Weather Classification in Traffic Scene Based on Joint Voting Network
-
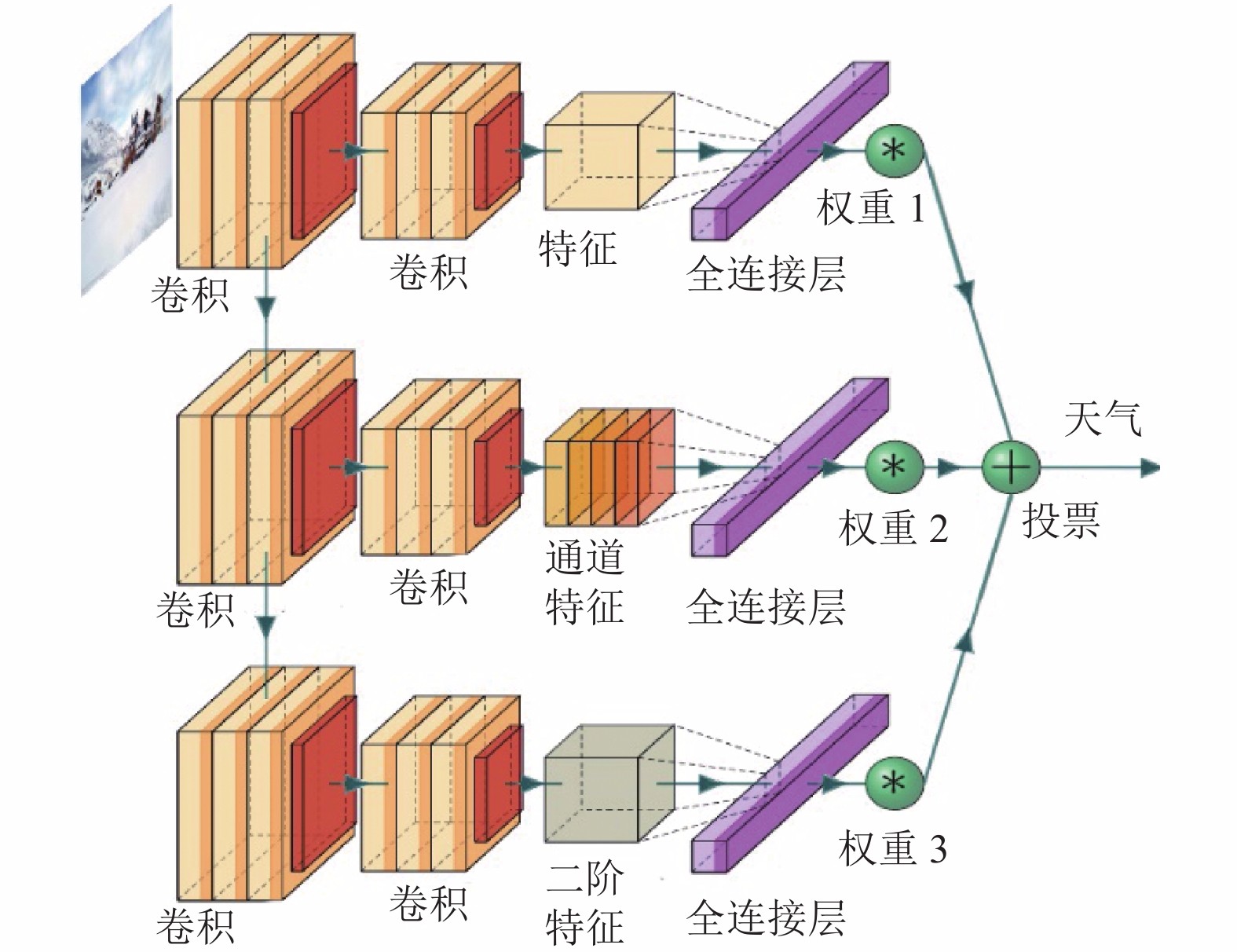
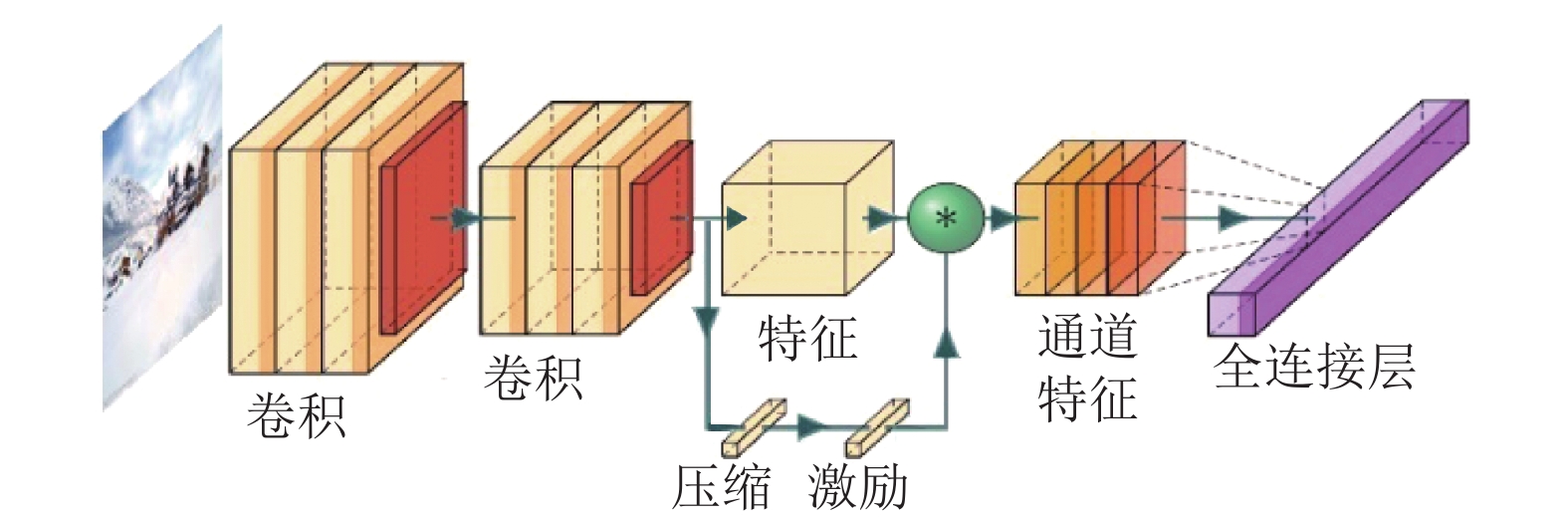
摘要: 基于交通视频监控图像的天气识别已经成为智能交通系统中重要的研究课题. 虽然卷积神经网络(convolutional neural network,CNN)在图像识别技术获得了巨大的发展,但是针对复杂交通场景的天气识别问题,现有的模型在特征表达方面仍然面临着巨大的挑战. 为了提取丰富的语义特征,提出了基于联合投票机制的深度神经网络(deep neural network,DNN)模型. 所提出的模型包括两个核心模块:基于通道和空间注意力机制的二阶特征模块和基于复合特征结果联合投票机制的分类模块, 用以提取不同天气图像中的判别性信息,提高在复杂交通场景下的天气识别性能. 最后,在两个基准天气分类数据集上进行了验证试验,结果表明:对于复杂场景条件下的天气识别问题,所提出的基于联合投票机制的深度神经网络模型的识别正确率优于目前最好的天气识别方法的1.97%.Abstract: Weather classification based on road monitoring images has become an important research topic in intelligent traffic system. With the application of convolutional neural network (CNN), image recognition has been greatly developed. However, the existing deep learning methods still face great challenges in weather recognition of complex traffic scenarios. A novel deep neural network (DNN) model based on joint voting framework is proposed to extract rich semantic features. The proposed model consists of two core modules: the second-order feature module based on channel and spatial attention mechanism and the joint voting classification module based on composite features, which can extract discriminant information from different weather images and improve the weather recognition performance in complex scenarios. Extensive experiments conducted on two benchmark weather classification datasets demonstrate that the proposed joint voting DNN outperforms the existing weather recognition method by 1.97%.
-
表 1 试验测试模型在6CWD和2CWD数据集上的正确率
Table 1. Model accuracy on 6CWD and 2CWD
% 网络模型 6CWD 2CWD VSM with Voters[8] 76.60 Weather-CNN[13] 91.10 AlexNet[9] 77.40 93.30 Inception_v3[10] 79.50 93.25 ResNet-101[11] 81.34 94.40 SE-ResNet-101[18] 81.47 94.50 DRN_D_105[15] 81.60 94.65 CBAM-ResNet-101[19] 82.00 94.65 MPN-COV-ResNet-101[20] 83.18 94.65 *MPN-COV-512-ResNet-101 82.39 95.05 *JVNet 85.15 95.50 注:*表示本文提出的优化模型. 表 2 6CWD数据集下不同网络特征的可视化结果
Table 2. Visualization results of different network on 6CWD
分类 输入 ResNet SENet CBAM MPN-COV JVNet 晴天 





雨天 





薄雾 





中雾 





浓雾 





雪天 





表 3 平均置信度加权和不等置信度加权复合模型在6CWD数据集上的试验结果
Table 3. Experimental results of weighted composite model with equal confidence and unequal confidence on 6CWD
% 网络模型 正确率 网络模型 正确率 JVNet-6-A 83.23 JVNet-6-NA 83.21 JVNet-5-A 83.44 JVNet-5-NA 83.31 JVNet-4-A 83.18 JVNet-4-NA 83.44 JVNet-3-A 83.71 JVNet-3-NA 84.10 注:JVNet-6-A和JVNet-6-NA分别表示对复合了6种模型的复合模型做平均加权处理和不等加权处理;其余类推. 表 4 模式G和模式B结果投票复合方法在6CWD数据集上的试验结果
Table 4. Experimental results of composite model with model G and model B on 6CWD
% 网络模型 正确率 网络模型 正确率 JVNet-6-V-G 83.72 JVNet-6-V-B 84.36 JVNet-5-V-G 84.63 JVNet-5-V-B 85.15 JVNet-4-V-G 84.36 JVNet-4-V-B 84.89 JVNet-3-V-G 83.84 JVNet-3-V-B 83.97 注:JVNet-6-V-G和JVNet-6-V-B分别表示复合了6种模型的模式G和模式B的复合模型;其余类推. -
公安部交通管理局. 中华人民共和国道路交通事故统计年报(2010年度)[R]. 北京: 公安部交通管理局, 2011. ROSER M, MOOSMANN F. Classification of weather situations onsingle color images[C]//2008 IEEE Intelligent Vehicles Symposium. Eindhoven: IEEE, 2008: 798-803. YAN Xunshi, LUO Yupin, ZHENG Xiaoming. Weather recognition based on images captured by vision system in vehicle[C]//International Symposium on Neural Networks. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer, 2009: 390-398. GEIGER A, LAUER M, URTASUN R. A generative model for 3d urban scene understanding from movable platforms[C]//2011 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2011: 1945-1952. ZHAO P, FANG T, XIAO J X, et al. Rectilinear parsing of architecture in urban environment[C]//2010 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. San Francisco: IEEE, 2010: 342-349. LOWE D G. Distinctive image features from scale-invariant keypoints[J]. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2004, 60(2): 91-110. doi: 10.1023/B:VISI.0000029664.99615.94 DALAL N, TRIGGS B. Histograms of oriented gradients for human detection[C]//2005 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. San Diego: IEEE, 2005: 886-893 LECUN Y, BOTTOU L, BENGIO Y, et al. Gradient-based learning applied to document recognition[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 1998, 86(11): 2278-2324. doi: 10.1109/5.726791 LU C, LIN D, JIA J, et al. Two-class weather classification[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2014: 3718-3725. KRIZHEVSKY A, SUTSKEVER I, HINTON G. ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks[C]//Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems. [S.l.]: Curran Associates Inc, 2012: 1097-1105. SZEGEDY C, LIU W, JIA Y, et al. Going deeper with convolutions[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2015: 1-9. HE K, ZHANG X, REN S, et al. Deep residual learning for image recognition[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2016: 770-778. HE K, ZHANG X, REN S, et al. Identity mappings in deep residual networks[C]//Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision. Cham: Springer, 2016: 630-645. ELHOSEINY M, HUANG S, ELGAMMAL A. Weather classification with deep convolutional neural networks[C]//IEEE International Conference on Image Processing. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2015: 3349-3353 LIN D, LU C, HUANG H, et al. RSCM:region selection and concurrency model for multi-class weather recognition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2017, 26(9): 4154-4167. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2017.2695883 YU F, KOLTUN V, FUNKHOUSER T. Dilated residual networks[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2017: 472-480. JADERBERG M, VEDALDI A, ZISSERMAN A. Speeding up convolutional neural networks with low rank expansions[J/OL]. Computer Science, 2014, 1: 1-15[2020-03-06]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1405.3866. CHOLLET F. Xception: deep learning with depthwise separable convolutions[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2017: 1251-1258. HU J, SHEN L, SUN G. Squeeze-and-excitation networks[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2018: 7132-7141. WOO S, PARK J, LEE J Y, et al. Cbam: convolutional block attention module[C]//Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision. Cham: Springer, 2018: 3-19. LI P, XIE J, WANG Q, et al. Is second-order information helpful for large-scale visual recognition?[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2017: 2070-2078. RUSSAKOVSKY O, DENG J, SU H, et al. Imagenet large scale visual recognition challenge[J]. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2015, 115(3): 211-252. doi: 10.1007/s11263-015-0816-y SELVARAJU R R, COGSWELL M, DAS A, et al. Grad-CAM: visual explanations from deep networks via gradient-based localization[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2017: 618-626. -




 下载:
下载: