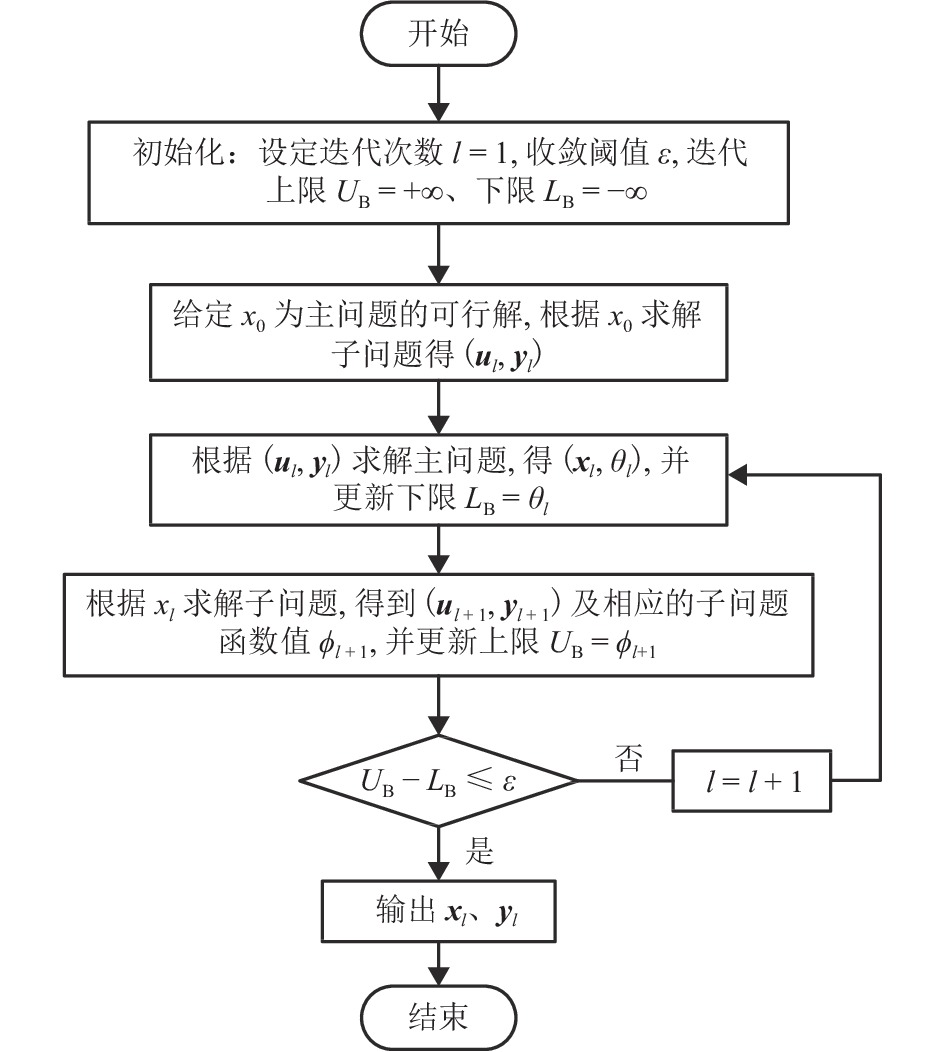
Two-Stage Robust Scheduling Optimization of AC/DC Hybrid Microgrid with Electric Vehicles
-
摘要:
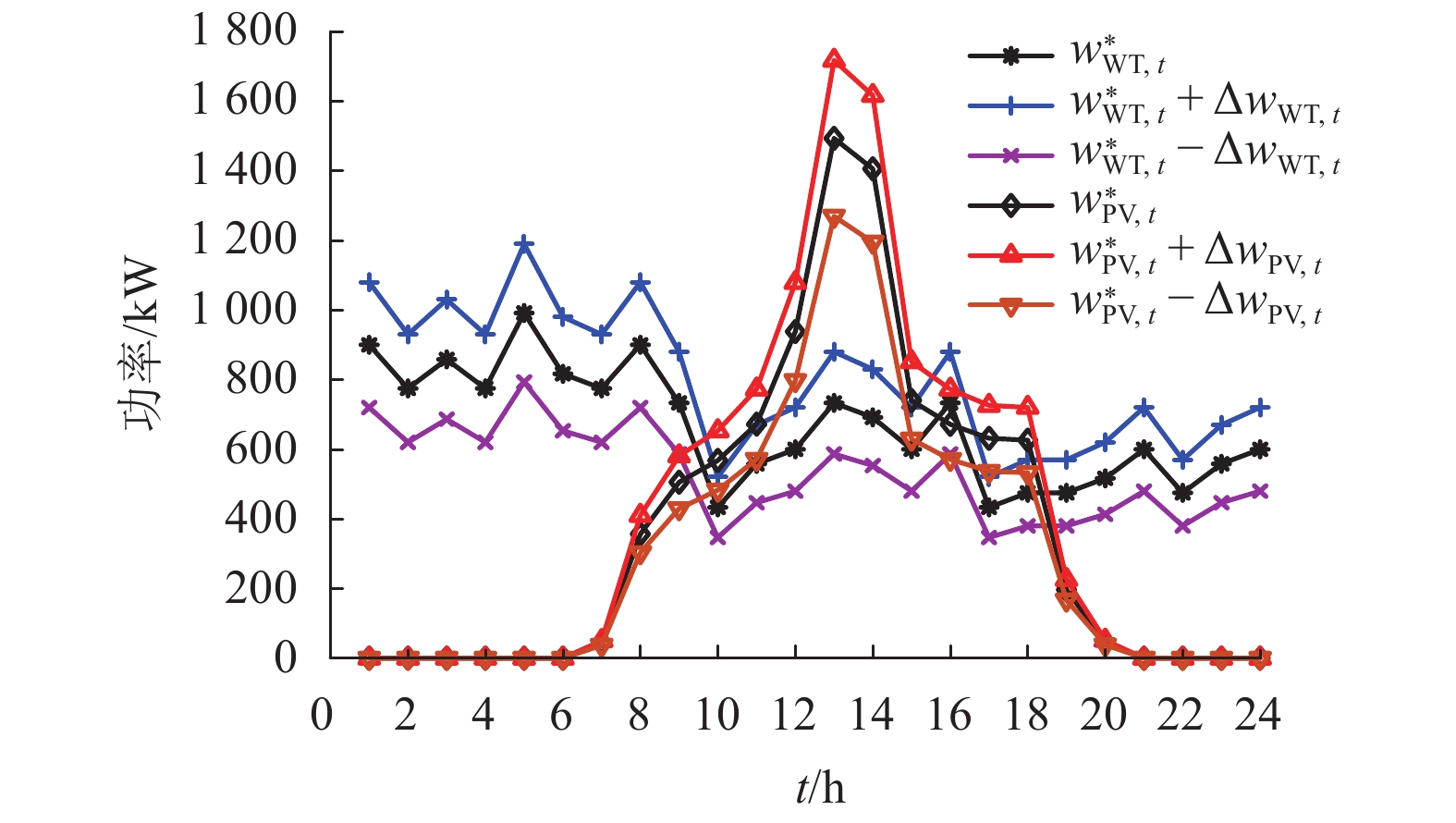
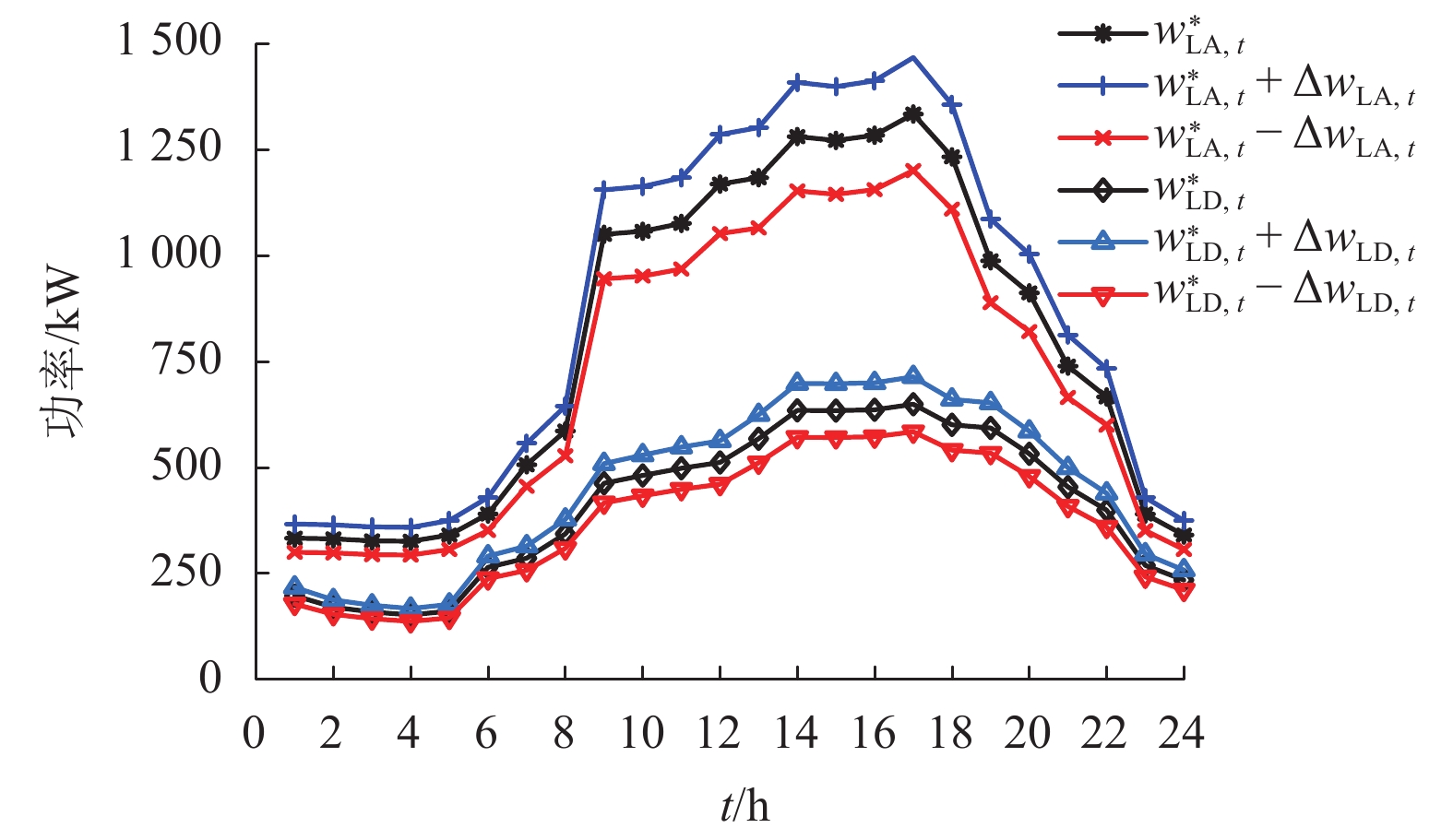
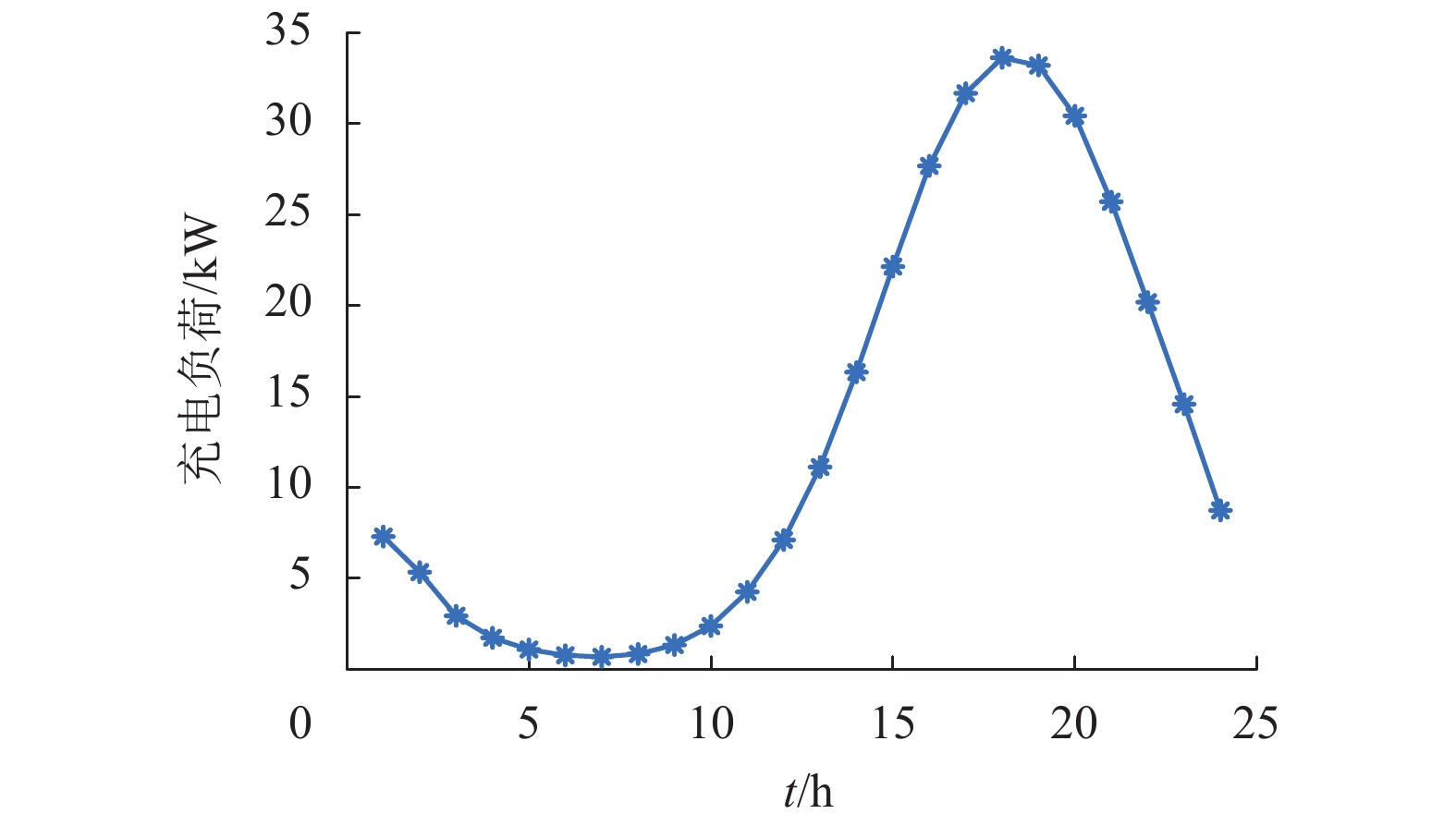
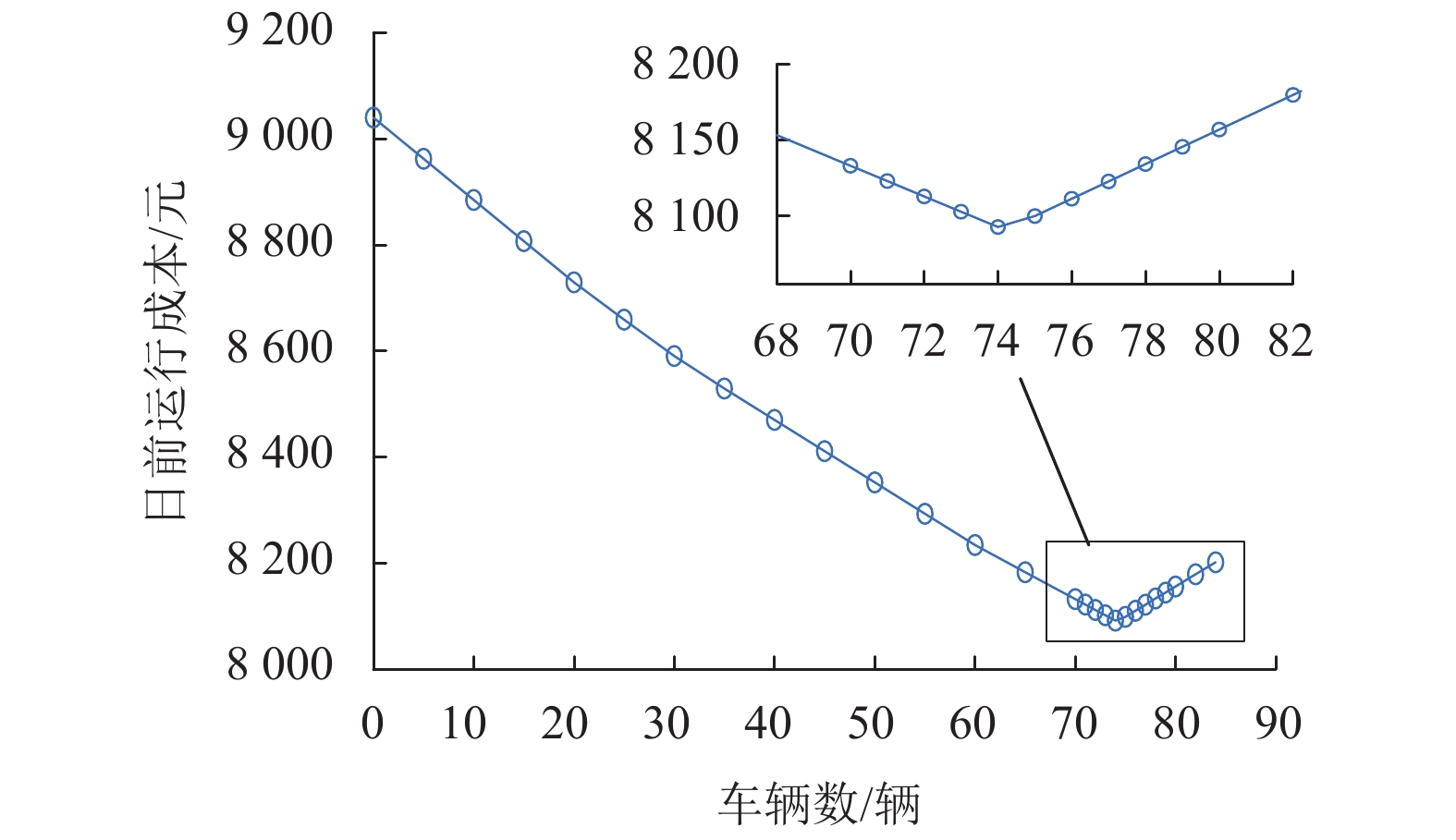
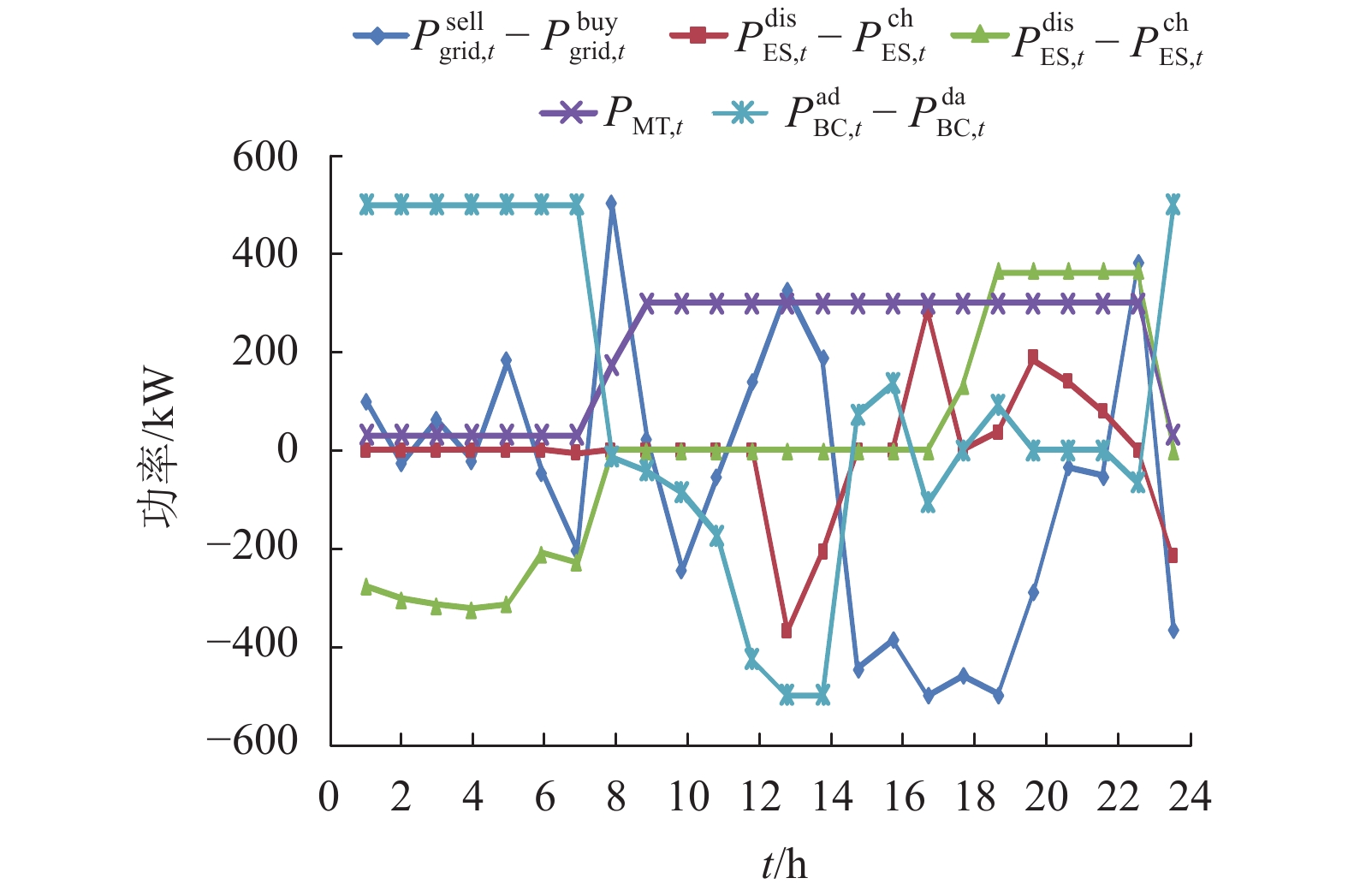
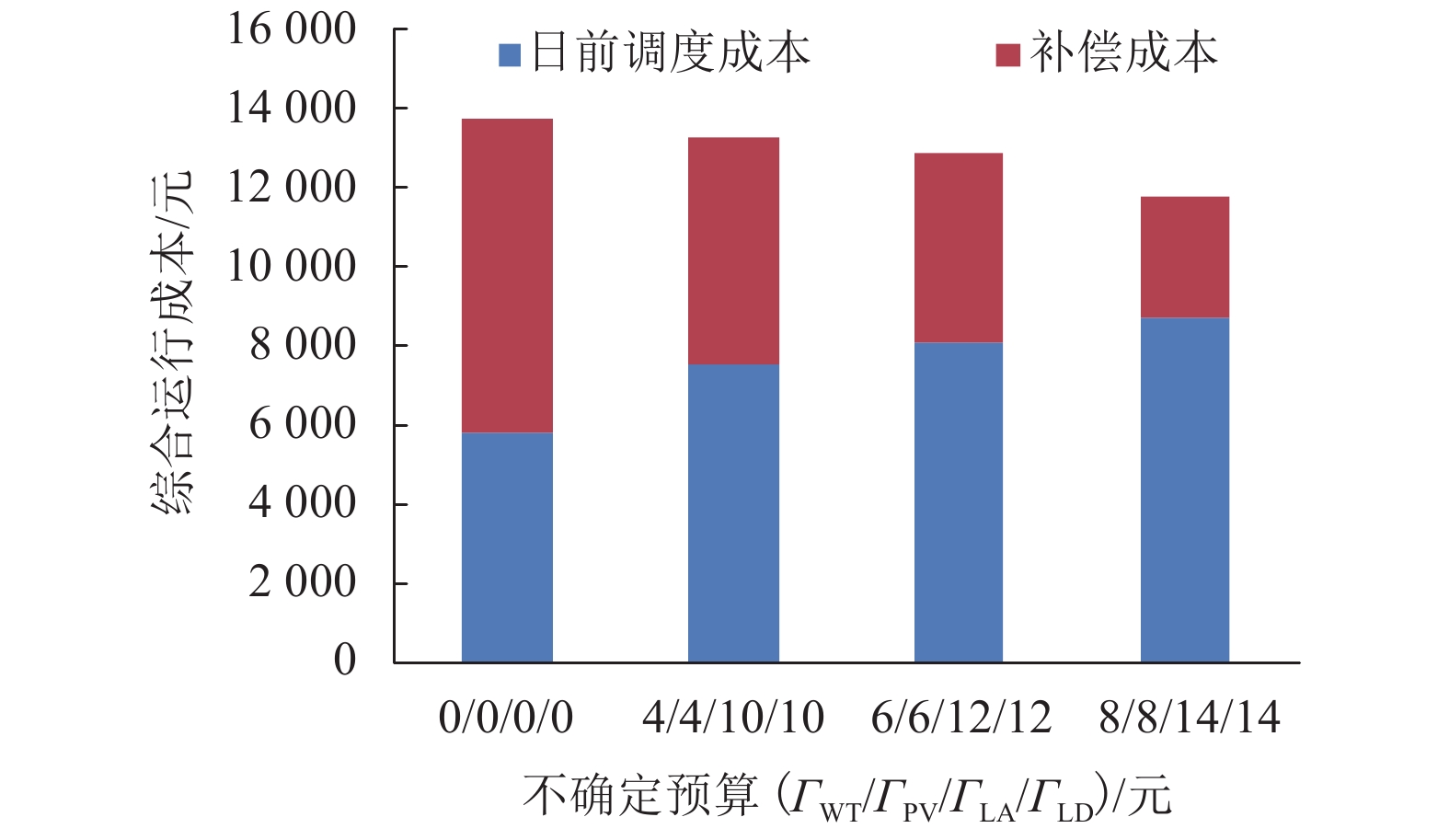
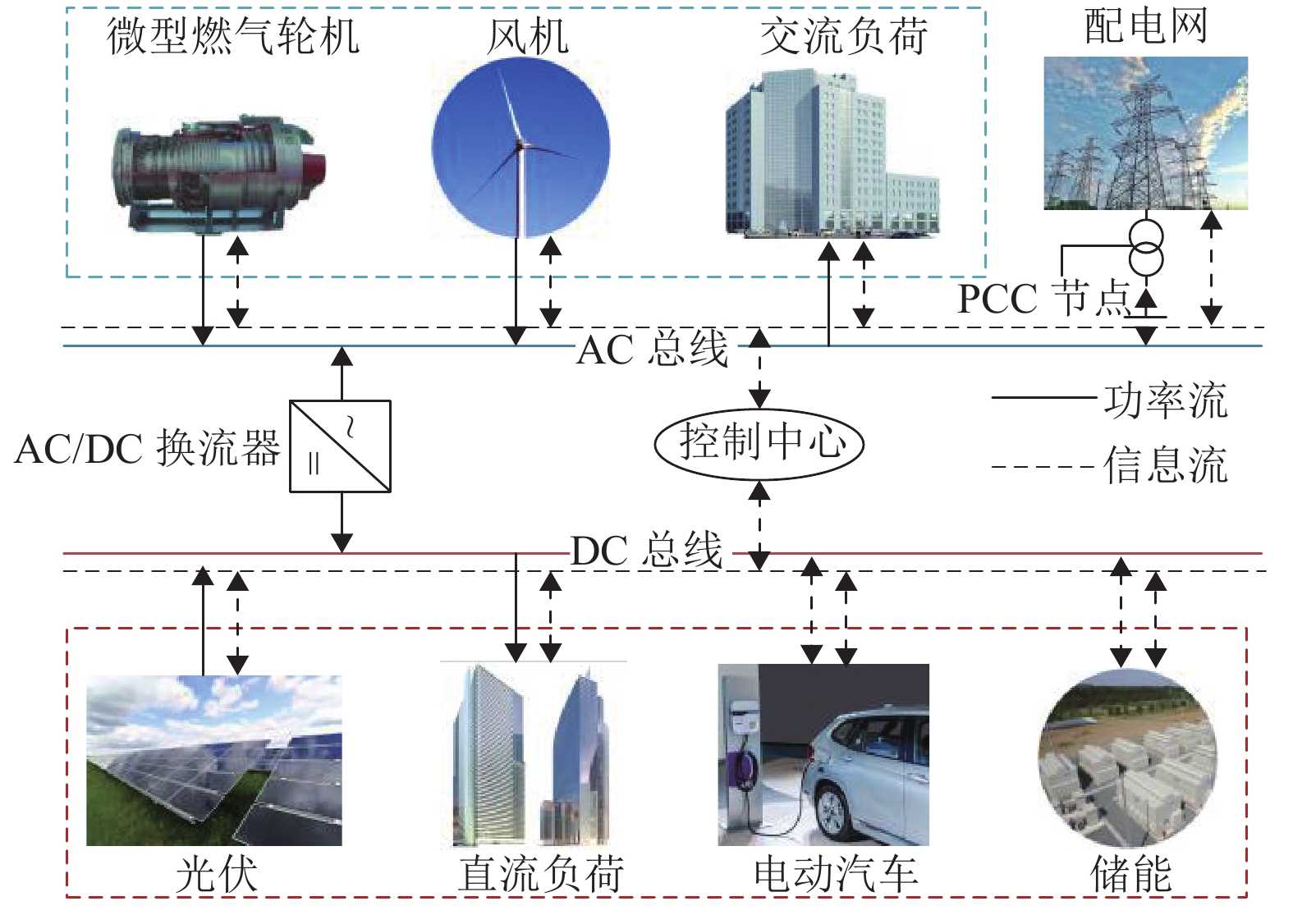
随着电动汽车(electric vehicles,EVs)技术的快速发展,EVs数量激增,将其接入微电网中参与充放电调度成为了降低大规模EVs对电网负面影响的有效途径. 为此,将EVs接入交直流混合微电网的直流侧,考虑EVs的源荷双重特性,针对微电网系统中微源出力及负荷的不确定性,搭建了计及EVs充放电的交直流混合微电网两阶段鲁棒调度模型,以寻求系统在极端场景下的经济最优方案. 该模型采用盒式不确定集描述不确定性,通过不确定性预算灵活调节模型保守性;基于系统各单元运行约束条件,建立最小成本目标函数,并通过强对偶理论和BIG-M法将模型转化为混合整数线性规划模型;最后通过列约束生成算法对模型进行迭代求得最优解,结合算例进行了仿真. 结果发现:合理运用EVs的源荷特性能够有效降低微电网的日运行成本,其中,当50辆EVs并网运行时,无序充电模式下的运行成本较有序充放电模式下的成本高出1069.7元;在换流功率的限制下,随着EVs接入数量的增加,运行成本呈现先下降后上升的趋势;考虑实时调整成本,鲁棒调度模型的经济性更佳.
Abstract:Due to the rapid development of electric vehicles (EVs), the number of EVs has surged. Connecting EVs to micro-grid in charge-discharge scheduling become an effective way to reduce the negative impact of large-scale EVs on the power grid. Thus, given the source-charge characteristics of the EVs, with the access of EVs to DC side in micro AC/DC hybrid power grid, the two-phase robust scheduling model is built to settle the uncertainty in micro-source output and load of the microgrid system and find most economical solution in extreme situations. The model uses a box uncertainty set to describe the uncertainty, and flexibly adjusts the conservatism of the model through uncertain budget. Based on the operation constraints of each unit in the system, the objective function of minimum cost is established, and the model is transformed into a mixed integer linear programming model by the strong duality theory and BIG-M method. Finally, the model is iterated to obtain the optimal solution through the column and constraint generation algorithm. The simulation results of an example simulation show that reasonably utilizing the source-load characteristics of EVs can effectively reduce the microgrid daily operation cost. In the case of 50 EVs in parallel operation, the operation cost in the randomly charging mode is higher than that in the orderly charging and discharging mode by 1069.7 Yuan. In addition, under the restriction of power commutation, with the increase in the number of EV access, the operation cost also shows a trend of declining and then rising. In terms of real-time adjustment costs, the robust scheduling model has favorable economic benefits.
-
Key words:
- uncertainty /
- AC/DC hybrid microgrid /
- electric vehicle /
- two-stage robust model /
- uncertainty budget
-
表 1 基本参数设置
Table 1. Basic parameter setting
参数 数值 参数 数值 mPV、mWT/
(元/(kW•h)−1)0.01 $P_{{\rm{MT}}}^{\max }{\text{、}}P_{{\rm{MT}}}^{\min }$/kW 30 mMT、mBC/
(元/(kW•h)−1)0.1 $P_{{\rm{ES}}}^{{\rm{ch}},\max }$、$P_{{\rm{ES}}}^{{\rm{dis}},\max }$/kW 500 aMT/(元/(kW•h)−1) 0.79 $P_{{\rm{BC}}}^{{\rm{ad,max}}}$、$P_{{\rm{BC}}}^{{\rm{da,max}}}$/kW 500 mES/(元/(kW•h)−1) 0.35 $P_{{\rm{grid}}}^{{\rm{buy,max}}}$、$P_{{\rm{grid}}}^{{\rm{sell,max}}}$/kW 500 mEV/(元/(kW•h)−1) 0.8125 $P_{{\rm{EV}}i}^{{\rm{ch,max}}}$、$P_{{\rm{EV}}i}^{{\rm{dis,max}}}$/kW 3.6 $E_{{\rm{ES}}}^{\max }{\text{、}}E_{{\rm{ES}}}^{\min }$/(kW•h) 2400、500 $\eta _{{\rm{EV}}}^{{\rm{ch}}}{\text{、}}\eta _{{\rm{EV}}}^{{\rm{dis}}}$ 0.9 $E_{{\rm{EV}}i}^{{\rm{max}}}{\text{、}}E_{{\rm{EV}}i}^{{\rm{min}}}$/(kW•h) 30、6 $\eta _{{\rm{BC}}}^{{\rm{ad}}}{\text{、}}\eta _{{\rm{BC}}}^{{\rm{da}}}$ 0.95 $E_{{\rm{ES}},0}$/(kW•h) 800 $R_{{\rm{BC}}}^{{\rm{up}}}$、$R_{{\rm{BC}}}^{{\rm{down}}}$/kW 1000 $E_{{\rm{EV}}i,0}$/(kW•h) 9.6 $\eta _{{\rm{ES}}}^{{\rm{ch}}}{\text{、}}\eta _{{\rm{ES}}}^{{\rm{dis}}}$ 0.95 ΓWT、ΓPV 6 ΓLA、ΓLD 12 表 2 配电网分时电价
Table 2. Time-of-use prices for distribution network
时段类型 时段 电价/元 峰时 09:00—12:00 1.3 谷时 23:00—24:00 及 00:00—08:00 0.5 平时 其余时段 0.9 表 3 电动汽车随机充电与有序充放电仿真结果对比
Table 3. Simulation results of randomly charging and orderly charging and discharging for electric vehicles
项目 电动汽车
补贴/元日运行
成本/元净购电
量/kW随机充电 9421.9 2128.3 有序充放电 1099.9 8352.2 1735.2 -
[1] 王成山,武震,李鹏. 微电网关键技术研究[J]. 电工技术学报,2014,29(2): 1-12. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6753.2014.02.001WANG Chengshan, WU Zhen, LI Peng. Research on key technologies of microgrid[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2014, 29(2): 1-12. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6753.2014.02.001 [2] 王成山,李鹏. 分布式发电、微网与智能配电网的发展与挑战[J]. 电力系统自动化,2010,34(2): 10-14, 23.WANG Chengshan, LI Peng. Development and challenges of distributed generation,the micro-grid and smart distribution system[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2010, 34(2): 10-14, 23. [3] KATIRAEI F, IRAVANI M R. Power management strategies for a microgrid with multiple distributed generation units[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Systems, 2006, 21(4): 1821-1831. doi: 10.1109/TPWRS.2006.879260 [4] 丁涛,李澄,胡源,等. 考虑非预期条件的电力系统多阶段随机规划建模理论与方法[J]. 电网技术,2017,41(11): 3566-3573.DING tao, LI Cheng, HU Yuan, et al. Multi-stage stochastic programming for power system planning considering nonanticipative constraints[J]. Power Grid Technology, 2017, 41(11): 3566-3573. [5] 龙军,莫群芳,曾建. 基于随机规划的含风电场的电力系统节能优化调度策略[J]. 电网技术,2011,35(9): 133-138.LONG Jun, MO Qunfang, ZENG Jian. A stochastic programming based short-term optimization scheduling strategy considering energy conservation for power system containing wind farms[J]. Power Grid Technology, 2011, 35(9): 133-138. [6] ZHAO C YGUAN Y P. Unified stochastic and robust unit commitment[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Systems, 2013, 28(3): 3353-3361. doi: 10.1109/TPWRS.2013.2251916 [7] 刘一欣,郭力,王成山. 微电网两阶段鲁棒优化经济调度方法[J]. 中国电机工程学报,2018,38(14): 4013-4022,4307.LIU Yixin, GUO Li, WANG Chengshan. Economic dispatch of microgrid based on two stage robust optimization[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2018, 38(14): 4013-4022,4307. [8] QIU H F, GU W, XU Y L, et al. Interval-partitioned uncertainty constrained robust dispatch for AC/DC hybrid microgrids with uncontrollable renewable generators[J]. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid, 2019, 10(4): 4603-4614. doi: 10.1109/TSG.2018.2865621 [9] QIU H F, ZHAO B, GU W, et al. Bi-level two-stage robust optimal scheduling for AC/DC hybrid multi-microgrids[J]. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid, 2018, 9(5): 5455-5466. doi: 10.1109/TSG.2018.2806973 [10] LI F C, GUO H X, JING Z, et al. Peak and valley regulation of distribution network with electric vehicles[J]. The Journal of Engineering, 2019, 2019, 16: 2488-2492. doi: 10.1049/joe.2018.8540 [11] 茆美琴,孙树娟,苏建徽. 包含电动汽车的风/光/储微电网经济性分析[J]. 电力系统自动化,2011,35(14): 30-35.MAO Meiqin, SUN Shujuan, SU Jianhui. Economic analysis of a microgrid with wind/photovoltaic/storages and electric vehicles[J]. Power System Automation, 2011, 35(14): 30-35. [12] 侯慧,薛梦雅,陈国炎,等. 计及电动汽车充放电的微电网多目标分级经济调度[J]. 电力系统自动化,2019,43(17): 55-67. doi: 10.7500/AEPS20180930001HOU Hui, XUE Mengya, CHEN Guoyan, et al. Multi-objective hierarchical economic dispatch for microgrid considering charging and discharging of electric vehicles[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2019, 43(17): 55-67. doi: 10.7500/AEPS20180930001 [13] 梁子鹏,陈皓勇,王勇超,等. 含电动汽车的微网鲁棒经济调度[J]. 电网技术,2017,41(8): 2647-2658.LIANG Zipeng, CHEN Haoyong, WANG Yongchao, et al. Robust economic dispatch of microgrids containing electric vehicles[J]. Power System Technology, 2017, 41(8): 2647-2658. [14] HUANG Q L, JIA Q S, GUAN X H. Robust scheduling of EV charging load with uncertain wind power integration[J]. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid, 2018, 9(2): 1043-1054. [15] SHI R F, SUN C H, ZHOU Z Y, et al. A robust economic dispatch of residential microgrid with wind power and electric vehicle integration[C]//2016 Chinese Control and Decision Conference (CCDC). Yinchuan: IEEE, 2016: 3672-3676. [16] 李鹏,郑苗苗,陈安伟,等. 基于文化基因算法的交直流混合微网优化运行[J]. 中国电机工程学报,2018,38(11): 3226-3234.LI Peng, ZHENG Miaomiao, CHEN Anwei, et al. Optimal operation of hybrid AC/DC microgrid based on memetic algorithm[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2018, 38(11): 3226-3234. [17] 魏韡,刘锋,梅生伟. 电力系统鲁棒经济调度:(一)理论基础[J]. 电力系统自动化,2013,37(17): 43-49.WEI Wei, LIU Feng, MEI Shengwei. Robust and economical scheduling methodology for power systems: part one,theoretical foundations[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2013, 37(17): 43-49. [18] 徐秋实,邓长虹,赵维兴,等. 含风电电力系统的多场景鲁棒调度方法[J]. 电网技术,2014,38(3): 653-661.XU Qiushi, DENG Changhong, ZHAO Weixing, et al. A multi-scenario robust dispatch method for power grid integrated with wind farms[J]. Power System Technology, 2014, 38(3): 653-661. [19] ZENG B, ZHAO L. Solving two-stage robust optimization problems using a column-and-constraint generation method[J]. Operations Research Letters, 2013, 41(5): 457-461. doi: 10.1016/j.orl.2013.05.003 [20] DANTZIG G B, GLYNN P W, AVRIEL M, et al. Decomposition techniques for multi-area generation and transmission planning under uncertainty[R]. [S. l.]: EPRI, 1989. [21] 刘健辰,刘山林. 基于二阶锥松弛和Big-M法的配电网分布式电源优化配置[J]. 电网技术,2018,42(8): 2604-2611.LIU Jianchen, LIU Shanlin. Optimal distributed generation allocation in distribution network based on second order conic relaxation and big-M method[J]. Power System Technology, 2018, 42(8): 2604-2611. [22] 国家能源局. 光伏发电站功率预测系统技术要求: NB/T 32011—2013[S]. 北京: 新华出版社, 2013. [23] RAWAT T, NIAZI K R. Impact of EV charging/ discharging strategies on the optimal operation of islanded microgrid[J]. The Journal of Engineering, 2019, 18: 4819-4823. doi: 10.1049/joe.2018.9335 [24] 郭尊,李庚银,周明,等. 考虑网络约束和源荷不确定性的区域综合能源系统两阶段鲁棒优化调度[J]. 电网技术,2019,43(9): 3090-3100.GUO Zun, LI Gengyin, ZHOU Ming, et al. Two-stage robust optimal scheduling of regional integrated energy system considering network constraints and uncertainties in source and load[J]. Power System Technology, 2019, 43(9): 3090-3100. -




 下载:
下载: