Fuzzy Dual-Adaptive Zero-Power Control for Permanent Electromagnetic Magnet Hybrid Suspension System
-
摘要:
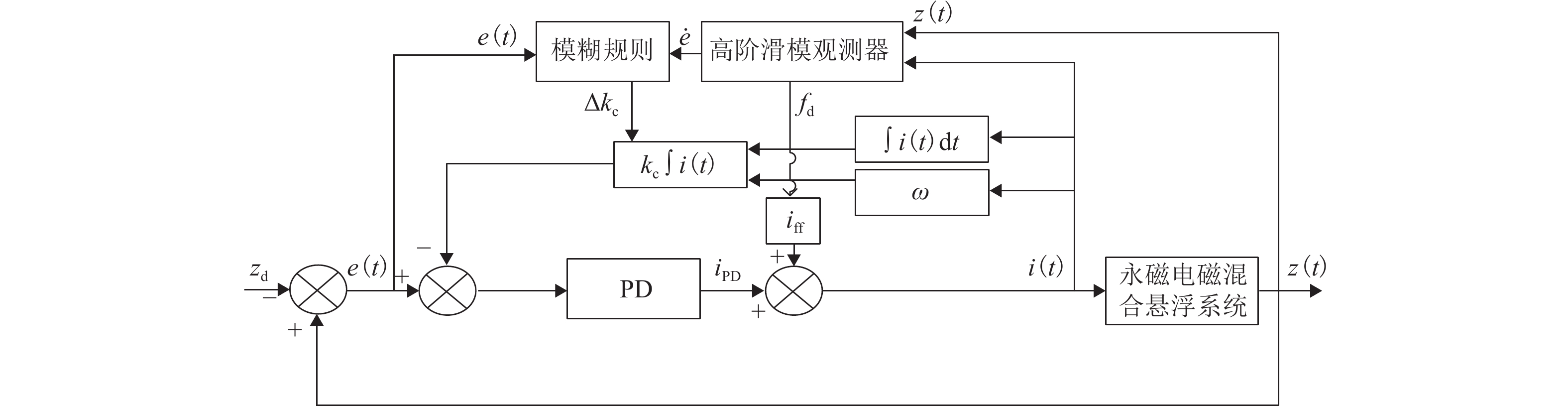
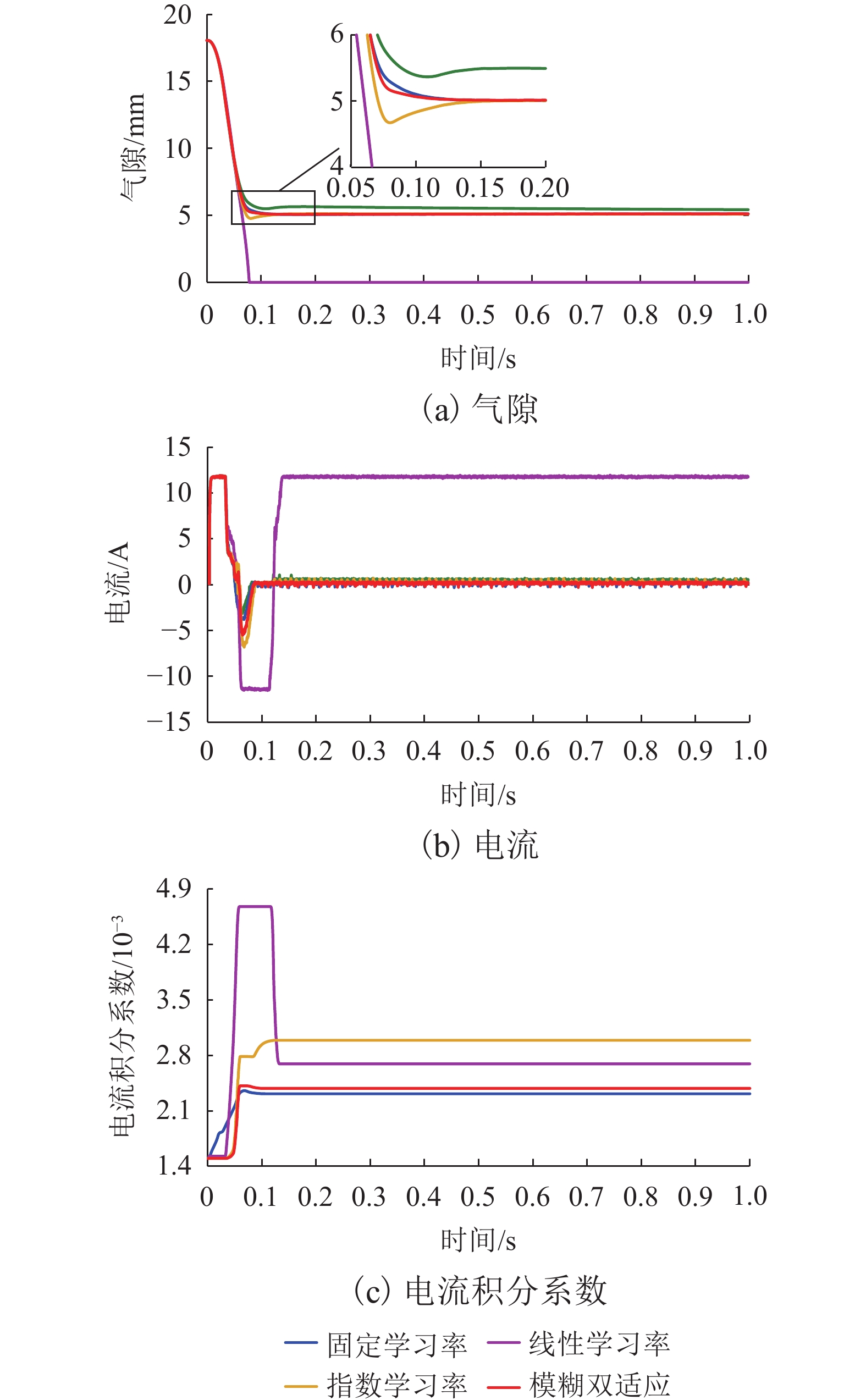
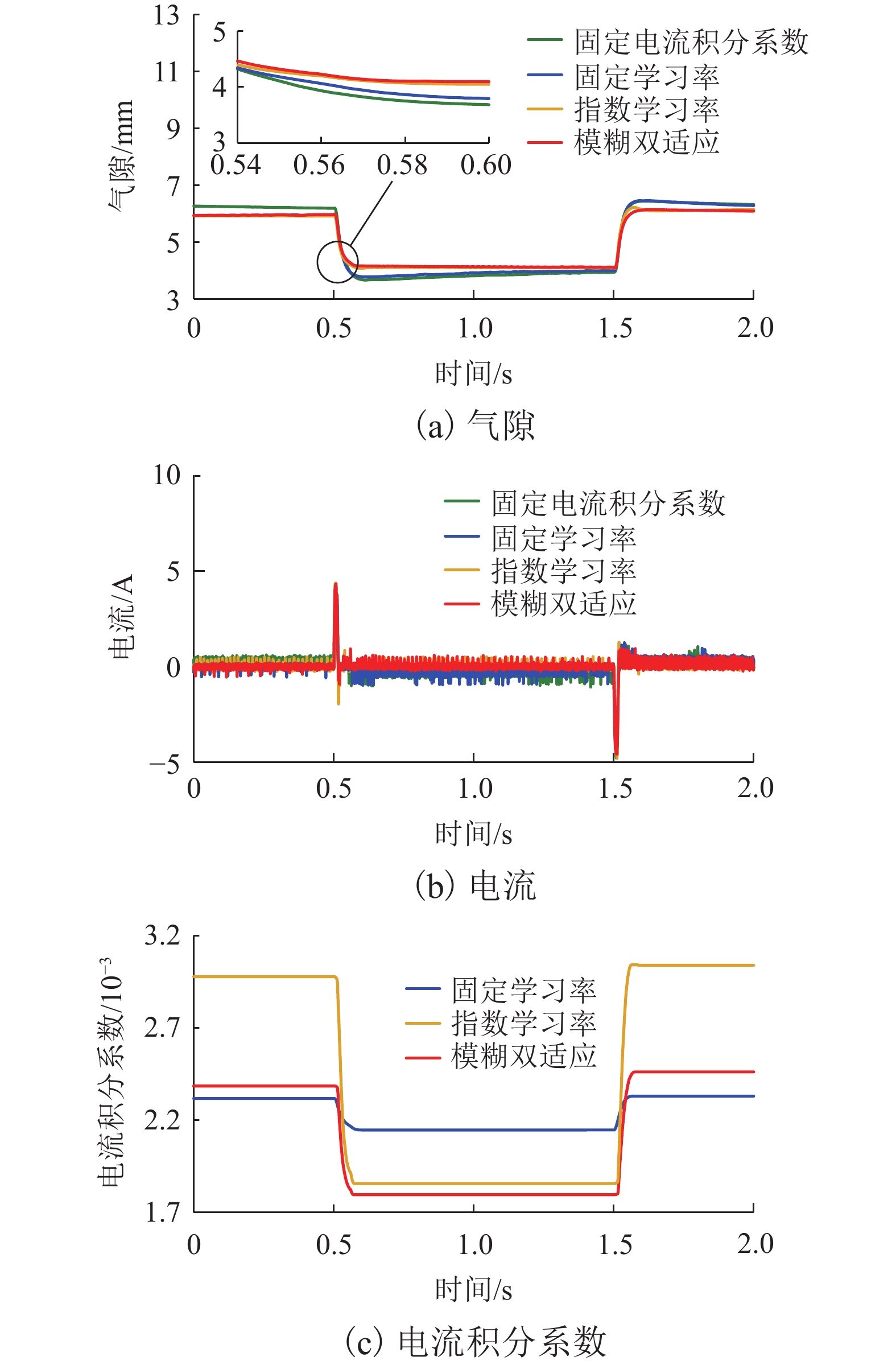
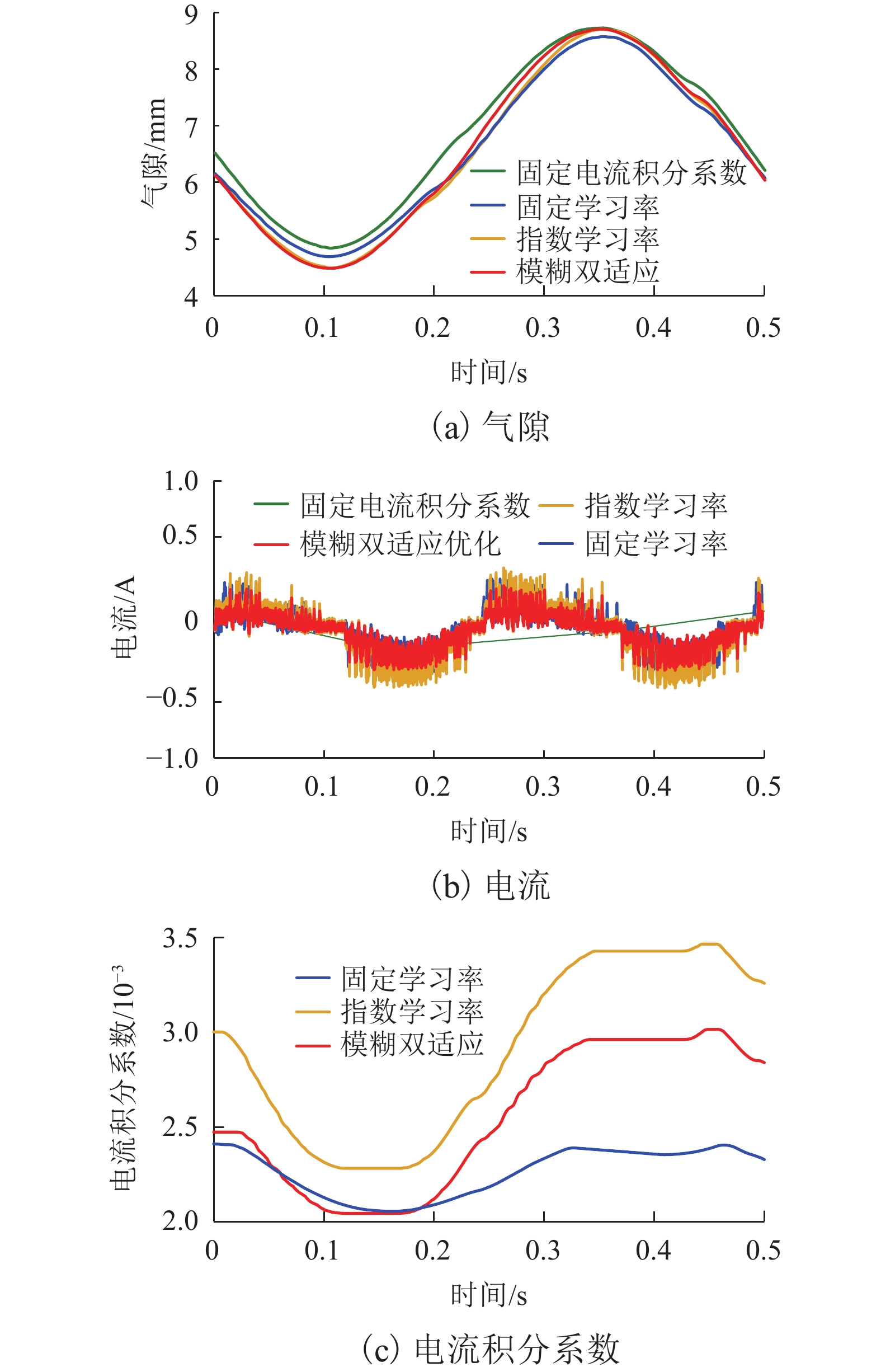
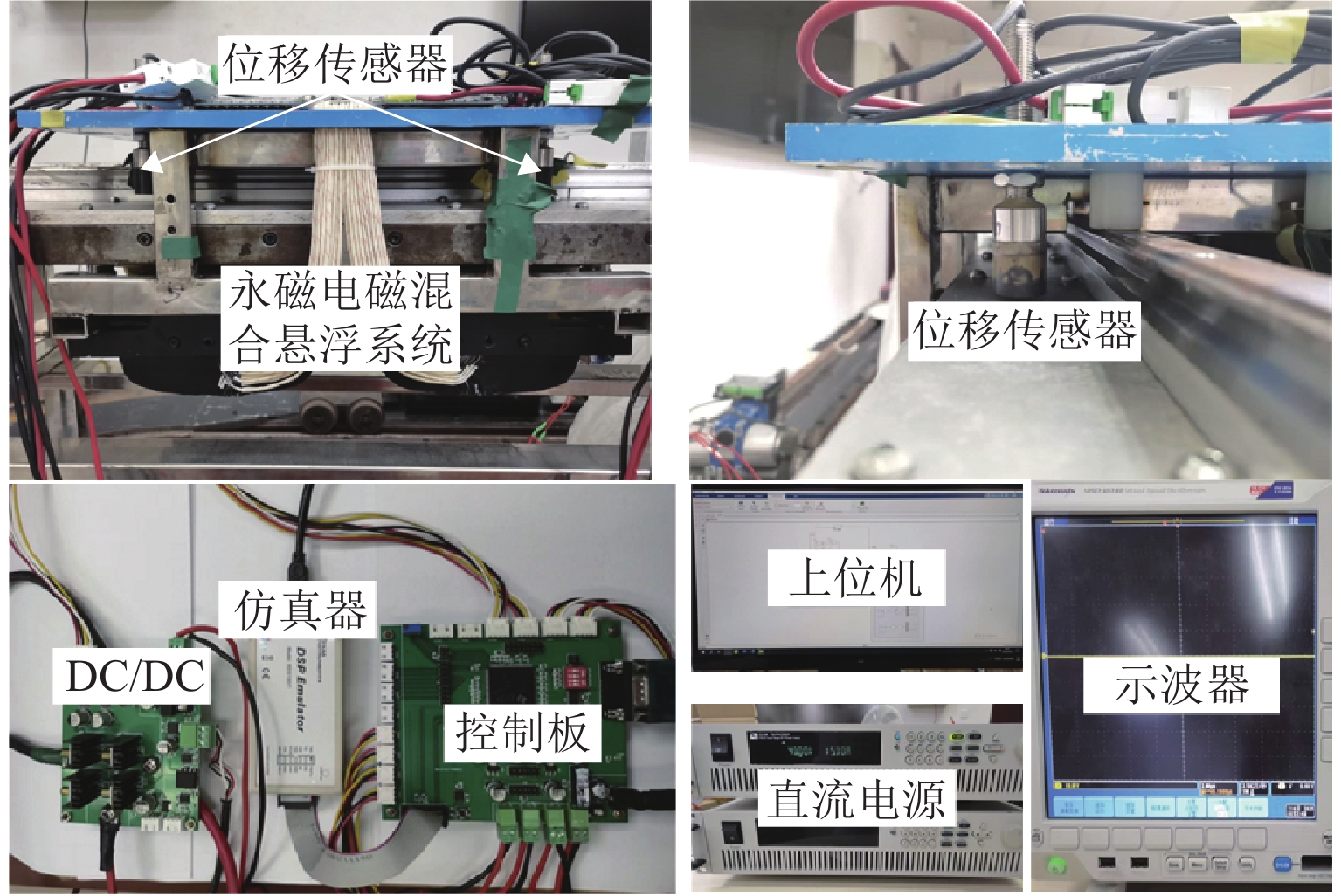
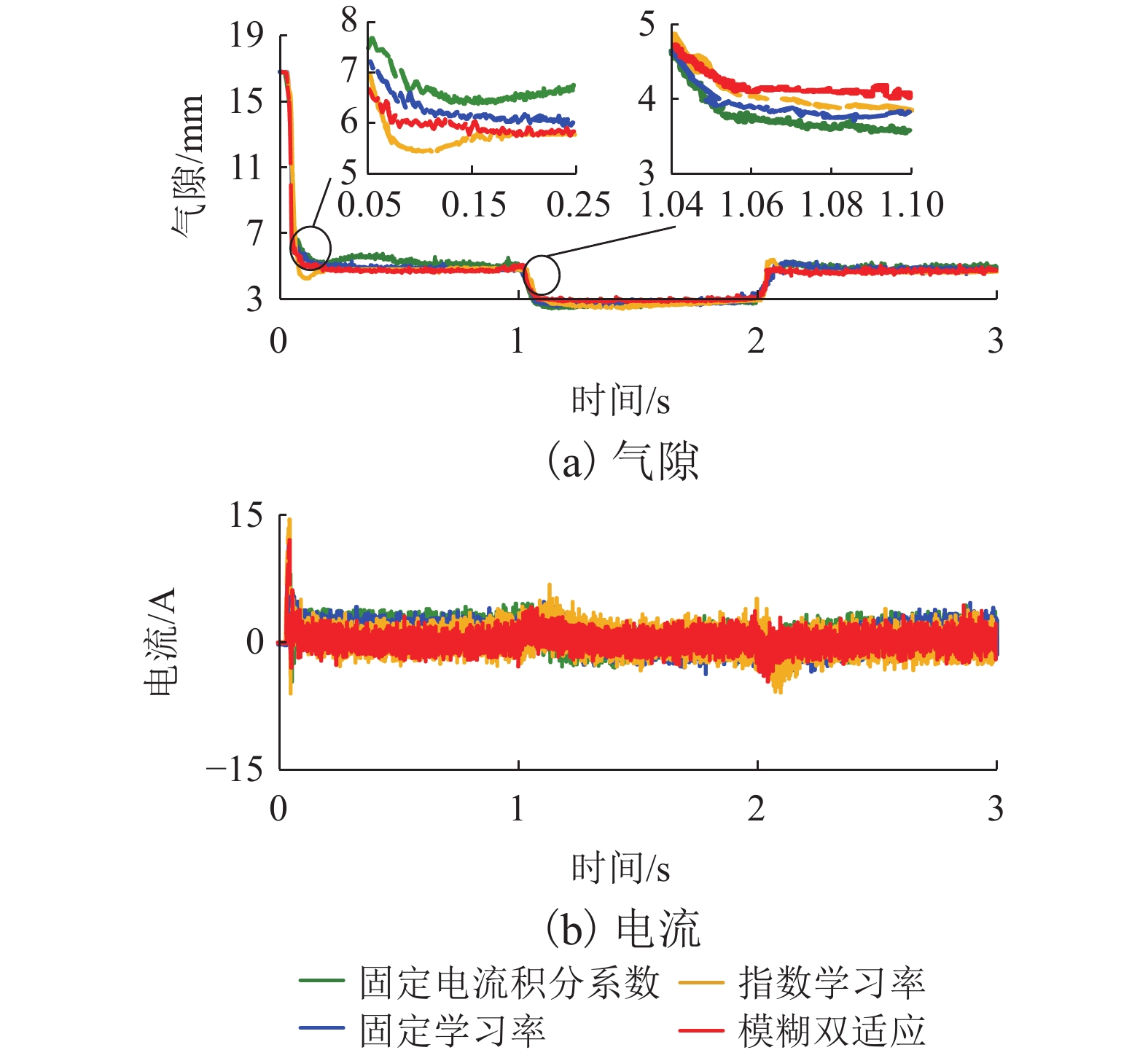
针对永磁电磁混合悬浮系统零功率控制中电流积分导致的饱和、响应滞后与抗扰能力不足的问题,综合考虑系统空载起浮和负载变化两种工况,提出一种基于高阶滑模观测器的模糊双适应零功率控制方法. 首先,基于系统数学模型,设计高阶滑模观测器,实现对集总干扰和误差变化率的估计;其次,根据观测器输出在PD控制器中引入前馈补偿,完成对悬浮间隙的快速稳定跟踪和干扰力的动态补偿;进一步分析电流积分在系统空载起浮和负载变化工况下对系统动稳态性能的影响;最后,提出模糊双适应算法,借助二维模糊算法在线优化电流环积分系数,并基于双曲正切函数的动态调节学习率,从而根据系统动态特性自适应调整积分增益权重,有效抑制积分饱和并提高系统响应速度. 研究结果表明:在空载起浮工况下,所提方法的仿真与实验响应时间分别为0.12 s和0.25 s,且均无超调;在负载突变工况下,仿真与实验响应时间分别为0.10 s和0.15 s,亦无超调;在负载连续变化工况下,电流误差不超过±0.35 A,且无超调;与固定学习率和固定电流积分系数方法相比,所提方法响应时间最少缩短了14.2%,且超调为0.
-
关键词:
- 永磁电磁混合悬浮系统 /
- 高阶滑模观测器 /
- 电流积分反馈 /
- 模糊双适应算法
Abstract:A fuzzy dual-adaptive zero-power control method based on a high-order sliding mode observer was proposed to address issues of saturation, response lag, and insufficient disturbance rejection caused by current integration in the zero-power control of permanent magnet electromagnetic hybrid suspension systems. The method comprehensively considered both no-load lifting and load variation operating conditions. First, based on the system mathematical model, a high-order sliding mode observer was designed to estimate the lumped disturbance and error variation rate. Second, feedforward compensation was introduced into the proportional derivative (PD) controller according to the observer output, achieving fast and stable tracking of the suspension gap and dynamic compensation of disturbance forces. Further analysis was conducted on the impact of current integration on dynamic and steady-state performance under both no-load lifting and load variation conditions. Finally, a fuzzy dual-adaptive algorithm was proposed. A two-dimensional fuzzy algorithm was used to optimize the integral coefficient of the current loop online, while the learning rate was dynamically adjusted based on a hyperbolic tangent function, enabling adaptive adjustment of the integral gain weight according to the system dynamics. This effectively suppressed integral saturation and improved system response speed. The research results show that under no-load lifting conditions, the simulation and experimental response time of the proposed method is 0.12 s and 0.25 s, respectively, with no overshoot. Under sudden load variation conditions, the simulation and experimental response time is 0.10 s and 0.15 s, without overshoot. Under continuous load variation conditions, the current error does not exceed ±0.35 A, and no overshoot occurs. Compared with methods using fixed learning rates and fixed current integral coefficients, the proposed method reduces response time by at least 14.2% with zero overshoot.
-
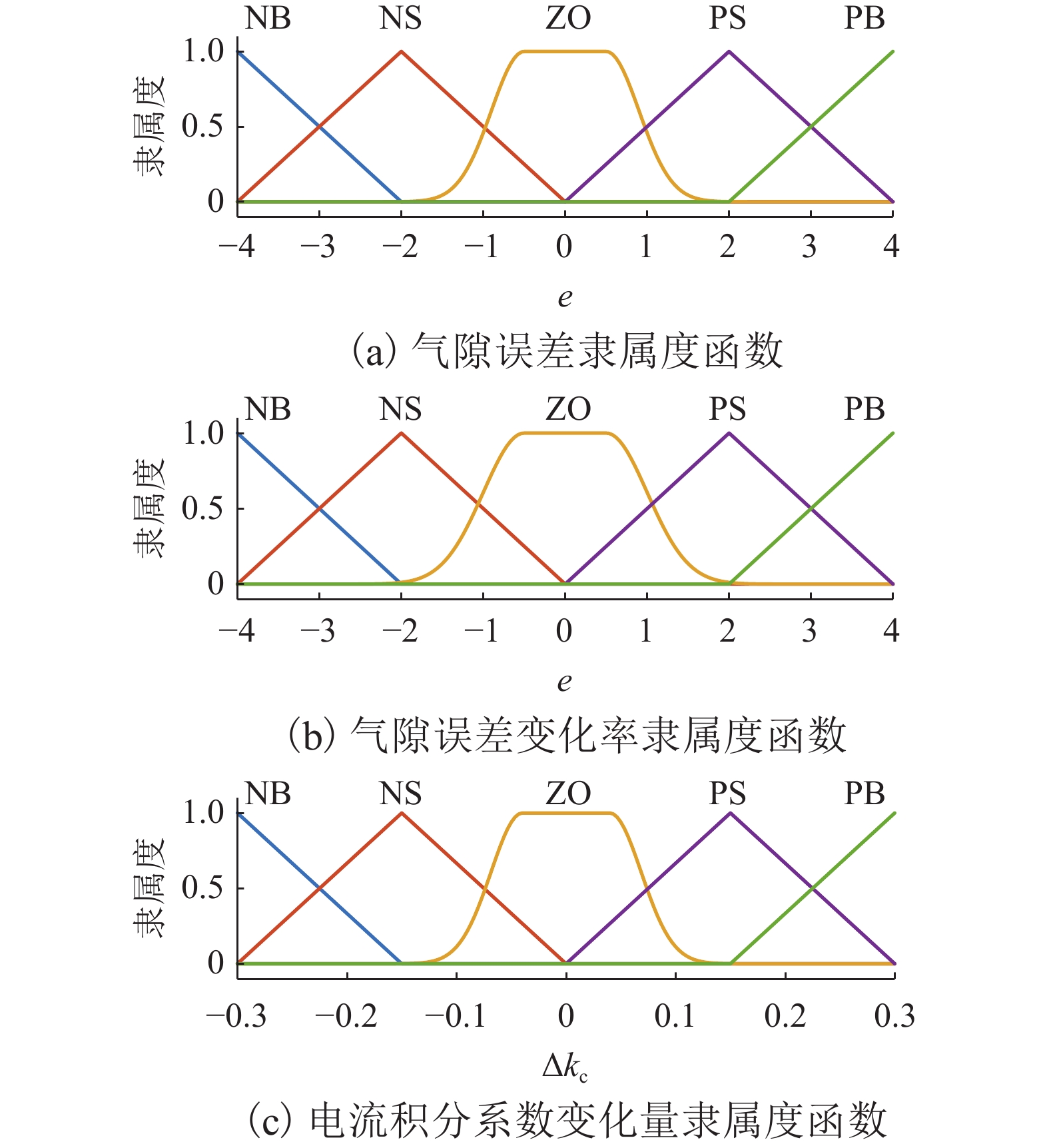
表 1 电流积分系数整定规则
Table 1. Setting rules for current integral coefficient
e $ \dot{e} $ NB NS ZO PS PB NB NB NS ZO PB PB NS NS NB ZO PS PB ZO ZO ZO ZO ZO ZO PS PS PB ZO ZO ZO PB PS PS ZO PB PS 表 2 仿真参数
Table 2. Simulation parameters
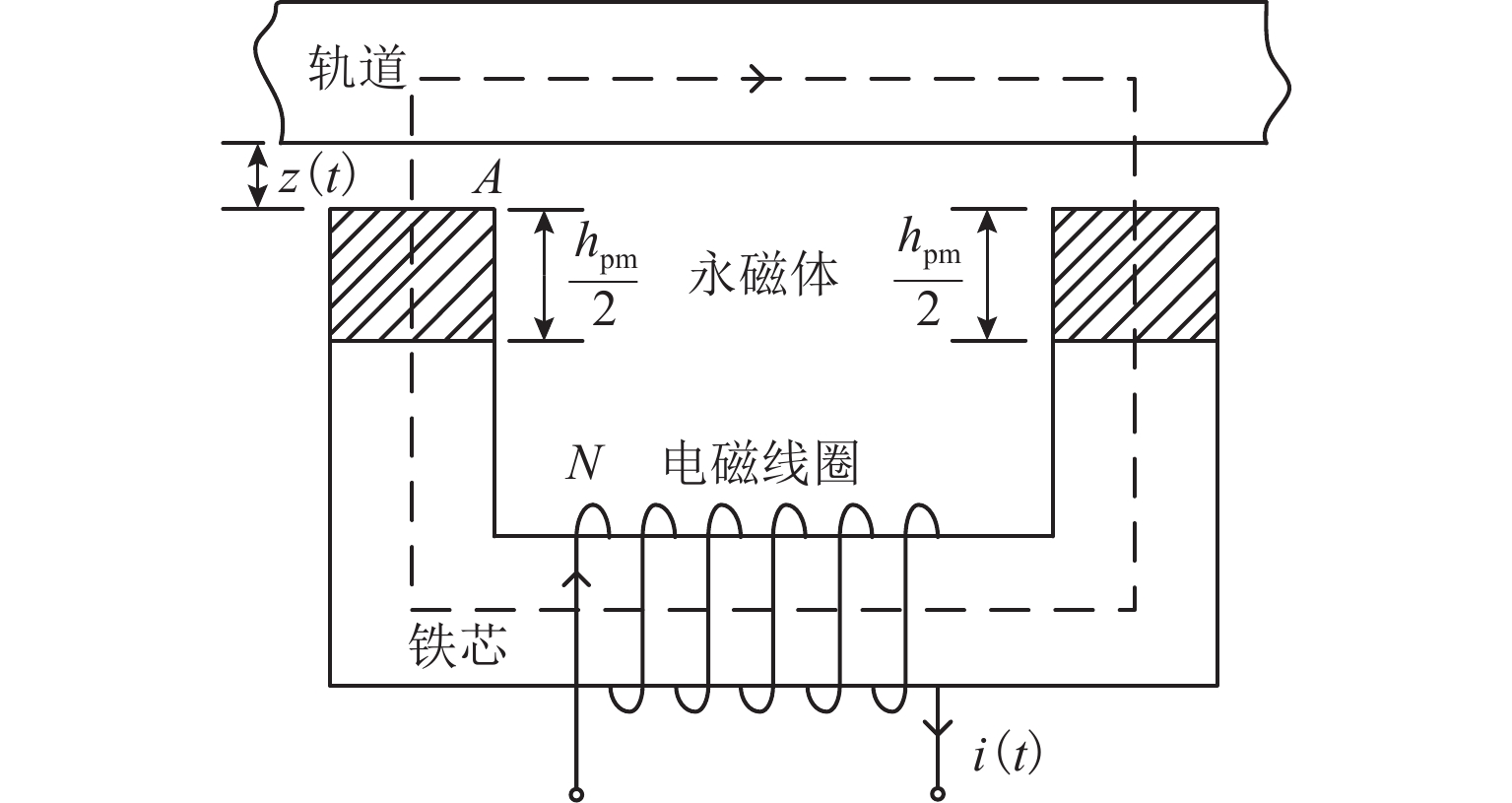
参 数 数 值 永磁体总厚度hpm/mm 6 线圈匝数N 550 永磁体矫顽力Hc/Am 5.8×105 参考气隙$ {{\textit{z}}}_{\text{ref}} $/mm 7 空载零功率稳态气隙$ {{\textit{z}}}_{\max } $/mm 5.96 满载零功率稳态气隙$ {{\textit{z}}}_{\min } $/mm 4.09 观测器增益l 2000 比例系数$ {k}_{{\mathrm{p}}} $ 4500 微分系数$ {k}_{{\mathrm{d}}} $ 80 预设电流积分系数$ {k}_{{\mathrm{c}}0} $ 0.0015 预设学习率$ {\omega }_{0} $ 0.8 -
[1] 马卫华, 胡俊雄, 李铁, 等. EMS型中低速磁浮列车悬浮架技术研究综述[J]. 2023(4): 720-733.MA Weihua, HU Junxiong, LI Tie, et al. Technologies research review of electro-magnetic suspension medium—low-speed maglev train levitation frame [J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2023(4): 720-733. [2] 邓自刚, 刘宗鑫, 李海涛, 等. 磁悬浮列车发展现状与展望[J]. 西南交通大学学报, 2022, 57(3): 455-474, 530.DENG Zigang, LIU Zongxin, LI Haitao, et al. Development status and prospect of maglev train[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2022, 57(3): 455-474,530. [3] GOU J S. Development status and global competition trends analysis of maglev transportation technology based on patent data[J]. Urban Rail Transit, 2018, 4(3): 117-129. doi: 10.1007/s40864-018-0087-3 [4] TZENG Y K, WANG T C. Optimal design of the electromagnetic levitation with permanent and electro magnets[J]. IEEE Transactions on Magnetics, 1994, 30(6): 4731-4733. doi: 10.1109/20.334204 [5] HUANG Z H, LI C H, ZHOU Z M, et al. Magnetic bearing: structure, model, and control strategy[J]. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 2024, 131(5): 3287-3333. [6] 孙凤, 裴文哲, 金俊杰, 等. 可变磁路式永磁悬浮平台的起浮控制方法[J]. 西南交通大学学报, 2022, 57(3): 531-539.SUN Feng, PEI Wenzhe, JIN Junjie, et al. Floating control method for permanent magnetic levitation platform with variable flux path[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2022, 57(3): 531-539. [7] 李旭春, 张鹏, 严乐阳, 等. 具有参数辨识的永磁同步电机无位置传感器控制[J]. 电工技术学报, 2016, 31(14): 139-147, 164. doi: 10.19768/j.cnki.dgjs.2022.15.018LI Xuchun, ZHANG Peng, YAN Leyang, et al. Sensorless control of permanent magnet synchronous motor with parameter identification[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2016, 31(14): 139-147,164. doi: 10.19768/j.cnki.dgjs.2022.15.018 [8] 蒋雪, 侯汉, 马庆军, 等. 用于紫外光谱仪的探测器温度控制系统[J]. 中国光学(中英文), 2024(1): 209-216.JIANG Xue, HOU Han, MA Qingjun, et al. Detector temperature control system for ultraviolet spectrometer[J]. Chinese Optics, 2024(1): 209-216. [9] HOROWITZ I M, LIAO Y K. Quantitative non-linear compensation design for saturating unstable uncertain plants[J]. International Journal of Control, 1986, 44(4): 1137-1146. doi: 10.1080/00207178608933655 [10] OHISHI K, HAYASAKA E, NAGANO T, et al. High-performance speed servo system considering Voltage saturation of a vector-controlled induction motor[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2006, 53(3): 795-802. doi: 10.1109/TIE.2006.874274 [11] 付金宝, 张洪文, 黄厚田, 等. 航空光电载荷串级动态复合限幅分幅步进控制[J]. 光学精密工程, 2023, 31(13): 1922-1932.Cascade dynamic hybrid amplitude limitation frame division step control of airborne optical electronic load[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2023, 31(13): 1922-1932. [12] JIA L, ZHAO X Q. An improved particle swarm optimization (PSO) optimized integral separation PID and its application on central position control system[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2019, 19(16): 7064-7071. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2019.2912849 [13] CHOI J W, LEE S C. Antiwindup strategy for PI-type speed controller[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2009, 56(6): 2039-2046. doi: 10.1109/TIE.2009.2016514 [14] 左静, 严龙刚, 杨乔礼, 等. 虚拟编组下基于扩张状态观测器的城轨列车多车协同自适应滑模控制[J]. 铁道科学与工程学报, 2025, 22(10): 4412-4423.ZUO Jing, YAN Longgang, YANG Qiaoli, et al. Multi-train coordination adaptive sliding mode control for urban rail trains based on extended state observer under virtual grouping[J]. Journal of Railway Science and Engineering, 2025, 22(10): 4412-4423. [15] 谭草, 宋亚东, 李波, 等. 基于超扭曲扩张状态观测器的电子机械制动器夹紧力改进滑模控制[J/OL]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024: 1-10. (2024-06-27). https://link.cnki.net/doi/10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20240264.TAN Cao, SONG Yadong, LI Bo, et al. Improved sliding mode control of clamping force in electronic mechanical brake based on super-twisting extended state observer[J/OL]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024: 1-10. (2024-06-27). https://link.cnki.net/doi/10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20240264. [16] 许鹏, 邢伯阳, 刘宇飞, 等. 基于扩张状态观测器和模型预测方法的四足机器人抗干扰复合控制[J]. 兵工学报, 2023, 44(增2): 12-21.XU Peng, XING Boyang, LIU Yufei, et al. Anti-disturbance composite controller design of quadruped robot based on extended state observer and model predictive control technique[J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2023, 44(S2): 12-21. [17] 朱孝勇, 彭忠飞, 张丽, 等. 基于自适应扰动补偿观测器的漏磁可控永磁电机无位置传感器控制研究[J]. 中国科学: 技术科学, 2024, 54(5): 911-923.ZHU Xiaoyong, PENG Zhongfei, ZHANG Li, et al. Research on sensorless control of flux leakage controllable permanent magnet motor based on an adaptive disturbance compensation observer[J]. Scientia Sinica (Technologica), 2024, 54(5): 911-923. [18] 高升, 张海龙, 张伟, 等. 基于自适应超螺旋观测器的空间机械臂鲁棒故障诊断[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2024, 46(4): 1287-1296.GAO Sheng, ZHANG Hailong, ZHANG Wei, et al. Robust fault diagnosis for space robot manipulator based on adaptive super-twisting observer[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2024, 46(4): 1287-1296. [19] 徐建安, 刘浩博, 刘华东, 等. 基于干扰观测器的自适应反演滑模主动升沉补偿控制策略[J]. 哈尔滨工程大学学报, 2025, 46(3): 558-566.XU Jian’an, LIU Haobo, LIU Huadong, et al. Disturbance observer based adaptive backstepping sliding mode control strategy for active heave compensation[J]. Journal of Harbin Engineering University, 2025, 46(3): 558-566. [20] 李擎, 孙鹏, 郭祥贵. 基于非线性干扰观测器和类故障模型的车辆队列预设时间容错滑模控制[J]. 控制理论与应用, 2025, 42(8): 1659-1668.LI Qing, SUN Peng, GUO Xianggui. Preset-time fault-tolerant sliding-mode control of vehicular platoon based on nonlinear disturbance observer and fault-like model[J]. Control Theory & Applications, 2025, 42(8): 1659-1668. [21] XU J W, YU X, QIAO J Z. Hybrid disturbance observer-based anti-disturbance composite control with applications to Mars landing mission[J]. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems, 2021, 51(5): 2885-2893. [22] QUE N N, DENG W X, ZHOU N, et al. Disturbance observer-based prescribed-time tracking control of nonlinear systems with non-vanishing uncertainties[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems Ⅱ: Express Briefs, 2024, 71(6): 3131-3135. [23] LEVANT A. Higher-order sliding modes, differentiation and output-feedback control[J]. International Journal of Control, 2003, 76(9/10): 924-941. [24] SHTESSEL Y B, SHKOLNIKOV I A, LEVANT A. Smooth second-order sliding modes: missile guidance application[J]. Automatica, 2007, 43(8): 1470-1476. [25] LI S H, SUN H B, YANG J, et al. Continuous finite-time output regulation for disturbed systems under mismatching condition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2015, 60(1): 277-282. -




 下载:
下载: