Fire Prevention Strategies for Min-Zhe Timber Arch Lounge Bridges Based on Digital Reconstruction
-
摘要:
当前闽浙木拱廊桥大都存在详尽图纸资料缺失问题,导致保护效果不佳,且在火灾蔓延规律和防灾方面的研究较为匮乏. 为解决这些问题,提出基于三维扫描-BIM参数化的数字重建技术构建木拱廊桥数字孪生体,基于BIM-FDS (fire dynamics simulator)分析木拱廊桥火灾蔓延规律和防火策略. 首先,通过现场三维扫描获得合龙桥原始点云模型,经配准、去噪、抽稀处理后,建立BIM参数化数字孪生体,计算其火灾荷载密度;其次,采用IFC格式文件实现BIM与FDS交互,建立木拱廊桥火灾数字孪生体,通过热释放速率(HRR)、火灾蔓延现象、能见度、温度、有害气体浓度等进行仿真分析,在FDS中通过模拟分析多个典型火源场景工况得出火灾蔓延规律;最后,探讨材料阻燃处理、桥面非燃化改造及喷淋布设等防火优化策略. 研究结果表明:木拱廊桥火灾荷载密度高达
4017.764 MJ/m2,远超国内外典型建筑,具有极高的火灾风险性;多个典型火源场景中,除去HRR突变值,拱结构、桥底工况的HRR峰值分别稳定在100、95 MW,桥中心、桥头工况的HRR峰值分别稳定在88、70 MW,桥侧底、桥顶工况的HRR在1000 s内未达到峰值,最大值分别为55、22 MW,因此,桥下起火的火灾风险性最大,桥面起火次之,屋顶起火和桥侧底面起火的火灾风险性相对较低;通过火灾仿真和多个火灾参数量化分析,证实了3种防火措施能延缓木拱廊桥火灾蔓延,且上下防火分区、木材阻燃、喷淋系统分别使得HRR峰值下降23、39、63 MW. 研究成果可作为木拱廊桥的信息存储、火灾蔓延量化分析以及预防性保护的依据,也可为文物建筑的长效安全运维提供技术支撑.Abstract:Currently, most Min-Zhe timber arch lounge bridges suffer from the lack of detailed blueprint documentation, leading to unsatisfactory preservation effects and insufficient research on fire spread patterns and disaster prevention. To solve these problems, a digital reconstruction technology based on three-dimensional scanning and BIM parameterization was proposed to construct the digital twins of timber arch lounge bridges, and a BIM-fire dynamics simulator (FDS) was used to analyze the fire spread patterns and fire prevention strategies of such bridges. Firstly, the original point cloud model of Helong Bridge was obtained through on-site three-dimensional scanning, and after registration, denoising, and thinning processes, a BIM parametric digital twin was established to calculate its fire load density. Secondly, the IFC format was adopted to realize the interaction between BIM and FDS, and the fire digital twin of the timber arch lounge bridge was established. Simulation analysis was conducted through parameters such as heat release rate (HRR), fire spread phenomenon, visibility, temperature, and harmful gas concentration, and the fire spread patterns were derived by simulating and analyzing multiple typical fire source scenarios in FDS. Finally, fire prevention optimization strategies such as material flame-retardant treatment, bridge deck non-combustible transformation, and sprinkler system layout were discussed. The research results indicate that the fire load density of the timber arch lounge bridge is as high as 4 017.764 MJ/m2, far exceeding that of typical Chinese and foreign buildings, thus posing an extremely high fire risk. Among multiple typical fire source scenarios, excluding HRR mutation values, the HRR peaks of the arch structure and bridge bottom working conditions are stable at 100 MW and 95 MW, respectively. The HRR peaks of the bridge center and bridge head working conditions are stable at 88 MW and 70 MW, respectively. The HRR of the bridge side bottom and bridge top working conditions does not reach the peak within 1 000 seconds, with maximum values of 55 MW and 22 MW. Therefore, the fire risk of ignition under the bridge is the highest, followed by ignition on the bridge deck, while the fire risks of roof ignition and ignition at the bridge side bottom are relatively low. Through fire simulation and quantitative analysis of multiple fire parameters, it is confirmed that the three fire prevention measures can delay the fire spread of timber arch lounge bridges, and the upper and lower fire compartments, wood flame retardancy, and sprinkler systems reduce the HRR peak by 23 MW, 39 MW, and 63 MW, respectively. The research results can serve as the basis for information storage, quantitative analysis of fire spread, and preventive protection of timber arch lounge bridges and provide technical support for the long-term safe operation and maintenance of cultural heritage buildings.
-
Key words:
- Min-Zhe timber arch lounge bridge /
- digital twin /
- fire prevention strategy /
- BIM /
- FDS
-
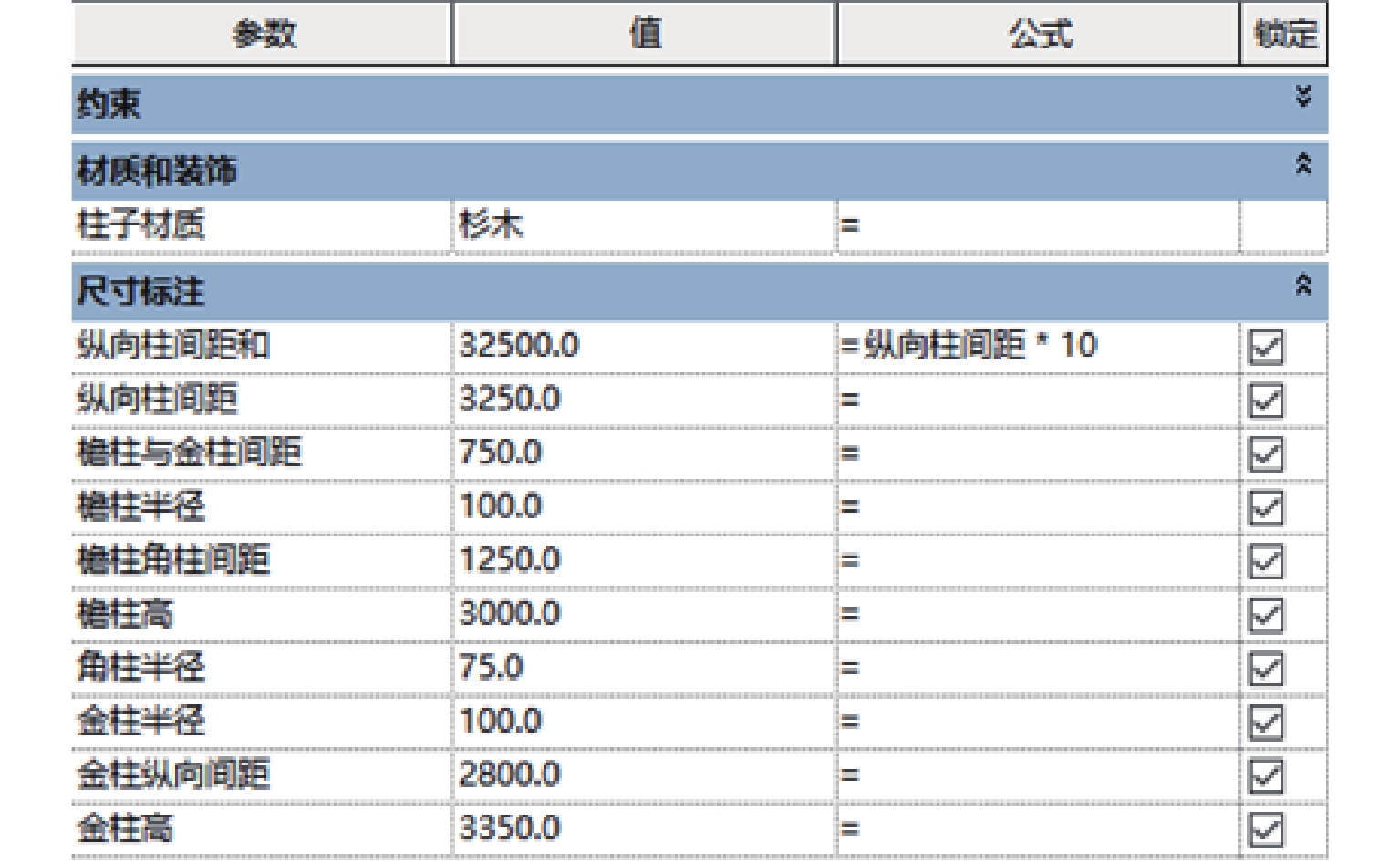
表 1 合龙桥固定火灾荷载统计
Table 1. Statistics of fixed fire load of Helong Bridge
可燃物 材质 V/m3 ρ/(kg·m3) q/(MJ·kg) QF/MJ 廊屋结构 杉木 39.440 400 18.77 296118.974 桥面结构 杉木 17.382 400 18.77 130504.056 拱结构 杉木 32.000 400 18.77 240256.000 松木 5.296 500 19.22 50894.560 表 2 不同火源位置下的火灾蔓延场景
Table 2. Fire spread scenarios under different fire source locations
工况 200 s 400 s 600 s 800 s 桥头 



桥中心 



桥底 



拱结构 



桥侧底 



桥顶 



表 3 木材阻燃处理前后热释放速率变化
Table 3. Variation in heat release rate of timber before and after flame-retardant treatment
材料类型 时间/s 热释放速率/(kw•m−2) 杉木 0 0 150 450 阻燃杉木 0 0 25 150 50 15 150 90 表 4 喷淋参数
Table 4. Sprinkler parameters
激活温
度/℃响应时间
指数/(m•s)0.5流量/
(L•min−1)射流
类型射流速
度/(m•s−1)粒子数/
(个•s)68.33 50 49.05 圆锥形 5 5000 -
[1] 杨艳, 陈宝春. 现存中国木拱桥结构调查与分析[J]. 福州大学学报(自然科学版), 2015, 43(6): 809-814.YANG Yan, CHEN Baochun. Investigation and analysis on existing China timber arch bridge structures[J]. Journal of Fuzhou University (Natural Science Edition), 2015, 43(6): 809-814. [2] 陈舒洁, 刘永健, 秋原雅人, 等. 基于文化遗产价值的闽浙木拱廊桥防火策略[J]. 建筑科学与工程学报, 2022, 39(6): 163-174.CHEN Shujie, LIU Yongjian, AKIHARA M, et al. Fire prevention strategy of wooden arch covered bridge in Min-Zhe area based on cultural heritage value[J]. Journal of Architecture and Civil Engineering, 2022, 39(6): 163-174. [3] 龚迪发. 福建木拱桥调查报告[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2013. [4] 国家质量监督检验检疫总局, 中国国家标准化管理委员会. 建筑材料及制品燃烧性能分级: GB 8624—2012[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2013. [5] HAN Y W, LIN Z C, PENG H J, et al. Public participation in architectural heritage conservation—the case of wooden arch corridor bridge “Qiansheng bridge”[J]. Sustainability, 2024, 16(4): 1581. doi: 10.3390/su16041581 [6] 刘妍. 匠艺的秘密与门槛——闽浙编木拱桥技术人类学研究[J]. 建筑学报, 2020(6): 28-33.LIU Yan. Thresholds and secrets of bridge-building craftsmanship an anthropological study on the building technology of woven arch bridges in southeast China[J]. Architectural Journal, 2020(6): 28-33. [7] CHEN S J, YANG Y, SHEN Z J. Impact of new construction activities of Min-Zhe wooden arch bridge in the conservation of its traditional building craftsmanship[J]. International Journal of Architectural Heritage, 2023, 17(8): 1207-1220. doi: 10.1080/15583058.2021.2023694 [8] CHEN S J, YANG Y, SHEN Z J, et al. Reconstruction of Min-Zhe wooden arch bridges and its legitimation as tangible and intangible heritage[J]. International Journal of Architectural Heritage, 2022, 16(12): 1779-1796. doi: 10.1080/15583058.2021.1908444 [9] YANG Y, NAKAMURA S, CHEN B C, et al. Mechanical behavior of Chinese woven timber arch bridges[J]. Engineering Structures, 2019, 195: 340-357. doi: 10.1016/j.engstruct.2019.05.068 [10] 张铮, 张博恒, 李振, 等. 闽浙木拱廊桥榫卯节点受力性能研究[J]. 林产工业, 2023, 60(7): 58-63, 74.ZHANG Zheng, ZHANG Boheng, LI Zhen, et al. Research on mechanical performance of mortise-tenon joints of Minzhe timber arch bridge[J]. China Forest Products Industry, 2023, 60(7): 58-63, 74. [11] 杨艳, 郑裔, 黄聪燕, 等. 闽浙编木拱桥燕尾榫节点力学模型[J]. 交通运输工程学报, 2024, 24(5): 113-130.YANG Yan, ZHENG Yi, HUANG Congyan, et al. Mechanical model of dovetail joints of Min-Zhe woven timber arch bridges[J]. Journal of Traffic and Transportation Engineering, 2024, 24(5): 113-130. [12] 姜绍飞, 李朋泽, 项程, 等. 基于无人机与图像轮廓提取的古石拱桥逆向建模方法[J/OL]. 西南交通大学学报, 2025: 1-9. (2025-09-22). https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/51.1277.U.20250922.1409.004.html. [13] 韩宜丹, 淳庆. 强风作用下木拱廊桥的风振响应分析——以文兴桥为例[J]. 文物保护与考古科学, 2021, 33(5): 102-112.HAN Yidan, CHUN Qing. Research on the response of arched timber lounge bridges under strong wind action: a case study of Wenxing Lounge Bridge[J]. Sciences of Conservation and Archaeology, 2021, 33(5): 102-112. [14] DENG H. Application of BIM technology in the seismic performance of “wood weaving” structure of wooden arcade bridges[J]. Shock and Vibration, 2022, 1: 8033059. [15] LI X R, CHUN Q, YUAN Y, et al. Research on flood resistance performance of traditional corridor woven arch bridges[J]. NPJ Heritage Science, 2025, 13: 328. doi: 10.1038/s40494-025-01909-2 [16] 缪小龙. 闽浙木拱廊桥防火研究[J]. 消防科学与技术, 2009, 28(12): 945-948.MIAO Xiaolong. Fire protection research on covered bridge in Fujian and Zhejiang[J]. Fire Science and Technology, 2009, 28(12): 945-948. [17] 陈秉安. 一起古木拱廊桥火灾事故的认定与分析[J]. 消防科学与技术, 2025, 44(1): 136-140.CHEN Bing’an. Identification and analysis of a fire accident of an ancient wooden arch covered bridge[J]. Fire Science and Technology, 2025, 44(1): 136-140. [18] 官丽莉, 周小勇, 罗艳. 我国植物热值研究综述[J]. 生态学杂志, 2005, 24(4): 452-457.GUAN Lili, ZHOU Xiaoyong, LUO Yan. A review on the study of plant caloric value in China[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2005, 24(4): 452-457. [19] 何介南, 康文星, 王东. 不同年龄阶段杉木人工林植物热值分析[J]. 生态学报, 2015, 35(2): 449-459.HE Jienan, KANG Wenxing, WANG Dong. The plant calorific values in the Chinese fir (cunninghamia lanceolata) plantations at different ages[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2015, 35(2): 449-459. [20] 刘妍. 编木拱桥: 技术与社会史[M]. 北京: 清华大学出版社, 2021. [21] 王金平. 我国典型既有建筑火灾荷载的标准值[C]//2013中国消防协会科学技术年会论文集. 北京: 中国科学技术出版社, 2013: 136-137. [22] 李胜利, 李孝斌. FDS火灾数值模拟[M]. 北京: 化学工业出版社, 2019. [23] 林鹏, 王国元, 司有亮, 等. 隧道火灾排烟口位置对排烟效率的影响[J]. 西南交通大学学报, 2019, 54(5): 1055-1062, 1112.LIN Peng, WANG Guoyuan, SI Youliang, et al. Influence of vent location on efficiency of smoke extraction in tunnel fire[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2019, 54(5): 1055-1062, 112. [24] HUANG H, SONG S S, SHUAI C X, et al. Layered double hydroxide-polyaniline nanofibers in lightweight aerogels for bioinspired flame-retardant wood[J]. ACS Applied Nano Materials, 2023, 6(6): 4105-4111. doi: 10.1021/acsanm.3c00195 [25] XUE M M, XU J, LI Y, et al. Flame retardant effect of lignin/carbon nanohorns/potassium carbonate composite flame retardant on fir pretreated under different methods[J]. Thermochimica Acta, 2024, 731: 179641. doi: 10.1016/j.tca.2023.179641 [26] TIAN F Y, MAO W, XU X W. Effect of a layered combination of APP and TBC on the mechanics and flame retardancy of poplar strandboards[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2023, 401: 132881. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2023.132881 [27] 陈希磊. 阻燃丙烯酸酯单体/低聚物的合成及其涂层热降机理与性能研究[D]. 合肥: 中国科学技术大学, 2008. [28] PING P, GAO X Z, KONG D P, et al. Experimental study on the synergistic strategy of liquid nitrogen and water mist for fire extinguishing and cooling of lithium-ion batteries[J]. Process Safety and Environmental Protection, 2024, 188: 713-725. doi: 10.1016/j.psep.2024.05.077 -





 下载:
下载: