Word Sense Disambiguation Based on Semi-Supervised Convolutional Neural Networks
-
摘要:
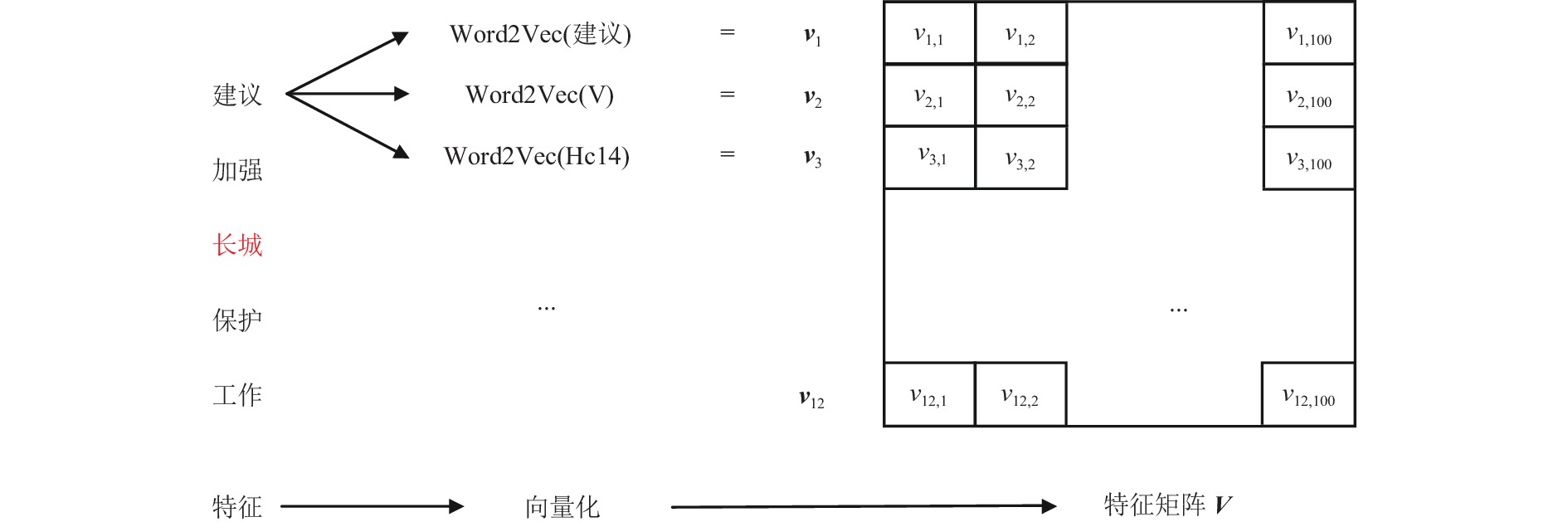
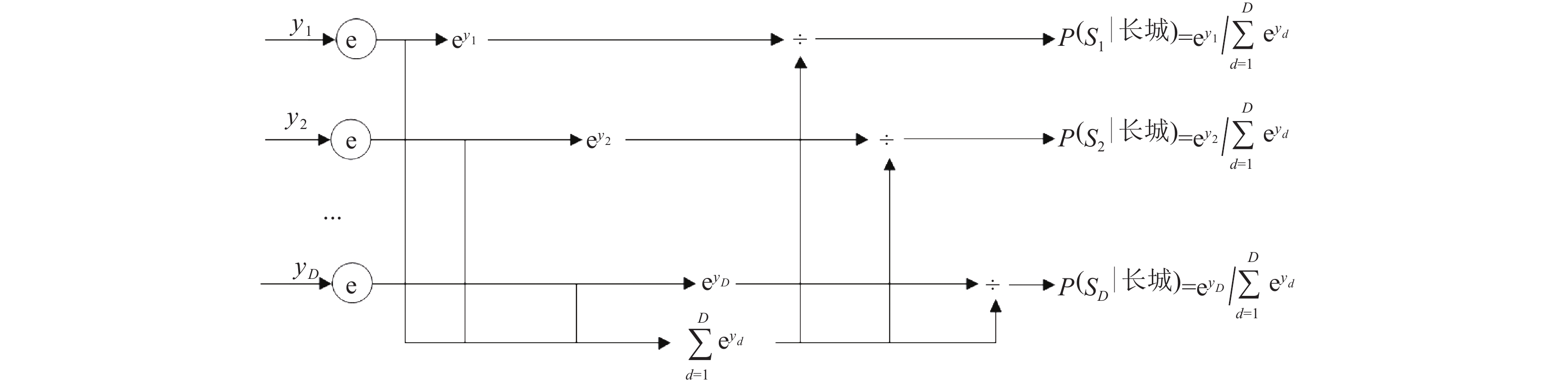
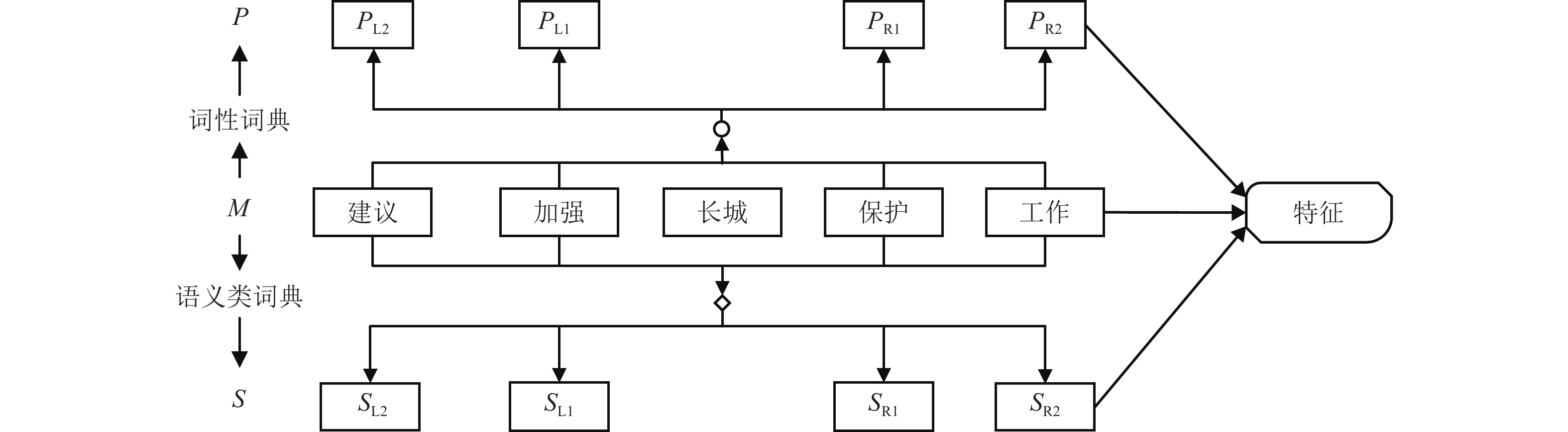
为了解决有标签语料获取困难的问题,提出了一种半监督学习的卷积神经网络(convolutional neural networks, CNN)汉语词义消歧方法. 首先,提取歧义词左右各2个词汇单元的词形、词性和语义类作为消歧特征,利用词向量工具将消歧特征向量化;然后,对有标签语料进行预处理,获取初始化聚类中心和阈值,同时,使用有标签语料对卷积神经网络消歧模型进行训练,利用优化后的卷积神经网络对无标签语料进行语义分类,选取满足阈值条件的高置信度语料添加到训练语料之中,不断重复上述过程,直到训练语料不再扩大为止;最后,使用SemEval-2007:Task#5作为有标签语料,使用哈尔滨工业大学无标注语料作为无标签语料进行实验. 实验结果表明:所提出方法使CNN的消歧准确率提高了3.1%.
Abstract:In order to solve the difficulty of acquiring tagged corpus, a Chinese word sense disambiguation method is proposed on the basis of semi-supervised learning convolutional neural networks (CNN). Firstly, the word, part of speech and semantic category are extracted as discriminative features, which are acquired from 2 word units on the both left and right adjacent to ambiguous word. Word vector tool is used to denote discriminative features as vector. Secondly, tagged corpus is preprocessed to obtain initialized clustering centers and thresholds. At the same time, it is used to train convolutional neural networks. The optimized CNN is applied for determining the semantic categories of ambiguous words in the untagged corpus. Corpus with high confidence that meets threshold conditions is selected into the training corpus. The above process is repeated until the training corpus is no longer expanded. In the last, SemEval-2007: Task#5 is used as the tagged corpus, and the unannotated corpus from Harbin Institute of Technology is used as the untagged corpus. Experimental results show that the proposed method improve disambiguation accuracy of CNN by 3.1%.
-
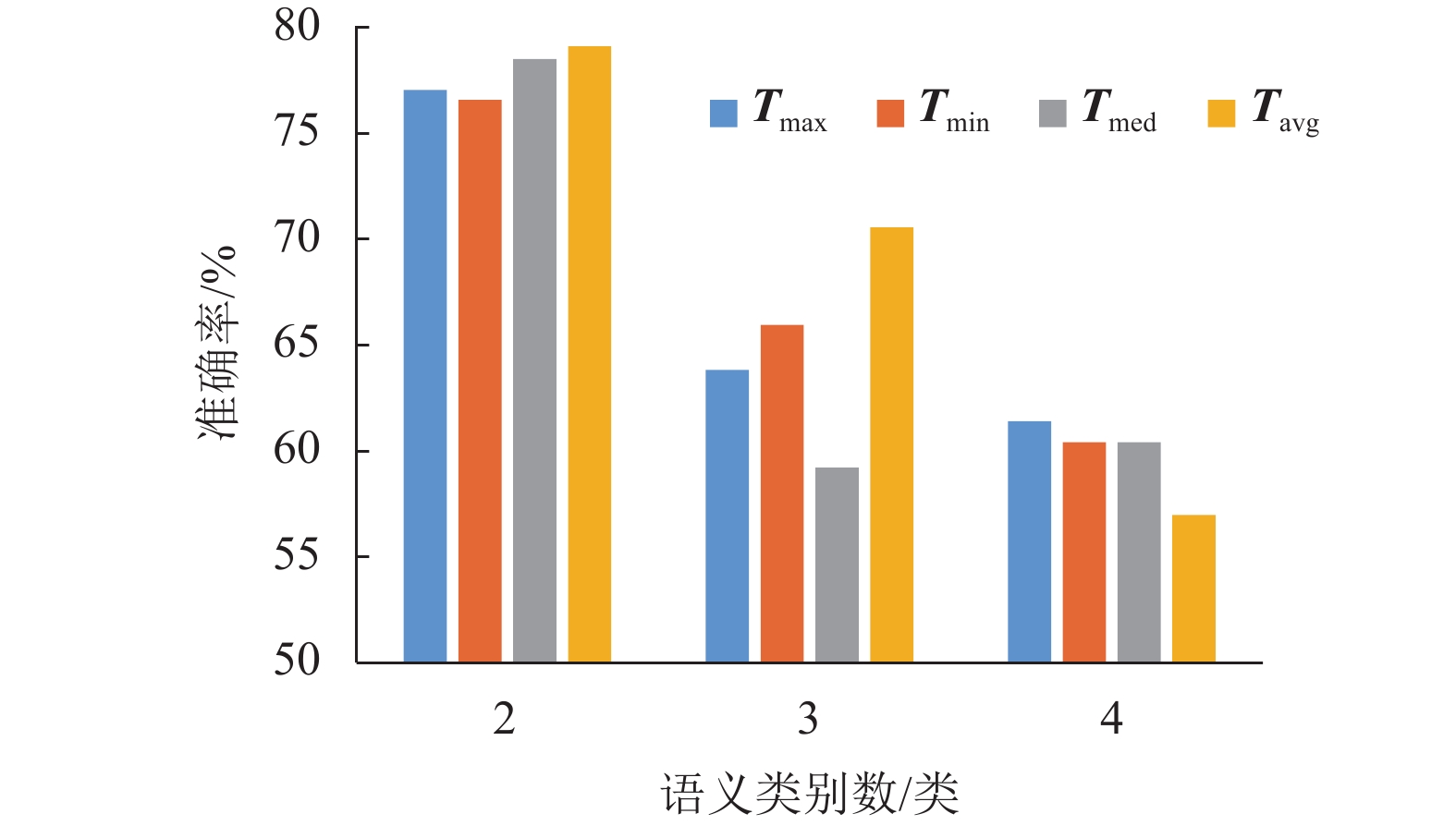
表 1 不同阈值的平均消歧准确率
Table 1. Average disambiguation accuracy of different thresholds
% 类别
数/类歧义
词汇T = Tmax T = Tmin T = Tmed T = Tavg 2 表面
菜
单位
动摇
儿女
镜头
开通
气息
气象
使
眼光88.3
88.9
77.8
86.7
90.2
50.0
60.5
64.2
93.8
70.2
76.982.4
72.2
94.4
80.0
86.3
57.1
58.8
66.5
87.5
72.5
84.676.4
88.9
94.4
93.3
92.4
50.0
58.8
68.6
87.5
76.3
76.982.4
88.9
94.4
73.3
96.3
50.7
58.8
67.3
93.8
79.6
84.63 补
成立
赶
旗帜
日子
长城62.0
84.6
66.7
50.0
51.6
68.061.9
88.2
66.7
62.5
48.4
68.052.4
80.8
55.6
50.0
48.4
68.071.4
76.9
77.8
68.8
48.4
80.04 吃
动
叫56.0
66.7
61.556.0
61.1
64.156.0
61.1
64.156.0
61.1
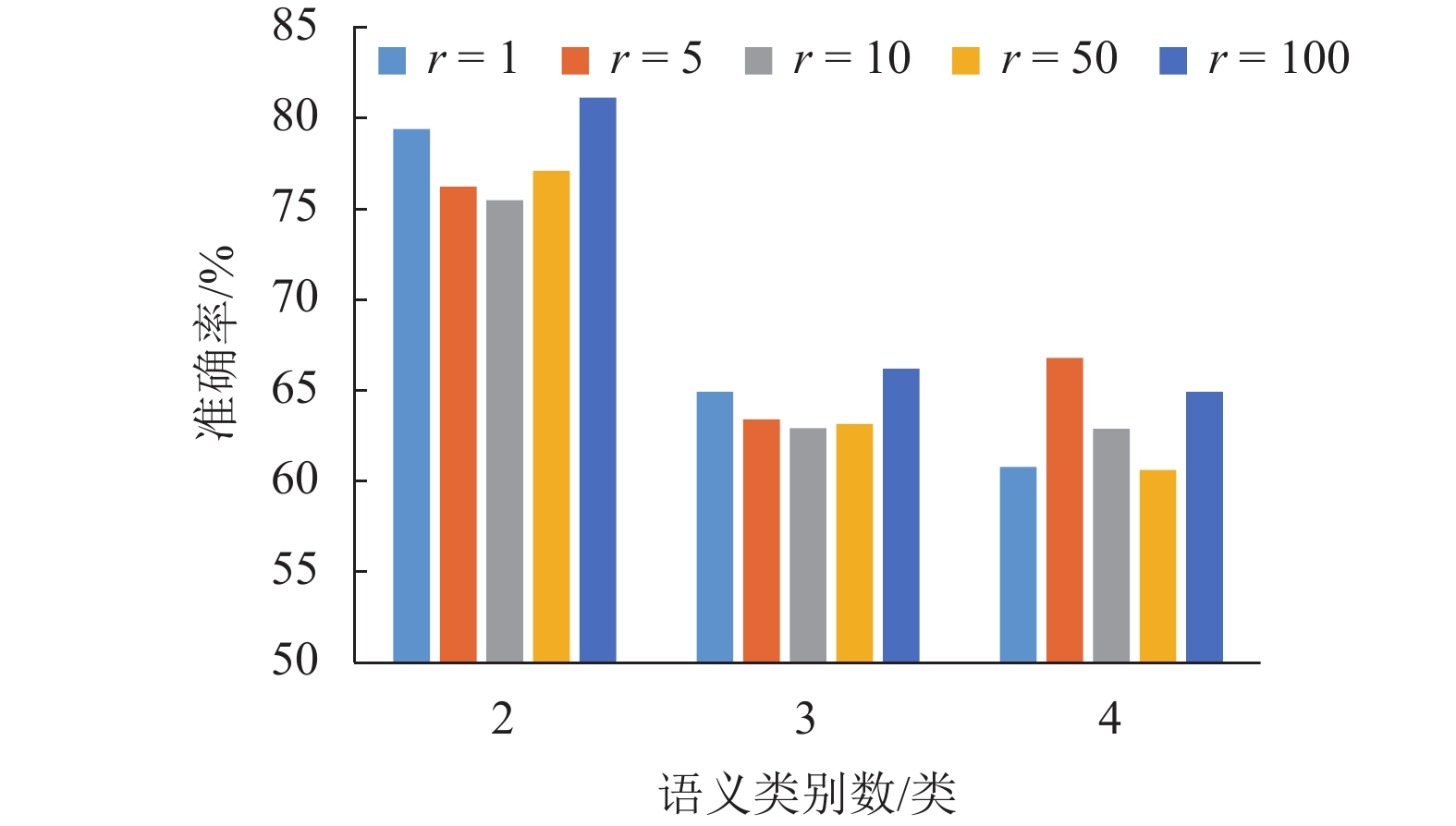
53.8平均准确率 70.7 71.0 70.0 73.2 表 2 不同比率下的平均消歧准确率
Table 2. Average disambiguation accuracy of different rates
% 类别
数/类歧义
词汇r = 1 r = 5 r = 10 r = 50 r = 100 2 表面
菜
单位
动摇
儿女
镜头
开通
气息
气象
使
眼光82.4
88.9
94.5
86.7
82.2
64.3
58.8
64.2
93.8
72.5
84.682.4
77.8
94.5
80.0
88.9
50.0
58.8
68.6
87.5
72.5
76.976.0
83.3
88.9
80.0
84.6
57.1
58.8
66.5
87.5
70.2
76.982.4
88.9
83.3
80.0
90.7
50.0
58.8
66.5
87.5
74.9
84.688.3
88.9
94.5
86.7
92.4
57.1
58.8
68.0
93.8
75.4
88.03 补
成立
赶
旗帜
日子
长城71.4
76.9
72.2
60.5
48.4
60.061.9
84.6
61.1
56.3
48.4
68.052.4
76.9
72.2
56.3
51.6
68.061.9
76.9
61.1
62.5
48.4
68.071.4
80.8
66.7
62.5
51.6
64.04 吃
动
叫60.0
55.6
66.764.0
72.2
64.160.0
67.1
61.560.0
50.0
71.864.0
66.7
64.0平均准确率 72.2 70.9 69.8 70.4 74.2 表 3 3 组实验的平均消歧准确率
Table 3. Average disambiguation accuracy of three groups of experiments
% 类别
数/类歧义词汇 DBN CNN 本文方法 2 表面
菜
单位
动摇
儿女
镜头
开通
气息
气象
使
眼光61.1
55.6
58.8
62.5
70.0
53.3
70.0
71.4
62.5
62.5
71.482.3
72.2
82.3
93.7
94.9
53.3
85.0
64.2
87.5
81.2
71.482.4
88.9
94.4
73.3
96.3
50.7
58.8
67.3
93.8
79.6
84.63 补
成立
赶
旗帜
日子
长城50.0
63.3
50.0
55.6
46.9
38.164.9
66.6
55.5
72.2
50.0
71.471.4
76.9
77.8
68.8
48.4
80.04 吃
动
叫43.5
50.0
30.052.1
50.0
70.056.0
61.1
53.8平均准确率 56.3 71.0 73.2 -
[1] LESK M. Automatic sense disambiguation using machine readable dictionaries: how to tell a pine code from an ice cream[C]//The Figth Annual International Conference on Systems Documentation. Toronto: ACM Press, 1986: 24-26 [2] 杨安,李素建,李芸. 基于领域知识和词向量的词义消歧方法[J]. 北京大学学报(自然科学版),2017,53(2): 204-210.YANG An, LI Sujian, LI Yun. Word sense disambiguation based on domain knowledge and word vector model[J]. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Pekinensis, 2017, 53(2): 204-210. [3] FRANCO R L, IVAN L A , PINTO D, et al. Context expansion for domain-specific word sense disambiguation[J]. IEEE Latin America Transactions, 2015, 13(3): 784-789. doi: 10.1109/TLA.2015.7069105 [4] 唐共波,于东,荀恩东. 基于知网义原词向量表示的无监督词义消歧方法[J]. 中文信息学报,2015,29(6): 23-29. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0077.2015.06.004TANG Gongbo, YU Dong, XUN Endong. An unsupervised word sense disambiguation method based on sememe vector in HowNet[J]. Journal of Chinese Information Processing, 2015, 29(6): 23-29. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0077.2015.06.004 [5] ARAB M, JAHROMI M Z, FAKHRAHMAD S M. A graph-based approach to word sense disambiguation. An unsupervised method based on semantic relatedness[C]//2016 24th Iranian Conference on Electrical Engineering (CEE). Shiraz: IEEE, 2016: 250-255. [6] 孟禹光,周俏丽,张桂平,等. 引入词性标记的基于语境相似度的词义消歧[J]. 中文信息学报,2018,32(8): 9-18. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0077.2018.08.003MENG Yuguang, ZHOU Qiaoli, ZHANG Guiping, et al. Word sense disambiguation based on context simila- rity with POS tagging[J]. Journal of Chinese Information Processing, 2018, 32(8): 9-18. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0077.2018.08.003 [7] 鹿文鹏,黄河燕,吴昊. 基于领域知识的图模型词义消歧方法[J]. 自动化学报,2014,40(12): 2836-2850.LU Wenpeng, HUANG Heyan, WU Hao. Word sense disambiguation with graph model based on domain knowledge[J]. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2014, 40(12): 2836-2850. [8] DUQUE A, STEVENSON M, MARTINEZ-ROMO J, et al. Co-occurrence graphs for word sense disambiguation in the biomedical domain[J]. Artificial Intelligence in Medicine, 2018, 87: 9-19. doi: 10.1016/j.artmed.2018.03.002 [9] TRIPODI R, PELILLO M. A game-theoretic approach to word sense disambiguation[J]. Computational Linguistics, 2017, 43(1): 31-70. doi: 10.1162/COLI_a_00274 [10] XU Xueping, YU Jianping, PIAO Xiaoyu. Contribution of governors to word sense disambiguation of English preposition[J]. ICIC Express Letters, 2015, 6(3): 723-730. [11] 杨陟卓. 基于上下文翻译的有监督词义消歧研究[J]. 计算机科学,2017,44(4): 252-255, 280. doi: 10.11896/j.issn.1002-137X.2017.04.053YANG Zhizhuo. Supervised WSD method based on context translation[J]. Computer Science, 2017, 44(4): 252-255, 280. doi: 10.11896/j.issn.1002-137X.2017.04.053 [12] CARDELLINO C, ALONSO ALEMANY L. Exploring the impact of word embeddings for disjoint semisupervised Spanish verb sense disambiguation[J]. Inteligencia Artificial, 2018, 21(61): 67-81. doi: 10.4114/intartif.vol21iss61pp67-81 [13] HUANG Z H, CHEN Y D, SHI X D. A novel word sense disambiguation algorithm based on semi-supervised statistical learning[J]. International Journal of Applied Mathematics and Statistics, 2013, 43(13): 452-458. [14] MAHMOODVAND M, HOURALI M. Semi-supervised approach for Persian word sense disambiguation[C]// 2017 7th International Conference on Computer and Knowledge Engineering (ICCKE). Mashhad: IEEE, 2017: 104-110. [15] 刘子图,全紫薇,毛如柏,等. NT-EP:一种无拓扑结构的社交消息传播范围预测方法[J]. 计算机研究与发展,2020,57(6): 1312-1322. doi: 10.7544/issn1000-1239.2020.20190584LIU Zitu, QUAN Ziwei, MAO Rubai, et al. NT-EP:a non-topology method for predicting the scope of social message propogation[J]. Journal of Computer Research and Development, 2020, 57(6): 1312-1322. doi: 10.7544/issn1000-1239.2020.20190584 [16] 刘勇,谢胜男,仲志伟,等. 社会网中基于主题兴趣的影响最大化算法[J]. 计算机研究与发展,2018,55(11): 2406-2418. doi: 10.7544/issn1000-1239.2018.20170672LIU Yong, XIE Shengnan, ZHONG Zhiwei, et al. Topic-interest based influence maximization algorithm in social networks[J]. Journal of Computer Research and Development, 2018, 55(11): 2406-2418. doi: 10.7544/issn1000-1239.2018.20170672 [17] 薛涛,王雅玲,穆楠. 基于词义消歧的卷积神经网络文本分类模型[J]. 计算机应用研究,2018,35(10): 2898-2903. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3695.2018.10.004XUE Tao, WANG Yaling, MU Nan. Convolutional neural network based on word sense disambiguation for text classification[J]. Application Research of Computers, 2018, 35(10): 2898-2903. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3695.2018.10.004 [18] PESARANGHADER A, MATWIN S, SOKOLOVA M, et al. DeepBioWSD:effective deep neural word sense disambiguation of biomedical text data[J]. Journal of the American Medical Informatics Association, 2019, 26(5): 438-446. doi: 10.1093/jamia/ocy189 [19] BORDES A, GLOROT X, WESTON J, et al. A semantic matching energy function for learning with multi-relational data[J]. Machine Learning, 2014, 94(2): 233-259. doi: 10.1007/s10994-013-5363-6 [20] CHEN S J, HUNG C. Word sense disambiguation based sentiment lexicons for sentiment classification[J]. Knowledge-Based Systems, 2016, 110: 224-232. doi: 10.1016/j.knosys.2016.07.030 -




 下载:
下载: