Research on Key Technology of Magnetic Suspension Bearings
-
摘要:
磁悬浮轴承是一种通过磁力作用使旋转轴悬浮在平衡位置,从而消除转子与定子之间接触摩擦的装置. 区别于传统轴承的支撑方式,磁轴承凭借无接触特性,在转速提升、控制精度优化及低能耗方面展现出显著优势,能够实现高速运转、精确控制与零摩擦运行的核心需求,已广泛应用于工业生产、飞轮储能、航空航天、高速机床等关键领域. 然而,随着现代工业对高性能轴承需求的不断增长和低碳环保理念的持续深入,磁悬浮轴承的技术升级与性能突破成为行业发展的迫切需求,相关研究也受到学术界与产业界的广泛关注. 本文系统综述了磁悬浮轴承的研究进展,依据悬浮力产生方式(吸力型、斥力型)明确其分类体系,进而围绕磁轴承系统的拓扑结构设计、数学建模、控制策略等核心研究内容展开梳理,全面呈现当前技术研究现状. 当前研究虽在基础理论与工程应用层面取得阶段性成果,但仍面临高温/高速工况下的稳定性控制、永磁体退磁防护、系统集成小型化、成本控制等关键技术瓶颈. 未来研究应聚焦多场耦合机理深化、智能控制算法融合、轻量化与低成本设计等方向,为磁悬浮轴承在更极端工况与更广泛领域的规模化应用提供技术支撑.
Abstract:Magnetic suspension bearings are devices that suspend the rotating shaft at an equilibrium position by magnetic force action, thereby eliminating the contact friction between rotors and stators. Different from the support methods of traditional bearings, magnetic suspension bearings exhibit significant advantages in rotational speed increase, control precision optimization, and low energy consumption, achieving the core demands of high-speed operation, precise control, and zero-friction operation. Magnetic suspension bearings have been widely applied in key fields such as industrial manufacturing, flywheel energy storage, aerospace, and high-speed machine tools. However, with the increasing demand of modern industries for high-performance bearings and the continuous deepening of the concept of low carbon and environmental protection, the technical improvement and performance breakthrough of magnetic suspension bearings have become an urgent requirement of industry development. The relevant research also catches extensive attention from academia and industry. Research progress in magnetic suspension bearings was reviewed systematically. The classification system was first clarified based on the magnetic suspension force generation method (attractive type and repulsive type), followed by reviewing core research content of magnetic suspension bearing systems such as topological structure design, mathematical modeling, and control strategies. The current state of the art in technical research was comprehensively presented. Although phased achievement has been made in basic theory and engineering applications, core technical bottlenecks remain, including stability control under high-temperature/high-speed operating conditions, permanent magnet demagnetization protection, system integration and miniaturization, and cost control. Future research should focus on deepening of multi-field coupling mechanisms, the integration of intelligent control algorithms, and the design of lightweight and low-cost systems, so as to provide technical support for the large-scale application of magnetic suspension bearings under more extreme operating conditions and in broader fields.
-
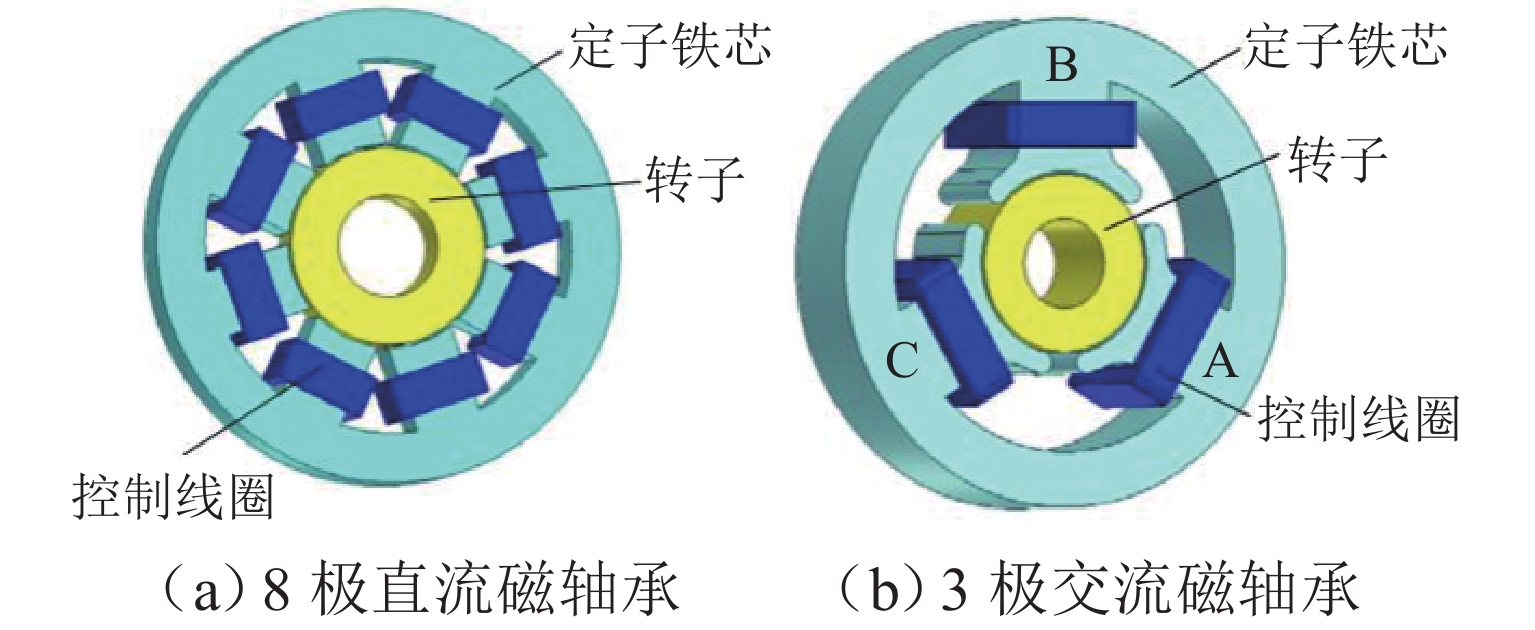
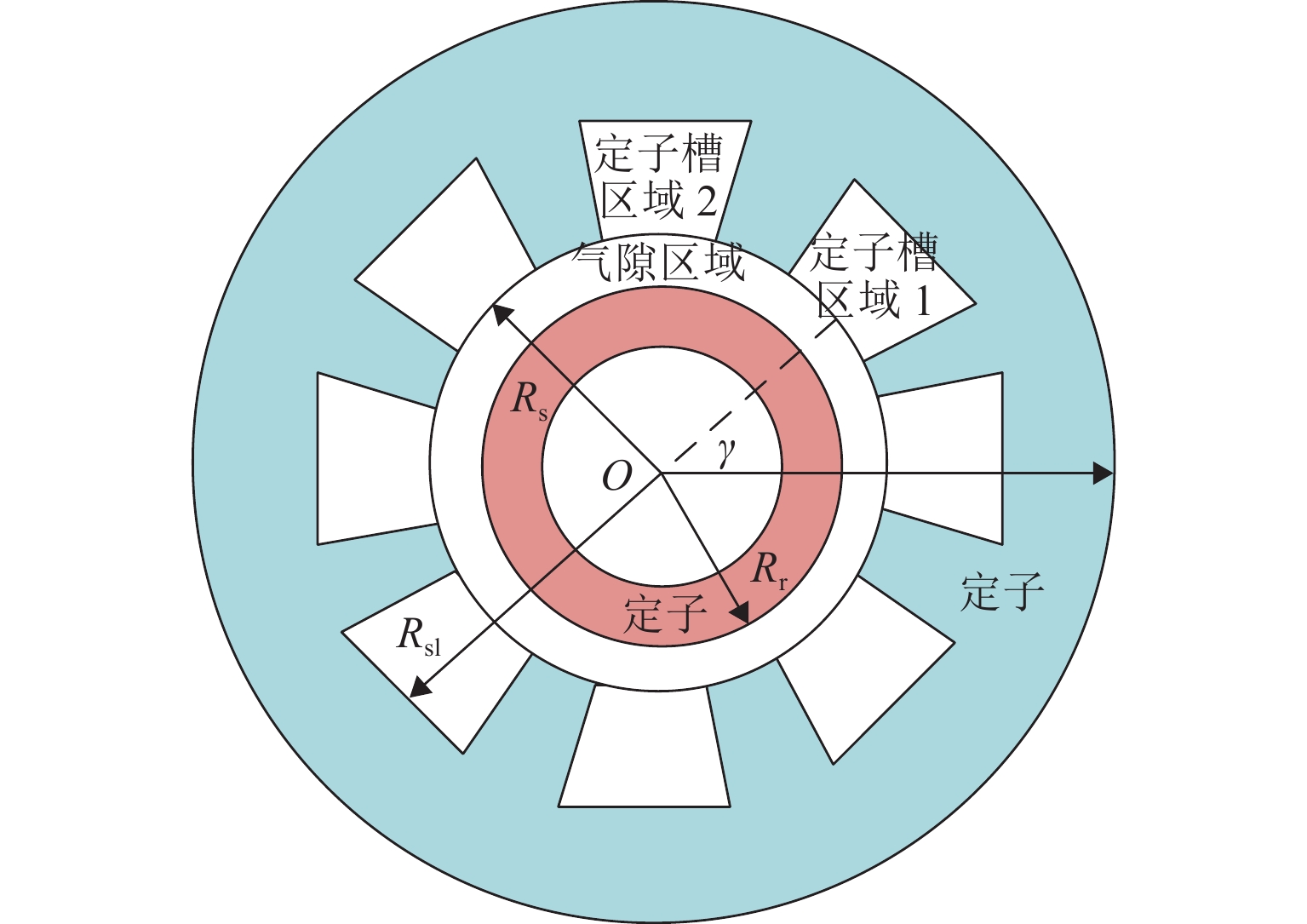
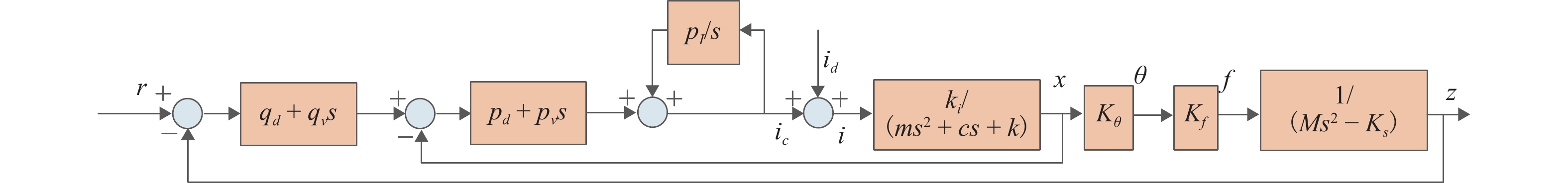
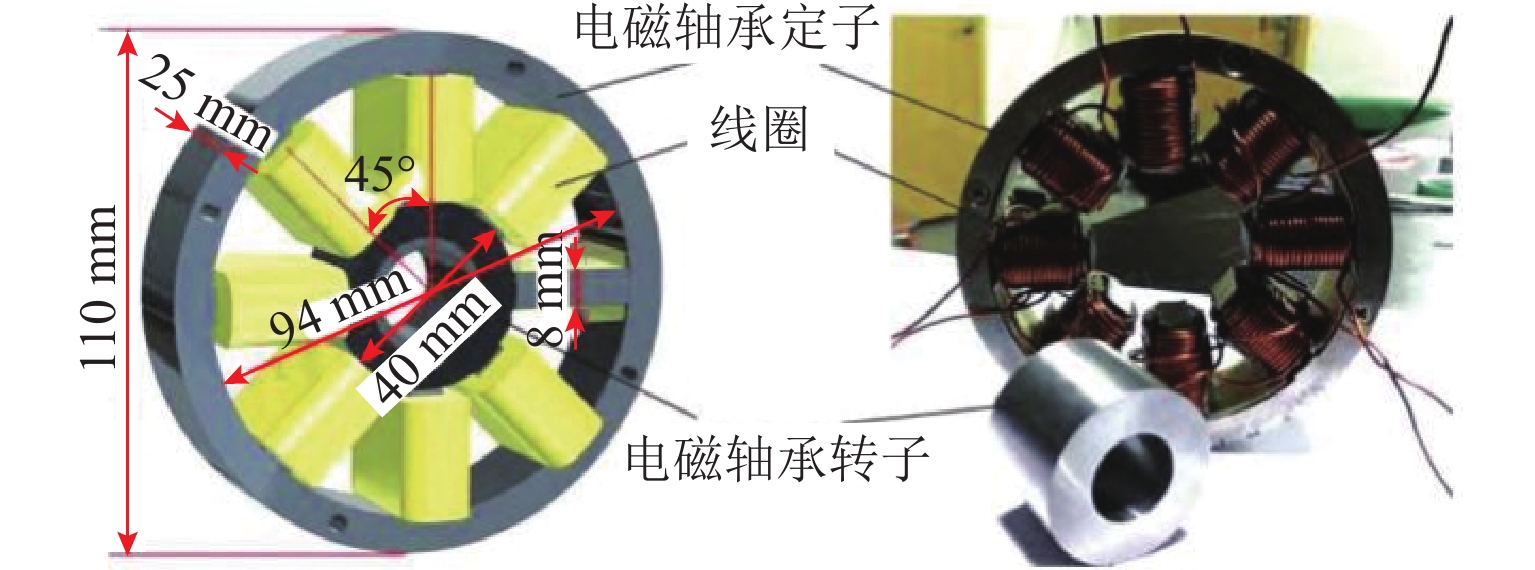
图 1 8极主动磁轴承结构[20]
Figure 1. Structure of 8-pole active magnetic suspension bearing
表 1 磁轴承之间的统计比较
Table 1. Statistical comparison between magnetic suspension bearings
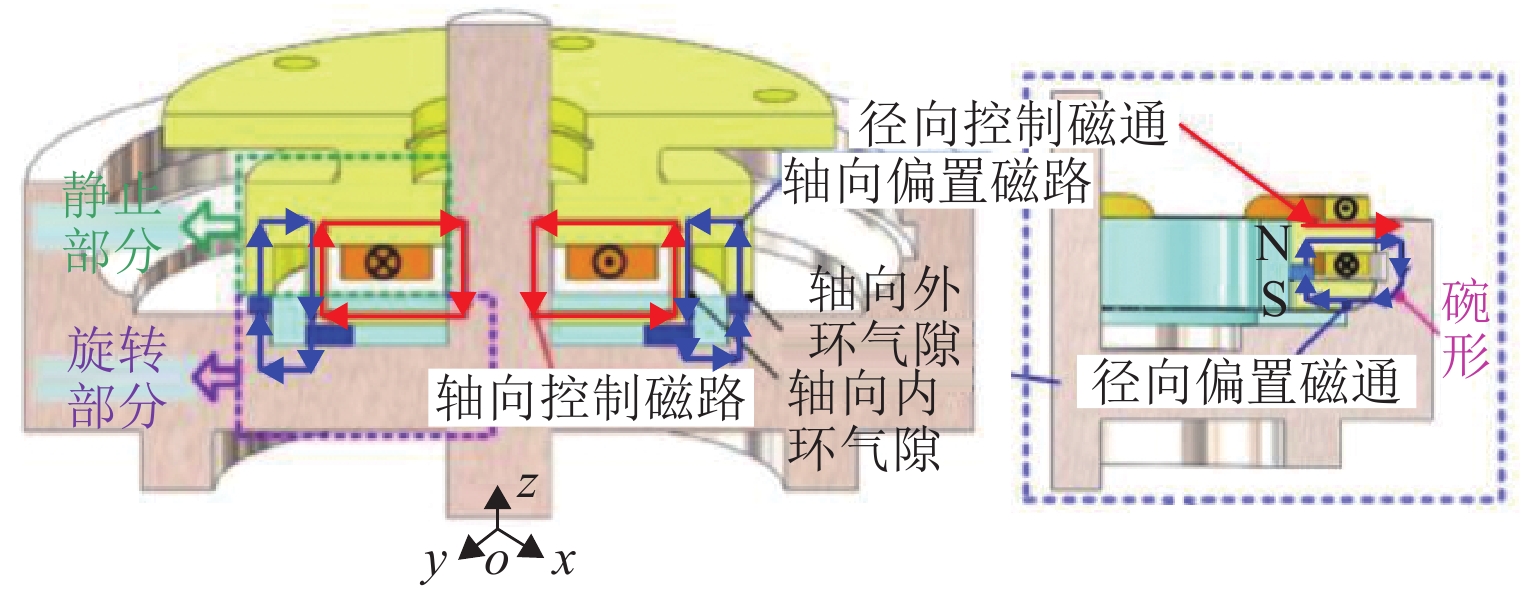
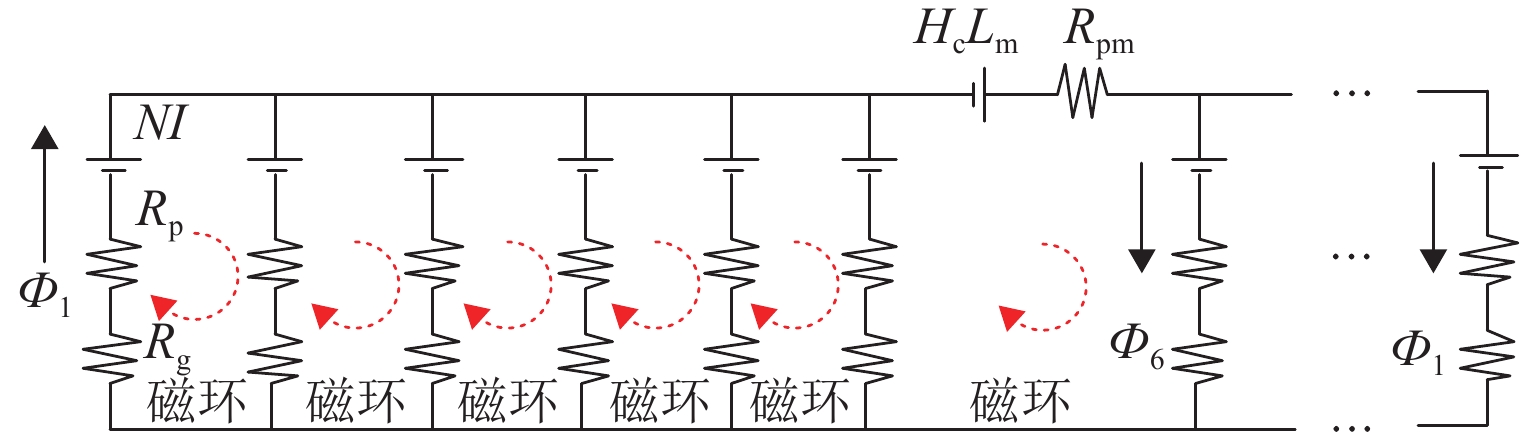
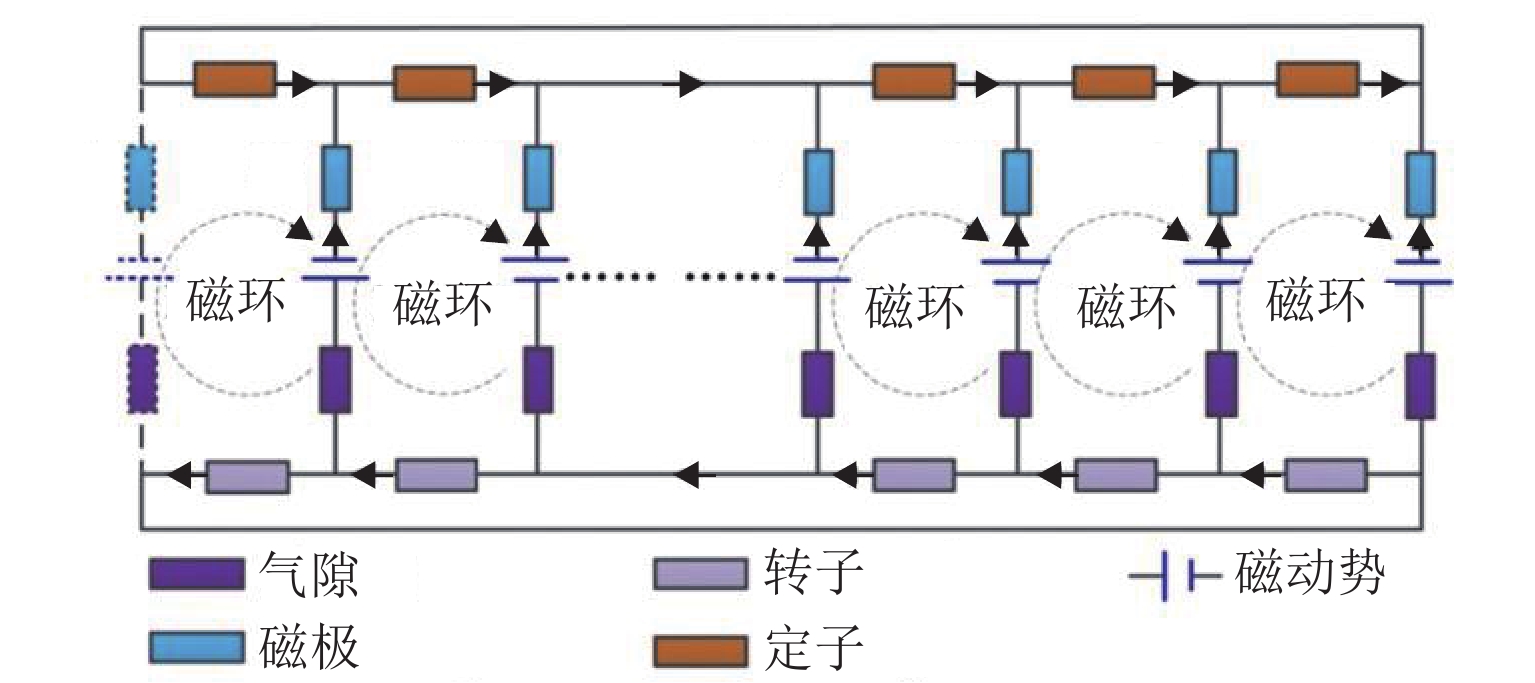
磁悬浮轴承类型 静态性能 悬浮力 应用 局限性 吸力磁悬浮轴承 主动(电)磁轴承 电磁铁提供底座悬浮力,实时可调,刚度、阻尼可通过控制算法灵活调节,承载力和刚度大 文献[23]中,当转子在z方向偏移量为30 mm时,悬浮磁力为21 N,位移刚度为0.7 N/μm. z轴力的最大变化率为0.29% 航空发动机、卫星姿态控制、高速电机、涡轮分子泵等 高硬件和维护成本、高系统复杂性以及易受电磁干扰 混合磁轴承 永磁提供基本悬浮力,电磁铁调节悬浮力;整体刚度高,刚度可调. 被动阻尼和主动阻尼的结合可以优化阻尼性能 文献[24]中,当转子在x方向偏移为0.2 mm时,悬浮磁力为16 N 高速电机、航空发动机、卫星姿态控制、飞轮储能等 复杂的磁场设计、高精度的制造要求、高昂的材料、维护成本以及复杂的控制系统 被动磁轴承 永磁提供吸力,在一定范围内具有自平衡能力;刚度非线性,刚度与气隙密切相关,固有阻尼小,依赖于结构阻尼 文献[31]中,当转子在z方向偏移量为2 mm时,悬浮磁力为10 kN,位移刚度为2 N/m 小型旋转设备、精密天平、陀螺仪、真空环境设备、高温环境设备等 悬浮力和承载能力有限,受永磁性能和气隙限制,稳定性受非线性特性影响,缺乏主动调节能力,对环境敏感 斥力磁悬浮轴承 被动磁轴承 永磁斥力产生悬浮,悬浮力与距离强相关;刚度非线性,刚度调整困难,固有阻尼小,可通过结构设计增加阻尼 在文献[23]中,当转子在z方向偏移量为30 mm时,悬浮磁力为21 N,位移刚度为0.7 N/μm 小型电机、微型泵、精密天平、光学陀螺仪、真空环境设备、放射性环境等 局限性与吸力式被动磁轴承相似,悬浮力和负载能力受限于永磁性能和气隙,稳定性受非线性特性影响,缺乏主动调节能力,对温度和磁场敏感 抗磁磁轴承 抗磁效应产生悬浮力,悬浮力相对较小且稳定;刚度较低,刚度与材料和磁场分布有关,固有阻尼较小,可通过附加结构增加 文献[43]中,当转子在z方向偏移量为3 mm时,悬浮磁力为13 kN 光学斩波器、陀螺仪、生物芯片、晶体全息干涉仪、高精度力传感器等 悬浮受力和承载能力有限,刚度和稳定性不足,应用范围有限 表 2 磁轴承分类特点
Table 2. Magnetic suspension bearing classification characteristics
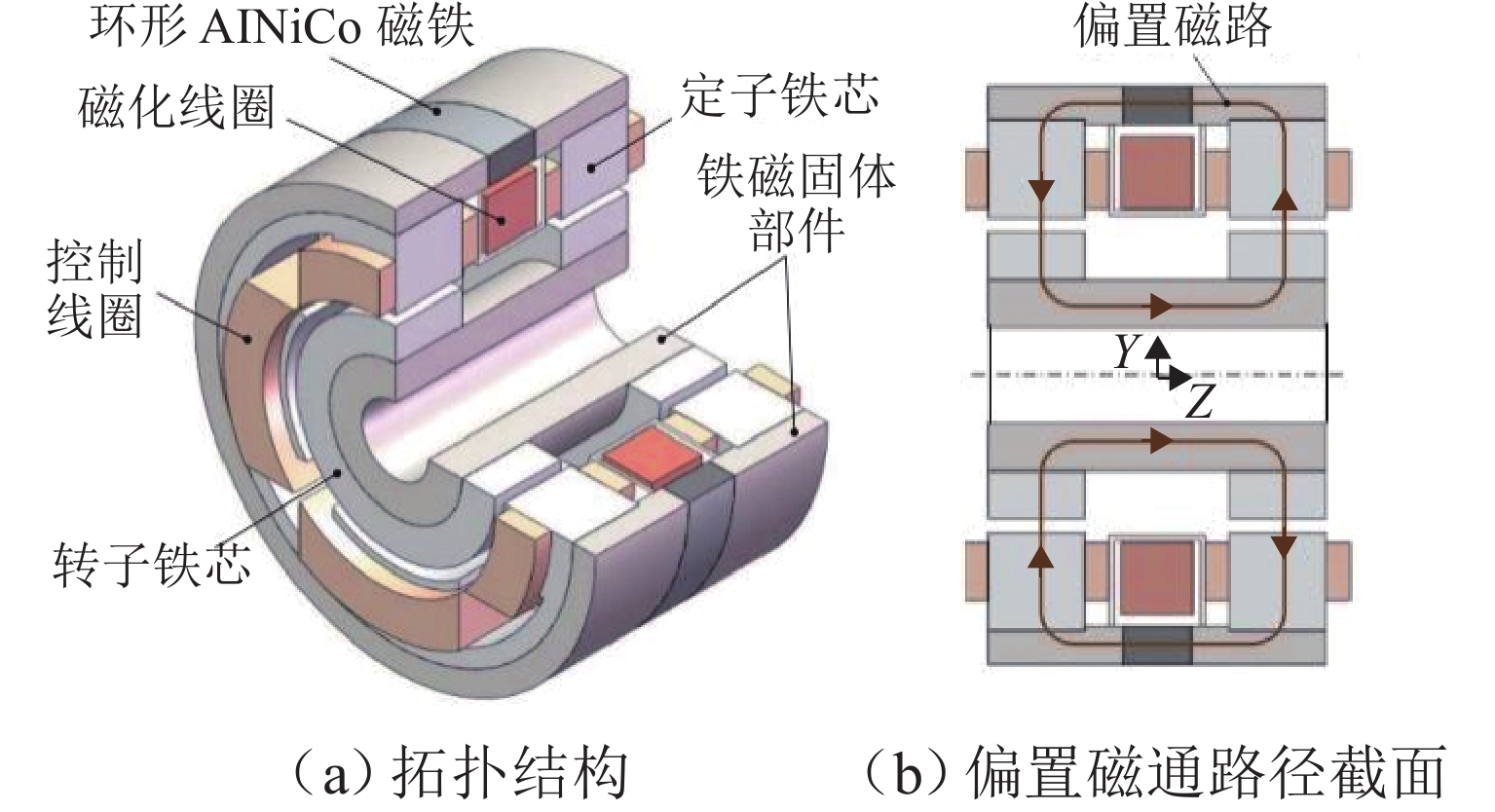
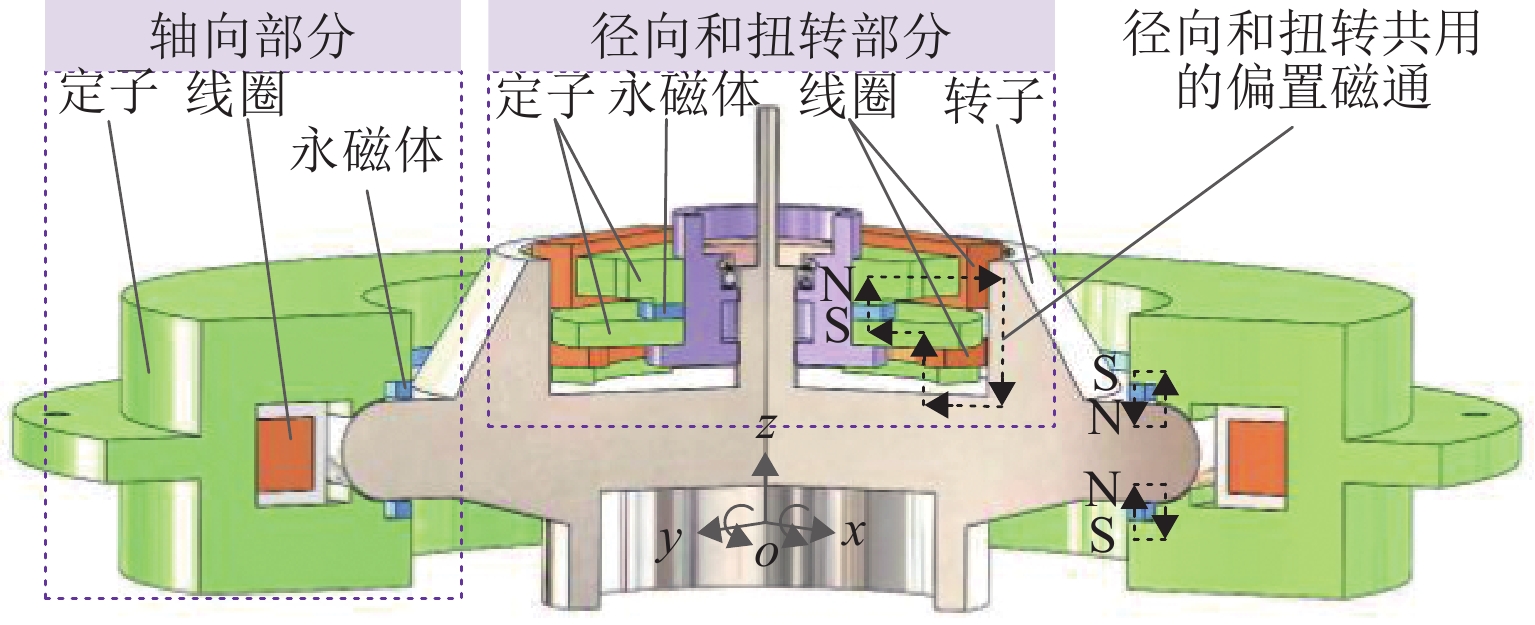
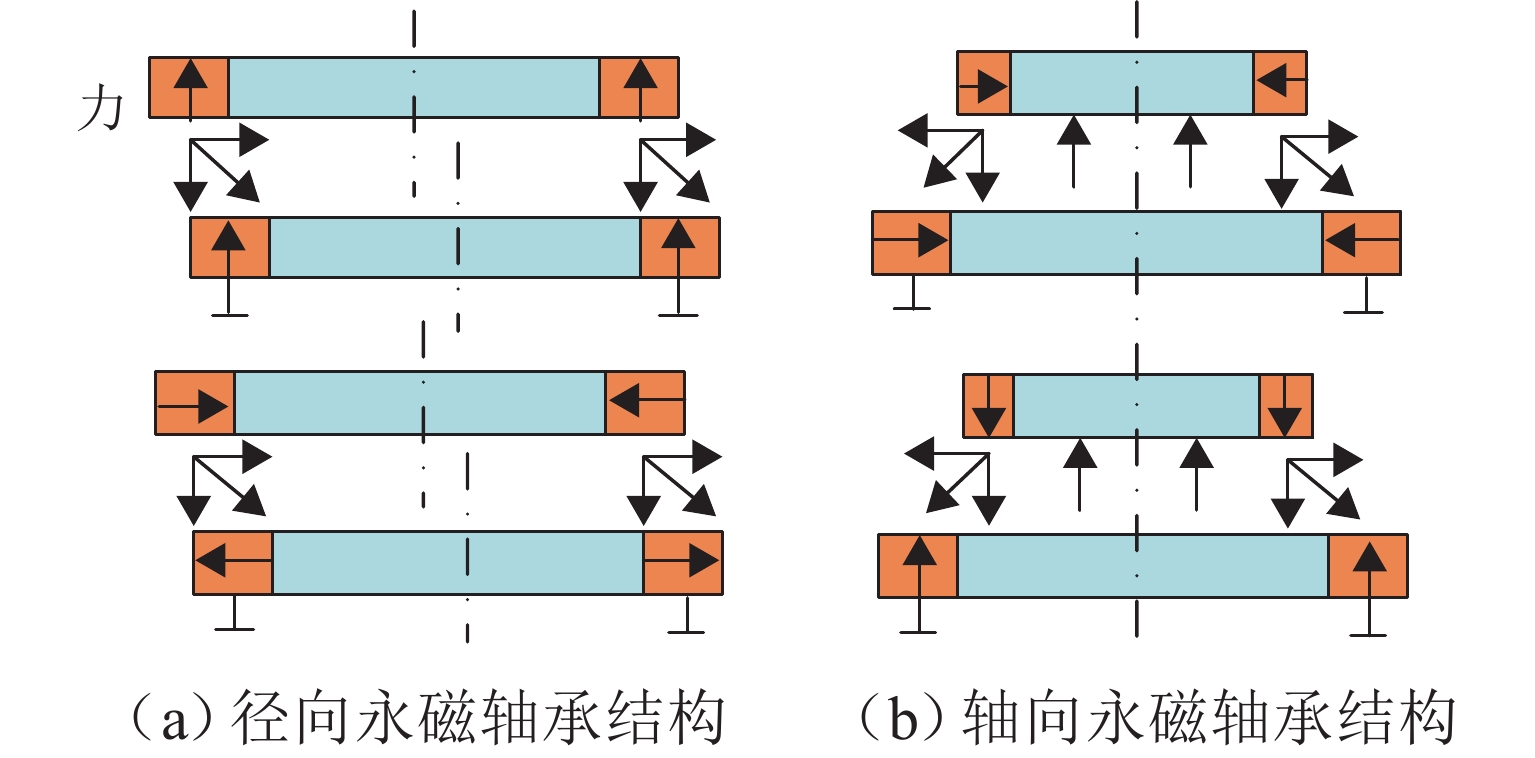
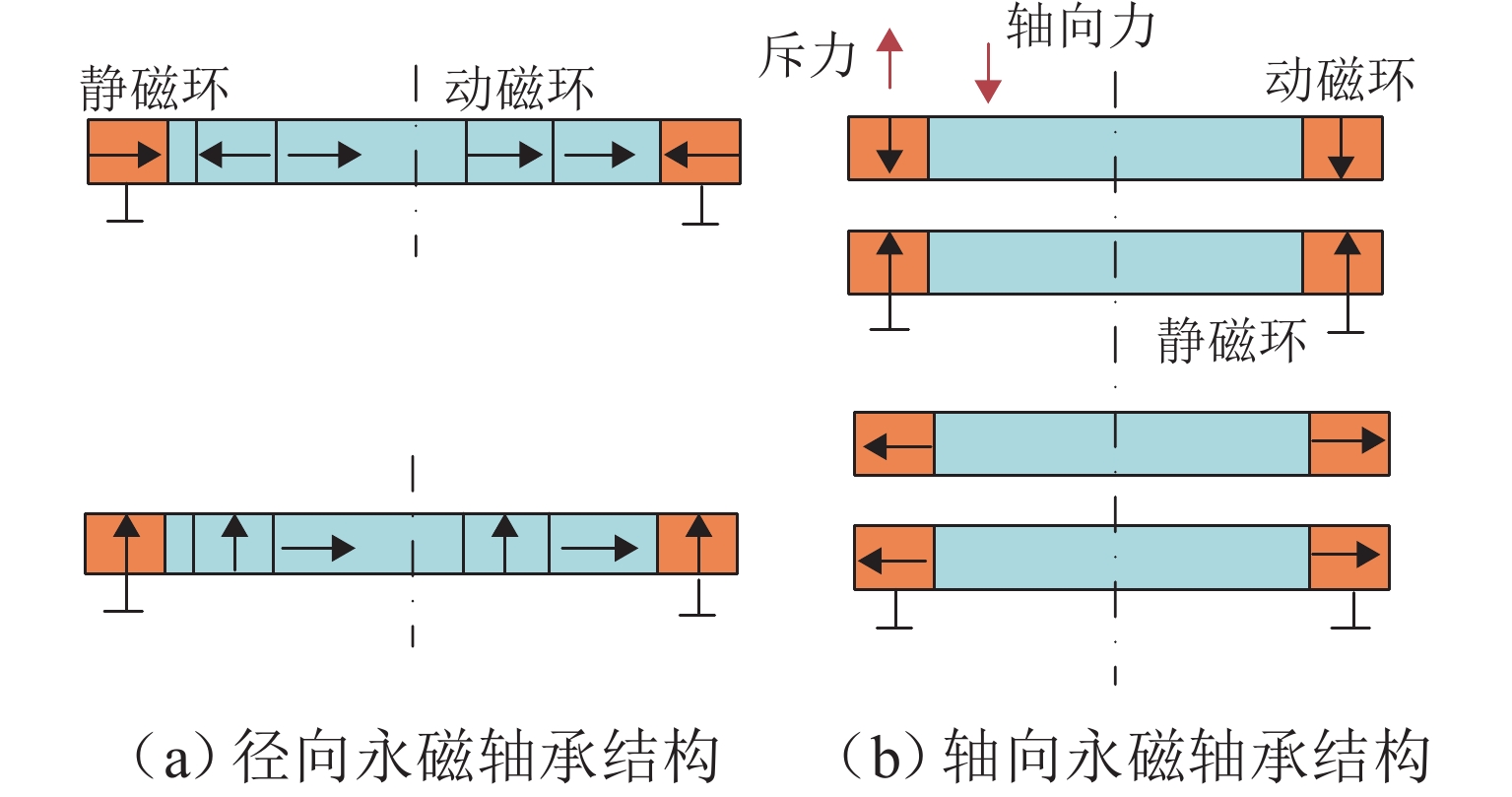
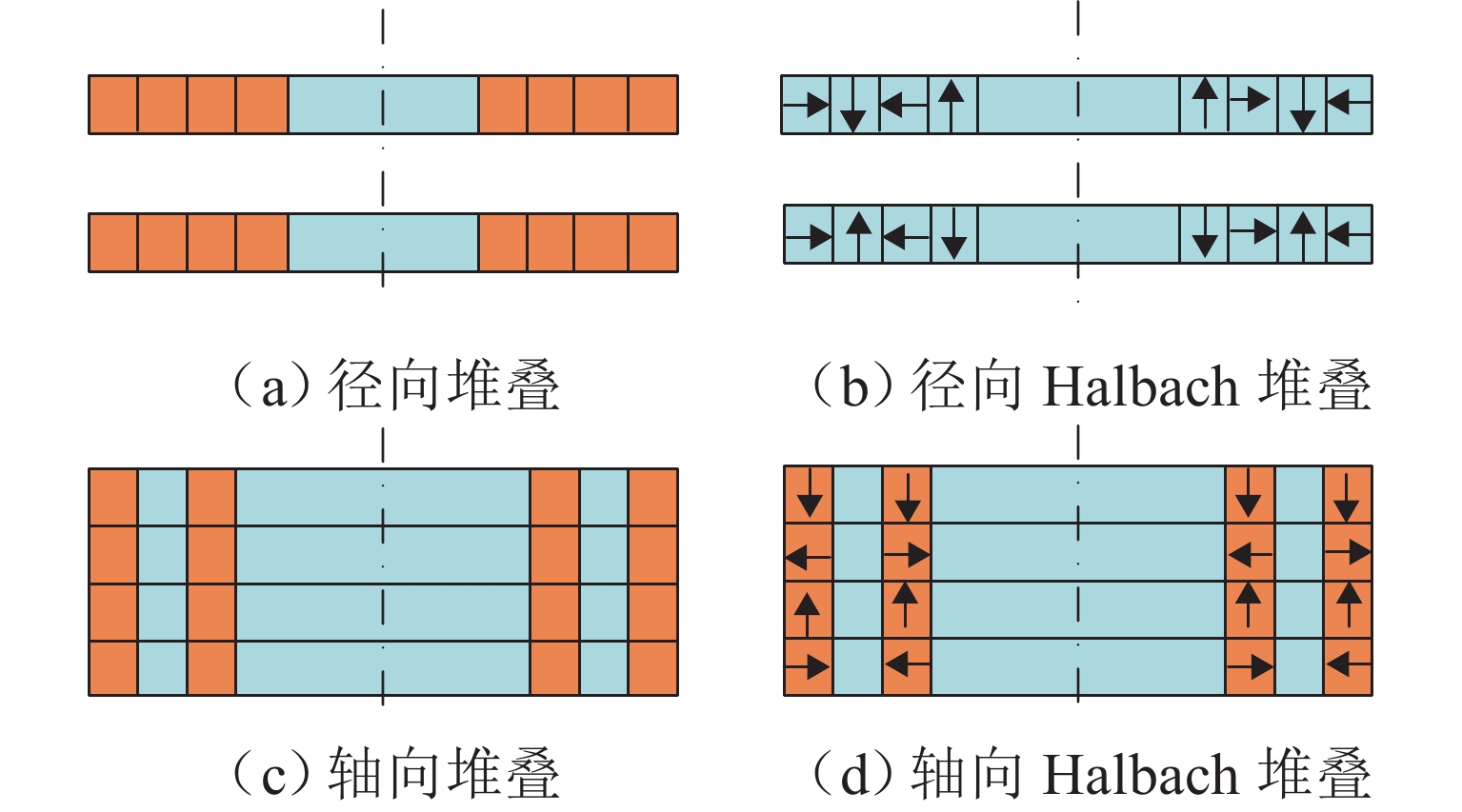
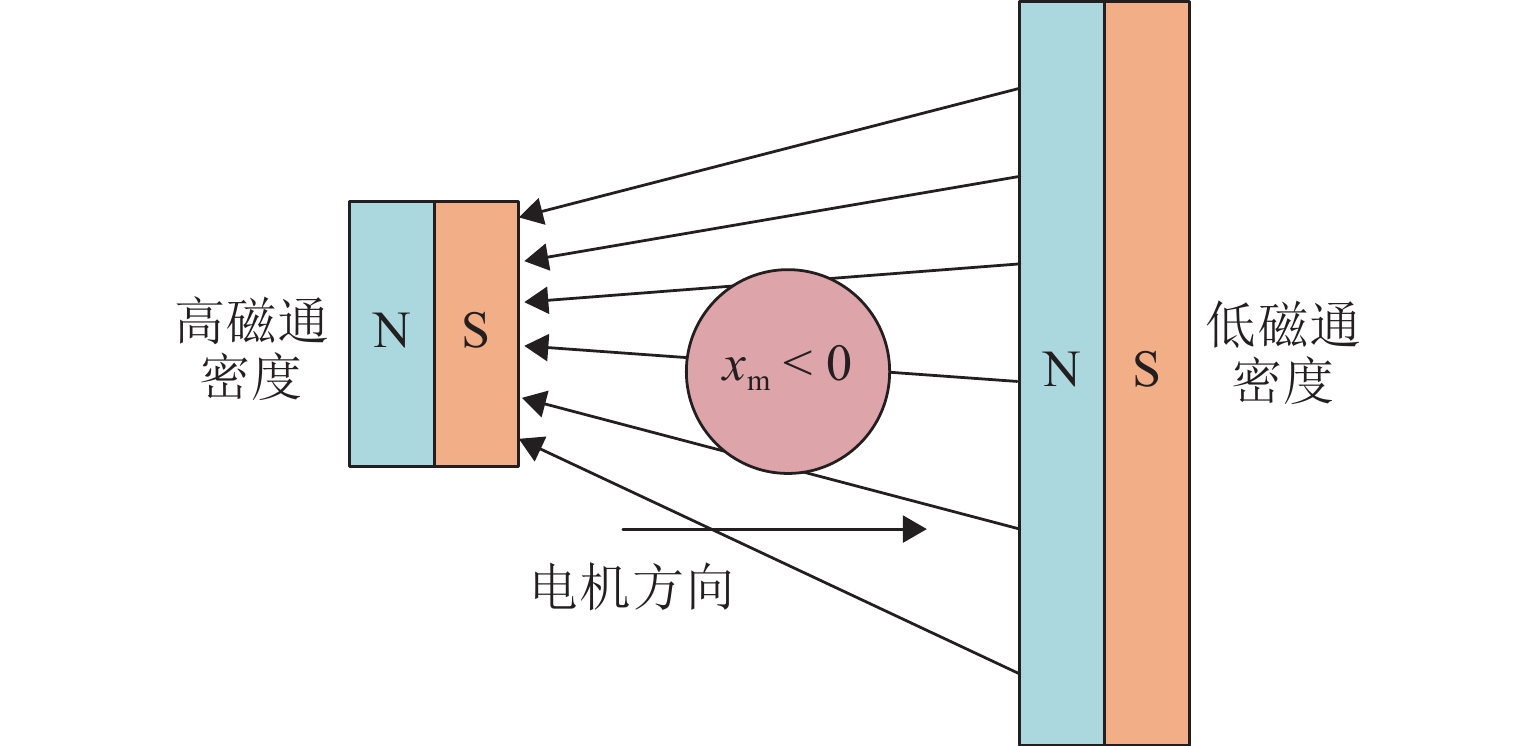
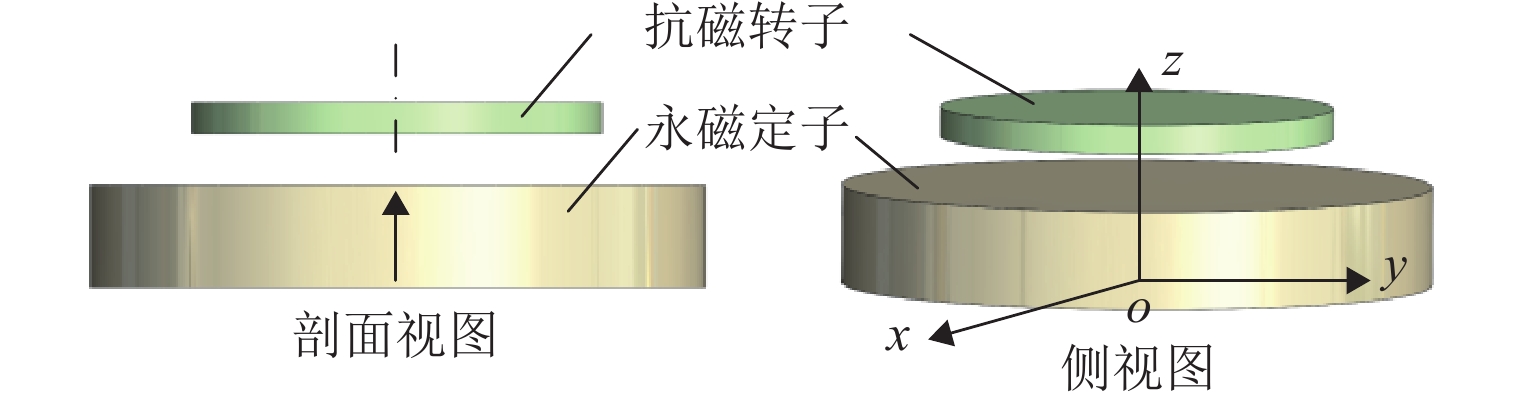
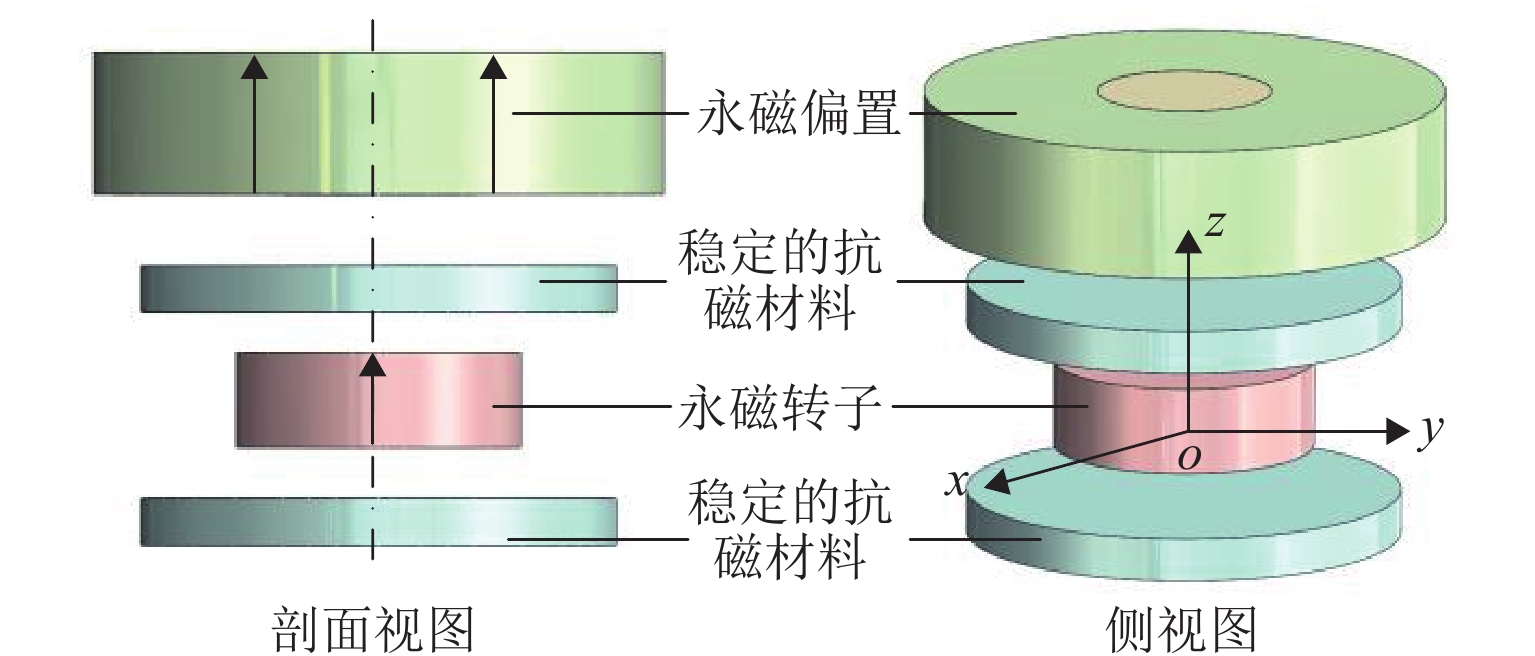
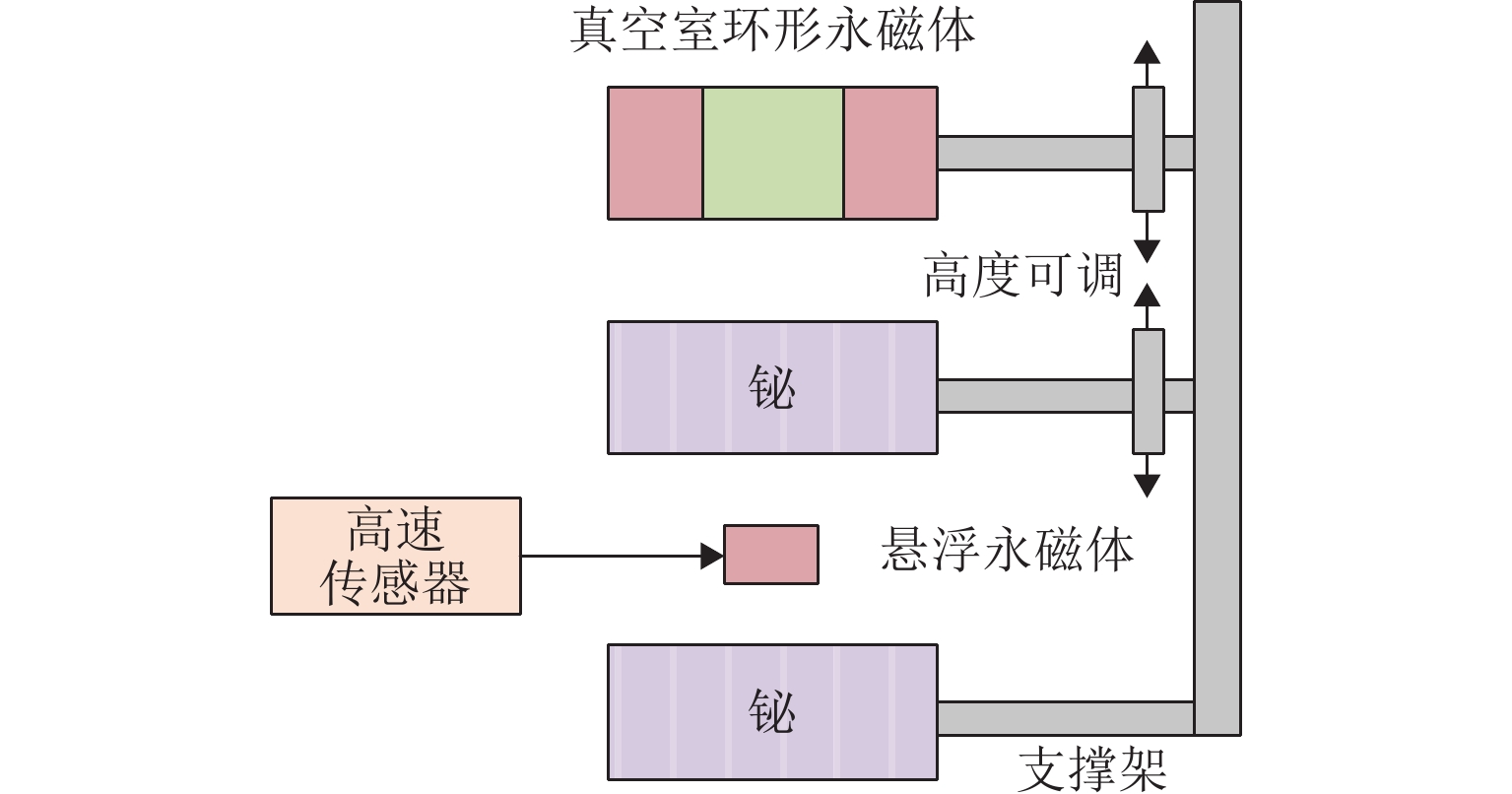
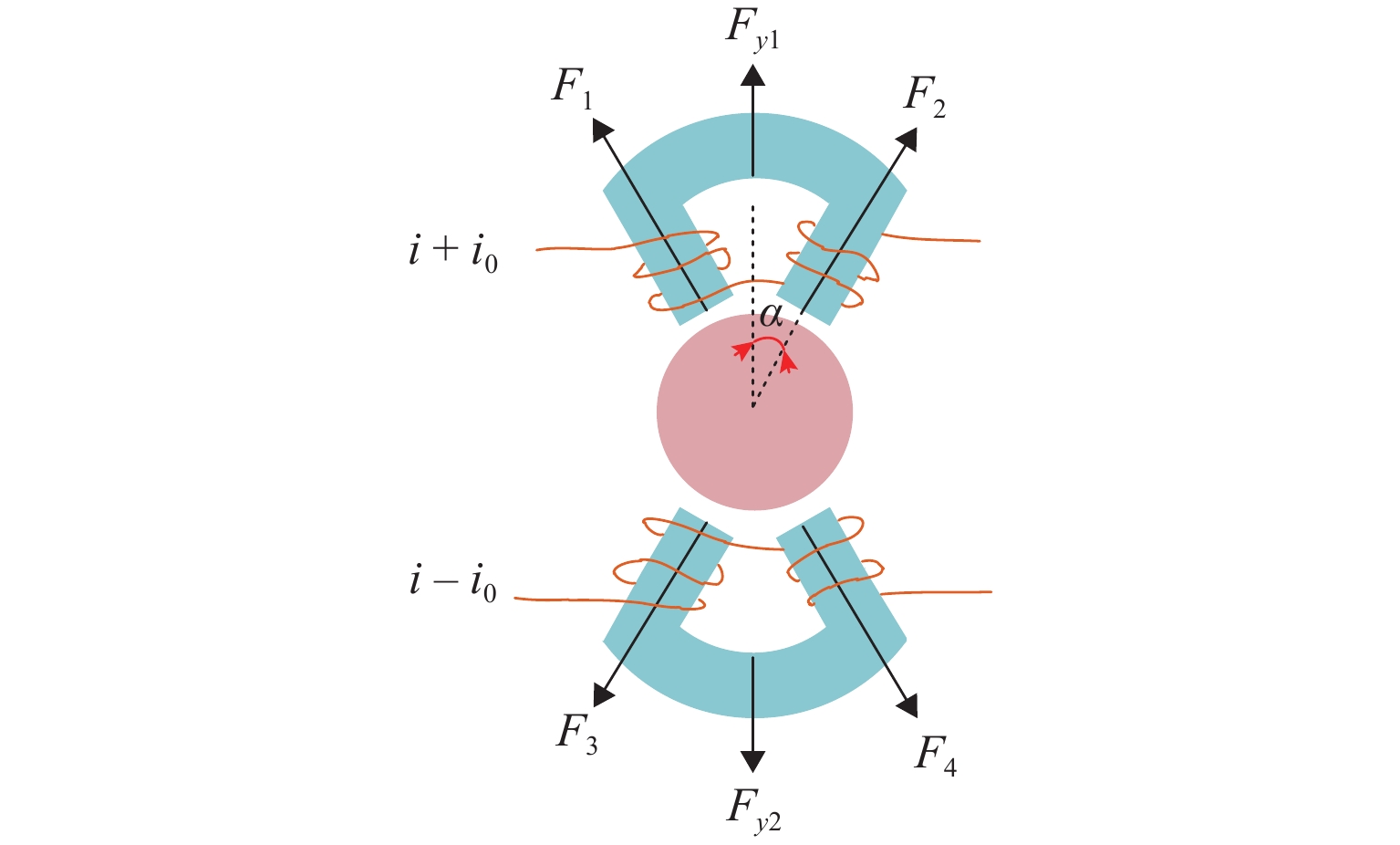
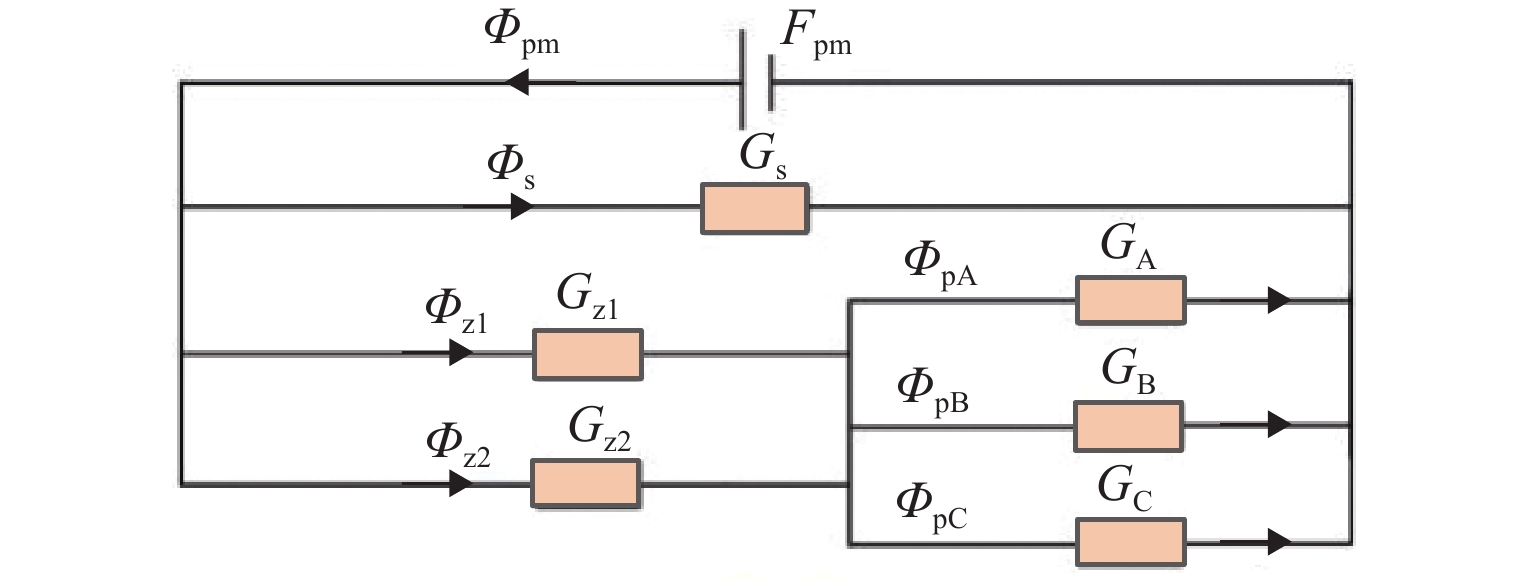
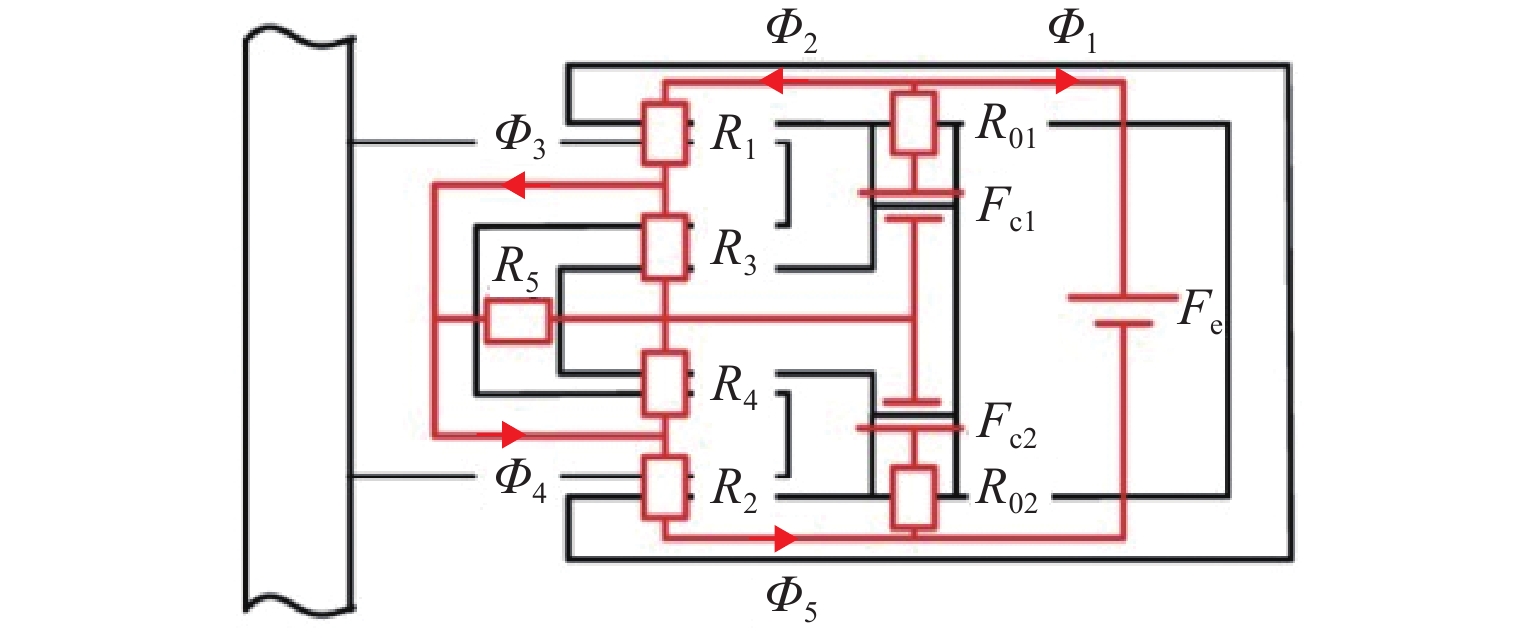
磁悬浮轴承类型 作用原理 特点 吸力磁悬浮轴承 主动(电)磁轴承 通过电磁体产生的悬浮力支撑转子,利用位移传感器精确定位转子的位置. 控制系统通过调节电流强度调整磁力大小,以纠正并维持转子在预定轨迹上的稳定运行. 该装置主要由电磁体、位移传感器、转子、功率放大器及控制器构成 逆变器驱动,体积小,非线性强,技术成熟 混合磁轴承 该轴承融合了主动式与被动式磁悬浮轴承的技术特点,在结构设计上以主动式磁悬浮轴承为核心,通过加入永磁体或超导体来形成偏置磁场,以此提供辅助的悬浮力,同时配备了机械保护轴承 结构稍复杂,但由于减少了电磁线圈匝数,从而降低整体轴承体积并节约成本 被动磁轴承 利用永磁体产生的悬浮力,通过控制定子和转子之间的吸引力使转子实现了无接触稳定悬浮. 结构简单,无需控制和消耗电能,使用方便,承载力小,精度低 斥力磁悬浮轴承 被动磁轴承 由不同永磁体的磁化方向排列形式产生的斥力维持转子悬浮,有轴向阵列、径向阵列以及Halbach阵列 为了克服同性相斥所导致的退磁现象,其永磁体需具备较高的矫顽力 抗磁磁轴承 利用超导体的抗磁性和磁通钉扎性或常温抗磁材料产生与外界相反的磁场,与永磁体产生斥力,从而实现转子无接触悬浮的磁力轴承 无源和完全无接触摩擦,结构简单,刚度可变,超导磁轴承要求低温环境. 常温抗磁材料磁轴承要求负载重量轻 表 3 磁悬浮轴承悬浮力建模方式
Table 3. Modeling methods of suspension force of magnetic suspension bearing
表 4 不同控制策略的比较
Table 4. Comparison of different control strategies
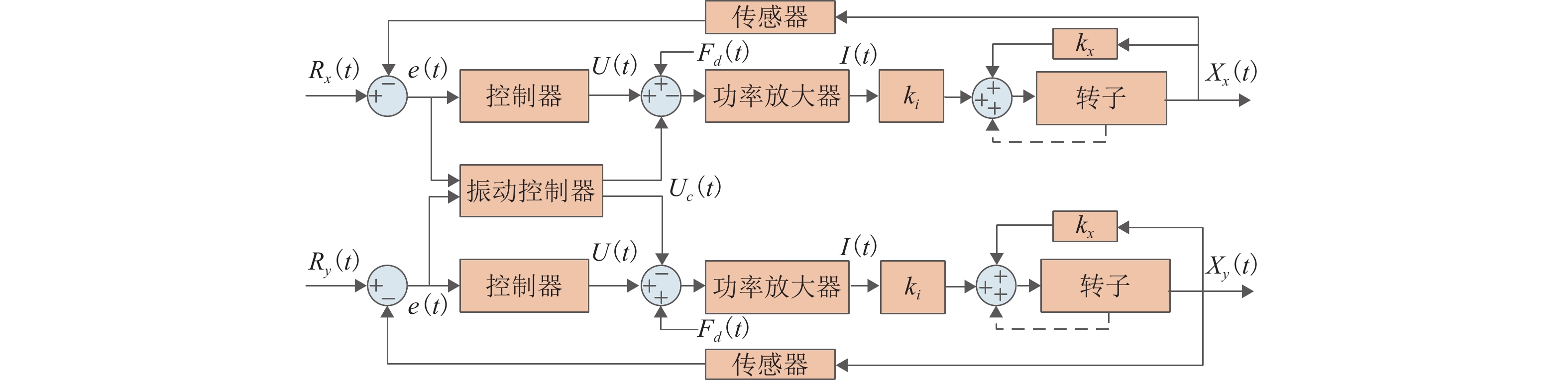
控制策略 优势 劣势 吸力式磁轴承控制策略 低功耗 1.引入多种非线性控制算法.
2.将电流积分项作为外环进行独立控制.降低能耗、减少热量、提高系统效率、便于设备小型化和便携化. 控制算法复杂、对传感器精度要求高、稳定性和鲁棒性面临挑战. 零位移 1.电流补偿.
2. 位移电压补偿.定位精度高、减少振动、响应速度快、优化系统能量. 对传感器要求高、控制算法复杂、系统稳定性存在挑战、成本高. 鲁棒控制 PID 控制、线性二次型调节器(LQR)控制、其他鲁棒控制. 抗干扰能力强、对参数变化的适应性好、提高系统可靠性、拓宽应用场景. 控制性能折中、设计难度大、偏保守、调试复杂. 无传感器 高频信号注入法、凸极跟踪法、占空比补偿法、状态观测法、卡尔曼滤波法. 降低成本、抗干扰能力强、响应速度快、避免传感器误差. 对模型依赖性高、估计精度有限、故障诊断困难、控制算法复杂. 斥力式磁轴承控制策略 PID、最小均方(LMS)自适应法、陷波滤波器(Notch Filter, NF)、通用陷波滤波器. PID:控制简单、鲁棒性好.
LMS:自适应能力强,不依赖精确模型.
陷波滤波器:自适应能力强、通用性和可扩展性好.PID:抗干扰能力有限、参数整定复杂.
LMS:收敛速度与稳态精度存在矛盾.
陷波滤波器:对特定频率依赖性高、系统适应性有限、设计和调试难度大. -
[1] EARNSHAW S. On the nature of the molecular forces which regulate the constitution of the lumiferous ether[J]. Transactions of the Cambridge Philharmonical Society, 1842, 3: 97-112. [2] KEMPER H. Schwebebahn mit raederlosen fahrzeugen, die an eisernen fahrschienen mittels magnetischer felder schwebend entlang gefuehrt werden: German Patent 644, 302[P]. 1937-4-5. [3] KEMPER H. Suspension by electromagnetic forces: a possibility for a radically new method of transportation[J]. Elektrotechnische Zeitschrift, 1938, 59: 391-395. [4] BEAMS J W. Magnetic suspension for small rotors[J]. Review of Scientific Instruments, 1950, 21(2): 182-184. doi: 10.1063/1.1745523 [5] SCHWEITZER G. Ein aktives magnetisches Rotorlager- Auslegung und Anwendung/An active magnetic hub bearing: design and application[J]. Auto, 1978, 26(1/2/3/4/5/6/7/8/9/10/11/12): 10-15. [6] 楚云凌, 汪希平, 雷永锋, 等. 电磁轴承系统中信息存储与接口技术的智能化方法[J]. 轴承, 2007(9): 4-6, 14. doi: 10.19533/j.issn1000-3762.2007.09.002CHU Yunling, WANG Xiping, LEI Yongfeng, et al. Intelligent method of information storage and interface in magnetic bearing system[J]. Bearing, 2007(9): 4-6,14. doi: 10.19533/j.issn1000-3762.2007.09.002 [7] KNOSPE C, COLLINS E G. Introduction to the special issue on magnetic bearing control [guest editorial[J]. IEEE Transactions on Control Systems Technology, 1996, 4(5): 481. doi: 10.1109/tcst.1996.531914 [8] BRUNET M. Practical applications of active magnetic bearing to the industrial world[C]//In: Proceedings of the 1st International Symposium on Magnetic Bearings. Zurich: [s. n. ], 1988. [9] TANIGUCHI M. Cutting performance of digital controlled milling AMB-spindle[C]//In: Proceedings of the 5th International Symposium on Magnetic Bearings. Kanazawa: [s. n. ], 1996. [10] 孙津济, 房建成. 磁悬浮飞轮用新型永磁偏置径向磁轴承的设计[J]. 轴承, 2008(3): 8-13.SUN Jinji, FANG Jiancheng. Design on new permanent magnet biased radial magnetic bearing in magnetic suspending flywheel[J]. Bearing, 2008(3): 8-13. [11] HOFFMAN W. Behaviour and control of an inverter-fed three-pole active radial magnetic bearing[C]//2003 IEEE International Symposium on Industrial Electronics. Brazil: IEEE, 2003: 974-979. [12] SCHMIDT E, HOFER M. Parameter evaluation of a hybrid magnetic bearing by using 3D finite element analyses[C]//2008 Australasian Universities Power Engineering Conference. Sydney: IEEE, 2008: 1-6. [13] KIM S H, SHIN J W, ISHIYAMA K. Magnetic bearings and synchronous magnetic axial coupling for the enhancement of the driving performance of magnetic wireless pumps[J]. IEEE Transactions on Magnetics, 2014, 50(1): 4003404. doi: 10.1109/tmag.2013.2278837 [14] GONG L, ZHU C S. The influence of PID controller parameters on polarity switching control for unbalance compensation of active magnetic bearings rotor systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2024, 71(8): 8324-8338. doi: 10.1109/TIE.2023.3323751 [15] DUTTA D, KUMAR BISWAS P, DEBNATH S, et al. Advancements and challenges in active magnetic bearings: a comprehensive review of performance, control, and future prospects[J]. IEEE Access, 2024, 13: 3051-3071. doi: 10.1109/access.2024.3523205 [16] 吴华春, 龙志强, 周瑾, 等. 磁力轴承: 过去、现在和未来[J]. 轴承, 2024(7): 1-13.WU Huachun, LONG Zhiqiang, ZHOU Jin, et al. Magnetic bearings: past, present and future[J]. Bearing, 2024(7): 1-13. [17] ZHANG W Y, ZHU H Q. Radial magnetic bearings: an overview[J]. Results in Physics, 2017, 7: 3756-3766. doi: 10.1016/j.rinp.2017.08.043 [18] LEE R-M, WU Z-B, WANG C-C, et al. Multi-hybrid active magnetic bearing design for milling spindle applications[J]. Sensors and Materials, 2020, 32(1): 375. doi: 10.18494/sam.2020.2600 [19] 刘欣, 袁鹏禹. 新型异极径向混合磁悬浮轴承的建模及仿真[J]. 西南交通大学学报, 2025, 60(4): 944-953.LIU Xin, YUAN Pengyu. Modeling and simulation of a novel heteropolar radial hybrid magnetic bearing[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2025, 60(4): 944-953. [20] 万少可, 奚航航, 李小虎, 等. 基于电磁轴承混合支承的主动式主轴系统[J]. 轴承, 2022(12): 17-22. doi: 10.19533/j.issn1000-3762.2022.12.003WAN Shaoke, XI Hanghang, LI Xiaohu, et al. Active spindle system hybrid-supported with active magnetic bearing[J]. Bearing, 2022(12): 17-22. doi: 10.19533/j.issn1000-3762.2022.12.003 [21] 姜豪, 苏振中, 姜亚鹏. 高承载力密度磁轴承优化设计[J]. 西南交通大学学报, 2025, 60(4): 965-975, 985.JIANG Hao, SU Zhenzhong, JIANG Yapeng. Optimized design of high-load capacity magnetic bearings[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2025, 60(4): 965-975, 985. [22] GARCÍA P, GUERRERO J M, BRIZ F, et al. Sensorless control of three-pole active magnetic bearings using saliency-tracking-based methods[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industry Applications, 2010, 46(4): 1476-1484. doi: 10.1109/TIA.2010.2049973 [23] XU S L, FANG J C. A novel conical active magnetic bearing with claw structure[J]. IEEE Transactions on Magnetics, 2014, 50(5): 8101108. doi: 10.1109/tmag.2013.2295060 [24] ZHANG W Y, WANG J P, ZHU P F, et al. A novel vehicle-mounted magnetic suspension flywheel battery with a virtual inertia spindle[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2021, 69(6): 5973-5983. doi: 10.1109/tie.2021.3088375 [25] XU S L, SUN J J, REN H L. An active magnetic bearing with controllable permanent-magnet bias field[J]. IEEE/ASME Transactions on Mechatronics, 2022, 27(5): 3474-3481. doi: 10.1109/TMECH.2022.3142517 [26] ZHANG W Y, ZHU H Q. Control system design for a five-degree-of-freedom electrospindle supported with AC hybrid magnetic bearings[J]. IEEE/ASME Transactions on Mechatronics, 2015, 20(5): 2525-2537. doi: 10.1109/TMECH.2014.2387151 [27] MASUZAWA T, KOJIMA J, ONUMA H, et al. Micro magnetic bearing for an axial flow artificial heart[C]//Proceedings of the 9th International Symposium on Magnetic Bearings. Lexington: University of Kentucky, 2004: 89-94. [28] BLUMENSTOCK K, BROWN G. Novel integrated radial and axial magnetic bearing[C]//Proceedings of the 7th International Symposium on Magnetic Bearings. Zurich: International Center for Magnetic Bearings, 2000: 467-471. [29] ZHANG W Y, WANG J W, LI A, et al. Multiphysics fields analysis and optimization design of a novel saucer-shaped magnetic suspension flywheel battery[J]. IEEE Transactions on Transportation Electrification, 2023, 10(3): 5473-5483. doi: 10.1109/tte.2023.3318305 [30] 胡佳成, 吴华春, 方康平, 等. 永磁轴承结构综述[J]. 轴承, 2023(7): 1-7. doi: 10.19533/j.issn1000-3762.2023.07.001HU Jiacheng, WU Huachun, FANG Kangping, et al. Overview on structure of permanent magnetic bearings[J]. Bearing, 2023(7): 1-7. doi: 10.19533/j.issn1000-3762.2023.07.001 [31] VAN BENEDEN M, KLUYSKENS V, DEHEZ B. Optimal sizing and comparison of permanent magnet thrust bearings[J]. IEEE Transactions on Magnetics, 2017, 53(2): 8300110. doi: 10.1109/tmag.2016.2625275 [32] 杨里. 不同矩形截面永磁环构成的Halbach永磁轴承轴向磁力研究[D]. 西安: 西安理工大学, 2016. [33] YOO S Y, KIM W Y, KIM S J, et al. Optimal design of non-contact thrust bearing using permanent magnet rings[J]. International Journal of Precision Engineering and Manufacturing, 2011, 12(6): 1009-1014. doi: 10.1007/s12541-011-0134-4 [34] 刘洋. 飞轮电池永磁被动磁力支承系统的研究及应用[D]. 宜昌: 三峡大学, 2019. [35] HAN B C, ZHENG S Q, LE Y, et al. Modeling and analysis of coupling performance between passive magnetic bearing and hybrid magnetic radial bearing for magnetically suspended flywheel[J]. IEEE Transactions on Magnetics, 2013, 49(10): 5356-5370. doi: 10.1109/TMAG.2013.2263284 [36] JANSSEN J L G, PAULIDES J J H, LOMONOVA E. Passive limitations for a magnetic gravity compensator[J]. Journal of System Design & Dynamics, 2009, 3(4): 671-680. doi: 10.1299/jsdd.3.671 [37] ARKADIEV V. A floating magnet[J]. Nature, 1947, 160(4062): 330. [38] BRAUNBEK W. Freischwebende Körper im elektrischen und magnetischen Feld[J]. Zeitschrift Für Physik, 1939, 112(11): 753-763. doi: 10.1007/bf01339979 [39] 许吉敏, 张飞, 金英泽, 等. 高温超导磁悬浮轴承的发展现状及前景[J]. 中国材料进展, 2017, 36(5): 321-328, 351.XU Jimin, ZHANG Fei, JIN Yingze, et al. Development status and prospects of high-tc superconducting magnetic bearing[J]. Materials China, 2017, 36(5): 321-328,351. [40] CHEN J Y, ZHOU J B, MENG G, et al. Evaluation of eddy-current effects on diamagnetic bearings for microsystems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2009, 56(4): 964-972. doi: 10.1109/TIE.2008.2011346 [41] CANSIZ A, HULL J R. Stable load-carrying and rotational loss Characteristics of diamagnetic bearings[J]. IEEE Transactions on Magnetics, 2004, 40(3): 1636-1641. doi: 10.1109/TMAG.2004.827181 [42] CANSIZ A. Static and dynamic analysis of a diamagnetic bearing system[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 2008, 103(3): 034510. doi: 10.1063/1.2841699 [43] LEE E. A micro HTS renewable energy/attitude control system for micro/nano satellites[J]. IEEE Transactions on Applied Superconductivity, 2003, 13(2): 2263-2266. doi: 10.1109/TASC.2003.813061 [44] 苏宇锋, 叶志通, 张坤. 抗磁悬浮石墨转子理论分析与实验[J]. 中国机械工程, 2017, 28(9): 1039-1043.SU Yufeng, YE Zhitong, ZHANG Kun. Theoretical analyses and experiments of micromachined graphite rotor based on diamagnetic levitation[J]. China Mechanical Engineering, 2017, 28(9): 1039-1043. [45] 王泽霖. 主动磁悬浮轴承的结构设计及电控系统研究[D]. 北京: 华北电力大学, 2022. [46] SHAKIBAPOUR F, RAHIDEH A, MARDANEH M. 2D analytical model for heteropolar active magnetic bearings considering eccentricity[J]. IET Electric Power Applications, 2018, 12(5): 614-626. doi: 10.1049/iet-epa.2017.0669 [47] DU T C, GENG H P, ZHANG Y Y, et al. Exact analytical method for active magnetic bearings with rotor eccentricity[J]. IEEE Transactions on Magnetics, 2019, 55(12): 8301112. doi: 10.1109/tmag.2019.2942023 [48] WANG K, WANG D, SHEN Y, et al. Subdomain method for permanent magnet biased homo-polar radial magnetic bearing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Magnetics, 2016, 52(7): 8300405. doi: 10.1109/tmag.2015.2508046 [49] KANG K, PALAZZOLO A. Homopolar magnetic bearing saturation effects on rotating machinery vibration[J]. IEEE Transactions on Magnetics, 2012, 48(6): 1984-1994. doi: 10.1109/TMAG.2012.2182776 [50] JIANG H, SU Z Z, WANG D. Analytical calculation of active magnetic bearing based on distributed magnetic circuit method[J]. IEEE Transactions on Energy Conversion, 2021, 36(3): 1841-1851. doi: 10.1109/TEC.2020.3040975 [51] 朱熀秋, 张仲, 诸德宏, 等. 交直流三自由度混合磁轴承结构与有限分析[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2007, 27(12): 77-81.ZHU Huangqiu, ZHANG Zhong, ZHU Dehong, et al. Structure and finite element analysis of an AC-DC three degrees of freedom hybrid magnetic bearing[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2007, 27(12): 77-81. [52] WANG K, WANG D, LIN H Y, et al. Analytical modeling of permanent magnet biased axial magnetic bearing with multiple air gaps[J]. IEEE Transactions on Magnetics, 2014, 50(11): 8002004. doi: 10.1109/tmag.2014.2330843 [53] ZHANG W Y, YANG H K, CHENG L, et al. Modeling based on exact segmentation of magnetic field for a centripetal force type-magnetic bearing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2020, 67(9): 7691-7701. doi: 10.1109/tie.2019.2945275 [54] 张维煜, 朱熀秋. 基于麦克斯韦张量法的交流磁轴承径向悬浮力建模[J]. 科学通报, 2012, 57(11): 976-986.ZHANG Weiyu, ZHU Huangqiu. A novel modeling method for radial suspension forces of AC magnetic bearings[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2012, 57(11): 976-986. [55] YONNET J P. Analytical calculation of magnetic bearings[C]//The 5th International Workshop on Rare Earth-Cobalt Permanent Magnets and Their Applications. Roanoke: [s. n. ], 1981, 3: 199-216. [56] DELLINGER S J, SMITH A O, STMAT K J. Field and force calculations for use in passive magnetic bearing systems employing rare earth magnets[C]//The 8th International Workshop on Rare Earth-Cobalt Permanent Magnets And Their Applications. Dayton: [s. n. ], 1985, 6: 153-164. [57] 谭庆昌, 刘明洁, 孟慧琴, 等. 永磁向心轴承承载能力与刚度的计算[J]. 摩擦学学报, 1994, 14(4): 337-344.TAN Qingchang, LIU Mingjie, MENG Huiqin, et al. Study on bearing capacity and stiffness of radial magnetic bearing[J]. Tribology, 1994, 14(4): 337-344. [58] 修世超, 谭庆昌, 孟慧琴. 同轴环形磁铁磁作用力计算的等效磁荷法[J]. 沈阳黄金学院学报, 1995(3): 359-363.XIU Shichao, TAN Qingchang, MENG Huiqin. A method of equivalent magnetic charge for the calculation of the acting force of coaxial magnet rings[J]. Gold Journal, 1995(3): 359-363. [59] 梅柏杉, 翁兴华. 圆盘式Halbach结构永磁轴承解析模型[J]. 微电机, 2021, 54(7): 39-43, 86.MEI Boshan, WENG Xinghua. Analytical model of magnetic and stiffness of disc-type halbach structure permanent magnetic bearing[J]. Micromotors, 2021, 54(7): 39-43,86. [60] 陈殷, 张昆仑. Halbach永磁阵列空间磁场的解析计算[J]. 磁性材料及器件, 2014, 45(1): 1-4, 9.CHEN Yin, ZHANG Kunlun. Analytic calculation of the magnetic field created by Halbach permanent magnets array[J]. Journal of Magnetic Materials and Devices, 2014, 45(1): 1-4,9. [61] 徐飞鹏, 李铁才. 采用Halbach磁场的新型被动磁轴承仿真[J]. 电机与控制学报, 2007, 11(5): 538-541.XU Feipeng, LI Tiecai. Simulation of new type of passive magnetic bearing using Halbach magnetic field[J]. Electric Machines and Control, 2007, 11(5): 538-541. [62] TIAN L L, AI X P, TIAN Y Q. Analytical model of magnetic force for axial stack permanent-magnet bearings[J]. IEEE Transactions on Magnetics, 2012, 48(10): 2592-2599. [63] CHANG P ‐ Z, MOON F C, HULL J R, et al. Levitation force and magnetic stiffness in bulk high‐temperature superconductors[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 1990, 67(9): 4358-4360. [64] HAN Y H, PARK B J, JUNG S Y, et al. The improved damping of superconductor bearings for 35kWh superconductor flywheel energy storage system[J]. Physica C: Superconductivity, 2013, 485: 102-106. [65] 徐园平, 凌日旺, 周瑾, 等. 抗磁悬浮静电电机悬浮与驱动特性研究[J]. 机械工程学报, 2022, 58(19): 104-114.XU Yuanping, LING Riwang, ZHOU Jin, et al. Research on levitation and driven characteristics of diamagnetic levitation electrostatic motor[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2022, 58(19): 104-114. [66] SIMON I, EMSLIE A G, STRONG P F, et al. Sensitive tiltmeter utilizing a diamagnetic suspension[J]. Review of Scientific Instruments, 1968, 39(11): 1666-1671. [67] 虞烈, 袁祟军 译, 谢友柏 校. 主动磁轴承基础、性能及应用[M]. 北京: 新时代出版社, 1997. [68] TSIOTRAS P, ARCAK M. Low-bias control of AMB subject to voltage saturation: state-feedback and observer designs[J]. IEEE Transactions on Control Systems Technology, 2005, 13(2): 262-273. [69] 龙志强, 王水泉, 尹力明. 磁悬浮系统中的零功率、大刚度控制研究[J]. 机电工程, 1998, 15(2): 45-46.LONG Zhiqiang, WANG Shuiquan, YIN Liming. Research on zero power and large stiffness control in magnetic suspension system[J]. Journal of Mechanical & Electrical Engineering, 1998, 15(2): 45-46. [70] EMDADUL HOQUE M, MIZUNO T, ISHINO Y, et al. A six-axis hybrid vibration isolation system using active zero-power control supported by passive weight support mechanism[J]. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 2010, 329(17): 3417-3430. [71] LUM K Y, COPPOLA V T, BERNSTEIN D S. Adaptive autocentering control for an active magnetic bearing supporting a rotor with unknown mass imbalance[J]. IFAC Proceedings Volumes, 1996, 29(1): 5351-5356. [72] KIM C S, LEE C W. In situ runout identification in active magnetic bearing system by extended influence coefficient method[J]. IEEE/ASME Transactions on Mechatronics, 1997, 2(1): 51-57. [73] RANJAN G, TIWARI R. Application of active magnetic bearings for in situ flexible rotor residual balancing using a novel generalized influence coefficient method[J]. Inverse Problems in Science and Engineering, 2019, 27(7): 943-968. [74] ZHOU J, WU H C, WANG W Y, et al. Online unbalance compensation of a maglev rotor with two active magnetic bearings based on the LMS algorithm and the influence coefficient method[J]. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 2022, 166: 108460. [75] MAO C, ZHU C S. Unbalance compensation for active magnetic bearing rotor system using a variable step size real-time iterative seeking algorithm[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2018, 65(5): 4177-4186. [76] SCHUHMANN T, HOFMANN W, WERNER R. Improving operational performance of active magnetic bearings using Kalman filter and state feedback control[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2012, 59(2): 821-829. [77] 吴海同, 周瑾, 纪历. 基于单相坐标变换的磁悬浮转子不平衡补偿[J]. 浙江大学学报(工学版), 2020, 54(5): 963-971.WU Haitong, ZHOU Jin, JI Li. Unbalance compensation of magnetically suspended rotor based on single phase coordinate transformation[J]. Journal of Zhejiang University (Engineering Science), 2020, 54(5): 963-971. [78] 宋腾, 韩邦成, 郑世强, 等. 基于最小位移的磁悬浮转子变极性LMS反馈不平衡补偿[J]. 振动与冲击, 2015, 34(7): 24-32.SONG Teng, HAN Bangcheng, ZHENG Shiqiang, et al. Variable polarity LMS feedback based on displacement nulling to compensate unbalance of magnetic bearing[J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2015, 34(7): 24-32. [79] 鞠金涛. 磁悬浮电主轴三极混合磁轴承非线性研究与结构优化[D]. 镇江: 江苏大学, 2016. [80] 邱洪, 黄苏丹, 曹广忠. 基于DSP的磁悬浮球模糊PID数字控制器[J]. 武汉理工大学学报(信息与管理工程版), 2009, 31(6): 933-936.QIU Hong, HUANG Sudan, CAO Guangzhong. Development of fuzzy PID controller for magnetic levitated ball system based on DSP[J]. Journal of Wuhan University of Technology (Information & Management Engineering), 2009, 31(6): 933-936. [81] 李杰, 齐晓慧, 夏元清, 等. 线性/非线性自抗扰切换控制方法研究[J]. 自动化学报, 2016, 42(2): 202-212.LI Jie, QI Xiaohui, XIA Yuanqing, et al. On linear/nonlinear active disturbance rejection switching control[J]. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2016, 42(2): 202-212. [82] 刘贺. 主动磁悬浮轴承的H∞控制研究[D]. 大连: 大连理工大学, 2021. [83] 宋鹏云, 张克跃, 张继业. 能量回馈式主动悬挂的鲁棒控制器设计[J]. 西南交通大学学报, 2011, 46(4): 572-578.SONG Pengyun, ZHANG Keyue, ZHANG Jiye. Robust controller of self-powered active suspension[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2011, 46(4): 572-578. [84] KUSEYRI İ S. Robust control and unbalance compensation of rotor/active magnetic bearing systems[J]. Journal of Vibration and Control, 2012, 18(6): 817-832. [85] NONAMI K, ITO T. Synthesis of flexible rotor-magnetic bearing systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Control Systems Technology, 1996, 4(5): 503-512. [86] SUN J B, ZHU H Q. Self-sensing technology of rotor displacement for six-pole radial active magnetic bearing using improved quantum particle swarm optimized cubature Kalman filter[J]. IEEE Journal of Emerging and Selected Topics in Power Electronics, 2022, 10(3): 2881-2889. [87] 张雯柏, 林国斌, 康劲松, 等. 考虑相移补偿的磁浮列车长定子高频注入无传感控制方法[J]. 西南交通大学学报, 2025, 60(4): 1032-1041.ZHANG Wenbai, LIN Guobin, KANG Jinsong, et al. Sensorless control method of high-frequency injection for long-stator synchronous motor of maglev trains considering phase shift compensation[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2025, 60(4): 1032-1041. [88] SUN J J, CHEN D, REN H L. Modeling and control of an integrated axial passive and radial active magnetic bearing system[C]//2013 IEEE International Conference on Information and Automation (ICIA). Yinchuan: IEEE, 2013: 682-687. [89] CHAKRABORTY A, SANTRA T, ROY D, et al. Modelling and stability analysis of a repulsive type magnetic bearing[C]//2015 International Conference on Energy, Power and Environment: Towards Sustainable Growth (ICEPE). Shillong: IEEE, 2015: 1-6. [90] FANG J C, REN Y. High-precision control for a single-gimbal magnetically suspended control moment gyro based on inverse system method[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2011, 58(9): 4331-4342. [91] PENG C, HE J X, DENG Z Q, et al. Parallel mode Notch filters for vibration control of magnetically suspended flywheel in the full speed range[J]. IET Electric Power Applications, 2020, 14(9): 1672-1678. -




 下载:
下载: