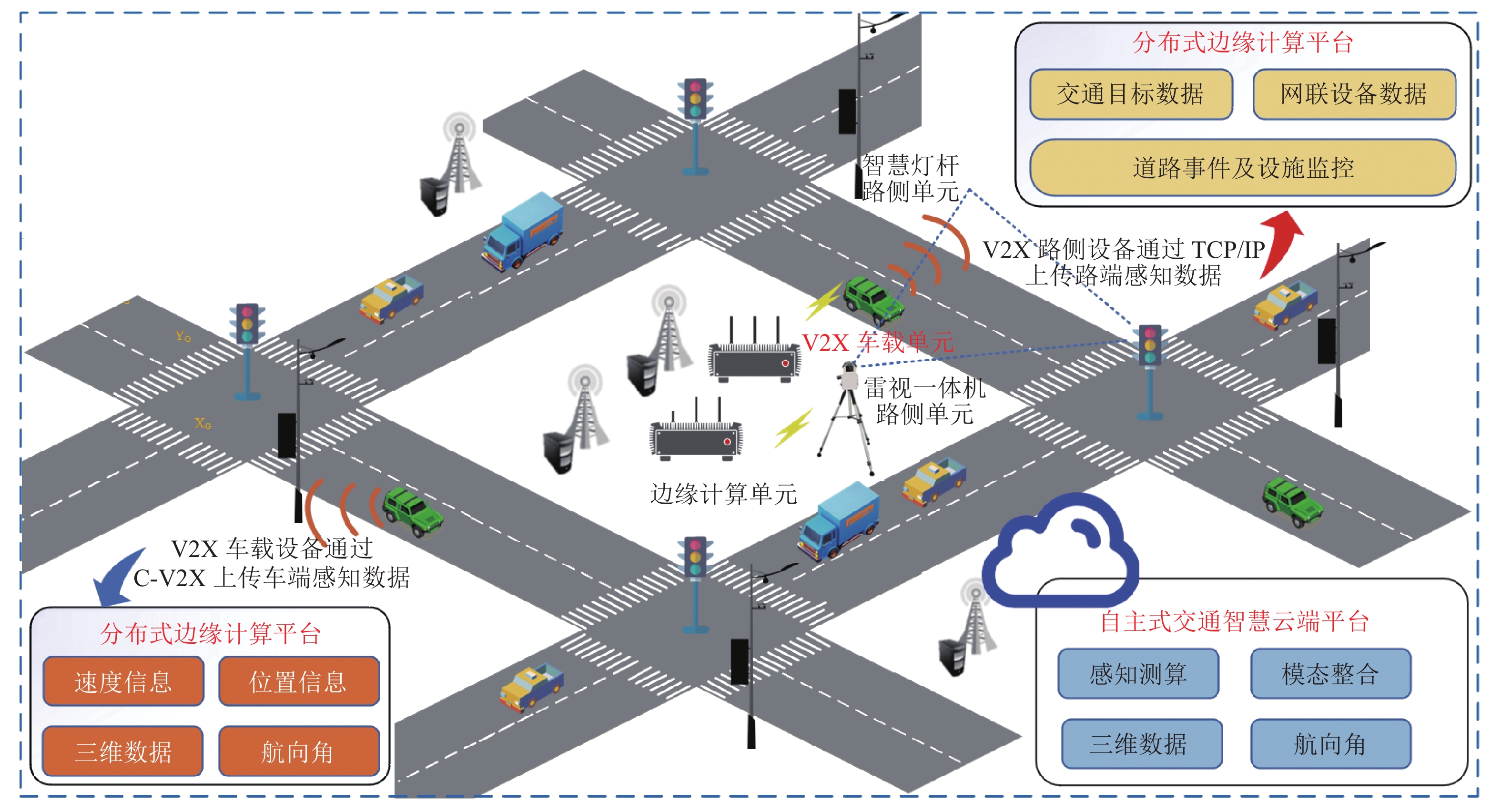
Urban Autonomous Traffic System Situation Evolution Modeling Based on Multimodal Semantic Cognition
-
摘要:
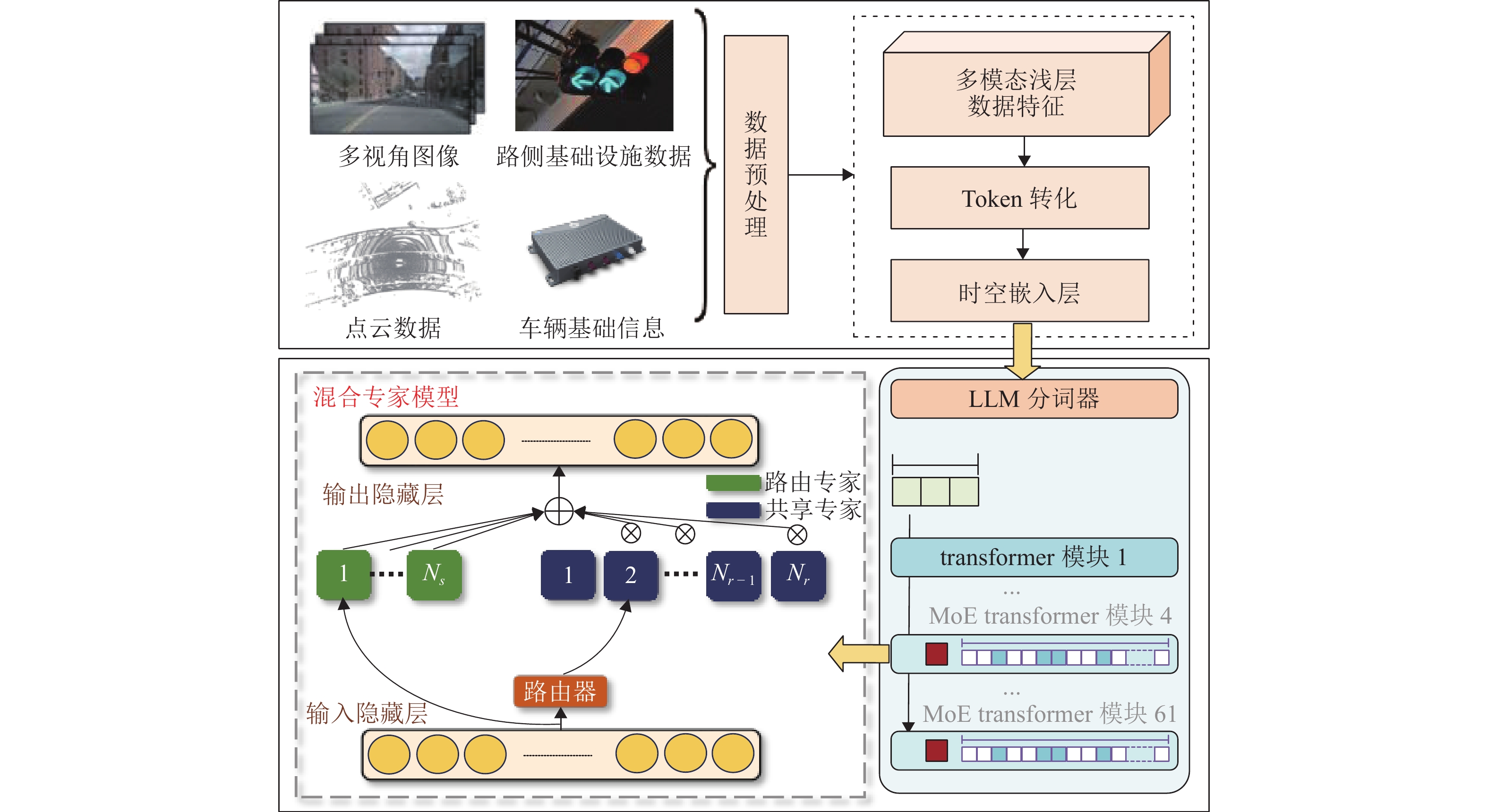
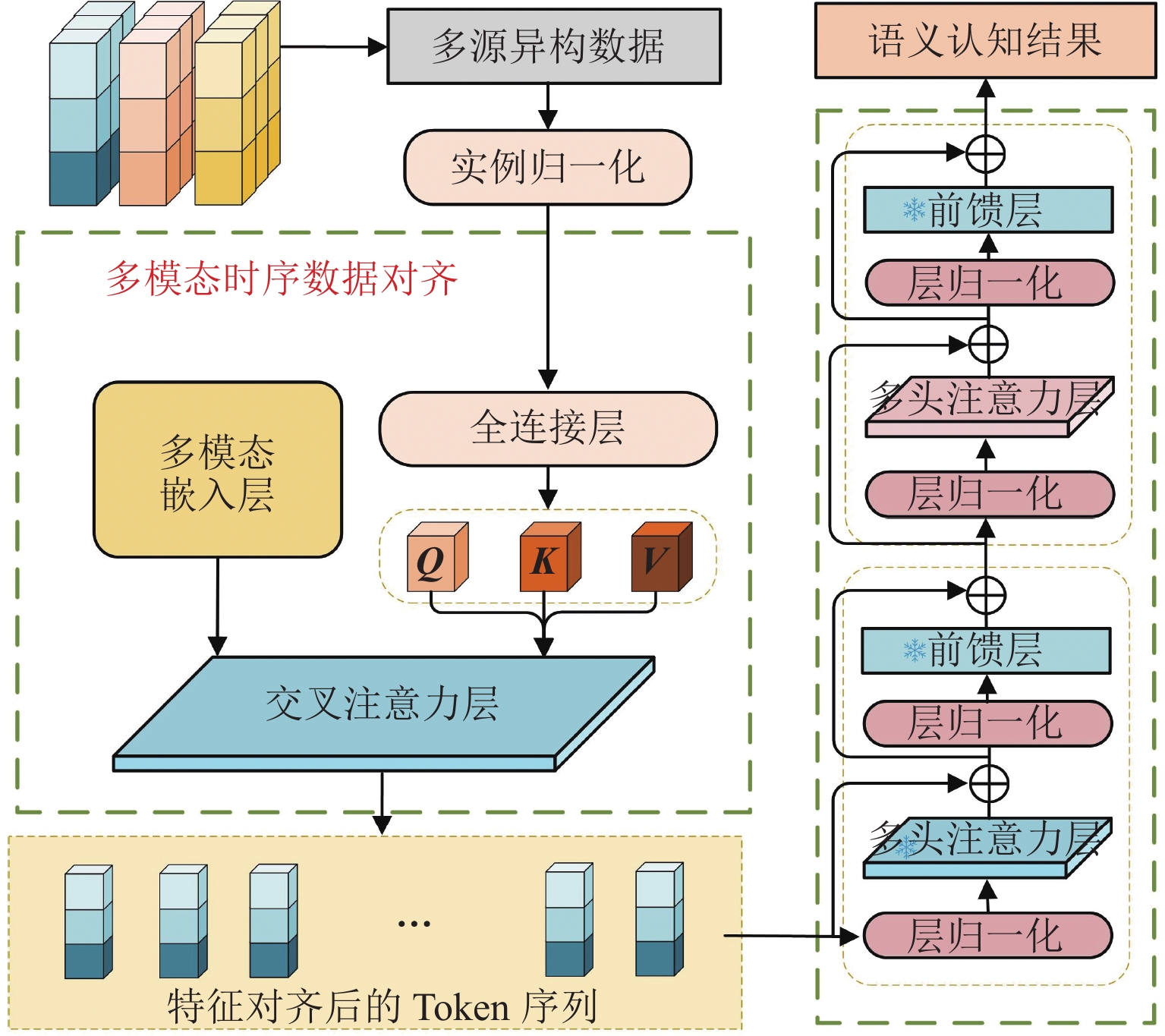
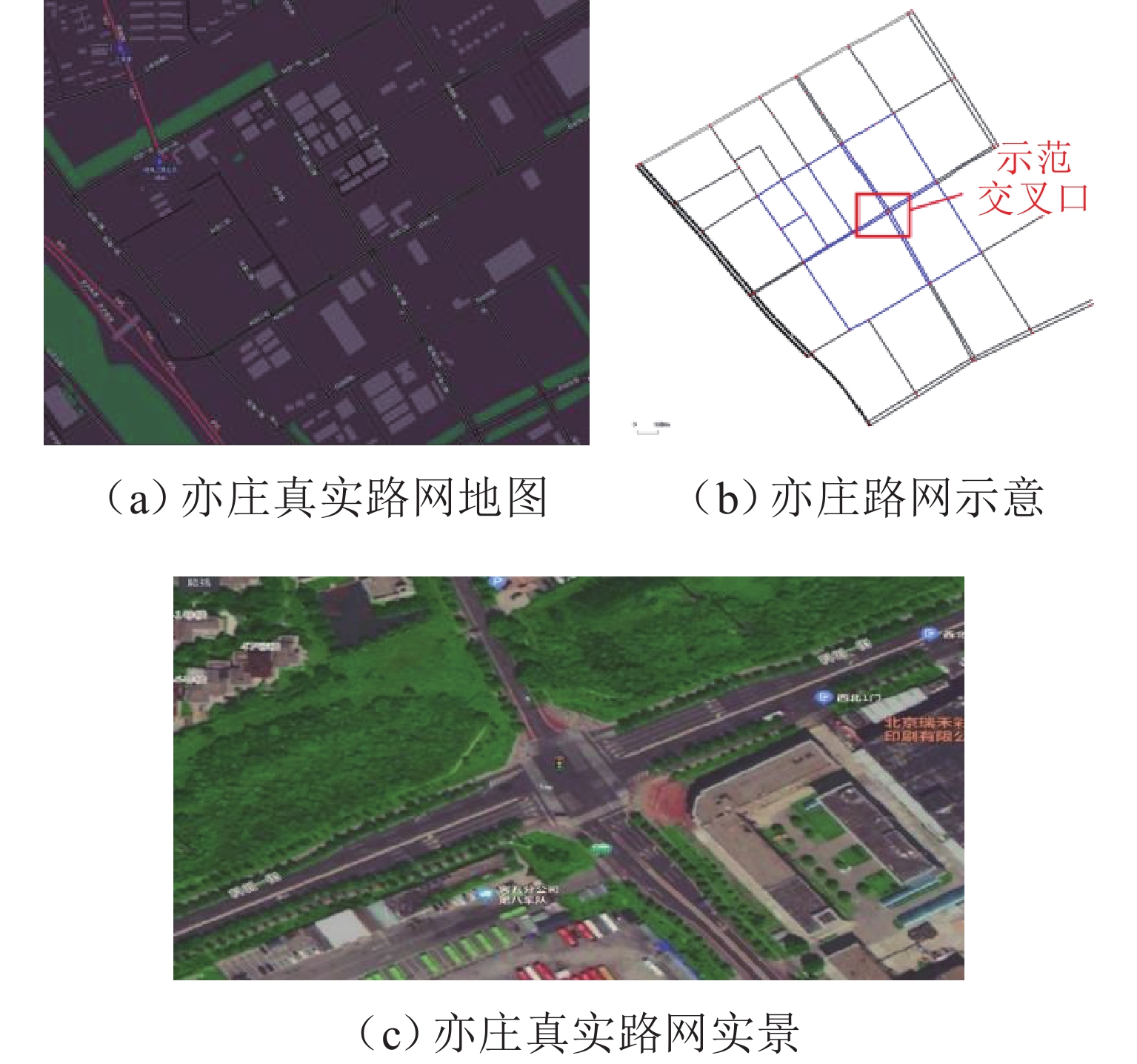
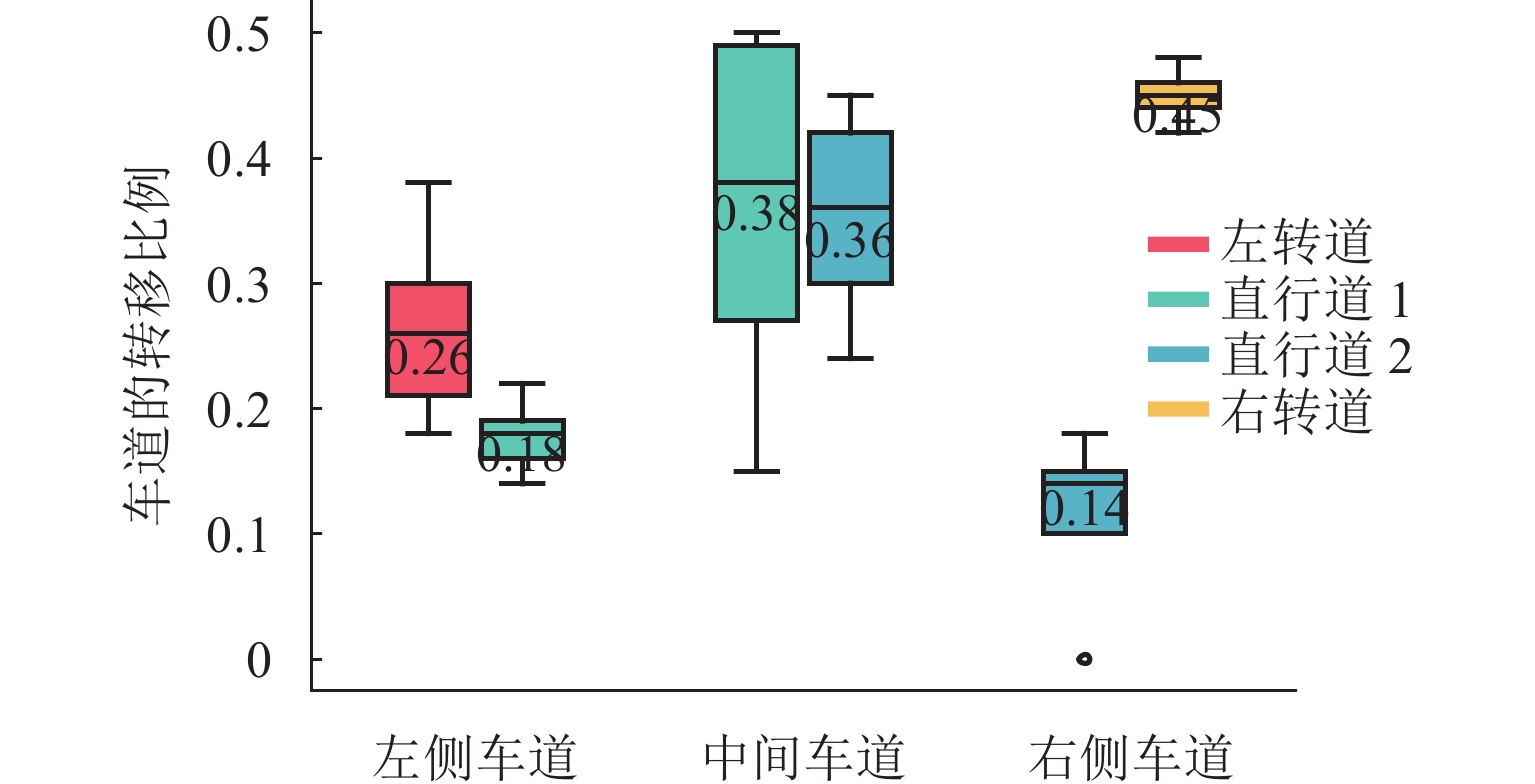
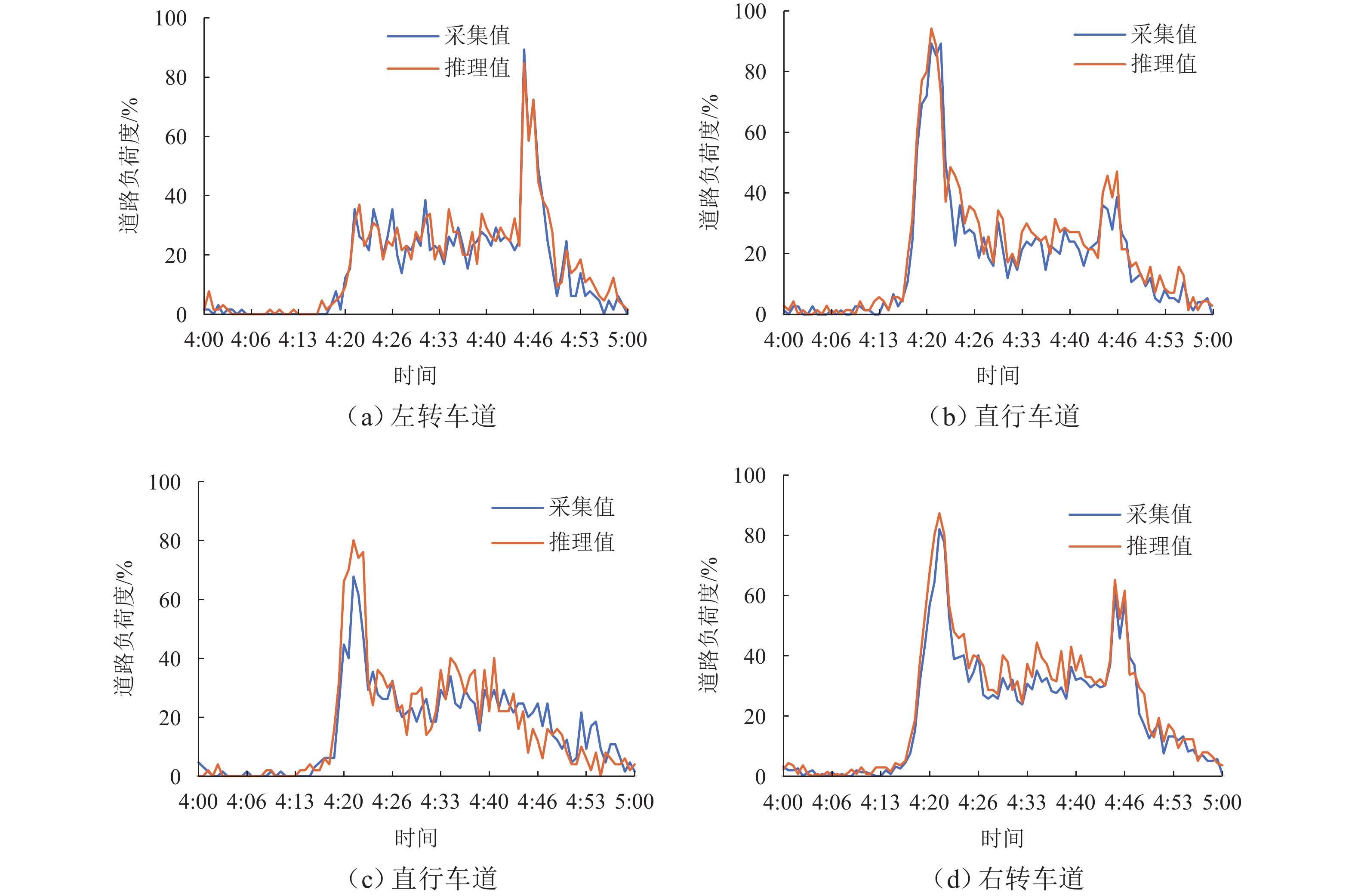
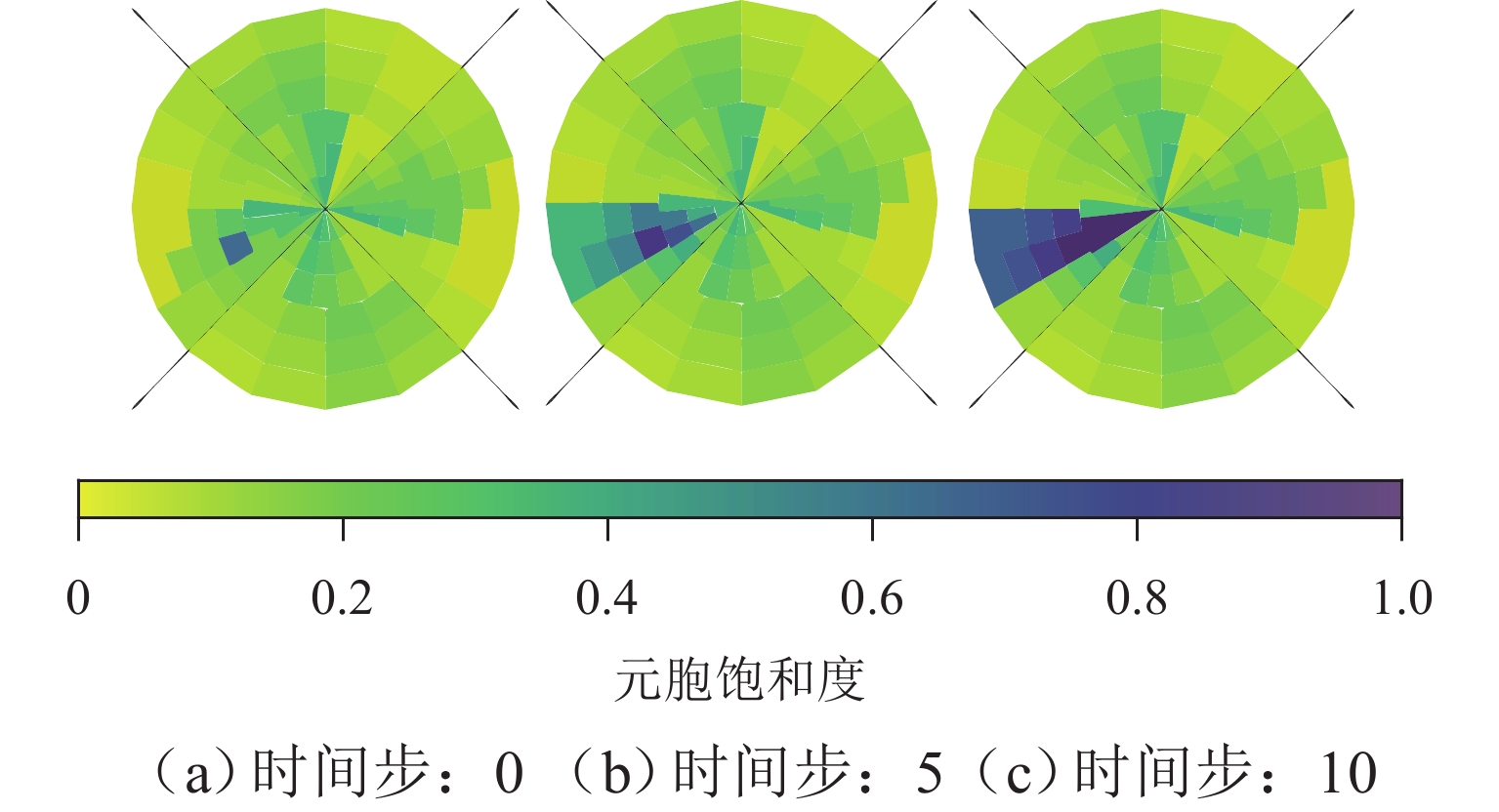
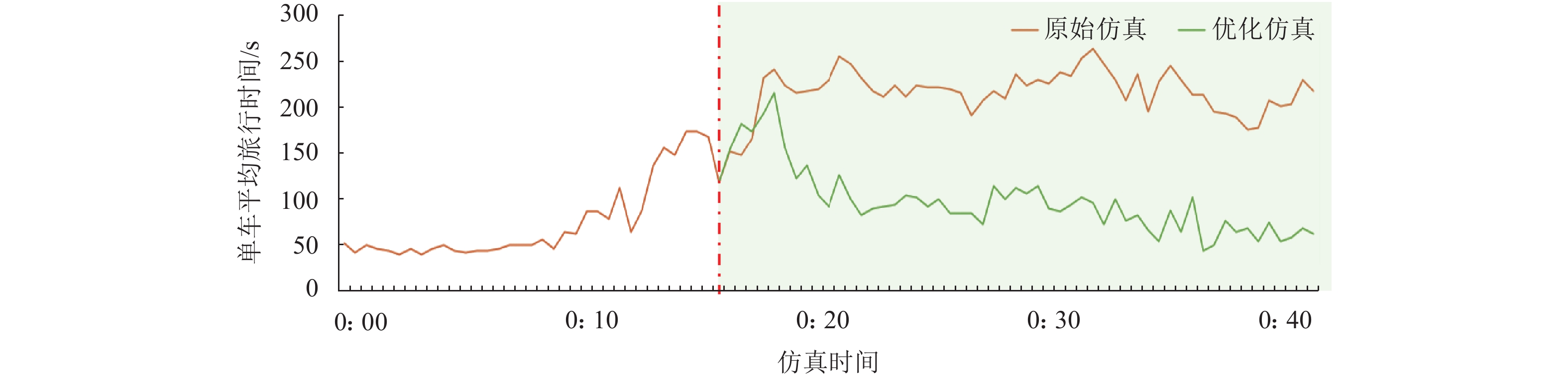
针对城市交通拥堵态势传播问题,从微观层面提出一种车道级的元胞传输模型Micro-CTM(micro cell transmission model),结合大语言模型(large language model,LLM)的多模态语义认知优势,构建车道级交通拥堵态势演化模型(coupled map lattice-driven lane congestion evolution model,CML-LCEM). 首先,构建一种融合混合专家架构大语言模型的交通流特征辨识框架,通过跨模态语义对齐及模型微调方法实现城市交通多模态语义认知;其次,结合转移熵研究车道元胞间状态因果关系,构建车道级交通拥堵演化模型,预测拥堵态势关键元胞;最后,在北京市高级别自动驾驶示范区局域路网开展实验,划分多类型元胞并验证模型对车道级饱和度及拥堵传播的刻画能力. 研究结果表明:本文方法在高峰时段车道级预测精度较传统模型提升显著,对关键元胞的提前干预可降低车辆平均行驶时间达28.3%,为智能交通系统的实时拥堵预警、疏导策略制定及车路云一体化应用提供了数据驱动的大模型解决方案.
Abstract:To address urban traffic congestion propagation, a lane-level Micro Cell Transmission Model (Micro-CTM) was proposed from a microscopic perspective. By leveraging the multimodal semantic cognition capabilities of a large language model (LLM), a lane-level traffic congestion evolution model, the coupled map lattice-driven lane congestion evolution model (CML-LCEM), was constructed. First, a traffic flow feature recognition framework was constructed by integrating an LLM with a mixture-of-experts (MoE) architecture, enabling multimodal semantic cognition of urban traffic through cross-modal semantic alignment and model fine-tuning. Secondly, transfer entropy was employed to analyze the causal relationships between lane-level cells, based on which a lane-level traffic congestion evolution model was constructed to predict key cells in traffic congestion situations. Finally, experiments were conducted on a local road network within the Beijing High-level Autonomous Driving Demonstration Zone, and multiple types of cells were classified to validate the model’s ability to characterize lane-level saturation and congestion propagation. The results show that the proposed method significantly improves lane-level prediction accuracy during peak hours compared to traditional models. Early intervention on key cells can reduce average vehicle travel time by 28.3%, providing a data-driven large-model solution for real-time congestion warning, mitigation strategy formulation, and integrated vehicle-road-cloud applications in intelligent transportation systems.
-
表 1 Qwen3-30b数据流
Table 1. Data flow of Qwen3-30B
数据流 参数 类型 输入 model 字符串 messages 列表 result_format 字符串 输出 request_id 字符串 output 列表 usage.input_tokens 整数 usage.output_tokens 整数 表 2 多模态语义认知数据集示例
Table 2. Multimodal semantic cognition dataset
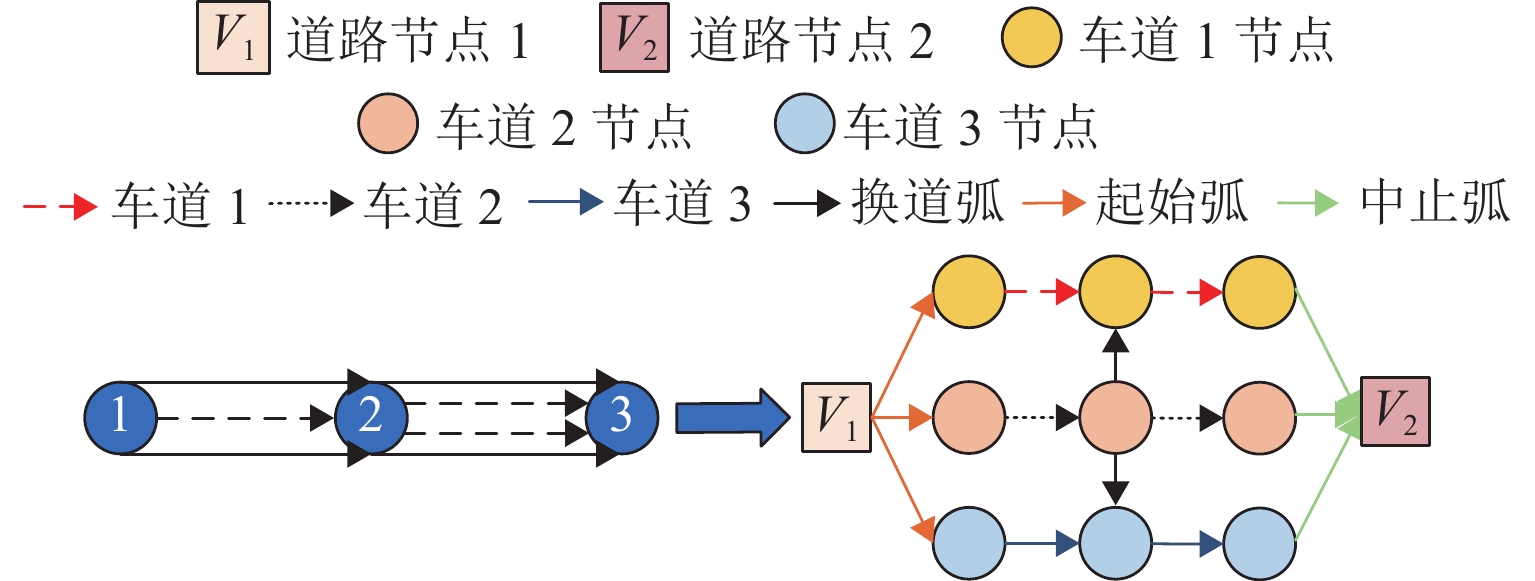
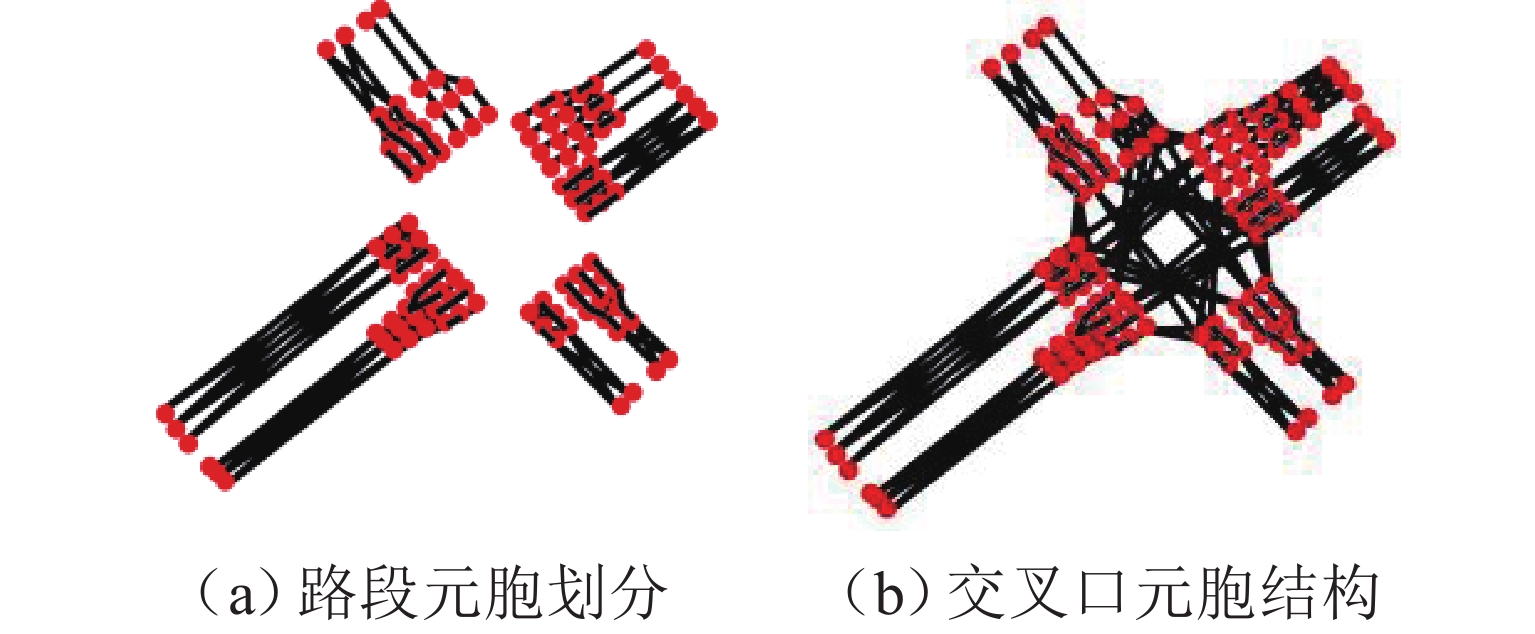
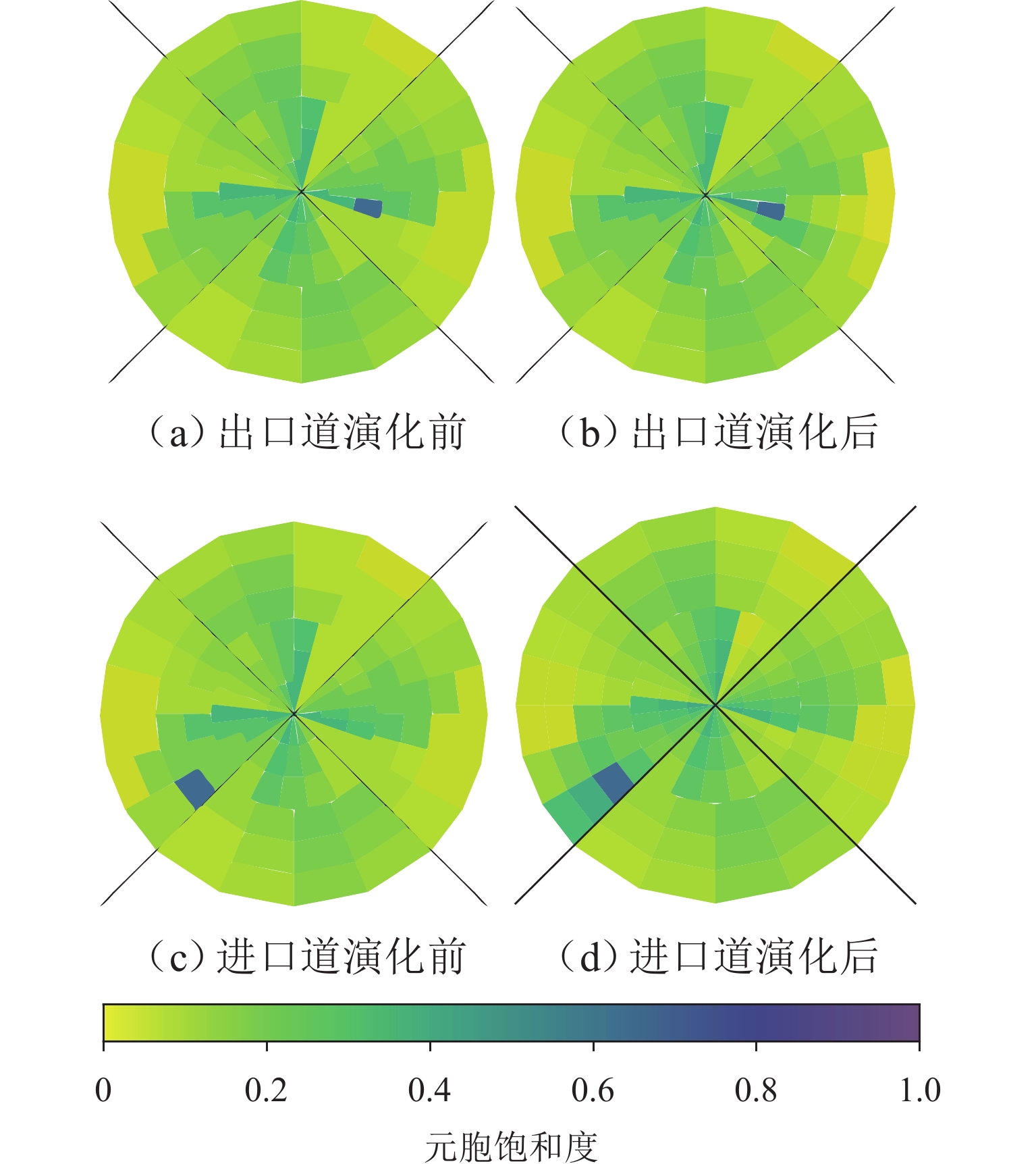
obj_id position_x position_y position_z speed_x speed_y speed_z heading 17863 39.81342 116.5163 21.37064 6.128467 8.729830 0 144.9297 17872 39.81393 116.5157 21.55035 0 0 0 145.8901 17911 39.81384 116.5158 21.46605 0 0 0 178.1357 17929 39.81352 116.5162 21.39956 5.745960 8.207440 0 145.0007 17940 39.81404 116.5158 21.49099 6.401353 − 9.664500 0 146.4705 17944 39.81464 116.5156 21.71785 0.525014 0.530456 0 44.61958 17951 39.81388 116.5158 21.58009 2.459119 − 3.6298800 0 146.3079 表 3 单交叉口元胞划分属性表
Table 3. Attribute table of cell partitioning for single intersection
元胞类型 数量/个 处理单元 交通流移动范围 拥堵传播方向 普通路段元胞 58 路段MEC 各元胞向下游与横向传播 各元胞间全向传播 交叉口进口元胞 42 路口MEC 各元胞向下游传播 展宽段纵向 + 出口道全向 超级元胞 20 云端 其他交叉口向当前超级元胞 超级元胞向上游普通元胞 表 4 各模型态势推演结果评估指标
Table 4. Evaluation indicators for situation evolution results
模型 MAE RMSE MAPE/% HA 2.88 5.59 6.80 ARIMA 1.62 3.30 3.50 STGCN 1.36 2.96 2.90 DCRNN 1.38 2.95 2.90 GWNet 1.30 2.74 2.73 Micro-CTM 1.05 2.11 2.10 -
[1] 卢春房, 马成贤, 江媛, 等. 中国车路协同产业研究与发展对策建议[J]. 中国公路学报, 2023, 36(3): 225-233.LU Chunfang, MA Chengxian, JIANG Yuan, et al. Countermeasure suggestions of development and research for vehicle infrastructure cooperation industry in China[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2023, 36(3): 225-233. [2] 肖建力, 邱雪, 张扬, 等. 交通大模型综述[J]. 交通运输工程学报, 2025, 25(01): 8-28.XIAO Jianli, QIU Xue, ZHANG Yang, et al. Review of Traffic Foundation Model[J]. Journal of Traffic and Transportation Engineering, 2025, 25(01): 8-28. [3] 潘磊, 袁鸿霄, 钟准, 等. 基于大模型构建图网络的事件因果关系识别[J/OL]. 西南交通大学学报: 1-10[2025-09-05]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/51.1277.u.20250408.1541.004.html.PAN Lei, YUAN Hongxiao, ZHONG Zhun, et al. Event Causal Identification Based on Large Language Model-Constructed Graph Networks [J/OL]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2025: 1-10[2025-09-05]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/51.1277.u.20250408.1541.004.html. [4] 童旭东, 周强, 顾晶晶, 等. 基于预训练时空自注意力大模型的交通流量预测[J/OL]. 小型微型计算机系统: 1-8[2025-09-05]. https://doi.org/10.20009/j.cnki.21-1106/TP.2025-0155.TONG Xudong, ZHOU Qiang, GU Jingjing, et al. Pre-trained Spatio-Temporal Attention Model for Traffic Flow Prediction [J/OL]. Journal of Chinese Computer Systems: 1-8[2025-09-05]. https://doi.org/10.20009/j.cnki.21-1106/TP.2025-0155. [5] 冯婷薇, 杨达, 刘家威, 等. 融合多源时序数据的车辆换道全过程检测方法研究[J/OL]. 西南交通大学学报, 1-12[2025-09-11]. https://link.cnki.net/urlid/51.1277.u.20250417.1012.002.FENG Tingwei, YANG Da, LIU Jiawei, et al. Research on the Whole Vehicle Lane-changing Process Detection Method Based on Multi-source Temporal Data Fusion [J/OL]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 1-12[2025-09-11]. https://link.cnki.net/urlid/51.1277.u.20250417.1012.002. [6] 王庞伟, 何昕泽, 张龙, 等. 智能网联环境下城市道路多源交通数据补全方法[J]. 中国公路学报, 2025, 38(01): 281-293.WANG Pangwei, HE Xinze, ZHANG Long, et al. Multisource Traffic Data Completion Method for Urban Roads in Intelligent Connected Scenarios[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2025, 38(01): 281-293. [7] WANG Pangwei, LIU Cheng, ZHANG Juan, et al. DS-UKF-based positioning method for intelligent connected vehicles in urban intersection scenarios[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2023, 25(6): 6118-6132. doi: 10.1109/tits.2023.3336770 [8] ZUO Zhiqiang, LIU Zhengxuan, WANG Yijing. A survey of optimal control for mixed traffic system with vehicle-roadcloud integration[J]. Control and Decision, 2023, 38(3): 577-594 [9] ZHANG Siyao, FU Daocheng, LIANG Wenzhe, et al. Trafficgpt: viewing, processing and interacting with traffic foundation models[J]. Transport Policy, 2024, 150: 95-105. doi: 10.1016/j.tranpol.2024.03.006 [10] CUI Yaodong, HUANG Shucheng; ZHONG Jiaming, et al. Drivellm: Charting the path toward full autonomous driving with large language models[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Vehicles, 2023. [11] TANG Yihong , WANG Zhaokai, QU Ao, et al. Synergizing Spatial Optimization with Large Language Models for Open-Domain Urban Itinerary Planning[J/OL]. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2402.07204, 2024. [12] TIAN Yonglin, LI Xuan, ZHANG Hui, et al. VistaGPT: Generative parallel transformers for vehicles with intelligent systems for transport automation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Vehicles, 2023. [13] LI Xuan, LIU Enlu, SHEN Tianyu, et al. ChatGPT-based scenario engineer: A new framework on scenario generation for trajectory prediction[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Vehicles, 2024. [14] 吴精乙, 景峻, 贺熠凡, 等. 基于多模态大模型的高速公路场景交通异常事件分析方法[J]. 图学学报, 2024, 45(06): 1266-1276.WU Jingyi, JING Jun, HE Yifan, et al. Analysis Method for Traffic Abnormal Events in Highway Scenarios Based on Multimodal Foundation Model[J]. Journal of Graphics, 2024, 45(06): 1266-1276. [15] 王祥, 任浩, 谭国真, 等. 大语言模型协同强化学习的自动驾驶决策方法[J]. 交通运输系统工程与信息, 2025, 25(04): 137-146 + 161.WANG Xiang, REN Hao, TAN Guozhen, et al. Autonomous Driving Decision-Making Method Based on Large Language Model Collaborative Reinforcement Learning[J]. Journal of Transportation Systems Engineering and Information Technology, 2025, 25(04): 137-146 + 161. [16] WANG Maonan, PANG Aoyu, KAN Yuheng, et al. LLM-assisted light: leveraging large language model capabilities for human-mimetic traffic signal control in complex urban environments[J/OL]. (2024-03-13). https://arxiv.org/abs/2403.08337. [17] 周臻, 顾子渊, 曲小波, 等. 城市多模式交通大模型MT-GPT: 点线面的分层技术与应用场景[J]. 中国公路学报, 2024, 37(2): 253-274. doi: 10.19721/j.cnki.1001-7372.2024.02.020ZHOU Zhen, GU Ziyuan, QU Xiaobo, et al. Urban multimodal transportation generative pretrained transformer foundation model: hierarchical techniques and application scenarios of spot-corridor-network decomposition[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2024, 37(2): 253-274. doi: 10.19721/j.cnki.1001-7372.2024.02.020 [18] LIU C X, YANG S, XU Q X, et al. Spatial-temporal large language model for traffic prediction[C]//2024 25th IEEE International Conference on Mobile Data Management (MDM). Brussels: IEEE, 2024: 31-40. [19] KUMAR S V, VANAJAKSHI L. Short-term traffic flow prediction using seasonal ARIMA model with limited input data[J]. European Transport Research Review, 2015, 7(3): 21. doi: 10.1007/s12544-015-0170-8 [20] S V Kumar, L Vanajakshi. Short-term traffic flow prediction using seasonal arima model with limited input data[J]. European Transport Research Review, 7(3): 1–9, 2015. [21] CHANG S Y, WU H C, KAO Y C. Tensor extended Kalman filter and its application to traffic prediction[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2023, 24(12): 13813-13829. doi: 10.1109/TITS.2023.3299557 [22] 李珣, 程硕, 吴丹丹, 等. 车路协同下基于元胞自动机的精细交通流模型[J]. 西南交通大学学报, 2025, 60(01): 225-232. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.20220830LI Xun, CHENG Shuo, WU Dandan, et al. Refined Traffic Flow Model Based on Cellular Automaton Under Cooperative Vehicle Infrastructure System[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2025, 60(01): 225-232. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.20220830 [23] ZHAI C, WU W T, XIAO Y P. The jamming transition of multi-lane lattice hydrodynamic model with passing effect[J]. Chaos, Solitons & Fractals, 2023, 171: 113515. [24] AKOPOV A S, BEKLARYAN L A. Traffic improvement in Manhattan Road networks with the use of parallel hybrid biobjective genetic algorithm[J]. IEEE Access, 2024, 12: 19532-19552. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2024.3361399 [25] LI R N, QIN Y, LIU J, et al. Multipath based congestion propagation via information network interaction in IIoT[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2024, 20(6): 8512-8523. doi: 10.1109/TII.2024.3354306 [26] YE H N, LUO X, YE H N, et al. Cascading failure analysis on Shanghai metro networks: an improved coupled map lattices model based on graph attention networks[J]. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 2021, 19(1): 204. doi: 10.3390/ijerph19010204 [27] CHEN S Q, LÜ X. Adaptive network traffic control with approximate dynamic programming based on a non-homogeneous Poisson demand model[J]. Transportmetrica B: Transport Dynamics, 2024, 12(1): 2336029. doi: 10.1080/21680566.2024.2336029 [28] CHEN T, WANG Z W, XIANG J, et al. Analysis of mixed traffic flow characteristics based on cellular automata model under lane management measures[J]. Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and Its Applications, 2024, 654: 130177. doi: 10.1016/j.physa.2024.130177 -




 下载:
下载: