Assessment for External Influence Factors of High-Speed Train Transmission Reliability
-
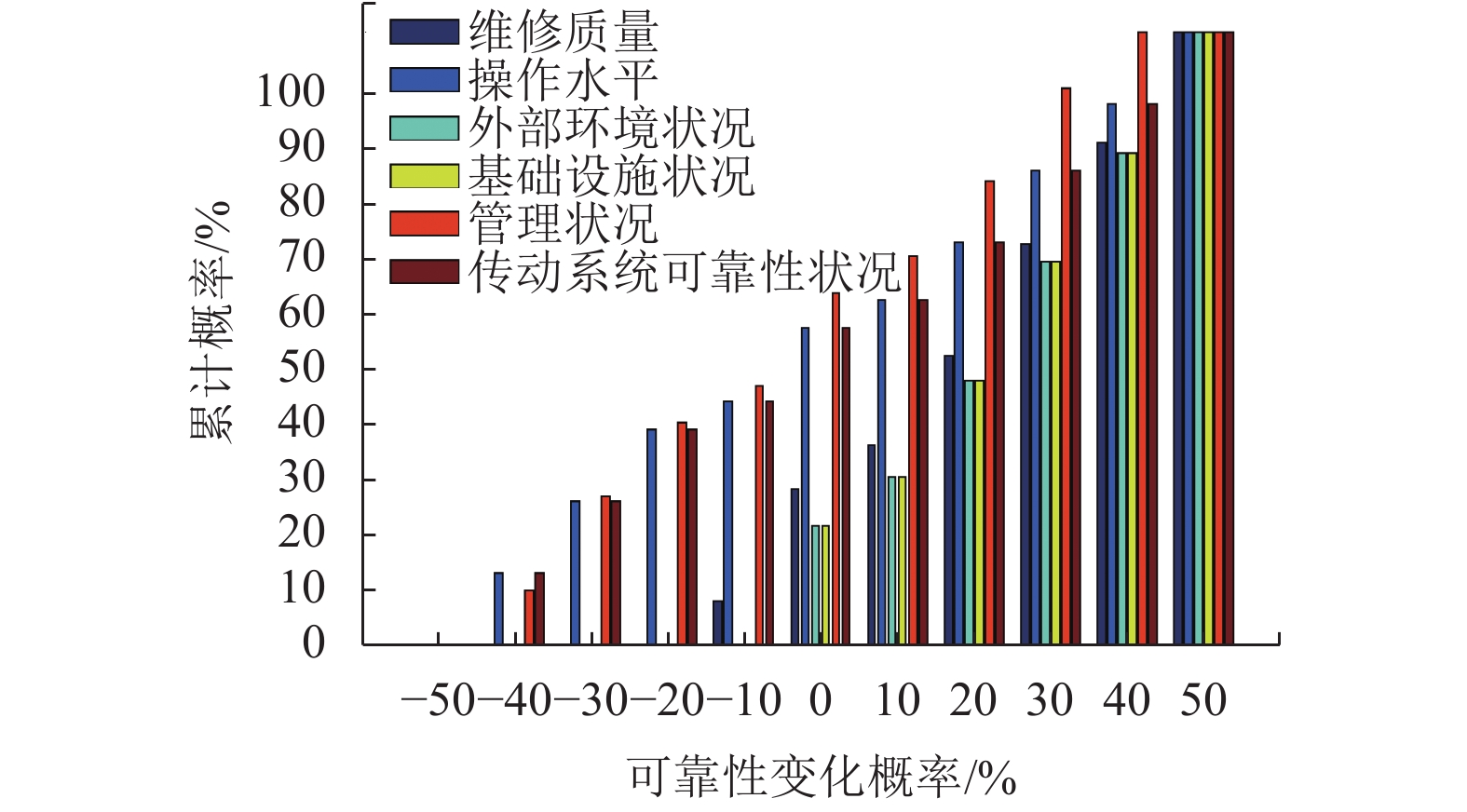
摘要: 为研究除自身构件外的外部影响因素对高速列车传动系可靠性的影响,以现役CHR3型高速列车为研究对象,基于FID (fuzzy influence diagram)理论,对影响高速列车传动系统可靠性的外部因素进行评估分析. 首先通过业内权威专家问卷,建立外部影响因素的FID频率模糊集、状态模糊集和模糊关系,并构建影响传动系统可靠性的FID关系层、数值层及函数层;其次依据模糊集合理论对人员、基础设施、环境、维修、管理等外部影响因素的频率矩阵进行计算;最后得出各项外部影响因素的状态降低及提高的累积概率. 研究结果表明:人员状况和管理水平的状态降低的累积概率分别为39.9%、42.5%,两项因素在保持当前状态基础上累积提高30%的概率分别为77.6%和90.9%,并且二者的累计概率分布与该型传动系的可靠性概率分布相近,说明人员和管理状况为首要影响因素,其他因素次之.Abstract: For the study of external influence factors besides its components impact on the high-speed train transmission reliability, the external influence factors of the CHR3 high-speed train transmission reliability are analyzed based on fuzzy influence diagram (FID). First, Frequency fuzzy sets, state fuzzy sets and fuzzy relation were built by the expert questionnaires. The relational layer, number layer and function layer of FID were constructed for the transmission reliability. Furthermore, the frequency matrix of extrinsic impact factors such as personnel, infrastructure, environment, maintenance and management is calculated based on the fuzzy set theory. Finally, get the reduced state cumulative probability and the cumulative increase probability of external influence factors. The reduced state cumulative probability of the personnel situation and the management level is 39.9% and 42.5%, and the cumulative increase probability is 77.6% and 90.9%, and the cumulative probability distribution is similar to the reliability of transmission probability distribution..In summary, the staff and management are the key extrinsic impact factors for the transmission reliability, and other factors are secondary.
-
Key words:
- FID /
- high-speed train transmission system /
- external influence factors /
- reliability
-
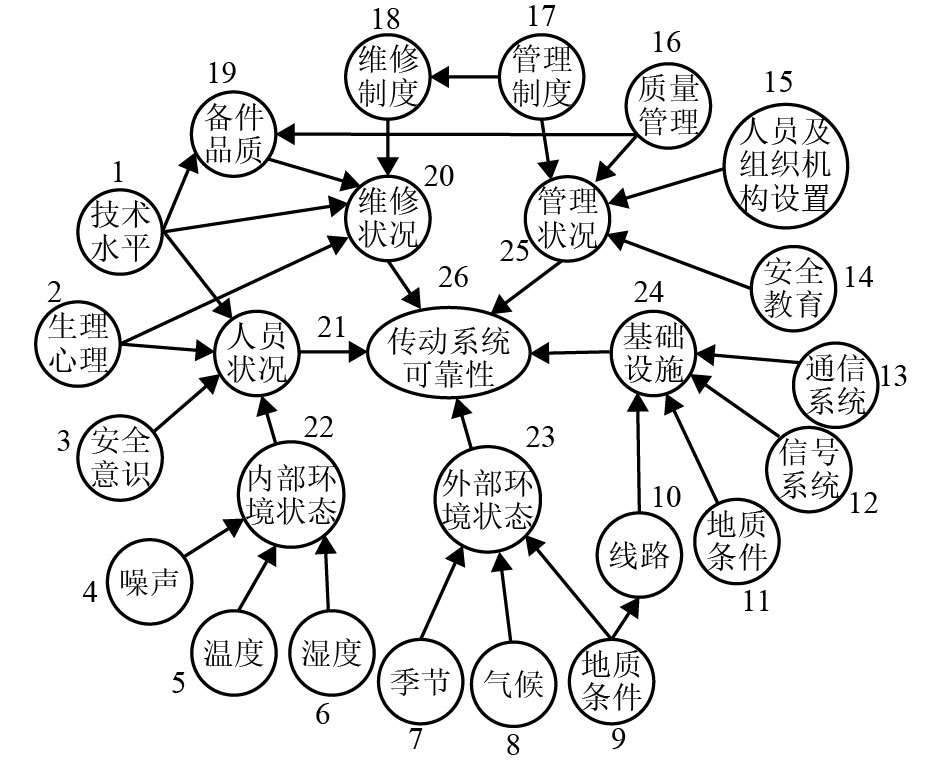
表 1 独立结点的数值层
Table 1. Numerical layer of independent nodes
结点 状态 E G M B 技术水平1 ${V_{ H}}$ ${{H}}$ ${{I}}$ ${V_{ L}}$ 生理心理2 ${V_{ H}}$ ${{H}}$ ${{H}}$ ${{L}}$ 安全意识3 ${{V_H}}$ ${{H}}$ ${{I}}$ ${{V_L}}$ 内部作业噪声4 ${{I}}$ ${{V_H}}$ ${{H}}$ $L$ 内部作业温度5 ${{I}}$ ${{V_H}}$ ${{H}}$ ${{V_L}}$ 内部作业湿度6 ${{I}}$ ${{V_H}}$ ${{H}}$ ${{V_L}}$ 季节7 ${{V_L}}$ ${{V_H}}$ ${{H}}$ ${{L}}$ 气候8 ${{I}}$ ${{H}}$ ${{V_H}}$ ${{L}}$ 地质条件9 ${{H}}$ ${{V_H}}$ ${{I}}$ ${{V_L}}$ 供电系统11 ${{V_H}}$ ${{H}}$ ${{L}}$ ${{V_L}}$ 信号系统12 ${{V_H}}$ ${{H}}$ ${{L}}$ ${{V_L}}$ 通信系统13 ${{V_H}}$ ${{H}}$ ${{L}}$ ${{V_L}}$ 安全教育14 ${{L}}$ ${{V_H}}$ ${{I}}$ ${{V_L}}$ 人员及组织机构设置15 ${{I}}$ ${{V_H}}$ ${{H}}$ ${{V_L}}$ 质量管理16 ${{H}}$ ${{V_H}}$ ${{I}}$ ${{L}}$ 制度管理17 ${{H}}$ ${{V_H}}$ ${{I}}$ ${{V_L}}$ 表 2 结点变量间的模糊关系
Table 2. Fuzzy relationship between the node variables
结点 模糊关系 结点 模糊关系 2-20 If 2 is E, then 20 is MI 2-21 If 2 is E, then 21 is HI If 2 is G, then 20 is NO If 2 is G, then 21 is NO If 2 is M, then 20 is MD If 2 is M, then 21 is MO If 2 is B, then 20 is HD If 2 is B, then 21 is HD 表 3 随机结果的概率
Table 3. Probability of random results
频率变化/% 节点 20 21 23 24 25 26 –50 0 0 0 0 0 0 – 40 0 0.117 0 0 0.091 0.117 –30 0 0.118 0 0 0.152 0.118 –20 0 $0.117$ $0$ $0$ $0.121$ $0.117$ –10 $0.073$ $0.047$ $0$ $0$ $0.061$ $0.047$ 0 $0.182$ $0.118$ 0.196 0.196 0.150 0.118 10 0.073 0.047 0.078 0.078 0.061 0.047 20 0.145 0.094 0.157 0.157 0.121 0.094 30 0.182 0.118 0.196 0.196 0.152 0.118 40 0.164 0.106 0.177 0.177 0.091 0.106 50 0.181 0.118 0.196 0.196 0 0.118 -
李宛瞳. 高速列车运用安全评估方法及实例研究[D]. 北京: 北京交通大学, 2016 向泽锐,徐伯初,支锦亦. 中国高速列车工业设计研究综述与展望[J]. 铁道学报,2013,35(12): 12-13.XIANG Zerui, XU Bochu, ZHI Jinyi. Review and prospect of research of industrial design of high-speed train in China[J]. Journal of The China Railway Society, 2013, 35(12): 12-13. 刘玉梅,赵聪聪,熊明烨,等. 高速列车传动系统特征参数经典域优化[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2016,51(1): 85-90,120.LIU Yumei, ZHAO Congcong, XIONG Mingye, et al. Optimization of classical domains for high-speed train transmission system[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2016, 51(1): 85-90,120. 杨靖. 侧风下高速列车运行安全性分析[J]. 机械工程与自动化,2016,10(5): 19-20, 24.YANG Jing. Safety analysis of high-speed train under crosswind[J]. Mechanical Engineering and Automation, 2016, 10(5): 19-20, 24. DIEHL M, HAIMES Y Y. Influence diagrams with multiple objectives and trade off analysis[J]. IEEE Transactions on Systems,Man and Cybernetics-Part A:Systems and Humans (S1083−4427), 2004, 24(3): 293-304. 杨娜. 基于模糊影响图的铁路电气化改造施工安全风险评价[D]. 成都: 西南交通大学, 2014 刘合香. 模糊数学理论及其应用[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2012: 2-12 赵聪聪. 高速列车传动系可靠性分析与评估[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 2016 程铁信,王平,张伟波. 模糊影响图评价算法的探讨[J]. 系统工程学报,2004(2): 177-182. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-5781.2004.02.012CHENG Tiexin, WANG Ping, ZHANG Weibo. Investigation on fuzzy influence diagrams evaluation algorithm[J]. Journal of Systems Engineering, 2004(2): 177-182. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-5781.2004.02.012 常志朋,王永利,程龙生. 基于模糊影响图与D-S证据理论的多属性群决策方法[J]. 模糊系统与数学,2014,28(4): 100-109.CHANG Zhipeng, WANG Yongli, CHENG Longsheng. Multiple attribute group decision making method based on fuzzy influence diagram and D-S evidence theory[J]. Fuzzy Systems and Mathematics, 2014, 28(4): 100-109. 方学进. 基于模糊影响图的隧道施工安全风险评价研究[D]. 重庆: 重庆交通大学, 2009 樊红,冯恩德. 概率影响图在船舶综合安全评估中的应用[J]. 船舶工程,2004(5): 3-5.FAN Hong, FENG Endeng. The application of probabilistic influence diagram in FSA[J]. Ship Ocean Engineering, 2004(5): 3-5. HOWARD R A, MATHESON J E. Reading on the principle and application of decision analysis[M]. New York: American Mathematical Society, 1993: 25-30 SHACHTER R D. Probabilistic inference and influence diagrams[J]. Operation Research, 1988, 36(4): 589-605. doi: 10.1287/opre.36.4.589 黄文静. 概率模糊集理论研究及其建模[D]. 长沙: 中南大学, 2013 -




 下载:
下载: