Construction Method of Monitoring System of Preventive Conservation for Lugou Bridge Based on Three Principles
-
摘要:
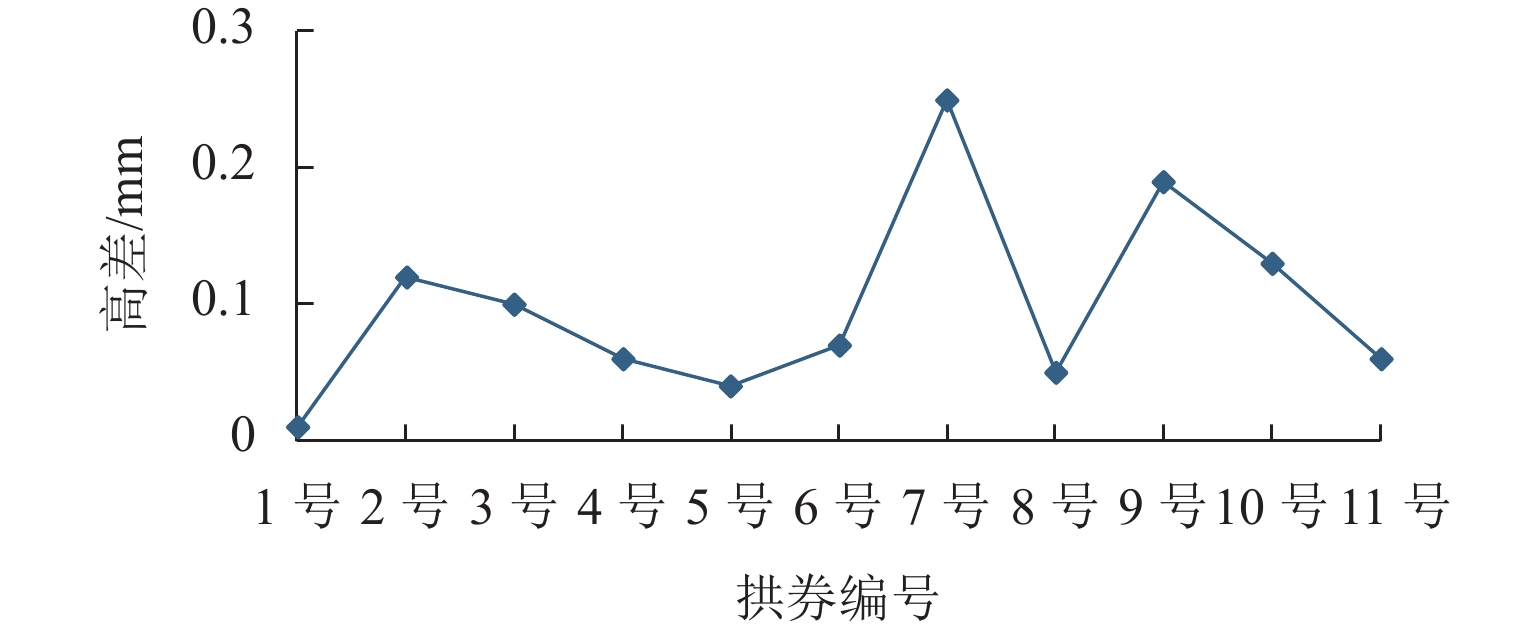
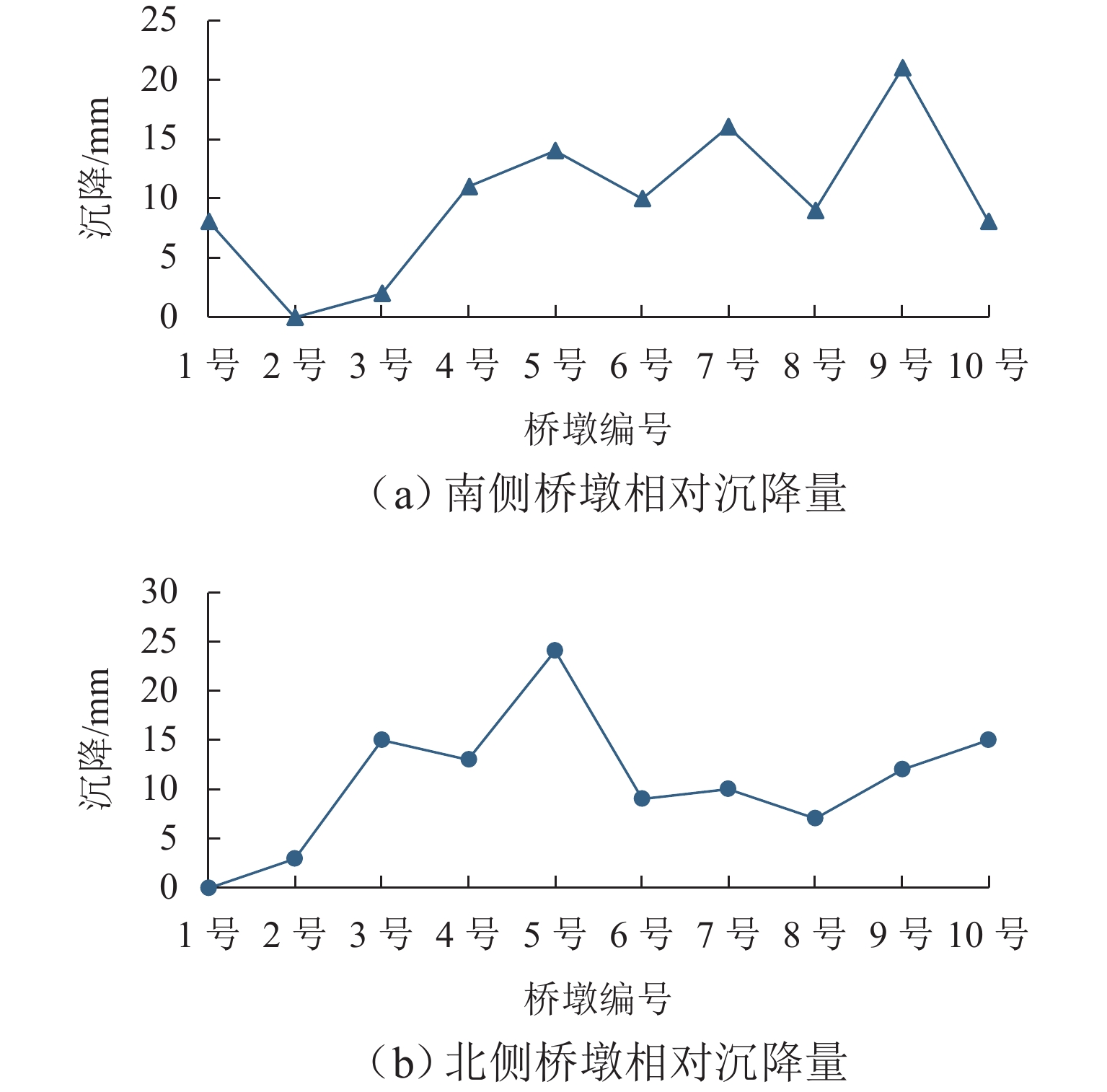
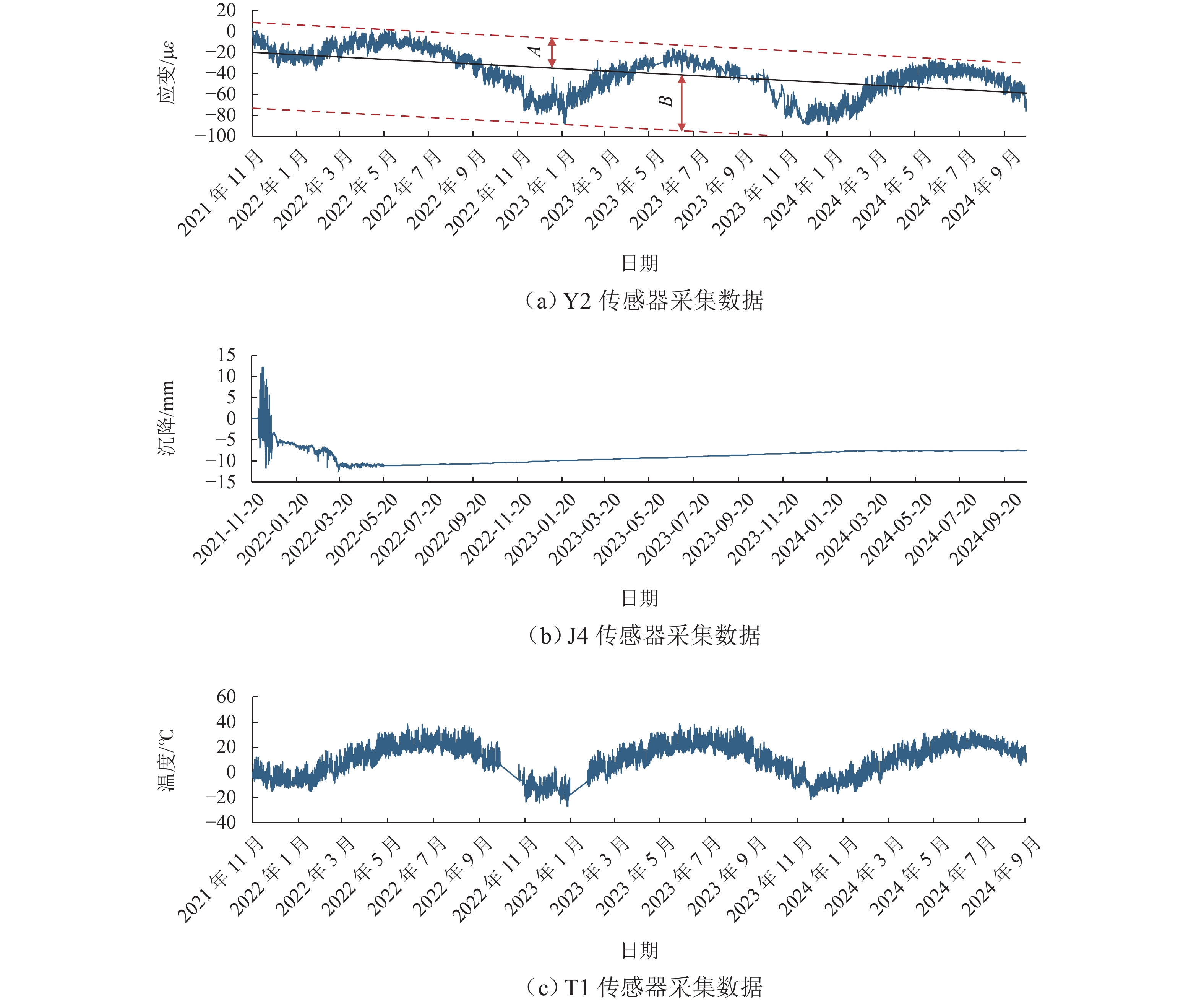
为构建古代砖石拱桥的预防性保护监测系统,开展面向风险识别的监测方法研究. 首先,采用残损评定等级、Von Mises应力和构件重要性分别作为残损最严重、受力最不利、构件最重要3项原则的量化表示;其次,基于残损矩阵、受力矩阵和重要性矩阵求解卢沟桥64个构件的监测目标值;最后,制定卢沟桥基于三原则的传感器优化布置方案. 研究结果表明:该方法能够定位待监测的高目标值构件,并且监测信息可提取卢沟桥的结构季节性波动规律和累积损伤风险;除沉降项目基本不受季节变化影响,其余监测项目存在明显的季节性波动规律,波动波峰位于每年6月—7月,波谷位于每年1月;应变传感器的冬季与夏季峰值之比为1.577,东起第7孔位移传感器的冬季与夏季峰值之比为0.849,东起第9孔位移传感器的冬季与夏季峰值之比为1.206,横桥向倾斜传感器的冬季与夏季峰值之比为1.549,季节性波动比率平均介于20%~60%. 沉降传感器监测到东起第5桥墩沉降量为第9桥墩的1.156倍;靠近拱桥中部或位于损伤严重构件的传感器在同类型传感器中具有更大的峰值. 研究结果可为古代砖石拱桥的预防性保护监测提供科学基础.
Abstract:To construct a monitoring system of preventive protection for ancient masonry arch bridges, a monitoring method for risk identification was investigated. Three indicators, which were damage assessment grade, Von Mises stress, and component importance, were used to quantify the most severe damage, unfavorable stress, and critical components. The monitoring target values were solved for the 64 components of the Lugou Bridge based on the loss matrix, force matrix, and importance matrix, and a sensor placement scheme was made accordingly. The results have shown that the method can identify high-value components for monitoring and capture the seasonal fluctuation patterns and cumulative damage risks of Lugou Bridge. Except for the settlement, monitoring data exhibits significant seasonal fluctuation patterns, with peaks in June to July and troughs in January each year. The ratio of winter to summer peak values is 1.577 for strain sensors, 0.849 for displacement sensors at the seventh pier from the east, 1.206 for displacement sensors at the ninth pier from the east, and 1.549 for transverse inclination sensors. The average seasonal fluctuation ratio ranges from 20% to 60%. The settlement of the fifth pier from the East is 1.156 times that of the ninth pier from the East. Sensors near the central arch bridge or located in severely damaged areas have higher peak values among the same type of sensors. The study provides a scientific basis for the monitoring of preventive conservation of ancient masonry arch bridges.
-
Key words:
- masonry arch bridge /
- architectural heritage /
- preventive conservation /
- monitoring /
- sensor
-
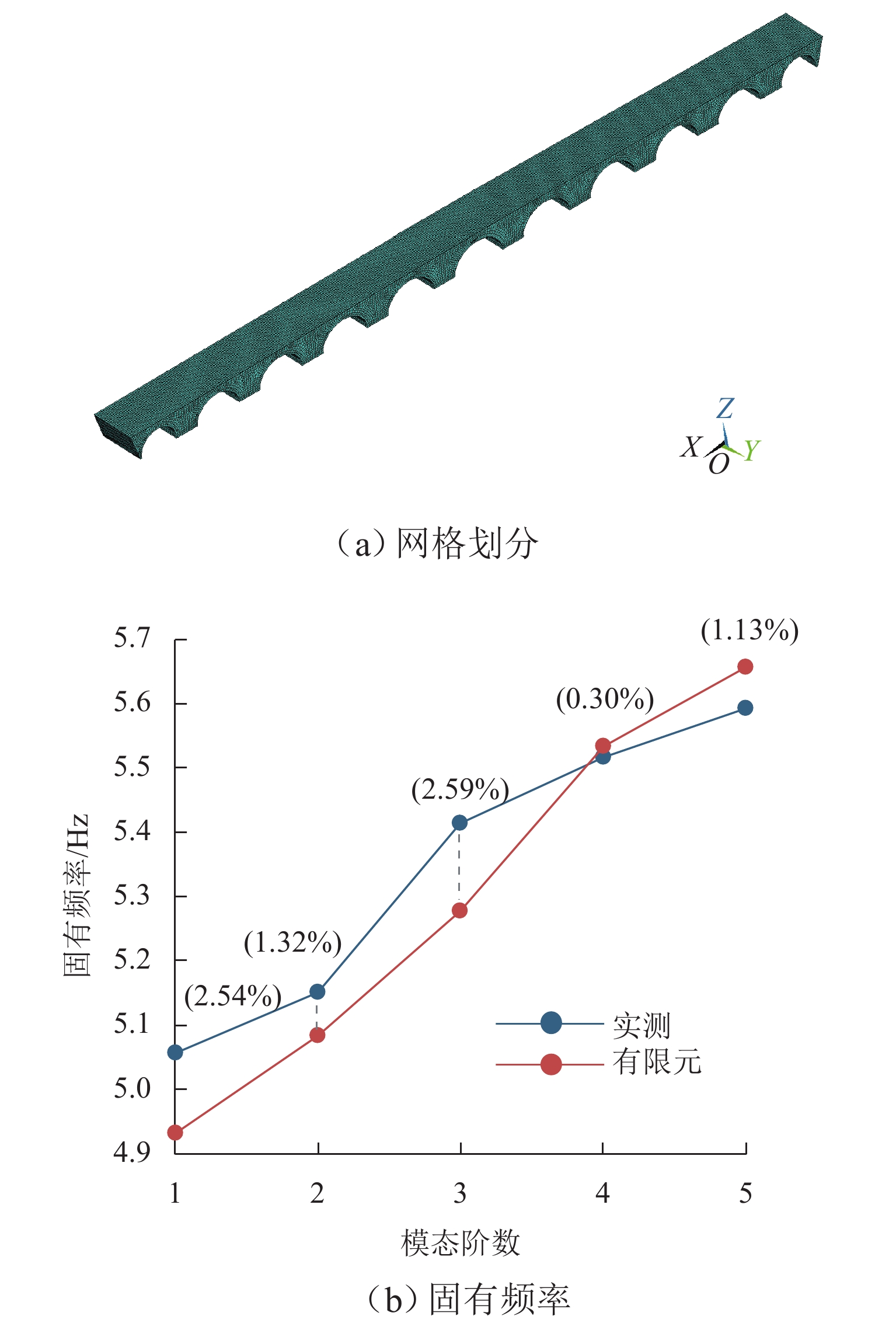
表 1 材料参数
Table 1. Material parameters
材料 弹性模量/MPa 泊松比 密度/(kg•m−3) 砖砌块 2250 0.15 2000 石砌块 6750 0.15 2500 填土 40 0.20 1900 表 2 三原则矩阵
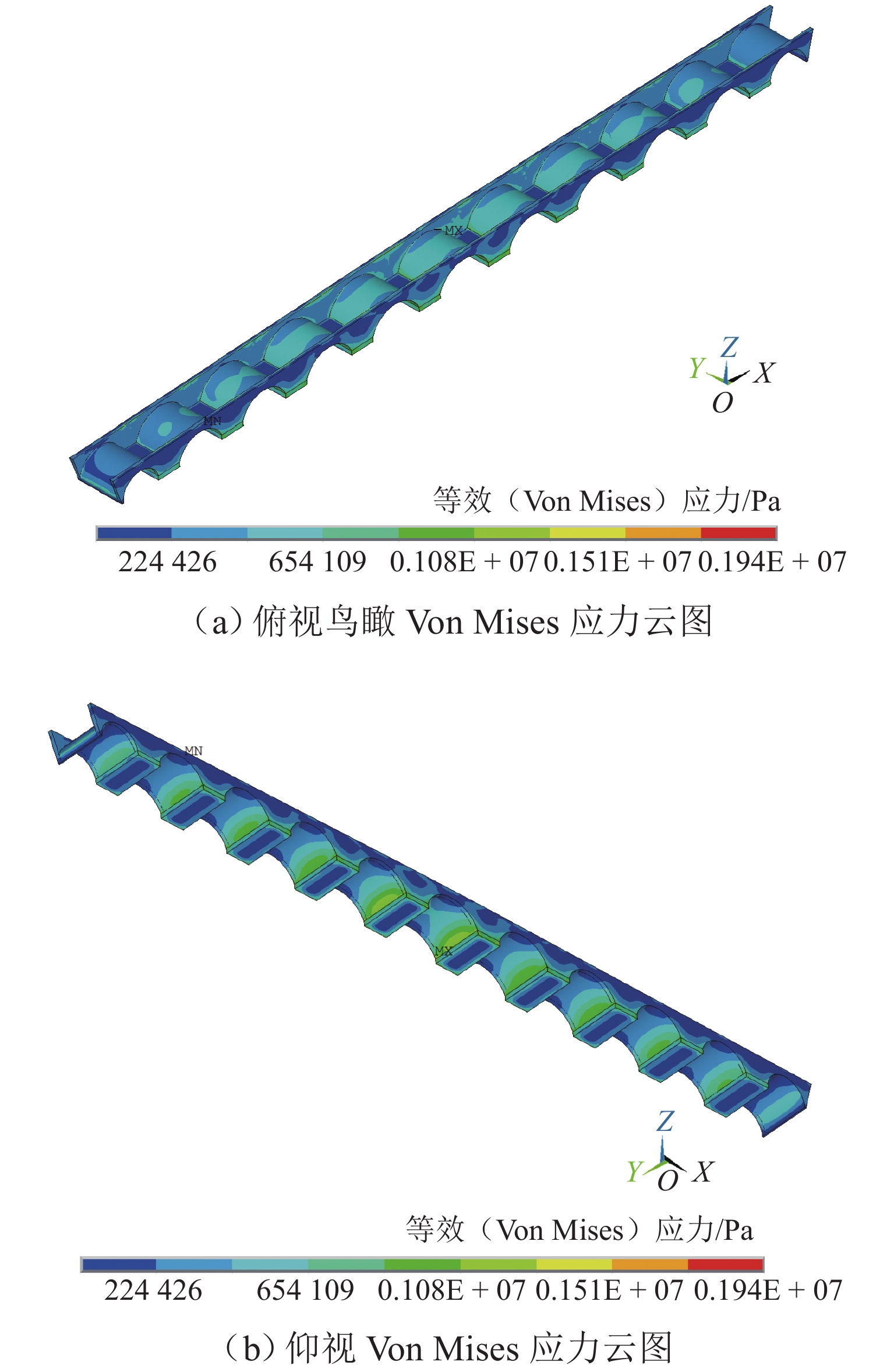
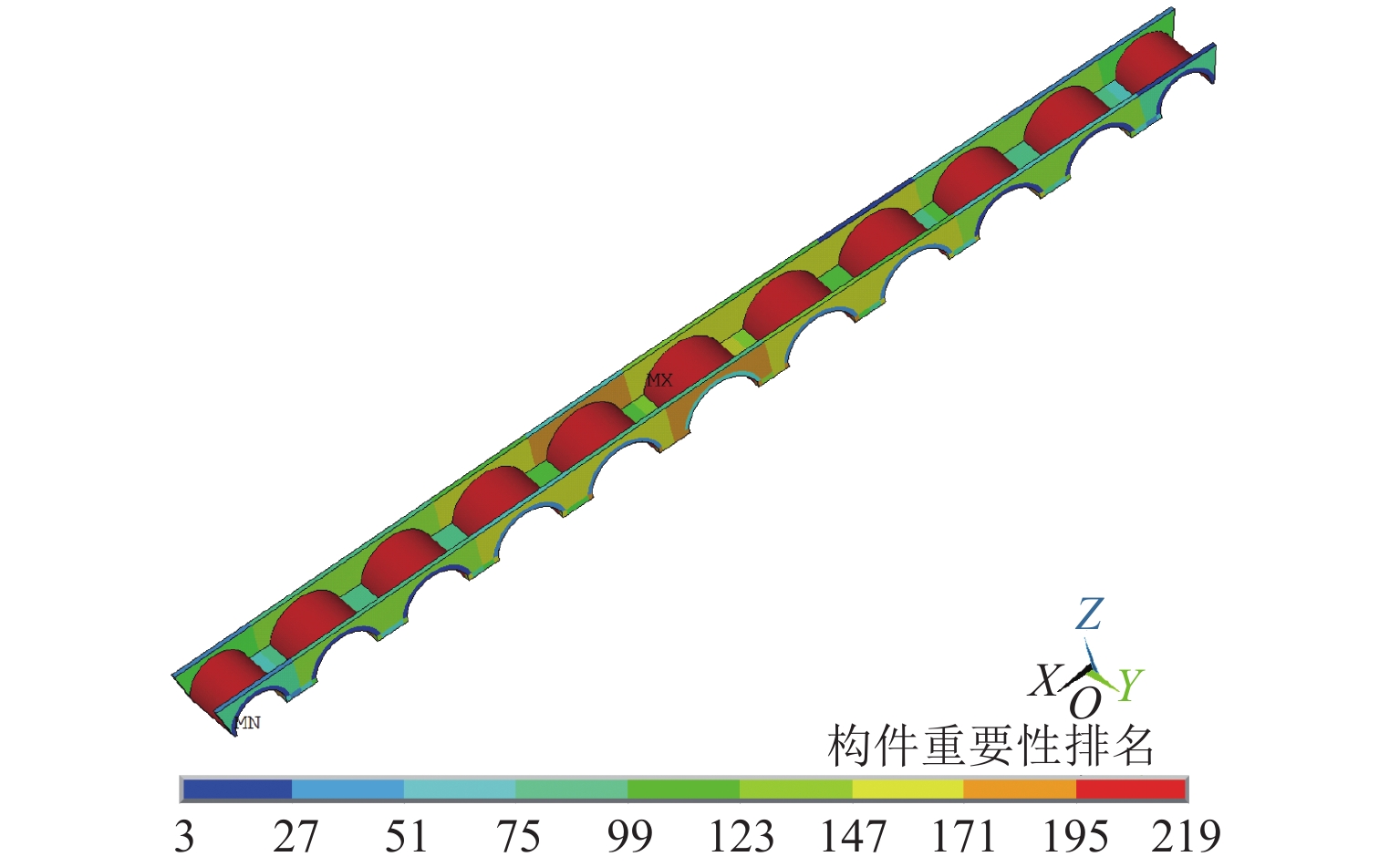
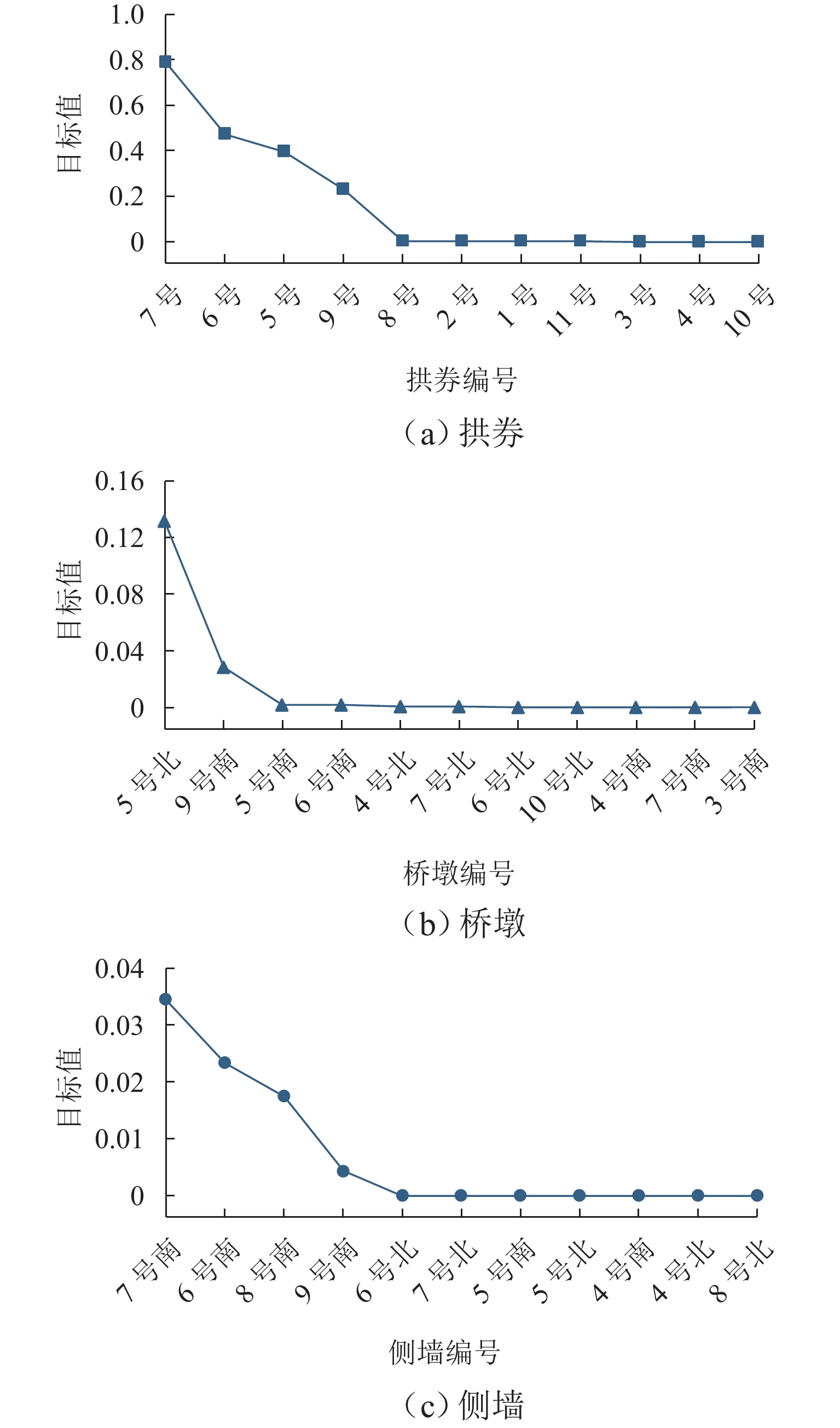
Table 2. Three principles matrix
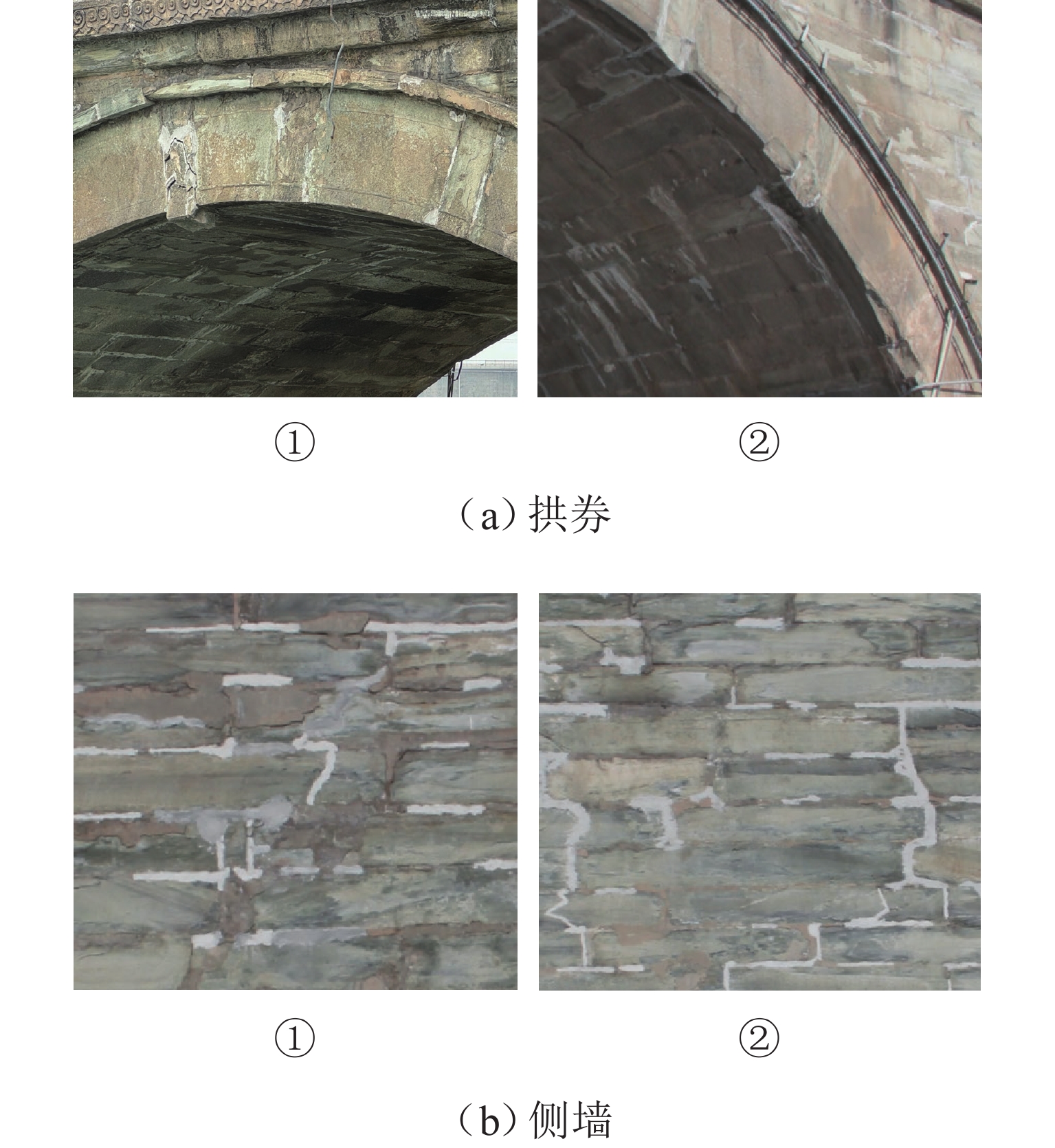
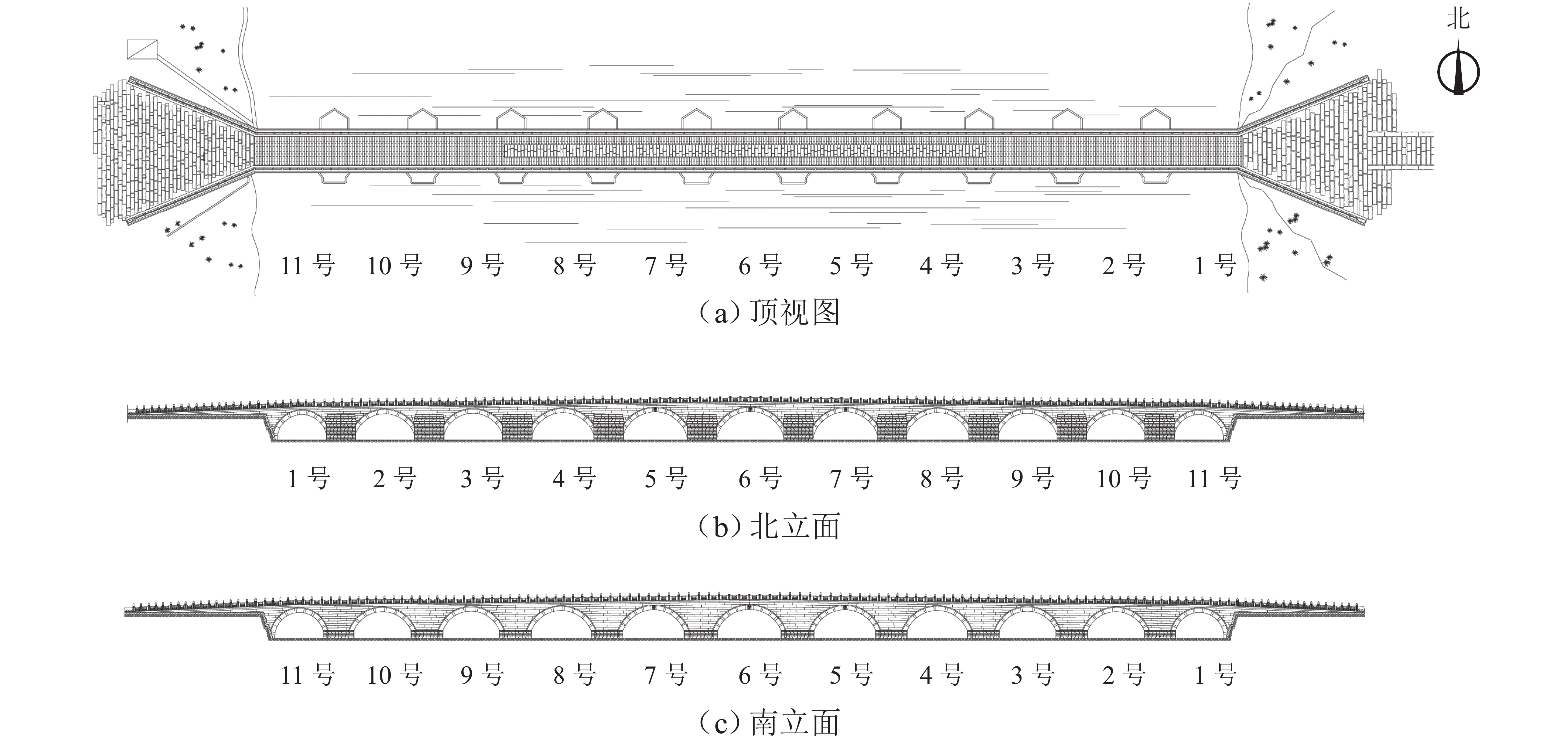
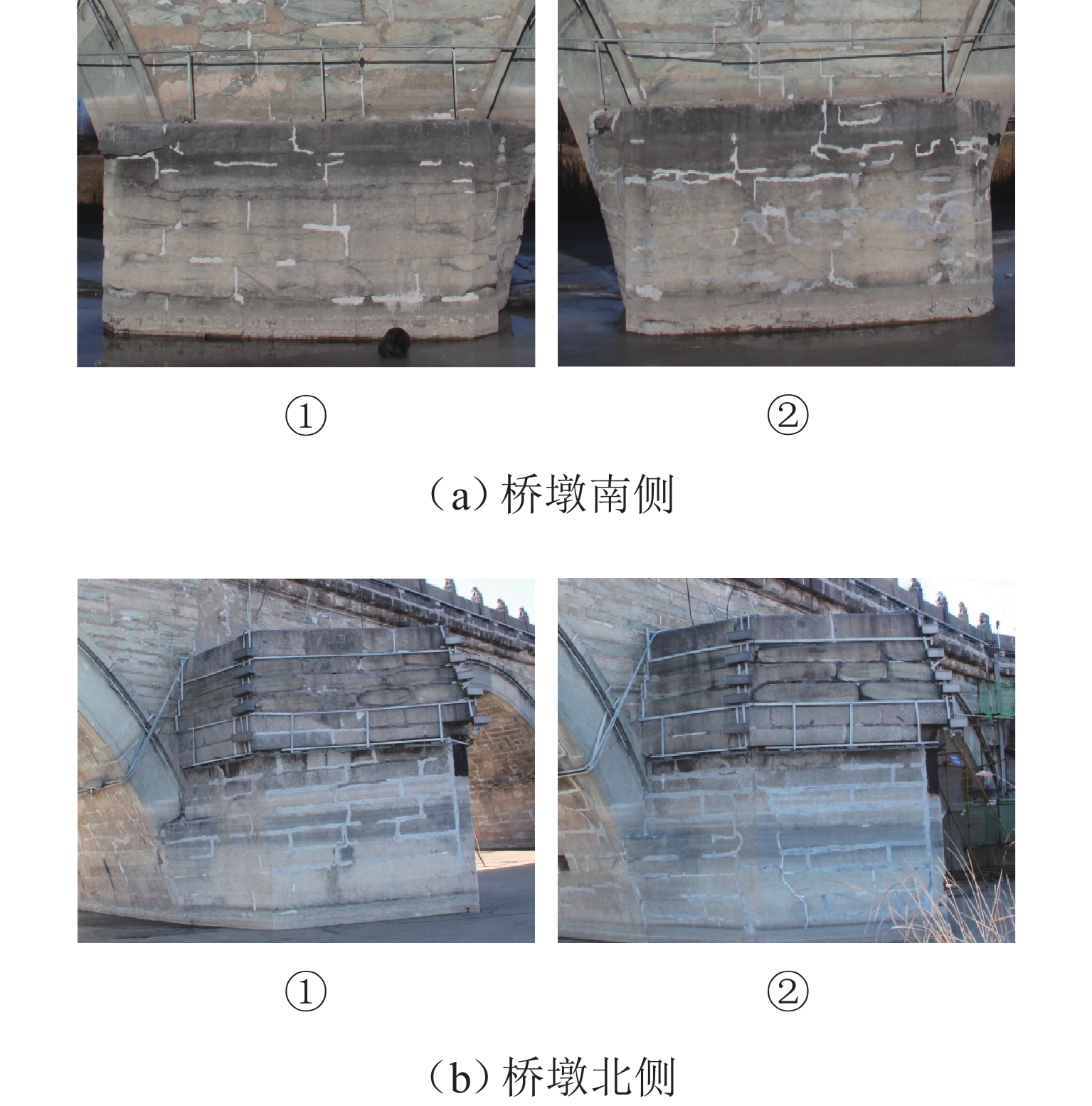
构件 残损 受力 重要性 位置 编号 损伤劣化 变形位移 拱券 1 号 0.75 0.50 0.237 0.617 2 号 0.75 0.50 0.312 0.885 3 号 0.50 0.50 0.356 0.899 1 号 0.50 0.50 0.351 0.912 5 号 0.50 0.75 0.484 0.962 6 号 0.50 0.75 0.535 1.000 7 号 0.50 1.00 0.484 0.962 8 号 0.75 0.50 0.351 0.912 9 号 0.75 0.75 0.356 0.899 10 号 0.50 0.75 0.312 0.885 11 号 0.75 0.50 0.237 0.617 南侧桥墩 1 号 0.50 0.50 0.257 0.169 2 号 0.50 0.50 0.347 0.218 3 号 0.50 0.50 0.388 0.245 4 号 0.50 0.50 0.434 0.277 5 号 0.75 0.50 0.557 0.350 6 号 0.75 0.50 0.557 0.350 7 号 0.50 0.50 0.434 0.277 8 号 0.50 0.50 0.388 0.245 9 号 1.00 0.75 0.347 0.218 10 号 0.50 0.50 0.257 0.169 北侧桥墩 1 号 0.50 0.50 0.257 0.169 2 号 0.50 0.50 0.347 0.218 3 号 0.50 0.50 0.388 0.245 4 号 0.75 0.50 0.434 0.277 5 号 0.50 0.75 0.557 0.350 6 号 0.50 0.50 0.557 0.350 7 号 0.75 0.50 0.434 0.277 8 号 0.50 0.50 0.388 0.245 9 号 0.50 0.50 0.347 0.218 10 号 0.75 0.50 0.257 0.169 南侧侧墙 1 号 0.50 0.50 0.150 0.119 2 号 0.5 0.5 0.187 0.153 3 号 0.50 0.50 0.190 0.160 4 号 0.50 0.50 0.251 0.185 5 号 0.50 0.50 0.291 0.200 6 号 0.50 0.75 0.321 0.214 7 号 0.50 1.00 0.297 0.200 8 号 0.50 1.00 0.238 0.185 9 号 0.50 0.75 0.219 0.160 10 号 0.50 0.50 0.198 0.153 11 号 0.50 0.50 0.144 0.119 北侧侧墙 1 号 0.50 0.50 0.150 0.119 2 号 0.50 0.50 0.187 0.153 3 号 0.50 0.50 0.190 0.160 4 号 0.50 0.50 0.251 0.185 5 号 0.50 0.50 0.291 0.200 6 号 0.50 0.50 0.321 0.214 7 号 0.50 0.50 0.297 0.200 8 号 0.50 0.50 0.238 0.185 9 号 0.50 0.50 0.219 0.160 10 号 0.50 0.50 0.198 0.153 11 号 0.50 0.50 0.144 0.119 表 3 传感器编号
Table 3. Sensor codes
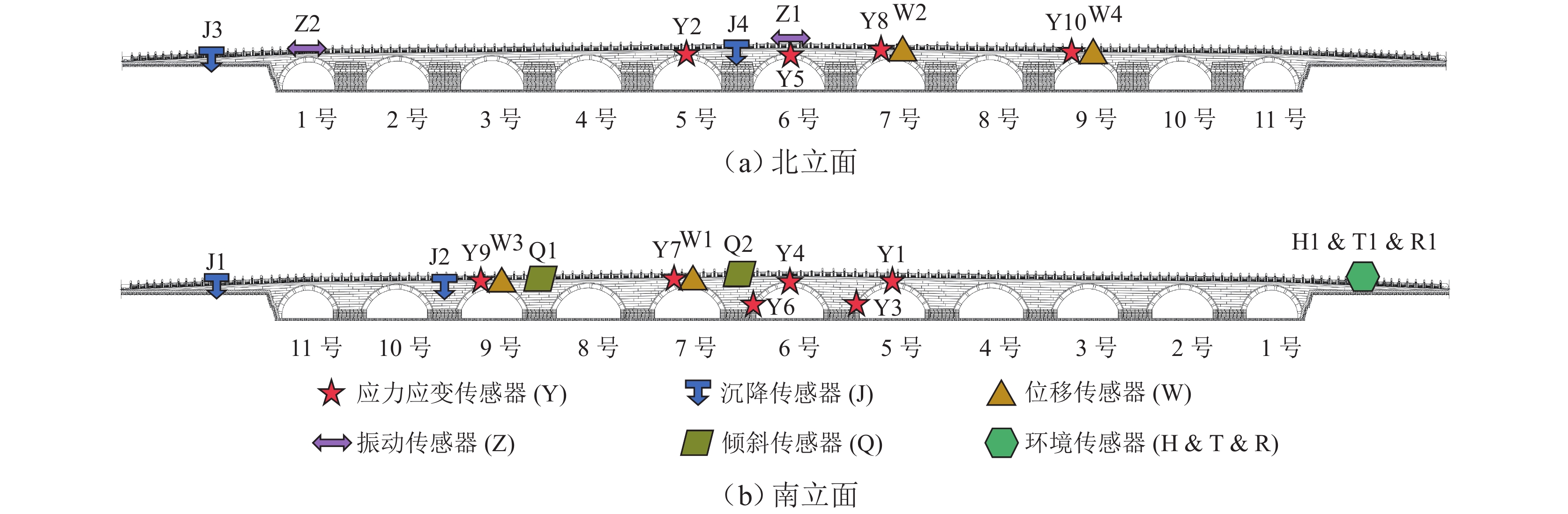
传感器类型 编号 安装位置 应力应变计 Y1 5 号拱券南侧拱顶 Y2 5 号拱券北侧拱顶 Y3 5 号拱券南侧拱脚 Y4 6 号拱券南侧拱顶 Y5 6 号拱券北侧拱顶 Y6 6 号拱券南侧拱脚 Y7 7 号拱券南侧拱顶 Y8 7 号拱券北侧拱顶 Y9 9 号拱券南侧拱顶 Y10 9 号拱券北侧拱顶 静力水准仪 J1 西侧桥头相对稳定点 J2 9 号桥墩对应桥面南侧 J3 西侧桥头相对稳定点 J4 5 号桥墩对应桥面北侧 智能位移计 W1 7 号拱券南侧拱顶 W2 7 号拱券北侧拱顶 W3 9 号拱券南侧拱顶 W4 9 号拱券北侧拱顶 智能倾斜计 Q1 8、9 号孔间侧墙南侧 Q2 6、7 号孔间侧墙南侧 振动传感器 Z1 6 号孔北侧栏板外侧 Z2 1 号孔北侧栏板外侧 湿度传感器 H1 温度传感器 T1 东侧桥头南面护堤 雨量计 R1 表 4 数据分析结果
Table 4. Data analysis results
传感器编号 A B |B/A| Y1 27.81 −45.37 1.631 Y2 28.88 −52.89 1.831 Y3 43.76 −19.43 0.444 Y4 27.77 −45.56 1.641 Y5 36.30 −64.73 1.783 Y6 28.71 −49.39 1.720 Y7 29.22 −45.59 1.560 Y8 21.05 −28.62 1.360 Y9 27.89 −41.55 1.490 Y10 26.86 −61.97 2.307 W1 1.40 −1.01 0.721 W2 1.23 −1.20 0.976 W3 0.74 −0.79 1.068 W4 0.58 −0.78 1.345 Q1X 方向 0.16 −0.22 1.375 Q1Y 方向 0.25 −0.24 0.960 Q2X 方向 0.18 −0.31 1.722 Q2Y 方向 0.13 −0.13 1.000 -
[1] 淳庆, 汤晔峥, 潘建伍, 等. 明代石拱桥襟湖桥保护技术研究[J]. 文物保护与考古科学, 2016, 28(3): 65-72.CHUN Qing, TANG Yezheng, PAN Jianwu, et al. Research on conservation of Jin Hu Bridge, a Stone arch bridge built in the Ming Dynasty[J]. Sciences of Conservation and Archaeology, 2016, 28(3): 65-72. [2] 淳庆, 韩宜丹, 李可镜, 等. 桥梁文物预防性保护技术的研究现状与展望[J]. 世界建筑, 2024(10): 57-64.CHUN Qing, HAN Yidan, LI Kejing, et al. Current situation and prospect on preventive conservation technologies for bridge heritage[J]. World Architecture, 2024(10): 57-64. [3] 吴美萍. 国际遗产保护新理念: 建筑遗产的预防性保护探析[J]. 中国文物科学研究, 2011(2): 90-95.WU Meiping. A new concept of international heritage protection: analysis on the preventive protection of architectural heritage[J]. China Cultural Heritage Scientific Research, 2011(2): 90-95. [4] 吴美萍, 朱光亚. 建筑遗产的预防性保护研究初探[J]. 建筑学报, 2010(6): 37-39.WU Meiping, ZHU Guangya. Preliminary study on preventive conservation of architectural heritage[J]. Architectural Journal, 2010(6): 37-39. [5] 朱淳, 龚逸非, 宋盛渊, 等. 滑坡多源监测技术及预警模型研究进展与展望[J/OL]. 西南交通大学学报, 2024: 1-19. (2024-09-29). https: //kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=XNJT20240913001&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ. [6] 何庆, 周思源, 万秋实, 等. 基于数据分析和物理模型的高速铁路梁端一体化装置监测管理建议[J/OL]. 西南交通大学学报, 2025: 1-10. (2025-03-11). https://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=XNJT20250225001&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ. [7] 王旭东. 基于风险管理理论的莫高窟监测预警体系构建与预防性保护探索[J]. 敦煌研究, 2015(1): 104-110.WANG Xudong. Construction of a monitoring and precaution system and exploration of preventive conservation at the Mogao Grottoes based on risk management theory[J]. Dunhuang Research, 2015(1): 104-110. [8] 梅雯. 园林遗产监测预警体系研究: 以苏州古典园林为例[D]. 杭州: 浙江农林大学, 2019. [9] 郭明, 闫冰男, 周腾飞, 等. 激光雷达技术在应县木塔形变分析中的应用[J]. 建筑科学与工程学报, 2020, 37(2): 109-117.GUO Ming, YAN Bingnan, ZHOU Tengfei, et al. Application of LiDAR technology in deformation analysis of Yingxian wooden pagoda[J]. Journal of Architecture and Civil Engineering, 2020, 37(2): 109-117. [10] 淳庆, 林怡婕, 张承文. 宁波保国寺大殿的结构机制和健康监测关键技术研究[J]. 东方建筑遗产, 2020: 143-151. [11] 李爱群, 周坤朋, 解琳琳, 等. 中国建筑遗产预防性保护再思考[J]. 中国文化遗产, 2021(1): 13-22.LI Aiqun, ZHOU Kunpeng, XIE Linlin, et al. Rethinking on preventive protection of architectural heritage in China[J]. China Cultural Heritage, 2021(1): 13-22. [12] 邢国华, 陈思锦, 苗鹏勇, 等. 基于改进遗传算法的大型体育场馆传感器优化布置研究[J]. 建筑科学与工程学报, 2024, 41(6): 19-30.XING Guohua, CHEN Sijin, MIAO Pengyong, et al. Optimal sensor placement for large-scale stadium based on improved genetic algorithm[J]. Journal of Architecture and Civil Engineering, 2024, 41(6): 19-30. [13] 胡莹迪, 张令心. 一种结构台阵传感器优化布设的单位刚度能量-驱动点留数法[J]. 地震工程与工程振动, 2025, 45(1): 28-37.HU Yingdi, ZHANG Lingxin. A unit stiffness energy-drive point retention method for the optimal layout of structural array sensors[J]. Earthquake Engineering and Engineering Dynamics, 2025, 45(1): 28-37. [14] 周鹏飞, 张雍. 基于改进多目标粒子群算法的码头结构传感器优化布置[J]. 振动与冲击, 2025, 44(1): 243-251.ZHOU Pengfei, ZHANG Yong. Wharf structural optimal sensor placement based on IMOPSO algorithm[J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2025, 44(1): 243-251. [15] 王雅琼. 以风险识别为目的的门式起重机传感器优化布置研究[D]. 南京: 东南大学, 2015. [16] 孔祥萸, 李卫, 张龙. 卢沟桥的选址与营造技术研究[J]. 中国文化遗产, 2023(6): 118-125.KONG Xiangyu, LI Wei, ZHANG Long. Site selection and construction technology of Lugou Bridge[J]. China Cultural Heritage, 2023(6): 118-125. [17] 史聪怡, 乔亚军, 张龙. 卢沟桥景观演进与营修史研究[J]. 建筑学报, 2024(增1): 66-71.SHI Congyi, QIAO Yajun, ZHANG Long. Research on the landscape evolution and the restoration history of Lugou Bridge[J]. Architectural Journal, 2024(S1): 66-71. [18] 迟宇, 邓扬, 李爱群, 等. 卢沟桥形变监测分析[J]. 测绘科学, 2021, 46(8): 63-72, 126.CHI Yu, DENG Yang, LI Aiqun, et al. The analysis for the deformation monitoring of Lugou bridge[J]. Science of Surveying and Mapping, 2021, 46(8): 63-72, 126. [19] 郝务宸, 董友强, 迟宇, 等. 基于模糊层次分析法的石拱桥适用性评价分析[J]. 地理信息世界, 2022, 29(4): 65-69.HAO Wuchen, DONG Youqiang, CHI Yu, et al. Applicability evaluation analysis of stone arch bridge based on fuzzy analytic hierarchy process[J]. Geomatics World, 2022, 29(4): 65-69. [20] 张承文, 淳庆, 花全均, 等. 基于元遗传算法的石拱桥传感器优化布置及评价方法研究[J/OL]. 西南交通大学学报, 2024: 1-11. (2024-10-10). https: //kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=XNJT20240913002&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ. [21] 张承文, 淳庆, 马宇坤, 等. 基于时空差分图卷积神经网络的古代石拱桥损伤识别研究[J]. 东南大学学报(自然科学版), 2025, 55(2): 370-379.ZHANG Chengwen, CHUN Qing, MA Yukun, et al. Research on damage detection of ancient stone arch bridges based on spatio-temporal difference graph convolutional neural network[J]. Journal of Southeast University (Natural Science Edition), 2025, 55(2): 370-379. [22] 张时琦, 淳庆. 明代石拱桥永昌桥的加固修缮技术研究[J]. 文物保护与考古科学, 2019, 31(6): 54-61.ZHANG Shiqi, CHUN Qing. Research on strengthening techniques for Yongchang Bridge, a stone arch bridge built in the Ming dynasty[J]. Sciences of Conservation and Archaeology, 2019, 31(6): 54-61. [23] 赵丹. 石拱桥的健康监测与保护研究[D]. 聊城: 聊城大学, 2015. [24] 刘聪. 石拱桥极限承载能力分析与影响因素[D]. 长沙: 长沙理工大学, 2015. [25] DR M Y, HABIBI H. Residual capacity evaluation of masonry arch bridges by extended finite element method[J]. Structural Engineering International, 2023, 33(1): 183-194. doi: 10.1080/10168664.2021.1944454 [26] 徐睦. 基于预防性保护理论的德胜门箭楼监测系统研究[D]. 北京: 北京建筑大学, 2023. [27] 中华人民共和国住房和城乡建设部. 民用建筑可靠性鉴定标准: GB 50292—2015[S]. 北京: 中国建筑工业出版社, 2016. [28] 国家市场监督管理总局, 国家标准化管理委员会. 古建筑砖石结构维修与加固技术规范: GB/T 39056—2020[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2020. [29] 龚晓进. 石拱桥病害分析及维修加固方法研究[D]. 成都: 西南交通大学, 2007. [30] HEYMAN J. The safety of masonry arches[J]. International Journal of Mechanical Sciences, 1969, 11(4): 363-385. doi: 10.1016/0020-7403(69)90070-8 [31] 钱令希. 赵州桥的承载能力分析[J]. 土木工程学报, 1987, 20(4): 39-48.QIAN Lingxi. The carrying capacity of Zhaozhou stone arch bridge[J]. China Civil Engineering Journal, 1987, 20(4): 39-48. [32] 陈荣刚, 郑振飞. 石拱桥极限承载能力分析[J]. 福州大学学报(自然科学版), 2002, 30(1): 92-97.CHEN Ronggang, ZHENG Zhenfei. Ultimate bearing capacity analysis of stone arch bridges[J]. Journal of Fuzhou University (Natural Sciences Edtion), 2002, 30(1): 92-97. [33] 聂建国, 樊健生. 700年石拱桥的静力加载试验与结构分析[J]. 清华大学学报(自然科学版), 2003, 43(6): 840-843.NIE Jianguo, FAN Jiansheng. Static loading test and structural analysis of a 700 year old masonry arch bridge[J]. Journal of Tsinghua University (Science and Technology), 2003, 43(6): 840-843. [34] HAN Y D, CHUN Q, GAO X Y. Flood-induced forces and collapse mechanism of historical multi-span masonry arch bridges: The Putang Bridge case[J]. Engineering Failure Analysis, 2023, 153: 107564. doi: 10.1016/j.engfailanal.2023.107564 [35] ALPASLAN E, YILMAZ M F, ŞENGÖNÜL B D. Rating and reliability assessment of a historical masonry arch bridge[J]. Journal of Civil Structural Health Monitoring, 2023, 13(4): 1003-1021. [36] 蔡建国, 王蜂岚, 冯健, 等. 连续倒塌分析中结构重要构件的研究现状[J]. 工业建筑, 2011, 41(10): 85-89.CAI Jianguo, WANG Fenglan, FENG Jian, et al. Review of the key element for progressive collapse of structures[J]. Industrial Construction, 2011, 41(10): 85-89. [37] 朱丽华, 王宁娟, 戴军. 基于客观赋权法的构件重要性评估[J]. 建筑科学与工程学报, 2015, 32(4): 46-52.ZHU Lihua, WANG Ningjuan, DAI Jun. Evaluation on element importance based on objective weighting method[J]. Journal of Architecture and Civil Engineering, 2015, 32(4): 46-52. [38] YI H, BALAKRISHNAN N. Importance measures for two semi-coherent systems with shared components[J]. Reliability Engineering & System Safety, 2024, 250: 110306. [39] 叶列平, 林旭川, 曲哲, 等. 基于广义结构刚度的构件重要性评价方法[J]. 建筑科学与工程学报, 2010, 27(1): 1-6, 20.YE Lieping, LIN Xuchuan, QU Zhe, et al. Evaluating method of element importance of structural system based on generalized structural stiffness[J]. Journal of Architecture and Civil Engineering, 2010, 27(1): 1-6, 20. [40] 卢啸, 陆新征, 张劲泉, 等. 某石拱桥连续倒塌模拟及构件重要性评价[J]. 兰州交通大学学报, 2010, 29(6): 25-30.LU Xiao, LU Xinzheng, ZHANG Jinquan, et al. Progressive collapse simulation and components importance evaluation of a stone arch bridge[J]. Journal of Lanzhou Jiaotong University, 2010, 29(6): 25-30. [41] 淳庆, 孟哲, 贾肖虎, 等. 典型江南传统木构建筑的构件重要性分析方法[J]. 华侨大学学报(自然科学版), 2019, 40(1): 64-71.CHUN Qing, MENG Zhe, JIA Xiaohu, et al. Evaluation methods of component importance of typical traditional timber buildings in Yangtze River regions[J]. Journal of Huaqiao University (Natural Science), 2019, 40(1): 64-71. [42] 彭贝. 明代砖砌无梁殿结构安全评估方法研究[D]. 南京: 东南大学, 2023. [43] 中华人民共和国住房和城乡建设部. 砌体结构设计规范: GB 50003—2011[S]. 北京: 中国计划出版社, 2012. [44] SEVIM B, BAYRAKTAR A, ALTUNIŞIK A C, et al. Assessment of nonlinear seismic performance of a restored historical arch bridge using ambient vibrations[J]. Nonlinear Dynamics, 2011, 63(4): 755-770. doi: 10.1007/s11071-010-9835-y -





 下载:
下载: