Experimental Study on Ductile Seismic Performance of Rectangular Hollow Concrete Columns
-
摘要:
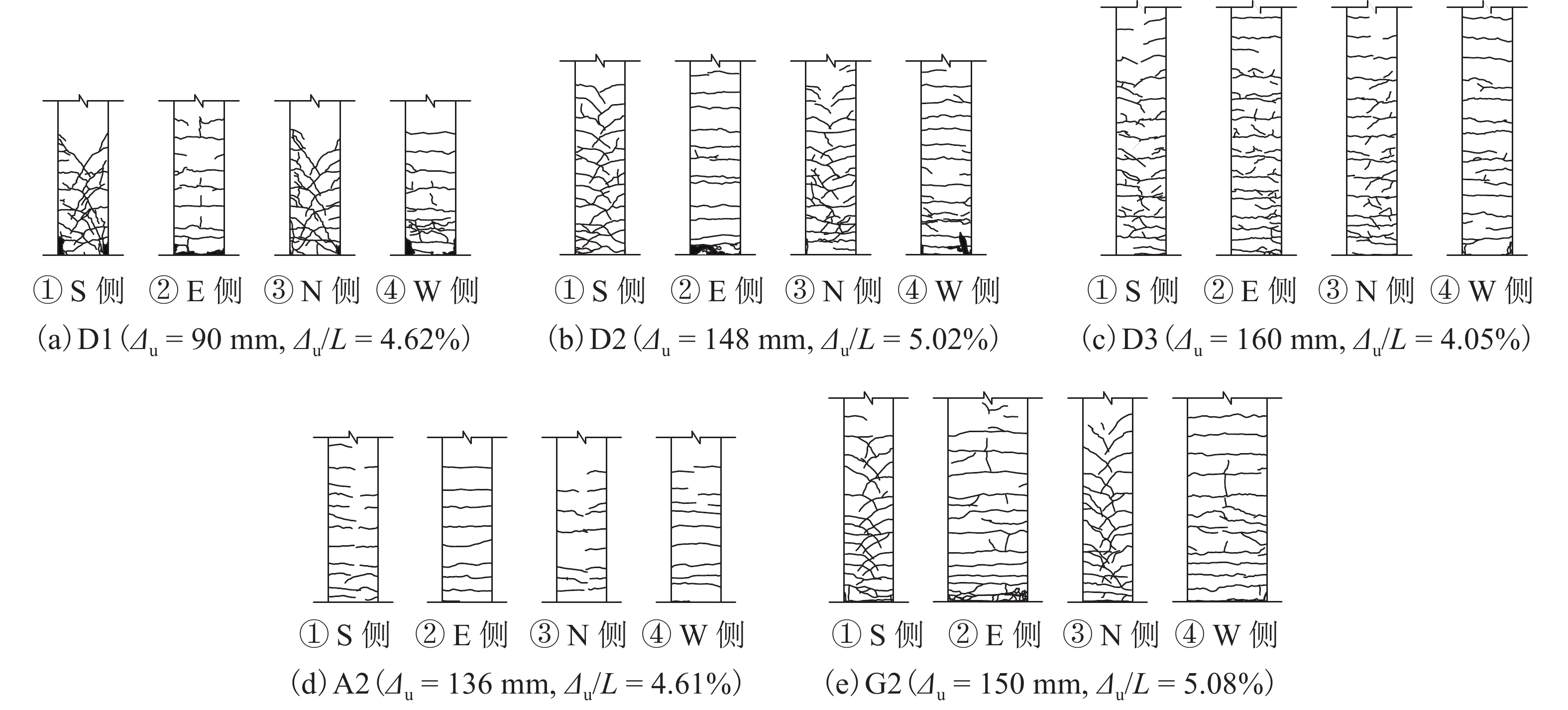
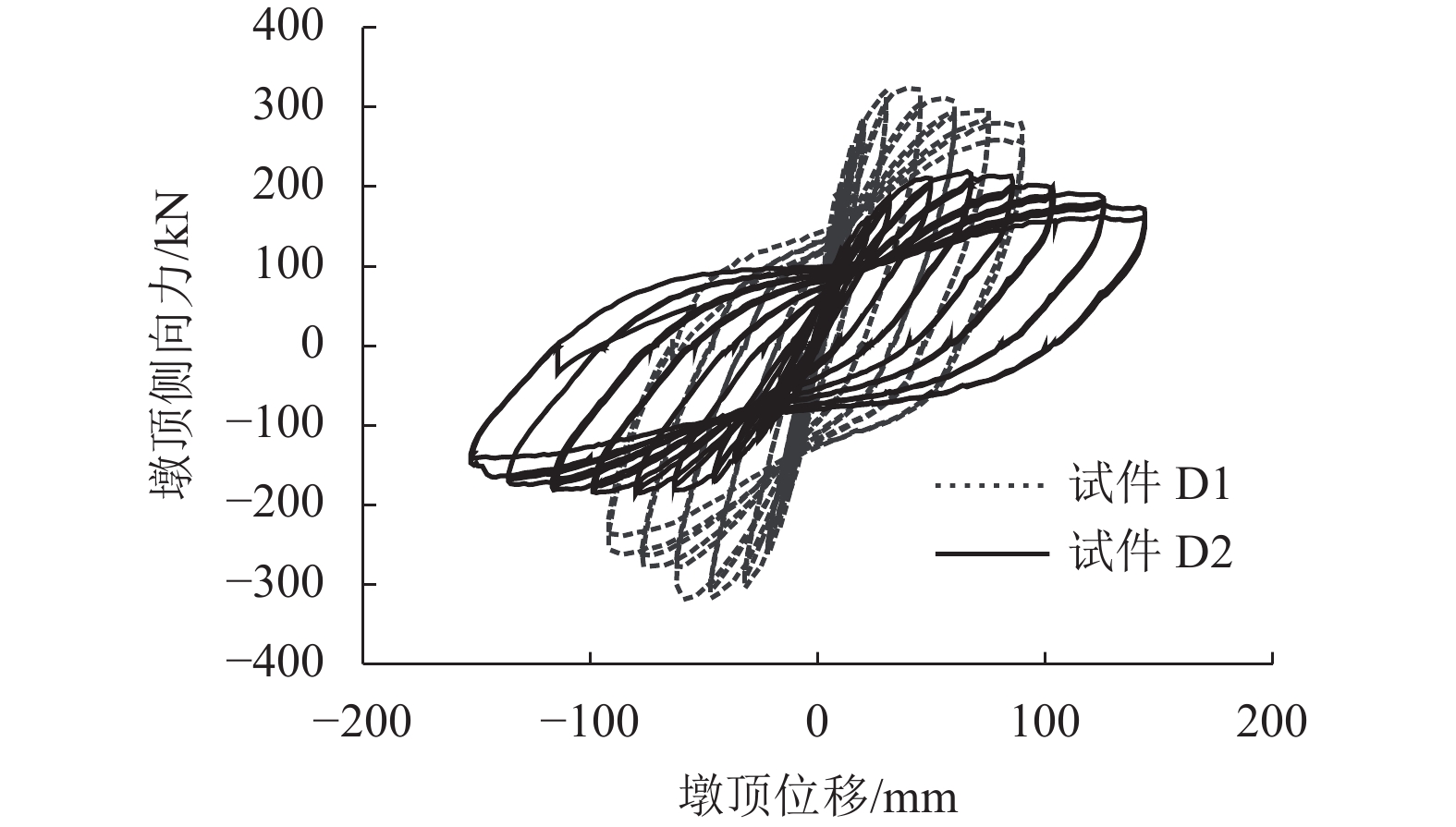
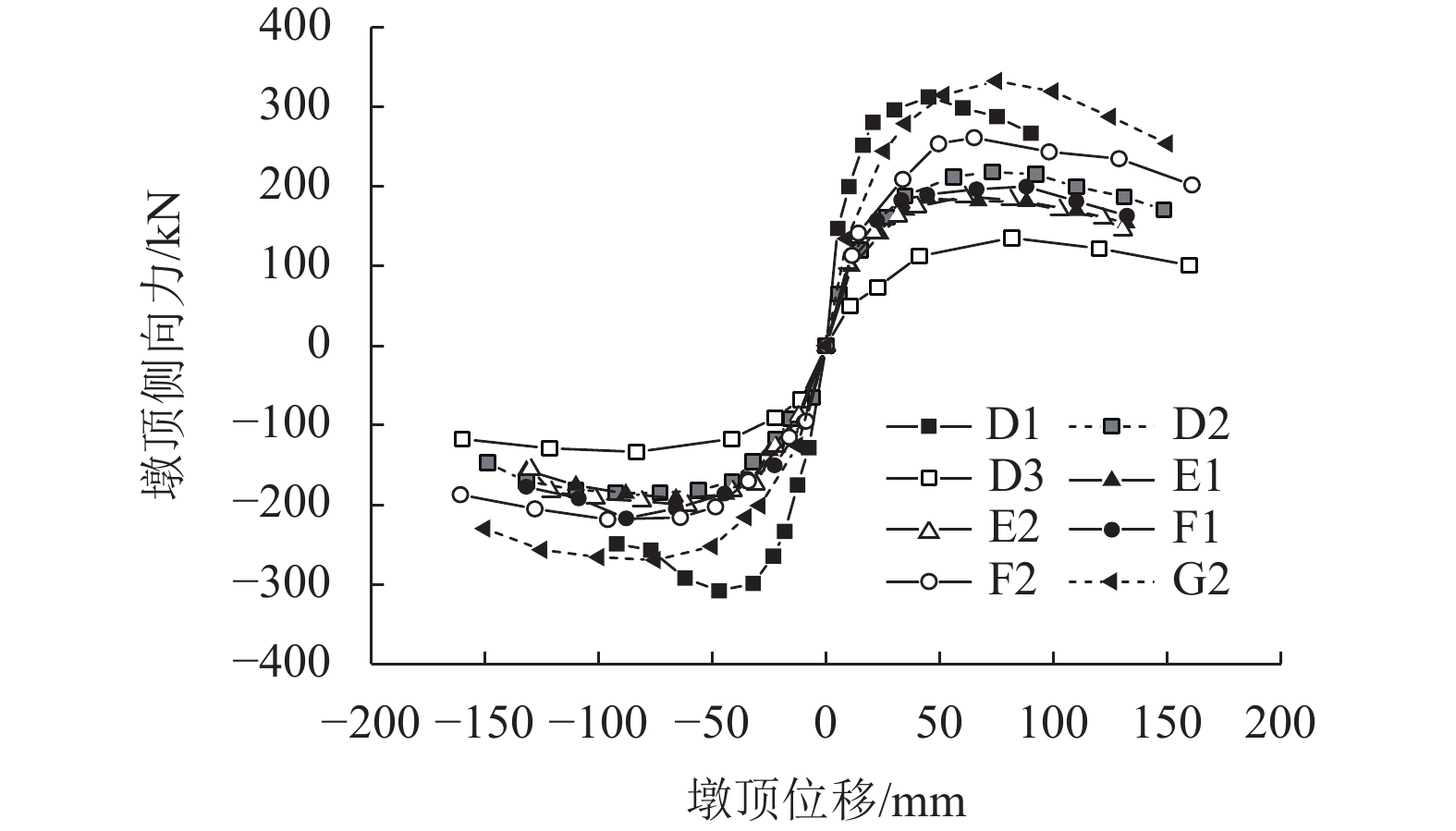
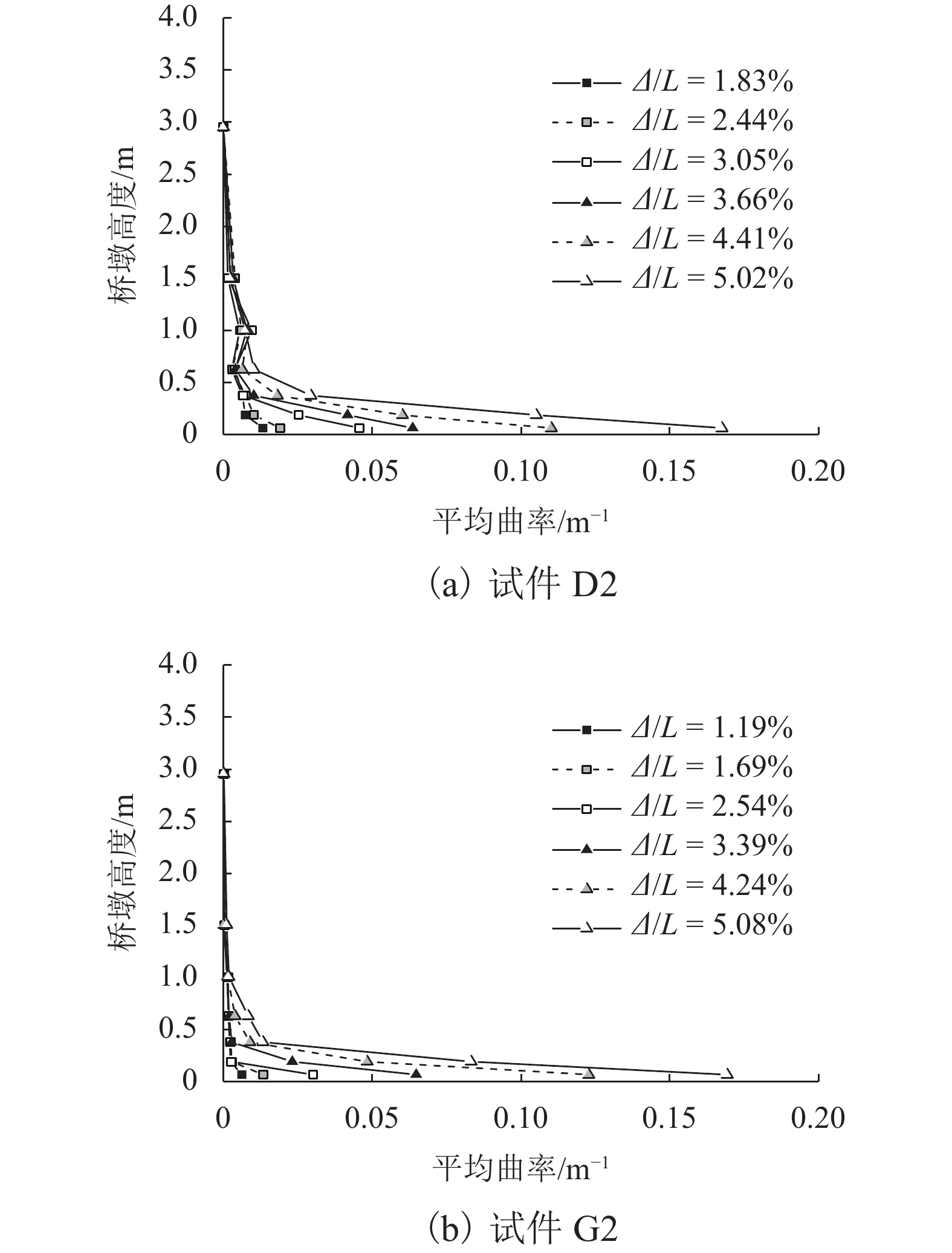
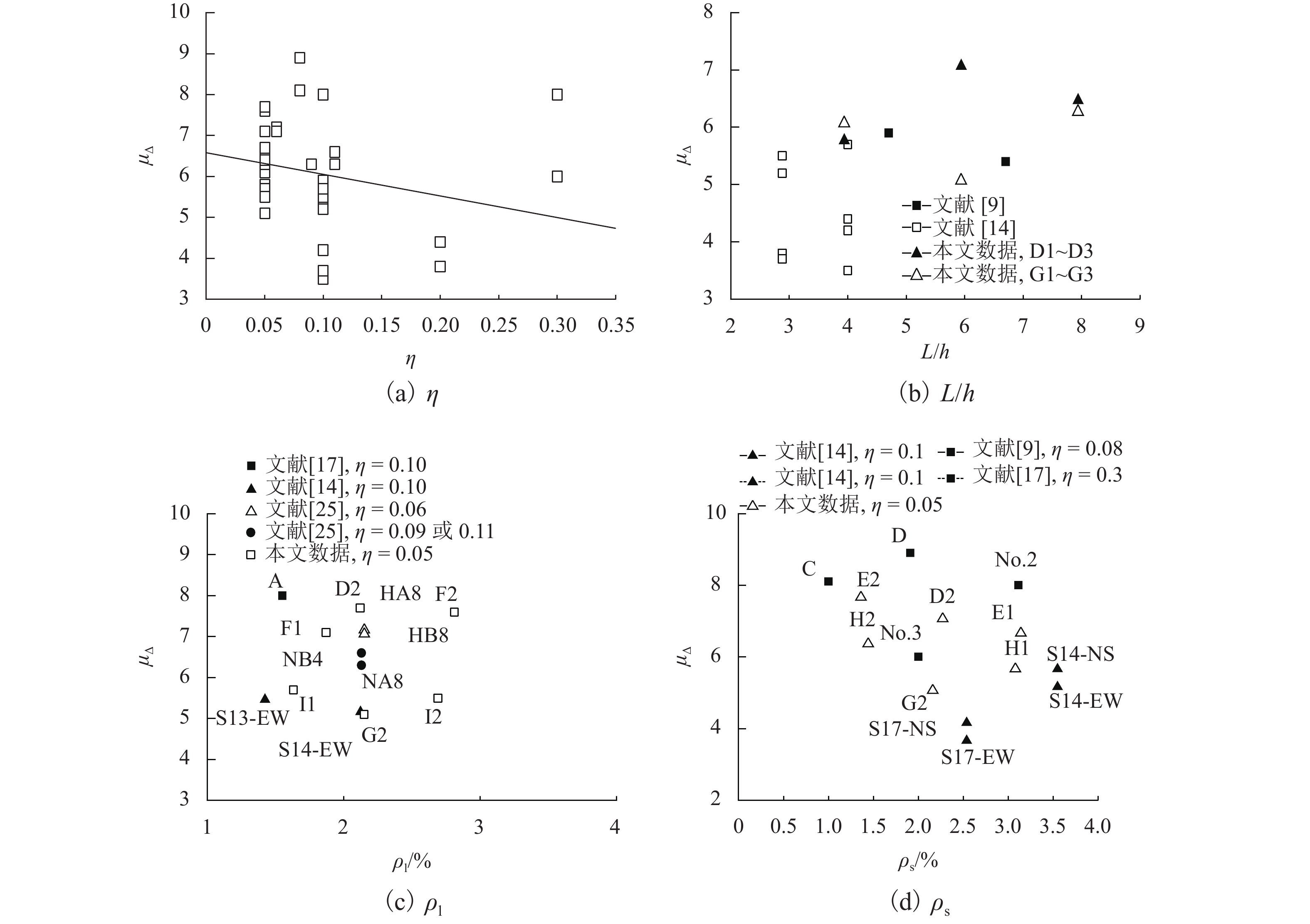
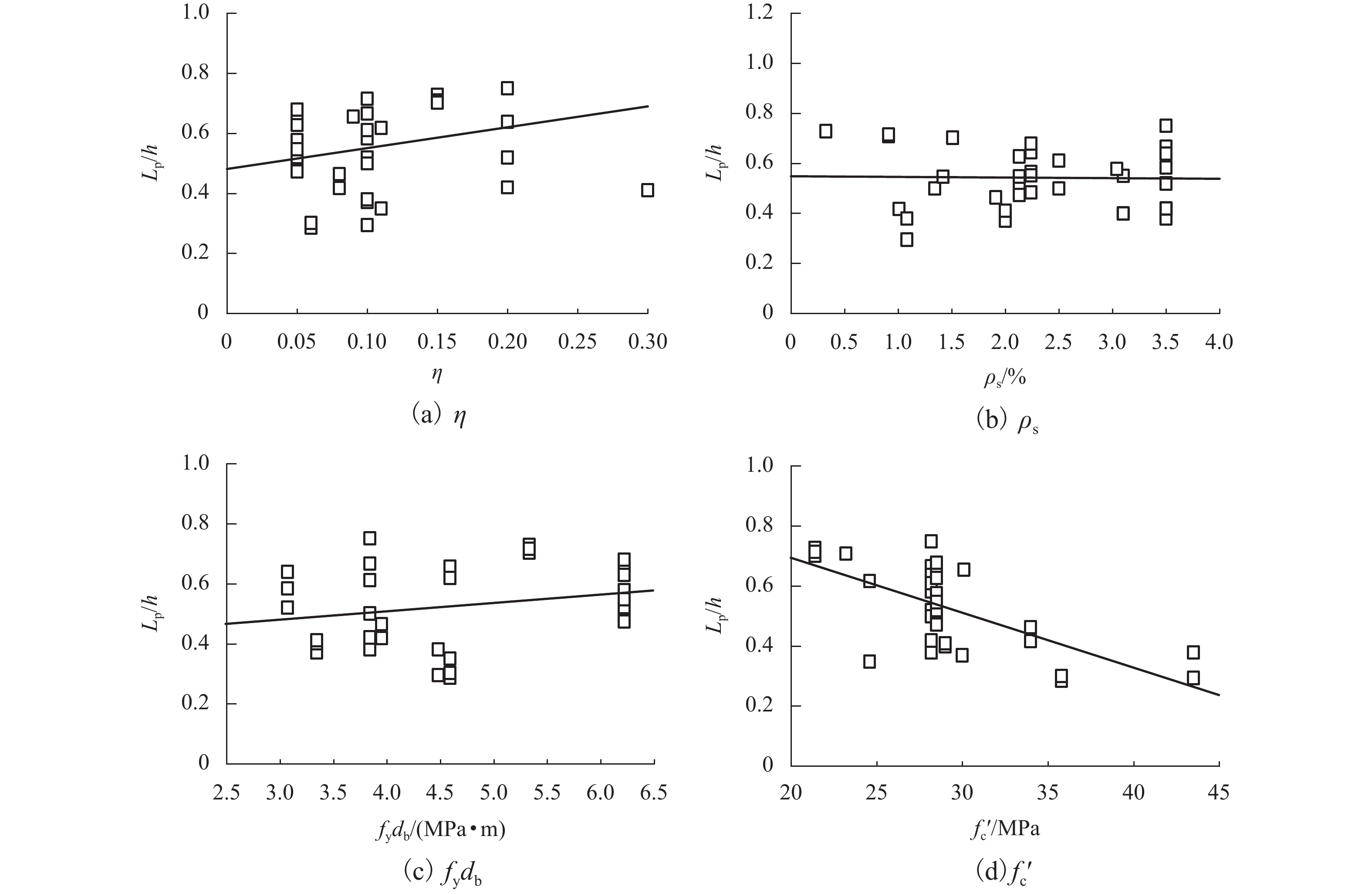
为深入认识混凝土空心墩地震损伤机理并评估其延性能力,对不同剪跨比、纵筋率及配箍率的方形和矩形空心墩试件开展拟静力加载试验. 观测各墩裂缝分布和损伤情况,分析桥墩的滞回性能、曲率及位移延性,并结合文献试验数据探讨既有塑性铰公式对空心墩顶部位移能力计算的适用性. 研究结果表明:各空心墩试件呈弯曲破坏特征,延性系数均在5.0以上,抗震性能良好;相同剪跨比下空心墩抗剪性能弱于相同外尺寸实心墩;增加纵向率能够适当提升空心墩侧向承载力和极限位移;在低轴压比下,纵筋率和箍筋用量对空心墩位移延性系数的影响规律不明显;空心墩塑性铰长度随剪跨比、纵筋强度或直径、轴压比的增加而提高,随混凝土强度的增加而降低,而配箍率的影响不显著;Mander、孙治国和JRA塑性铰模型预测值与试验值误差不超过5%,其中Mander公式计算效果最佳,可用于评估空心墩等效塑性铰长度;规范中较多采用的Paulay-Priestley模型高估了空心墩塑性铰长度,会使得桥墩抗震设计偏于不安全.
Abstract:To deeply explore the seismic damage mechanism and evaluate the ductile capacity of hollow RC columns, square and rectangular hollow specimens with different aspect ratios, longitudinal rebar ratios, and stirrup ratios were tested under quasi-static loading. The crack distribution and damage state were observed. The hysteretic behavior, curvature and displacement ductility were analyzed. According to the experimental data in literature, applicability of the existing plastic hinge formulas to estimate the tip displacement capacity of hollow columns was discussed. The results show that all hollow specimens suffer flexural failure with ductility factor over 5.0, resulting in excellent seismic performance. The shear performance of hollow columns is weaker than that of solid members with the same external size and aspect ratio. The lateral bearing capacity and ultimate displacement can be properly improved by increasing longitudinal rebar ratio. However, the longitudinal steel and stirrup amount exert vague effects on the displacement ductility factor of hollow columns with low axial load ratio. The plastic hinge length of hollow columns increases with increased aspect ratio, longitudinal rebar strength/diameter, or axial load ratio, but decreases with the increment in concrete strength. The influence of stirrup on the plastic hinge is not obvious. The relative errors between the test and calculation of Mander, Sun and JRA models are less than 5%. Mander supplies the best result, which can be used to evaluate the equivalent plastic hinge length of a hollow column. The Paulay-Priestley model, adopted in many codes, overestimates the length of the plastic hinge of hollow members, leading to unsafe seismic design.
-
表 1 桥墩模型设计参数
Table 1. Design parameters of pier samples
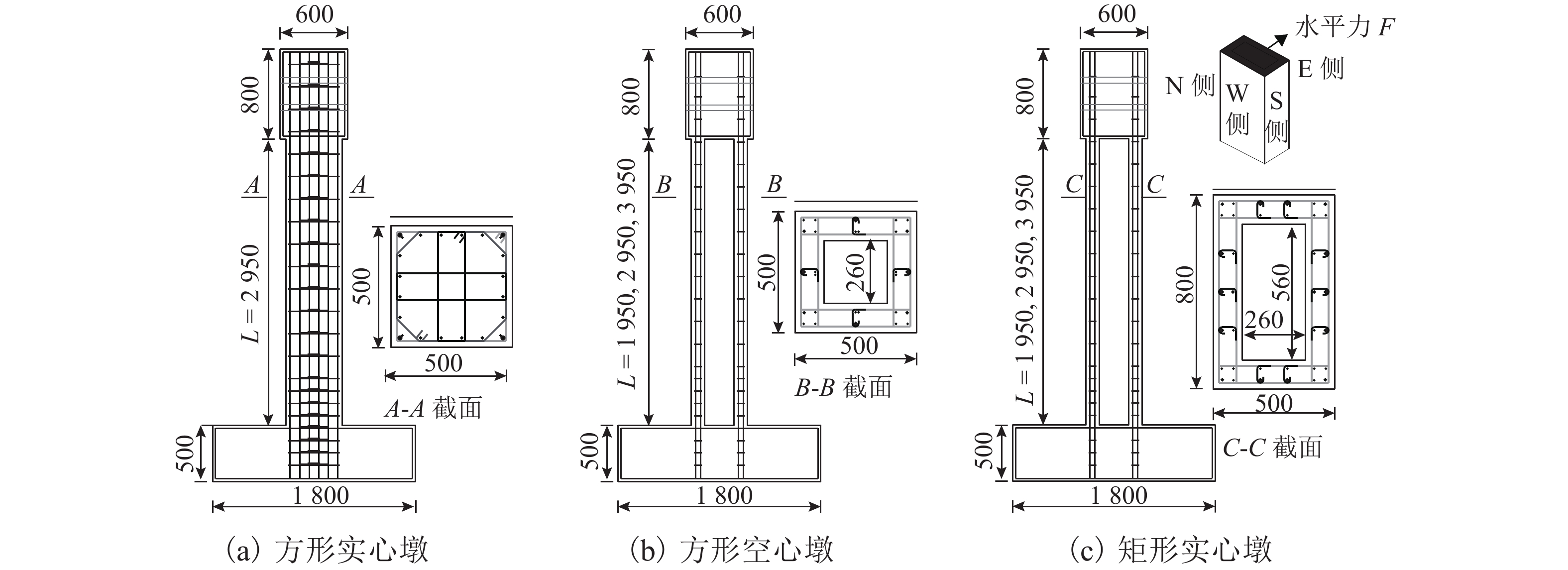
桥墩类型 试件
名称L/m L/h ρl/% 纵筋布置 ρs/% s/mm 方形实心墩 A2 2.95 5.9 1.79 20ϕ16 + 4ϕ12 2.35 110 方形空心墩 D1 1.95 3.9 2.12 20ϕ12 + 8ϕ16 2.24 90 D2 2.95 5.9 2.12 20ϕ12 + 8ϕ16 2.24 90 D3 3.95 7.9 2.12 20ϕ12 + 8ϕ16 2.24 90 E1 2.95 5.9 2.12 20ϕ12 + 8ϕ16 3.10 65 E2 2.95 5.9 2.12 20ϕ12 + 8ϕ16 1.34 150 F1 2.95 5.9 1.87 16ϕ12 + 8ϕ16 2.24 90 F2 2.95 5.9 2.81 24ϕ12 + 12ϕ16 2.24 90 矩形空心墩 G1 1.95 3.9 2.15 20ϕ12 + 16ϕ16 2.13 100 G2 2.95 5.9 2.15 20ϕ12 + 16ϕ16 2.13 100 G3 3.95 7.9 2.15 20ϕ12 + 16ϕ16 2.13 100 H1 2.95 5.9 2.15 20ϕ12 + 16ϕ16 3.04 70 H2 2.95 5.9 2.15 20ϕ12 + 16ϕ16 1.42 150 I1 2.95 5.9 1.63 26ϕ12 + 6ϕ16 2.13 100 I2 2.95 5.9 2.69 32ϕ12 + 16ϕ16 2.13 100 表 2 延性系数和塑性铰长度实测值
Table 2. Measured ductility factors and plastic hinge length
试件 Δy /mm Φy/( × 10−3 m−1) Δu /mm Φu/m−1 延性系数 μΔ Lp /mm D1 15.6 12.30 90.0 0.180 5.8 242.0 D2 20.8 7.17 148.0 0.167 7.1 283.0 D3 24.7 4.75 160.0 0.104 6.5 362.0 E1 19.6 6.76 132.0 0.152 6.7 275.0 E2 16.9 5.83 130.0 0.166 7.7 250.0 F1 17.3 5.96 132.0 0.154 7.6 276.0 F2 20.1 6.93 154.0 0.149 7.7 340.0 G1 18.6 14.70 113.6 0.215 6.1 261.0 G2 29.2 10.10 148.7 0.166 5.1 273.0 G3 29.0 5.58 181.3 0.134 6.3 314.0 H1 26.2 9.03 149.7 0.161 5.7 289.0 H2 20.5 7.07 131.1 0.151 6.4 274.0 I1 24.2 8.34 137.7 0.178 5.7 237.0 I2 30.4 10.50 168.6 0.190 5.5 274.0 表 3 等效塑性铰计算模型
Table 3. Equivalent plastic hinge length models
编号 来源 计算式 M1 Mander[17] (1983年) $ {L_{\text{p}}} = 0.06L + 32\sqrt {{d_{\text{b}}}} $ M2 Priestley-Park[16] (1987年) ${L_{\text{p}}} = 0.08L + 6{d_{\text{b}}}$ M3 Paulay-Priestley[18] (1992年),
Caltrans[19] (2006年)${L_{\text{p}}} = 0.08L + 0.022{f_{\text{y}}}{d_{\text{b}}} \geqslant 0.044{f_{\text{y}}}{d_{\text{b}}}$ M4 Watson-Park[20](1994年) ${L_{\rm{p} } } = h\left( {1 + 2.8\mathop P\nolimits_{\rm{u} } /\left( {{\varphi \mathop f\nolimits{'}}_{\rm{c} } {A_{\rm{g} } } } \right)} \right)$ M5 Berry[21](2008年) ${L_p} = 0.05L + 0.1{ { {f_{\text{y} } }{d_{\text{b} } } } \mathord{\left/ {\vphantom { { {f_{\text{y} } }{d_{\text{b} } } } {\sqrt { { {f'}_{\text{c} } } } } } } \right. } {\sqrt { { {f}'_{\text{c} } } } } }$ M6 孙治国[22] (2011年) $\begin{gathered} {L_{\rm{p} } }{ { = } }0.10L - 0.165h + 7.32{d_{\rm{b} } }, \quad 0.2h \leqslant {L_{\rm{p} } } \leqslant 0.7h \end{gathered}$ M7 JRA[23] (2002年) $\begin{gathered} {L_{\rm{p} } } = 0.2L - 0.1h, \quad 0.1h \leqslant {L_{\rm{p} } } \leqslant 0.5h \end{gathered}$ M8 Eurocode 8[24](2005年) ${L_{\text{p}}} = 0.1L + 0.015{f_{\text{y}}}{d_{\text{b}}}$ M9 《细则》[2](2008年) $\begin{array}{l}{L_{ {\rm{p1} } } } = 0.08L + 0.022{f_{\rm{y} } }{d_{\rm{b} } } \geqslant 0.044{f_{\rm{y} } }{d_{\rm{b} } },\; {L_{ {\rm{p} }2} } = \dfrac{2}{3}h,\; {L_{\rm{p} } } = \min \left\{ { {L_{ {\rm{p} }1} },\; {L_{ {\rm{p} }2} }\left. {} \right\} } \right.\end{array}$ 表 4 文献中试件参数及Lp
Table 4. Parameters and Lp of specimens in literature
编号 来源 试件 ρl
/%fy
/MPaρs
/%fc'
/MPaη μΔ Lp/mm 1 文献[17] A 1.55 335 2.0 30.0 0.10 8.0 278 2 C 1.55 335 3.1 29.0 0.30 8.0 300 3 D 1.55 335 2.0 29.0 0.30 6.0 308 4 文献[25] NB4 2.13 460 30.1 0.09 6.3 328 5 NA8 2.13 460 24.6 0.11 6.6 309 6 NB8 2.13 460 24.6 0.11 6.3 175 7 HA8 2.13 460 35.8 0.06 7.2 143 8 HB8 2.13 460 35.8 0.06 7.1 151 9 文献[9] No.2 1.92 330 1.91 34.0 0.08 8.9 232 10 No.3 1.92 330 1.01 34.0 0.08 8.1 209 11 文献[11] 405 1.93 374 1.08 43.5 0.10 5.9 177 12 805 1.93 374 1.08 43.5 0.10 5.4 228 13 文献[14] S13-NS 1.40 385 3.5 28.2 0.10 3.5 210 14 S13-EW 1.40 385 3.5 28.2 0.10 5.5 260 15 S14-NS 2.10 385 3.5 28.2 0.10 5.7 240 16 S14-EW 2.10 385 3.5 28.2 0.10 5.2 190 17 S15-NS 1.40 385 3.5 28.2 0.20 4.4 230 18 S15-EW 1.40 385 3.5 28.2 0.20 3.8 260 19 S16-NS 2.10 385 3.5 28.2 0.20 4.4 270 20 S16-EW 2.10 385 3.5 28.2 0.20 3.8 210 21 S17-NS 2.10 385 2.5 28.2 0.10 4.2 220 22 S17-EW 2.10 385 2.5 28.2 0.10 3.7 250 -
[1] 宗周红,夏坚,徐绰然. 桥梁高墩抗震研究现状及展望[J]. 东南大学学报(自然科学版),2013,43(2): 445-452.ZONG Zhouhong, XIA Jian, XU Chaoran. Seismic study of high piers of large-span bridges:an overview and research development[J]. Journal of Southeast University (Natural Science Edition), 2013, 43(2): 445-452. [2] 中华人民共和国交通运输部. 公路桥梁抗震设计细则: JTG/TB 02-01—2008[S]. 北京: 人民交通出版社, 2008. [3] 中华人民共和国铁道部. 铁路工程抗震设计规范: GB 50111—2006[S]. 北京: 中国计划出版社, 2009. [4] 孙治国,王东升,李宏男,等. 钢筋混凝土空心桥墩应用及抗震性能综述[J]. 交通运输工程学报,2013,13(3): 22-32. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1637.2013.03.004SUN Zhiguo, WANG Dongsheng, LI Hongnan, et al. Application of RC hollow bridge pier and review of seismic behavior research[J]. Journal of Traffic and Transportation Engineering, 2013, 13(3): 22-32. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1637.2013.03.004 [5] MANDER J B, PRIESTLEY M J N, PARK R. Behavior of ductile hollow reinforced concrete columns[J]. Bulletin of the New Zealand National Society for Earthquake Engineering, 1983, 16(4): 273-290. doi: 10.5459/bnzsee.16.4.273-290 [6] YEH Y K, MO Y L, YANG C Y. Full-scale tests on rectangular hollow bridge piers[J]. Materials and Structures, 2002, 35(2): 117-125. [7] ACI committee. Building code requirements for reinforced concrete: ACI 318-95[S]. Detroit: American Concrete Institute, 1995. [8] MO Y L, NIEN I C. Seismic performance of hollow high-strength concrete bridge columns[J]. Journal of Bridge Engineering, 2002, 7(6): 338-349. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)1084-0702(2002)7:6(338) [9] 宋晓东. 桥梁高墩延性抗震性能的理论和试验研究[D]. 上海: 同济大学, 2002. [10] 杜修力,陈明琦,韩强. 钢筋混凝土空心桥墩抗震性能试验研究[J]. 振动与冲击,2011,30(11): 254-259. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3835.2011.11.051DU Xiuli, CHEN Mingqi, HAN Qiang. Experimental evaluation of seismic performance of reinforced concrete hollow bridge columns[J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2011, 30(11): 254-259. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3835.2011.11.051 [11] 罗征,李建中. 低周往复荷载下空心矩形墩抗震性能试验研究[J]. 振动与冲击,2013,32(8): 183-188. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3835.2013.08.032LUO Zheng, LI Jianzhong. Tests for a seismic performance of rectangular hollow thin-walled bridge columns under low-cycle reversed loading[J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2013, 32(8): 183-188. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3835.2013.08.032 [12] 韩强,周雨龙,杜修力. 钢筋混凝土矩形空心桥墩抗震性能[J]. 工程力学,2015,32(3): 28-40.HAN Qiang, ZHOU Yulong, DU Xiuli. Seismic performance of reinforced concrete rectangular hollow bridge columns[J]. Engineering Mechanics, 2015, 32(3): 28-40. [13] 宗周红,陈树辉,夏樟华. 钢筋混凝土箱型高墩双向拟静力试验研究[J]. 防灾减灾工程学报,2010,30(4): 369-374.ZONG Zhouhong, CHEN Shuhui, XIA Zhanghua. Bi-axial quasi-static testing research of high hollow reinforced concrete piers[J]. Journal of Disaster Prevention and Mitigation Engineering, 2010, 30(4): 369-374. [14] HAN Q, DU X L, ZHOU Y H, et al. Experimental study of hollow rectangular bridge column performance under vertical and cyclically bilateral loads[J]. Earthquake Engineering and Engineering Vibration, 2013, 12(3): 433-445. doi: 10.1007/s11803-013-0184-y [15] PARK R, PAULAY T. Reinforced Concrete Structures [M]. New York: John Wiley & Sons, 1975. [16] PRIESTLEY M J N, PARK R. Strength and ductility of reinforced concrete bridge columns under seismic loading[J]. ACI Structural Journal, 1987, 84(1): 61-76. [17] MANDER J B. Seismic design of bridge columns[D]. Christchurch: University of Canterbury, 1983. [18] PAULAY T, PRIESTLEY M J N. Seismic design of reinforced concrete and masonry buildings[M]. New York: John-Wiley & Sons, 1992. [19] CALTRANS. Caltrans seismic design criteria: version 1.4[S]. Sacramento: California Department of Transportation, 2006. [20] WATSON S, PARK R. Simulated seismic load tests on reinforced concrete columns[J]. Journal of Structural Engineering, 1994, 120(6): 1825-1849. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9445(1994)120:6(1825) [21] BERRY M P, LEHMAN D E, LOWES L N. Lumped-plasticity models for performance simulation of bridge columns[J]. ACI Structural Journal, 2008, 10(3): 270-279. [22] 孙治国,王东升,郭迅,等. 钢筋混凝土墩柱等效塑性铰长度研究[J]. 中国公路学报,2011,24(5): 56-64.SUN Zhiguo, WANG Dongsheng, GUO Xun, et al. Research on equivalent plastic hinge length of reinforced concrete bridge column[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2011, 24(5): 56-64. [23] Japan Road Association. Design specifications for highway bridges, part V: seismic design[S]. Tokyo: Japan Road Association, 2002 [24] European Committee for Standardization. Eurocode 8: design provisions for earthquake resistance of structures, part 2: bridges: EN 1998-2[S]. Brussels: European Committee for Standardization (CEN), 2005. [25] MO Y L, WONG D C, MAEKAWA K. Seismic performance of hollow bridge columns[J]. ACI Structural Journal, 2003, 100(3): 337-348. -




 下载:
下载: