Ancient Stone Arch Bridge Inverse Modeling Method Based on UAV and Image Contour Extraction
-
摘要:
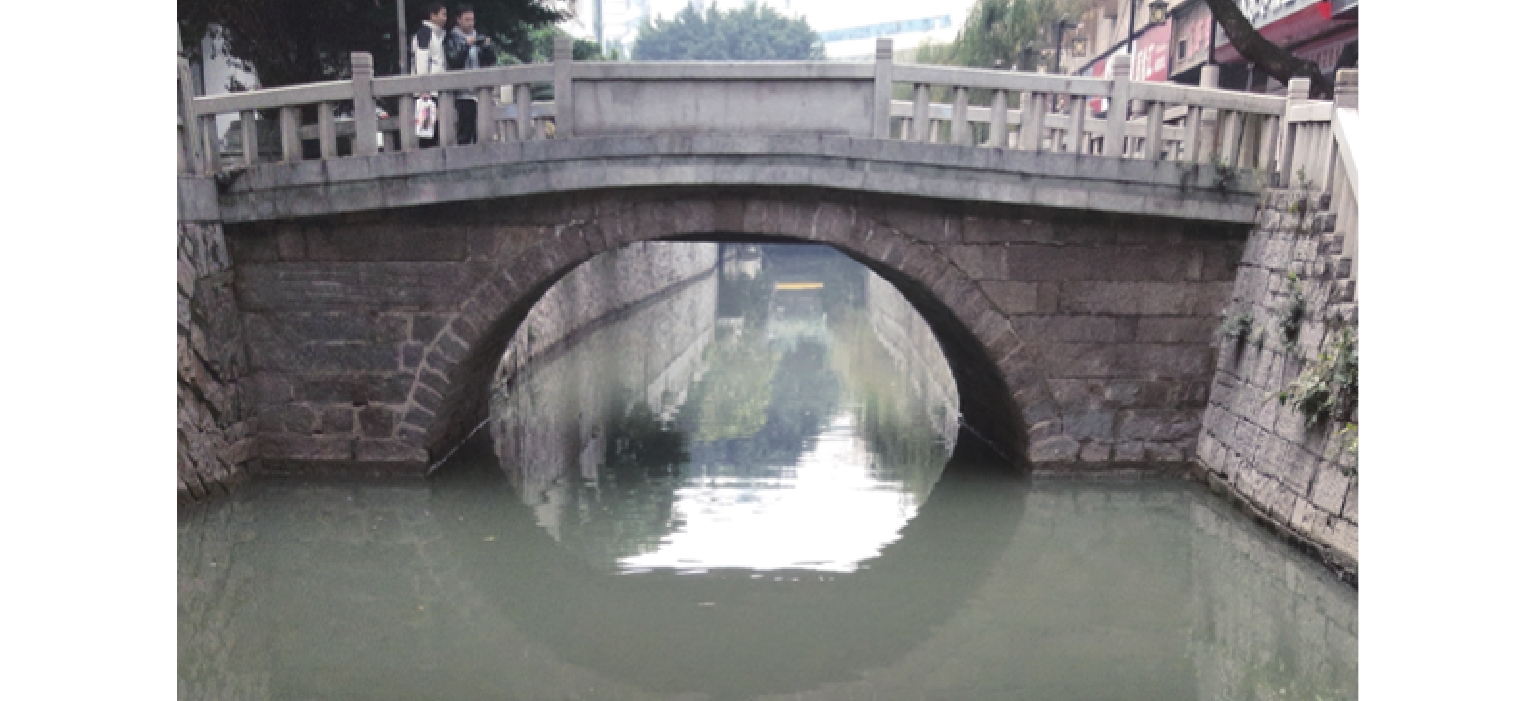
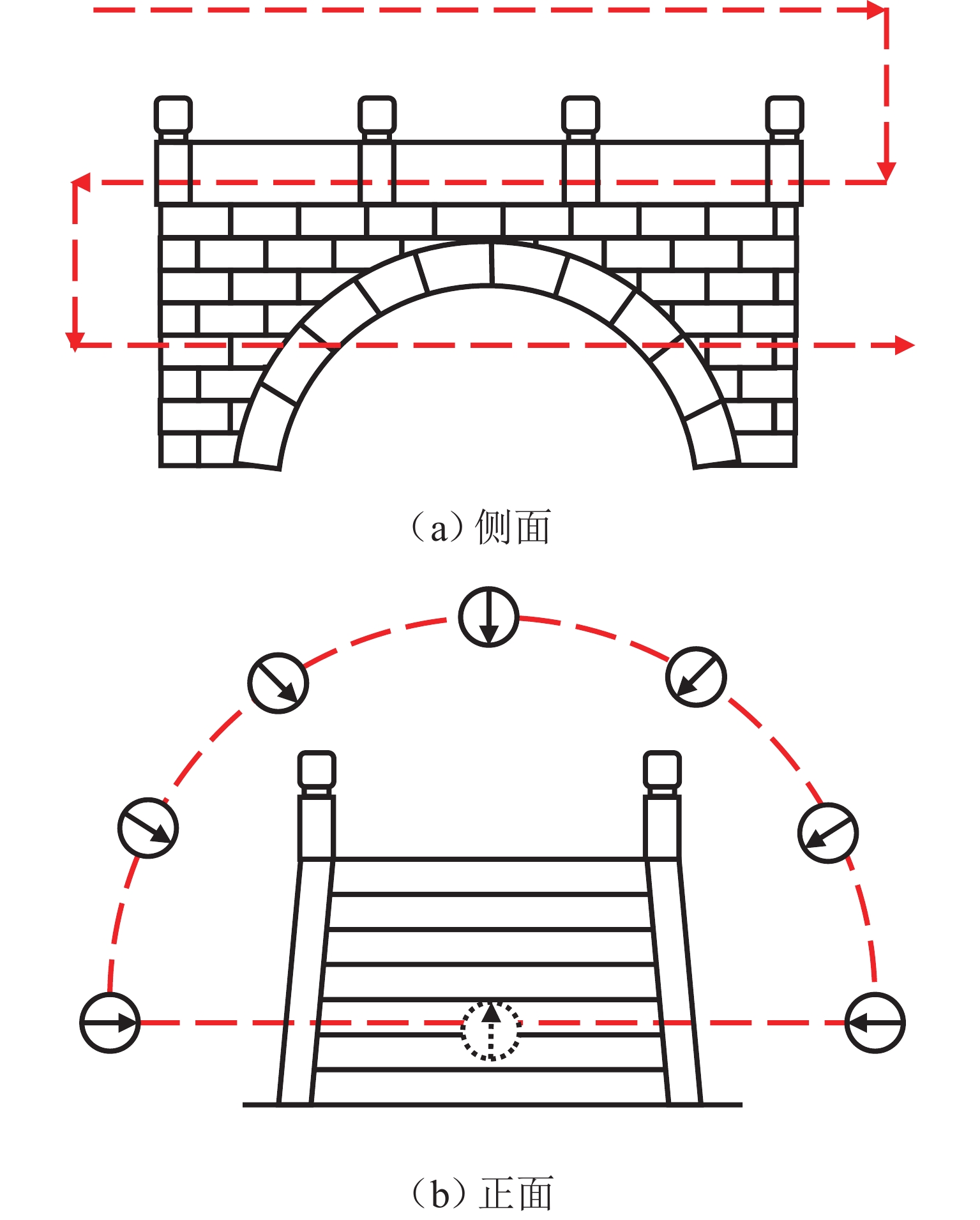
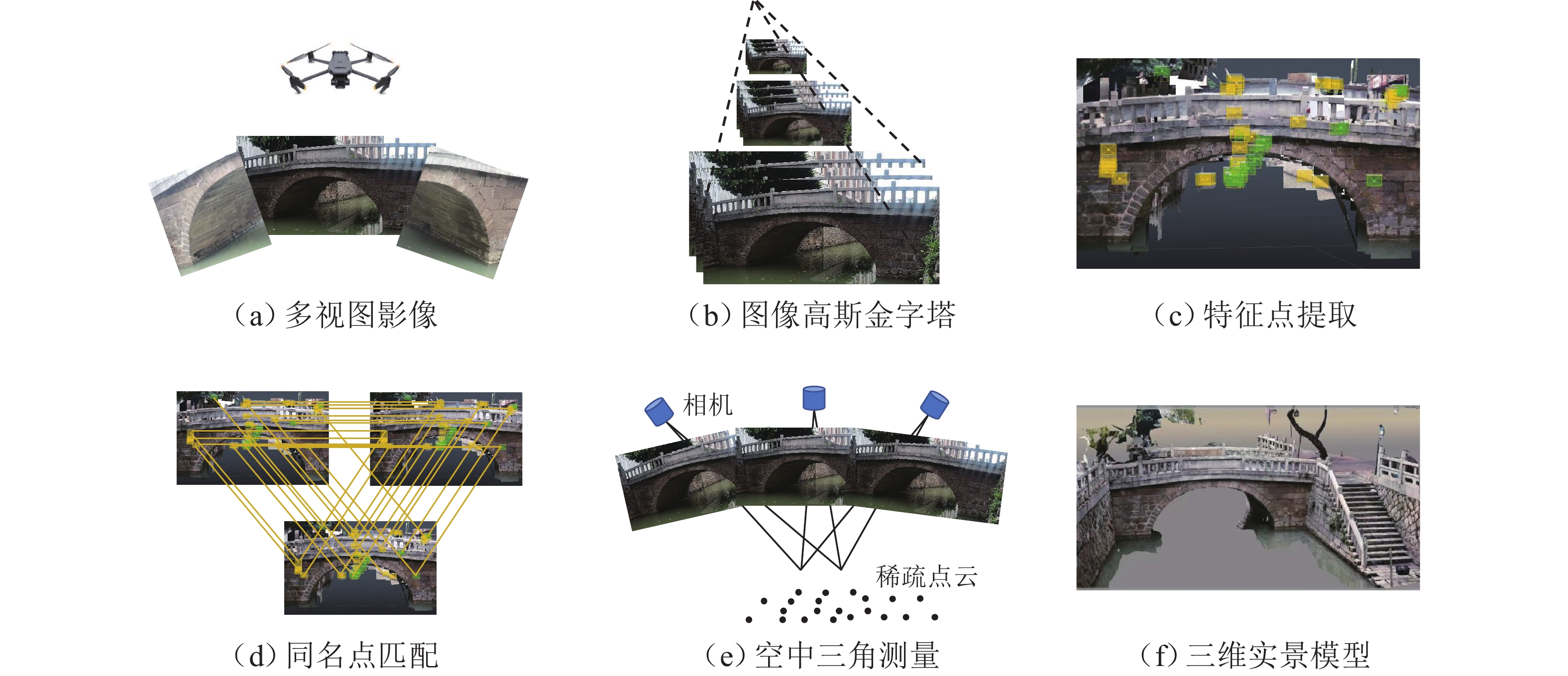
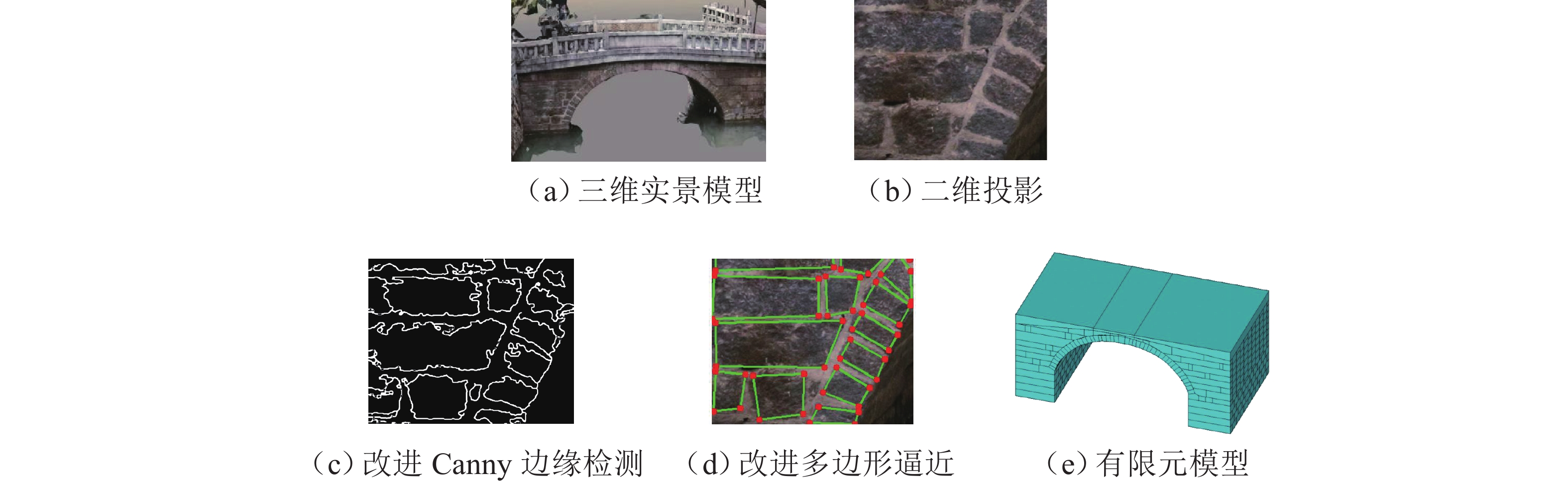
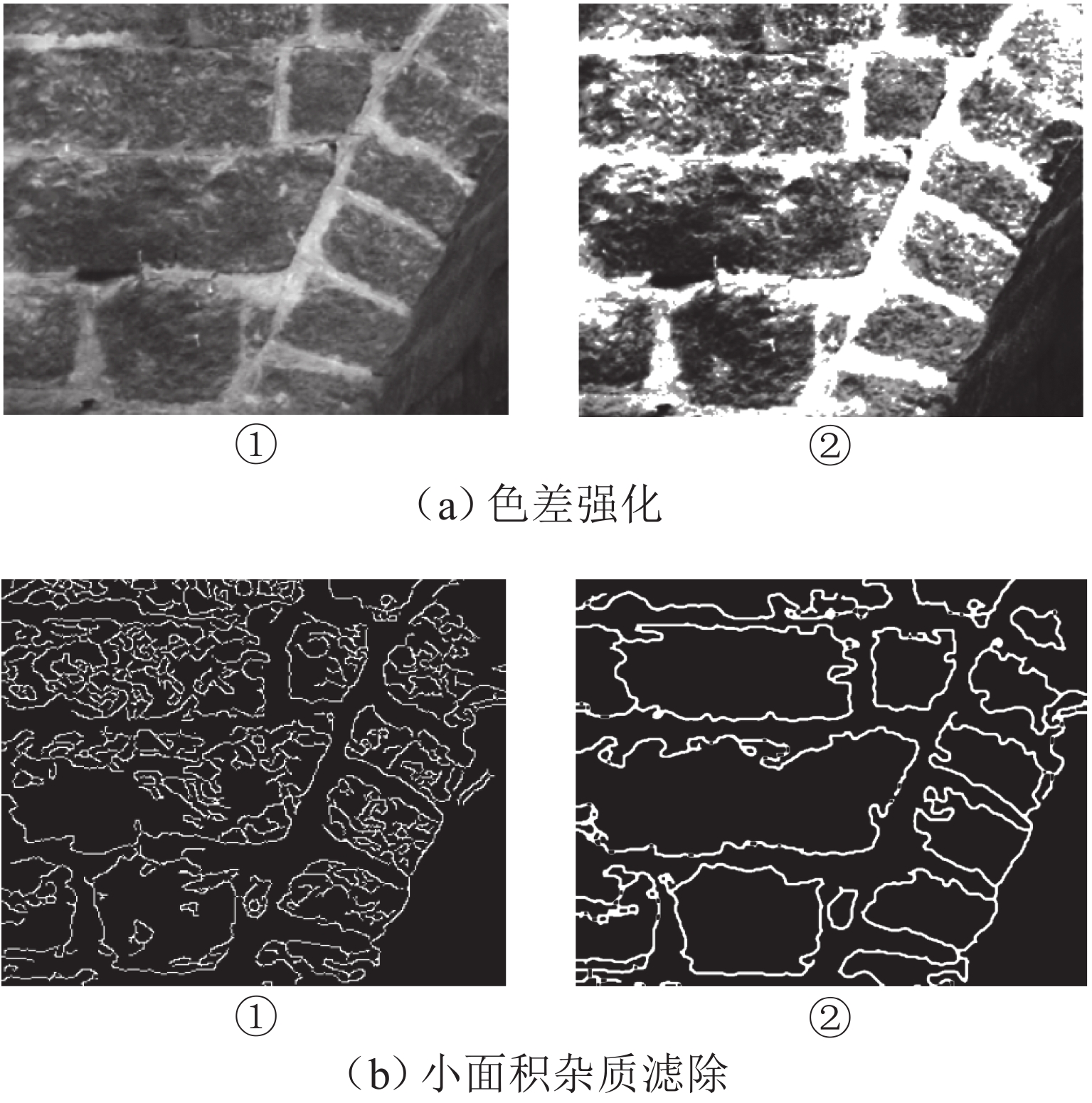
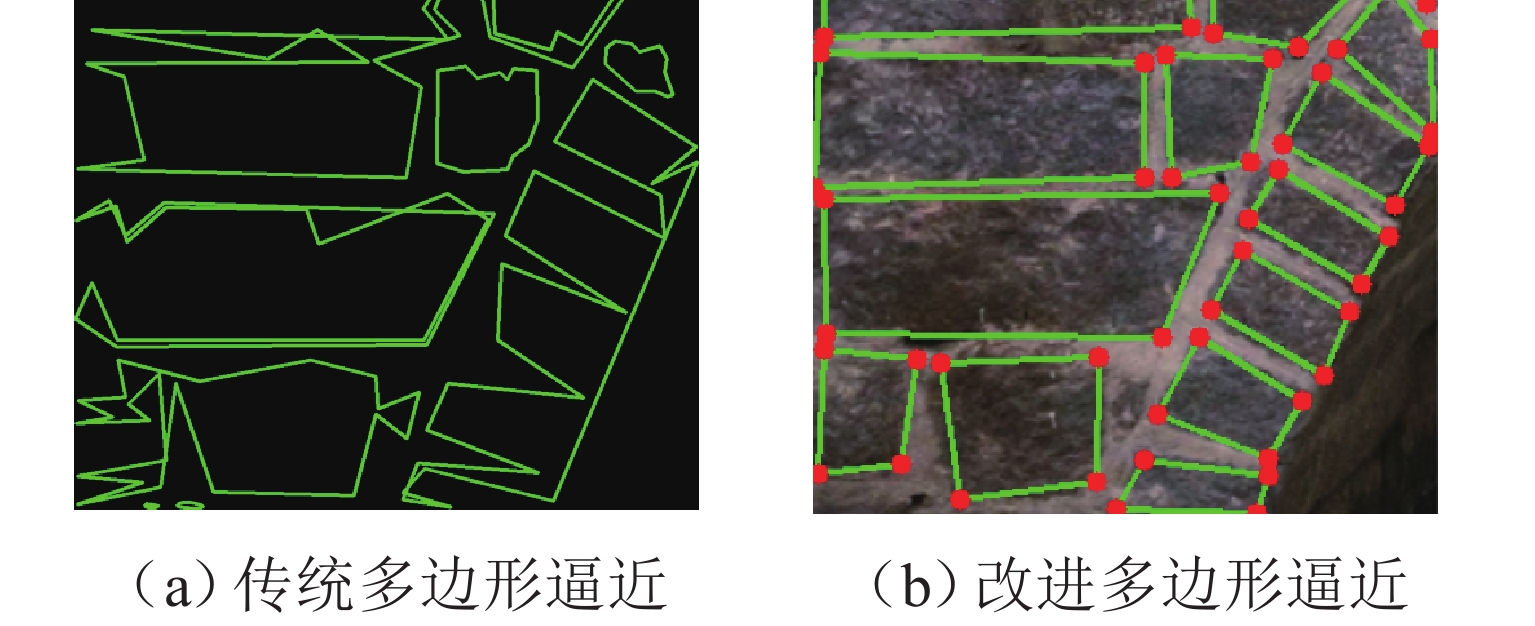
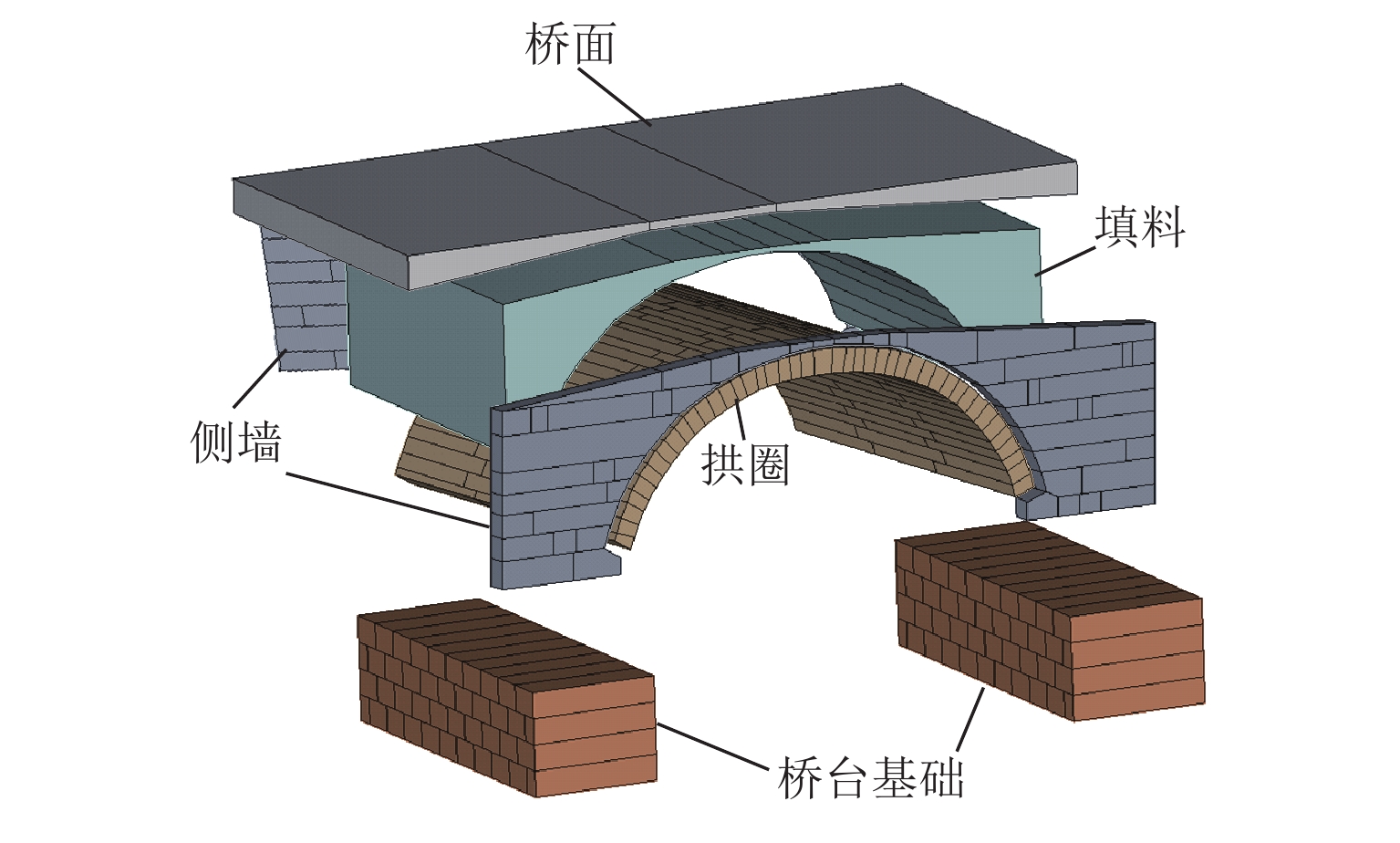
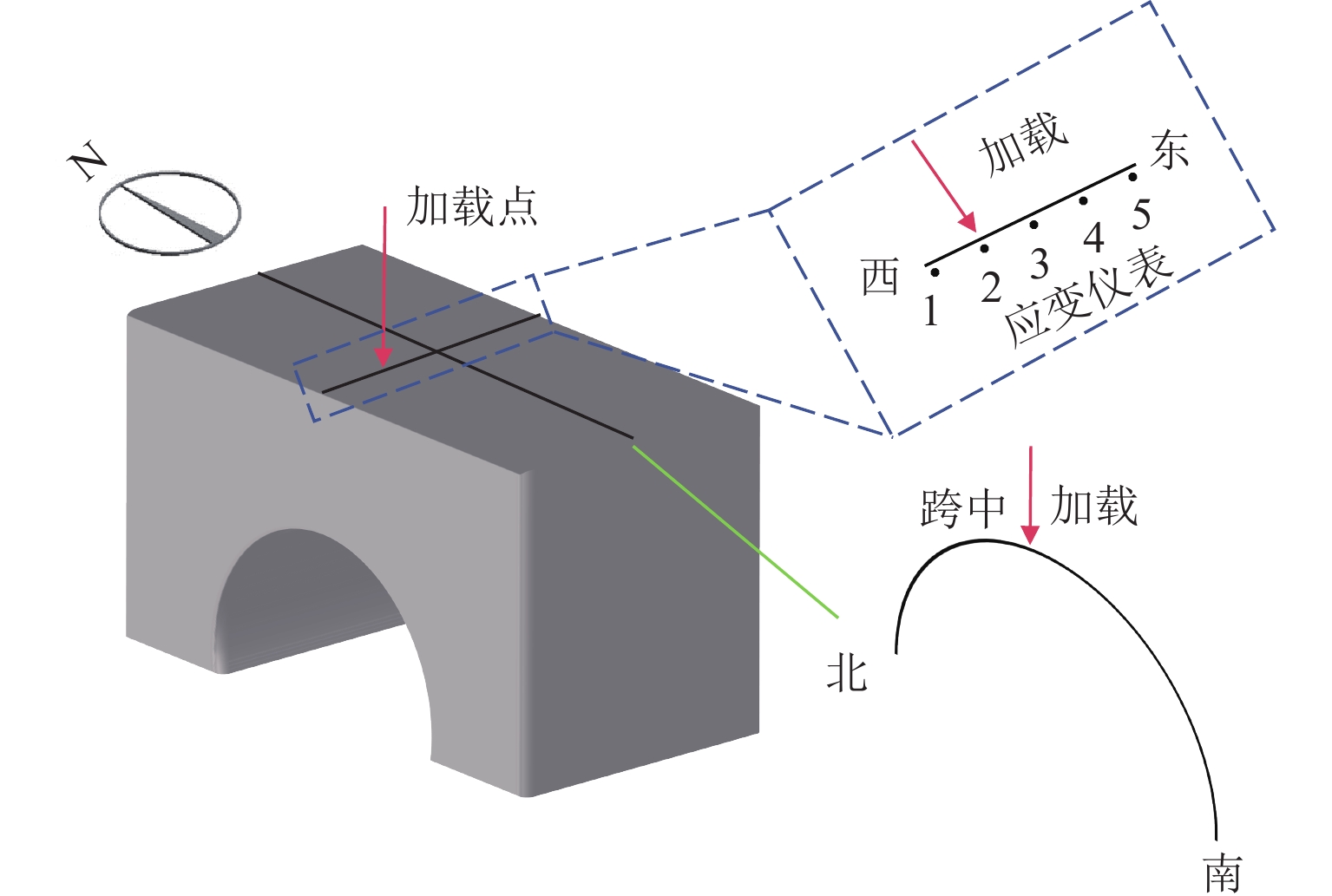
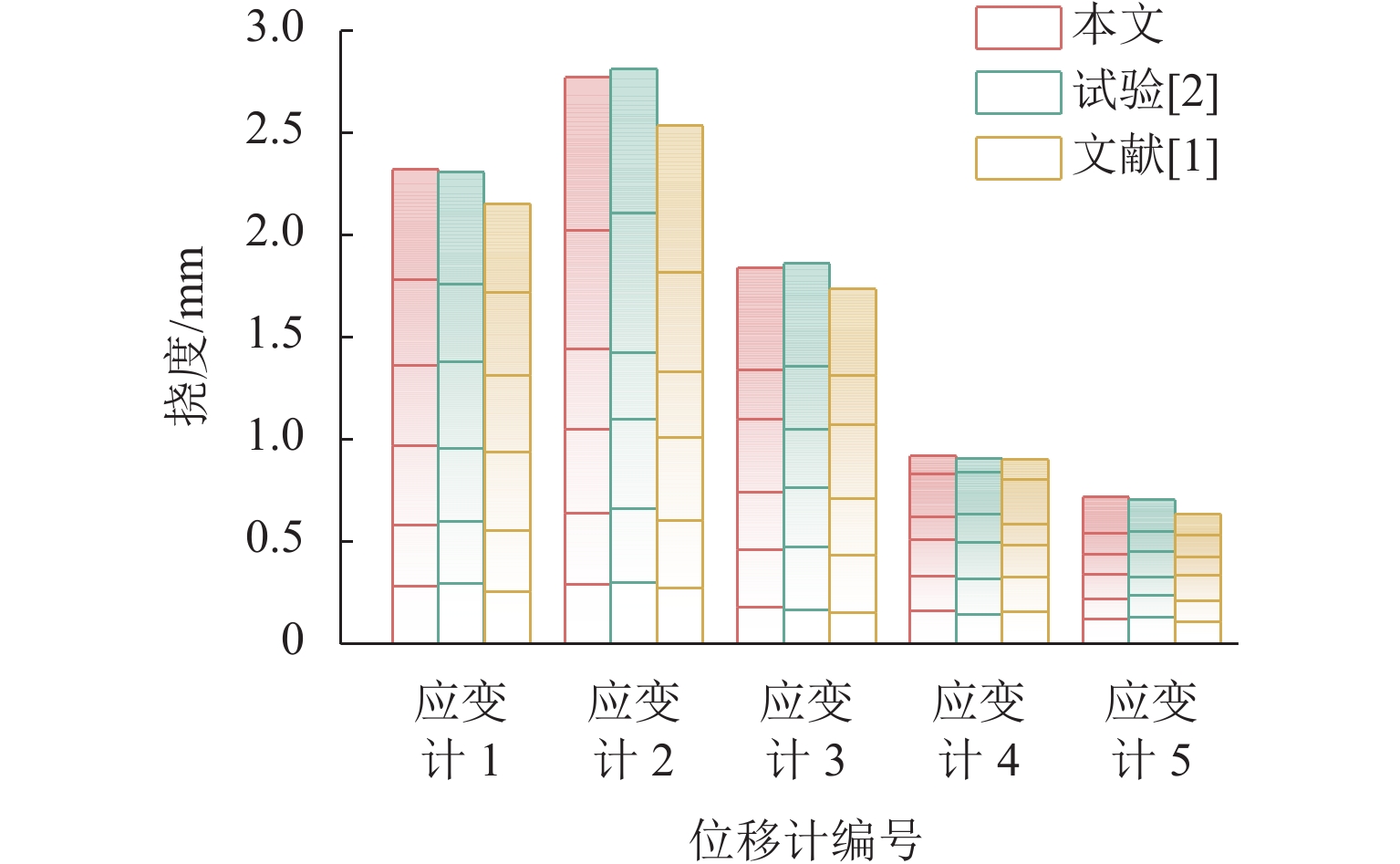
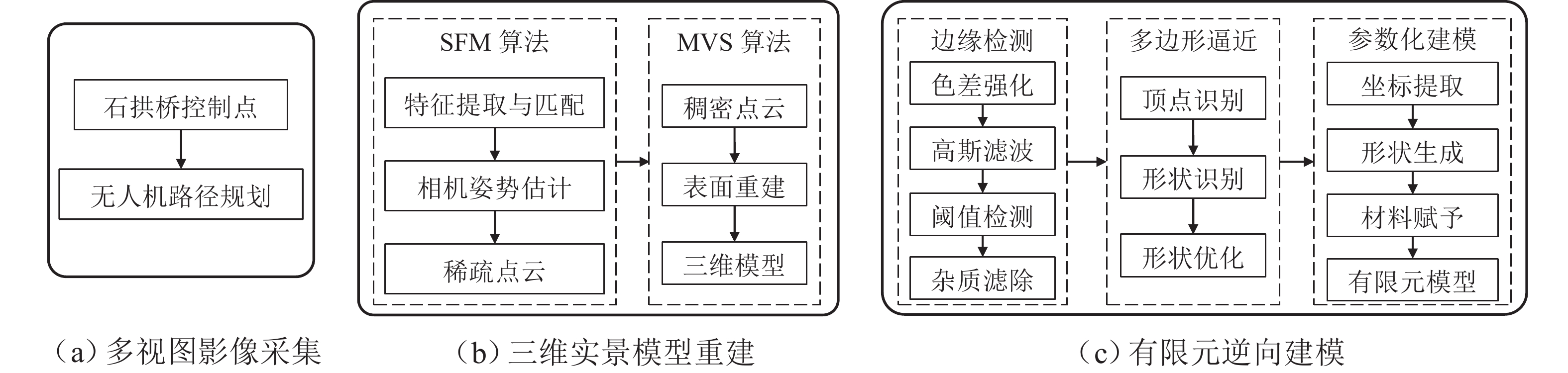
为实现古石拱桥数字化建模与性能评估,基于无人机倾斜摄影和图像轮廓提取技术开展古石拱桥逆向建模方法研究. 首先,使用无人机采集石拱桥的多视角序列图像;其次,基于运动恢复结构(SfM)和多视图立体匹配(MVS)算法,构建石拱桥的三维(3D)实景模型;接着,基于石块与砂浆存在色差和石块几何规则性的特点,提出色差强化与小面积杂质滤除策略,改进Canny边缘检测,引入循环识别四边形与形状优化改进多边形逼近算法,实现表面轮廓的自动化识别;然后,基于地面控制点标定真实尺度,利用提取的轮廓坐标参数化建模,生成有限元模型;最后,使用提出方法对透龙桥进行建模和性能分析,并与试验结果进行对比. 研究结果表明:透龙桥3D实景模型表面未检出明显病害,最大尺寸误差为0.8%;有限元模型的挠度最大计算误差为2.1%. 该方法能够准确反映古石拱桥的几何形态和力学性能,为其数字化保护与性能评估提供技术支持.
Abstract:To achieve digital modeling and performance evaluation of ancient stone arch bridges, the reverse modeling method was explored based on unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) oblique photography and image contour extraction technology. Firstly, the UAV was used to collect multi-view sequence images of the stone arch bridge. Secondly, based on the structure from motion (SfM) and multi-view stereo (MVS) algorithms, a three-dimensional (3D) model of stone arch bridges was constructed. Then, based on the characteristics of color difference between stone blocks and mortar, as well as the geometric regularity of stone blocks, strategies of color difference enhancement and small-area impurity filtering were proposed to improve the Canny edge detection. Subsequently, the real scale was calibrated based on ground control points, and the finite element model was generated through parametric modeling using the extracted contour coordinates. Finally, the proposed method was applied to model the Toulong Bridge and analyze its performance, and compared with experimental results. The study has shown that no obvious diseases are detected on the surface of the 3D real-scene model of the Toulong Bridge, with the maximum dimensional error of 0.8%. The maximum calculation error of the deflection of the finite element model is 2.1%. These indicate that the method can accurately reflect the geometric shape and mechanical properties of ancient stone arch bridges, providing technical support for their digital protection and performance evaluation.
-
[1] MAJTAN E, CUNNINGHAM L S, ROGERS B D. Numerical study on the structural response of a masonry arch bridge subject to flood flow and debris impact[J]. Structures, 2023, 48: 782-797. doi: 10.1016/j.istruc.2022.12.100 [2] 罗英, 唐寰澄. 中国石拱桥研究[M]. 北京: 人民交通出版社, 1993. [3] 张承文, 淳庆, 花全均, 等. 基于元遗传算法的石拱桥传感器优化布置及评价方法研究[J/OL]. 西南交通大学学报, 2024: 1-11. (2024-10-10). https://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=XNJT20240913002&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ. [4] 王威, 姜绍飞, 宋华霖, 等. 基于轻量化网络与迁移学习的桥梁水下桩墩结构表观病害轮廓提取[J]. 中国公路学报, 2024, 37(2): 88-99.WANG Wei, JIANG Shaofei, SONG Hualin, et al. Extracting surface defect contours of bridge underwater pile-pier structures based on lightweight network and transfer learning[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2024, 37(2): 88-99. [5] XIE Y, TEO M X, LI S Y, et al. As-built BIM reconstruction of piping systems using smartphone videogrammetry and terrestrial laser scanning[J]. Automation in Construction, 2023, 156: 105120. doi: 10.1016/j.autcon.2023.105120 [6] TRUONG-HONG L, LINDENBERGH R. Automatically extracting surfaces of reinforced concrete bridges from terrestrial laser scanning point clouds[J]. Automation in Construction, 2022, 135: 104127. doi: 10.1016/j.autcon.2021.104127 [7] 朱军, 张传军, 赵剑峰, 等. 知识引导的铁路站场接触网点云导线特征智能提取方法[J]. 西南交通大学学报, 2026, 60(6): 1333-1341.ZHU Jun, ZHANG Chuanjun, ZHAO Jianfeng, et al. Intelligent extraction method of overhead catenary point cloud wire features of railway stations guided by knowledge[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2026, 60(6): 1333-1341. [8] HU D F, GAN V J L, YIN C. Robot-assisted mobile scanning for automated 3D reconstruction and point cloud semantic segmentation of building interiors[J]. Automation in Construction, 2023, 152: 104949. doi: 10.1016/j.autcon.2023.104949 [9] 朱庆, 姜兆奕, 吴浩宇, 等. 基于体素的隧道破碎围岩多特征融合建模方法[J/OL]. 西南交通大学学报, 2025: 1-10. (2025-06-09). https://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=XNJT20250530001&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ. [10] LI W J, HU Z H, MENG L X, et al. Weakly supervised 3-D building reconstruction from monocular remote sensing images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2024, 62: 5615315. [11] CUSSON D, STEWART H. Satellite synthetic aperture radar, multispectral, and infrared imagery for assessing bridge deformation and structural health: a case study at the Samuel de Champlain bridge[J]. Remote Sensing, 2024, 16(4): 614. doi: 10.3390/rs16040614 [12] 孙彪, 韩珣, 杨时俊, 等. 基于因子组稀疏正则的多时相遥感图像去云方法[J/OL]. 西南交通大学学报, 2025: 1-11. (2025-01-02). https://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=XNJT2024123000A&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ. [13] XU Y, ZHANG J. UAV-based bridge geometric shape measurement using automatic bridge component detection and distributed multi-view reconstruction[J]. Automation in Construction, 2022, 140: 104376. doi: 10.1016/j.autcon.2022.104376 [14] YASIN YIĞIT A, UYSAL M. Virtual reality visualisation of automatic crack detection for bridge inspection from 3D digital twin generated by UAV photogrammetry[J]. Measurement, 2025, 242: 115931. [15] GIL-DOCAMPO M L, PERALEDA-VÁZQUEZ S, ORTIZ SANZ J, et al. 3D scanning of hard-to-reach objects using SfM-MVS photogrammetry and a low-cost UAS[J]. IEEE Access, 2024, 12: 70405-70419. [16] OLASZEK P, MACIEJEWSKI E, RAKOCZY A, et al. Remote inspection of bridges with the integration of scanning total station and unmanned aerial vehicle data[J]. Remote Sensing, 2024, 16(22): 4176. doi: 10.3390/rs16224176 [17] 周云, 刘鹏, 郝官旺, 等. 基于无人机倾斜摄影技术的桥梁有限元逆向建模方法研究[J]. 湖南大学学报(自然科学版), 2023, 50(9): 13-23.ZHOU Yun, LIU Peng, HAO Guanwang, et al. Method on inverse establishment of bridge finite element model based on UAV oblique photography technology[J]. Journal of Hunan University (Natural Sciences), 2023, 50(9): 13-23. [18] 马如进, 董一庆, 潘子超, 等. 基于消费级无人机的古桥三维重构分析[J]. 华南理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2019, 47(6): 94-100, 126.MA Rujin, DONG Yiqing, PAN Zichao, et al. Analysis of 3D reconstruction of ancient bridge based on consumer-grade unmanned aerial vehicle[J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2019, 47(6): 94-100, 126. [19] VAN BOGAERT P, DE BACKER H. The effects of river torrents and debris on historic masonry vaulted arch bridges[J]. Buildings, 2024, 14(1): 54. [20] TUBALDI E, MACORINI L, IZZUDDIN B A. Three-dimensional mesoscale modelling of multi-span masonry arch bridges subjected to scour[J]. Engineering Structures, 2018, 165: 486-500. doi: 10.1016/j.engstruct.2018.03.031 [21] SCOZZESE F, RAGNI L, TUBALDI E, et al. Modal properties variation and collapse assessment of masonry arch bridges under scour action[J]. Engineering Structures, 2019, 199: 109665. doi: 10.1016/j.engstruct.2019.109665 [22] PANTÒ B, ORTEGA J, GROSMAN S, et al. Advanced calibration of a 3D masonry arch bridge model using non-destructive testing and numerical optimisation[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2024, 438: 137131. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2024.137131 [23] 王子娟, 刘新荣, 傅晏, 等. 两种岩石试件的“超声-回弹-密度” 综合筛选法研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2018, 37(增1): 3575-3583.WANG Zijuan, LIU Xinrong, FU Yan, et al. Study on comprehensive screening method of “ ultrasonic-rebound-density ” for two kinds of rock specimens[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2018, 37(S1): 3575-3583. [24] HAN Y D, CHUN Q, GAO X Y. Flood-induced forces and collapse mechanism of historical multi-span masonry arch bridges: the Putang bridge case[J]. Engineering Failure Analysis, 2023, 153: 107564. doi: 10.1016/j.engfailanal.2023.107564 [25] 沈圣, 孙宇, 王耀, 等. 基于力学性能指标与耐久性能指标联合的夯土改性配比优化设计方法[J]. 土木工程学报, 2024, 57(5): 1-14.SHEN Sheng, SUN Yu, WANG Yao, et al. Design method for optimum mix proportion of modified rammed earth based on combination of mechanical and durability performance indexes[J]. China Civil Engineering Journal, 2024, 57(5): 1-14. -




 下载:
下载: