Hydrodynamic Pressures Study of Barrier Lake under Coaction of Earthquake and Clastic Flow Landslide
-
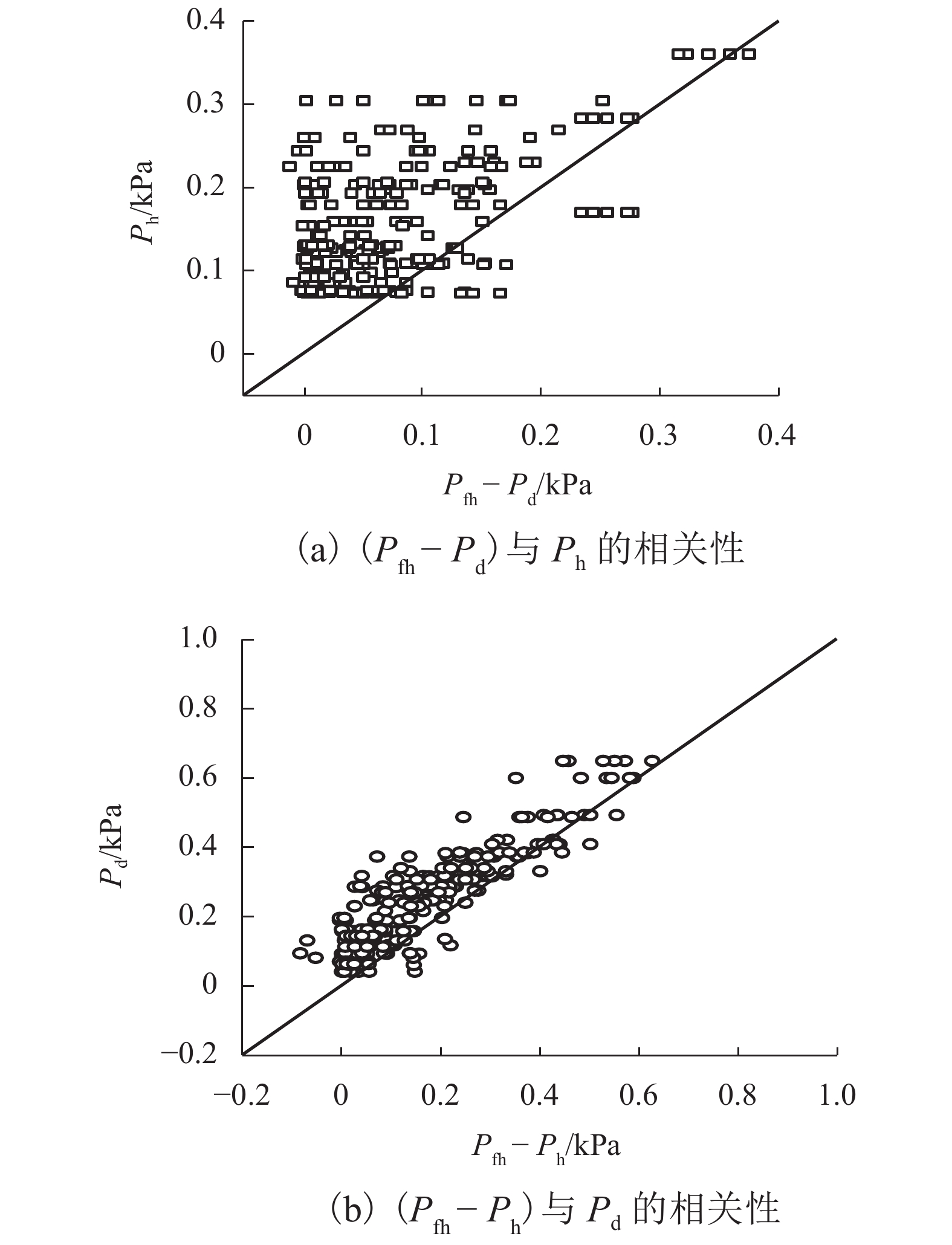
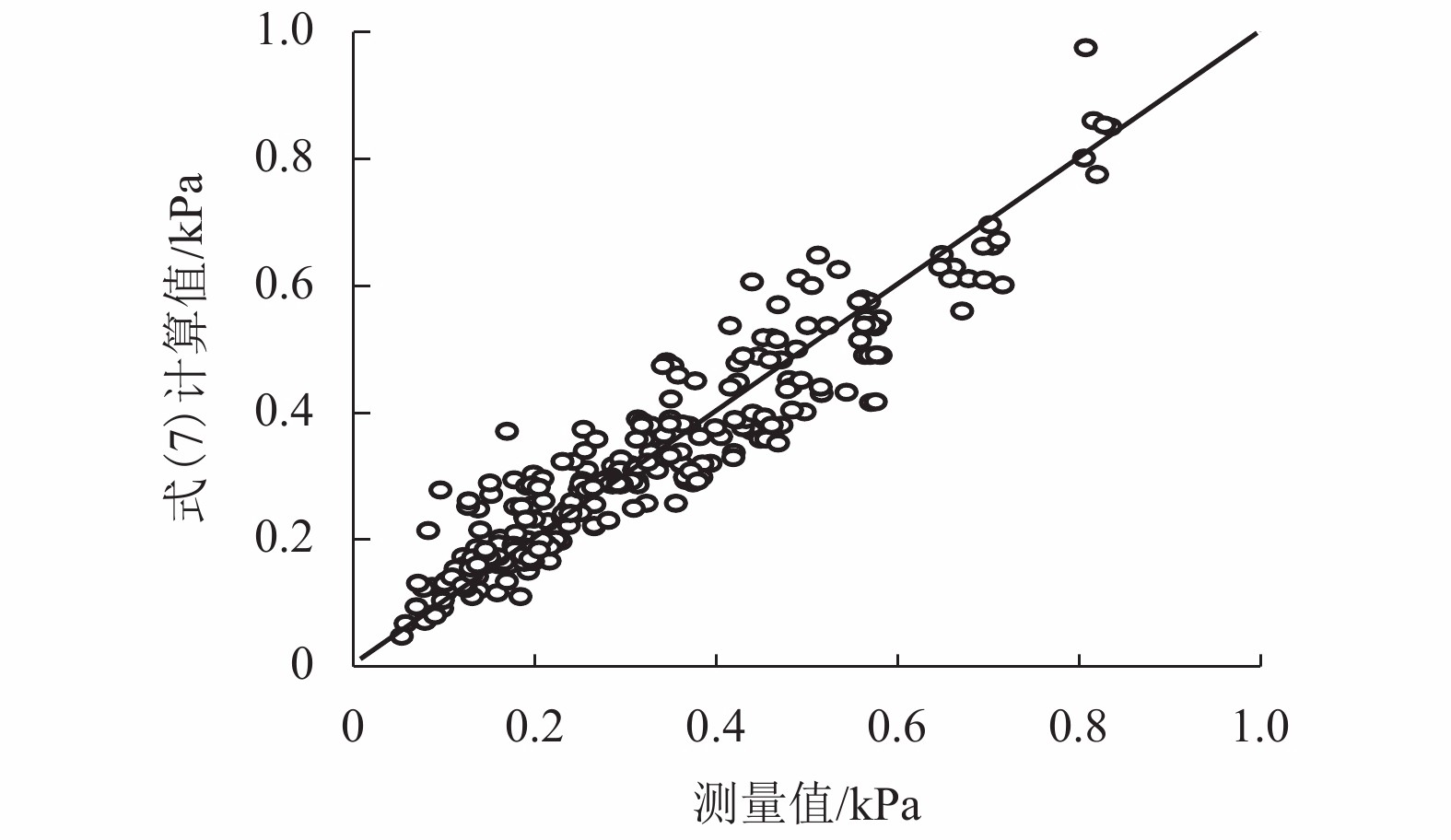
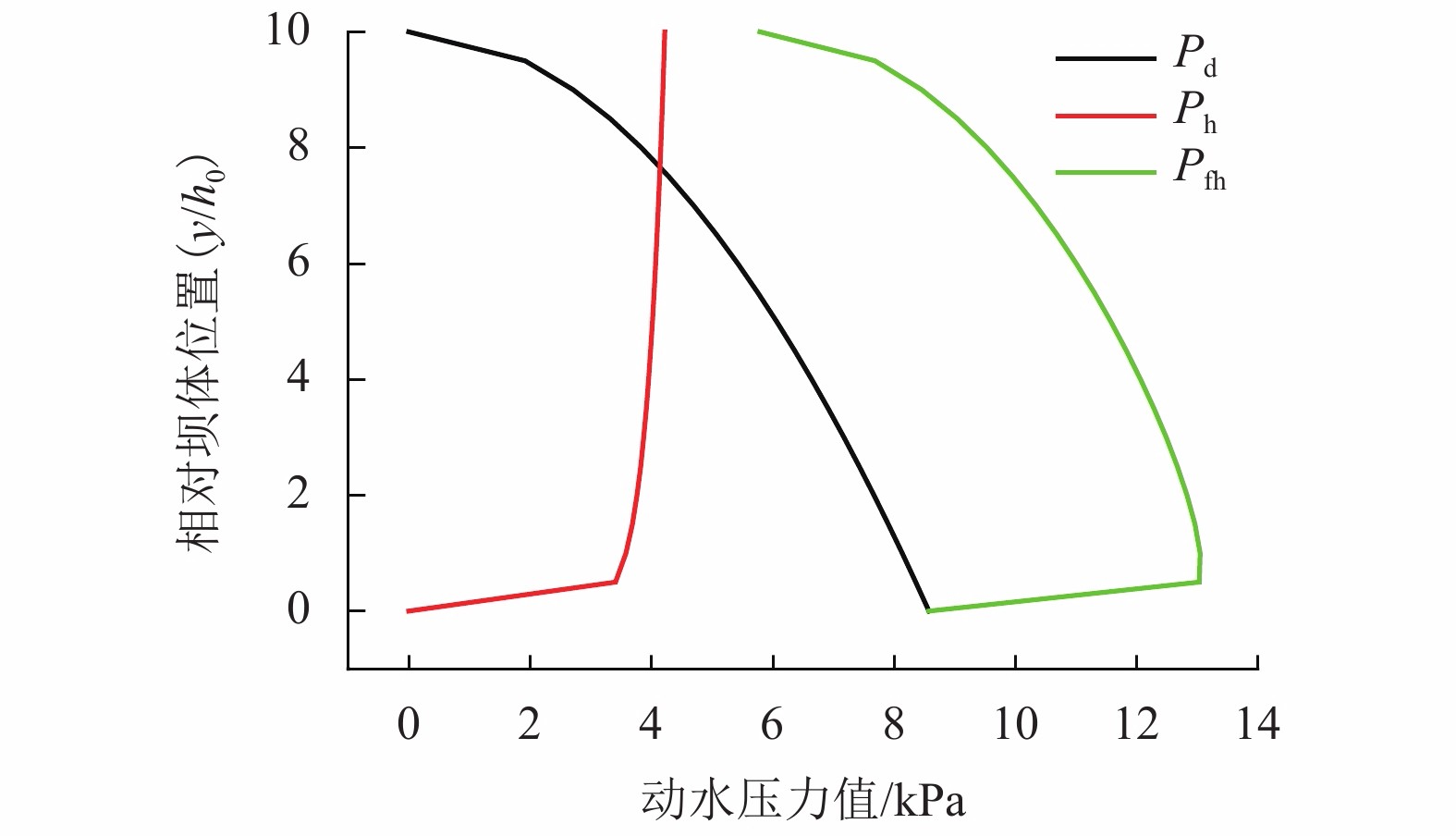
摘要: 为了研究堰塞湖水体在地震以及同震滑坡碎屑流共同作用下产生的涌浪动水压力,设计了振动台造波模型试验,开展了地震作用下堰塞湖涌浪动水压力试验,获取单独地震作用下动水压力数据并同已有地震动水压力计算公式进行比较;开展了滑坡碎屑流作用下的堰塞湖涌浪动水压力试验,获取单独滑坡碎屑流作用下动水压力数据,进而建立了计算滑坡碎屑流作用下的堰塞湖涌浪动水压力的统计公式;开展了地震和滑坡碎屑流综合作用下的堰塞湖涌浪动水压力试验,最终建立了复合动水压力的计算公式. 研究结果表明:地震涌浪动水压力与水深和地震峰值加速度的关系可用Westergaard公式描述;滑坡碎屑流涌浪动水压力与初始水深负相关,与碎屑流入水速度和碎屑流体积正相关;复合动水压力小于单独地震动水压力和单独滑坡碎屑流动水压力二者之和,约为二者和的51%~95%.Abstract: A shaking table model experiment was designed to study the hydrodynamic pressures of the barrier lake under the action of an earthquake and a clastic flow landslide. Firstly, an experiment was carried to study the hydrodynamic pressure of the barrier lake under the action of an earthquake to obtain the hydrodynamic pressure data, which was compared with the existing calculation formula of seismic hydrodynamic pressure. Then, an experiment was carried to study the hydrodynamic pressure caused by the surge of the barrier lake under the action of a clastic flow landslide to obtain the hydrodynamic pressure data and a statistical formula was established. Finally, an experiment was carried to study the combined hydrodynamic pressure under the effect of an earthquake and a co-seismic clastic flow landslide and a formula for calculating the combined hydrodynamic pressure caused by an earthquake and a clastic flow landslide was established. The results show that the relationship between the hydrodynamic pressure caused by an earthquake and water depth and seismic peak acceleration can be described by Westergaard’ formula. The hydrodynamic pressure caused by a clastic flow landslide is negatively related to the initial water depth, positively related to the inflow velocity and volume of landslide. The combined hydrodynamic pressure is less than the sum of the single hydrodynamic pressure under the action of an earthquake and the single hydrodynamic pressure under the action of a clastic flow landslide, which is about 51% − 95% of the sum of two.
-
Key words:
- earthquake /
- clastic flow landslide /
- barrier lake /
- combined hydrodynamic pressures
-
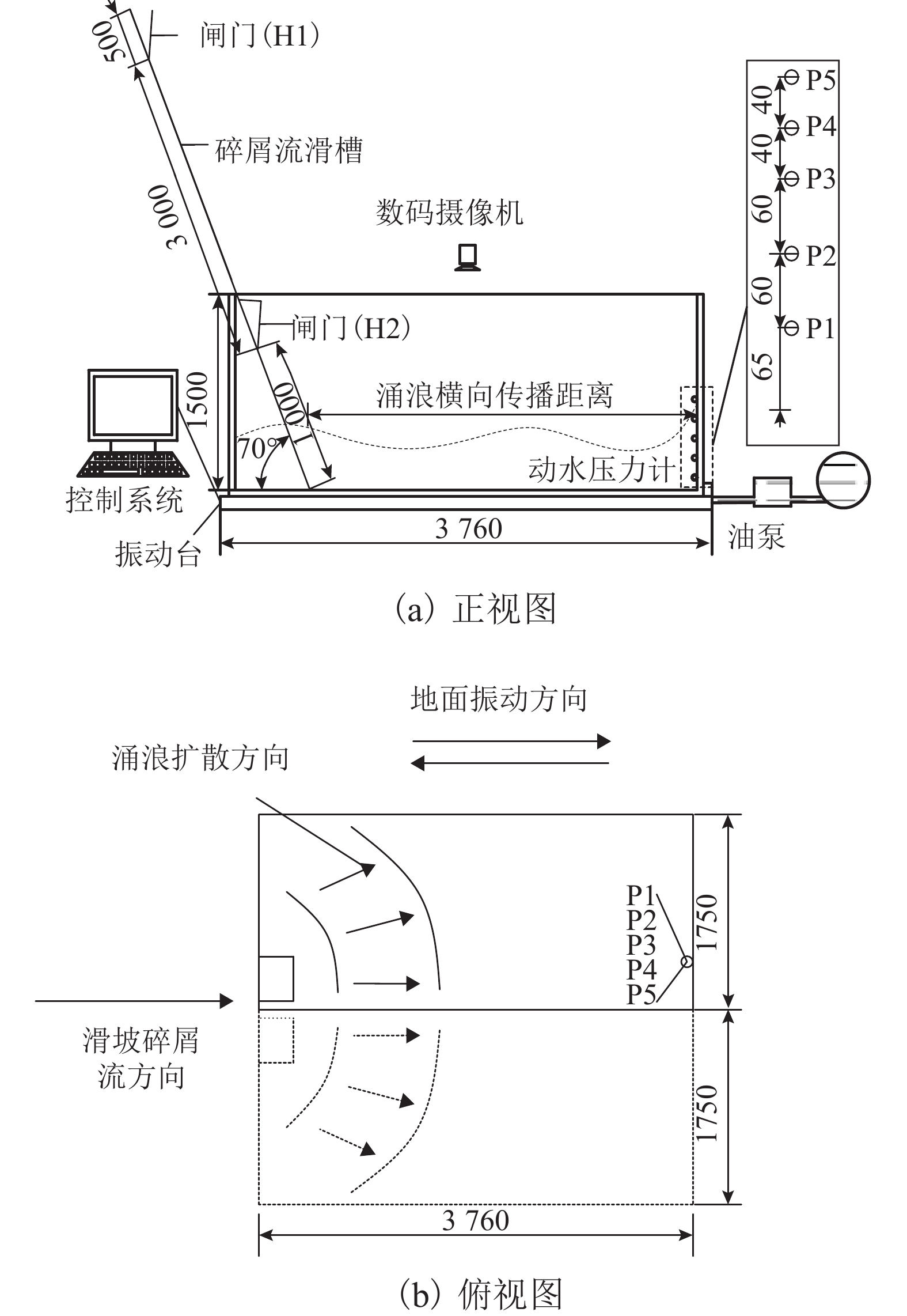
表 1 123组试验组合
Table 1. Experimental conditions for 123 laboratory tests
组号 编号 地震波地震动加速度峰值(PGA)/(×g) 碎屑质量 s/kg 初始水深/m 入水速度/(m•s−1) A 1~15 0.1,0.2,0.3,0.4,0.5 0.1,0.2,0.3 B 16~33 10,20,30 0.1,0.2,0.3 1.64,3.28 C 34~123 0.1,0.2,0.3,0.4,0.5 10,20,30 0.1,0.2,0.3 1.64,3.28 -
殷跃平. 汶川八级地震滑坡高速远程特征分析[J]. 工程地质学报,2009,17(2): 153-166. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9665.2009.02.002YIN Yueping. Rapid and long run-out features of landslides triggered by the Wenchuan earthquake[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2009, 17(2): 153-166. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9665.2009.02.002 CUI P, ZHU X. Surge generation in reservoirs by landslides triggered by the wenchuan earthquake[J]. Journal of Earthquake & Tsunami, 2011, 5(5): 461-474. FRITZ H M. Lituya bay case rockslide impact and wave run-up[J]. Science of Tsunami Hazards, 2001, 19(1): 3-19. HOLMEN J O. Fatigue of concrete by constant and variable amplitude loading[J]. Fatigue Concrete Structure, 1982, 75: 71-110. CORNELISSEN H, REINHARDT H. Uniaxial tensile fatigue failure of concrete underconstant-amplitude and programme loading[J]. Magazine Concrete Research, 1984, 36(129): 216-226. SALEH S, MADABHUSHI S P G. Response of concrete dams on rigid and soil foundations under earthquake loading[J]. Journal of Earthquake and Tsunami, 2011, 4(3): 251-268. 刘宁, 程尊兰, 崔鹏, 等. 堰塞湖及其风险控制[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2013: 16-21. KONG P, NA C, FINK D, et al. Moraine dam related to late quaternary glaciation in the Yulong mountains,southwest China,and impacts on the Jinsha river[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2009, 28(27): 3224-3235. WESTERGAARD H M. Water pressures on dams during earthquakes[J]. Transactions of the American Society of Civil Engineers, 1933, 98(3): 418-433. CHWANG A T, HOUSNER G W. Hydrodynamic pressures on sloping dams during earthquakes, part 1:momentum method[J]. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 1978, 87(2): 335-341. CHWANG A T. Hydrodynamic pressures on sloping dams during earthquakes, part 2:exact theory[J]. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 1978, 87(2): 343-348. PELECANOS L, KONTOE S, ZDRAVKOVIC L. Numerical modelling of hydrodynamic pressures on dams[J]. Computers and Geotechnics, 2013, 53: 68-82. 黄锦林. 库岸滑坡涌浪对坝体影响研究[D]. 天津: 天津大学, 2012. 杨艳. 山区河道型水库滑坡涌浪对架空直立式码头结构作用影响研究[D]. 重庆: 重庆交通大学, 2014. CHEN H Y, CUI P, CHEN X Q, et al. Laboratory experiments of water pressure loads acting on a downstream dam caused by ice avalanches[J]. Landslides, 2015, 12(6): 1131-1138. 游勇,程尊兰. 西藏波密米堆沟泥石流堵河模型试验[J]. 山地学报,2005,23(3): 288-293. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-2786.2005.03.006YOU Yong, CHENG Zunlan. Modeling experiment of debris flow in Midui gully,Tibet[J]. Journal of Mountain Research, 2005, 23(3): 288-293. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-2786.2005.03.006 李德基, 游勇. 西藏波密米堆冰湖溃决浅议[J]. 山地学报, 1992, 10(4): 219-224.LI Deji, YOU Yong. Bursting of the Midui moraine lake in Bomi, Xizang.[J]. Mountain Research, 1992, 10(4): 219-224. -




 下载:
下载: