Game-Theoretic Lane-Changing Decision-Making for Autonomous Vehicles
-
摘要:
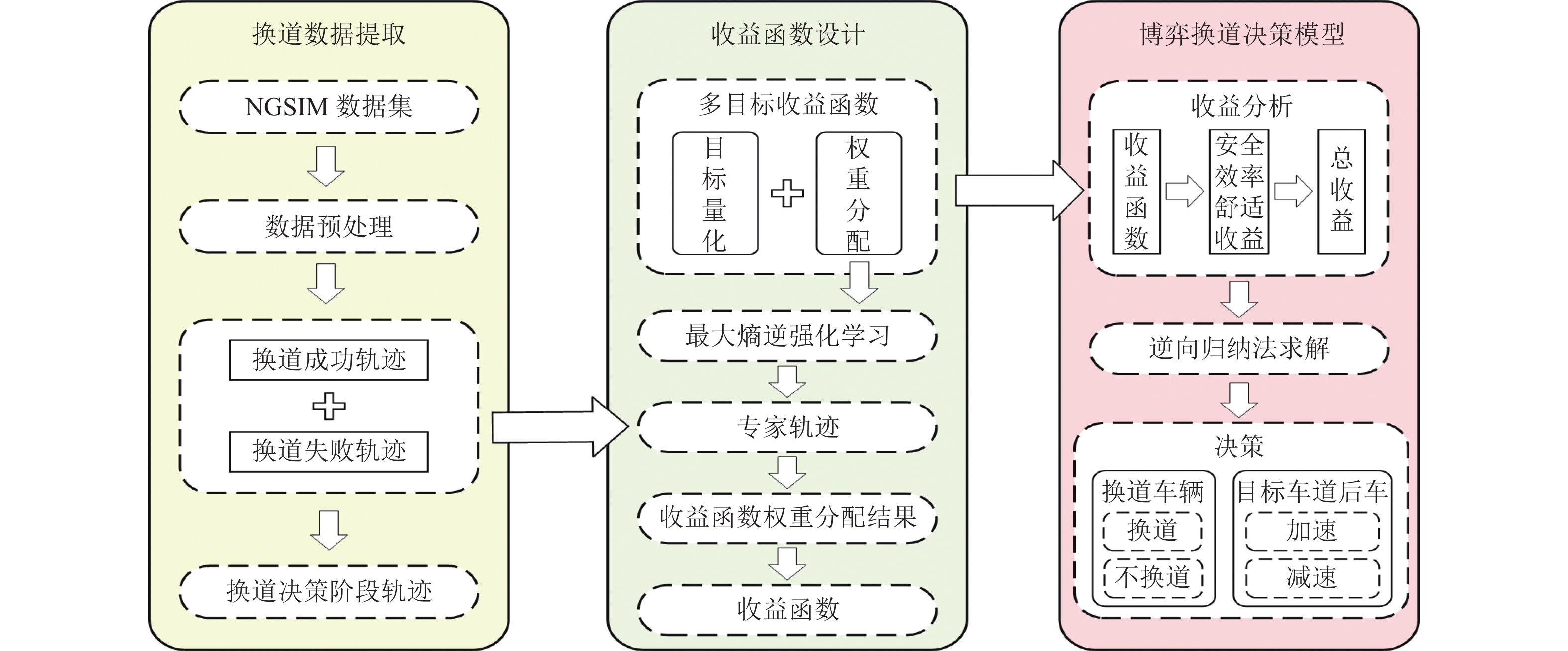
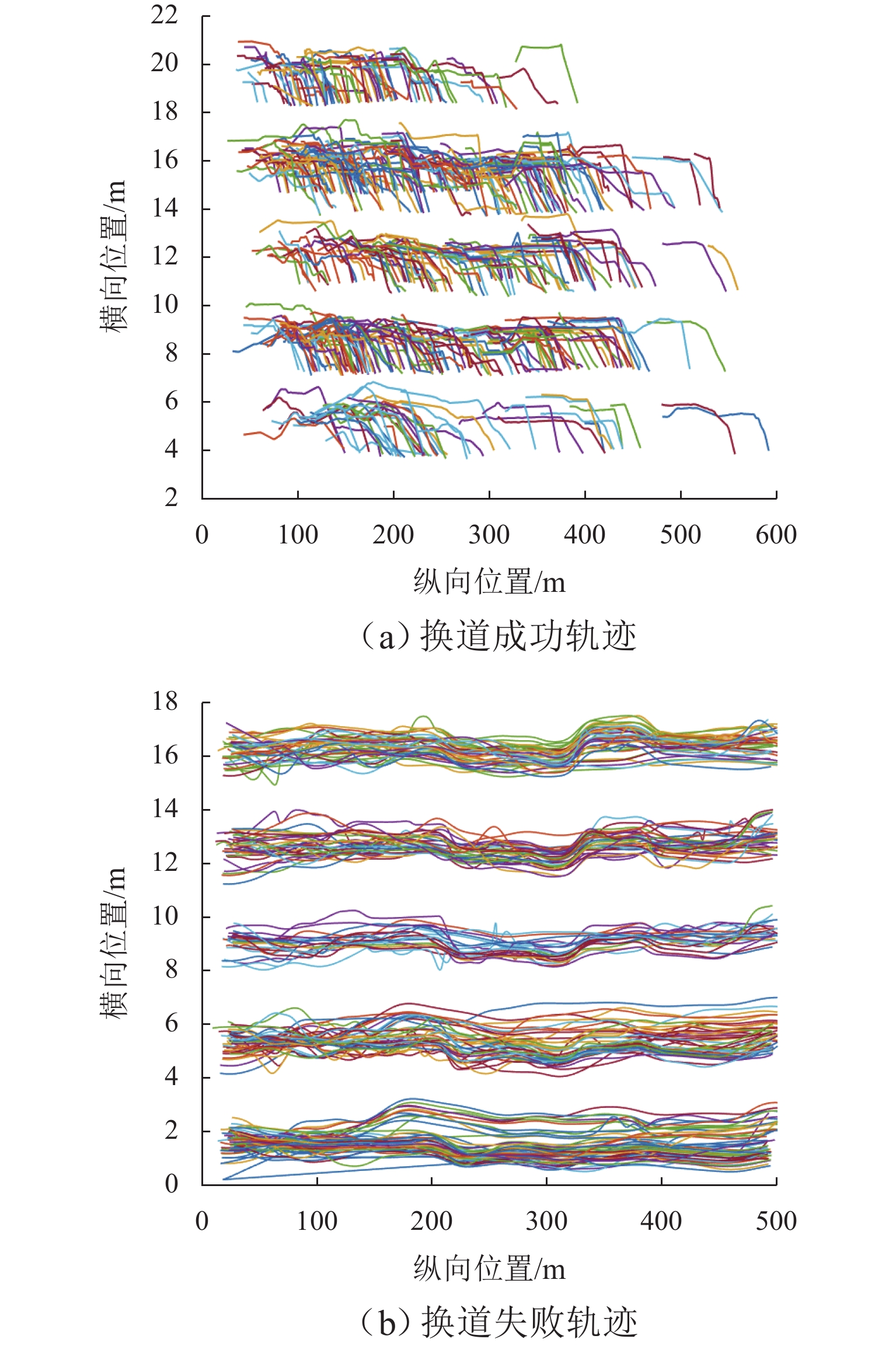
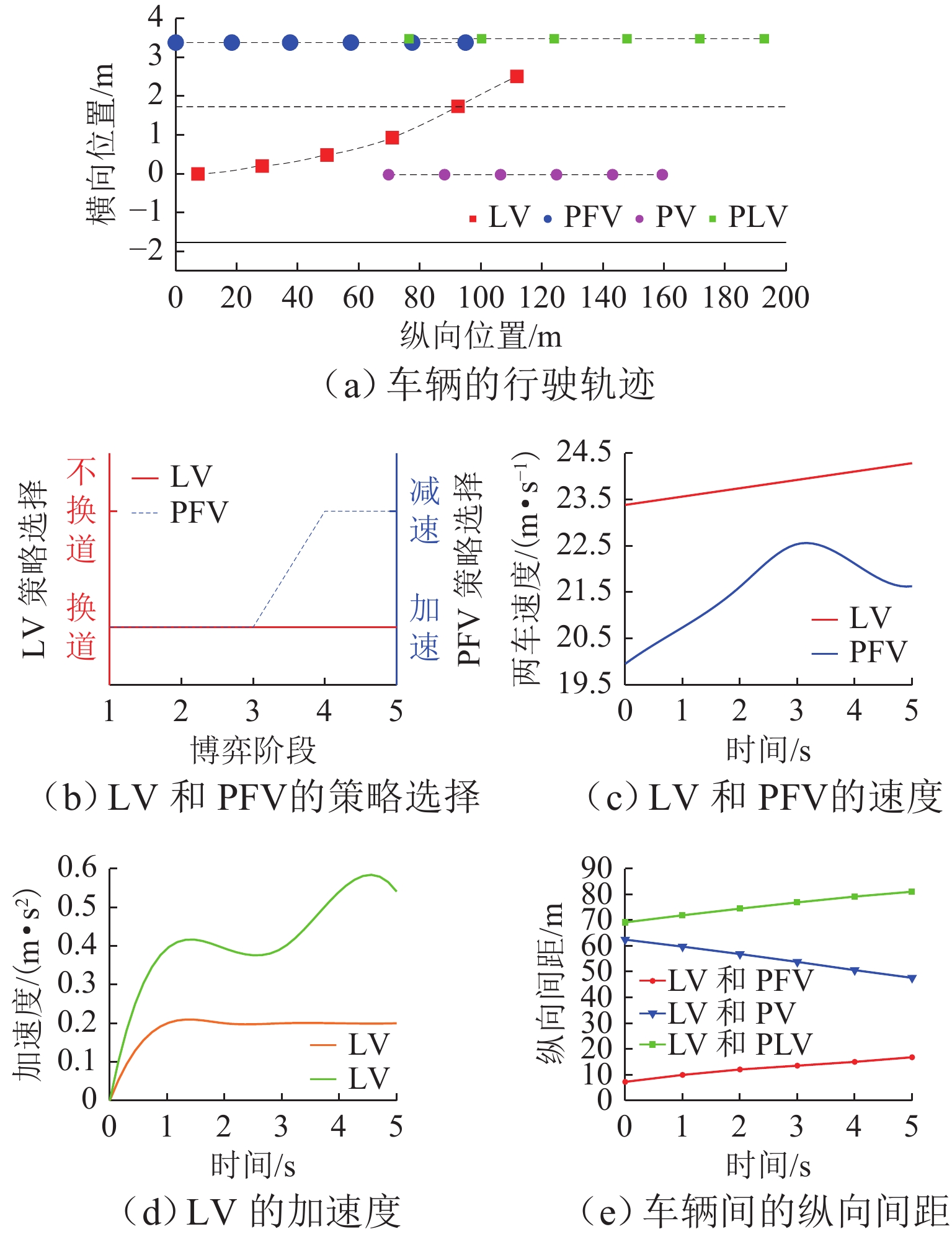
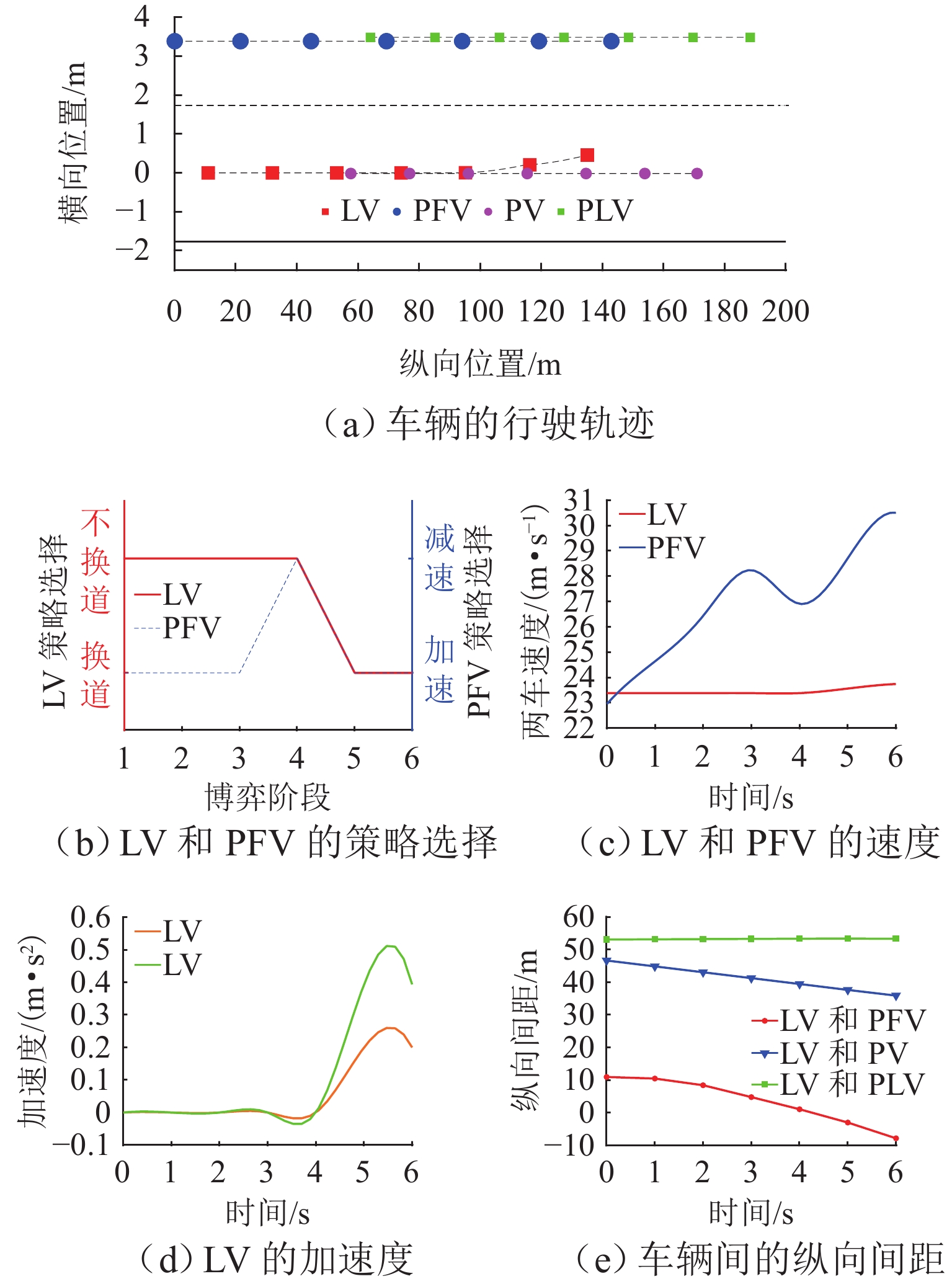
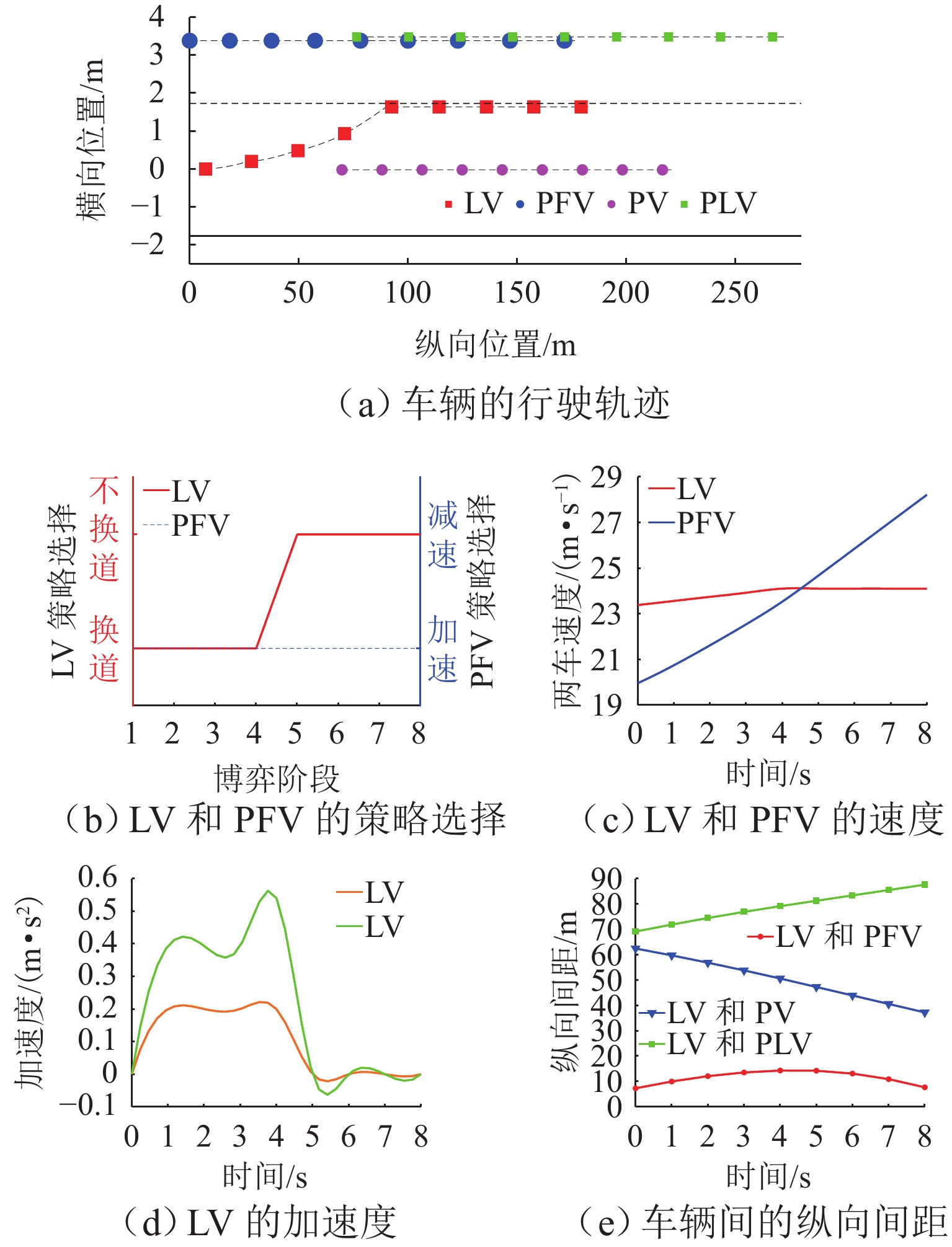
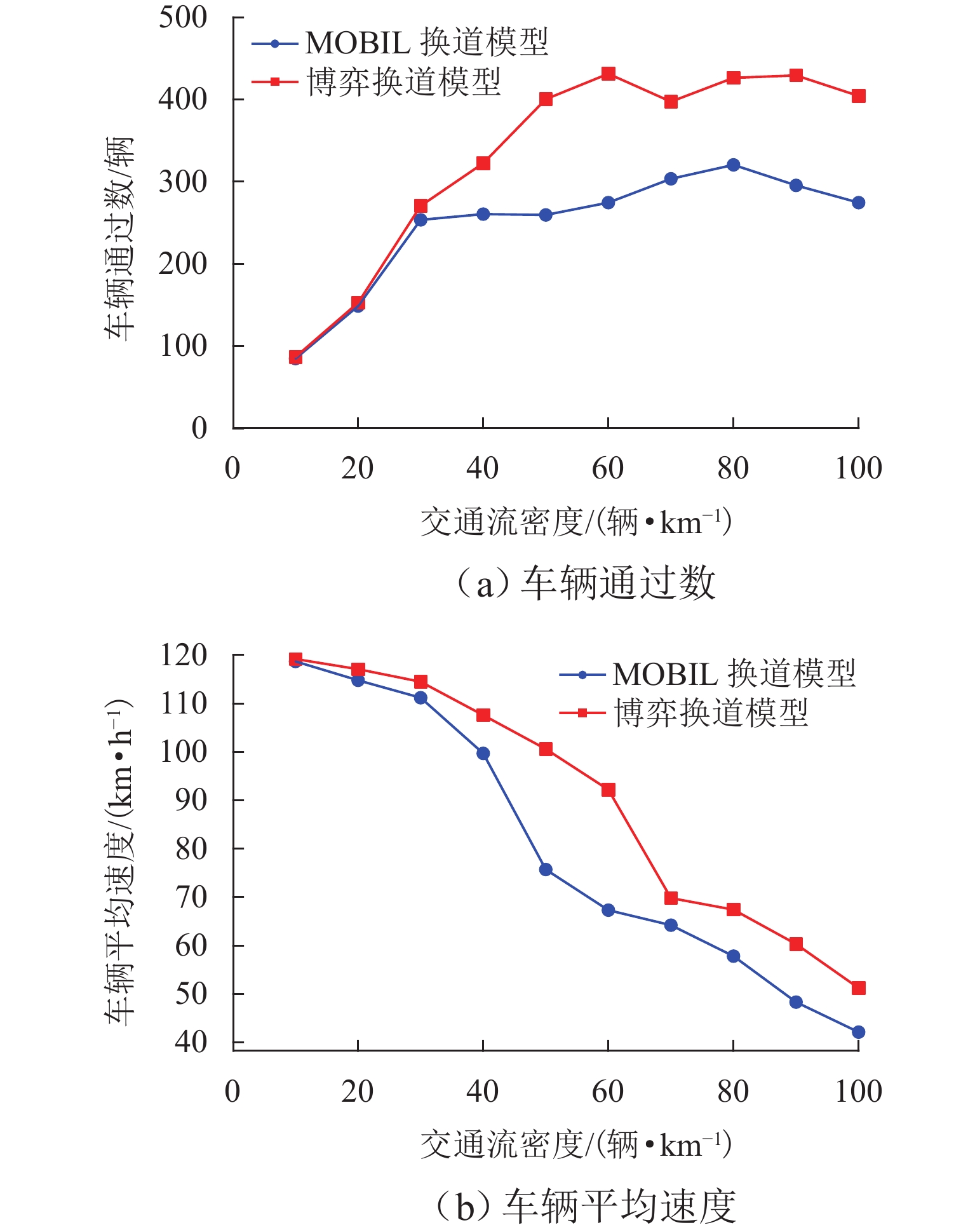
针对自主式交通系统中自动驾驶车辆的换道决策难题,提出一种基于不完全信息动态博弈的换道决策模型. 首先,基于博弈论思想,明确换道意图判断、博弈换道条件以及模型求解等核心问题,并建立相应的博弈框架;为优化收益函数,构建一个综合考虑安全性、效率性和舒适性的多目标收益函数,选择合适的特征对各目标收益进行量化处理,并结合逆强化学习方法从NGSIM数据中学习权重分配,确保了决策的多维度考量. 实验结果显示:无论是在博弈成功还是失败的交通场景中,所提模型都能有效提升决策的安全性和效率;相较于传统的防御型换道模型,该模型在提高行驶效率方面表现更为优越,展现了其在自动驾驶换道决策中的实用性和优势;此外,通过SUMO仿真验证,模型在真实高速公路场景中表现出良好的安全性和通行效率,能有效适应交通流变化,保障车辆安全高效行驶,验证了其在自动驾驶换道决策中的实用价值.
Abstract:To address the lane-changing decision-making challenge of autonomous vehicles in autonomous transportation systems, a lane-changing decision model based on an incomplete-information dynamic game was proposed. First, grounded in game-theoretic principles, core issues such as lane-changing intention recognition, game-based lane-changing conditions, and model solution methods were delineated, and a corresponding game framework was established. To optimize the payoff function, a multi-objective payoff function that comprehensively considers safety, efficiency, and comfort was constructed, with appropriate features selected to quantitatively evaluate the payoff of each objective. In conjunction with inverse reinforcement learning, the weight allocation was learned from the NGSIM dataset, ensuring multi-dimensional consideration in decision-making. Experimental results indicate that the proposed model effectively enhances decision safety and efficiency in both successful and failed game traffic scenarios. Compared with traditional defensive lane-changing models, the proposed model demonstrates superior performance in improving driving efficiency, demonstrating its practicality and advantages in autonomous vehicle lane-changing decision-making. Furthermore, validation through SUMO simulation shows that the model exhibits good safety and traffic efficiency performance in realistic highway scenarios, effectively adapts to variations in traffic flow, and supports safe and efficient vehicle operation, thereby verifying its practical value in autonomous vehicle lane-changing decision-making.
-
表 1 收益矩阵
Table 1. Payoff matrix
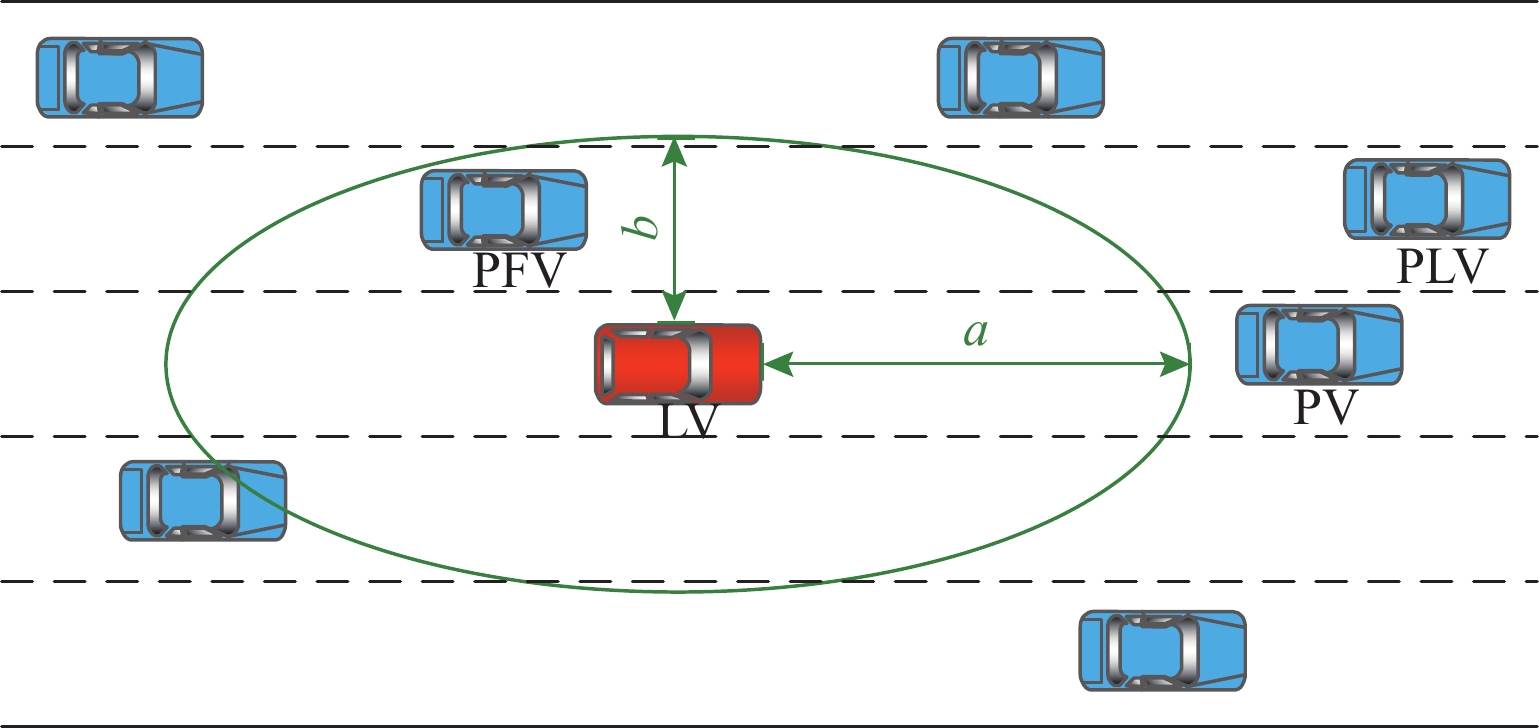
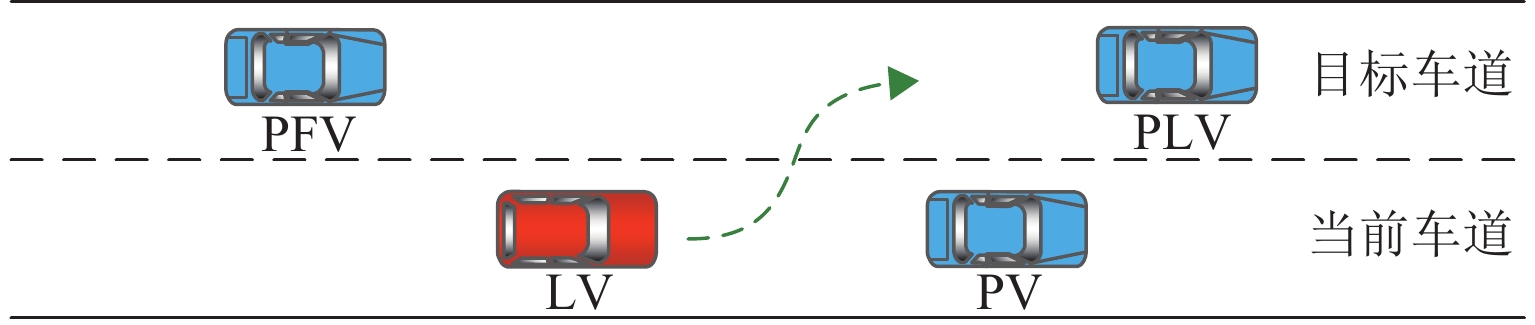
车辆类型 换道策略 PFV 加速 减速 LV 换道 $ \left(U_{\text{LV},11},U_{\text{PFV},11}\right) $ $ \left(U_{\text{LV},12},U_{\text{PFV},12}\right) $ 不换道 $ \left(U_{\text{LV},21},U_{\text{PFV},21}\right) $ $ \left(U_{\text{LV},22},U_{\text{PFV},22}\right) $ 表 2 状态集和动作集
Table 2. State set and action set
参数 状态集 动作集 相对
距离/m相对
速度/(m•s−1)本车
速度/(m•s−1)转向/
rad纵向加
速度/(m•s−2)符号 dr vr vx θ ax 表 3 多目标收益函数权重的学习结果
Table 3. Learning results of multi-objective payoff function weights
收益函数维度 特征 权重 安全性 $ {f}_{thwf} $ 0.15 $ {f}_{thwr} $ 0.28 效率性 $ {f}_{\text{v}} $ 0.42 舒适性 $ {f}_{\text{jerk}} $ 0.15 表 4 实验配置表
Table 4. Experimental configuration table
符合 描述 数值 $ {L}_{\text{car}} $ 车辆长度/m 4.976 $ {W}_{\text{car}} $ 车辆宽度/m 1.908 $ {L}_{\text{lane}} $ 道路长度/m 640 $ {W}_{\text{lane}} $ 道路宽度/m 3.75 $ {v}_{\min } $ 最小行驶速度/(m•s−1) 15 $ {v}_{\max } $ 最大行驶速度/(m•s−1) 36 $ a $ 加速度/(m•s−2) 0~5 $ d $ 减速度/(m•s−2) 0~5 $ \delta $ 前轮转向角度/(°) −3~3 表 5 不同交通流密度下2种换道模型的事故发生数
Table 5. Number of accidents of two lane-changing models under different traffic flow densities
交通流密度/(辆•km−1) MOBIL换道模型 博弈换道模型 10 0 0 20 0 0 30 0 0 40 0 0 50 0 0 60 1 0 70 0 0 80 2 0 90 3 1 100 1 0 -
[1] 李升波, 陈晨, 方叙之, 等. 自动驾驶车辆的驾驶行为能力评估指标体系综述[J]. 中国公路学报, 2025, 38(1): 304-323. doi: 10.19721/j.cnki.1001-7372.2025.01.022LI Shengbo, CHEN Chen, FANG Xuzhi, et al. Review of indicator systems for driving behavioral ability evaluation of autonomous vehicles[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2025, 38(1): 304-323. doi: 10.19721/j.cnki.1001-7372.2025.01.022 [2] 李珣, 程硕, 吴丹丹, 等. 车路协同下基于元胞自动机的精细交通流模型[J]. 西南交通大学学报, 2025, 60(1): 225-232. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.20220830LI Xun, CHENG Shuo, WU Dandan, et al. Refined traffic flow model based on cellular automaton under cooperative vehicle infrastructure system[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2025, 60(1): 225-232. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.20220830 [3] 戴朝华, 杨帅, 叶圣永, 等. 供需双方博弈视角下的V2G优化策略[J]. 西南交通大学学报, 2025, 60(1): 166-174, 193. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.20230097DAI Chaohua, YANG Shuai, YE Shengyong, et al. Vehicle to grid optimization strategy from the perspective of supply and demand game[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2025, 60(1): 166-174,193. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.20230097 [4] LOPEZ V G, LEWIS F L, LIU M S, et al. Game-theoretic lane-changing decision making and payoff learning for autonomous vehicles[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2022, 71(4): 3609-3620. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2022.3148972 [5] ZHENG Y, DING W T, RAN B, et al. Coordinated decisions of discretionary lane change between connected and automated vehicles on freeways: a game theory-based lane change strategy[J]. IET Intelligent Transport Systems, 2020, 14(13): 1864-1870. doi: 10.1049/iet-its.2020.0146 [6] ARBIS D, DIXIT V V. Game theoretic model for lane changing: Incorporating conflict risks[J]. Accident Analysis & Prevention, 2019, 125: 158-164. doi: 10.1016/j.aap.2019.02.007 [7] WANG M, HOOGENDOORN S P, DAAMEN W, et al. Game theoretic approach for predictive lane-changing and car-following control[J]. Transportation Research Part C: Emerging Technologies, 2015, 58: 73-92. doi: 10.1016/j.trc.2015.07.009 [8] 张可琨, 曲大义, 宋慧, 等. 自动驾驶车辆换道博弈策略分析及建模[J]. 复杂系统与复杂性科学, 2023, 20(2): 60-67. doi: 10.13306/j.1672-3813.2023.02.008ZHANG Kekun, QU Dayi, SONG Hui, et al. Analysis and modeling for lane-changing game strategy of autonomous vehicles[J]. Complex Systems and Complexity Science, 2023, 20(2): 60-67. doi: 10.13306/j.1672-3813.2023.02.008 [9] 孙曼曼, 陈珍萍, 李海峰, 等. 基于博弈论的网联自动驾驶车辆协同换道研究[J]. 计算机仿真, 2023, 40(1): 161-166, 207. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-9348.2023.01.030SUN Manman, CHEN Zhenping, LI Haifeng, et al. Research on cooperative lane change of networked autonomous vehicles based on game theory[J]. Computer Simulation, 2023, 40(1): 161-166,207. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-9348.2023.01.030 [10] SMIRNOV N, LIU Y Z, VALIDI A, et al. A game theory-based approach for modeling autonomous vehicle behavior in congested, urban lane-changing scenarios[J]. Sensors (Basel, Switzerland), 2021, 21(4): 1523. doi: 10.3390/s21041523 [11] CHEN W H, REN G, CAO Q, et al. A game-theory-based approach to modeling lane-changing interactions on highway on-ramps: considering the bounded rationality of drivers[J]. Mathematics, 2023, 11(2): 402. doi: 10.3390/math11020402 [12] GUO J, HARMATI I. Lane-changing decision modelling in congested traffic with a game theory-based decomposition algorithm[J]. Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence, 2022, 107: 104530. doi: 10.1016/j.engappai.2021.104530 [13] HANG P, LV C, HUANG C, et al. Cooperative decision making of lane-change for automated vehicles considering human-like driving characteristics[C]//2021 40th Chinese Control Conference (CCC). Shanghai: IEEE, 2021: 6106-6111. [14] 巴兴强, 刘娇娇. 基于博弈论的公交进站换道决策行为研究[J]. 重庆理工大学学报(自然科学), 2019, 33(2): 111-116. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-8425(z).2019.02.019BA Xingqiang, LIU Jiaojiao. Research on decision making behavior of bus entering lane-changing based on game theory[J]. Journal of Chongqing University of Technology (Natural Science), 2019, 33(2): 111-116. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-8425(z).2019.02.019 [15] 梅生伟, 刘锋. 工程博弈论–工程优化决策中的博弈思想、原理及应用[J]. 控制理论与应用, 2024, 41(7): 1159-1171.MEI Shengwei, LIU Feng. Engineering game theory: motivations, principles, and applications in engineering decision-making problems[J]. Control Theory & Applications, 2024, 41(7): 1159-1171. [16] ZHAO F Q, WANG Q Y, WANG L. An inverse reinforcement learning framework with the Q-learning mechanism for the metaheuristic algorithm[J]. Knowledge-Based Systems, 2023, 265: 110368. doi: 10.1016/j.knosys.2023.110368 [17] 高振海, 闫相同, 高菲. 基于逆向强化学习的纵向自动驾驶决策方法[J]. 汽车工程, 2022, 44(7): 969-975. doi: 10.19562/j.chinasae.qcgc.2022.07.003GAO Zhenhai, YAN Xiangtong, GAO Fei. A decision-making method for longitudinal autonomous driving based on inverse reinforcement learning[J]. Automotive Engineering, 2022, 44(7): 969-975. doi: 10.19562/j.chinasae.qcgc.2022.07.003 [18] HUANG H, LIU J, SHI G, et al. Adaptive decision-making for autonomous vehicles: a learning-enhanced game-theoretic approach in interactive environments[EB/OL]. (2024-02-18). https://arxiv.org/abs/2402.11467. [19] EMUNA R, BOROWSKY A, BIESS A. Deep reinforcement learning for human-like driving policies in collision avoidance tasks of self-driving cars[EB/OL]. (2022-06-07). https://arxiv.org/abs/2006.04218 [20] PHAN-MINH T, HOWINGTON F, CHU T S, et al. DriveIRL: drive in real life with inverse reinforcement learning[C]//2023 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA). London: IEEE, 2023: 1544-1550. [21] WANG L T, SUN L T, TOMIZUKA M, et al. Socially-compatible behavior design of autonomous vehicles with verification on real human data[J]. IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters, 2021, 6(2): 3421-3428. doi: 10.1109/LRA.2021.3061350 [22] NAUMANN M, SUN L T, ZHAN W, et al. Analyzing the suitability of cost functions for explaining and imitating human driving behavior based on inverse reinforcement learning[C]//2020 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA). Paris: IEEE, 2020: 5481-5487. [23] XU D H, DING Z Z, HE X, et al. Learning from naturalistic driving data for human-like autonomous highway driving[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2020, 22(12): 7341-7354. doi: 10.1109/tits.2020.3001131 [24] YOU C X, LU J B, FILEV D, et al. Advanced planning for autonomous vehicles using reinforcement learning and deep inverse reinforcement learning[J]. Robotics and Autonomous Systems, 2019, 114: 1-18. doi: 10.1016/j.robot.2019.01.003 [25] TAN S L, WANG Y N, VASILAKOS A V. Distributed population dynamics for searching generalized Nash equilibria of population games with graphical strategy interactions[J]. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems, 2021, 52(5): 3263-3272. doi: 10.1109/tsmc.2021.3069059 [26] ZHENG Y, DING W T, RAN B, et al. Coordinated decisions of discretionary lane change between connected and automated vehicles on freeways: a game theory-based lane change strategy[J]. IET Intelligent Transport Systems, 2020, 14(13): 1864-1870. doi: 10.1049/iet-its.2020.0146 [27] JIA S, HUI F, WEI C, et al. Lane-changing behavior prediction based on game theory and deep learning[J]. Journal of Advanced Transportation, 2021, 2021(1): 6634960. [28] HUANG Z Y, WU J D, LV C. Driving behavior modeling using naturalistic human driving data with inverse reinforcement learning[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2022, 23(8): 10239-10251. doi: 10.1109/TITS.2021.3088935 [29] KIM C, LANGARI R. Game theory based autonomous vehicles operation[J]. International Journal of Vehicle Design, 2014, 65(4): 360. doi: 10.1504/ijvd.2014.063832 [30] 杨涛, 马玉琴, 刘梦, 等. 智能网联环境下信号交叉口车辆轨迹重构模型[J]. 西南交通大学学报, 2024, 59(5): 1148-1157. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.20220321YANG Tao, MA Yuqin, LIU Meng, et al. Vehicle trajectory reconstruction model of signalized intersection in connected automated environments[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2024, 59(5): 1148-1157. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.20220321 -




 下载:
下载: