A Column Generation Algorithm for Solving Wagon Flow Routing Optimization Problem
-
摘要:
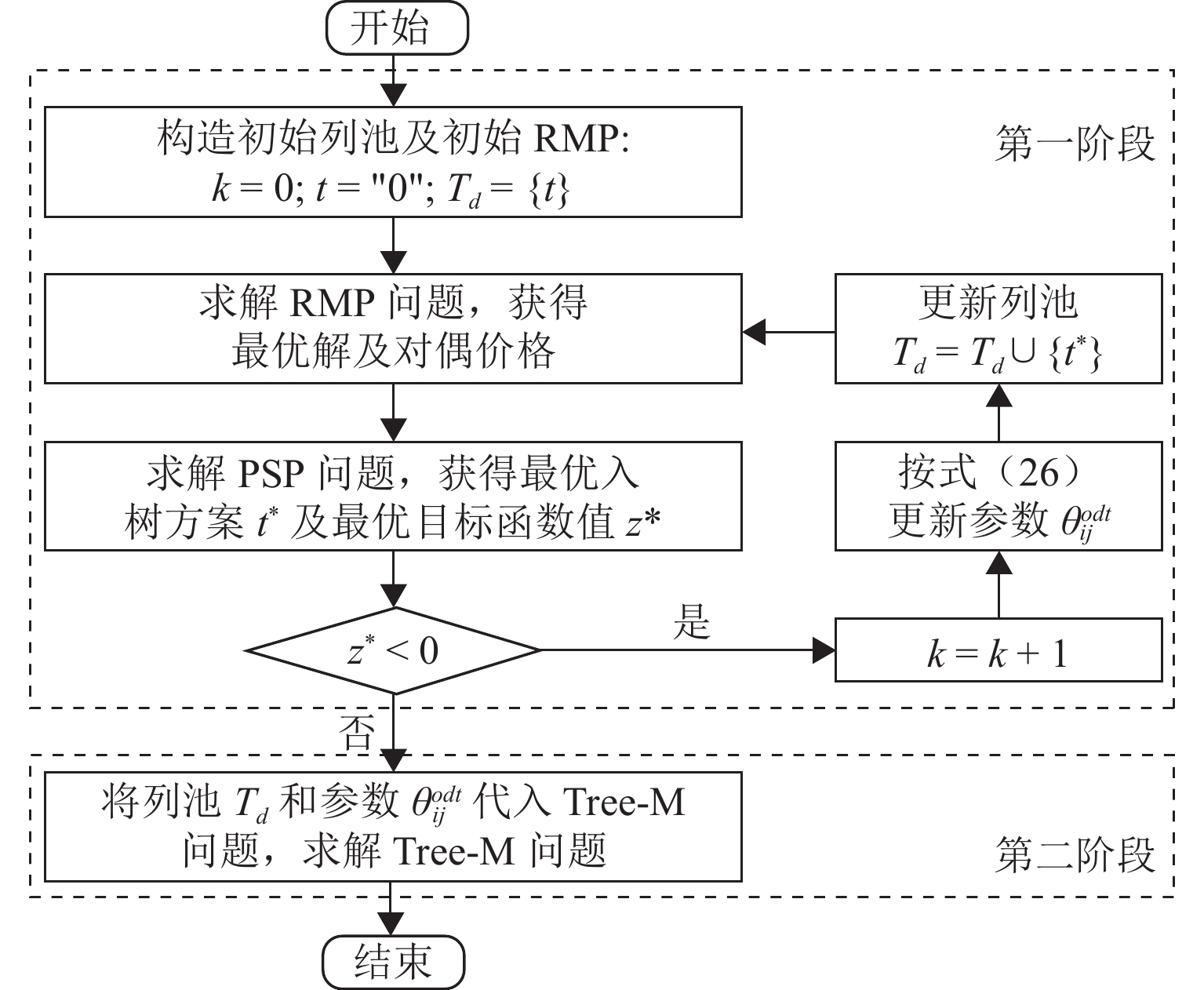
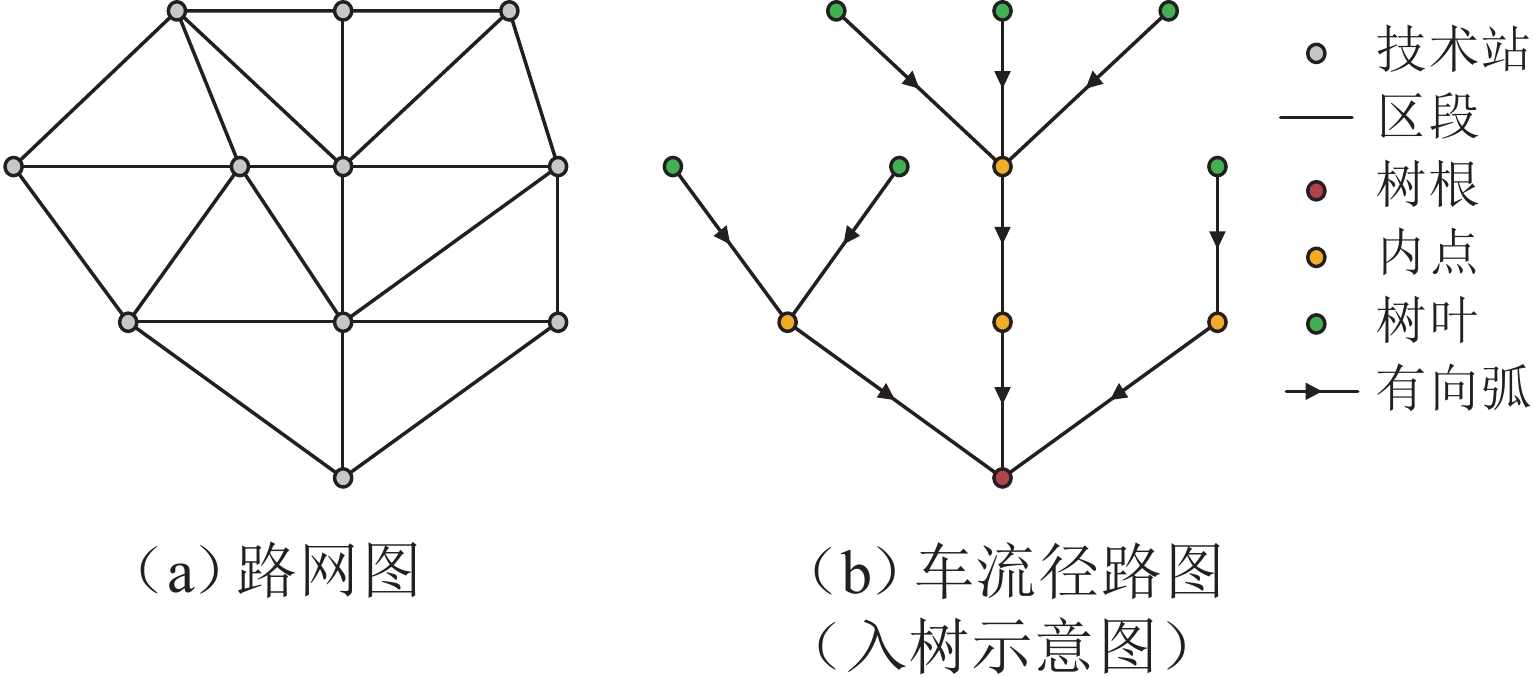
如何在考虑线路通过能力等复杂约束的基础上,快速编制高质量的车流径路方案,以期降低运输总成本,是铁路运输组织过程中面临的重要难题之一. 针对铁路车流径路的树形径路特征,将相同到站的所有车流视为一个整体,同步考虑并提出入树的概念,进而将问题转化为求解每个终到站(树根节点)的入树方案;在此基础上,对经典的基于弧段的多商品流模型采用入树选择变量进行重构;针对重构模型的结构特点,提出两阶段求解方法,第一阶段采用列生成算法得到有潜力的入树方案池,第二阶段在方案池中对每个树根优选出符合条件的入树方案,进而得到每支车流的径路;最后,利用中国西南地区路网数据构造不同规模路网的算例,对算法性能进行验证. 研究结果表明:本文方法能在较短时间内获得近似最优解,相较于CPLEX和模拟退化算法,列生成算法的求解效率更高、求解质量更佳;相较于弧段模型,入树模型具有更低的模型复杂度.
Abstract:One significant challenge in railway transportation organization is how to quickly develop high-quality wagon flow routing schemes while considering complex constraints such as line capacity, with the aim of minimizing total transportation costs. Given the distinct tree structure of wagon flow routes, all the wagon flow towards the same destination station was considered as a whole, and the concept of in-tree was proposed. By doing so, the flow routing problem could be transformed into determining the in-tree scheme for each destination station (i.e., root node). On this basis, the classic arc-based multi-commodity flow model was reformulated using the in-tree selection variables. Subsequently, a two-stage solution approach was proposed in consideration of the structure of the reformulated model. The first-stage model aimed to generate a pool of promising in-tree schemes by using the column generation algorithm. The second-stage model was intended to select the best in-tree scheme for each root and obtain the wagon flow routes. Finally, by using basic data from the railway network in Southwest China, test instances of varying network scales were constructed to evaluate the algorithm’s performance. The results demonstrate that the proposed method can obtain near-optimal solutions within a short computation time. Compared to CPLEX, the column generation algorithm achieves higher solution efficiency; compared to a simulated annealing algorithm, it delivers better solution quality. The in-tree model exhibits lower model complexity and higher computational efficiency than the traditional arc-based model.
-
表 2 按最短路配流与按优化方法配流的车流径路变化情况
Table 2. Changes in wagon routes resulting from using shortest-path assignment method and optimized assignment method
始发站 终到站 需求量/
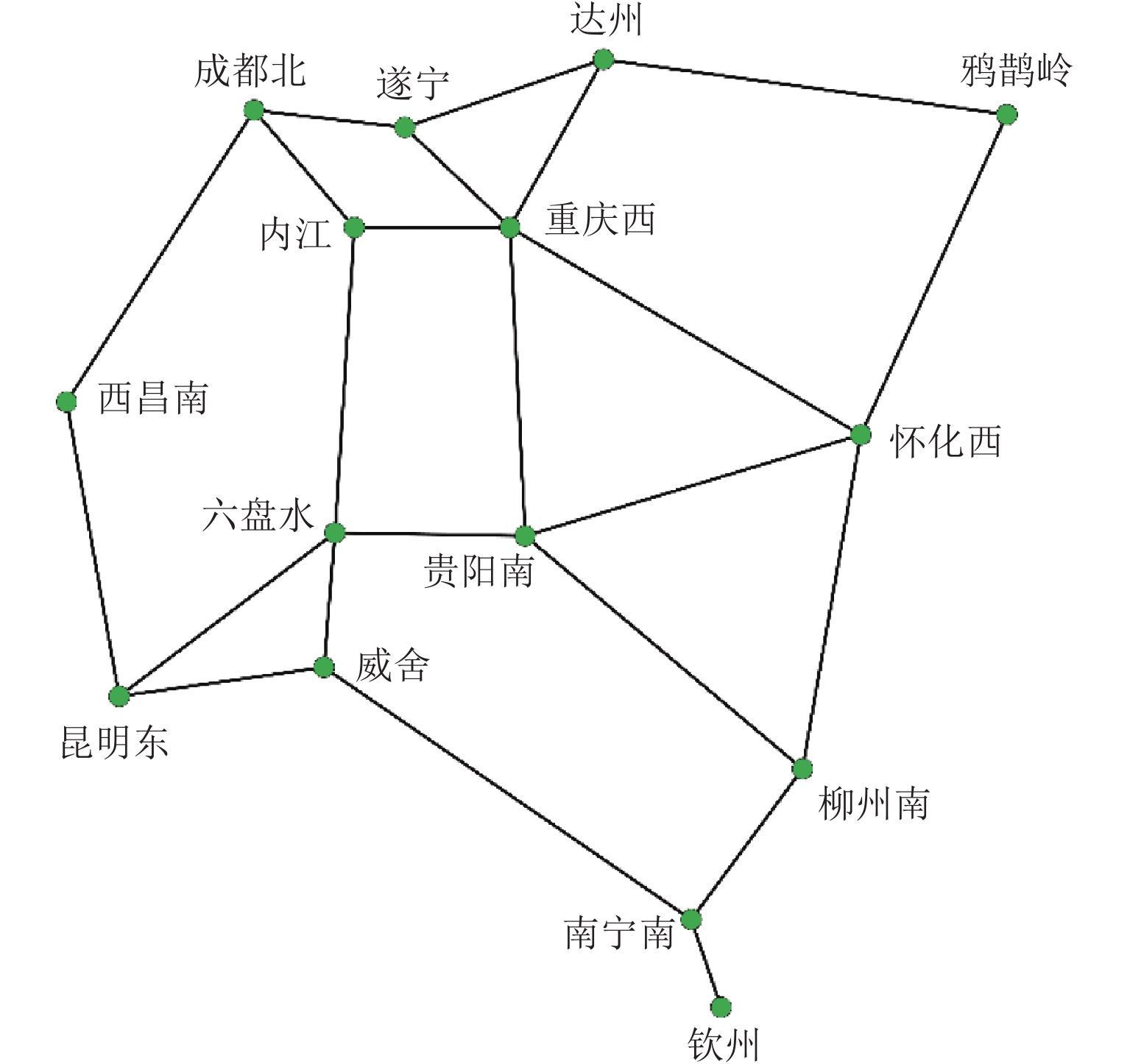
(车·d–1)按最短路配流 按优化方法配流 车流路径 径路长度/km 车流径路 径路长度/km 绕道率 成都北 柳州南 208 成都北→遂宁→重庆西→贵阳南→柳州南 1400 成都北→遂宁→重庆西→怀化西→柳州南 1442 1.03 重庆西 柳州南 105 重庆西→贵阳南→柳州南 1053 重庆西→怀化西→柳州南 1095 1.04 达州 柳州南 151 达州→重庆西→贵阳南→柳州南 1304 达州→重庆西→怀化西→柳州南 1346 1.03 内江 柳州南 89 内江→重庆西→贵阳南→柳州南 1317 内江→重庆西→怀化西→柳州南 1359 1.03 遂宁 柳州南 55 遂宁→重庆西→贵阳南→柳州南 1229 遂宁→重庆西→怀化西→柳州南 1271 1.03 遂宁 昆明东 125 遂宁→重庆西→贵阳南→六盘水→昆明东 1253 遂宁→成都北→西昌南→昆明东 1287 1.03 遂宁 六盘水 163 遂宁→重庆西→贵阳南→六盘水 872 遂宁→成都北→内江→六盘水 915 1.05 内江 达州 132 内江→重庆西→达州 515 内江→成都北→遂宁→达州 616 1.20 怀化西 西昌南 211 怀化西→重庆西→遂宁→成都北→西昌南 1571 怀化西→贵阳南→六盘水→昆明东→西昌南 1611 1.03 昆明东 遂宁 171 昆明东→六盘水→贵阳南→重庆西→遂宁 1253 昆明东→西昌南→成都北→遂宁 1287 1.03 注:本文的绕道率计算方法采用路径长度与最短路径长度之比. 表 1 区段参数
Table 1. Section parameters
编号 起始站 终到站 通过能力/
(车·d−1)区段长度/km 1 重庆西 怀化西 1 250 653 2 怀化西 柳州南 1 563 442 3 鸦鹊岭 怀化西 1 250 493 4 贵阳南 怀化西 1 250 439 5 成都北 内江 1 250 219 6 成都北 遂宁 1 875 171 7 成都北 西昌南 1 875 571 8 贵阳南 六盘水 2 813 246 9 重庆西 贵阳南 3 125 450 10 贵阳南 柳州南 1 875 603 11 内江 重庆西 1 250 264 12 遂宁 重庆西 1 563 176 13 重庆西 达州 1 563 251 14 柳州南 南宁南 2 813 260 15 昆明东 威舍 1 875 301 16 西昌南 昆明东 1 875 545 17 六盘水 昆明东 1 563 381 18 内江 六盘水 1 250 525 19 六盘水 威舍 1 875 247 20 南宁南 威舍 2 500 510 21 达州 鸦鹊岭 938 573 22 遂宁 达州 1 250 226 23 南宁南 钦州 2 500 119 表 3 算法对比
Table 3. Comparison of algorithms
求解算法 运输成本/元 最优间隙/% 求解时间/s CPLEX 62130354 0 19.58 模拟退火算法 63102249 1.56 2.00 列生成算法 62151900 0.03 0.43 表 4 路网规模及计算结果
Table 4. Network sizes and computational results
编号 节点
数/个弧段
数/条CPLEX 模拟退火算法 列生成算法 运输成本/元 求解时间/s 运输成
本/元求解时间/s 最优间隙/% 运输成
本/元求解时间/s 最优间隙/% 下界 上界 最优间隙 1 20 64 24 929 287 24 929 287 0 125.71 27 283 618 3.45 9.44 24 934 092 0.71 0.02 2 25 86 54 187 353 54 187 353 0 440.77 56 671 610 15.48 4.58 55 019 784 4.04 1.54 3 30 106 82 609 183 82 609 183 0 13 574.36 88 611 484 18.56 7.27 82 883 666 6.81 0.33 4 35 128 103 352 738 146 760 885 41.9 > 86 400.00 116249661 26.59 12.48 105 016 000 15.32 1.61 5 40 150 84 146 987 > 86 400.00 93 620 844 54.55 11.26 84 207 167 11.03 0.00 表 5 弧段模型与入树模型计算结果对比
Table 5. Comparison of computational results between arc-based model and in-tree model
节点数/个 弧段数/条 弧段模型 入树模型 变量数/个 约束数/个 运输成本/元 求解时间/s 变量数/个 约束数/个 运输成本/元 求解时间/s 15 46 10 350 13 486 62 130 354 19.58 58 61 62 130 354 3.42 20 64 25 536 33 038 24 929 287 125.71 564 84 24 928 862 48.44 -
[1] 林柏梁. 铁路车流理论[M]. 北京: 中国铁道出版社, 2022: 20-21. [2] AHUJA R K, MAGNANTI T L, ORLIN J B. Network flows: theory, algorithms, and applications[M]. New Jersey: Prentice Hall, 1993: 649-694. [3] EVEN S, ITAI A, SHAMIR A. On the complexity of timetable and multicommodity flow problems[J]. SIAM Journal on Computing, 1976, 5(4): 691-703. doi: 10.1137/0205048 [4] 薛锋, 周琳, 刘泳博. 铁路网车流分配问题研究综述[J]. 交通运输工程与信息学报, 2024, 22(1): 206-219.XUE Feng, ZHOU Lin, LIU Yongbo. Review of research on railway traffic distribution[J]. Journal of Transportation Engineering and Information, 2024, 22(1): 206-219. [5] 高旭敏, 周潮, 顾炎. 铁路网货车车流经路分配的优化模型及算法[J]. 铁道学报, 1992, 14(4): 43-48.GAO Xumin, ZHOU Chao, GU Yan. The optimization model and algorithm of the distribution of cars’ paths in a railway network[J]. Journal of the China Railway Society, 1992, 14(4): 43-48. [6] 纪丽君, 林柏梁, 乔国会, 等. 基于多商品流模型的铁路网车流分配和径路优化模型[J]. 中国铁道科学, 2011, 32(3): 107-110.JI Lijun, LIN Boliang, QIAO Guohui, et al. Car flow assignment and routing optimization model of railway network based on multi-commodity flow model[J]. China Railway Science, 2011, 32(3): 107-110. [7] 薛锋, 刘泳博, 户佐安, 等. 基于动态罚函数的铁路车流分配与径路优化模型[J]. 西南交通大学学报, 2022, 57(5): 941-948, 959.XUE Feng, LIU Yongbo, HU Zuoan, et al. Railcar traffic distribution and route optimization model based on dynamic penalty function[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2022, 57(5): 941-948, 959. [8] 赵伊楠, 林柏梁. 需求不确定的铁路车流径路优化模型[J]. 中国铁道科学, 2024, 45(1): 190-202.ZHAO Yinan, LIN Boliang. Optimization model of railway wagon flow path with uncertain demand[J]. China Railway Science, 2024, 45(1): 190-202. [9] 史峰, 李致中. 铁路车流路径的优选算法[J]. 铁道学报, 1993, 15(3): 70-76.SHI Feng, LI Zhizhong. An algorithm for the wagon path problem[J]. Journal of the China Railway Society, 1993, 15(3): 70-76. [10] LIN B L, ZHAO Y N, LIN R X, et al. Shipment path planning for rail networks considering elastic capacity[J]. IEEE Intelligent Transportation Systems Magazine, 2022, 14(3): 160-174. doi: 10.1109/MITS.2020.3014109 [11] FÜGENSCHUH A, HOMFELD H, SCHÜLLDORF H. Single-car routing in rail freight transport[J]. Transportation Science, 2013, 49(1): 130-148. doi: 10.1287/trsc.2013.0486 [12] 温旭红. 铁路车流分配的树状径路优化模型及算法[J]. 铁道学报, 2017, 39(3): 1-6.WEN Xuhong. An optimization model and algorithm for wagon-flow assignment and tree-form routing[J]. Journal of the China Railway Society, 2017, 39(3): 1-6. [13] 刘畅. 铁路货车车流径路、货物计费径路联合优化模型[J]. 铁道学报, 2023, 45(12): 26-36.LIU Chang. Joint optimization model for railway car flow path and freight charging path[J]. Journal of the China Railway Society, 2023, 45(12): 26-36. [14] 方波, 魏玉光, 马博文, 等. 不确定条件下的车流径路问题及其树形径路约束机制研究[J]. 铁道学报, 2024, 46(8): 10-20.FANG Bo, WEI Yuguang, MA Bowen, et al. Study of shipment routing problem under uncertainty and its tree-shaped path constraint mechanism[J]. Journal of the China Railway Society, 2024, 46(8): 10-20. [15] 赵军, 李愈, 任其亮, 等. 铁路枢纽内客运站分工的优化模型及算法[J]. 西南交通大学学报, 2011, 46(1): 148-153.ZHAO Jun, LI Yu, REN Qiliang, et al. Optimal model and algorithm for allocation of arrival and departure trains in railway passenger terminal[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2011, 46(1): 148-153. [16] 李冰, 任泽强, 轩华. 考虑多编组站转场作业的铁路枢纽车流组织优化[J]. 西南交通大学学报, 2023, 58(3): 489-498, 545.LI Bing, REN Zeqiang, XUAN Hua. Optimization of wagon flow assignment with transship work for multiple marshaling stations at railroad terminals[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2023, 58(3): 489-498, 545. [17] GILMORE P C, GOMORY R E. A linear programming approach to the cutting-stock problem[J]. Operations Research, 1961, 9(6): 849-859. doi: 10.1287/opre.29.6.1092 [18] BARNHART C, JOHNSON E L, NEMHAUSER G L, et al. Branch-and-price: column generation for solving huge integer programs[J]. Operations Research, 1998, 46(3): 316-329. doi: 10.1287/opre.46.3.316 [19] JIN J G, ZHAO J, LEE D H. A column generation based approach for the train network design optimization problem[J]. Transportation Research Part E: Logistics and Transportation Review, 2013, 50: 1-17. doi: 10.1016/j.tre.2012.11.004 [20] LI J, LI K P, TIAN Q N, et al. A column generation-based algorithm for gate assignment problem with combinational gates[J]. Expert Systems with Applications, 2024, 238: 121792. doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2023.121792 [21] 马亮, 郭进, 陈光伟. 编组站静态配流的约束传播和启发式回溯算法[J]. 西南交通大学学报, 2014, 49(6): 1116-1122. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2014.06.027MA Liang, GUO Jin, CHEN Guangwei. Constraint propagation and heuristics backtracking algorithm for static wagon-flow allocation at a marshalling station[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2014, 49(6): 1116-1122. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2014.06.027 [22] 陈东, 彭其渊, 李永辉. 列车到达晚点对技术站车流接续影响仿真分析[J]. 西南交通大学学报, 2014, 49(6): 1108-1115. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2014.06.026CHEN Dong, PENG Qiyuan, LI Yonghui. Simulation of effect of train arrival delay on wagon flow connection at technical stations[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2014, 49(6): 1108-1115. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2014.06.026 [23] 金伟, 李夏苗, 周凌云, 等. 基于列生成算法的高速铁路快捷货运组织方案优化研究[J]. 铁道学报, 2020, 42(9): 26-32. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8360.2020.09.004JIN Wei, LI Xiamiao, ZHOU Lingyun, et al. Research on optimization of high-speed railway freight transportation organization scheme based on column generation algorithm[J]. Journal of the China Railway Society, 2020, 42(9): 26-32. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8360.2020.09.004 [24] 赵天胤, 张永祥, 王蔚, 等. 考虑客流需求的高速铁路列车运行图加线模型与算法[J]. 西南交通大学学报, 2025, 60(3): 741-751. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.20240637ZHAO Tianyin, ZHANG Yongxiang, WANG Wei, et al. Optimization model and algorithm of additional trains scheduling in high-speed railway timetables considering passenger demand[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2025, 60(3): 741-751. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.20240637 [25] 薛锋, 王妗, 程代兵, 等. 基于模糊机会约束规划的列车编组计划优化[J]. 西南交通大学学报, 2025, 60(5): 1268-1277. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.20230325XUE Feng, WANG Jin, CHENG Daibing, et al. Optimization method for train formation plan with fuzzy chance-constrained programming[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2025, 60(5): 1268-1277. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.20230325 -




 下载:
下载: