Test and Evaluation Method for Filling Quality of Foamed Mixture Lightweight Filler Subgrade
-
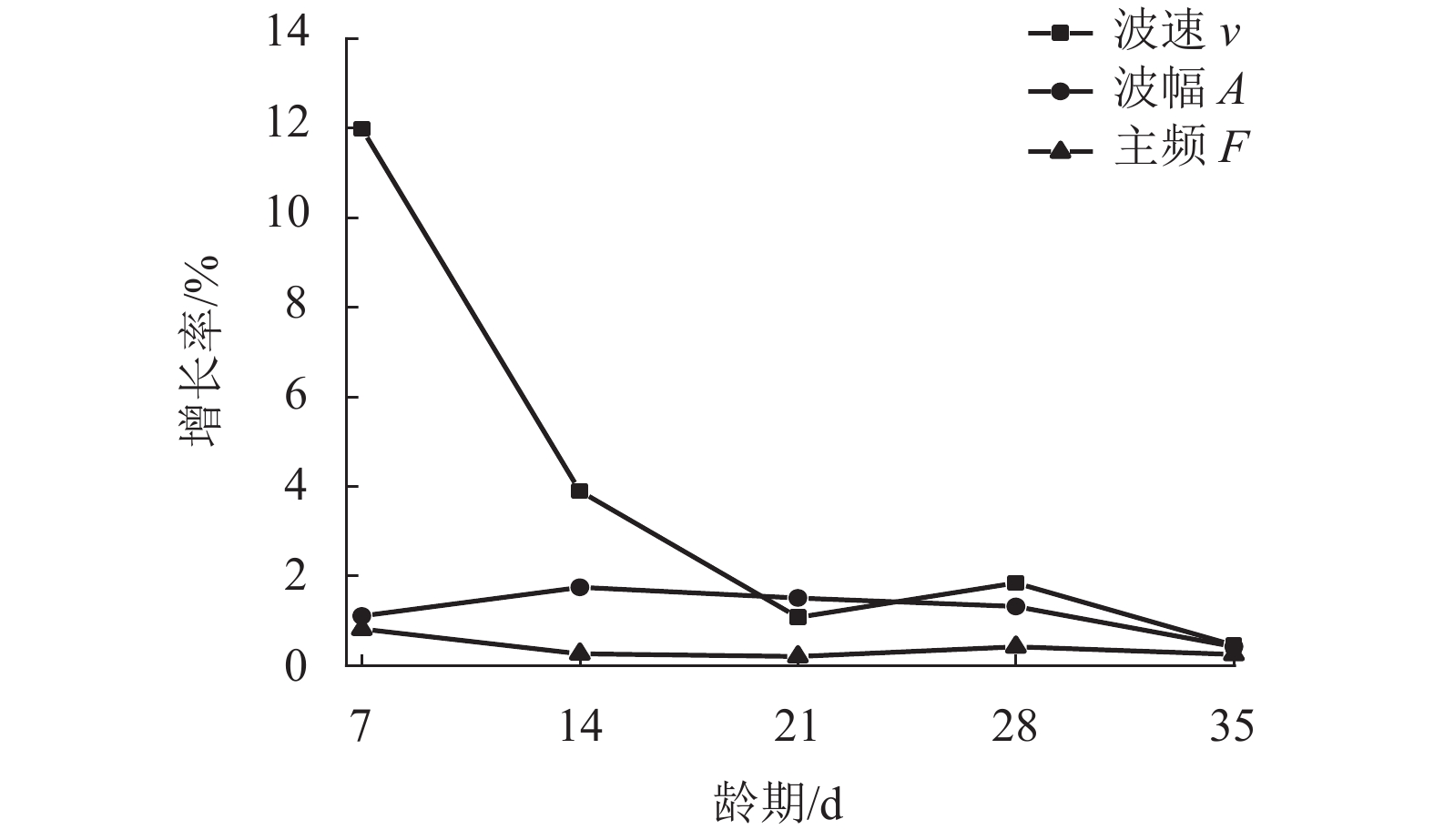
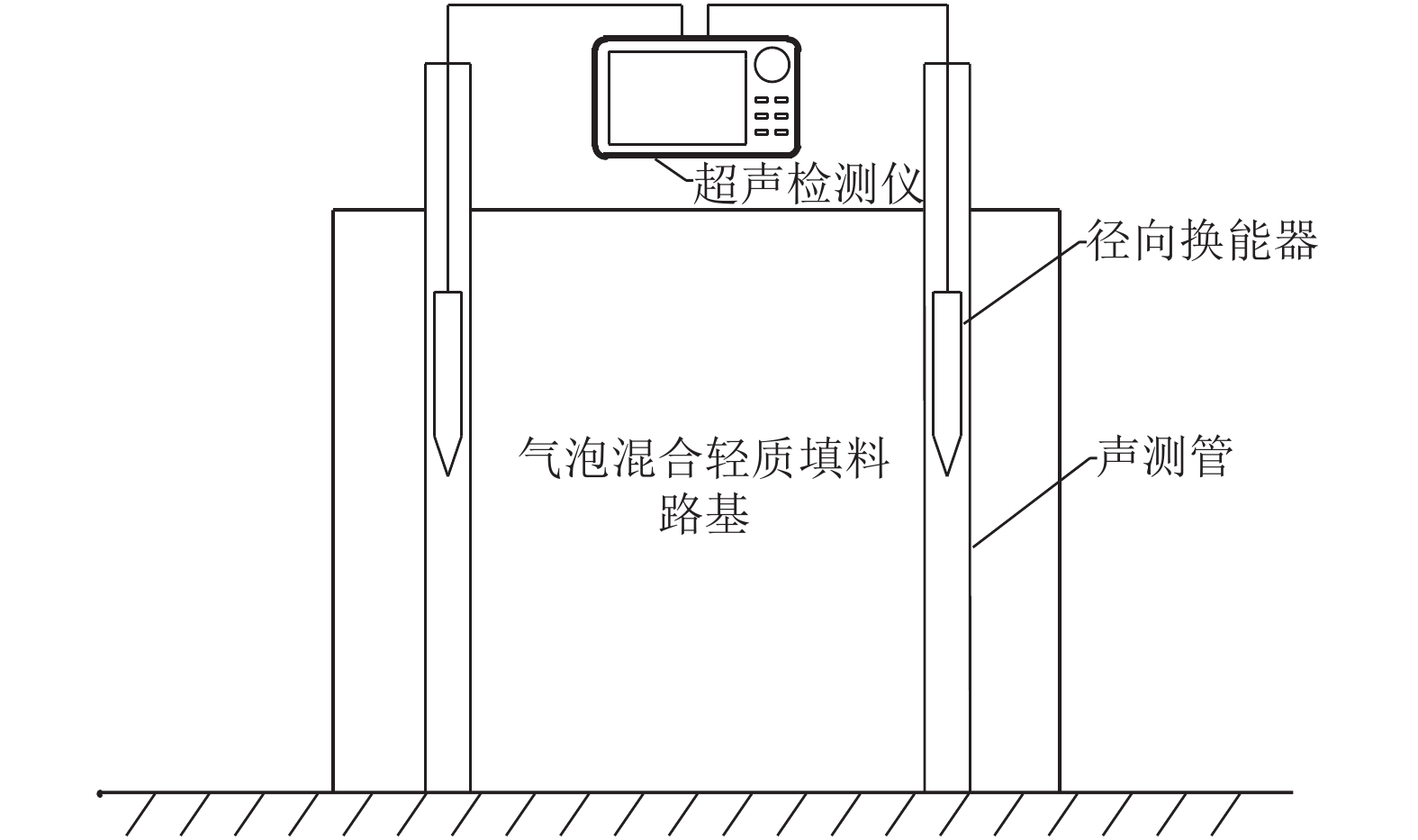
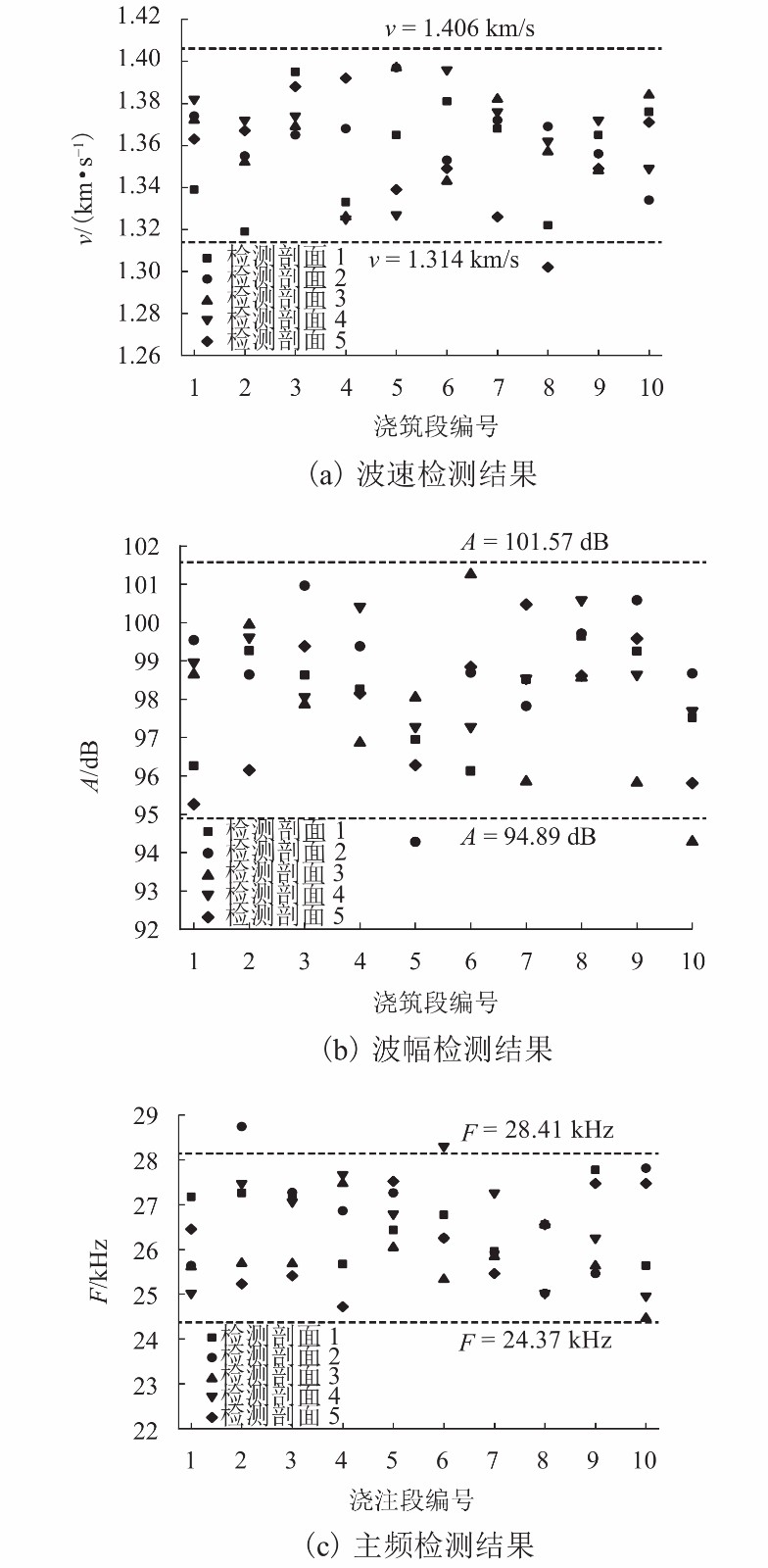
摘要: 为了评价气泡混合轻质填料路基的填筑质量,基于声波透射测试原理,依托实际工程开展了现场试验,选取波速、波幅和主频为评估指标,建立了气泡混合轻质填料路基的填筑质量测试与评估新方法. 评估方法分两级:第1级根据评估指标判断现场路基填筑质量是否合格;第2级在路基填筑质量合格的基础上,根据以熵权法为基础的路基填筑质量均匀性评估模型,进一步评估路基填筑质量是否优良. 研究结果表明:声测管布设间距为0.8 m时,气泡混合轻质填料路基的超声检测结果具有较好的稳定性和代表性;评估路基填筑质量是否合格时应采用波速最小值的95%作为波速低限值、波幅平均值的80%作为波幅低限值、主频平均值的86%作为主频低限值;根据路基填筑质量评估结果,试验段路基的填筑质量合格,填筑质量等级为良好.Abstract: To evaluate the quality of the foamed mixture lightweight filler subgrade, field tests were performed based on ultrasound technology in a practical project. Wave velocity, amplitude and main frequency were selected as evaluation indicators, and a novel method for detection and evaluation of foamed mixture lightweight filler subgrade was established. Evaluation method consisted of two steps: the first step judged whether the on-site subgrade was qualified by evaluation indicators; the second step evaluated quality grade of the qualified subgrade by entropy weight-based subgrade quality uniformity evaluation model. The results show that when testing distance is 0.8 m, the ultrasound test results of the foamed mixture lightweight filler subgrade are stable and representative. 95% of minimum wave velocity, 80% of average amplitude and 86% of average main frequency can be used as the low limits to judge whether the subgrade is qualified. The evaluation results show that the test section subgrade is qualified, and the subgrade quality grade is good.
-
表 1 气泡混合轻质填料施工配合比
Table 1. Mix ratio of foamed mixture lightweight soil
编号 水泥用量/
(kg•m−3)水的用量/
(kg•m−3)气泡群体积/
(L•m−3)S1 365 237 645 S2 325 211 684 S3 335 218 674 S4 345 224 665 S5 355 231 654 S5 375 244 635 S7 385 250 626 S8 395 257 616 S9 405 263 606 注:水泥采用海螺牌PO42.5普通硅酸盐水泥,发泡剂采用HTW-1型复合发泡剂,发泡剂稀释比为1∶50. 表 2 出现裂缝前后超声检测结果对比
Table 2. Comparison of ultrasonic test results before and after cracks appear
% 声参量 衰减量 最大值 平均值 最小值 波速 62.35 25.93 10.23 波幅 38.49 22.38 9.68 主频 70.03 14.87 6.13 表 3 各声参量对应权重
Table 3. Weights of acoustic parameters
声参量 波速 波幅 主频 权重 0.3361 0.3270 0.3369 表 4 路基填筑质量优良性分级
Table 4. Grading of subgrade filling quality
均匀性评估得分 优良评价 (3.75~5.00] 优秀 (2.50~3.75] 良好 (1.25~2.50] 中等 [0~1.25] 合格 表 5 上层路基填筑质量评估
Table 5. Filling quality evaluation of upper subgrade
浇筑段
编号合格评估 优良评估 抗压
强度浇筑
质量均匀性评估得分 填筑质量
等级1 合格 合格 3.1267 良好 2 合格 合格 2.7921 良好 3 合格 合格 3.1927 良好 4 合格 合格 2.6684 良好 5 合格 合格 2.7483 良好 6 合格 合格 3.0233 良好 7 合格 合格 3.2379 良好 8 合格 合格 3.0767 良好 9 合格 合格 3.2284 良好 10 合格 合格 2.4655 中等 表 6 中、下层路基填筑质量评估
Table 6. Filling quality evaluation of middle and lower subgrade
路基 浇筑段
编号合格评估 优良评估 抗压
强度浇筑
质量均匀性评估
得分填筑质量
等级中层 1 合格 合格 3.2316 良好 2 合格 合格 3.0241 良好 3 合格 合格 2.9817 良好 4 合格 合格 2.5498 良好 5 合格 合格 3.1504 良好 6 合格 合格 3.2219 良好 7 合格 合格 2.6916 良好 8 合格 合格 3.0149 良好 9 合格 合格 2.8413 良好 10 合格 合格 2.9816 良好 下层 1 合格 合格 2.9183 良好 2 合格 合格 3.0127 良好 3 合格 合格 3.1298 良好 4 合格 合格 2.8146 良好 5 合格 合格 2.7916 良好 6 合格 合格 3.0417 良好 7 合格 合格 2.4917 中等 8 合格 合格 3.1846 良好 9 合格 合格 2.5916 良好 10 合格 合格 2.9310 良好 -
MYDIN M A O, WANG Y C. Mechanical properties of foamed concrete exposed to high temperatures[J]. Construction & Building Materials, 2012, 26(1): 638-654. LIU X, SHENG K, LI Z L, et al. Experimental research on foamed mixture lightweight soil mixed with fly-ash and quicklime as backfill material behind abutments of expressway bridge[J]. Advances in Materials Science and Engineering, 2017, 2017(16): 1-11. 刘鑫,甘亮琴,盛柯,等. 基于加速应力试验方法的气泡混合轻质土使用寿命估计研究[J]. 岩土工程学报,2017,39(10): 1793-1799. doi: 10.11779/CJGE201710006LIU Xin, GAN Liangqin, SHENG Ke, et al. Experimental study on service life of foamed mixture lightweight soil based on method of accelerated stress tests[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2017, 39(10): 1793-1799. doi: 10.11779/CJGE201710006 HAJIMOHAMMADI A, NGO T, MENDIS P. Enhancing the strength of pre-made foams for foam concrete applications[J]. Cement and Concrete Composites, 2018, 87(1): 164-171. doi: 10.1016/j.cemconcomp.2017.12.014 CHAO S, YU Z, JIAN G, et al. Effects of foaming agent type on the workability,drying shrinkage,frost resistance and pore distribution of foamed concrete[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2018, 186: 833-839. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2018.08.019 NAMBIAR E, KUNHANANDAN K, RAMAMURTHY K. Fresh state characteristics of foam concrete[J]. Journal of Materials in Civil Engineering, 2008, 20(2): 111-117. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)0899-1561(2008)20:2(111) 朱俊杰,刘鑫,洪宝宁,等. 气泡混合轻质土路堤最佳浇筑厚度的确定方法[J]. 岩土力学,2008,20(2): 111-117.ZHU Junjie, LIU Xin, HONG Baoning, et al. A method for determining optimum casting thickness of foamed mixture lightweight soil embankment[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2008, 20(2): 111-117. HASSAN A M T, JONES S W. Non-destructive testing of ultra high performance fibre reinforced concrete (UHPFRC):a feasibility study for using ultrasonic and resonant frequency testing techniques[J]. Construction & Building Materials, 2012, 35: 361-367. SCHABOWICZ K. Ultrasonic tomography–the latest nondestructive technique for testing concrete members–description,test methodology,application example[J]. Archives of Civil and Mechanical Engineering, 2014, 14(2): 295-303. doi: 10.1016/j.acme.2013.10.006 中华人民共和国住房和城乡建设部. 建筑基桩检测技术规范: JGJ 106—2014[S]. 北京: 中国建筑工业出版社, 2014. 中国国家标准化管理委员会. 焊缝无损检测超声检测技术、检测等级和评定: GB/T 11345—2013[S]. 北京: 中国质检出版社, 2013. 中国工程建设标准化协会. 超声法检测混凝土缺陷技术规程: CECS 21—2000[S]. 北京: 中国城市出版社, 2000. 陈鹏宇,余宏明,师华鹏. 基于权重反分析和标准化模糊综合评价的岩爆预测模型[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2014,33(10): 2154-2160.CHEN Pengyu, YU Hongming, SHI Huaping. Prediction model for rockburst based on weighted back analysis and standardized fuzzy comprehensive evaluation[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2014, 33(10): 2154-2160. 阮航,张勇慧,朱泽奇,等. 一种改进的公路边坡稳定性模糊评价方法研究[J]. 岩土力学,2015,36(11): 3337-3344.RUAN Hang, ZHANG Yonghui, ZHU Zeqi, et al. An improved fuzzy method for evaluating stability of highway slopes[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2015, 36(11): 3337-3344. 翟友成, 曹文贵, 王江营, 等. 基于不确定型层次分析法的边坡稳定模糊评判方法[J]. 岩土力学, 2011, 32 (增刊2): 539-543.ZHAI Youcheng, CAO Wengui, WANG Jiangying, et al. Fuzzy evaluation method of slope stability based on uncertain analytic hierarchy process[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2011, 32 (S2): 539-543. -





 下载:
下载: