Chloride Ion Transport in Concrete of Ballastless Track under Fatigue Loading
-
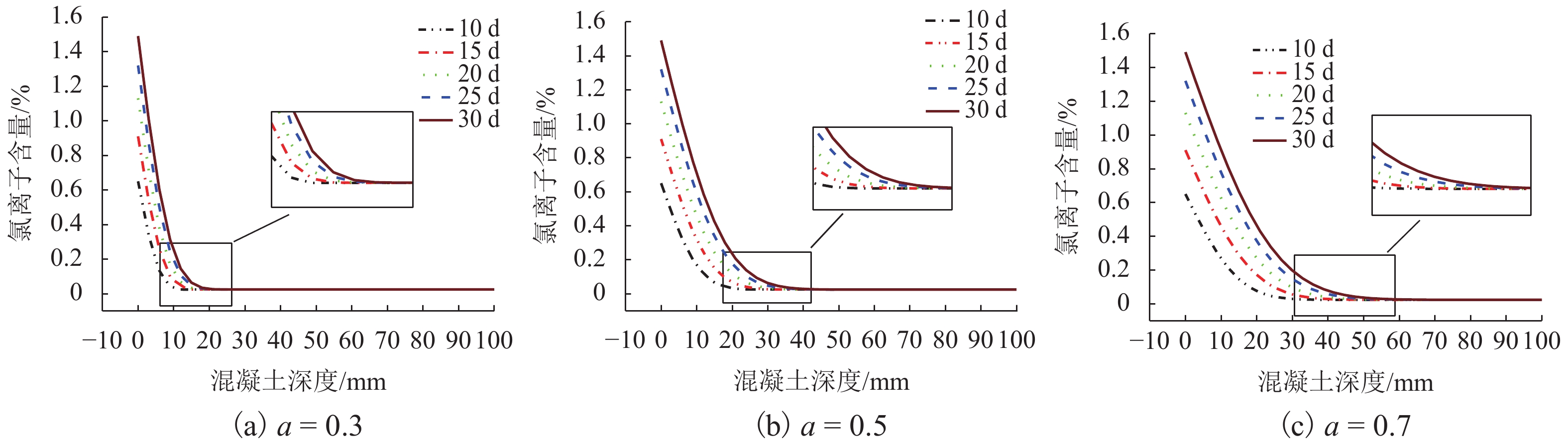
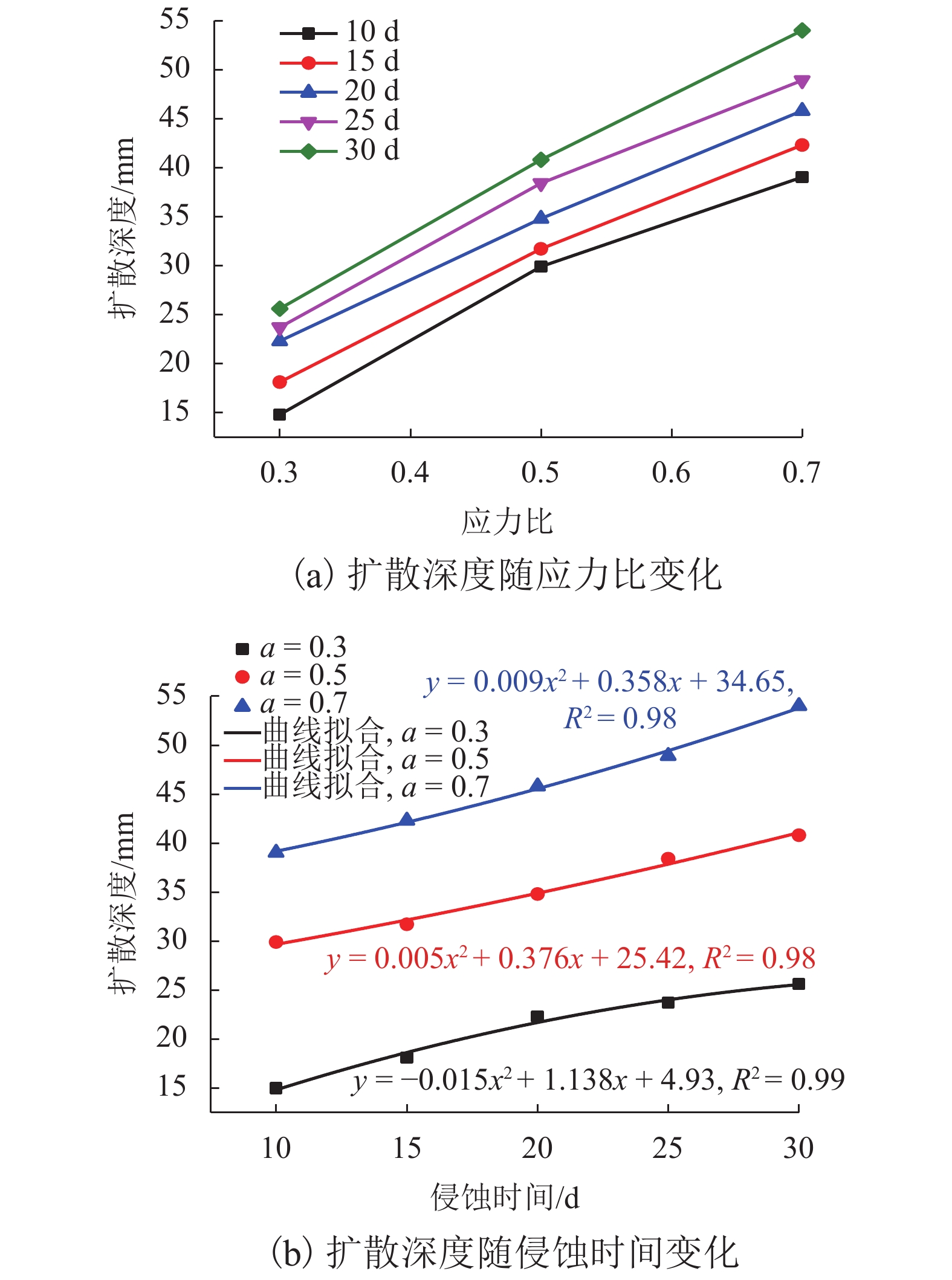
摘要: 疲劳荷载作用下,无砟轨道混凝土的抗氯离子渗透性能是影响其服役特性的主要因素之一. 为分析混凝土在疲劳荷载作用下氯离子的传输变化规律,首先针对浸泡于氯离子溶液的混凝土试件进行弯曲疲劳试验,然后利用COMSOL有限元软件建立结构力学场与氯离子传输场的两场耦合模型,模拟氯离子在混凝土中的扩散行为. 研究结果表明:当侵蚀时间为2 d时,应力比为0.3、0.5和0.7对应的氯离子扩散深度分别为7、11、16 mm,混凝土中氯离子扩散深度随荷载应力比的增大而增大;两场耦合有限元模型计算得到的氯离子含量与试验测试结果基本吻合,验证了模型的合理性;混凝土中氯离子扩散深度随侵蚀时间的增大而增大,采用一元二次多项式可较好地描述扩散深度与侵蚀时间的关系.Abstract: The chloride ion penetration resistance of concrete structure of ballastless track under fatigue load is one of the main factors affecting its service performance. In order to analyze the variation of chloride ion transport in concrete under fatigue load, the bending fatigue loading test of concrete specimens immersed in chloride solution was carried out. A two-field coupling model based on the structural mechanics field and the chloride transport field was then established with COMSOL finite element software to simulate the chloride diffusion behavior in concrete. The results show that when the erosion time is 2 d, the chloride ion diffusion depths corresponding to the stress levels of 0.3, 0.5, and 0.7 are 7, 11 and 16 mm, respectively, which indicates that the chloride diffusion depth in concrete increases with an increase in fatigue stress level. The chloride ion concentration calculated by the two-field coupling finite element model is basically consistent with the experimental test results, which proves that the model is reasonable. What’s more, the diffusion depth of chloride in concrete increases with the erosion time, and the relationship between them can be described well by a unary quadratic polynomial.
-
Key words:
- ballastless track /
- concrete /
- chloride ion transport /
- fatigue load
-
表 1 试验模拟工况
Table 1. Test simulation conditions
工况 应力比 a f/Hz 模拟车型 1 0.3 10 低速货车 2 0.3 15 低速客车 3 0.5 15 普速货车 4 0.7 15 普速货车(极限设计值) 5 0.3 20 普速客车 表 2 COMSOL中试件的力学参数
Table 2. Mechanical parameters of the specimen in COMSOL
参数名称 取值 弹性模量/(× 1010 Pa) 3.8 泊松比 0.2 抗压强度/MPa 69.2 极限荷载/kN 29.3 密度/(kg•m−3) 2 303 表 3 扩散模型相关参数
Table 3. Parameters of diffusion model
参数名称 取值 f/Hz 0.15 氯离子溶液质量分数 C 0.10 T/°C 0.28 初始氯离子质量分数 C0 2.42×10−4 t/d 2 表面氯离子质量分数 C1 0.001 46 ${\phi _0}$/% 4 水灰比 0.35 时间衰减因子 m 0.3 -
钟丽娟,黄庆华,顾祥林,等. 盐雾环境下混凝土中氯离子侵蚀加速试验的综述[J]. 结构工程师,2009,25(3): 144-149. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-0159.2009.03.028ZHONG Lijuan, HUANG Qinhua, GU Xianglin, et al. Analysis of accelerated chloride penetration tests for concrete in salt-fog environment[J]. Structural Engineers, 2009, 25(3): 144-149. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-0159.2009.03.028 孙培华. 循环荷载作用下混凝土渗透性试验研究[D]. 大连: 大连理工大学, 2012. YOON S, WANG K J, WEISS W J, et al. Interaction between loading,corrosion,and serviceability of reinforced concrete[J]. ACI Material Journal, 2000, 97(6): 637-644. CASTEL A, FRANCY O, FRANCOIS R, et al. Chloride diffusion in reinforced concrete beam under sustained loading[C]//CANMET/ACI Fifth International Conference on Recent Advances in Concrete Technology. Singapore: ACI SP, 2001: 647-662. AHN W, REDDY D V. Galvanostatic testing for the durability of marine concrete under fatigue loading[J]. Cement and Concrete Research, 2001, 31(3): 343-349. doi: 10.1016/S0008-8846(00)00506-8 SAMAHA H R, HOVER K C. Influence of microcracking on the mass transport properties of concrete[J]. ACI Material Journal, 1992, 89(4): 416-424. SATIO M, LSHIMORI H. Choride permeability of concrete under static and repeated compressive loading[J]. Cement and Concrete Research, 1995, 25(4): 803-808. doi: 10.1016/0008-8846(95)00070-S 李炜,蒋林华,王永亮,等. 疲劳作用对混凝土中氯离子扩散系数影响的研究[J]. 混凝土,2014(1): 31-34. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-3550.2014.01.009LI Wei, JIANG Linhua, WANG Yongliang, et al. Research on the effect of fatigue on chloride diffusion coefficient in concrete[J]. Concrete, 2014(1): 31-34. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-3550.2014.01.009 孙伟,蒋金洋,王晶,等. 弯曲疲劳载荷作用下HPC和HPFRCC抗氯离子扩散性能研究[J]. 中国材料进展,2009,28(11): 19-25,53.SUN Wei, JIANG Jinyang, WANG Jing, et al. Resistance to chloride ion diffusion of HPC and HPFRCC under bending fatigue load[J]. Materials China, 2009, 28(11): 19-25,53. 苏林王,蔡健,刘培鸽,等. 盐雾环境与交变荷载下混凝土梁的试验研究[J]. 华南理工大学学报(自然科学版),2017,45(5): 97-104. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-565X.2017.05.014SU Linwang, CAI Jian, LIU Peige, et al. Experimental investigation into RC beam under the action of alternating load in salt-spray environment[J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2017, 45(5): 97-104. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-565X.2017.05.014 於德美. 疲劳荷载与环境耦合作用下混凝土氯离子传输行为及模型研究[D]. 长安: 长安大学, 2017. 柳磊,吕毅刚,禹卓杰,等. 疲劳荷载与氯盐耦合作用下混凝土中氯离子扩散行为的试验研究[J]. 实验力学,2017,32(4): 517-524. doi: 10.7520/1001-4888-17-141LIU Lei, LV Yigang, YU Zhuojie, et al. Experimental study on diffusion behavior of chloride ion in concrete subjected to fatigue loading[J]. Journal of Experimental Mechanics, 2017, 32(4): 517-524. doi: 10.7520/1001-4888-17-141 王丹, 刘子键, 郑晓宁, 等. 海水干湿循环下疲劳损伤钢筋混凝土梁氯离子扩散试验研究[J]. 建筑结构学报, 2015, 36(增刊2): 250-256.WANG Dan, LIU Zijian, ZHENG Xiaoning, et al. Experimental study on chloride ion diffusion of fatigue damaged RC beams in seawater wet-dry cycles[J]. Journal of Building Structures, 2015, 36(S2): 250-256. 段一鸣. 盐雾与疲劳耦合下预应力箱梁氯离子扩散特性研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2015. 禹卓杰. 疲劳荷载作用下混凝土中氯离子渗透性能研究[D]. 长沙: 长沙理工大学, 2017. ZHANG W M, BA H, CHEN S. Effect of fly ash and repeated loading on diffusion coefficient in chloride migration test[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2011, 25(5): 2269-2274. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2010.11.016 NAKHI A E, XI Y, WILLAN K, et al. The effect of fatigue loading on chloride penetration in non-saturated concrete[C]//European Congress on Computational Methods in Applied Sciences and Engineering. Barcelona: [s.n.], 2000: 1-8. 刘丹. 振动荷载下无砟轨道耐久性特性与疲劳耐久性预测研究[D]. 成都: 西南交通大学, 2017. 中华人民共和国交通部. 水运工程混凝土试验规则: JTJ 270—98[S]. 北京: 人民交通出版社, 1999. REN J J, DENG S J, WEI K, et al. Mechanical property deterioration of the prefabricated concrete slab in mixed passenger and freight railway tracks[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2019, 208: 622-637. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2019.03.039 BENTZ D P, GARBOCZI E J. Modeling the leaching of calcium hydroxide from cement paste-effects on pore-space percolation and diffusivity[J]. Materials and Structures, 1992, 25(9): 523-533. KASSIR M K, GHOSN M. Chloride-induced corrosion of reinforced concrete bridge decks[J]. Cement and Concrete Research, 2002, 32(1): 139-14. doi: 10.1016/S0008-8846(01)00644-5 -





 下载:
下载: