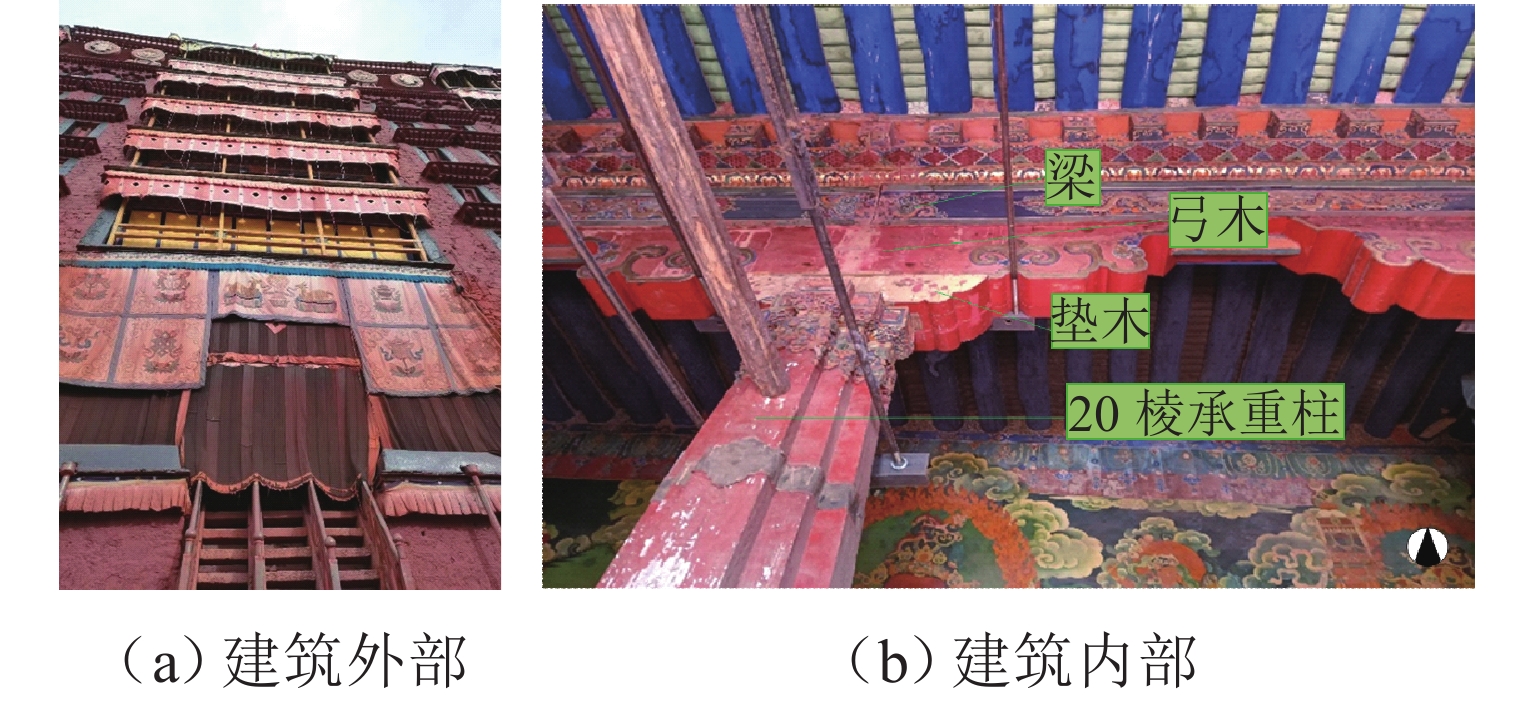
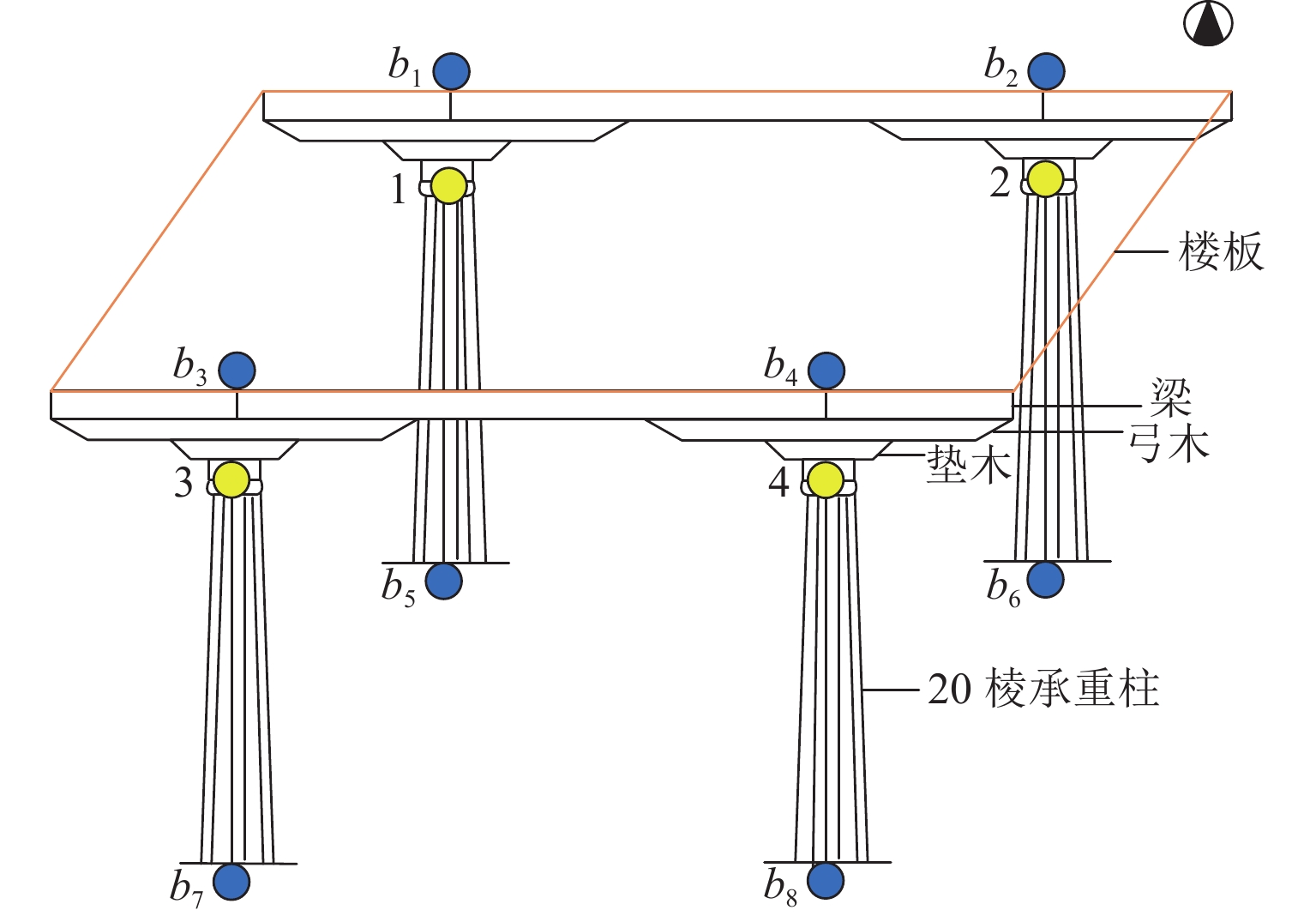
An Improved Isolated Substructure Method and Its Application in Dynamic Analysis of an Ancient Architecture
-
摘要:
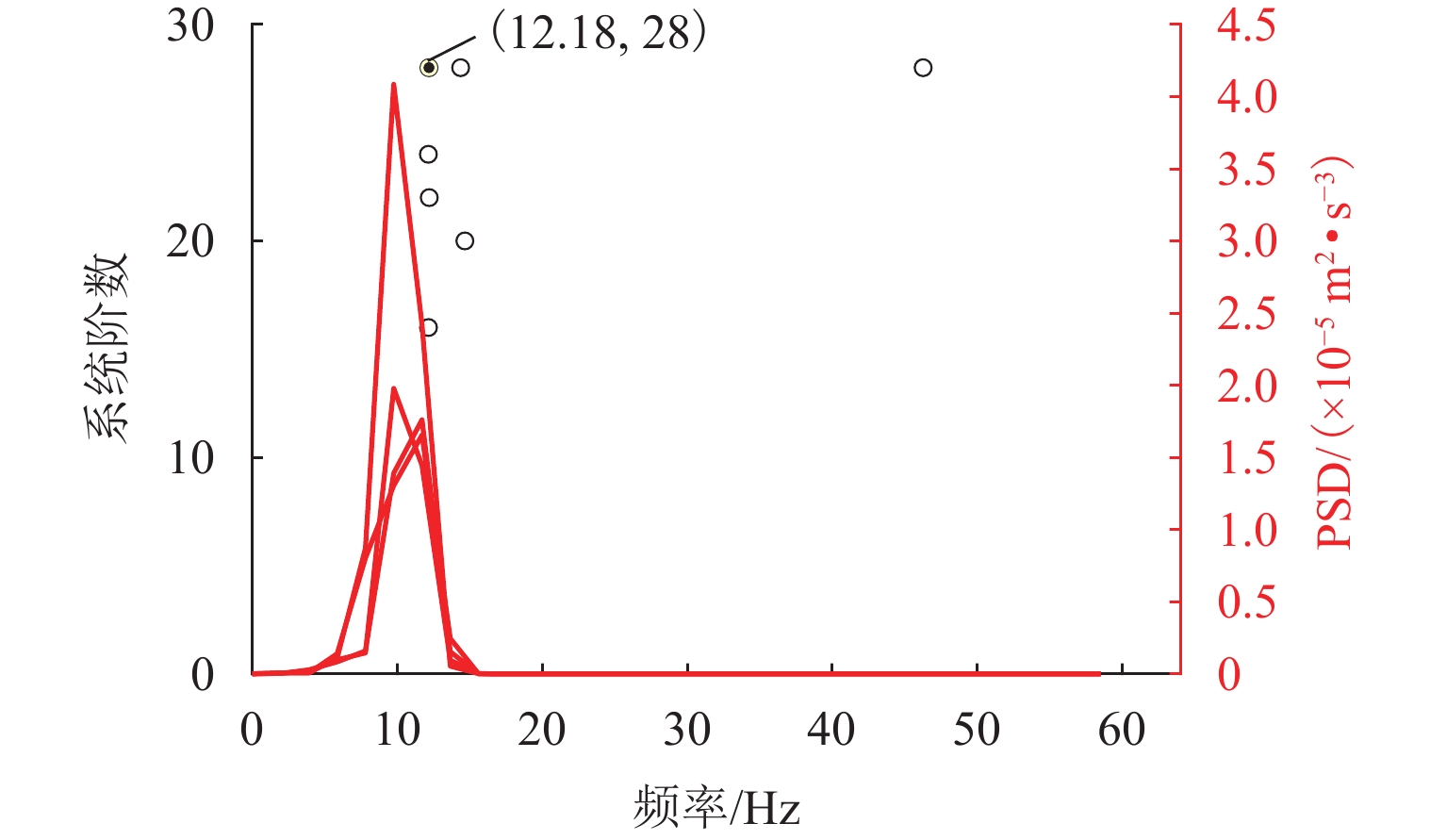
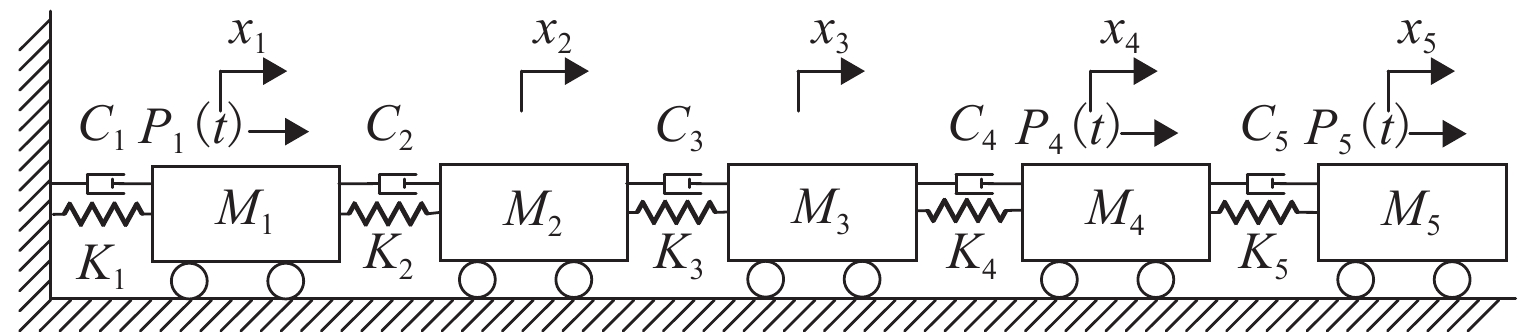
从全局结构中获取独立子结构的振动特性非常重要,针对现有基于时间序列的约束子结构法(SIM-TS),在噪声干扰下会因奇异值过小而出现计算误差增大的问题,提出一种改进的SIM-TS方法,以实现更高精度的子结构模态参数识别. 首先,以SIM-TS为基础,引入自适应截断奇异值分解技术,通过动态调整截断阈值来优化分解结果;同时,将ISIM-TS 方法与协方差驱动的随机子空间法(SSI-COV)相结合,构建新的ISIM-TS-SSI-COV子结构模态识别框架;然后,通过一个经典的5自由度数值算例验证方法可行性;最后,将该方法应用于某藏式古建筑子结构的动力特性识别中. 数值算例结果表明:在1%噪声情况下,改进后的方法提高了子结构的识别精度,尤其第二阶频率的识别误差较传统方法降低71.4%;基于环境激励下的响应数据,使用该方法成功识别出子结构的前两阶固有频率,分别为12.18 Hz和13.31 Hz. 本研究结果为后续结构模型修正与损伤识别提供了重要的数据基础.
Abstract:Obtaining the vibrational characteristics of independent substructures from global structures is crucial. The conventional isolated substructure method with time series (SIM-TS) suffers from increased computational errors due to excessively small singular values under noisy conditions. To address this, an improved ISM-TS method named ISIM-TS is proposed, aiming to achieve higher accuracy in substructure modal parameter identification. First, based on SIM-TS, an adaptive truncated singular value decomposition technique was introduced, optimizing the decomposition results by dynamically adjusting the truncation threshold. The ISIM-TS was combined with the covariance-driven stochastic subspace method (SSI-COV) to establish a new substructure modal identification framework, termed ISIM-TS-SSI-COV. Then, the feasibility of the proposed framework was verified via a classical five-degree-of-freedom (5-DOF) numerical simulation. Finally, this method was applied to identify the dynamic characteristics of a substructure in a Tibetan ancient architecture. The numerical results demonstrate that the improved method enhances the identification accuracy of the substructure, particularly reducing the identification error of the second-order frequency by 71.4%, under 1% noise. Furthermore, based on response data acquired under ambient excitation, the proposed method successfully identifies the first two natural frequencies of the substructure as 12.18 Hz and 13.31 Hz, respectively.
-
表 1 频率的理论值、识别值及其误差
Table 1. Theoretical and identified frequencies and their errors
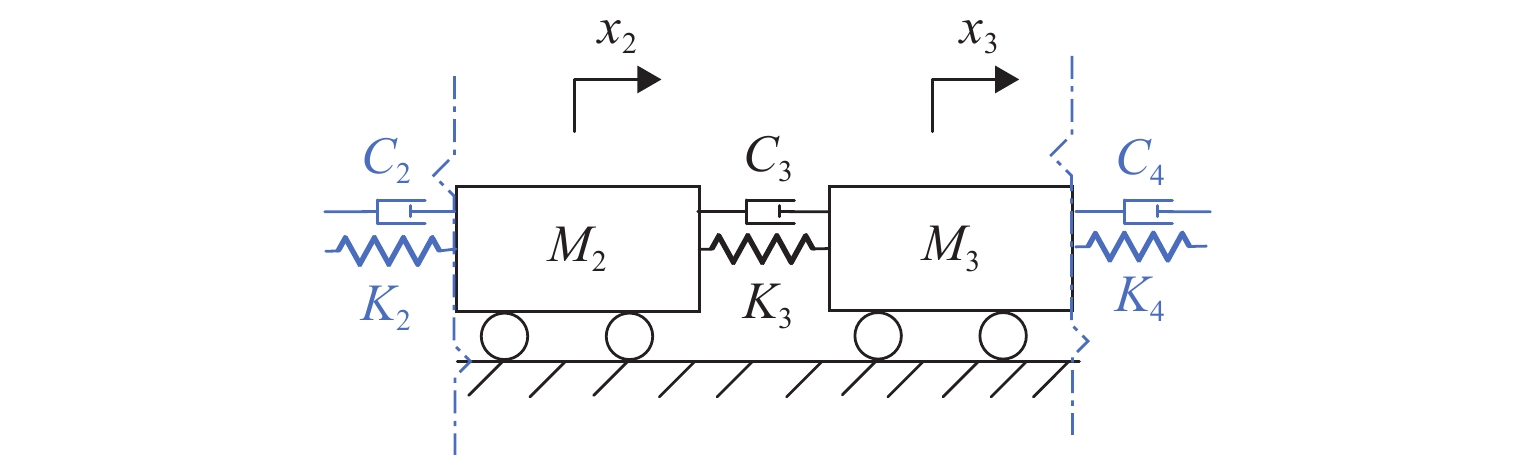
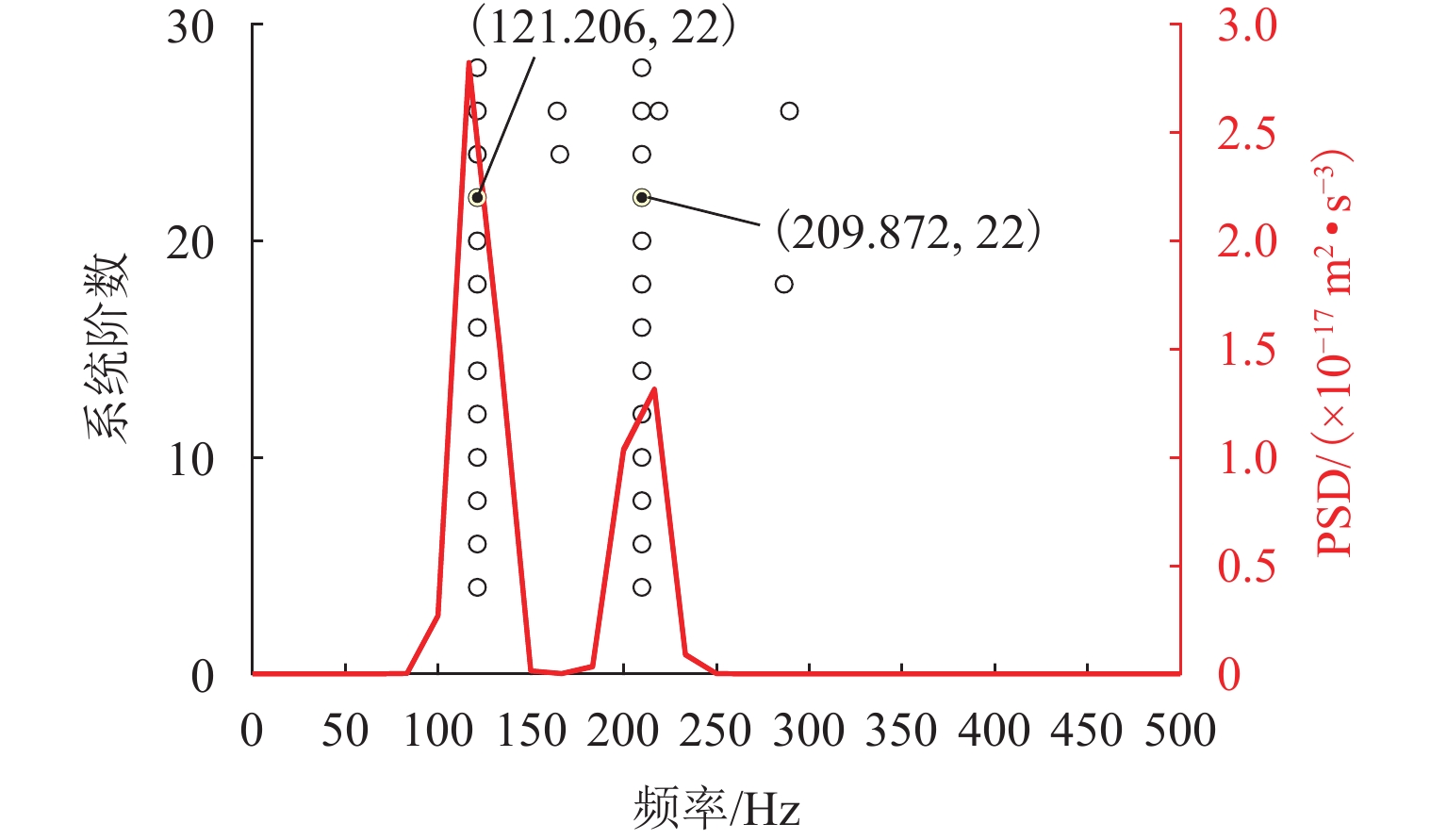
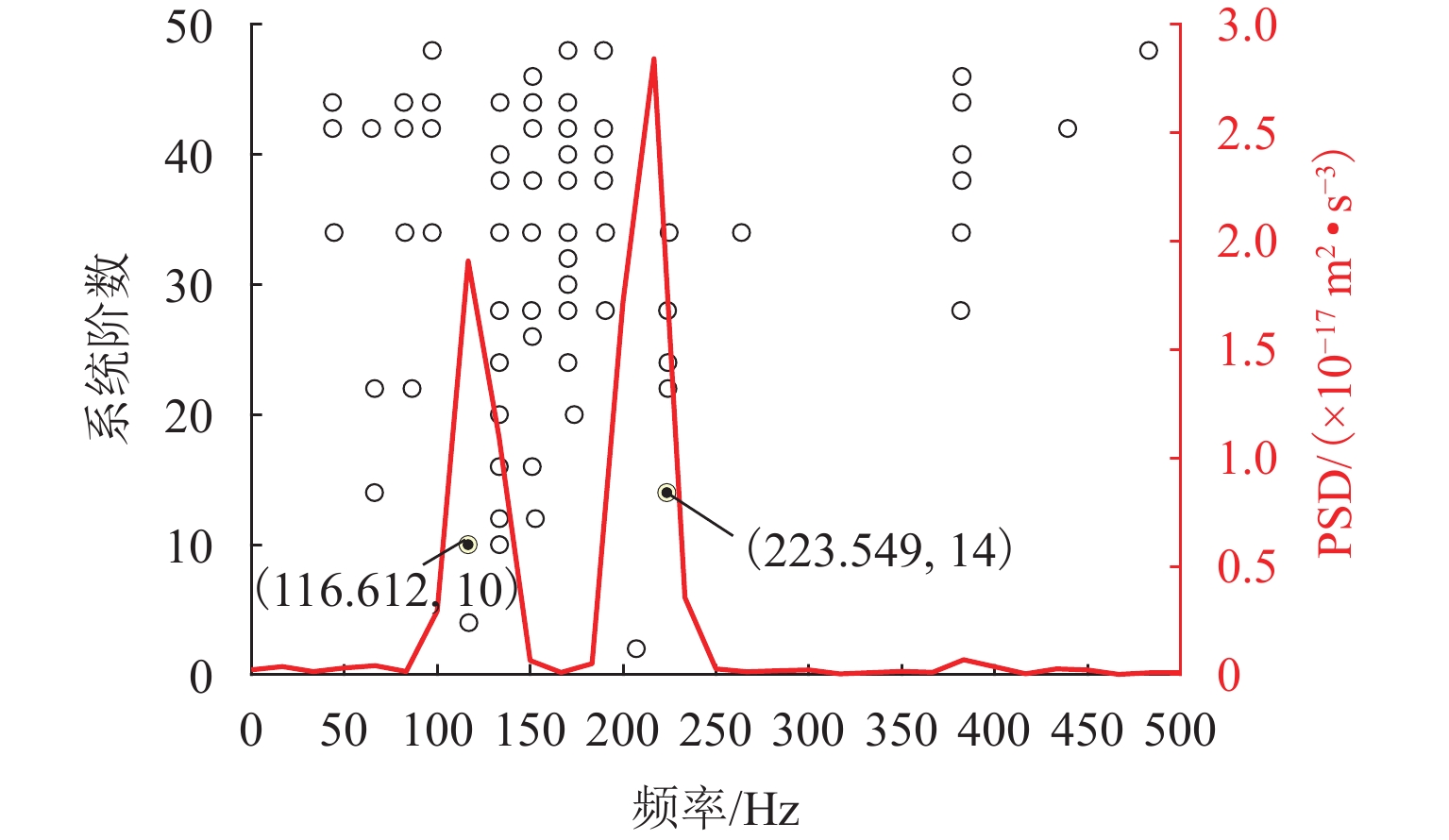
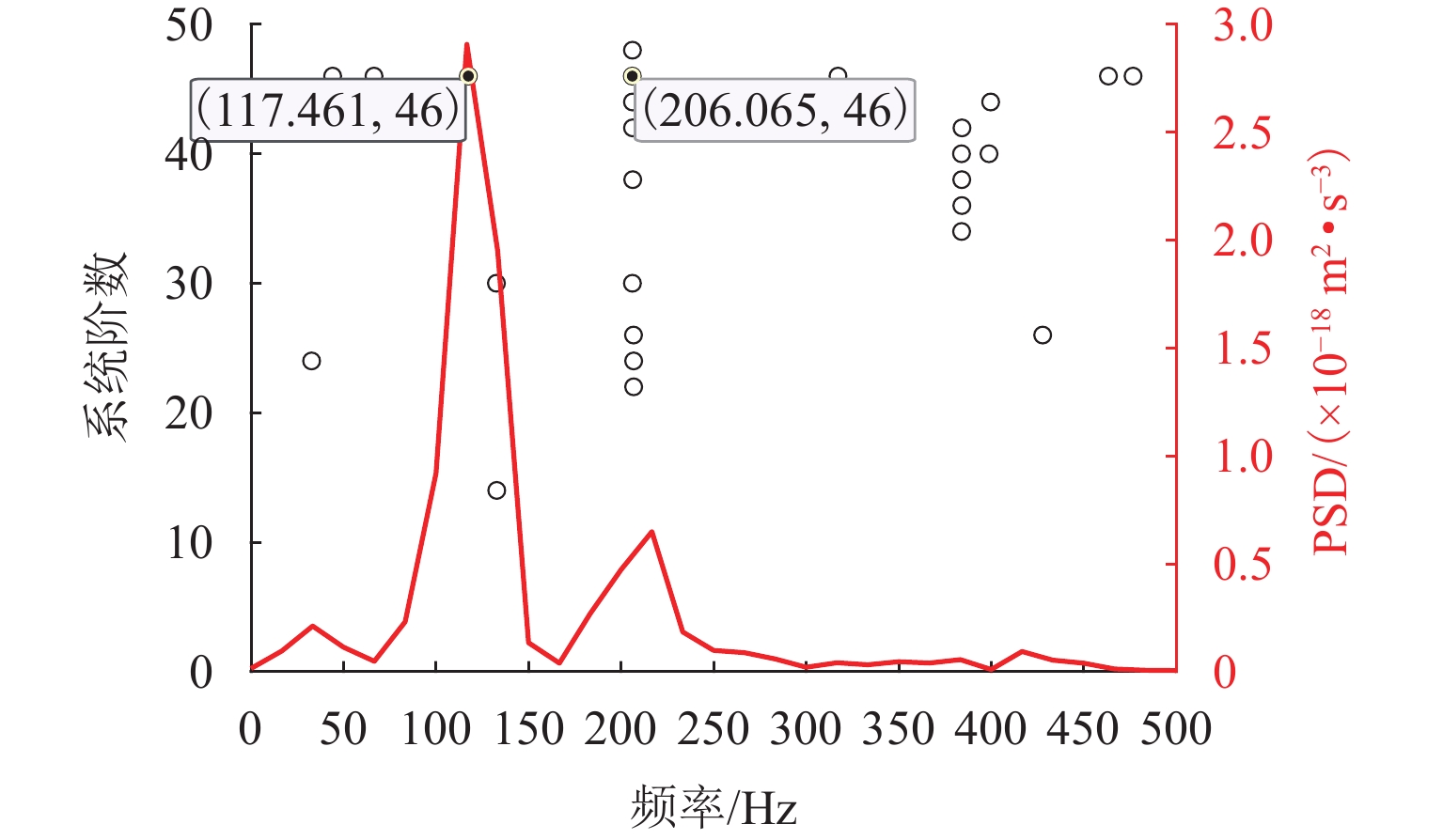
阶数 理论频率/Hz 识别频率/Hz 误差/% 1 121.21 121.21 0 2 209.94 209.87 −0.03 表 2 阻尼比的理论值、识别值及其误差
Table 2. Theoretical and identified damping ratios and their errors
% 阶数 理论阻尼比 识别阻尼比 误差 1 1.31 1.27 −3.05 2 2.27 2.29 0.88 表 3 振型系数的误差
Table 3. Errors of vibration mode coefficients
% 阶数 测点 1 误差 测点 2 误差 1 0 −0.23 2 −0.40 0 表 4 频率及阻尼比的识别结果
Table 4. Identification of frequencies and damping ratios
阶数 方向 频率/Hz 阻尼比/% 1 南北向 12.18 1.64 2 东西向 13.31 0.19 表 5 振型系数的识别结果
Table 5. Identification of vibration mode coefficients
阶数 方向 测点 1 测点 2 测点 3 测点 4 1 南北向 −0.59 −1.00 0.48 0.90 2 东西向 0.86 −0.88 −1.00 0.84 -
[1] 李兴泉, 邓兆祥, 李传兵, 等. 模态综合的子结构主模态截断方法[J]. 西南交通大学学报, 2014, 49(1): 173-178.LI Xingquan, DENG Zhaoxiang, LI Chuanbing, et al. Substructure normal modes selection method for component mode synthesis[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2014, 49(1): 173-178. [2] SENGUPTA P, CHAKRABORTY S. A state-of-the-art review on model reduction and substructuring techniques in finite element model updating for structural health monitoring applications[J]. Archives of Computational Methods in Engineering, 2025, 32(5): 3031-3062. doi: 10.1007/s11831-025-10231-w [3] UGALDE U, ANDUAGA J, SALGADO O, et al. SHM method for locating damage with incomplete observations based on substructure’s connectivity analysis[J]. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 2023, 200: 110519. doi: 10.1016/j.ymssp.2023.110519 [4] WENG S, ZHU H P, XIA Y, et al. A review on dynamic substructuring methods for model updating and damage detection of large-scale structures[J]. Advances in Structural Engineering, 2020, 23(3): 584-600. doi: 10.1177/1369433219872429 [5] KOH C G, SEE L M, BALENDRA T. Estimation of structural parameters in time domain: a substructure approach[J]. Earthquake Engineering & Structural Dynamics, 1991, 20(8): 787-801. [6] LEI Y, WU D T, JIANG Y Q. A two-stage Kalman estimation approach for the identification of large size structural parameters[J]. Advanced Materials Research, 2010, 163/164/165/166/167: 2603-2607. [7] LAW S S, LI J, DING Y. Structural response reconstruction with transmissibility concept in frequency domain[J]. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 2011, 25(3): 952-968. doi: 10.1016/j.ymssp.2010.10.001 [8] TEE K F, KOH C G, QUEK S T. Numerical and experimental studies of a substructural identification strategy[J]. Structural Health Monitoring, 2009, 8(5): 397-410. doi: 10.1177/1475921709102089 [9] 侯吉林, 欧进萍. 基于局部模态的约束子结构模型修正法[J]. 力学学报, 2009, 41(5): 748-756. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0459-1879.2009.05.018HOU Jilin, OU Jinping. Isolated substructure model updating based on local mode[J]. Chinese Journal of Theoretical and Applied Mechanics, 2009, 41(5): 748-756. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0459-1879.2009.05.018 [10] 侯吉林, 欧进萍. 基于局部时间序列的约束子结构修正法[J]. 振动工程学报, 2009, 22(3): 305-312. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-4523.2009.03.015HOU Jilin, OU Jinping. Isolated substructure model updating based on local time series[J]. Journal of Vibration Engineering, 2009, 22(3): 305-312. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-4523.2009.03.015 [11] HOU J L, JANKOWSKI Ł, OU J P. An online substructure identification method for local structural health monitoring[J]. Smart Materials and Structures, 2013, 22(9): 095017. doi: 10.1088/0964-1726/22/9/095017 [12] 张勇, 侯之超, 赵永玲. 基于频响函数截断奇异值响应面的有限元模型修正[J]. 振动工程学报, 2017, 30(3): 341-348. doi: 10.16385/j.cnki.issn.1004-4523.2017.03.001ZHANG Yong, HOU Zhichao, ZHAO Yongling. Finite element model updating based on response surface of the truncated singular values of frequency response functions[J]. Journal of Vibration Engineering, 2017, 30(3): 341-348. doi: 10.16385/j.cnki.issn.1004-4523.2017.03.001 [13] 仝瑶. 基于截断奇异值分解正则化改进识别移动荷载[D]. 郑州: 华北水利水电大学, 2021. [14] 杨秋伟, 陆晨, 李翠红. 基于奇异值截断的结构损伤识别方法研究[J]. 机械强度, 2019, 41(4): 976-982. doi: 10.16579/j.issn.1001.9669.2019.04.033YANG Qiuwei, LU Chen, LI Cuihong. Structural damage identification by singular value truncation method[J]. Journal of Mechanical Strength, 2019, 41(4): 976-982. doi: 10.16579/j.issn.1001.9669.2019.04.033 [15] 陆晨. 基于有偏估计的梁结构损伤识别方法研究[D]. 绍兴: 绍兴文理学院, 2019. [16] 万桂军, 黎剑安, 冯东明. 基于变分模态分解和分段多项式截断奇异值分解的桥梁影响线识别[J]. 浙江大学学报(工学版), 2025, 59(3): 460-468. doi: 10.3785/j.issn.1008-973X.2025.03.003WAN Guijun, LI Jianan, FENG Dongming. Bridge influence line identification based on variational mode decomposition and piecewise polynomial truncated singular value decomposition[J]. Journal of Zhejiang University (Engineering Science), 2025, 59(3): 460-468. doi: 10.3785/j.issn.1008-973X.2025.03.003 [17] 宁暑光, 何怡刚, 程彤彤, 等. 基于自适应S变换与截断紧致奇异值分解的局部放电源复杂染噪特征提取方法[J]. 电工技术学报, 2024, 44(5): 148-153. doi: 10.19595/j.cnki.1000-6753.tces.210987Ning Shuguang, He Yigang, Cheng Tongtong, et al. Feature extraction of partial discharge source with complex noise based on adaptive S-transform and truncated compact singular value decomposition[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2024, 44(5): 148-153. doi: 10.19595/j.cnki.1000-6753.tces.210987 [18] 周泰翔, 邬樱, 李爱群, 等. 非平稳环境激励下的明代厅堂式木构建筑模态识别研究: 以崇善寺大悲殿为例[J/OL]. 工程力学, 2025: 1-13. (2025-06-16). https://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=GCLX20250613001&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ. [19] 毛筱霏, 代兴鹏, 何洁美, 等. 武安州塔动力特性与抗震性能分析[J]. 北京建筑大学学报, 2024, 40(3): 102-108. doi: 10.19740/j.2096-9872.2024.03.12MAO Xiaofei, DAI Xingpeng, HE Jiemei, et al. Mechanical properties and seismic mechanism analysis of Wu’anzhou pagoda[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Civil Engineering and Architecture, 2024, 40(3): 102-108. doi: 10.19740/j.2096-9872.2024.03.12 [20] 刘威, 杨娜, 白凡, 等. 基于环境激励的藏式古城墙动力特性研究[J]. 土木工程学报, 2021, 54(4): 45-56. doi: 10.15951/j.tmgcxb.2021.04.006LIU Wei, YANG Na, BAI Fan, et al. Research on the dynamic characteristics of Tibetan ancient city wall based on ambient excitation[J]. China Civil Engineering Journal, 2021, 54(4): 45-56. doi: 10.15951/j.tmgcxb.2021.04.006 [21] 张允士, 张楠, 樊华, 等. 交通荷载作用下古木建筑结构的振动预测方法与验证[J]. 西南交通大学学报, 2017, 52(5): 902-909. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2017.05.009ZHANG Yunshi, ZHANG Nan, FAN Hua, et al. Method to predict vibrations induced in ancient wooden structures by traffic loads and its validation[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2017, 52(5): 902-909. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2017.05.009 [22] 吴晨伟, 薛建阳, 白福玉, 等. 历史文化建筑砖木混合结构原位动力特性试验及地震响应分析[J]. 工程力学, 2025, 42(增1): 145-152. doi: 10.6052/j.issn.1000-4750.2024.05.S035WU Chenwei, XUE Jianyang, BAI Fuyu, et al. In-situ dynamic characteristics test and seismic response analysis of brick-wood mixed structure in historical and cultural buildings[J]. Engineering Mechanics, 2025, 42(S1): 145-152. doi: 10.6052/j.issn.1000-4750.2024.05.S035 [23] ALTUNISIK A C, KALKAN E, OKUR F Y, et al. Non-destructive modal parameter identification of historical timber bridges using ambient vibration tests after restoration[J]. Measurement, 2019, 146: 411-424. doi: 10.1016/j.measurement.2019.06.051 [24] CHISARI C, ZIZI M, DE MATTEIS G. Dynamic model identification of the medieval bell tower of Casertavecchia (Italy)[J]. Engineering Failure Analysis, 2025, 167: 109055. doi: 10.1016/j.engfailanal.2024.109055 [25] ELYAMANI A, CASELLES O, ROCA P, et al. Dynamic investigation of a large historical cathedral[J]. Structural Control and Health Monitoring, 2017, 24(3): e1885. doi: 10.1002/stc.1885 [26] LIU-KUAN Y C, ESQUIVEL-SALAS L C. Análisis modal operacional de un edificio de concreto reforzado mediante métodos subespaciales estocásticos[J]. Ingeniería, 2024, 34(2): 38-53 [27] PENROSE R. A generalized inverse for matrices[J]. Mathematical Proceedings of the Cambridge Philosophical Society, 1955, 51(3): 406-413. doi: 10.1017/S0305004100030401 [28] HU S J, BAO X X, LI H J. Model order determination and noise removal for modal parameter estimation[J]. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 2010, 24(6): 1605-1620. doi: 10.1016/j.ymssp.2010.01.005 -




 下载:
下载: