Research on Long-Wave Irregularity of Metro Rail and Wheel-Rail Short-Wave Roughness Spectra
-
摘要:
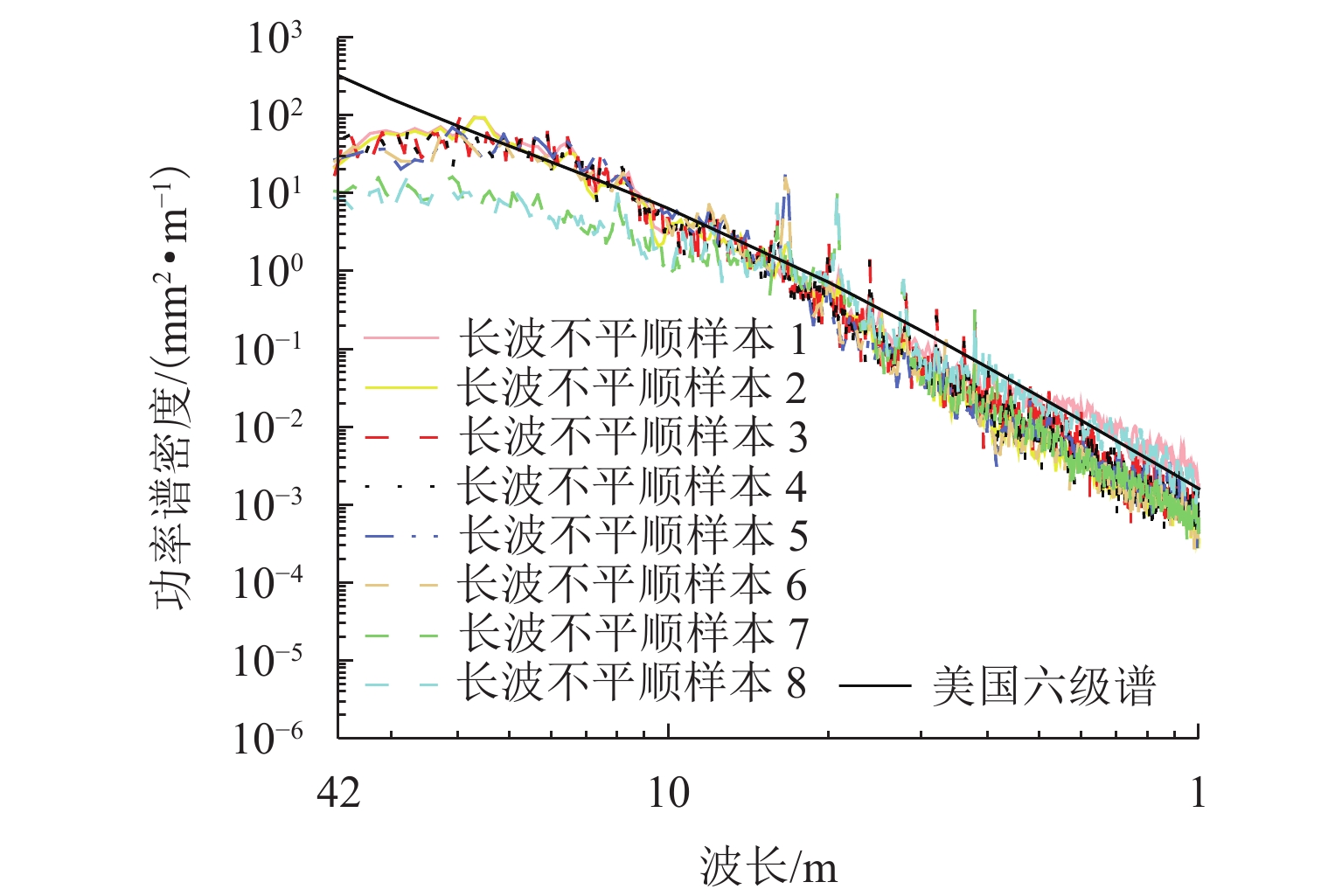
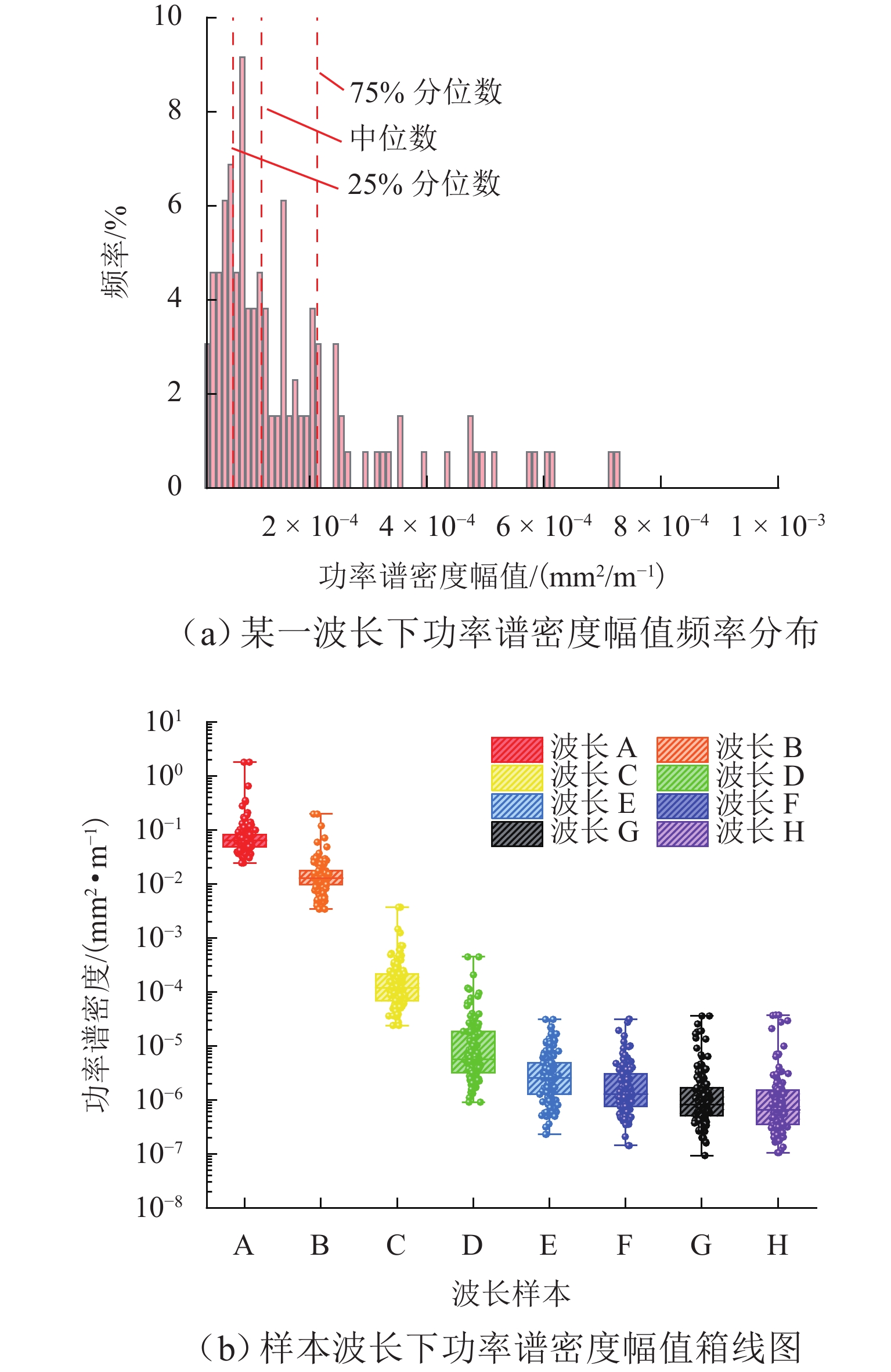
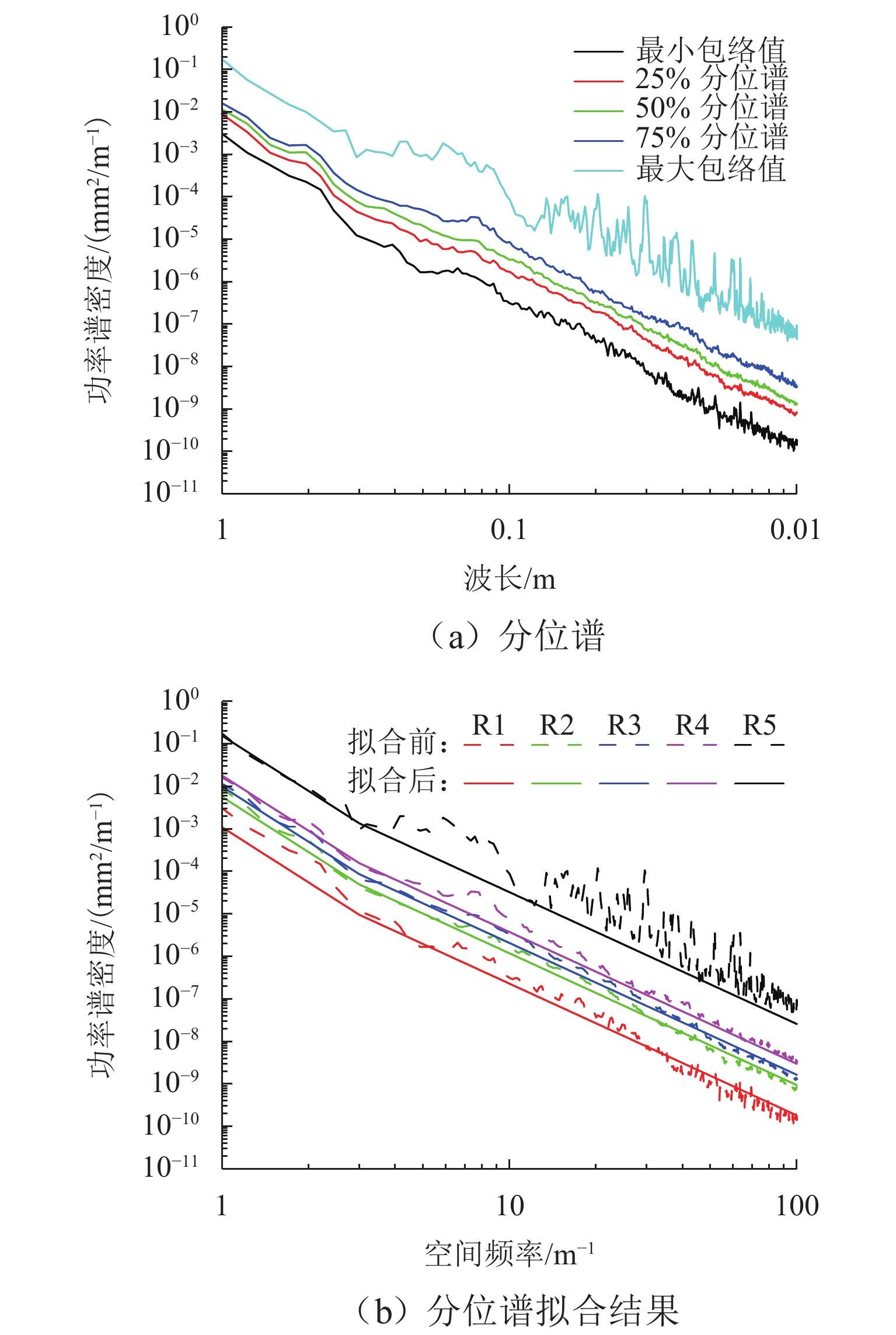
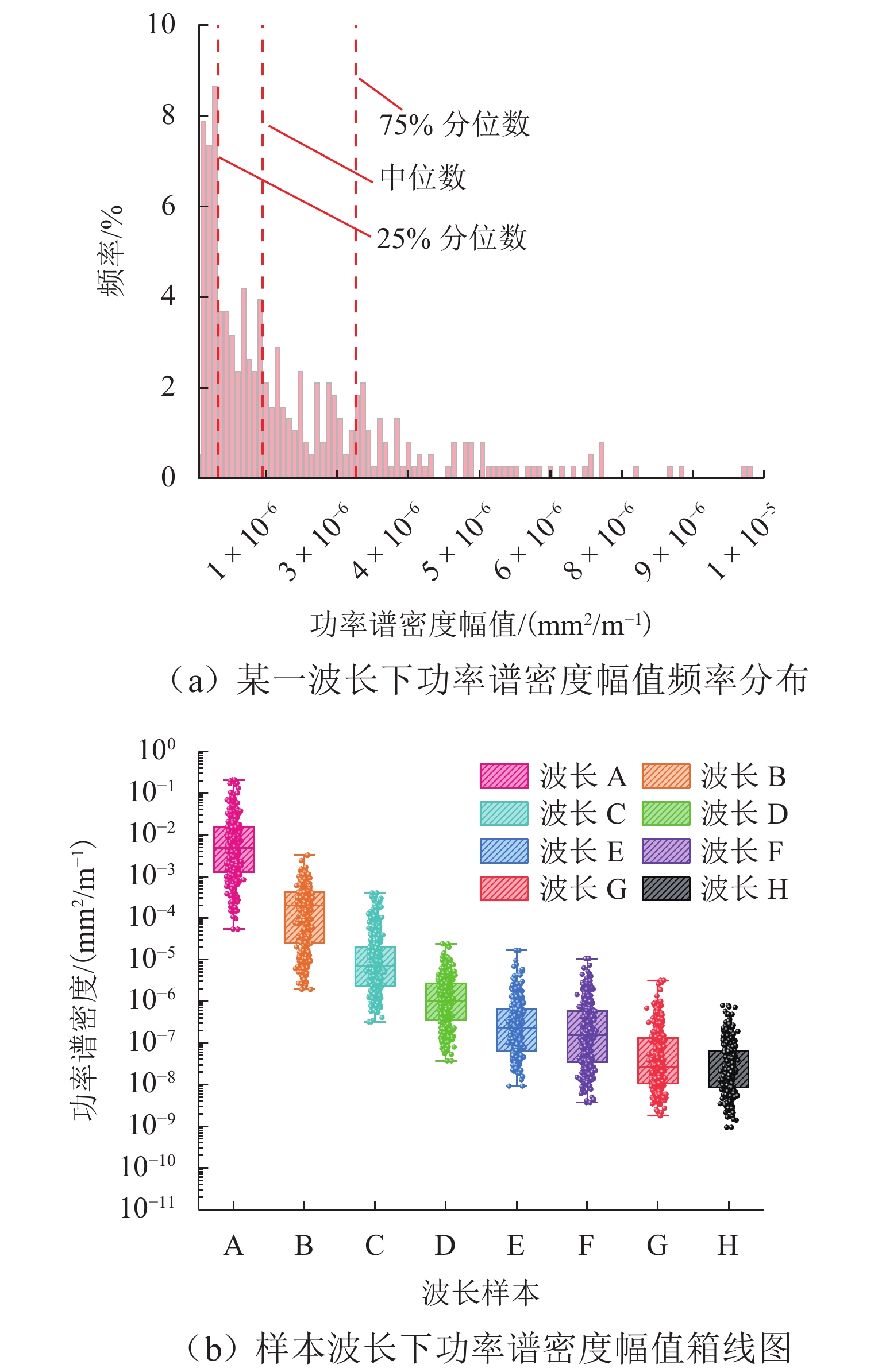
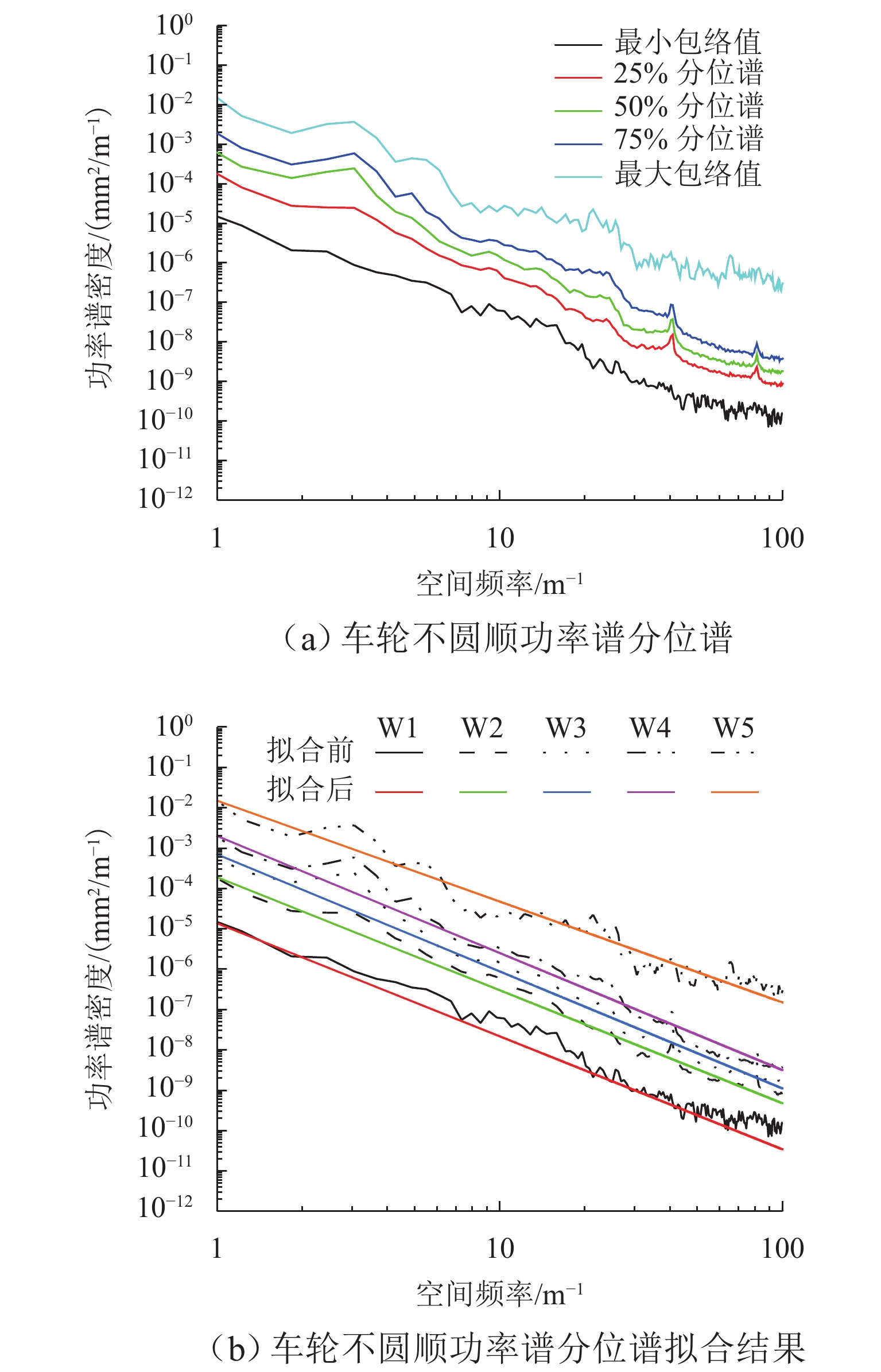
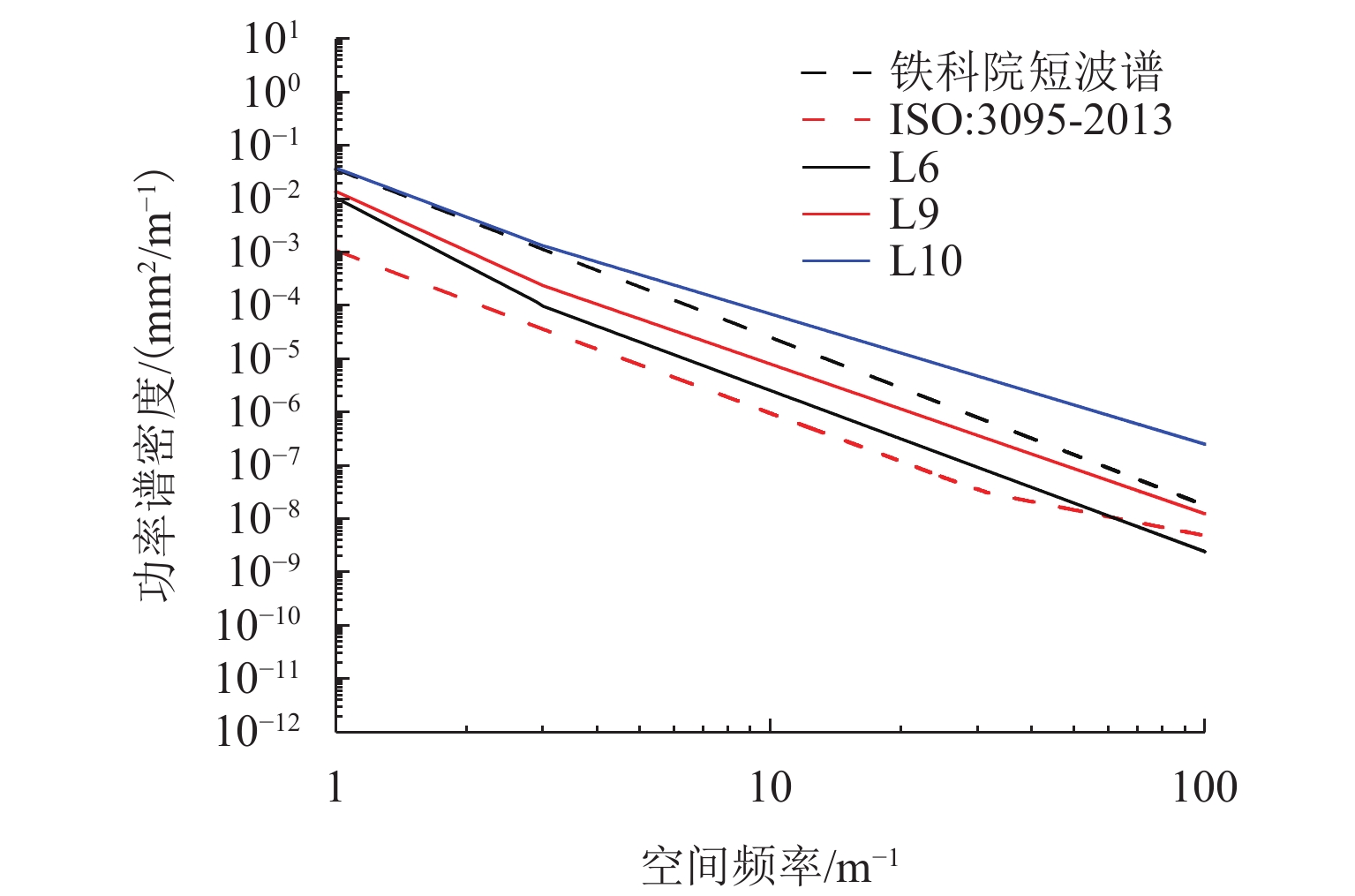
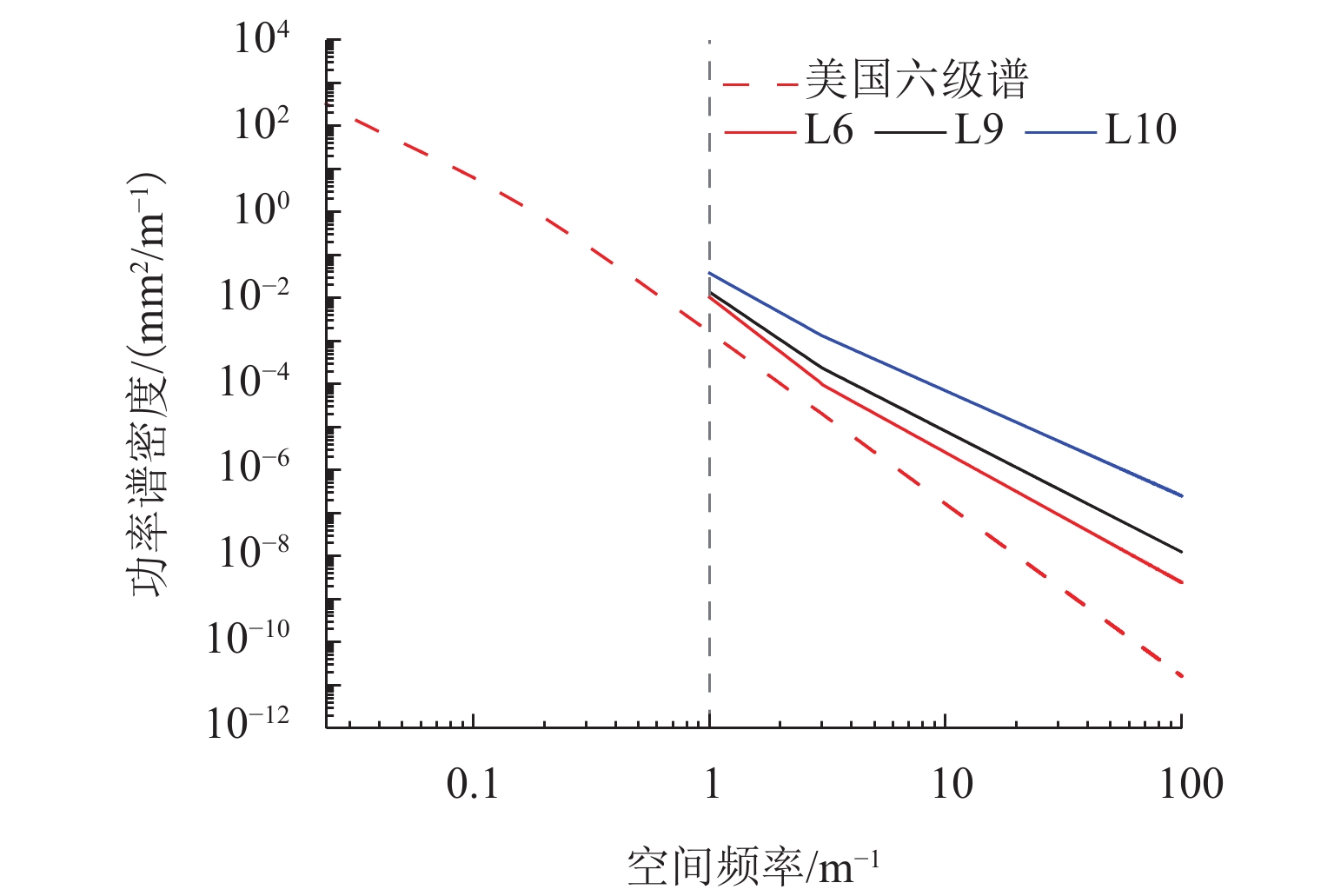
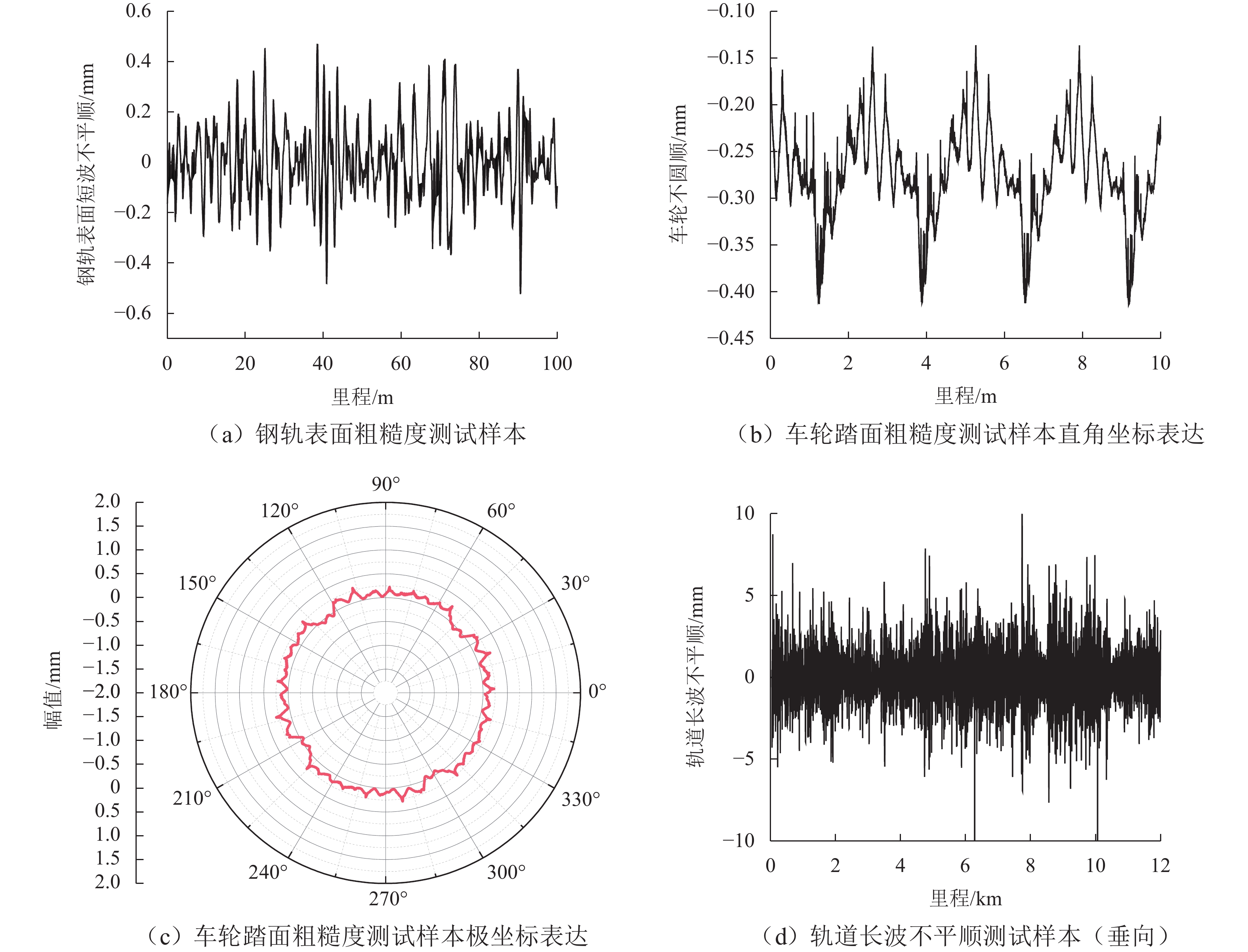
为建立用于地铁振动噪声数值仿真预测的轮轨宽频激励模型,依托北京地铁线路实测轨道长波不平顺、钢轨表面粗糙度和青岛地铁实测车轮踏面不圆顺数据,开展地铁轨道长波不平顺选取与轮轨短波粗糙度谱研究. 首先,采用Welch法对实测轨道不平顺数据进行功率谱密度估计,并给出了钢轨短波不平顺功率谱和车轮不圆顺功率谱表达式及其拟合参数;长波方面,以速度等级对应的单项高低TQI值相近原则选取典型轨道谱;短波方面,以四分位数分别将钢轨表面短波不平顺功率谱和车轮不圆顺功率谱划分为五个等级,并考虑二者相干性提出轮轨粗糙度谱. 研究结果表明:依据单项高低TQI值相近原则,选取的美国六级谱与北京设计速度80 km/h的地铁线路轨道长波(1~42 m)不平顺功率谱吻合良好;钢轨表面短波不平顺功率谱和车轮不圆顺功率谱在同一短波波长下幅值分布均具有显著的偏态分布特征;短波0.01~1.00 m内的不同等级大小轮轨粗糙度谱主要受车轮不圆顺谱主导,严重时甚至超过了铁科院短波谱.
Abstract:To establish a wheel-rail broadband excitation model for numerical simulation and prediction of metro vibration noise, a study was conducted on the selection for long-wave irregularity of metro rail and wheel-rail short-wave roughness spectra based on measured data of long-wave irregularity of metro rail and rail surface roughness from Beijing metro lines, as well as wheel tread out-of-roundness (OOR) from Qingdao metro lines. Firstly, the Welch method was applied to the measured data of rail irregularity to estimate the power spectral density, and the expressions for the short-wave irregularity power spectrum of rail and the OOR power spectrum of wheel, as well as their fitting parameters were provided. In terms of long wavelength, typical rail spectra were selected according to the principle of similarity in individual high and low TQI values corresponding to speed classes. Regarding short wavelength, the short-wave irregularity power spectrum of the rail surface and the OOR power spectrum of the wheel were respectively divided into five grades based on quartiles, and a wheel-rail roughness spectrum was proposed by considering their coherence. The results show that the selected American sixth grade spectrum aligns well with the long-wave (1–42 m) irregularity power spectrum of metro lines with 80 km/h designed by Beijing, according to the principle of similarity in individual high and low TQI values. Both the short-wave irregularity power spectrum of the rail surface and the wheel OOR power spectrum exhibit a significantly skewed amplitude distribution under the same short wavelength. The wheel-rail roughness spectra of different levels in the short-wave range of 0.01–1 m are mainly dominated by the wheel OOR spectrum, and in severe cases, it even exceeds the short-wave spectrum recommended by the China Academy of Railway Sciences.
-
表 1 (TG/GW102—2019)中规定的质量指数管理值
Table 1. Quality index management value specified in TG/GW102–2019
速度等级 左高低 右高低 左轨向 右轨向 轨距 水平 三角坑 TQI值 v≤80 km/h 2.2~2.5 2.2~2.5 1.8~2.2 1.8~2.2 1.4~1.6 1.7~1.9 1.9~2.1 13.0~15.0 80<v≤120 km/h 1.8~2.2 1.8~2.2 1.4~1.9 1.4~1.9 1.3~1.4 1.6~1.7 1.7~1.9 11.0~13.0 120<v≤ 160 km/h 1.5~1.8 1.5~1.8 1.1~1.4 1.1~1.4 1.1~1.3 1.3~1.6 1.4~1.7 9.0~11.0 v>160 km/h 1.1~1.5 1.1~1.5 0.9~1.1 0.9~1.1 0.9~1.1 1.1~1.3 1~1.4 7.0~9.0 表 2 常见典型轨道谱时域样本TQI值
Table 2. TQI values of time domain samples of common typical rail spectra
轨道不平顺 左高低 右高低 左轨向 右轨向 轨距 水平 三角坑 TQI值 美国五级谱 3.2~4.7 3.1~4.7 2.8~5.0 2.6~5.0 1.7~2.9 1.7~2.8 1.9~2.1 13.0~15.0 美国六级谱 2.1~3.6 2.3~3.6 2.0~3.4 2.2~3.5 1.3~2.3 1.6~2.0 1.7~1.9 11.0~13.0 德国高干扰谱 2.6~4.8 2.6~4.4 2.0~3.0 2.0~3.0 0.4~0.7 1.8~3.0 1.4~1.7 9.0~11.0 德国低干扰谱 1.8~2.4 1.8~2.4 1.3~2.0 1.3~2.0 0.4~0.5 1.2~1.7 1~1.4 7.0~9.0 中国高速谱 0.5~0.6 0.5~0.7 0.5~0.6 0.4~0.7 0.3~0.5 0.4~0.6 1~1.4 7.0~9.0 表 3 钢轨表面短波不平顺功率谱分级系数
Table 3. Classification coefficient of short-wave irregularity power spectrum on rail surface
等级 $ {A}_{1} $ $ {K}_{1} $ $ {A}_{2} $ $ {K}_{\text{2}} $ $ b $ R1 0.0098 4.31 0.0026 3.10 − 0.9559 R2 − 0.2423 R3 0 R4 0.2582 R5 2.1930 表 4 车轮不圆顺功率谱分级系数
Table 4. Classification coefficient of wheel OOR power spectrum
等级 A k W1 1.37 × 10−5 2.80 W2 1.9 × 10−4 2.8 W3 7 × 10−4 2.9 W4 2 × 10−3 2.9 W5 1.5 × 10−2 2.5 表 5 原始谱与轮轨粗糙度谱的关系
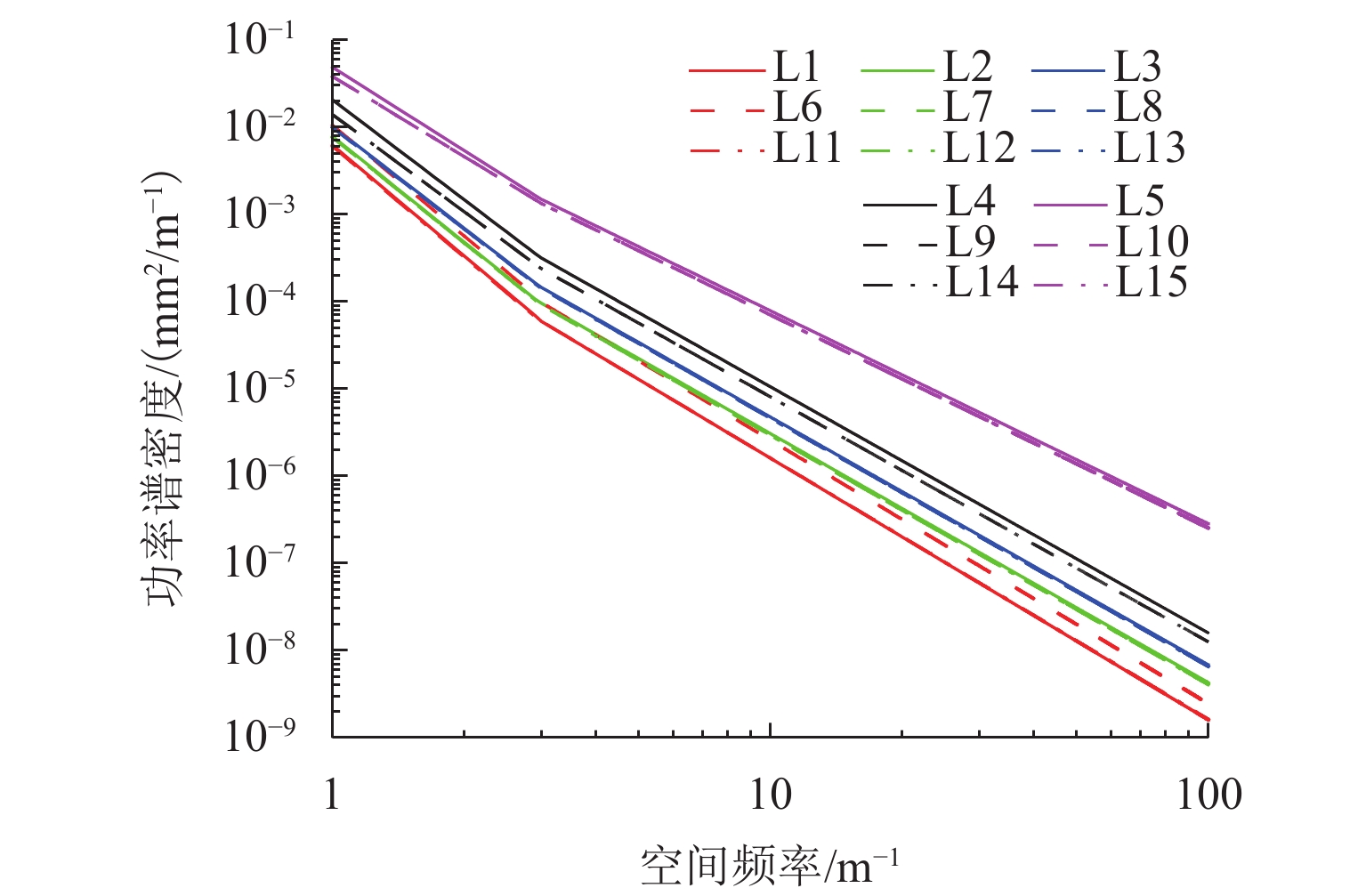
Table 5. Relationship between original spectrum and wheel-rail roughness spectrum
功率谱 W1 W2 W3 W4 W5 钢轨R2 L1 L2 L3 L4 L5 钢轨R3 L6 L7 L8 L9 L10 钢轨R4 L11 L12 L13 L14 L15 表 6 轮轨粗糙度谱公式参数取值
Table 6. Parameter value of wheel-rail roughness spectrum formula
等级 $ {A}_{1} $ $ {K}_{1} $ $ {A}_{2} $ $ {K}_{2} $ L1 6.2 × 10−3 4.2238 1.6 × 10−3 3.0005 L2 7.8 × 10−3 4.0307 2.2 × 10−3 2.8566 L3 1.02 × 10−2 3.8848 3.3 × 10−3 2.8430 L4 2.05 × 10−2 3.8082 7.0 × 10−3 2.8225 L5 4.85 × 10−2 3.1758 2.17 × 10−2 2.4426 L6 1.05 × 10−2 4.2440 2.7 × 10−3 3.0211 L7 7.6 × 10−3 4.0264 2.1 × 10−3 2.8544 L8 9.9 × 10−3 3.8785 3.2 × 10−3 2.8426 L9 1.39 × 10−2 3.7058 5.2 × 10−3 2.8089 L10 3.8 × 10−2 3.0519 1.95 × 10−2 2.4435 L11 6.0 × 10−3 4.2223 1.6 × 10−3 2.9991 L12 7.6 × 10−3 4.0257 2.1 × 10−3 2.8557 L13 9.9 × 10−3 3.8781 3.2 × 10−3 2.8435 L14 1.39 × 10−2 3.7057 5.2 × 10−3 2.8092 L15 3.80 × 10−2 3.0527 1.94 × 10−2 2.4421 -
[1] 罗林, 张格明, 吴旺青, 等. 轮轨系统轨道平顺状态的控制[M]. 北京: 中国铁道出版社, 2006: 3-4. [2] GARG V K, DUKKIPATI R V. Dynamics of Railway Vehicle Systems[M]. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 1984 [3] SCHIEHLEN W O. Dynamics of High-Speed Vehicles[M]. Cham: Springer Vienna, 1982. [4] SATO Y. Study on high-frequency vibrations in track operated with high-speed trains.[J]. Quarterly Report of RTRI, 1977, 18(3): 109-114. [5] Acoustics-Railway applications-Measurement of noise emitted by railbound vehicles: ISO 3095[S]. [S. l]: ISO, 2013. [6] Acoustics-Railway applications-Measurement of noise emitted by railbound vehicles: ISO 3095[S]. [S. l]: ISO, 2013. [7] Research Group on Random Vibration of Changsha Railway Institute etc. 关于机车车辆/轨道系统随机激励函数的研究[J]. 长沙铁道学院学报, 1985(2): 1-36. doi: 10.19713/j.cnki.43-1423/u.1985.02.001RESEARCH Group on Random Vibration of Changsha Railway Institute etc. Research on random excitation functions fo rolling stock/track system[J]. Journal of Railway Science and Engineering, 1985(2): 1-36. doi: 10.19713/j.cnki.43-1423/u.1985.02.001 [8] 王澜, 姚明初. 轨道结构随机振动理论及其在轨道结构减振研究中的应用[J]. 中国铁道科学, 1989, 10(2): 41-59.WANG Lan, YAO Mingchu. Random vibration theory of railtrack structure and it’s application in the study of railtrack vibration isolation[J]. China Railway Science, 1989, 10(2): 41-59. [9] 陈宪麦, 王澜, 陶夏新, 等. 我国干线铁路通用轨道谱的研究[J]. 中国铁道科学, 2008, 29(3): 73-77. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-4632.2008.03.014CHEN Xianmai, WANG Lan, TAO Xiaxin, et al. Study on general track spectrum for Chinese main railway lines[J]. China Railway Science, 2008, 29(3): 73-77. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-4632.2008.03.014 [10] 康熊, 刘秀波, 李红艳, 等. 高速铁路无砟轨道不平顺谱[J]. 中国科学(技术科学), 2014, 44(7): 687-696. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8360.2025.09.013KANG Xiong, LIU Xiubo, LI Hongyan, et al. PSD of ballastless track irregularities of high-speed railway[J]. Scientia Sinica (Technologica), 2014, 44(7): 687-696. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8360.2025.09.013 [11] 王平, 杨帆, 韦凯. 车-线-隧垂向环境振动预测辛模型及其应用[J]. 工程力学, 2017, 34(5): 171-178. doi: 10.6052/j.issn.1000-4750.2015.12.0973WANG Ping, YANG Fan, WEI Kai. Symplectic model and its application of vertical environment vibration prediction about vehicle-track-tunnel coupled system[J]. Engineering Mechanics, 2017, 34(5): 171-178. doi: 10.6052/j.issn.1000-4750.2015.12.0973 [12] 卢炜, 马帅, 高亮, 等. 北京地铁线路轨道不平顺谱分析[J]. 铁道工程学报, 2020, 37(3): 101-106. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2106.2020.03.017LU Wei, MA Shuai, GAO Liang, et al. Analysis of track irregularity spectrum of the Beijing subway lines[J]. Journal of Railway Engineering Society, 2020, 37(3): 101-106. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2106.2020.03.017 [13] 金锋, 肖宏, 崔旭浩. 基于Burg法的城市轨道交通快速线路轨道不平顺谱研究[J]. 铁道学报, 2020, 42(4): 99-106. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8360.2020.04.013JIN Feng, XIAO Hong, CUI Xuhao. Study on track irregularity spectrum of fast urban rail transit line based on burg method[J]. Journal of the China Railway Society, 2020, 42(4): 99-106. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8360.2020.04.013 [14] 马蒙, 张厚贵, 陈棋, 等. 钢轨表面短波不平顺对地铁振动源强影响[J]. 中国铁道科学, 2021, 42(3): 21-28. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4632.2021.03.03MA Meng, ZHANG Hougui, CHEN Qi, et al. Effect of rail surface shortwave irregularity on metro train induced vibration source intensity[J]. China Railway Science, 2021, 42(3): 21-28. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4632.2021.03.03 [15] 郝晓莉, 杨建, 杨飞, 等. 重载铁路轨道不平顺谱的分析和表征[J]. 铁道学报, 2023, 45(7): 115-125.HAO Xiaoli, YANG Jian, YANG Fei, et al. Analysis and expression of track irregularity spectrum of heavy-haul railway[J]. Journal of the China Railway Society, 2023, 45(7): 115-125. [16] 陈辉, 万壮. 成都地铁7号线轨道不平顺谱特征分析[J]. 城市轨道交通研究, 2023, 26(7): 1-6.CHEN Hui, WAN Zhuang. Characteristic analysis of Chengdu metro line 7 track irregularity spectrum[J]. Urban Mass Transit, 2023, 26(7): 1-6. [17] 陈宪麦, 董春敏, 魏子龙, 等. 高速铁路0.01~120 m波段轨道不平顺功率谱密度函数的构建[J]. 中南大学学报(自然科学版), 2023, 54(6): 2111-2121.CHEN Xianmai, DONG Chunmin, WEI Zilong, et al. Development on power spectral density function of track irregularity of 0.01-120 m waveband of high-speed railway[J]. Journal of Central South University (Science and Technology), 2023, 54(6): 2111-2121. [18] 陈小芳, 徐金辉, 刘庆杰, 等. 时速120 km地铁轨道几何不平顺谱研究[J]. 铁道标准设计, 2025, 69(7): 59-67.CHEN Xiaofang, XU Jinhui, LIU Qingjie, et al. Study on geometric irregularity spectrum of 120 km/h subway track[J]. Railway Standard Design, 2025, 69(7): 59-67. [19] 房建, 王宏轩, 郑稳稳, 等. 城市轨道交通轨面短波不平顺谱实测研究[J]. 北京交通大学学报, 2024, 48(1): 96-105. doi: 10.11860/j.issn.1673-0291.20230024FANG Jian, WANG Hongxuan, ZHENG Wenwen, et al. Research on short-wave irregularity spectrum of urban rail surface[J]. Journal of Beijing Jiaotong University, 2024, 48(1): 96-105. doi: 10.11860/j.issn.1673-0291.20230024 [20] 施以旋, 戴焕云, 毛庆洲, 等. 基于车轨耦合的地铁车轮多边形形成机理[J]. 西南交通大学学报, 2024, 59(6): 1357-1367, 1388.SHI Yixuan, DAI Huanyun, MAO Qingzhou, et al. Formation mechanism of metro wheel polygonal based on vehicle-track coupling[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2024, 59(6): 1357-1367,1388. [21] 董丙杰, 陈光雄, 冯晓航, 等. 钢轨波磨激励下的e 型弹条振动疲劳断裂机理[J]. 西南交通大学学报, 2025, 60(5): 1287-1295.DONG Bingjie, CHEN Guangxiong, FENG Xiaohang, et al. Vibration fatigue fracture mechanism of e-type clip under rail corrugation excitation[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2025, 60(5): 1287-1295. [22] 赖思成. 基于重载铁路轨检数据的轨道不平顺谱研究[D]. 成都: 西南交通大学, 2021. [23] 杨太. 现代谱估计理论在信号去噪中的应用研究[D]. 成都: 成都理工大学, 2013. [24] 程凡永. 高分辨谱估计及其在雷达信号处理中的应用研究[D]. 长沙: 湖南大学, 2009. [25] 赵泽明. 浮置板轨道系统弹性垫载频变动力响应特征及其老化预测研究[D]. 成都: 西南交通大学, 2022. [26] 康高亮, 王保国. 普速铁路线路修理规则: TGGW 102-2019[M]. 中国铁道出版社有限公司, 2019. [27] 国家质检总局. 城市轨道交通运营安全评估规范第1部分: 地铁和轻轨: GB/T 42334.1-2023[S]. 2023. [28] 韦凯, 王平. 铁路轨道高聚物弹性元件刚度设计方法与应用[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2023: 24-25. [29] 李明航, 马蒙, 谭新宇, 等. 随机车轮不圆顺及车辆参数对轨道频域振动响应影响分析[J]. 振动与冲击, 2021, 40(22): 104-111, 137. doi: 10.13465/j.cnki.jvs.2021.22.015LI Minghang, MA Meng, TAN Xinyu, et al. Influences of random wheel irregularity and vehicle parameters on the vibration of track in frequency domain[J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2021, 40(22): 104-111,137. doi: 10.13465/j.cnki.jvs.2021.22.015 [30] 马蒙, 李明航. 地铁列车振动环境影响预测及其不确定性[M]. 北京 科学出版社, 2024. [31] WANG Q S, ZHAO H, GONG D, et al. Compilation of wheel-rail comprehensive irregularity spectrum for subway vehicle[J]. Probabilistic Engineering Mechanics, 2024, 78: 103691. doi: 10.1016/j.probengmech.2024.103691 -




 下载:
下载: