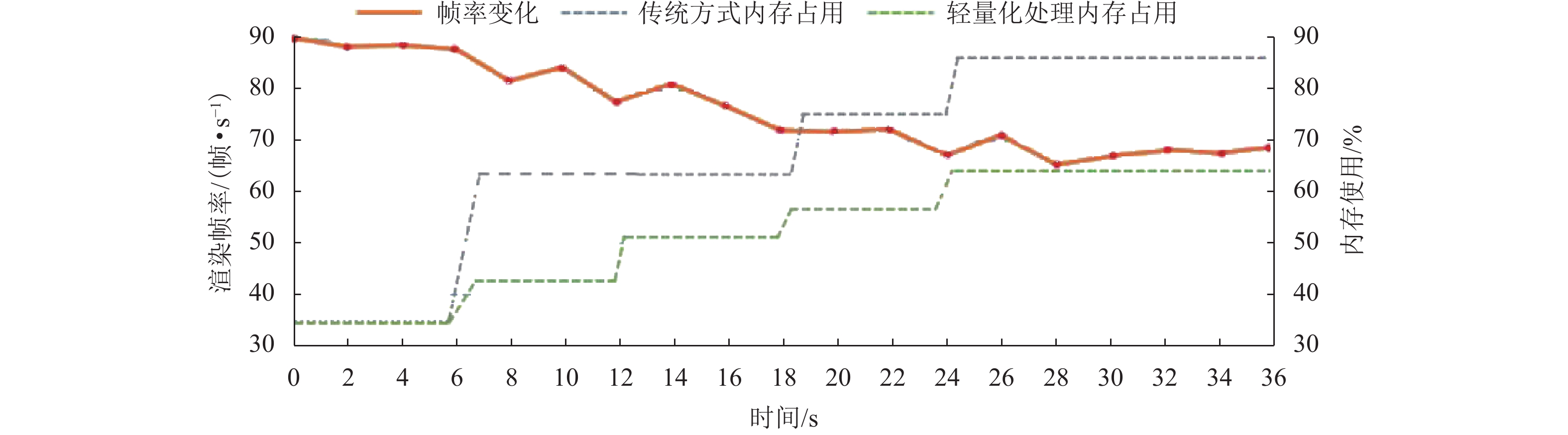
现有多源数据融合可视化方法对数据精度要求高,匹配过程复杂,且传统点云的组织索引方式冗余,面对复杂数据的动态性较差,索引效率较低,难以支撑在网络环境下进行多源数据高效可视化交互. 针对上述问题,提出面向网络轻量化应用的全景图与点云数据快速融合可视化方法. 探讨了二维影像与三维点云的快速映射匹配机制、非规则性八叉树点云优化组织与多细节层次(levels of detail,LOD)动态调度等关键技术;并设计了融合场景跨模态交互分析机制,以实现全景图和点云数据快速融合可视化;最后构建了原型系统并进行案例实验. 结果表明该方法缩短了全景图与点云数据融合匹配时间,并在网络环境中场景渲染帧数稳定在40帧/s以上,能够支持融合场景的高效可视化与交互分析.
Abstract:Existing data fusion visualization methods have high requirements on data accuracy, complex matching process, redundant organization mode of traditional point cloud, poor dynamics for complex data and low index efficiency, and thus it is difficult to efficiently visualize multi-source data in network environment. In view of the above problems, a fast fusion visualization method of panorama and point cloud is proposed for network lightweight application. Key technologies are discussed such as two-dimensional image mapping, fast matching of three-dimensional point cloud data, optimized organization of irregular octree-based point cloud and dynamic scheduling at multiple levels of detail (LOD). A fusion-scene cross-modal interaction mechanism is designed to realize fast fusion visualization of panorama and point cloud data. Finally, a prototype system is constructed and experiments are carried out. The results show that the method reduces the time in the matching and fusion of panoramic and point cloud, and the number of frames is stable above 40 frames/s, which can support the efficient visualization and interactive analysis of fusion scenes.
-
Key words:
- panorama /
- three-dimensional point cloud /
- data matching /
- network visualization
-
表 1 不同过程执行消耗时间
Table 1. Time consumed by different processes
执行过程 消耗时间/s 加载点云数据 5.8 加载视点点云细节数据 8.9 加载视点全景图数据 0.8 数据匹配融合可视化 0.6 表 2 传统方法与轻量化方法结果对比
Table 2. Comparison of results between traditional method and lightweight method
s 执行过程 常规方法耗时 轻量化方法耗时 点云组织 4.3 2.7 数据匹配融合 1.7 0.6 数据可视化 11.2 6.6 -
[1] 华一新,曹亚妮,李响. 地理空间可视分析及其研究方向综述[J]. 测绘科学技术学报,2012,29(4): 235-239. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-6338.2012.04.001HUA Yixin, CAO Yani, LI Xiang. Summarization of geospatial visual analytics and its research directions[J]. Journal of Geomatics Science and Technology, 2012, 29(4): 235-239. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-6338.2012.04.001 [2] 周志光,石晨,史林松,等. 地理空间数据可视分析综述[J]. 计算机辅助设计与图形学学报,2018,30(5): 747-763.ZHOU Zhiguang, SHI Chen, SHI Linsong, et al. A survey on the visual analytics of geospatial data[J]. Journal of Computer-Aided Design & Computer Graphics, 2018, 30(5): 747-763. [3] WONG P C, FOOTE H, KAO D L, et al. Multivariate visualization with data fusion[J]. Information Visualization, 2002, 1(3/4): 182-193. [4] HERMAN I, MELANCON G, MARSHALL M S. Graph visualization and navigation in information visualization:a survey[J]. IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics, 2000, 6(1): 24-43. doi: 10.1109/2945.841119 [5] 张靖,江万寿. 激光点云与光学影像配准:现状与趋势[J]. 地球信息科学学报,2017,19(4): 528-539.ZHANG Jing, JIANG Wanshou. Registration between laser scanning point cloud and optical images:status and trends[J]. Journal of Geo-Information Science, 2017, 19(4): 528-539. [6] ÖZDEMIR E, REMONDINO F. Segmentation of 3D photogrammetric point cloud for 3D building modeling[J]. The International Archives of the Photogrammetry,Remote Sensing and Spatial Information Sciences, 2018, XLII-4/W10: 135-142. [7] ZHENG J Y. Digital route panoramas[J]. IEEE MultiMedia, 2003, 10(3): 57-67. doi: 10.1109/MMUL.2003.1218257 [8] HUANG F, KLETTE R. Stereo panorama acquisition and automatic image disparity adjustment for stereoscopic visualization[J]. Multimedia Tools and Applications, 2010, 47(3): 353-377. doi: 10.1007/s11042-009-0328-2 [9] 李海亭,彭清山,王闪,等. 数字城市中的全景地图系统建设方法研究[J]. 测绘通报,2011(4): 71-73.LI Haiting, PENG Qingshan, WANG Shan, et al. Research on panoramic mapping system in digital city[J]. Bulletin of Surveying and Mapping, 2011(4): 71-73. [10] PARMEHR E G, FRASER C S, ZHANG C S, et al. Automatic registration of optical imagery with 3D LiDAR data using statistical similarity[J]. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 2014, 88: 28-40. doi: 10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2013.11.015 [11] 张帆,黄先锋,李德仁. 激光扫描与光学影像数据配准的研究进展[J]. 测绘通报,2008(2): 7-10.ZHANG Fan, HUANG Xianfeng, LI Deren. A review of registration of laser scanner data and optical image[J]. Bulletin of Surveying and Mapping, 2008(2): 7-10. [12] 马洪超,姚春静,邬建伟. 利用线特征进行高分辨率影像与LiDAR点云的配准[J]. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版),2012,37(2): 136-140,159.MA Hongchao, YAO Chunjing, WU Jianwei. Registration of LiDAR point clouds and high resolution images based on linear features[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 2012, 37(2): 136-140,159. [13] 朱庆,尚琪森,胡翰,等. 三角网模型多目标加权最短路径的特征线提取[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2021,56(1): 116-122.ZHU Qing, SHANG Qisen, HU Han, et al. Feature line extraction from 3D model of oblique photogrammetry based on multiobjective weighted shortest path[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2021, 56(1): 116-122. [14] LEBERL F, IRSCHARA A, POCK T, et al. Point clouds[J]. Photogrammetric Engineering & Remote Sensing, 2010, 76(10): 1123-1134. [15] 卢秀山,俞家勇,田茂义,等. 车载激光点云与序列化全景影像融合方法[J]. 中国激光,2018,45(5): 245-252.LU Xiushan, YU Jiayong, TIAN Maoyi, et al. Fusion method of vehicle laser point cloud and serialized panoramic image[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2018, 45(5): 245-252. [16] 冯文灏. 近景摄影测量: 物体外形与运动状态的摄影法测定[M]. 武汉: 武汉大学出版社, 2002. [17] 黄明,贾嘉楠,李闪磊,等. 多像位姿估计的全景纹理映射算法[J]. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版),2019,44(11): 1622-1632.HUANG Ming, JIA Jianan, LI Shanlei, et al. Panoramic texture mapping algorithm based on multi-image pose estimation[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 2019, 44(11): 1622-1632. [18] 王晏民,胡春梅. 一种地面激光雷达点云与纹理影像稳健配准方法[J]. 测绘学报,2012,41(2): 266-272.WANG Yanmin, HU Chunmei. A robust registration method for terrestrial LiDAR point clouds and texture image[J]. Acta Geodaetica et Cartographica Sinica, 2012, 41(2): 266-272. [19] 刘中华,李鹏飞,许章平. 基于点云数据的改进四叉树空间索引研究[J]. 测绘与空间地理信息,2019,42(5): 38-39,42,47. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-5867.2019.05.012LIU Zhonghua, LI Pengfei, XU Zhangping. Research on improved quadtree spatial index based on point cloud data[J]. Geomatics & Spatial Information Technology, 2019, 42(5): 38-39,42,47. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-5867.2019.05.012 [20] 曹文君,赵祚喜. Ladybug系列多目全景视觉技术的应用研究[J]. 机械与电子,2017,35(12): 27-30. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-2257.2017.12.007CAO Wenjun, ZHAO Zuoxi. Study on application of multi-view panoramic vision technology to Ladybug series[J]. Machinery & Electronics, 2017, 35(12): 27-30. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-2257.2017.12.007 [21] 欧阳峰,龚桂荣,何列松. 面向WebGL的矢量数据三维绘制技术[J]. 测绘科学技术学报,2016,33(6): 635-638, 643.OUYANG Feng, GONG Guirong, HE Liesong. Vector 3D rendering techniques based on WebGL[J]. Journal of Geomatics Science and Technology, 2016, 33(6): 635-638, 643. [22] 刘全海,鲍秀武,李楼. 激光点云与全景影像配准方法研究[J]. 现代测绘,2016,39(1): 21-25. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-4097.2016.01.007LIU Quanhai, BAO Xiuwu, LI Lou. Research of registration based on panoramic images and laser point cloud[J]. Modern Surveying and Mapping, 2016, 39(1): 21-25. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-4097.2016.01.007 -





 下载:
下载: