Extreme Value Inference of Axle Stress Spectrum for Intercity EMU
-
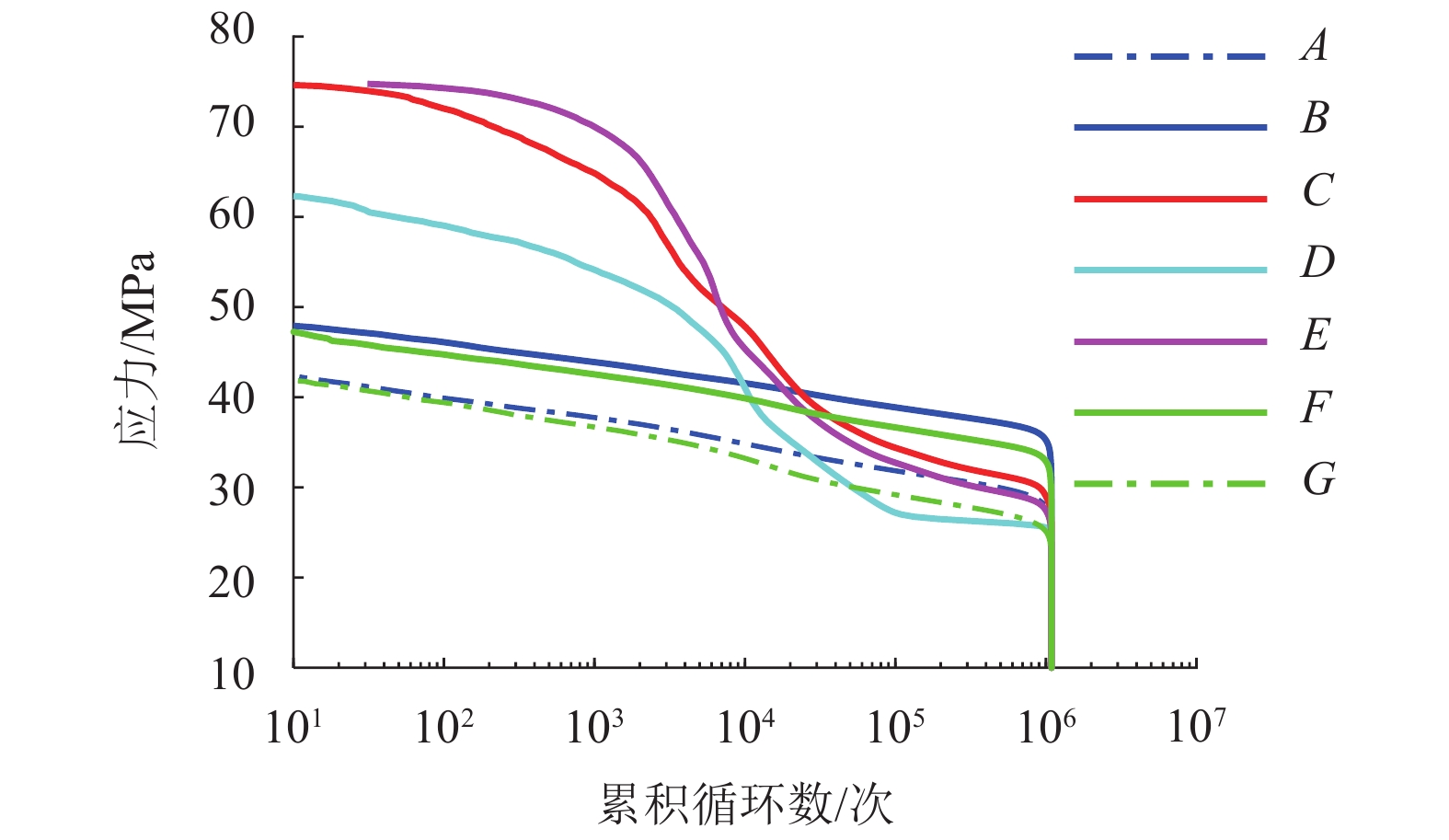
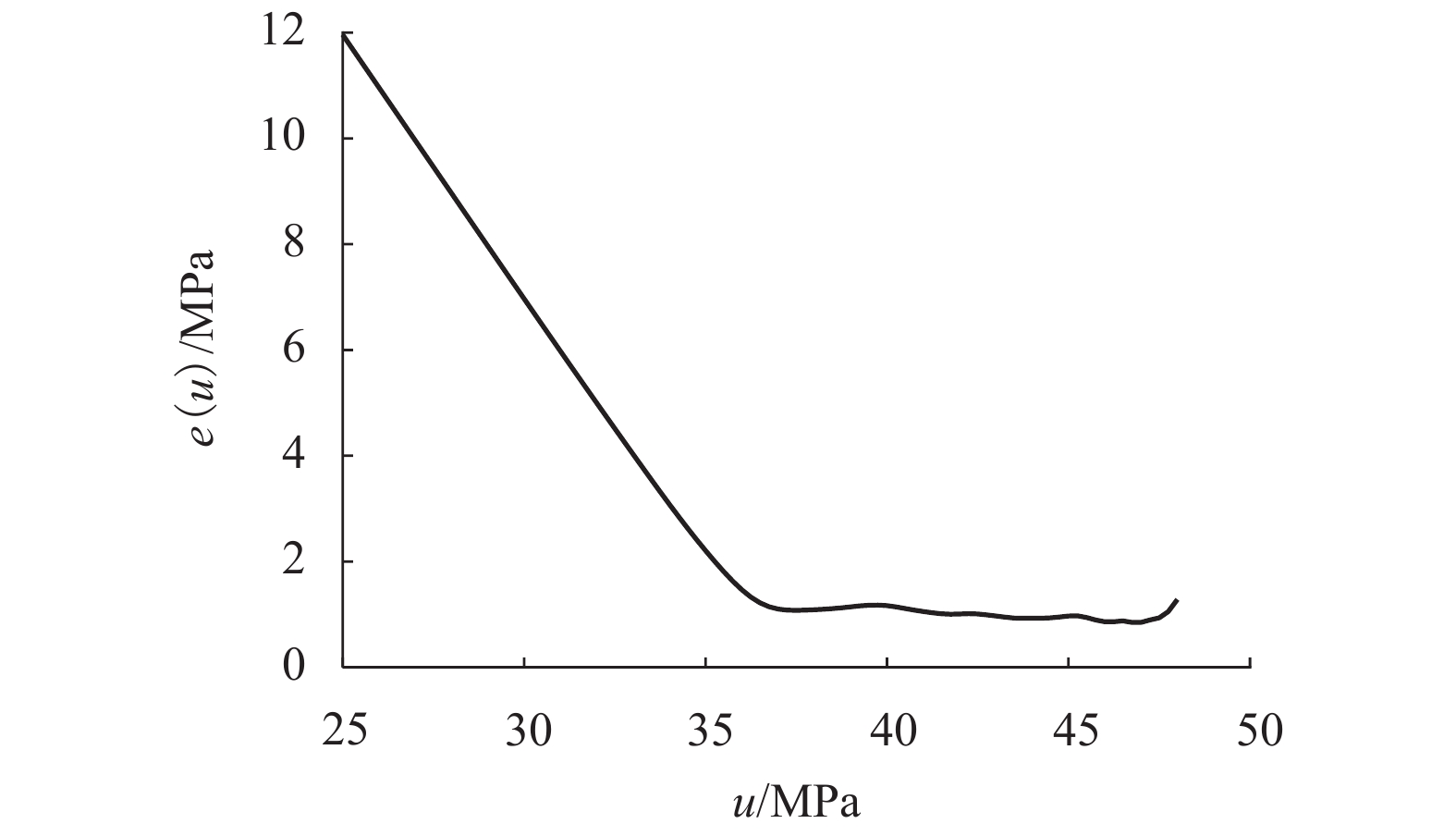
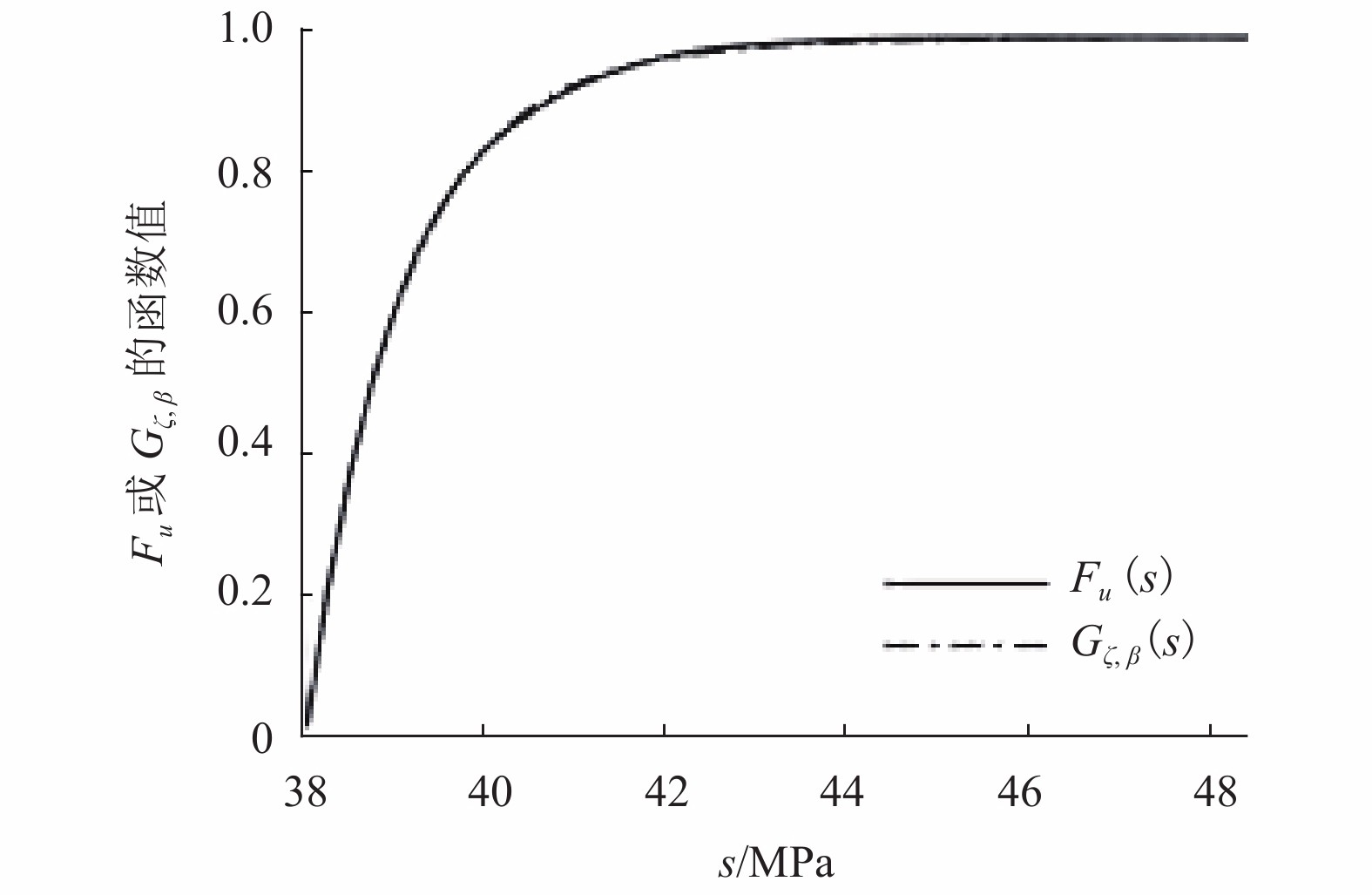
摘要: 为评估车轴的可靠性或扩展车轴的应力谱,需要预判车轴全寿命期内的最大应力. 首先,综合考虑推断精度和统计效率等因素,基于Sturges公式选取0.5 MPa为组距对实测车轴应力-时间历程进行雨流计数,得到车轴应力的经验累积分布函数. 其次,针对不同的门槛限值计算应力的经验均值超限函数,通过确定经验均值超限函数的拐点确定合理门槛限值. 然后,基于Pickands-Balkema-de Haan定理,利用广义帕累托分布拟合车轴应力的超限分布函数,并通过拟合分布外推车轴全寿命期内的最大应力. 最后,利用实测车轴应力数据进行了验证. 研究结果表明:为评估车轴寿命期内的最大应力,大约需要不少于 3000 km 的线路测试;基于13.5 t轴重实测数据推断的应力极值比基于14.1 t轴重计算的校核应力高出13%,因此完全按照设计轴重满载运营,需格外谨慎.Abstract: In order to evaluate the reliability and extend stress spectra of axles, the maximum stress during its full life need to be predicted. First, to obtain the empirical cumulative distribution function of axle stress, the bin width of 0.5 MPa is chosen, which is based on the Sturges formula as a tradeoff between the inferred accuracy and statistical efficiency, and the rain flow counting is performed against the measured axial stress-time history. Secondly, the empirical mean excess function is calculated according to different threshold values and the reasonable threshold is determined by identifying the turning point of the mean excess function. Then, based on Pickands-Balkema-de Haan theorem, the excess distribution function of the axle stress is fitted with the generalized Pareto distribution, and the maximum stress during the full life is inferred with the fitted distribution. Finally, this method is verified with the measured data. The results show that in order to assess the maximum axle stress during its full life, the tests of 3000 km are required at least. The inferred maximum stress with the measured data of 13.5 t wheel load is about 13% higher than that with the one of 14.1 t wheel load. Therefore it should be particularly cautious to operate at axle design weight.
-
Key words:
- axle /
- load spectrum analysis /
- extreme value inference /
- reliability theory
-
表 1 不同经验公式的组距计算结果
Table 1. Calculated results by different empirical formulas
公式名 表达式 h/MPa Sturges $k = {\rm{ent} }({\log _2}{n_{\rm{t}}}) + 1$ 0.50 square-root $k = {\rm{ent} }({\sqrt n _{\rm{t}}})$ 0.30 Scott $h = 3.5{\sigma _S} n_{\rm{t} }^{ - 1/3}$ 0.04 Freedman-Diaconis $h = 2{Q_S} n_{\rm{t} }^{ - 1/3}$ 0.03 表 2 截面 B 的分布拟合结果
Table 2. Fitted results of section B
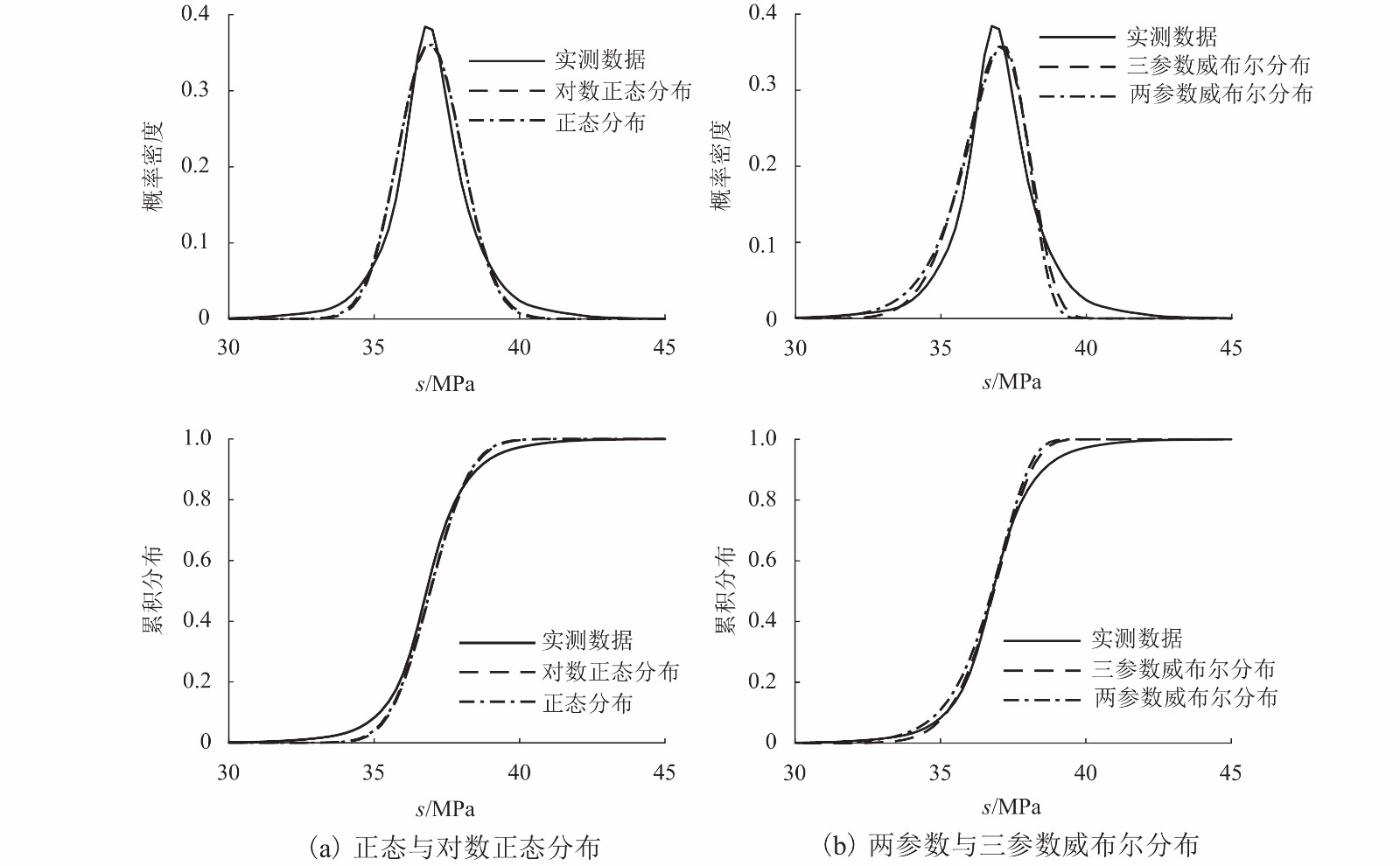
分布 位置参数 尺度参数 形状参数 $\chi _{{\rm{LN}}}^2/{\chi ^2} $ smax/MPa 正态 36.9 1.10 0.98 42.2 对数正态 3.6 0.03 1.00 42.6 两参数威布尔 37.20 36.3 0.52 39.9 三参数威布尔 30.0 7.20 6.9 0.66 40.5 表 3 各截面的实测最大值与应力的极值推断结果
Table 3. Measured maximum values and extreme value inferences of each section
截面 实测最大值/MPa $s_{\max }^*$/MPa $\hat \xi $ A 44 52 0.086 B 49 53 0.023 C 75 98 0.002 D 63 67 −0.350 E 75 78 −0.460 F 48 52 −0.140 G 43 47 −0.110 表 4
$s_{\max }^*$ 与校核应力的对比Table 4. Comparison between
$s_{\max }^*$ and allowable stressesMPa 截面 $s_{\max }^* $ 轴重/t 17.0 14.1 13.5 A 52 60 50 48 B 53 56 47 45 C 98 103 86 83 D 67 94 80 77 E 78 103 86 83 F 52 56 47 45 G 47 60 50 48 -
Japanese Industrial Standards Committee Divisional Council on Railways and Rolling Stock. Railway rolling stock−design methods for strength of axles: JIS E 4501[S]. Tokyo: Japanese Standards Association, 1995. European Committee for Standardization. Railway applications−wheelsets and bogies−non-powered axles−design method: EN13103[S]. Brussels: European Committee for Standardization Management Centre, 2001. European Committee for Standardization. Railway applications−wheelsets and bogies− powered axles−design method: EN13104[S]. Brussels: European Committee for Standardization Management Centre, 2001. 周素霞,谢基龙,赵方,等. 基于概率分布函数的动车组车轴应力谱试验分析[J]. 中国铁道科学,2013,34(2): 95-99. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4632.2013.02.16ZHOU Susia, XIE Jilong, ZHAO Fang, et al. Experimental analysis on the stress spectrum of emu axle based on probability distribution function[J]. China Railway Science, 2013, 34(2): 95-99. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4632.2013.02.16 周素霞,李福胜,谢基龙,等. 基于损伤容限的动车组车轴实测载荷谱等效应力评价[J]. 机械工程学报,2015,51(8): 131-136. doi: 10.3901/JME.2015.08.131ZHOU Suxia, LI Fusheng, XIE Jilong, et al. Equivalent stress evaluation of the load spectrum measured on the emu axle based on damage tolerance[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2015, 51(8): 131-136. doi: 10.3901/JME.2015.08.131 丁然,李强,任尊松. 城际动车组轮轨力统计特征研究[J]. 机械工程学报,2019,55(6): 108-115. doi: 10.3901/JME.2019.06.108DING Ran, LI Qiang, REN Zunsong. Statistics characters of wheel/rail loads of intercity EMU[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2019, 55(6): 108-115. doi: 10.3901/JME.2019.06.108 徐凯,李芾,安琪,等. 高速动车组车轮踏面磨耗特征分析[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2021,56(1): 92-100.XU Kai, LI Pei, AN Qi, et al. Wheel tread wear characteristics of high-speed electric multi-units[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2021, 56(1): 92-100. 王晨,罗世辉,邬平波,等. 动车组踏面凹型磨耗对车辆稳定性的影响[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2021,56(1)-91.WANG Chen, LUO Shihui, WU Pingbo, et al. Effect of hollow worn tread of electric multiple units on vehicle stability[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2021, 56(1)-91. 侯卫星. 统计推断理论在转向架载荷谱研究中的应用[J]. 铁道车辆,1990(7): 39-46. 白立国,李强,王斌杰. 120 km/h 重载货车摇枕载荷谱最大载荷的统计推断研究[J]. 铁道机车车辆,2008,28(4): 27-29. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-7842.2008.04.008BAI Liguo, LI Qiang, WANG Binjie. Statistical infertial research on ascertaining method of bolster max load in spectrum making when wagons run at 120 km/h with full load[J]. Railway Locomotive & Car, 2008, 28(4): 27-29. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-7842.2008.04.008 易当祥,吕国志,周雄伟. 用概率推断法确定多工况二维疲劳设计谱的载荷最大值[J]. 应用力学学报,2006,23(3): 484-487. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-4939.2006.03.032YI Dangxiang, LYU Guozhi, ZHOU Xiongwei. Maximal loading calculation for two dimensional fatigue design spectrum under multiple working conditions with probability extrapolation method[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Mechanics, 2006, 23(3): 484-487. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-4939.2006.03.032 陈道云,孙守光,李强. 高速列车载荷谱推断及扩展方法研究[J]. 机械工程学报,2018,54(10): 151-155. doi: 10.3901/JME.2018.10.151CHEN Daoyun, SUN Shouguang, LI Qiang. Study on deduction and extend of high-speed train load spectrum[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2018, 54(10): 151-155. doi: 10.3901/JME.2018.10.151 刘义伦,ZENNER H. 关于标准载荷累积频次谱的外推[J]. 中南矿冶学院学报,1991,22(5): 556-562.LIU Yilun, ZENNER H. Extrapolation about standard collection curves[J]. Journal of Central South University, 1991, 22(5): 556-562. 黄鹏,蔡玢,全涌,等. 基于实测的低矮房屋屋面风压极值计算方法[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2014,49(2): 247-253. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2014.02.010HUANG Peng, CAI Bin, QUAN Yong, et al. Peak pressure estimation method of wind loads on low-rise building based on field measurement[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2014, 49(2): 247-253. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2014.02.010 BALKEMA A A, DE HAAN L. Residual life time at great age[J]. The Annals of Probability, 1974, 2(5): 792-804. doi: 10.1214/aop/1176996548 EMBRECHTS P, KLÜPPELBERG C, MIKOSCH T. Modelling extremal events for insurance and finance[M]. Berlin: Springer, 1997. 邹骅. 城际动车组转向架构架载荷谱研究[D]. 北京: 北京交通大学, 2016. PICKANDS J. Statistical inference using extreme order statistics[J]. The Annals of Statistics, 1975, 3(1): 119-131. doi: 10.1214/aos/1176343003 -





 下载:
下载: