Influence of Various Fouling Materials on Geogrid-Reinforced Ballast Performance
-
摘要:
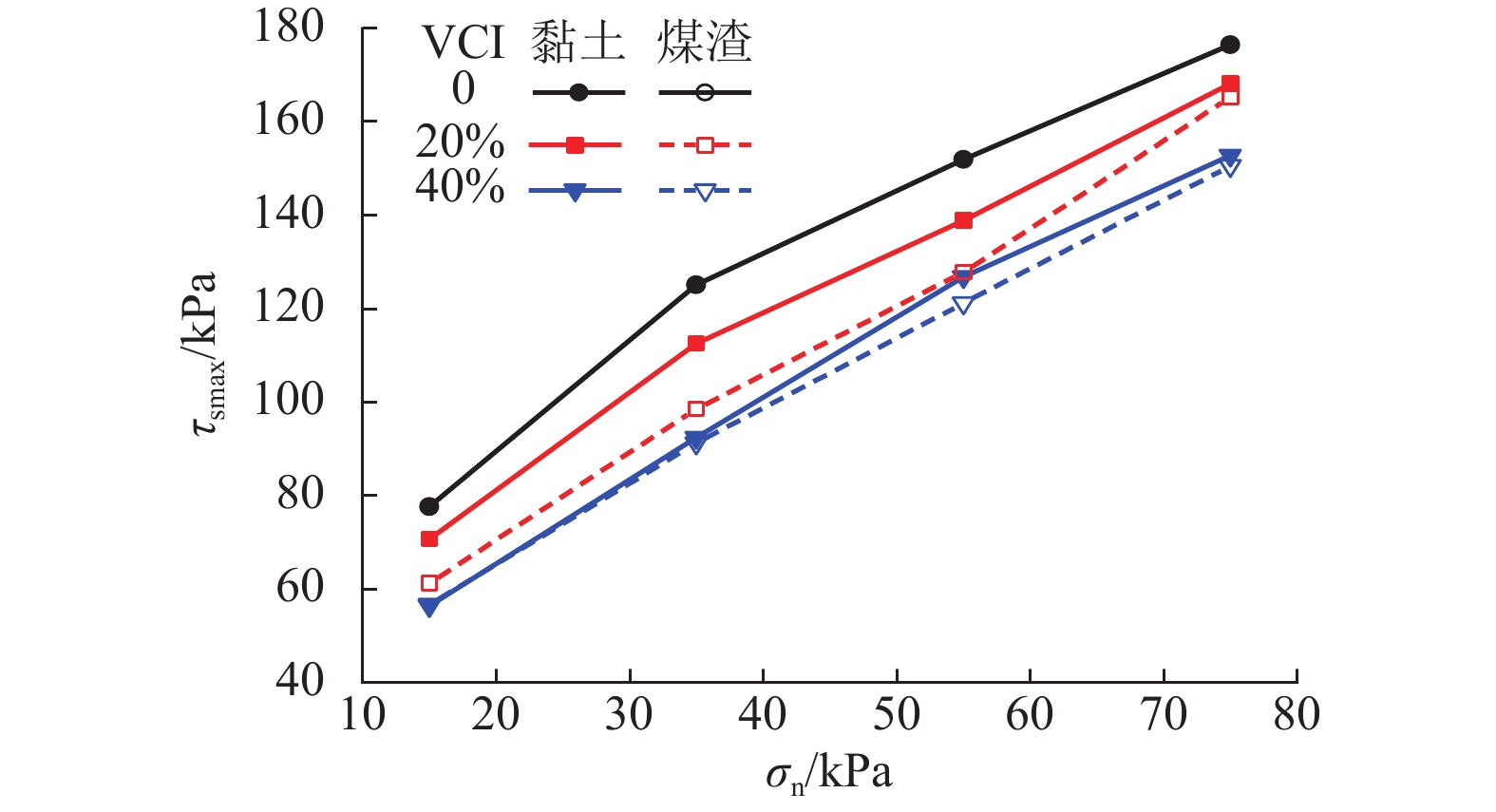
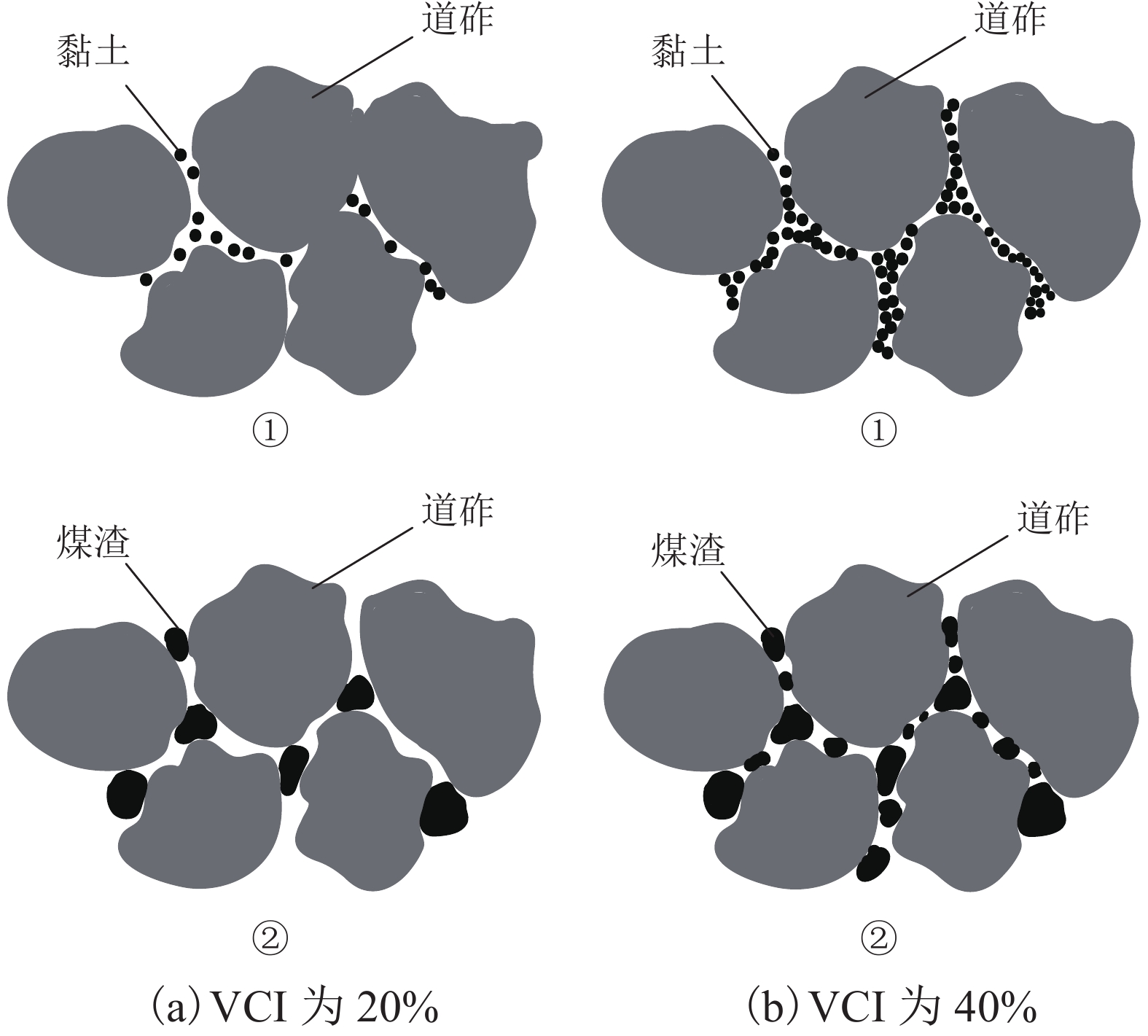
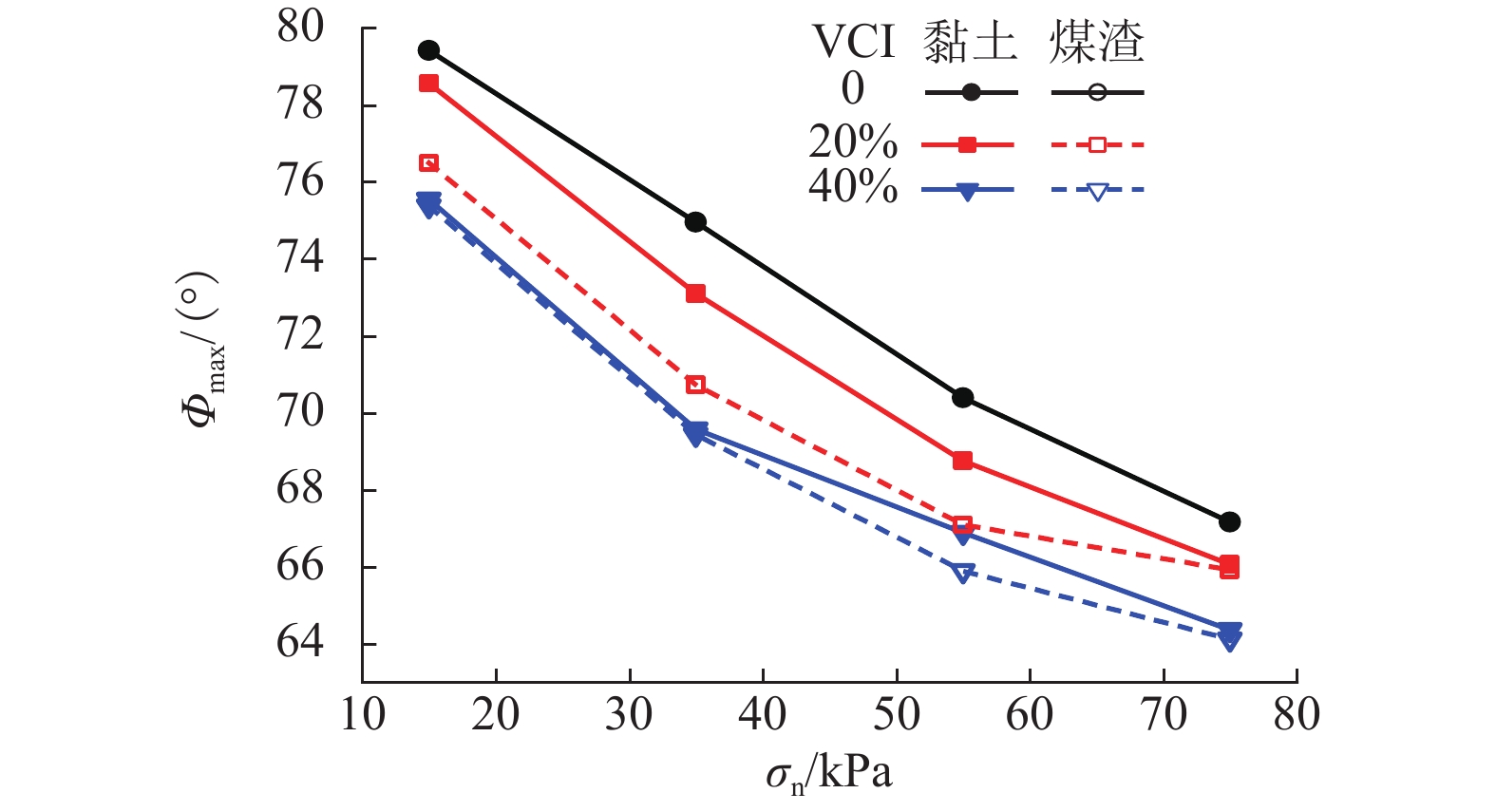
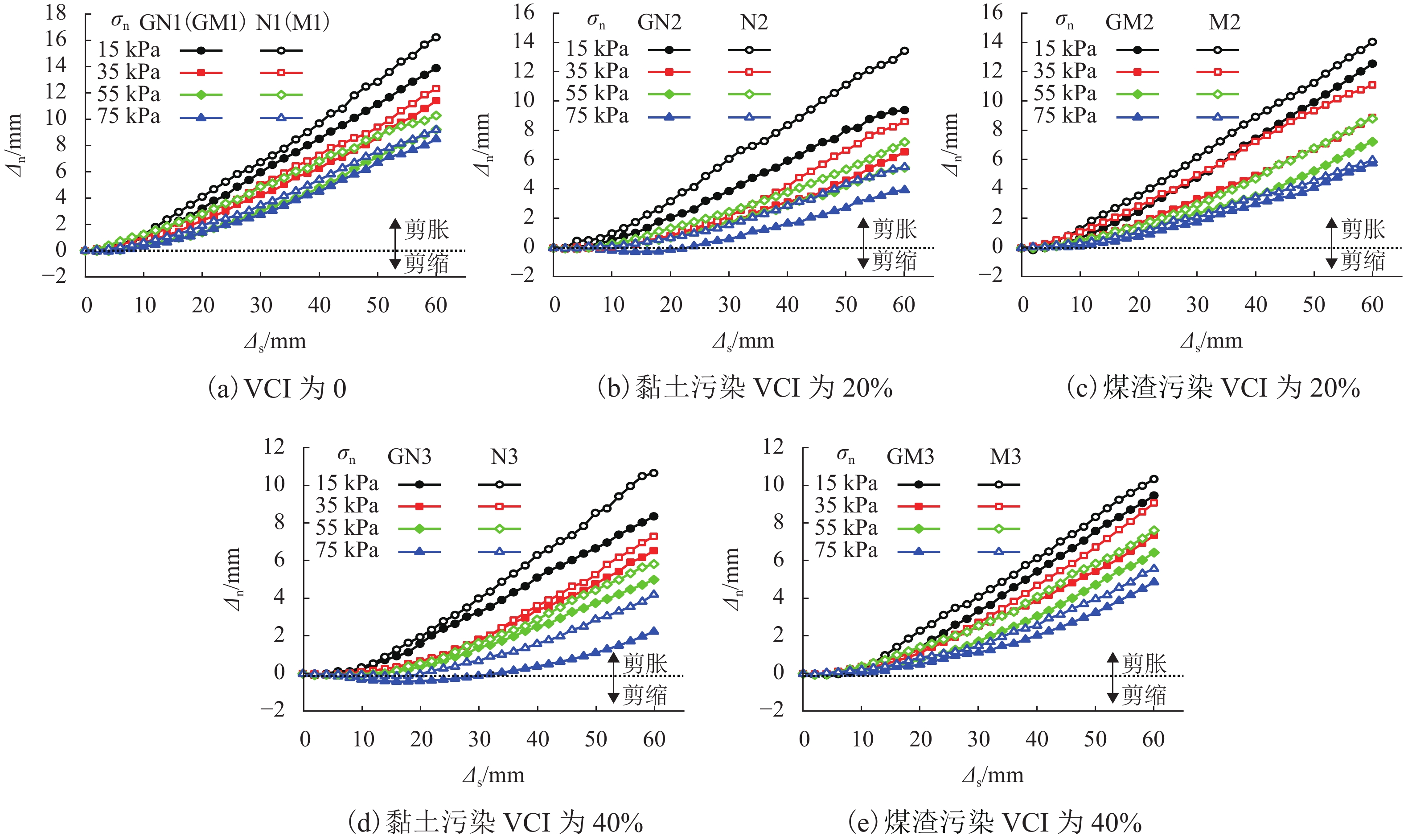
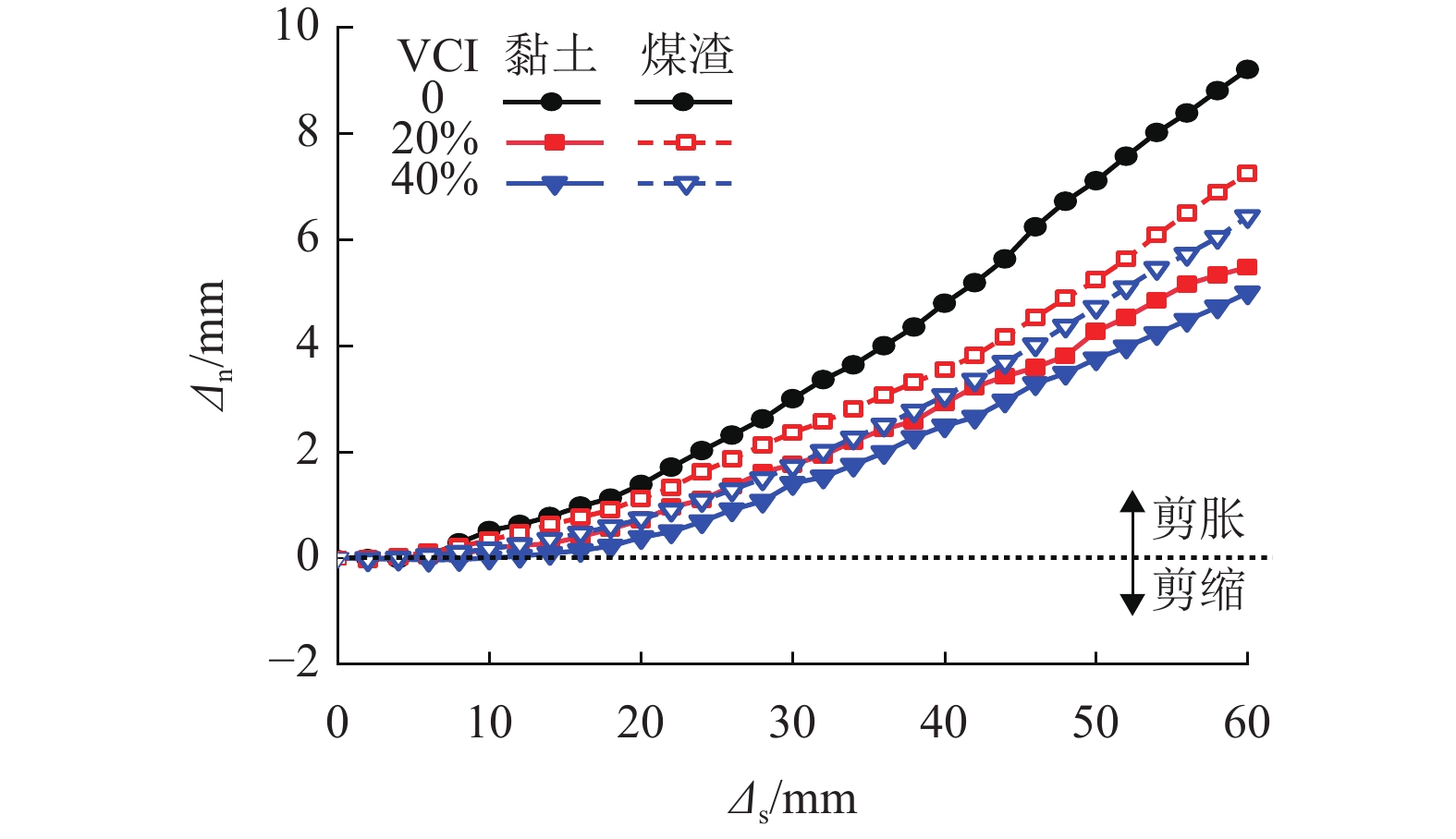
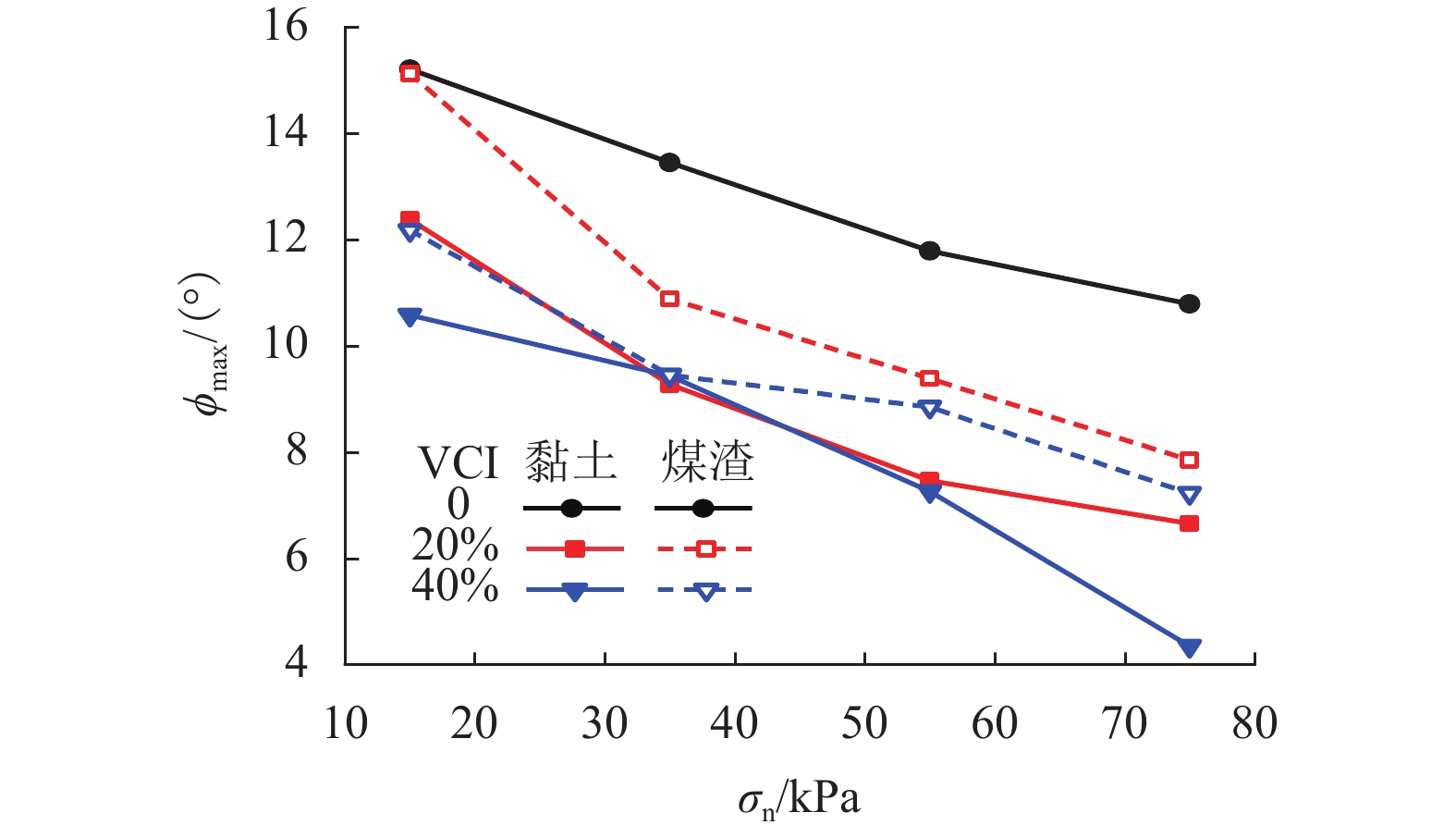
加筋格栅广泛应用于有砟轨道中以提高道床承载及侧向抗变形性能. 由于受到来自行进列车落下的煤渣或底砟及地基层翻冒的泥浆等的污染,格栅加筋道砟集料的力学性能会受到严重影响. 选用黏土、煤渣两种有砟铁路常见脏污杂质,对格栅加筋道砟开展了不同法向压力、不同脏污程度下的大型直剪试验,对比研究了不同脏污质对格栅加筋道砟的抗剪强度、峰值摩擦角、法向剪胀位移以及峰值剪胀角的影响差异,并分析了其差异产生的力学机制. 试验结果表明:脏污质的存在会降低格栅加筋道砟的抗剪强度和峰值摩擦角,并减小试样的法向剪胀位移和峰值剪胀角;相较于受黏土污染的格栅加筋道砟,受煤渣污染的集料具有更低的抗剪强度和峰值摩擦角,以及更高的法向剪胀位移和峰值剪胀角,表明煤渣脏污对格栅加筋道砟的力学性能会产生更加不利的影响.
Abstract:Geogrid has been widely adopted in ballasted railways to improve the bearing capacity of ballast and its resistance to lateral deformation. The mechanical properties of geogrid-reinforced ballast aggregate are seriously affected by contaminants of coals falling from the moving hauls or clay fines from ballast layer and subgrade. A series of large-scale direct shear tests of geogrid-reinforced ballast under different normal pressures and various fouling levels were performed using the two common fouling substances of ballasted railway, i.e., clays and coals. The effects of the two fouling materials on the shear strength, peak friction angle, vertical dilatant displacement, and peak dilatant angle of the geogrid-reinforced ballast were compared and analyzed, and the mechanical mechanism that contributes to the different performances was also explored. The results showed that the presence of fouling materials decreases the shear strength and peak friction angle of geogrid-reinforced ballast, but reduces its vertical dilatant displacement and peak dilatant angle. Compared with that fouled by clay fines, the ballast fouled by coals exhibits a lower shear strength and peak friction angle, and a larger vertical dilatant displacement and peak dilatant angle, indicating increasingly adverse impacts on the mechanical performances of geogrid-reinforced ballast.
-
Key words:
- geogrid reinforcement /
- ballast fouling /
- direct shear test /
- shearing performance
-
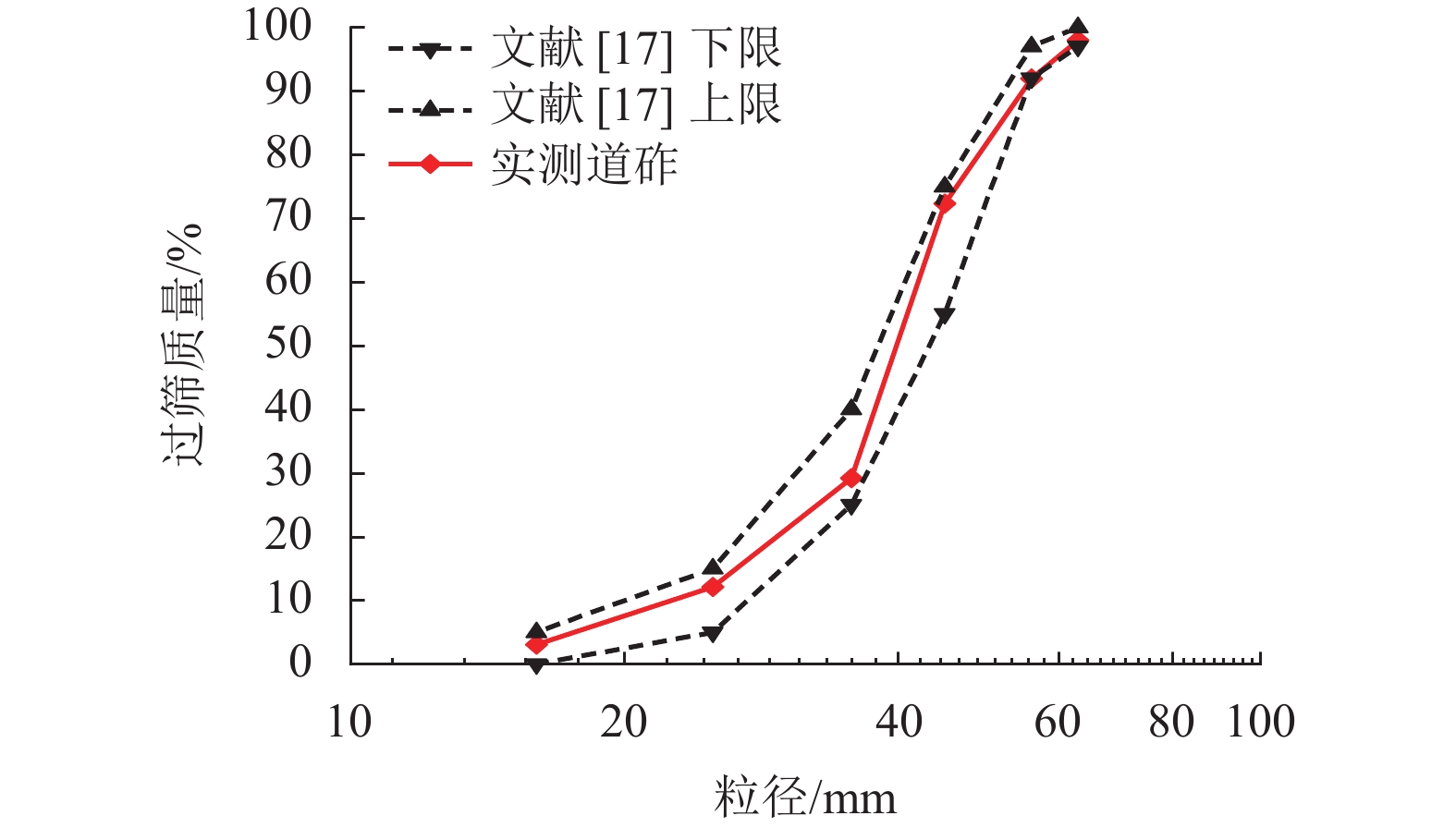
表 1 道砟及脏污质相关力学指标
Table 1. Mechanical indexes of ballast and fouling substances
名称 比重 堆积密度/
(kg•m−3)含水
率/%孔隙
比 e液限ωL/% 塑限ωP/% 道砟 2.66 1432 0.858 黏土 2.70 1178 22.2 1.207 42.10 22.40 煤渣 1.22 715 0.707 表 2 格栅参数
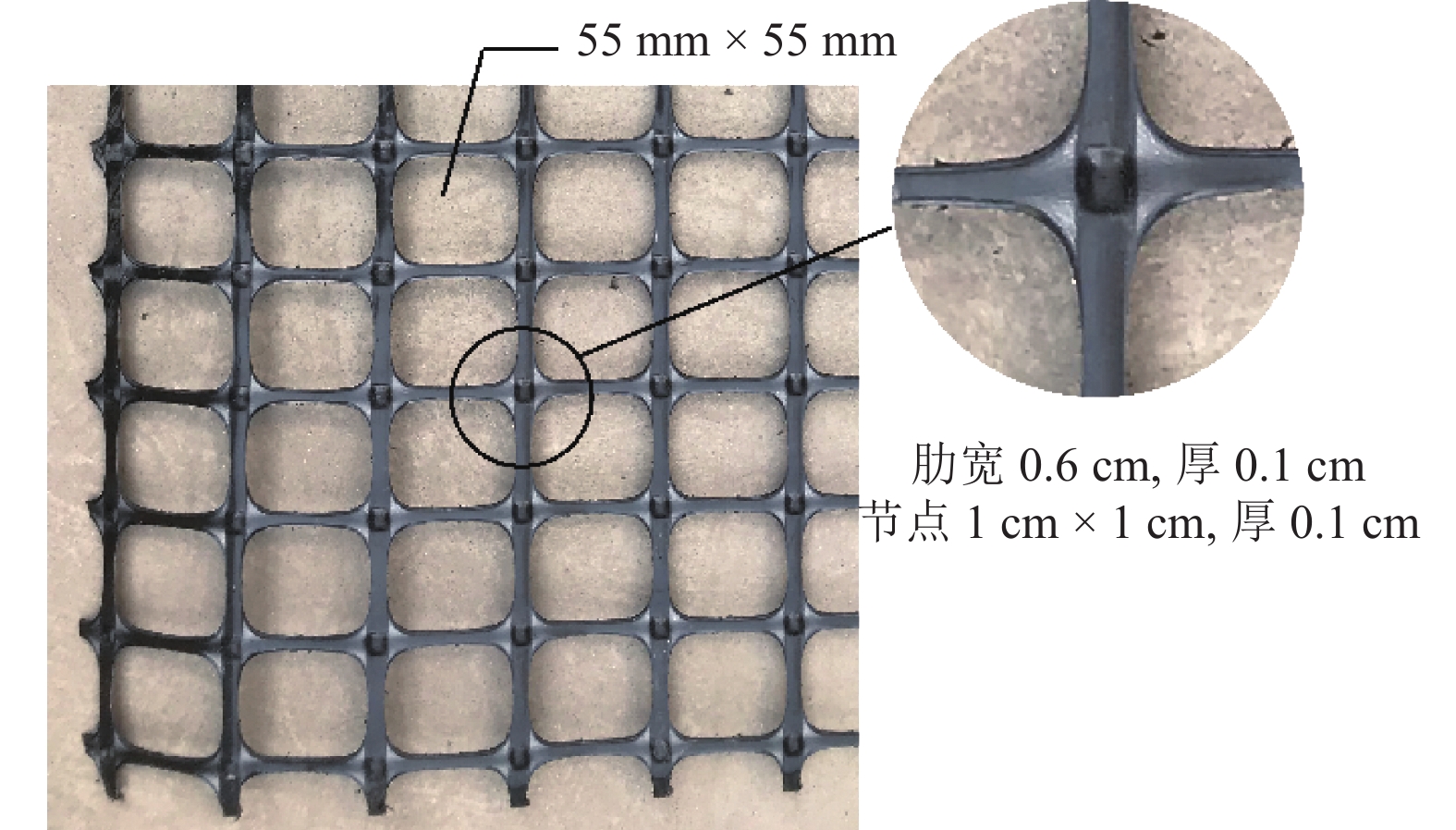
Table 2. Physical and technical properties of geogrid
格栅参数 数值 孔径形式 双向孔径 55 mm × 55 mm 材料 聚丙烯 2% 应变时抗拉强度/(kN•m−1) 11 5% 应变时抗拉强度/(kN•m−1) 15 峰值抗拉强度/(kN•m−1) 30 屈服点伸长率/% 13 表 3 试样设置情况
Table 3. Details of experimental specimens
类型 试样编号 脏污质种类 VCI/% 法向压力 σn/kPa 含格栅 GN1 黏土 0 15、35、55、75 GN2 20 GN3 40 GM1 煤渣 0 15、35、55、75 GM2 20 GM3 40 不含格栅 N1 黏土 0 15、35、55、75 N2 20 N3 40 M1 煤渣 0 15、35、55、75 M2 20 M3 40 -
[1] 高亮,徐旸,殷浩. 脏污材质对散体道床剪切力学性能影响的试验研究[J]. 北京交通大学学报,2017,41(1): 1-6. doi: 10.11860/j.issn.1673-0291.2017.01.001GAO Liang, XU Yang, YIN Hao. Experiment researchof shear behavior of railway ballast influenced by different fouling materials[J]. Journal of Beijing Jiaotong University, 2017, 41(1): 1-6. doi: 10.11860/j.issn.1673-0291.2017.01.001 [2] INDRARATNA B, NIMBALKAR S S, TENNAKOON N. The behaviour of ballasted track foundations: track drainage and geosynthetic reinforcement[C]//Advances in Analysis, Modeling & Design. Orlando: American Society of Civil Engineers, 2010: 2378-2387. [3] SELIG E T, WATERS J M. Track geotechnology and substructure management[M]. London: Thomas Telford, 1994. [4] KOOHMISHI M, PALASSI M. Effect of gradation of aggregate and size of fouling materials on hydraulic conductivity of sand-fouled railway ballast[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2018, 167: 514-523. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2018.02.040 [5] KASHANI H F, HO C L, HYSLIP J P. Fouling and water content influence on the ballast deformation properties[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2018, 190: 881-895. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2018.09.058 [6] INDRARATNA B, TENNAKOON N C, NIMBALKAR S, et al. Behaviour of clay-fouled ballast under drained triaxial testing[J]. Géotechnique, 2013, 63(5): 410-419. [7] NGO N T, INDRARATNA B, RUJIKIATKAMJORN C. Micromechanics-based investigation of fouled ballast using large-scale triaxial tests and discrete element modeling[J]. Journal of Geotechnical and Geoenvironmental Engineering, 2017, 143(2): 04016089.1-04016089.16. [8] SWETA K, HUSSAINI S K K. Behavior evaluation of geogrid-reinforced ballast-subballast interface under shear condition[J]. Geotextiles and Geomembranes, 2019, 47(1): 23-31. doi: 10.1016/j.geotexmem.2018.09.002 [9] BIABANI M M, INDRARATNA B. An evaluation of the interface behaviour of rail subballast stabilised with geogrids and geomembranes[J]. Geotextiles and Geomembranes, 2015, 43(3): 240-249. doi: 10.1016/j.geotexmem.2015.04.002 [10] 刘贵宪. 道砟基本力学特性及格栅加固机理研究[D]. 北京: 北京交通大学, 2015. [11] CHEN C, MCDOWELL G R, THOM N H. Investigating geogrid-reinforced ballast: experimental pull-out tests and discrete element modelling[J]. Soils and Foundations, 2014, 54(1): 1-11. [12] INDRARATNA B, HUSSAINI S K K, VINOD J S. The lateral displacement response of geogrid-reinforced ballast under cyclic loading[J]. Geotextiles and Geomembranes, 2013, 39: 20-29. doi: 10.1016/j.geotexmem.2013.07.007 [13] INDRARATNA B, NGO N T, RUJIKIATKAMJORN C. Deformation of coal fouled ballast stabilized with geogrid under cyclic load[J]. Journal of Geotechnical and Geoenvironmental Engineering, 2013, 139(8): 1275-1289. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)GT.1943-5606.0000864 [14] INDRARATNA B, NGO N T, RUJIKIATKAMJORN C. Behavior of geogrid-reinforced ballast under various levels of fouling[J]. Geotextiles and Geomembranes, 2011, 29(3): 313-322. [15] HUANG H, TUTUMLUER E, DOMBROW W. Laboratory characterization of fouled railroad ballast behavior[J]. Transportation Research Record, 2009, 2117: 93-101. [16] TUTUMLUER E, KENT P F, DOMBROW W, et al. Laboratory characterization of coal dust fouled ballast behavior[C]//AREMA 2008 Annual Conference & Exposition. Salt Lake City: [s.n.], 2008: 21-24. [17] 中华人民共和国铁道部. 铁道碎石道砟: TB/T 20140—2018[S]. 北京: 中国铁道出版社, 2008. [18] MCDOWELL G R, HARIRECHE O, KONIETZKY H, et al. Discrete element modelling of geogrid-reinforced aggregates[J]. Proceedings of the Institution of Civil Engineers-Geotechnical Engineering, 2006, 159(1): 35-48. doi: 10.1680/geng.2006.159.1.35 [19] INDRARATNA B, SU L, RUJIKIATKAMJORN C. A new parameter for classification and evaluation of railway ballast fouling[J]. Canadian Geotechnical Journal, 2011, 48(2): 322-326. doi: 10.1139/T10-066 -




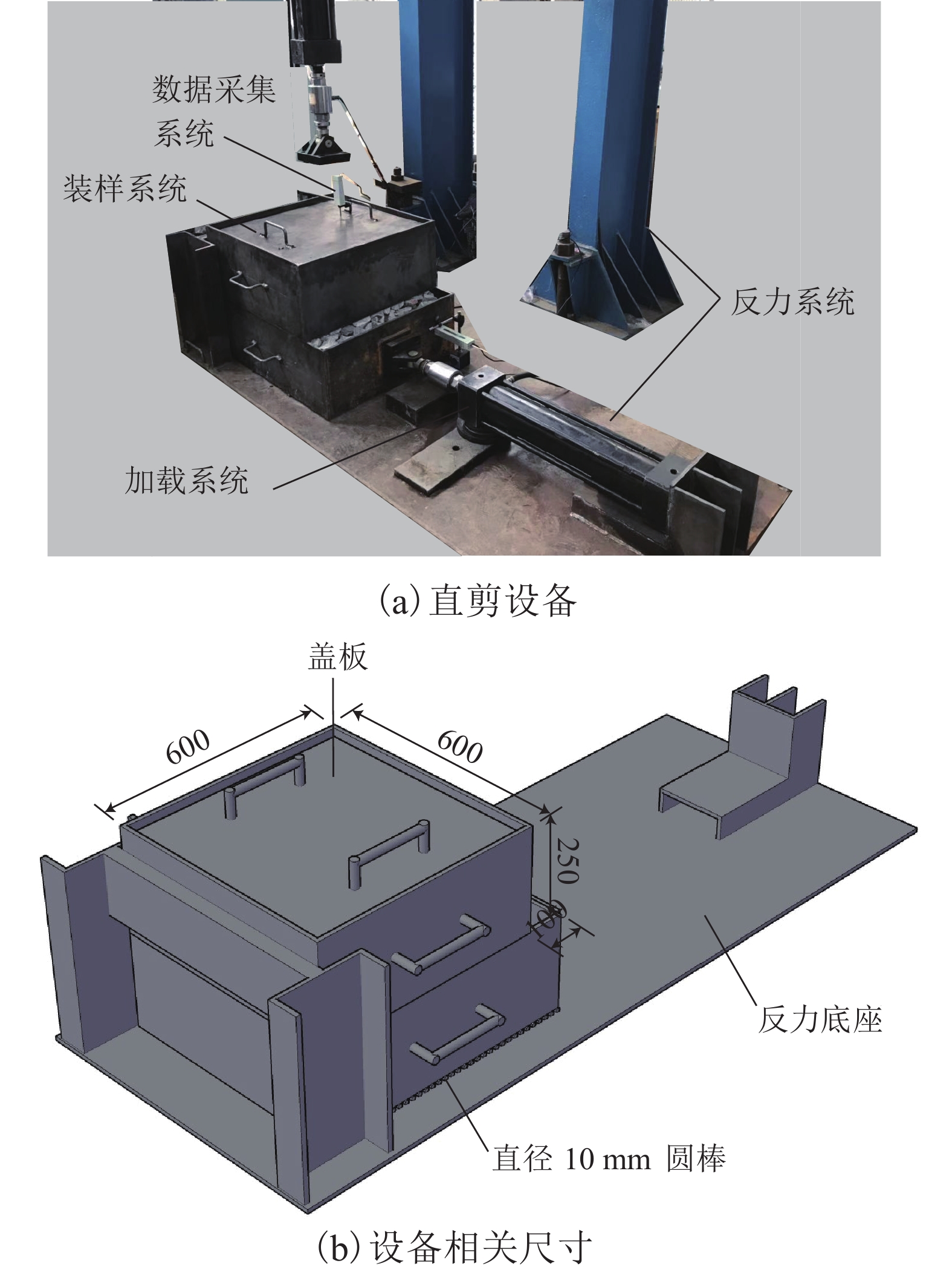
 下载:
下载: