Optimization of Wing Rail Lifting Value for Rigid Frog of Speed-Up Turnout
-
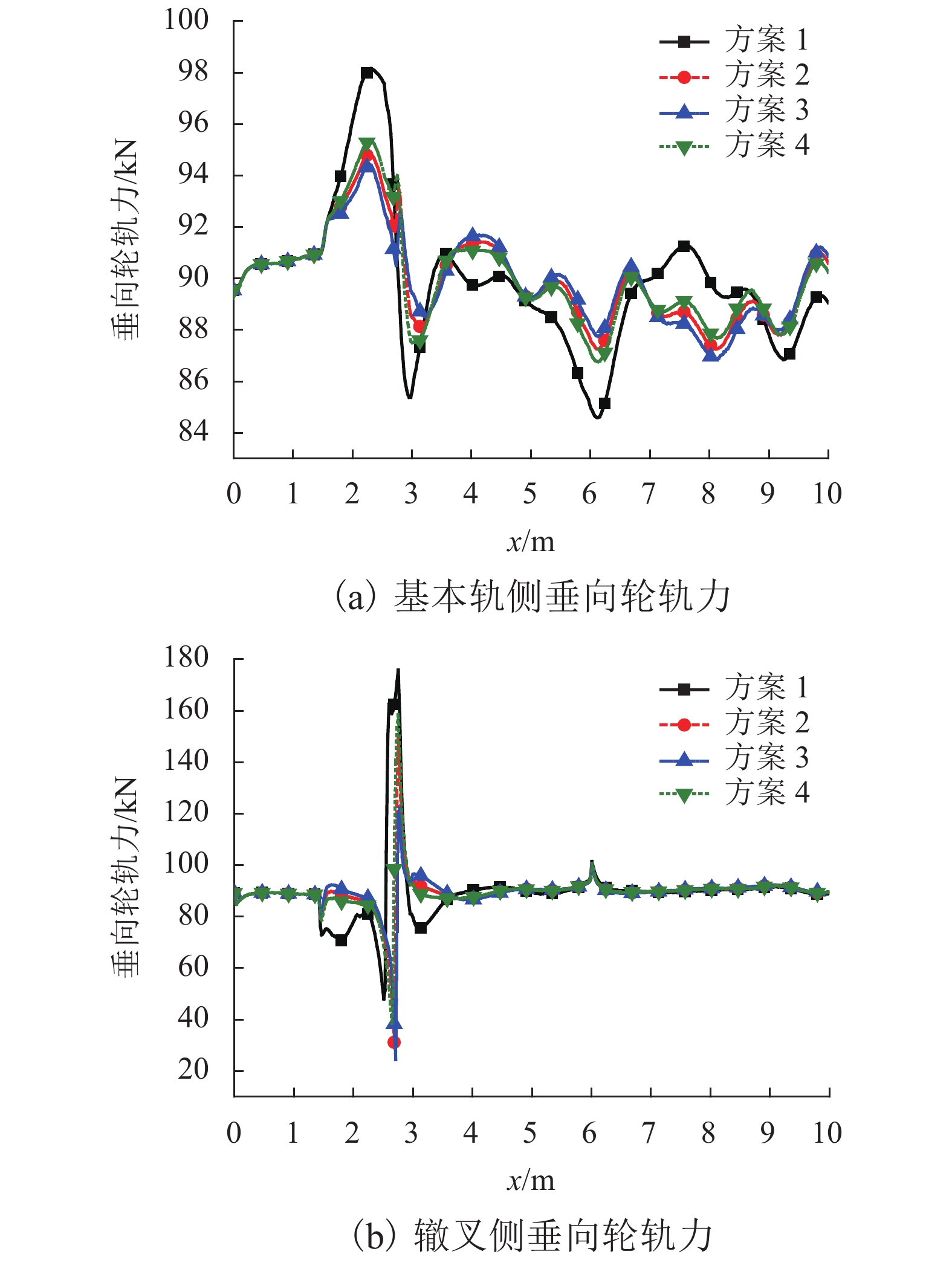
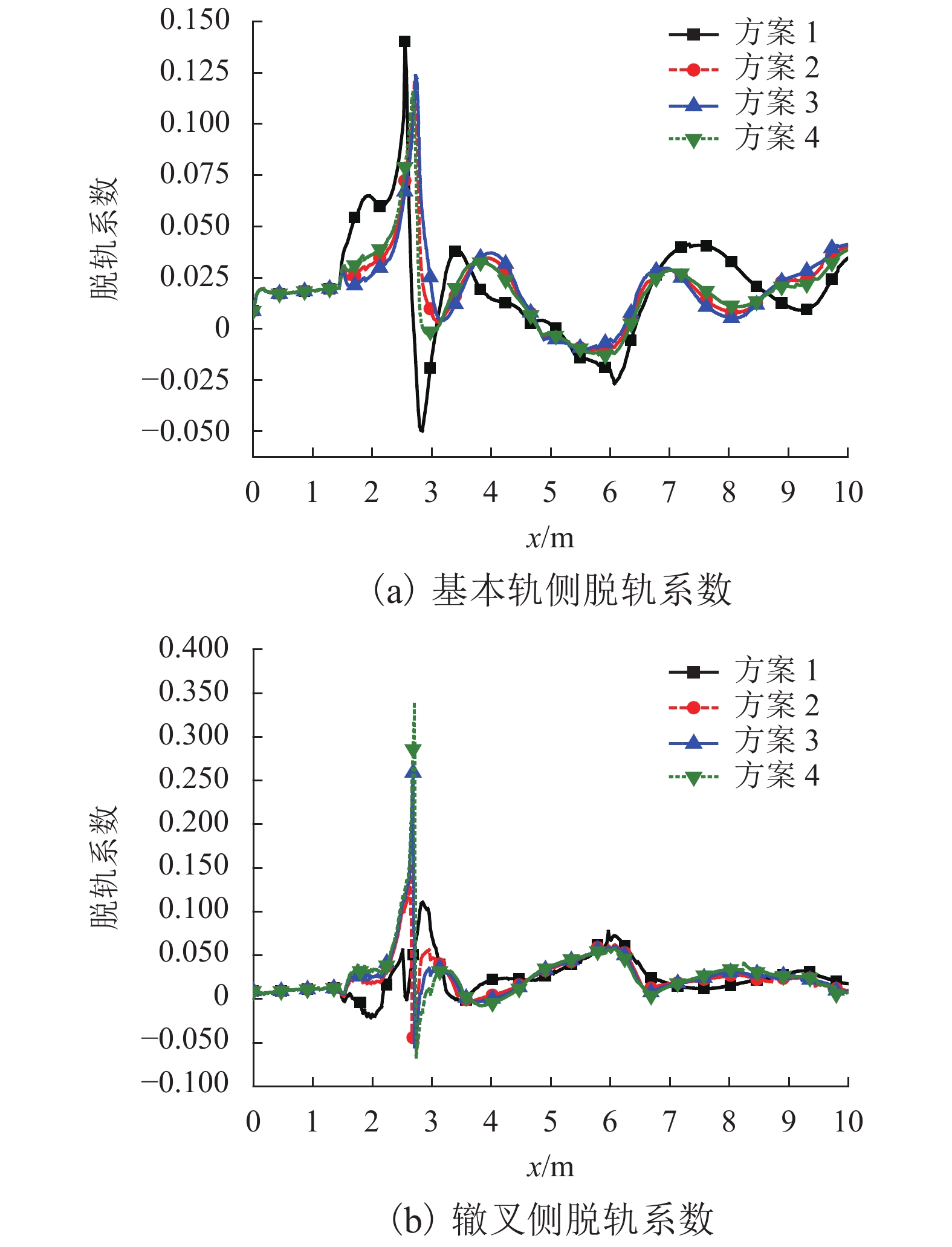
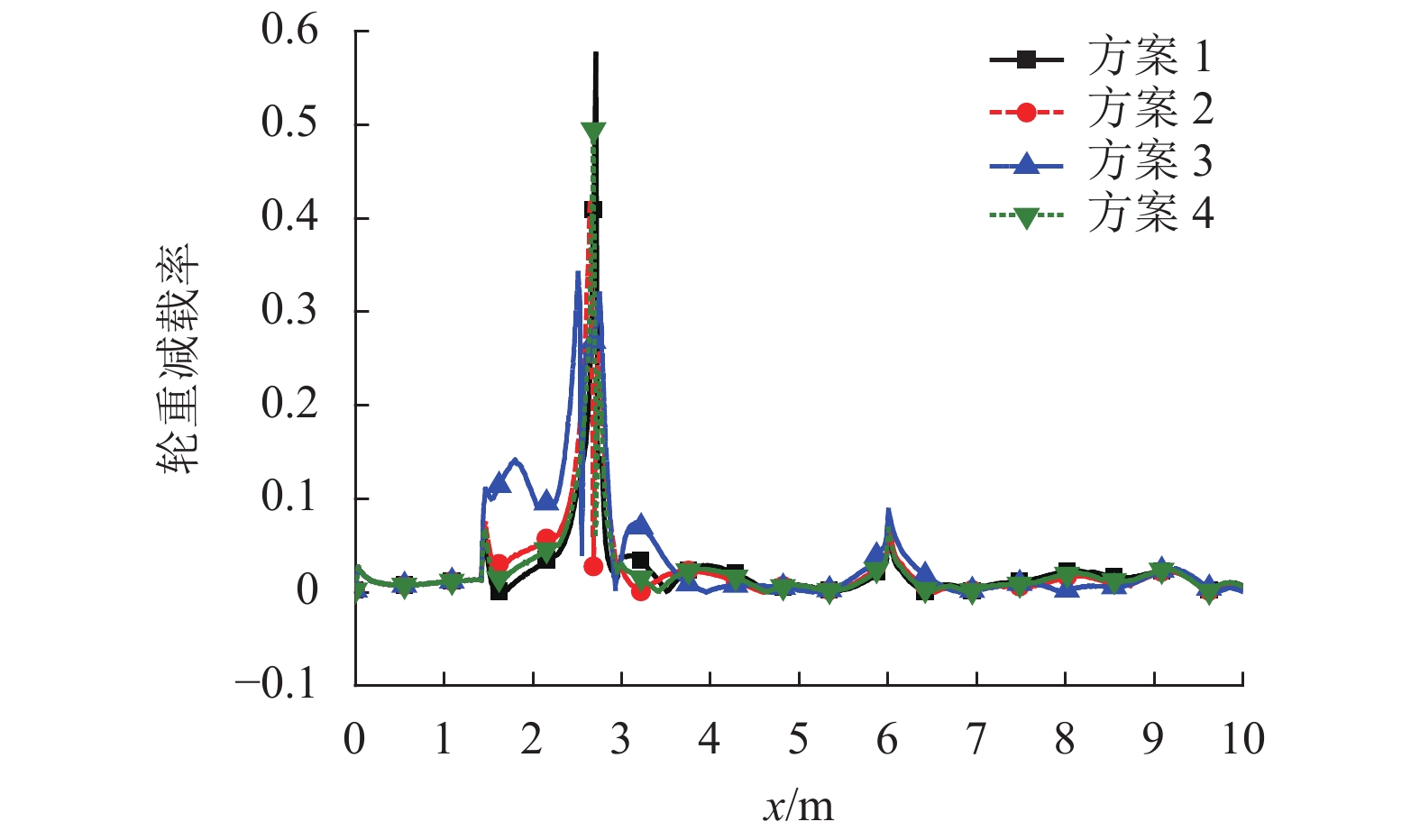
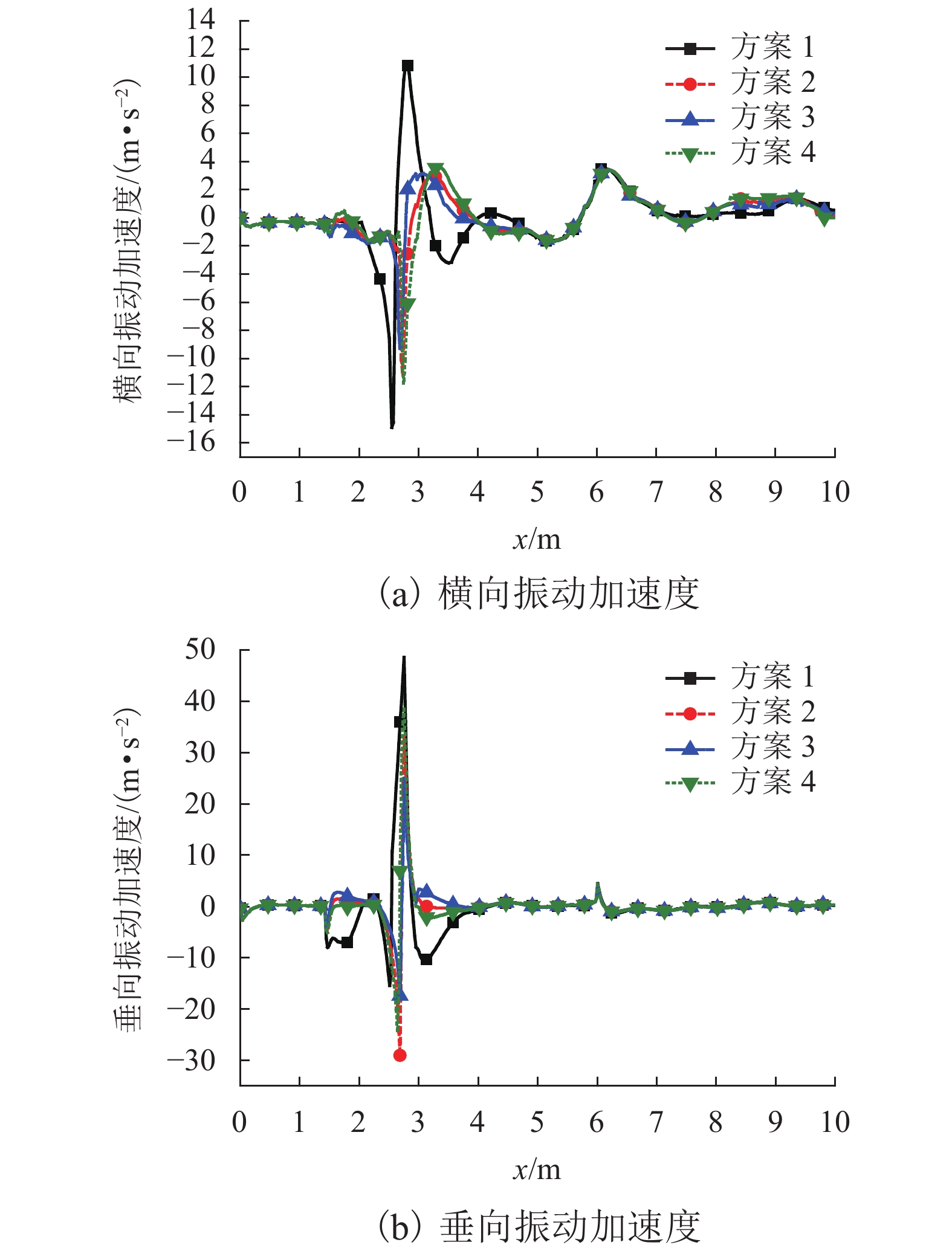
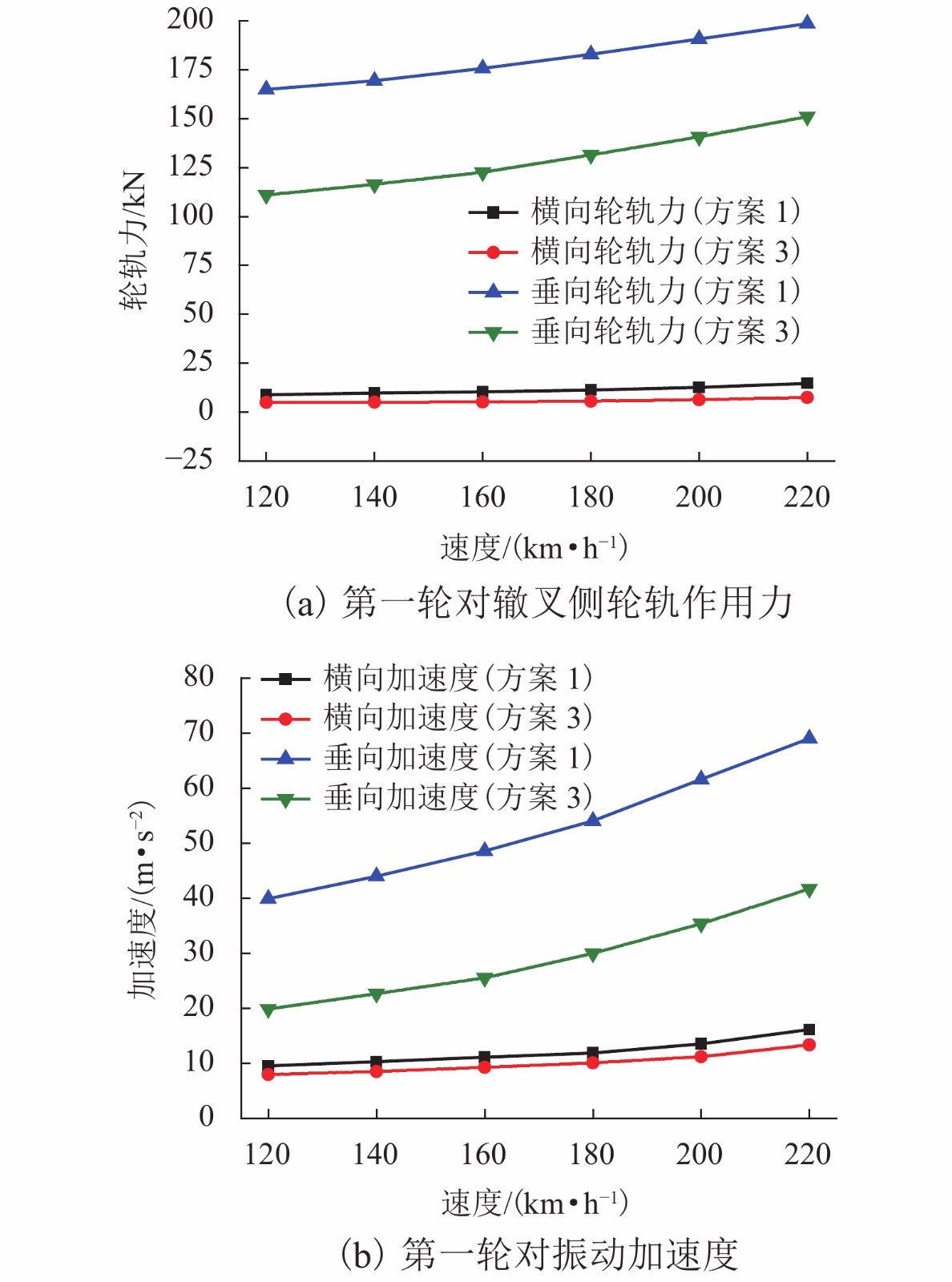
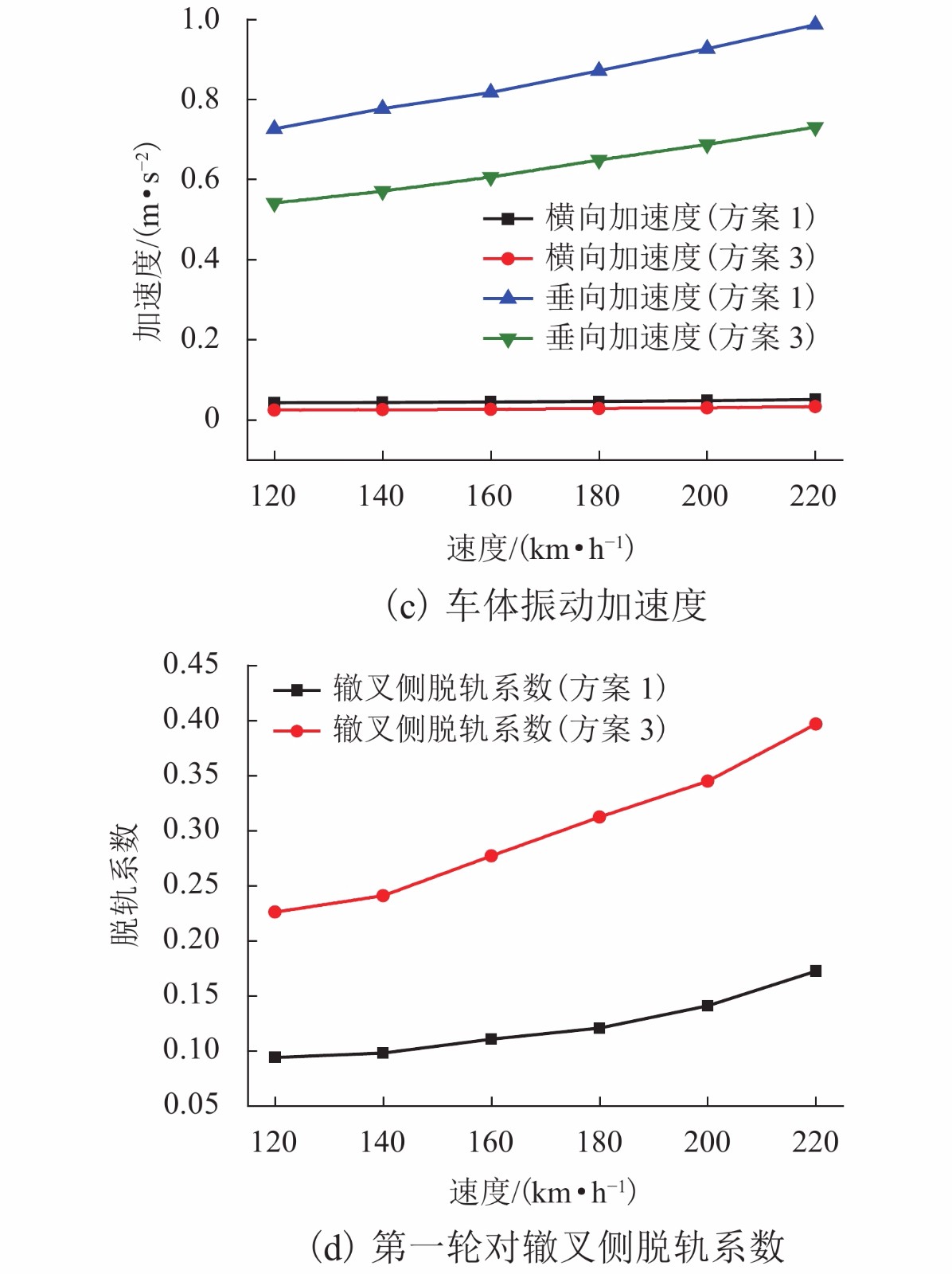
摘要: 为研究固定辙叉结构不平顺对列车过岔动力特性的影响,基于岔区轮轨系统动力学及轮轨接触关系理论,以12号提速道岔固定辙叉为例,分别建立了翼轨不同加高设计方案下的辙叉模型以及CRH2型车车辆模型,在此基础上,深入分析了翼轨加高设计对列车过岔动力特性、过岔速度以及行车平稳性的影响规律. 结果表明:列车过岔时,随着翼轨向外弯折,其轮轨接触区域开始外移,并由此造成辙叉区轮对质心垂向位置的降低;通过设置合理的翼轨加高值,可有效降低辙叉区轨道的竖向结构不平顺,进而抑制轮对质心垂向位置的降低,提高列车过岔的平稳性及旅客乘车舒适度;固定辙叉翼轨加高设计,可有效改善列车直向过岔动力特性,但对侧向过岔效果有限;当加高值设置为3 mm时,翼轨加高优化的效果最佳,与无加高设计相比,加高后列车直向过岔第一轮对横向和垂向轮轨力最大幅值分别降低了45.8%和30.3%,车体横向及垂向加速度则分别降低了42.2%和26.1%;随着列车运行速度的提高,过岔时的轮轨动力响应也开始逐渐加剧,合理的翼轨加高设计将有利于提高列车的过岔速度. 研究成果可为我国铁路线路道岔固定辙叉的结构优化设计提供理论参考.Abstract: In order to study the influence of the rigid frog structure irregularity on dynamic characteristics of trains passing through the turnout, based on the theory of wheel-rail contact and wheel-rail system dynamics, a frog model of switch and a CRH2 vehicle model under different wing rail lifting design schemes were established in the case of the rigid frog of Chinese No.12 single turnout. On this basis, the influence of wing rail elevation design on the dynamic characteristics, passing speed, and ride stability of trains crossing the turnout were analyzed. Results show that with the wing rail bending outwards the wheel-rail contact area begins to move outwards when the train crosses a switch, resulting in a reduction in the vertical position of the wheelset center of mass. The problem of lowering the vertical position of the wheel’s center of mass can be effectively solved by setting a reasonable wing rail lifting value, to improve the stability of the train crossing the switch and the comfort of passengers. The design of wing rail lifting can effectively improve the dynamic characteristics of the train passing through the turnout in the straight direction, but the effect on lateral crossing is limited. When the heightening value of the wing rail is set as 3 mm, the optimal effect of wing rail lifting is the best. Compared with the design without wing rail heightening, the maximum values of lateral and vertical wheel-rail forces of the first wheelset of the train passing through the turnout with heighted wing rail in the straight direction are reduced by 45.8% and 30.3%, respectively. In addition, the lateral and vertical accelerations of the vehicle body are also reduced by 42.2% and 26.1%, respectively. With the increase of the train running speed, the dynamic response of the wheels and rails at the time of crossing the turnout is gradually intensified, and a reasonable design of the wing rails will help to increase the speed of the train crossing the turnout. The research results can provide some theoretical reference for the structural optimization design of rigid frog for railway lines in China.
-
Key words:
- rigid frog /
- wing rail lifting value /
- dynamic characteristics /
- scheme optimization
-
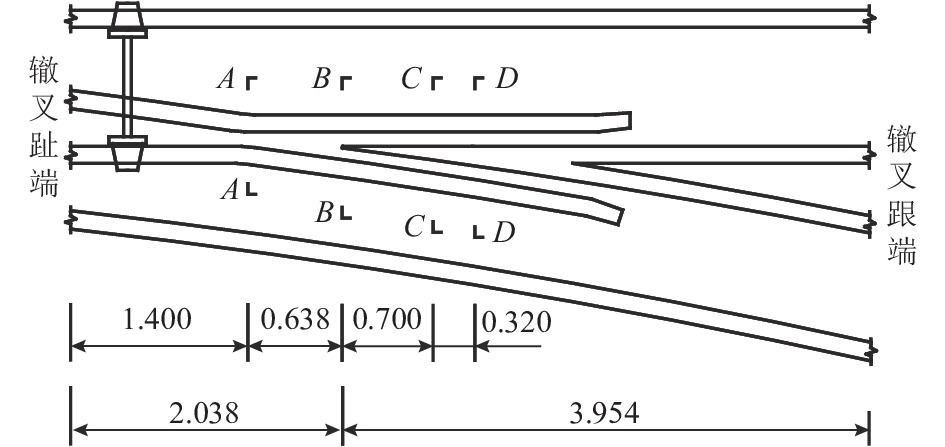
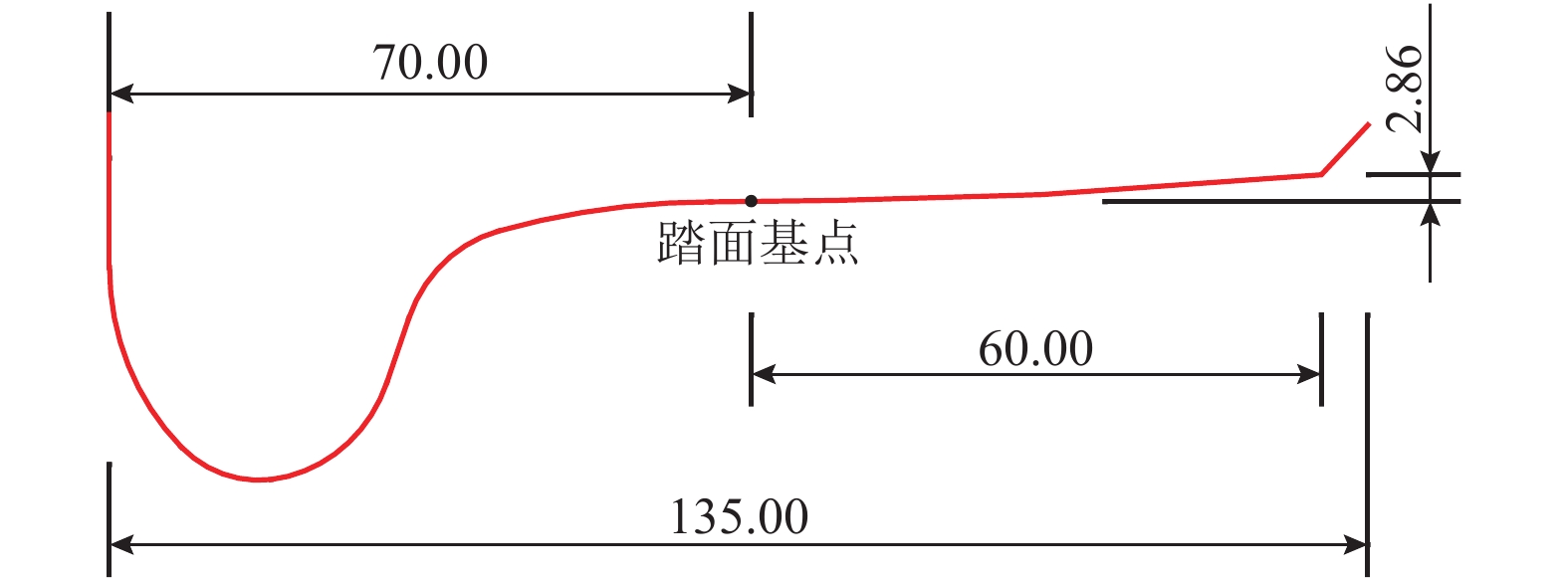
表 1 翼轨关键断面位置
Table 1. Position of key sections of wing rails
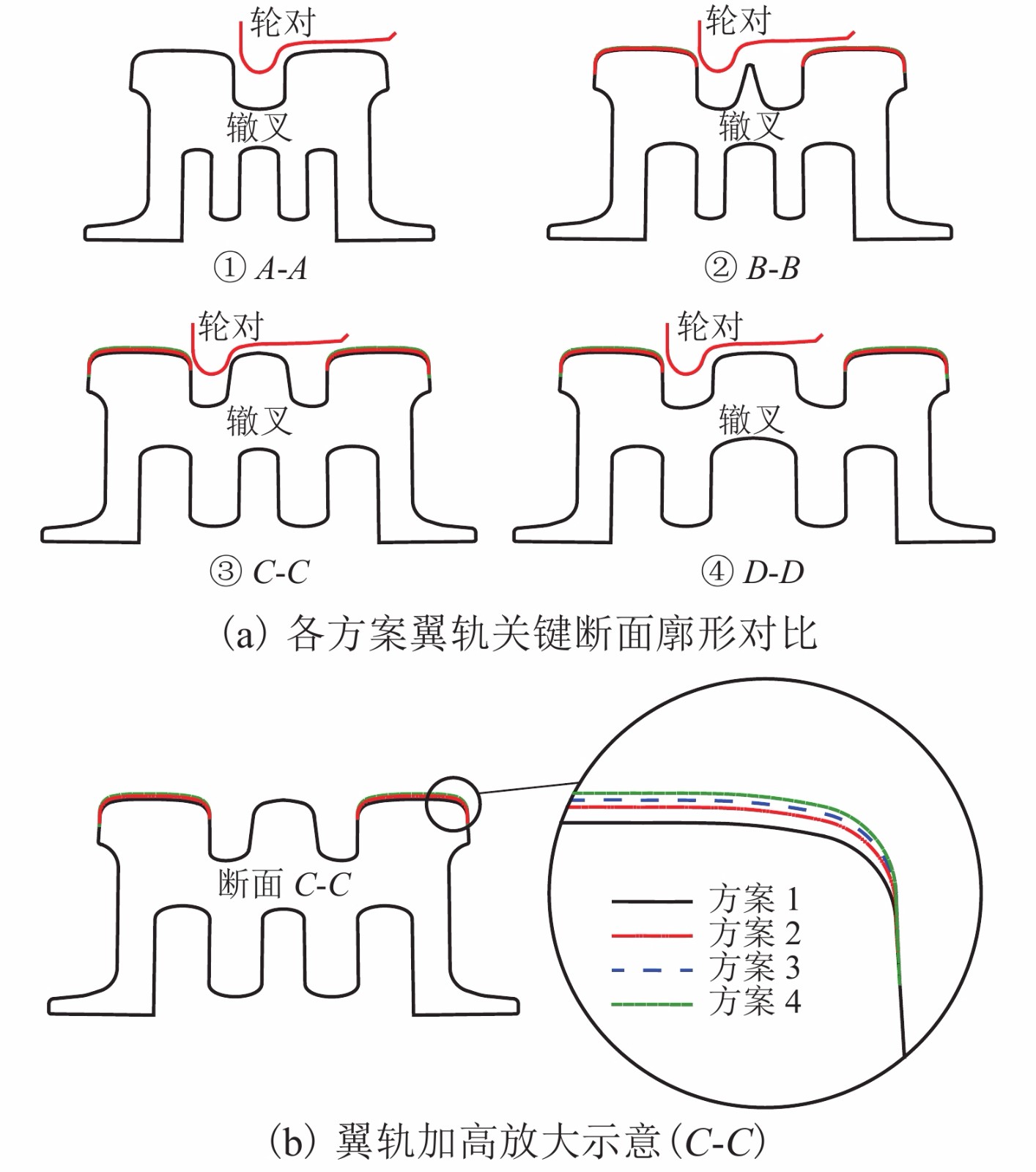
断面名称 心轨顶宽/mm 距辙叉趾端距离/m A-A 1.400 B-B 5 2.038 C-C 50 2.738 D-D 70 3.058 表 2 翼轨加高设计方案
Table 2. Design scheme for heightening the wing rail
方案 轨顶横坡 翼轨加高值/mm A-A B-B C-C D-D 1 1∶40 0 0 0 0 2 1∶40 0 0.95 2.00 2.00 3 1∶40 0 1.43 3.00 3.00 4 1∶40 0 1.91 4.00 4.00 表 3 CRH2型车基本计算参数
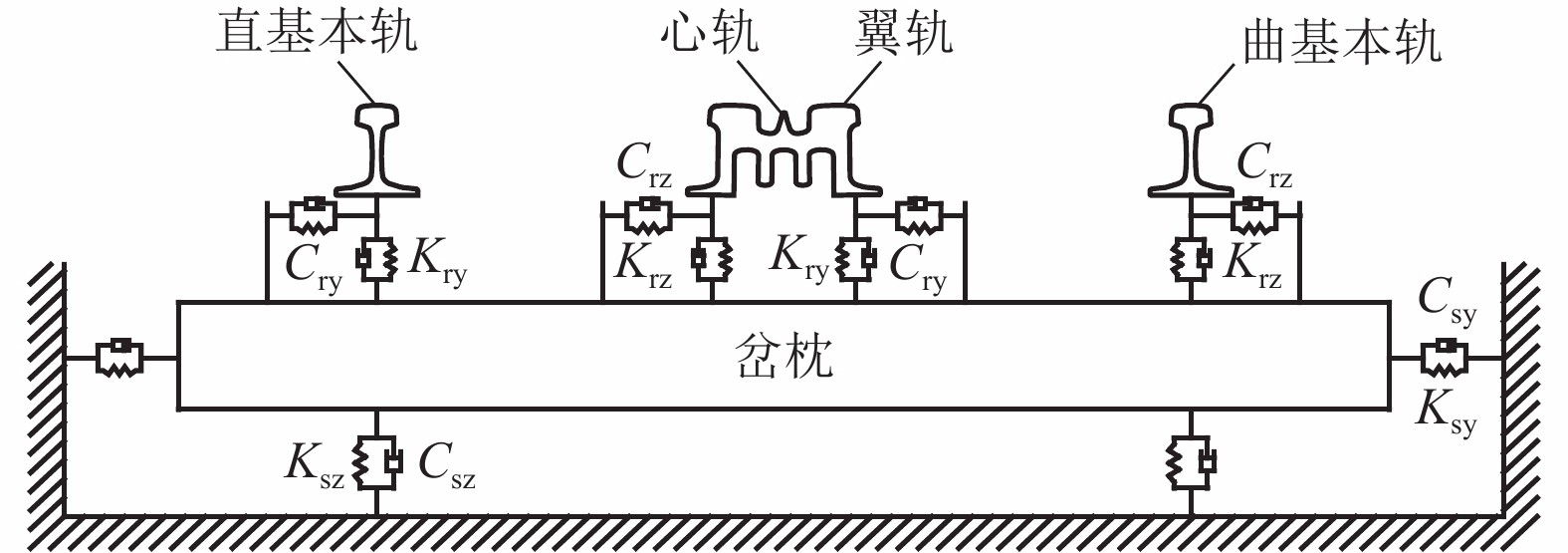
Table 3. Basic calculation parameters of CRH2 vehicle
符号 参数名称 取值 ${M_{\rm{c}}}$ 车体质量/${\rm{kg} }$ 42 400 ${I_{\rm{cx}}}$ 车体侧滚转动惯量/$({\rm{kg} } {\text{•} } { {\rm{m} }^2})$ 7.06 × 105 ${I_{{\rm{cy}}}}$ 车体点头转动惯量/$({\rm{kg} } {\text{•} } { {\rm{m} }^2})$ 2.27 × 106 ${I_{{\rm{cz}}}}$ 车体摇头转动惯量/$({\rm{kg} } {\text{•} } { {\rm{m} }^2})$ 2.08 × 106 ${M_{\rm{b}}}$ 构架质量/${\rm{kg}}$ 3 100 ${I_{{\rm{bx}}}}$ 构架侧滚转动惯量/$({\rm{kg} } {\text{•} } { {\rm{m} }^2})$ 5 045 ${I_{{\rm{by}}}}$ 构架点头转动惯量/$({\rm{kg} } {\text{•} } { {\rm{m} }^2})$ 2 806 ${I_{{\rm{bz}}}}$ 构架摇头转动惯量/$({\rm{kg} } {\text{•} } { {\rm{m} }^2})$ 2 247 ${M_{\rm{w} } }$ 轮对质量/${\rm{kg}}$ 1 850 ${I_{{\rm{wx}}}}$ 轮对侧滚转动惯量/$({\rm{kg} } {\text{•} } { {\rm{m} }^2})$ 717 ${I_{{\rm{wz}}}}$ 轮对摇头转动惯量/$({\rm{kg} } {\text{•} } { {\rm{m} }^2})$ 717 ${K_{1{\rm{x}}}}$ 一系悬挂纵向刚度之半/$({\rm{N} } {\text{•} } { {\rm{m} }^{ - 1} })$ 2.80 × 107 ${K_{1{\rm{y}}}}$ 一系悬挂横向刚度之半/$({\rm{N} } {\text{•} } { {\rm{m} }^{ - 1} } )$ 4.00 × 106 ${K_{1{\rm{z}}}}$ 一系悬挂垂向刚度之半/$({\rm{N} } {\text{•}} { {\rm{m} }^{ - 1} })$ 1.22 × 106 ${C_{1{\rm{x}}}}$ 一系悬挂纵向阻尼之半/$({\rm{N} } {\text{•}} {\rm{s} } {\text{•}} { {\rm{m} }^{ - 1} })$ 1.77 × 104 ${C_{1{\rm{y}}}}$ 一系悬挂横向阻尼之半/$({\rm{N} } {\text{•}} {\rm{s} } {\text{•}} { {\rm{m} }^{ - 1} })$ 0 ${C_{1{\rm{z}}}}$ 一系悬挂垂向阻尼之半/$({\rm{N} } {\text{•}} {\rm{s} } {\text{•}} { {\rm{m} }^{ - 1} })$ 0 ${K_{2{\rm{x}}}}$ 二系悬挂纵向刚度之半/$({\rm{N} } {\text{•}} { {\rm{m} }^{ - 1} })$ 1.45 × 105 ${K_{2{\rm{y}}}}$ 二系悬挂横向刚度之半/$({\rm{N} } {\text{•}} { {\rm{m} }^{ - 1} })$ 2.05 × 105 ${K_{2{\rm{z}}}}$ 二系悬挂垂向刚度之半/$({\rm{N} } {\text{•}} { {\rm{m} }^{ - 1} })$ 1.48 × 105 ${C_{{\rm{2x}}}}$ 二系悬挂纵向阻尼之半/$({\rm{N} } {\text{•}} {\rm{s} } {\text{•}} { {\rm{m} }^{ - 1} })$ 3.43 × 105 ${C_{2{\rm{y}}}}$ 二系悬挂横向阻尼之半/$({\rm{N} } {\text{•}} {\rm{s} } {\text{•}} { {\rm{m} }^{ - 1} })$ 2.45 × 104 ${C_{2{\rm{z}}}}$ 二系悬挂垂向阻尼之半/$({\rm{N} } {\text{•}} {\rm{s} } {\text{•}} { {\rm{m} }^{ - 1} })$ 3.16 × 104 ${ {{r} }_{\rm{0} } }$ 车轮名义滚动圆半径/m 0.460 表 4 计算结果对比
Table 4. Comparison of the calculative results
结果来源 轮轨力最大值/kN 车体加速度/(m•s−2) 横向 垂向 横向 垂向 文献[4] 12.540 152.440 0.080 0.300 本文 11.180 134.270 0.073 0.410 表 5 列车侧逆向过岔动力响应计算结果
Table 5. Calculation results of dynamic responses of the vehicle passing through the turnout in the flank direction
方案 横向轮轨力最大值/kN 垂向轮轨力最大值/kN 脱轨系数
最大值轮重减载率
最大值列车振动加速度最大值/(m•s−2) 车体 轮对 基本轨侧 辙叉侧 基本轨侧 辙叉侧 横向 垂向 横向 垂向 1 20.246 38.745 78.482 159.64 0.291 0.423 0.354 0.592 16.614 33.537 2 20.486 37.426 76.395 160.659 0.279 0.401 0.371 0.621 13.623 29.633 3 21.365 38.629 78.216 163.428 0.311 0.383 0.359 0.577 17.328 32.289 4 19.872 39.112 77.386 158.366 0.296 0.395 0.396 0.599 15.496 33.978 -
陈嵘,王平,李成辉. 75 kg/m钢轨12号重载道岔服役性能优化分析[J]. 铁道科学与工程学报,2011,8(6): 7-11. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7029.2011.06.002CHEN Rong, WANG Ping, LI Chenghu. Optimization of service performance of No.12 heavy haul railway turnout with 75 kg/m rail[J]. Journal of Railway Science and Engineering, 2011, 8(6): 7-11. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7029.2011.06.002 XIAO Junhua, ZHANG Fucheng, QIAN Lihe. Numerical simulation of stress and deformation in a railway crossing[J]. Engineering Failure Analysis, 2011, 18(8): 2296-2304. doi: 10.1016/j.engfailanal.2011.08.006 赵卫华,王平,黄惟. 固定辙叉轮轨接触关系算法研究及软件开发[J]. 铁道标准设计,2016,60(5): 15-24.ZHAO Weihua, WANG Ping, HUANG Wei. An algorithm of wheel/rail contact geometry for rigid frog and software development[J]. Railway Standard Design, 2016, 60(5): 15-24. 赵卫华. 固定辙叉轮轨关系优化及动力学仿真分析研究[D]. 成都: 西南交通大学, 2013. 徐井芒,王平. 基于轮轨廓型的固定辙叉优化设计方法[J]. 中国铁道科学,2014,35(2): 1-6. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4632.2014.02.01XU Jingmang, WANG Ping. Optimization design method for rigid frog based on wheel/rail profile type[J]. China Railway Science, 2014, 35(2): 1-6. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4632.2014.02.01 曹洋,王平,赵卫华. 基于轮轨接触参数的固定辙叉设计方法[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2012,47(4): 605-610. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2012.04.011CAO Yang, WANG Ping, ZHAO Weihua. Design method for rigid frog based on wheel/rail contact paramenters[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2012, 47(4): 605-610. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2012.04.011 曹洋,王平. 固定辙叉心轨轨顶降低值优化[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2015,50(6): 1067-1073. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2015.06.013CAO Yang, WANG Ping. Optimization of nose depth for rigid forg[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2015, 50(6): 1067-1073. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2015.06.013 任尊松. 车辆-道岔系统动力学研究[D]. 北京: 北京交通大学, 2000. KASSA E;ANDERSSON C;NIELSEN J C O. Simulation of dynamic interaction between train and railway turnout[J]. Vehicle System Dynamics, 2006, 44(3): 247-258. KASSA E, NIELSEN J C O. Dynamic train-turnout interaction in an extended frequency range using a detailed model of track dynamics[J]. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 2009, 320: 893-914. doi: 10.1016/j.jsv.2008.08.028 SUN Y Q, COLE C, MCCLANACHAN M. The calculation of wheel impact force due to the interaction between vehicle and a turnout[J]. Rail and Rail Transit, 2010, 224: 391-403. doi: 10.1243/09544097JRRT350 XU J M, WANG P, WANG L, et al. Effects of profile wear on wheel-rail contact conditions and dynamic internation of vehicle and turnout[J]. Advances in Mechanical Engieering, 2016, 8(1): 1-14. 曹洋. 道岔平面线型动力分析及其设计方法研究[D]. 成都: 西南交通大学, 2013. 吴安伟. 列车-变截面道岔动力学仿真分析[D]. 成都: 西南交通大学, 2006. 翟婉明. 车辆-轨道耦合动力学(上册)[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2015: 241. -




 下载:
下载: