An NLOS Environment Location Algorithm Based on Geometric Constraint and Iteration
-
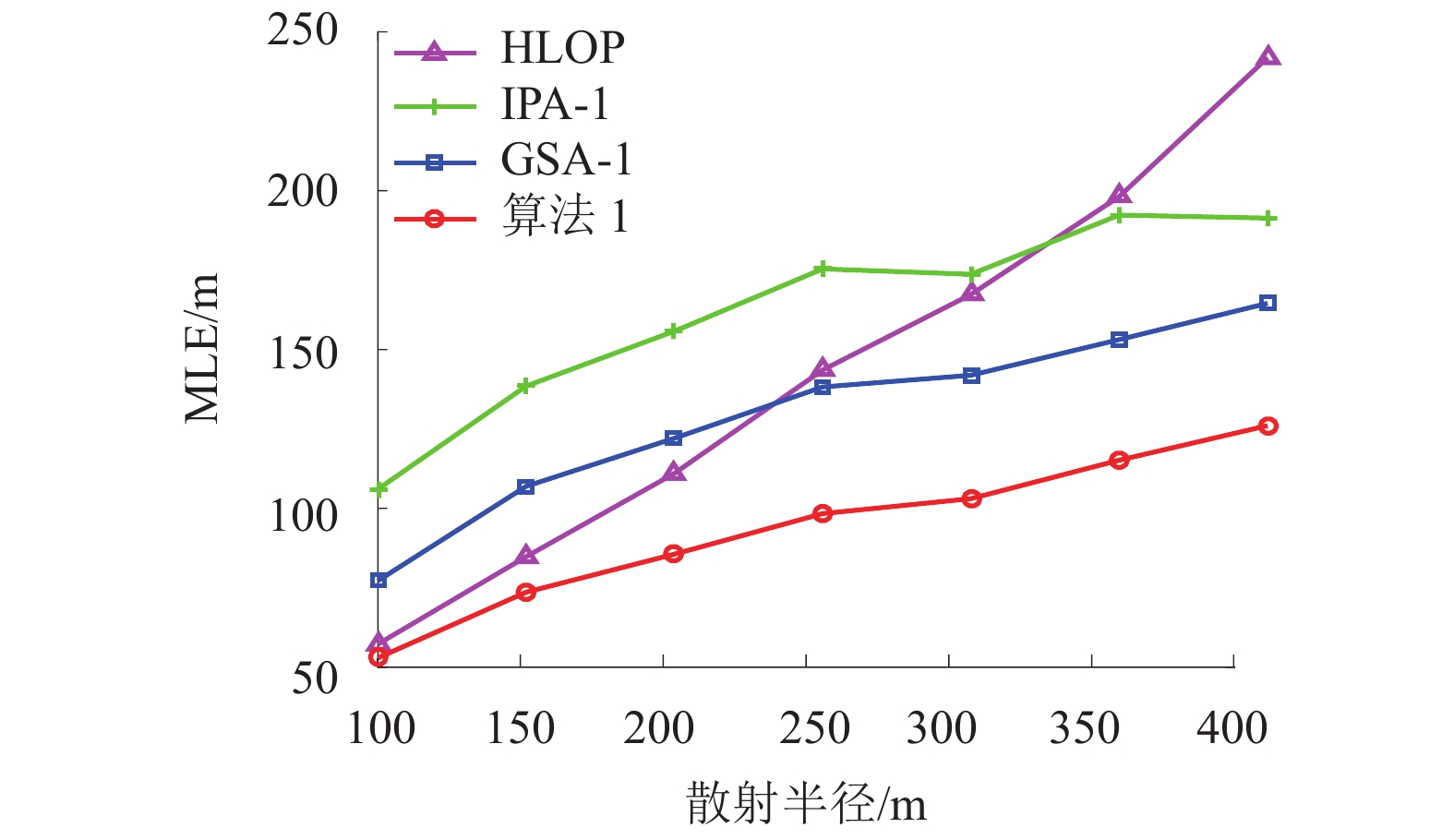
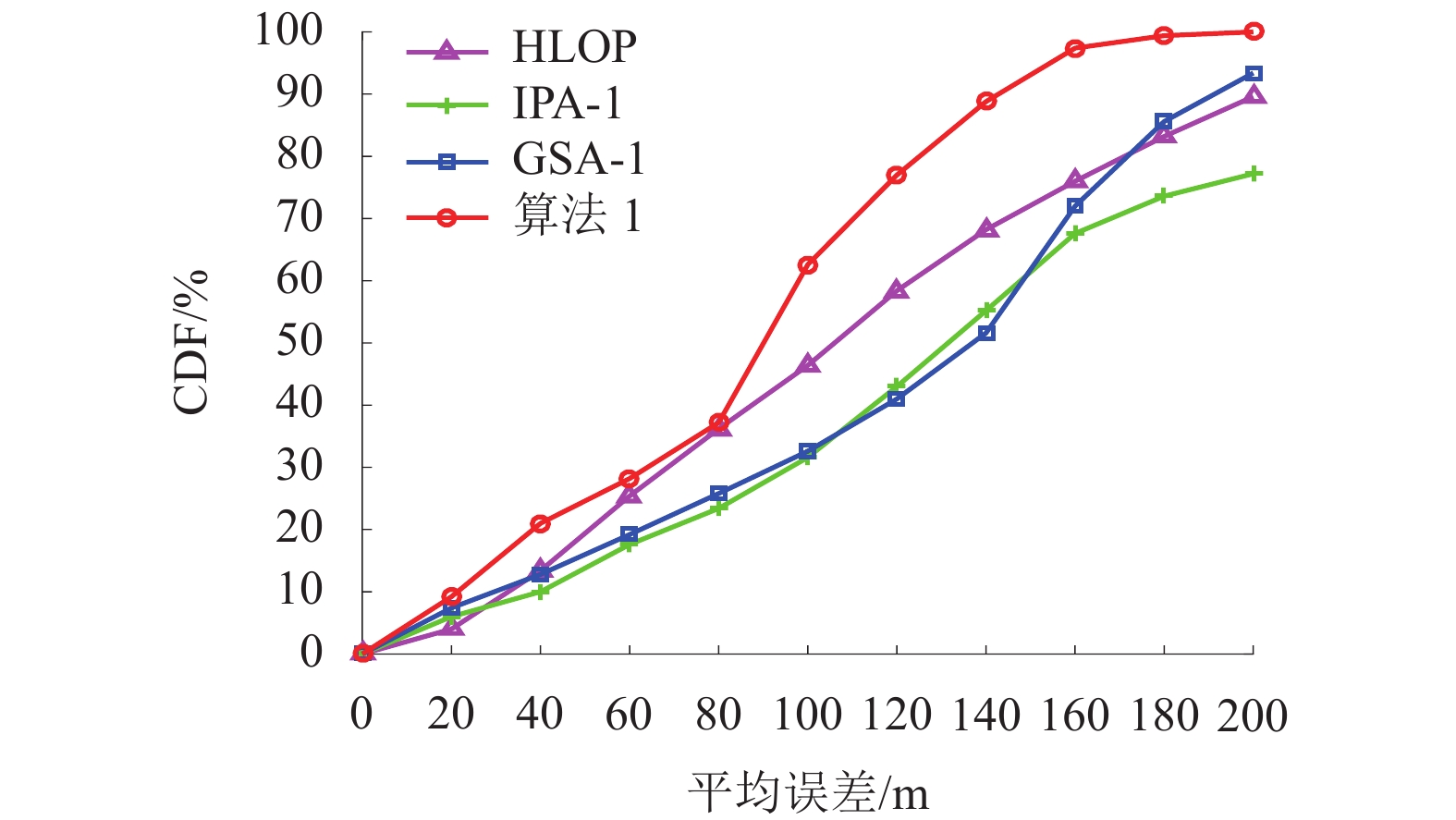
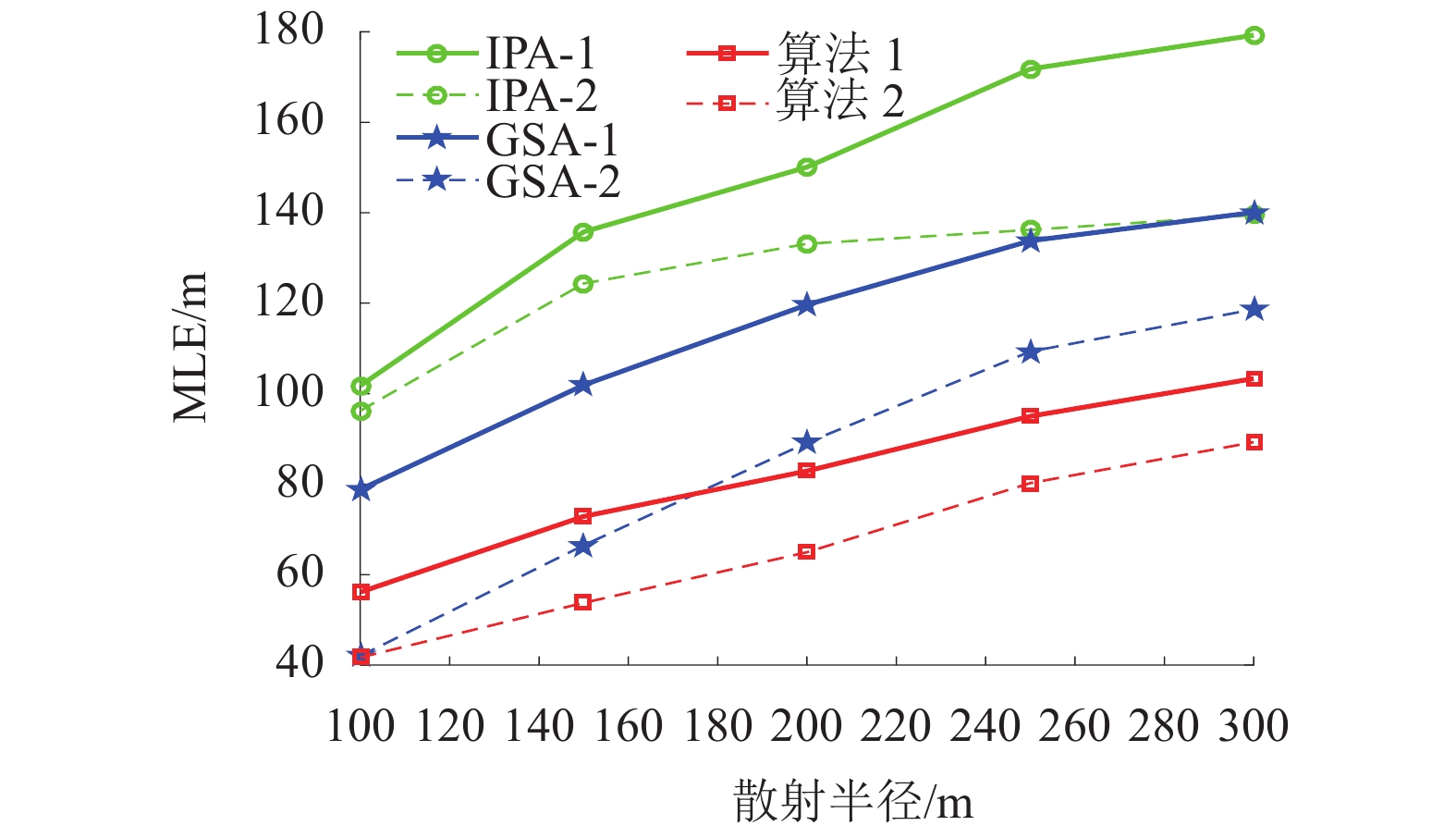
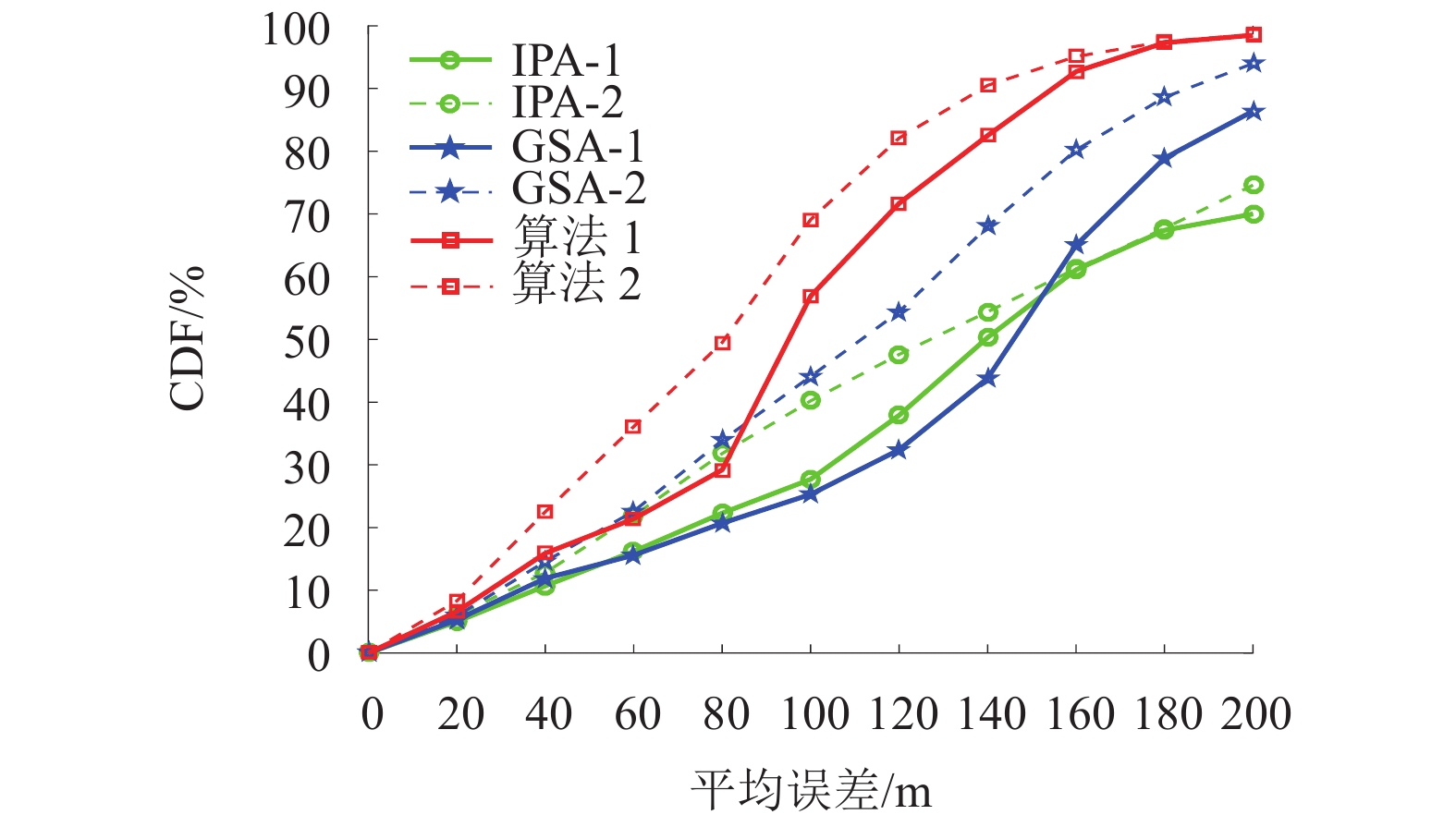
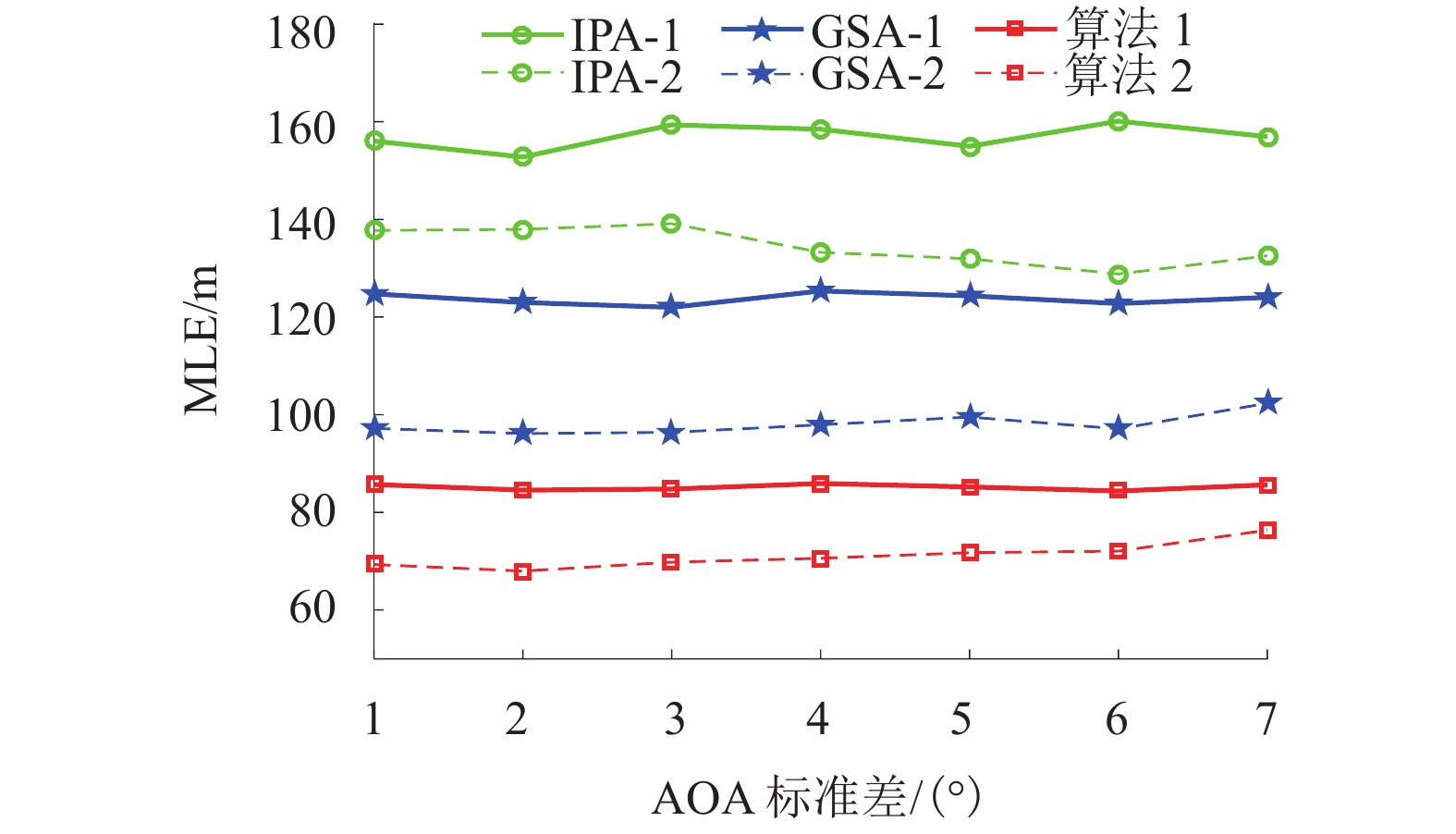
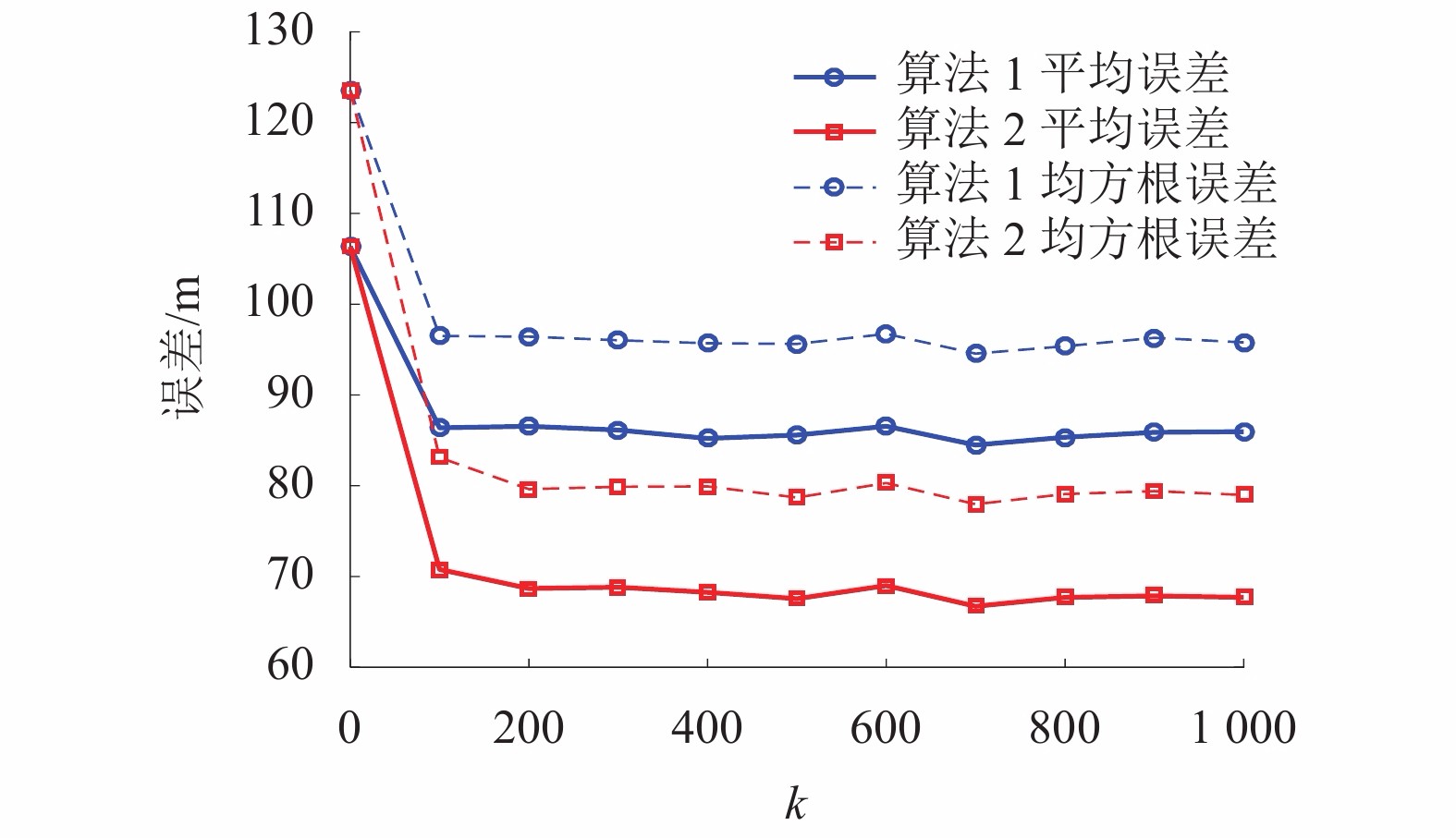
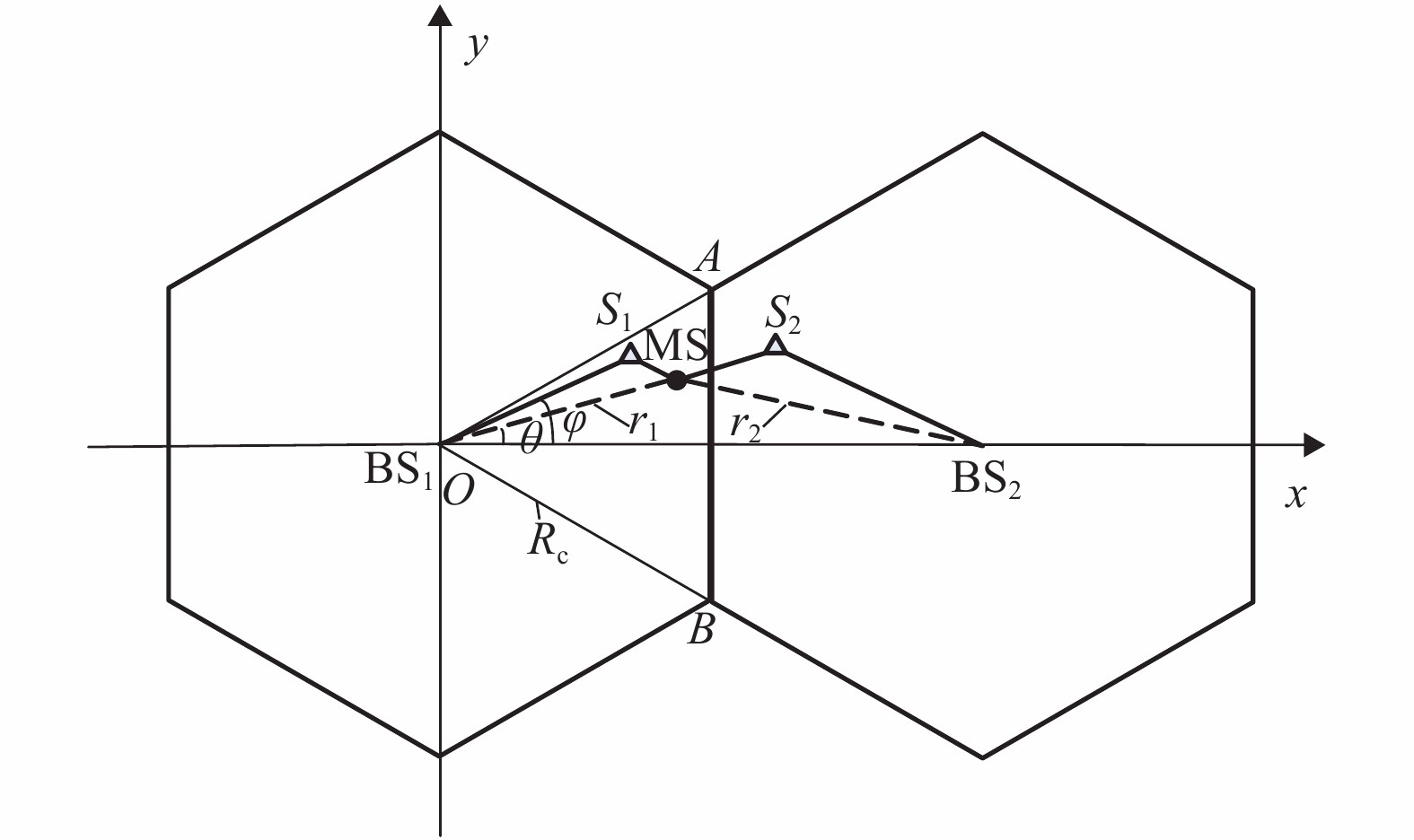
摘要: 针对在非视距 (non-line-of-sight,NLOS)环境中传统最优化定位算法抗NLOS误差能力较弱、且需要一个较准确的初始估计位置以确保算法收敛这一问题,提出一种应用在双基站场景下的基于几何约束及迭代的定位算法. 通过引入最大散射半径作为几何约束条件,以线性迭代方式进行一维全局搜索,并采用最小二乘算法获得移动台(mobile station,MS)初始估计位置,然后利用设定的阈值门限对各初始位置点进行筛选,最后通过加权平均获得MS的最终估计位置. 仿真结果表明:当散射半径为200 m时,本文算法的定位误差在200 m以下的概率能达到100%;在相同环境下,本文算法计算时间开销仅是网格搜索法的0.4%.Abstract: In non-line-of-sight (NLOS) environments, the traditional optimal localization algorithm is weak against NLOS errors and needs an accurate initial position value to guarantee the algorithm converge. To deal with this, a positioning algorithm based on geometric constraint and iteration in a scenario of two base station (BS) is proposed. By introducing the maximum scattering radius as the geometric constraint condition, the linear iterative method is used to perform a one-dimensional global search, and the initial estimation positions of mobile station (MS) are obtained by the least squares (LS) algorithm. Then the initial MS estimation positions are filtered by a distance threshold value, and finally its final position is obtained by weighted average. Simulation results show that when the scattering radius is 200 m, the probability of location error under 200 m can reach 100%, and in the same environment, the calculation time of this algorithm is only 0.4% of the grid search algorithm.
-
Key words:
- non-line-of-sight (NLOS) /
- geometric constraint /
- iteration /
- least squares /
- weighted average
-
表 1 算法描述
Table 1. Algorithm description
表 2 算法时间开销
Table 2. Algorithm time cost
s 算法 IPA GSA 本文迭代算法 约束条件 1 0.1786 0.1350 0.0059 约束条件 2 0.1644 0.1087 0.0050 -
VENKATRAMAN S, CAFFERY J. Hybrid TOA/AOA techniques for mobile location in non-line-of-sight environments[C]//Proceedings of IEEE Wireless Communications and Networking Conference. Atlanta: IEEE, 2004: 274-278. HASAN S, UKKUSURI S V. Reconstructing activity location sequences from incomplete check-in data:a semi-Markov continuous-time Bayesian network model[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2018, 19(3): 687-689. doi: 10.1109/TITS.2017.2700481 DIAO Hongxue, ZHAO Junhui. Cmd-based NLOS identification and mitigation in wireless sensor networks[C]//Proceedings of IEEE International Conference on Communications Workshops (ICC Workshops). Shanghai: IEEE, 2019: 1-6. DENG Ping. An NLOS error mitigation scheme based on tdoa reconstruction for cellular location services[J]. Chinese Journal of Radio Science, 2003, 18(3): 311-316. LIU Lin, DENG Ping, FAN Ping Zhi. A simple and efficient positioning algorithm based on geometry[C]// Proceedings of International Conference on Communications and Mobile Computing. Shenzheng: IEEE, 2010: 374-377. VENKATRAMAN S, CAFFERY J, YOU H R. A novel toa location algorithm using los range estimation for nlos environments[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2004, 53(5): 1515-1524. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2004.832384 AL-BAWRI S S, JAMLOS M F, ALJUNID S A. Outdoor location estimation for mobile based on single base station scattering distance[C]//Proceedings of IEEE International RF and Microwave Conference (RFM). Kuching: IEEE, 2015: 92-95. CHEN C S. A non-line-of-sight error mitigation method for location estimation[J]. International Journal of Distributed Sensor Networks, 2017, 13(1): 155014771688273.1-15501471688273.15. LI W, CHEN Y, ASIF M, A Wi-Fi-based indoor positioning algorithm with mitigating the influence of NLOS[C]//Proceedings of the 8th International Conference on Communication Software and Networks. Beijing: IEEE, 2016: 520-523. CHEN C S, CHIU Y J, LIN J M, et al. Geometrical positioning schemes for MS location estimation[C]// Proceedings of International Symposium on Computer, Consumer and Control, Taichung: IEEE, 2012: 487-490. XIE Yaqin, WANG Yan, WU Bo, et al. Localization by hybrid TOA, AOA and DSF estimation in NLOS environments[C]//Proceedings of the 72nd IEEE Vehicular Technology Conference. Ottawa: IEEE, 2010: 1-5. CHEN C S, HUANG J F, LIN S C, et al. Applying geometric dilution of precision approximation to adaptive neural network learning for precise mobile station positioning[C]//Proceedings of International Conference on Machine Learning and Cybernetics (ICMLC), Chengdu: IEEE, 2018: 474-479. WU Shixun, XU Dengyuan, TAN Jin, et al. Two base station location techniques with adjusted measurements in circular scattering environments[J]. International Journal of Communication Systems, 2016, 29(6): 1073-1083. doi: 10.1002/dac.3073 ANTCZAK T. A lower bound for the penalty parameter in the exact minimax penalty function method for solving nondifferentiable extremum problems[J]. Journal of Optimization Theory and Applications, 2013, 159(2): 437-453. doi: 10.1007/s10957-013-0335-3 ALJAZZAR S O, CAFFERY J, YOU H R. A scattering model based approach to nlos mitigation in TOA location systems[C]//Proceedings of the 55th Vehicular Technology Conference (VTC). Birmingham: IEEE, 2002: 861-865. -




 下载:
下载: