Applicability of Novel Pile-Plank Embankment in Seasonally Frozen Regions
-
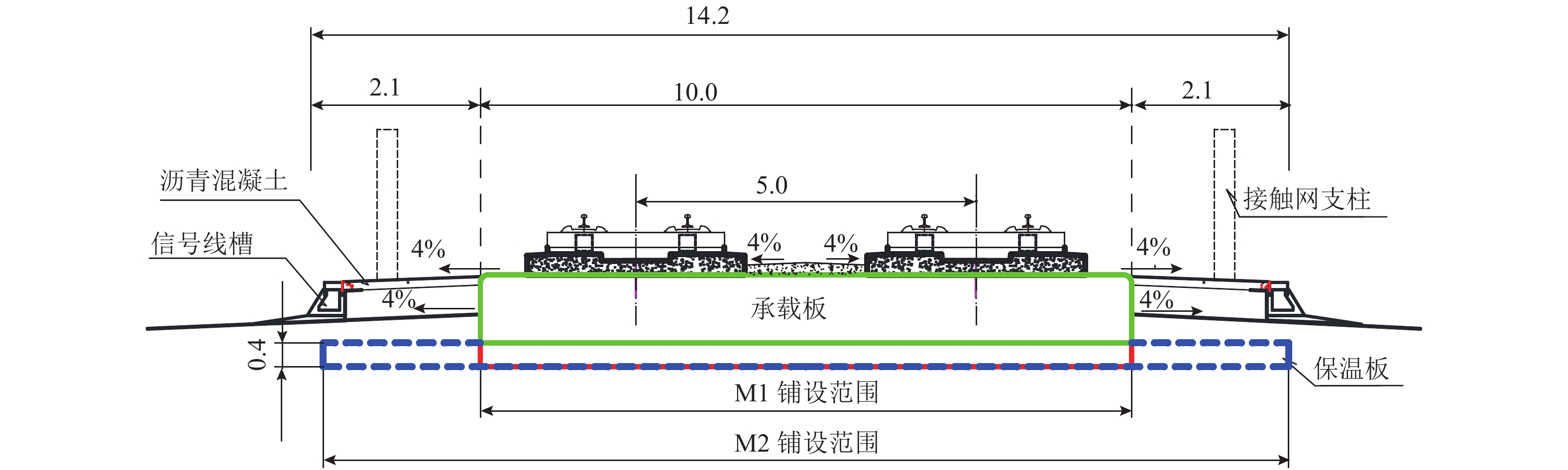
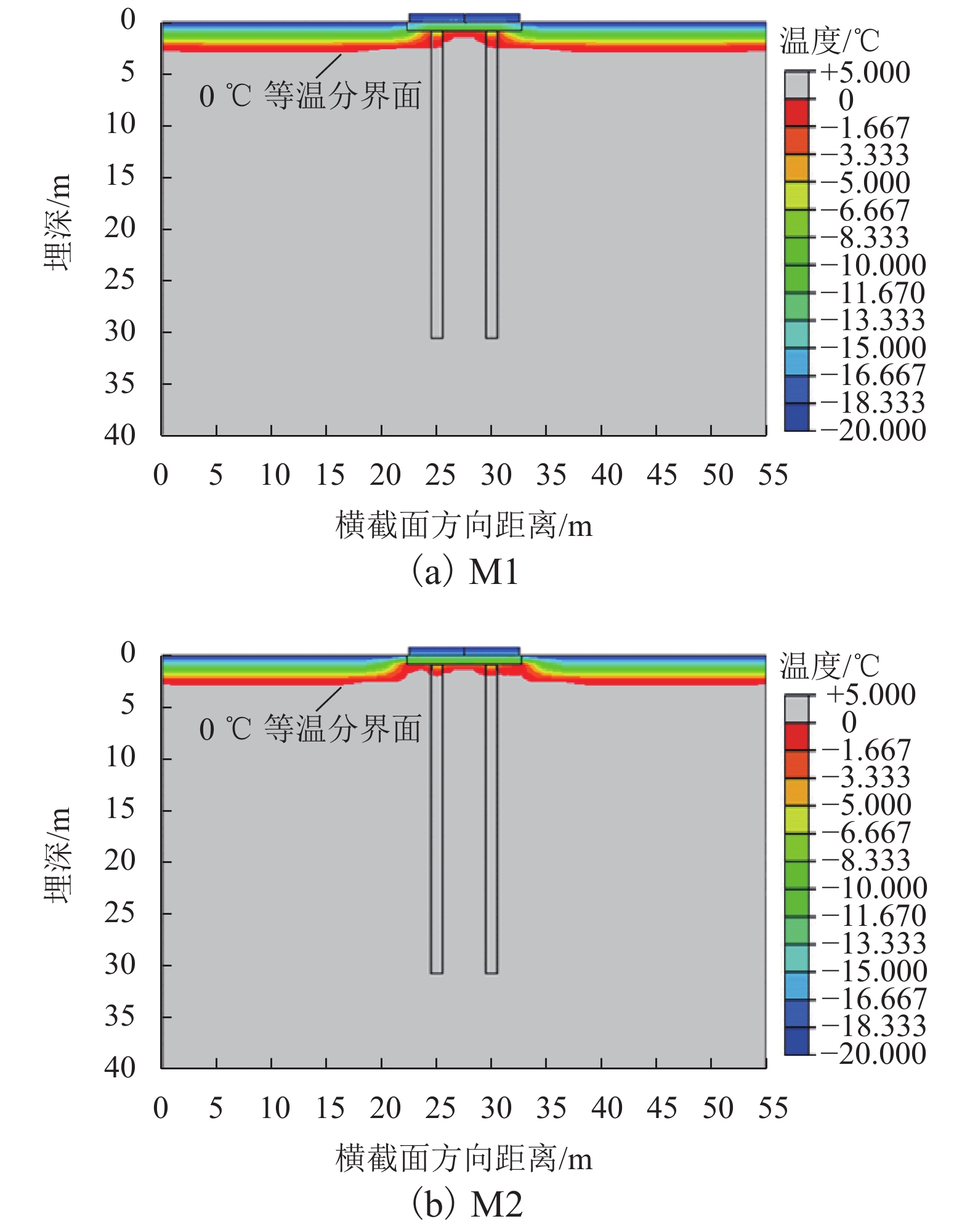
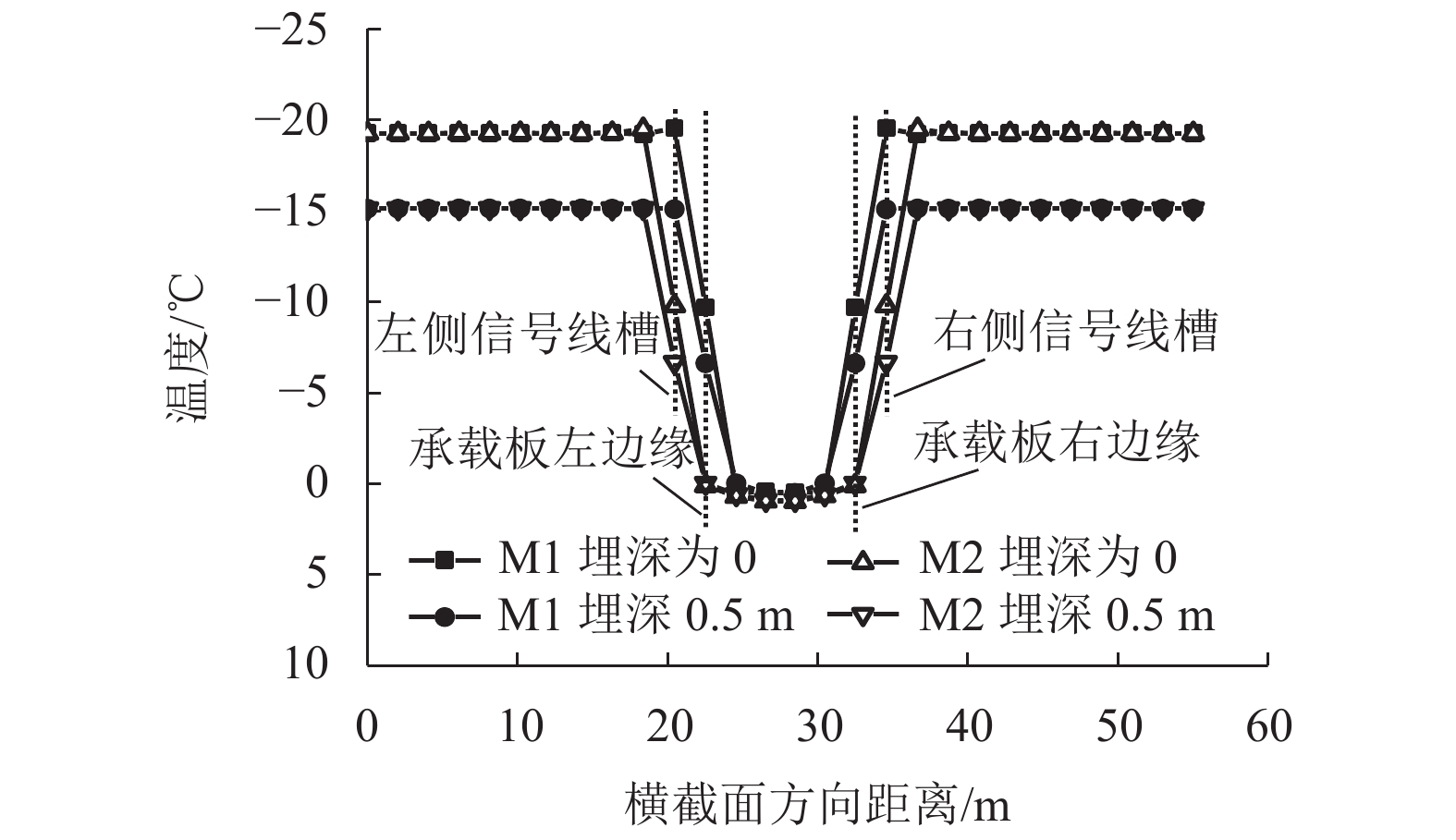
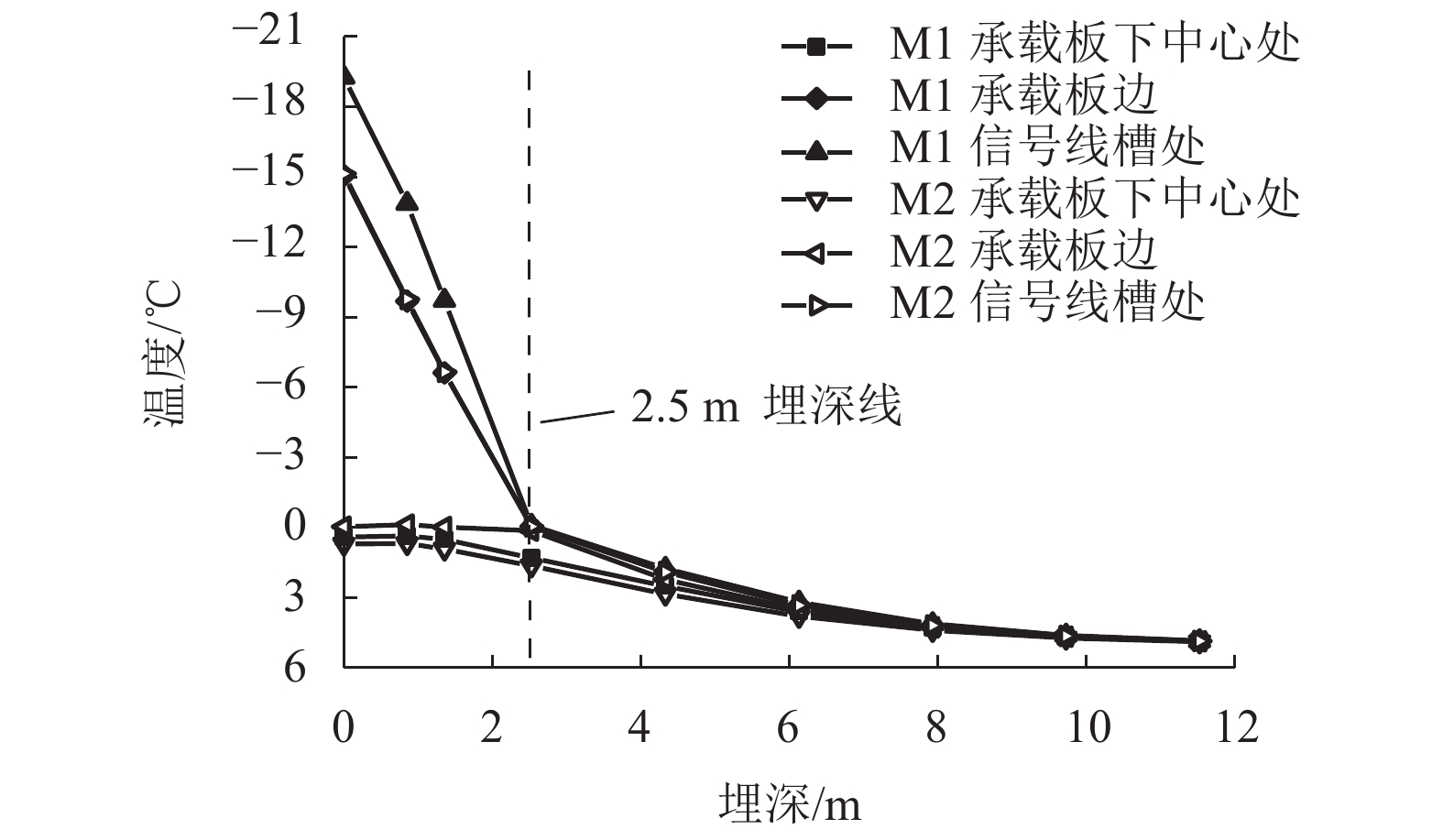
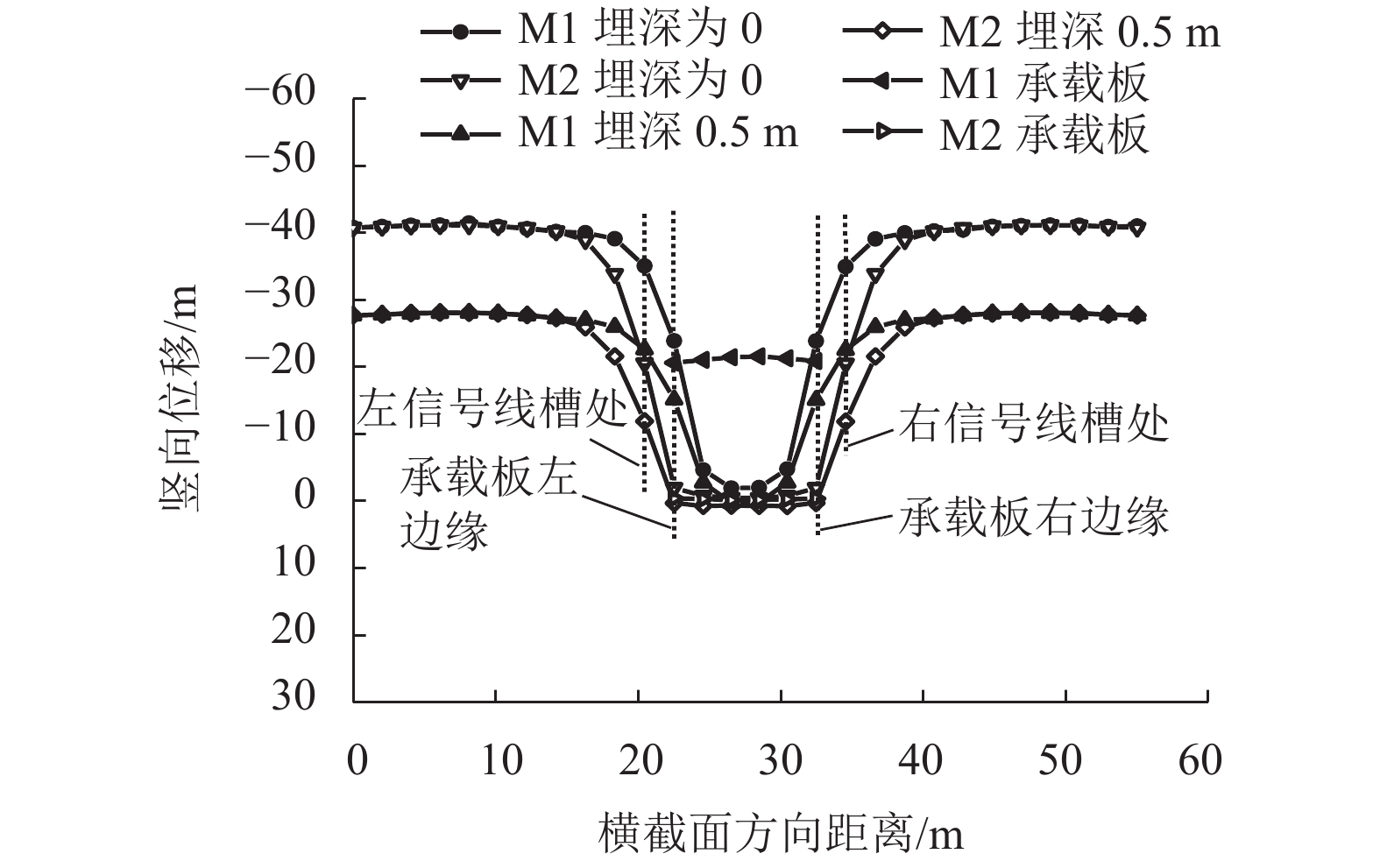
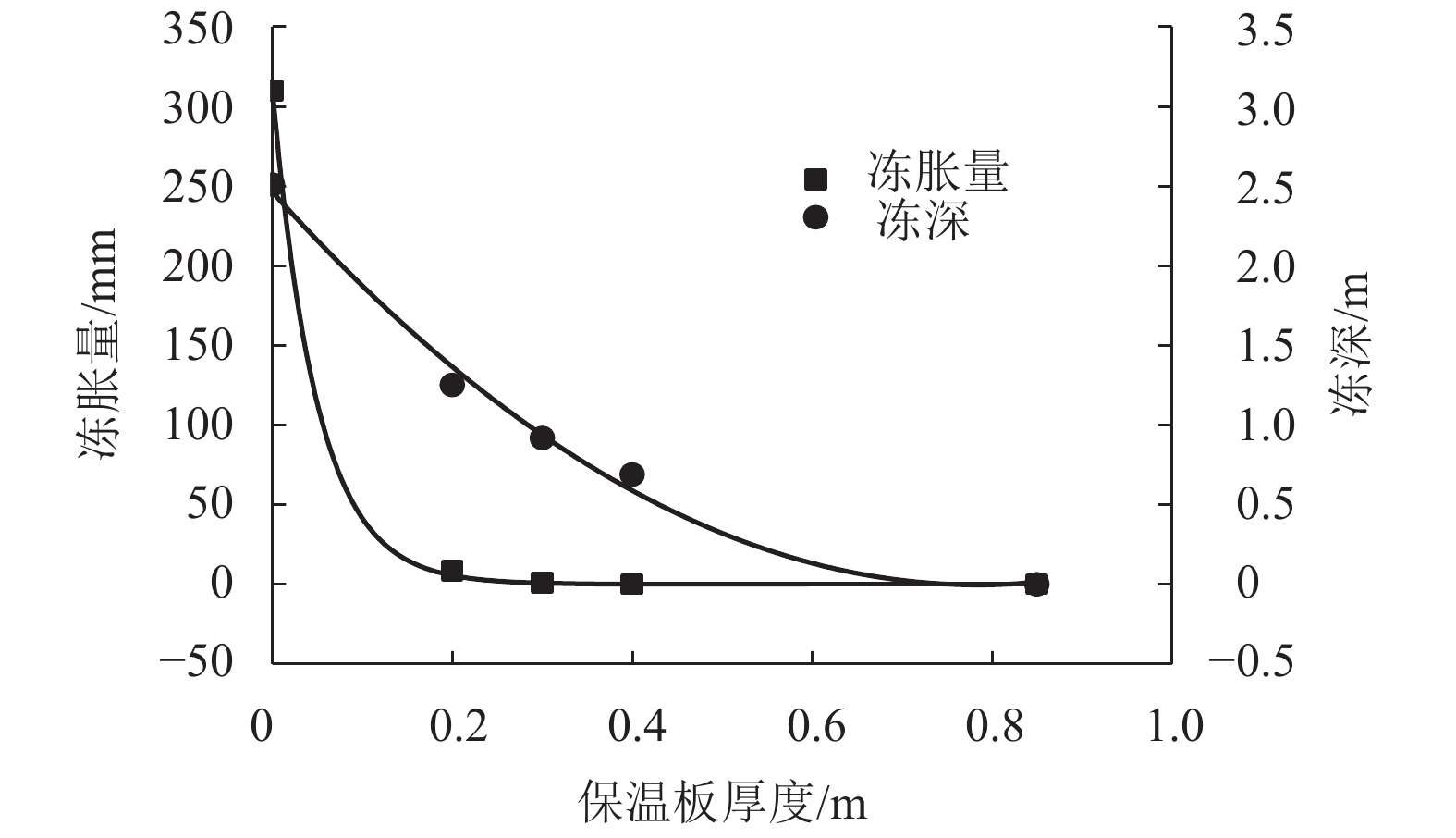
摘要: 针对莫喀(莫斯科—喀山)高速铁路季节性冻土区路基冻胀病害防治问题,提出了铺设保温板垫层的新型桩板结构路基. 通过对聚苯乙烯泡沫塑料板(EPS)、聚氨酯板(PU)和挤塑聚苯乙烯泡沫塑料板(XPS) 3种保温材料性能的对比分析,发现新型桩板结构路基中的保温板可采用在保温隔热、隔水防渗和抗压性能方面表现良好的XPS保温板. 通过建立热弹塑性冻胀计算模型,研究了冻胀力作用下保温板铺设范围、厚度、路基填高和外界温度对新型桩板结构路基受力变形的影响. 结果表明:当保温板铺设范围延伸到线路两端的信号线槽处时,可以更好地阻滞外界负温向下传递(减小冻深),抑制因桩板结构周边土体冻胀对结构物产生的不良影响;随着保温板厚度的增大,冻胀量呈指数形式减小,冻深呈抛物线形减小,保温板上表面处起到抑制外界负温向下传递的作用,下表面处起到控制下部土体温度耗散的作用;增大路基填高,有利于抑制路基冻胀量,减少保温板的使用厚度,当路基填高0.8 m时,保温板垫层厚度需大于0.40 m;当路基填高2.8 m时,保温板垫层厚度需大于0.31 m.Abstract: In order to control the frost heaving damage in the seasonally frozen regions of the Moscow−Kazan high-speed railway, a novel pile-plank subgrades with an insulation board was proposed. Comparing the performance of three kinds of thermal insulation materials, expanded polystyrene (EPS) foam board, polyurethane (PU) board and extruded polystyrene (XPS) foam board shows that the XPS insulation board could be used in the new subgrade for its better performance in heat insulation, waterproof, impervious and compressive properties. The thermo-elasto-plastic model was established to study the influences of laying range, insulation board thickness, filling height, and external temperature on the mechanical deformation of the new type subgrade. The results show that when the laying range of the insulation board is extended to the signal wire slot, it can do better to preventing the downward transfer of negative temperatures (reducing the frozen depth), and diminishing the harmful effect of soil frost heaving surrounding the pile-plank structure. With increasing board thickness, the heaving amount decreases exponentially and frozen depth decreases close to a parabolic curve. The upper surface of the insulation board can prevent the downward transfer of negative temperatures and its lower surface plays a role in controlling the soil temperature dissipating under embankment. Increasing the filling height of embankment is helpful to suppress the subgrade heaving amount and reduce the usage thickness of the insulation board. The insulation board thickness should be greater than 0.4 m when the filling height is 0.8 m; and the board thickness should be greater than 0.31 m when the filling height is 2.8 m.
-
表 1 保温板物性参数
Table 1. Physical parameters of insulation boards
材料类型 表观密度/(kg•m−3) 导热系数/(W•m−1•K−1) 体积吸水率/% 抗压强度/kPa EPS 30~40 0.030 0~0.044 0 3.60~6.00 300~345 PU 59 0.019 7 1.40 322 XPS 40~45 0.011 0~0.012 0 0.96~0.97 500~650 表 2 冻融条件下3种保温板稳定性对比
Table 2. Stability comparison of three kinds of insulation boards under freeze-thaw conditions
材料
类型冻融循
环/次导热系数/
(W•m−1•K−1)体积吸
水率/%抗压强
度/kPaEPS 5 0.025 3 2.60 347 10 0.024 9 2.50 335 20 0.025 3 2.80 352 30 0.024 2 2.50 326 PU 5 0.019 3 0.50 308 10 0.018 4 1.10 306 20 0.018 8 1.00 263 30 0.018 1 0.90 282 XPS 5 0.009 8 0.91 646 10 0.010 2 0.78 637 20 0.009 3 0.84 628 30 0.008 6 0.82 663 表 3 土层划分及参数
Table 3. Physical parameters by soil division
土层 高度/m 密度/(kg•m−3) 弹性模量/MPa 泊松比 黏聚力/kPa 内摩擦/(°) 路堤 2 000 50.00 0.25 75.4 34 微湿润粉砂 2.5 1 720 25.00 0.25 1.0 31 饱水细砂 9.0 1 940 46.45 0.25 2.0 34 饱水粉砂 6.0 1 980 26.80 0.25 3.0 28 饱水细砂 7.0 1 940 46.45 0.25 2.0 34 湿润及饱水细砂 25.5 2 040 69.65 0.25 4.0 34 表 4 桩板结构参数选取
Table 4. Parameter selection of pile-plank structure
构件
类型尺寸/m 密度/(kg•m−3) 弹性模量/MPa 泊松比 导热系数/(W•m−1•K−1) 承载板 长 22.48,宽 4.99 × 2(双线),高 0.80 2 500 32 500 0.18 1.58 托梁 长10.40,宽 1.30,高 0.85 2 500 32 500 0.18 1.58 桩基 长 30.00,直径 1.25,纵向桩间距 7.50,横向桩间距 5.00 2 500 30 000 0.20 1.58 -
TABER S. The mechanics of frost heaving[J]. The Journal of Geology, 1930, 38(4): 303-317. doi: 10.1086/623720 MILLER R D. Freezing and heaving of saturated and unsaturated soils[J]. Highway Research Record, 1972, 393: 1-11. DASH J G. Thermomolecular pressure in surface melting:motivation for frost heave[J]. Science, 1989, 246(4937): 1591-1593. doi: 10.1126/science.246.4937.1591 SHENG D, ZHANG S, NIU F J, et al. A potential new frost heave mechanism in high-speed railway embankments[J]. Geotechnique, 2014, 64(2): 144-154. doi: 10.1680/geot.13.P.042 李强,姚仰平,韩黎明,等. 土体的“锅盖效应”[J]. 工业建筑,2014,44(2): 69-71.LI Qiang, YAO Yangping, HAN Liming, et al. Pot-cover effect of soil[J]. Industrial Construction, 2014, 44(2): 69-71. THOMAS H R, CLEALL P J, LI Y, et al. Modelling of cryogenic processes in permafrost and seasonally frozen soils[J]. Geotechnique, 2009, 59(3): 173-184. doi: 10.1680/geot.2009.59.3.173 许健,牛富俊,李爱敏,等. 季节冻土区保温法抑制铁路路基冻胀效果研究[J]. 铁道学报,2010,32(6): 124-131. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8360.2010.06.021XU Jian, NIU Fujun, LI Aimin, et al. Analysis of the prevention effect of thermal-insulation method on frost heave of railway subgrade in seasonal frozen regions[J]. Journal of the China Railway Society, 2010, 32(6): 124-131. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8360.2010.06.021 许健,牛富俊,牛永红,等. 季节冻土区防冻胀护道对保温路基地温特征影响效果研究[J]. 铁道学报,2011,33(3): 84-90. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8360.2011.03.015XU Jian, NIU Fujun, NIU Yonghong, et al. Study on the temperature field of insulated roadbed with frost-resistant berm on seasonal frozen region[J]. Journal of the China Railway Society, 2011, 33(3): 84-90. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8360.2011.03.015 董元宏,牛永红,崔维孝,等. 哈尔滨—齐齐哈尔客运专线路基防冻工程模型试验研究[J]. 冰川冻土,2014,36(4): 828-835.DONG Yuanhong, NIU Yonghong, CUI Weixiao, et al. Model test study on the anti-frost engineering along the Harbin−Qiqihar passenger dedicated railway[J]. Journal of Glaciology and Geocryology, 2014, 36(4): 828-835. 田亚护,肖伟,沈宇鹏,等. 隔热层对季节冻土区无砟轨道路基冻胀防治的适应性分析[J]. 铁道学报,2014,36(5): 76-81. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8360.2014.05.013TIAN Yahu, XIAO Wei, SHEN Yupeng, et al. Adaptability of heat-insulating course to prevention of frost heave of unballasted railway track subgrade in seasonal frozen regions[J]. Journal of the China Railway Society, 2014, 36(5): 76-81. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8360.2014.05.013 国家铁路局. 高速铁路设计规范: TB10621—2014[S]. 北京: 中国铁道出版社, 2014. 詹永祥,蒋关鲁,魏永幸. 无碴轨道桩板结构路基在地震荷载下的动力响应分析[J]. 中国铁道科学,2006,27(6): 22-26. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-4632.2006.06.005ZHAN Yongxiang, JIANG Guanlu, WEI Yongxing. Dynamic response analysis on the pile-plank structure roadbed of ballastless track under earthquake load[J]. China Railway Science, 2006, 27(6): 22-26. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-4632.2006.06.005 詹永祥,蒋关鲁,胡安华,等. 遂渝线无碴轨道桩板结构路基动力响应现场试验研究[J]. 岩土力学,2009,30(3): 832-835. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2009.03.046ZHAN Yongxiang, JIANG Guanlu, HU Anhua, et al. Study of dynamic response of pile-plank embankment of ballastless track based on field test in Suining—Chongqing high-speed railway[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2009, 30(3): 832-835. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2009.03.046 詹永祥,蒋关鲁,牛国辉,等. 武广线高边坡陡坡地段桩板结构路基的设计理论探讨[J]. 铁道工程学报,2007(增刊1): 94-96,101.ZHAN Yongxiang, JIANG Guanlu, NIU Guohui, et al. Theoretical exploration on design of pile-plate structure subgrade in steep slope section of high side slop on Wuchang−Guangzhou railway passenger dedicated Line[J]. Journal of Railway Engineering Society, 2007(S1): 94-96,101. 董元宏,朱东鹏,张会建,等. 应用于冻土路基的XPS保温板力学性能[J]. 中国公路学报,2015,28(12): 64-68. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7372.2015.12.009DONG Yuanhong, ZHU Dongpeng, ZHAGN Huijian, et al. Mechanical properties of XPS thermal insulation board applied in permafrost embankment[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2015, 28(12): 64-68. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7372.2015.12.009 樊凯,章金钊,陈建兵. 保温材料在青藏公路路基工程中的应用[J]. 公路,2004(8): 163-166. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0451-0712.2004.08.038FAN Kai, ZHANG Jinzhao, CHEN Jianbing. Application of thermal insulating material in embankment engineering of Qinghai−Tibet highway[J]. Highway, 2004(8): 163-166. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0451-0712.2004.08.038 温智. 保温法在青藏高原多年冻土区道路工程中的应用评价研究[D]. 北京: 中国科学院研究生院, 2006. 赵丽萍. XPS板在冻土路基工程中的应用研究[D]. 西安: 长安大学, 2009. LAI Y M, WU Z W, ZHU Y L, et al. Nonlinear analysis for the coupled problem of temperature,seepage and stress fields in cod-region tunnels[J]. Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology, 1998, 13(4): 435-440. doi: 10.1016/S0886-7798(98)00086-8 -





 下载:
下载: