Influence of Strong Seepage Fractures on Stability of Water-Resistant Rock Mass at Tunnel Face
-
摘要:
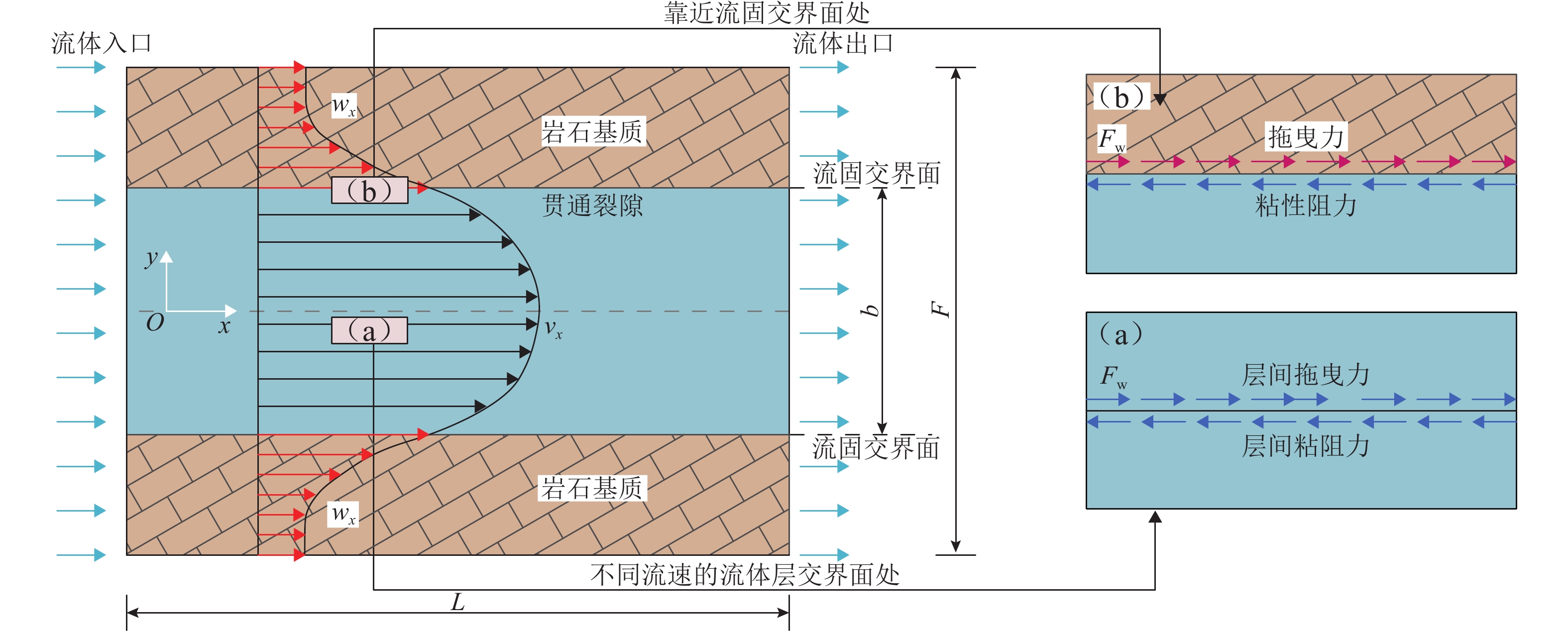
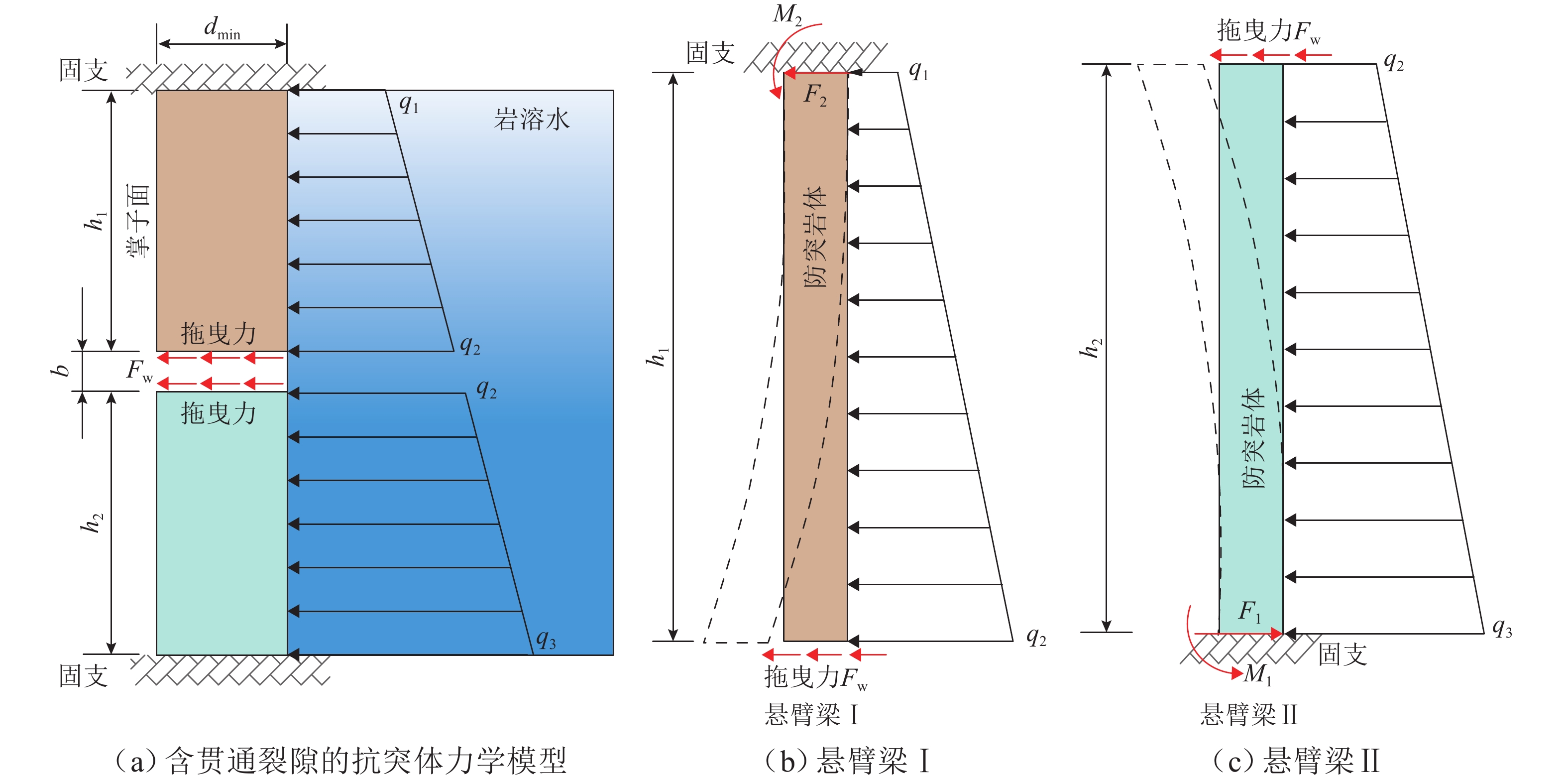
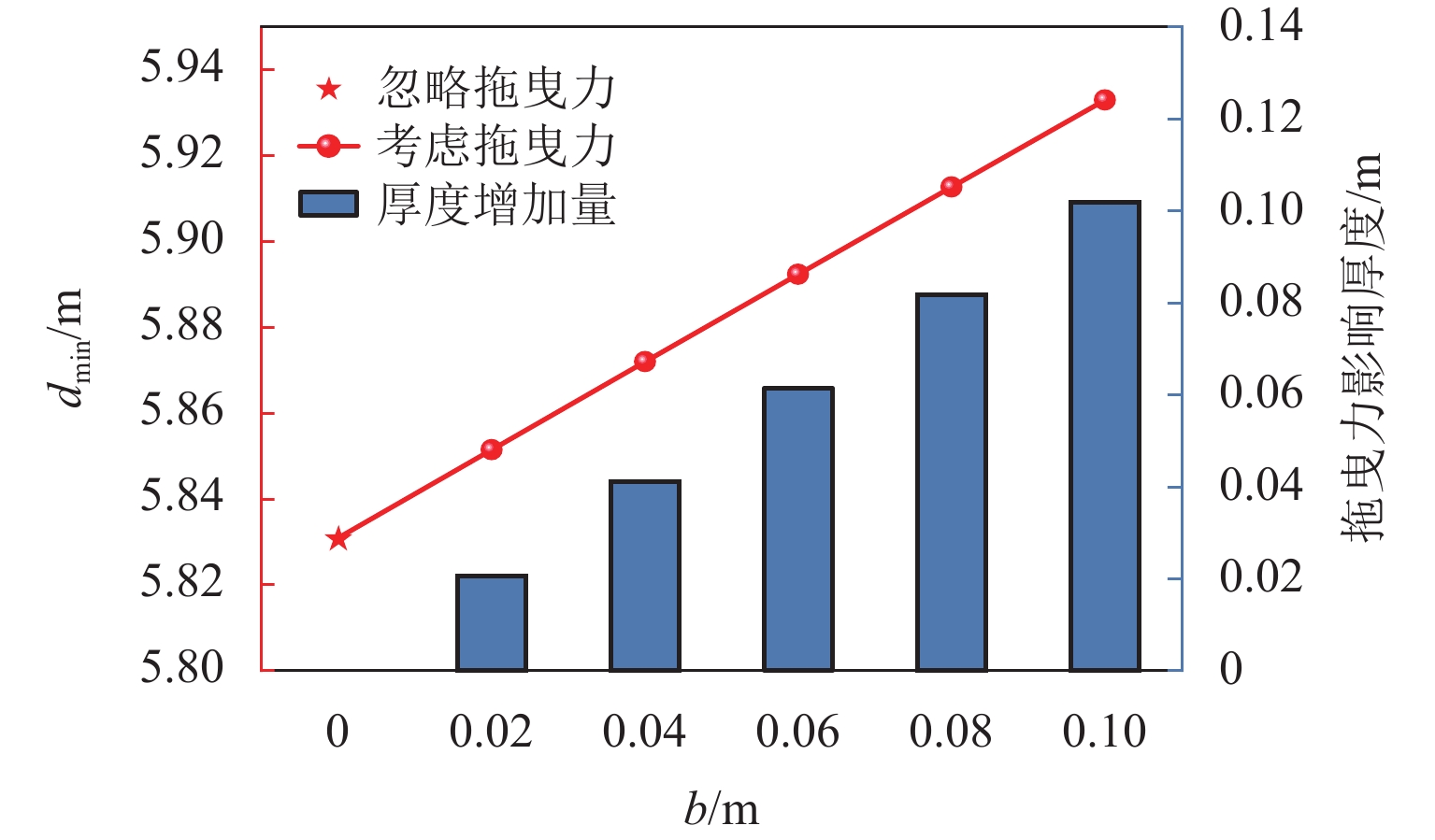
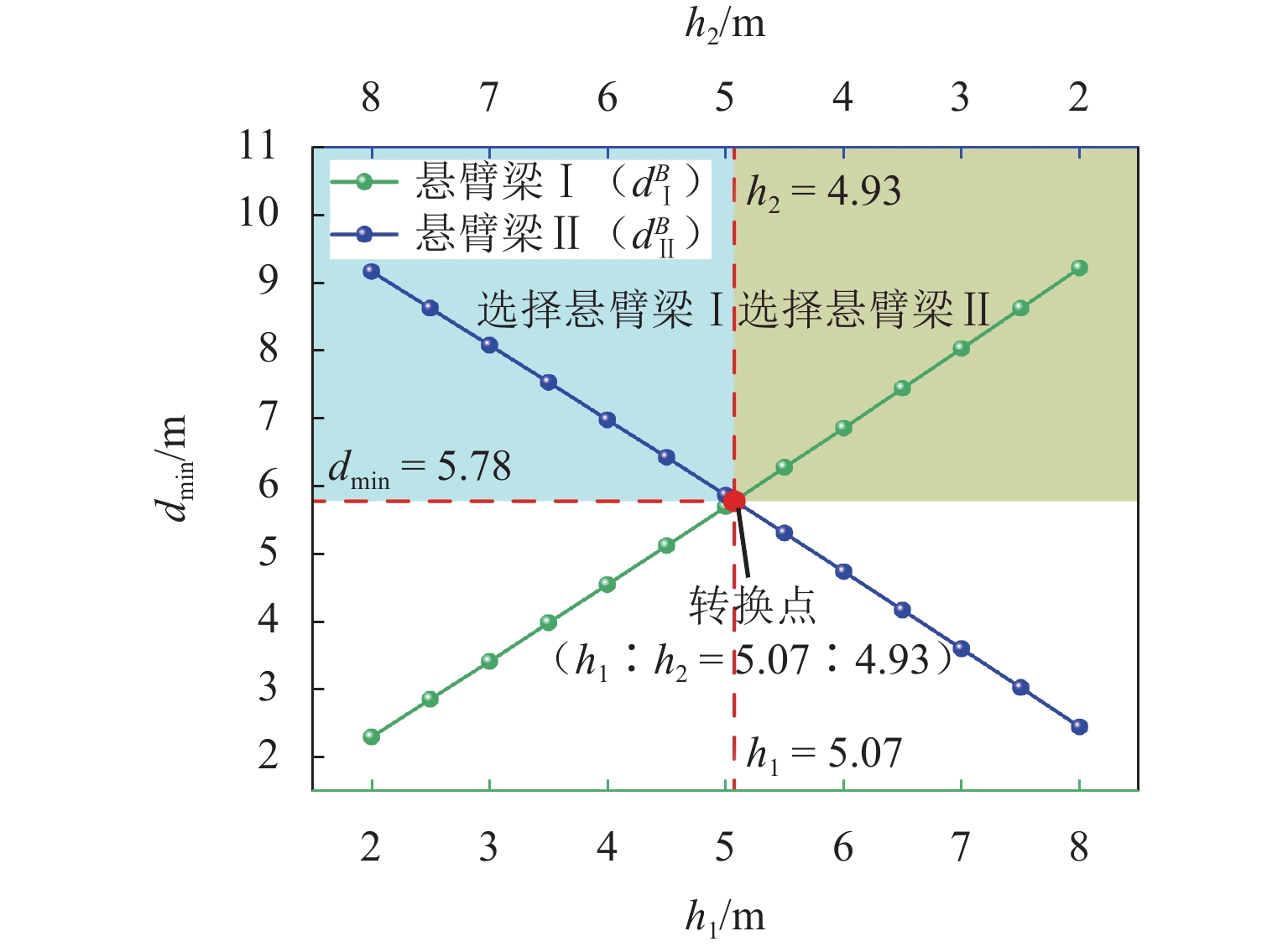
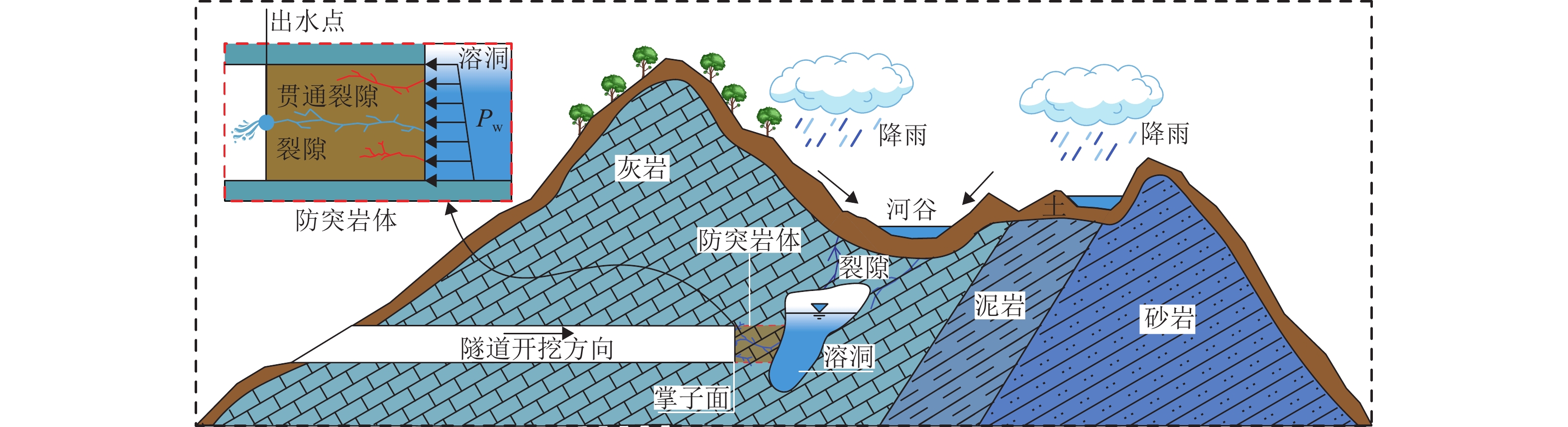
涌水突泥是岩溶隧道常见的地质灾害之一,对隧道施工安全和长期运营构成严重威胁,确保掌子面抗突体的安全性是防控涌水突泥灾害的关键. 本文围绕强渗流作用下掌子面抗突体的稳定性问题,构建隧道掌子面强渗流裂隙抗突体的力学分析模型;充分考虑水流在贯通裂隙壁面上产生的拖曳力效应,系统推导强渗流作用下岩溶隧道抗突体的最小安全厚度公式;结合参数敏感性分析和工程实例,采用有限差分软件FLAC3D进一步分析掌子面前方含贯通裂隙和富水溶腔下隧道开挖围岩的稳定性,深入探讨关键参数对抗突体稳定性的影响机制. 研究结果表明:裂隙开度的增大显著增强了拖曳力的作用效果;强渗流条件下,裂隙拖曳力对抗突体最小安全厚度具有显著的不利影响,且其影响程度随着裂隙开度的增加非线性增强;在不同位置分布,裂隙对最小安全厚度的影响有显著差异,存在一个临界过渡点(悬臂梁Ⅰ、Ⅱ长度比= 5.07∶4.93),在该过渡点,裂隙上、下梁板发生同步破坏,进一步揭示了裂隙位置与结构失稳之间的内在关联. 研究成果可为岩溶隧道掌子面抗突体厚度设计、岩溶灾害治理(如注浆封堵、裂隙加固与渗流控制)以及施工期风险分级与监测预警指标选取提供理论依据与工程指导.
Abstract:Water and mud inrush is one of the common geological disasters in karst tunnels, which poses a severe threat to the safety of tunnel construction and long-term operation. Therefore, ensuring the safety of water-resistant rock mass at the face is the key to the prevention and control of water and mud inrush disasters. To ensure the stability of water-resistant rock mass at the face under the action of strong seepage, a mechanical analysis model of water-resistant rock mass in strong seepage fractures at the tunnel face was constructed. The drag force effect generated by the water flow on the wall of the penetrating fracture was fully considered, and the minimum safe thickness formula of the water-resistant rock mass in the karst tunnel under the action of strong seepage was systematically derived. Parameter sensitivity analysis and engineering examples were employed; the stability of the surrounding rock during tunnel excavation was further investigated by using the finite-difference software FLAC3D, considering penetrating fractures and water-rich karst cavities ahead of the tunnel face; the influence mechanism of key parameters on the stability of the water-resistant rock mass was discussed in depth. The results show that the increase of fracture opening significantly enhances the effect of the drag force. Under the condition of strong seepage, the fracture drag force has a significant adverse effect on the minimum safe thickness of the water-resistant rock mass, and its influence degree increases nonlinearly with the increase of fracture opening. In addition, the influence of fracture at different location distributions on the minimum safe thickness shows significant differences. It is found that there is a critical transition point (height ratio of cantilever beams I and II = 5.07∶4.93) at which the upper and lower beams and slabs of the fracture are destroyed synchronously, which further reveals the internal relationship between the fracture location and structural instability. The findings of this study can provide a theoretical basis and engineering guidance for designing the thickness of water-resistant rock mass in karst tunnel face, mitigating karst-related disasters (e.g., grouting sealing, fracture reinforcement, and seepage control), selecting monitoring and early-warning indicators, and conducting risk classification during construction.
-
Key words:
- karst tunnel /
- water and mud inrush /
- strong seepage fracture /
- water-resistant rock mass /
- drag force
-
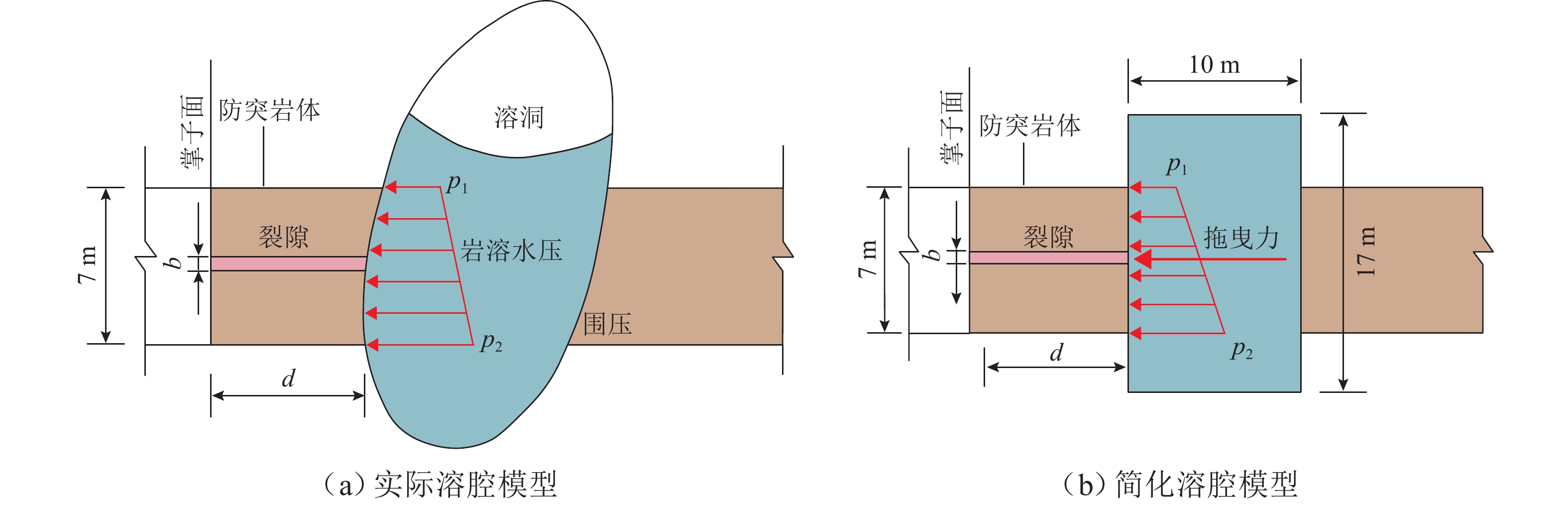
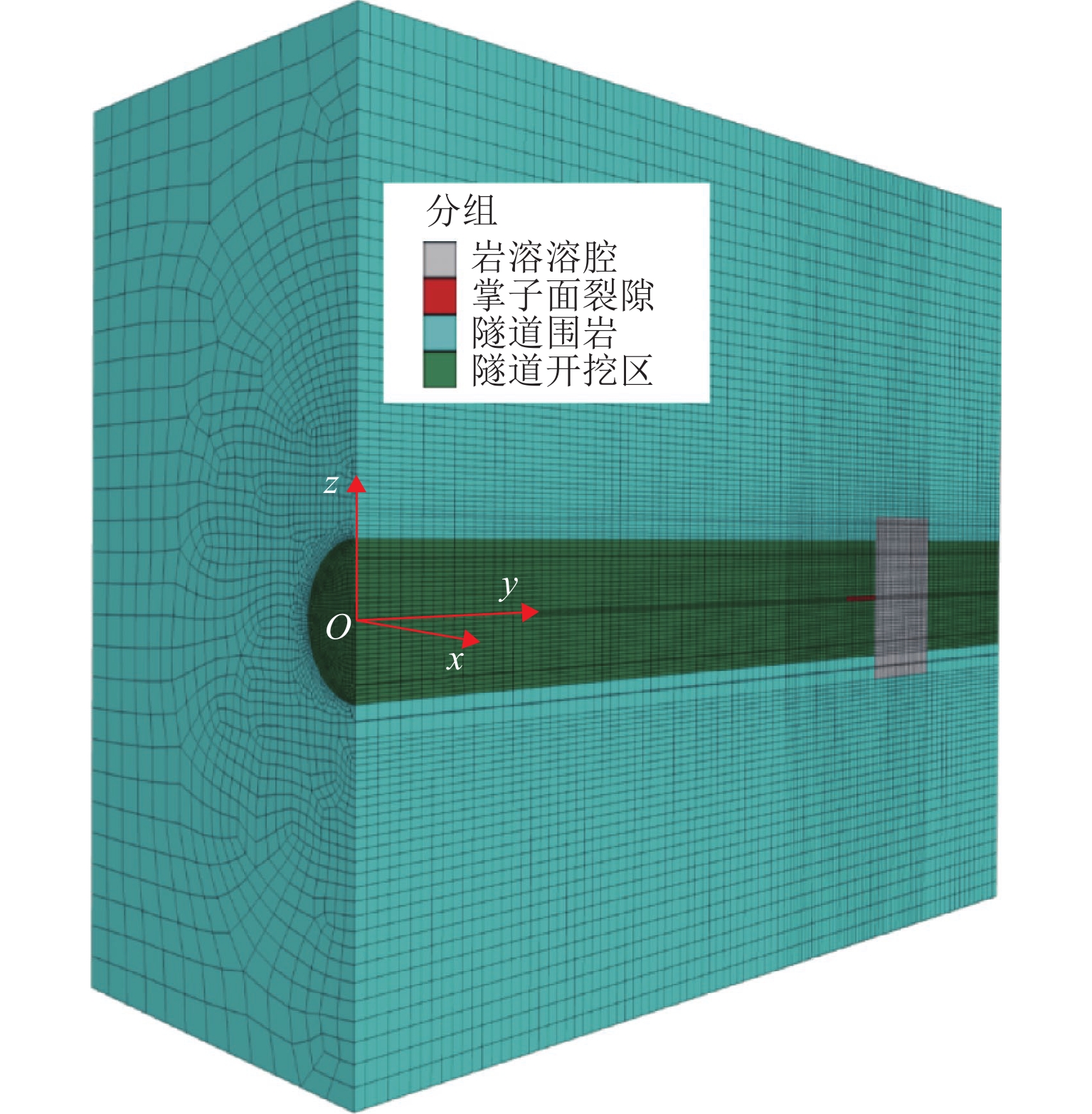
参数分类 参数 取值范围 取值 隧道 h1/m 2~10 5 h2/m 2~10 5 h1∶h2 1∶4~4∶1 1∶1 富水溶腔 γw/kN∙m–3 / 10 h/m 35~135 50 围岩 围岩等级 / Ⅲ [σt]/MPa 1~15 5 裂隙 b/m 0~0.1 0.04 ∆p/MPa 0.1~2 1 安全系数 k / 2 表 2 隧道围岩物理、力学性质参数取值
Table 2. Parameter values of physical and mechanical properties of surrounding rock in tunnel
岩样
性质密度/
(kg∙m−3)弹性模量/
GPa抗压强度/
MPa抗拉强度/
MPa泊松比 粘聚力/MPa 摩擦角/(°) 渗透系数/(m2/Pa-s) 围岩 2670 3.15 32.5 1.0 0.23 1.27 36.22 1.0 × 10−10 表 3 3种模拟突水过程的方案
Table 3. Three schemes for simulating water inrush process
模拟
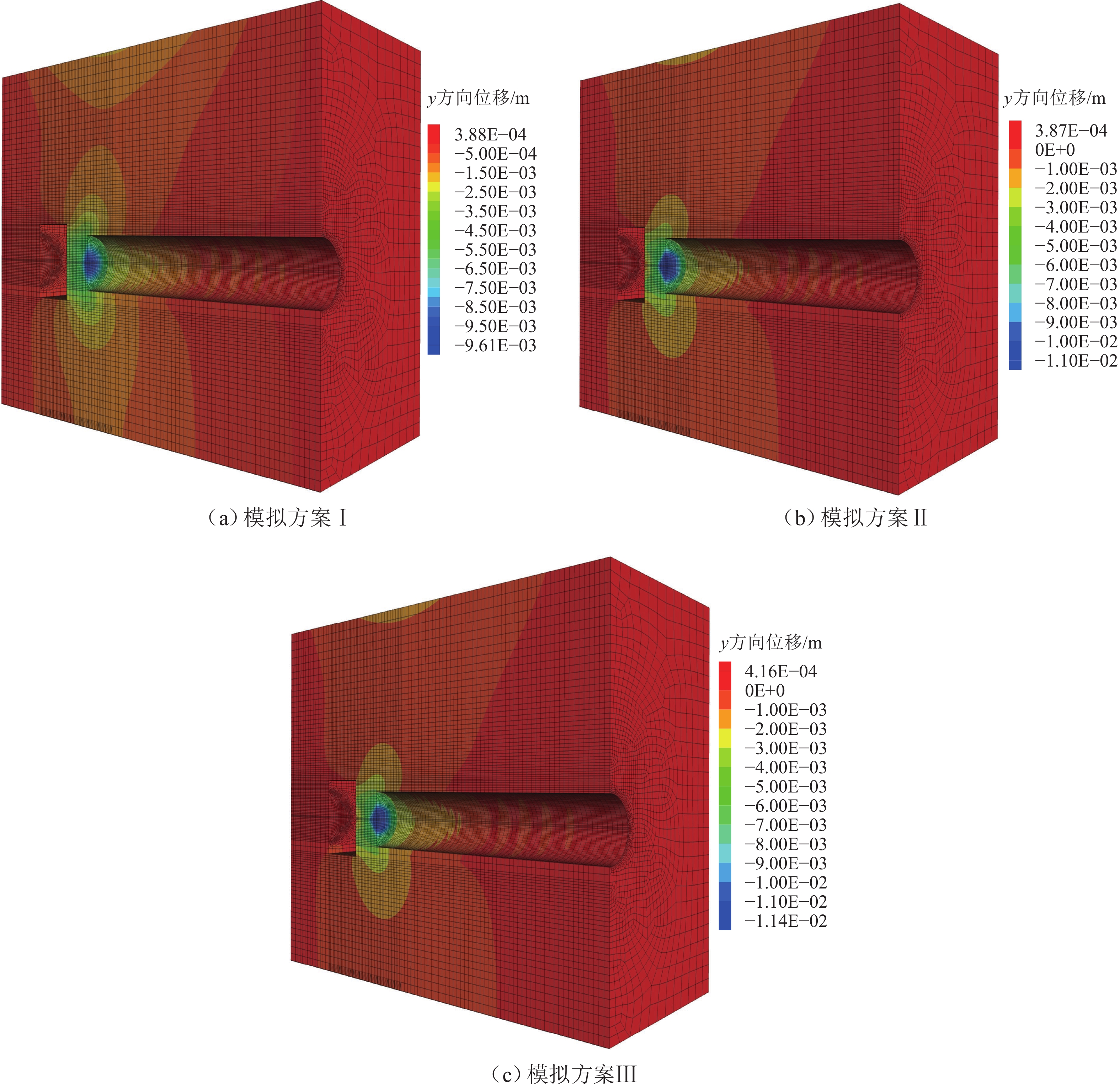
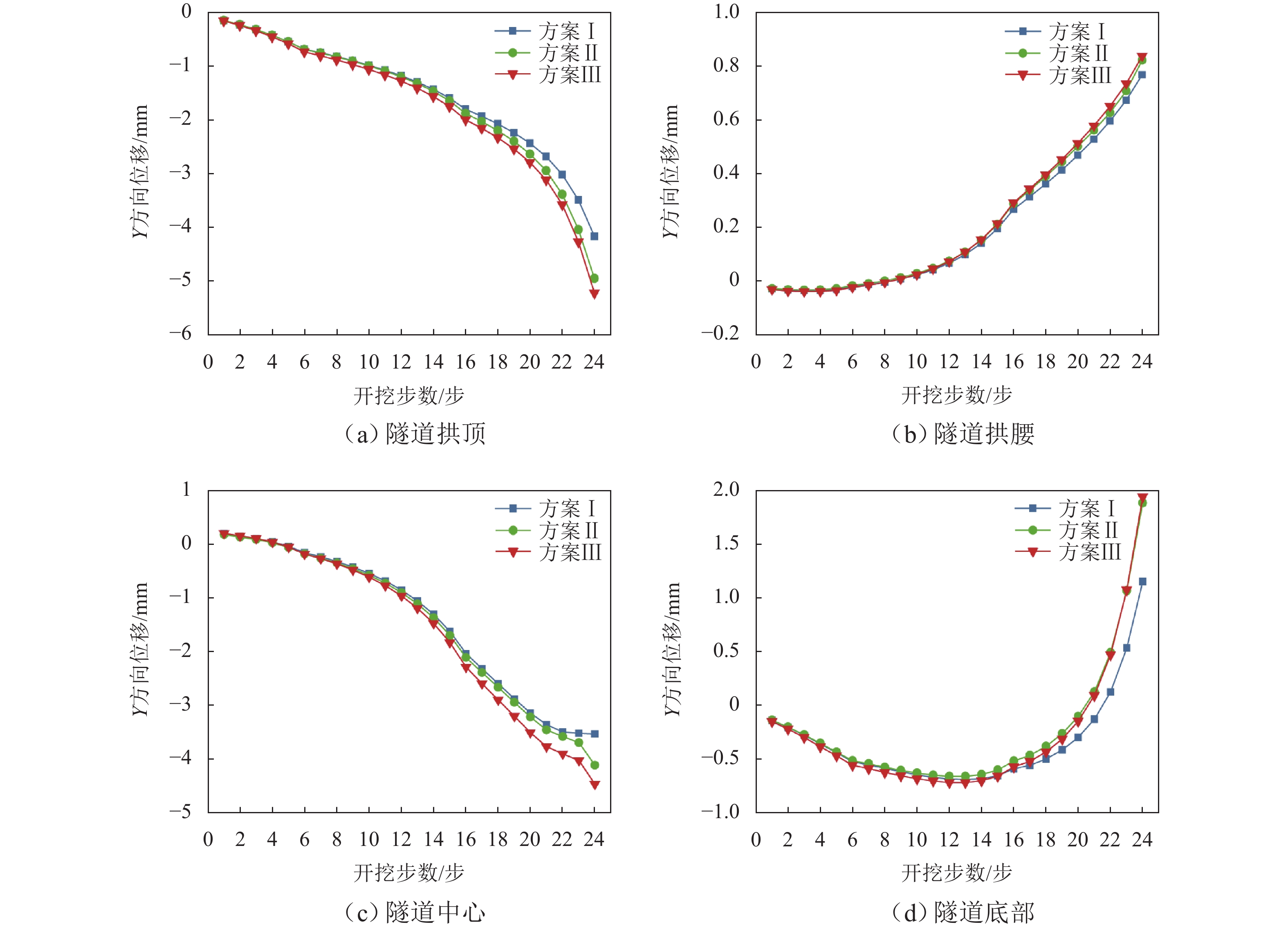
方案裂隙 拖曳力 b/m 岩溶水压 qm1/MPa qm2/MPa Ⅰ 不考虑 不考虑 / 0.8 0.85 Ⅱ 考虑 不考虑 0.5 III 考虑 考虑 0.5 -
[1] 高树全, 蒋良文, 牟元存, 等. 西南复杂艰险山区铁路隧道超前地质预报技术[J]. 现代隧道技术, 2024, 61(2): 52-59.GAO Shuquan, JIANG Liangwen, MOU Yuancun, et al. Advanced geological forecasting techniques for railway tunnels in the complex and treacherous mountainous areas of southwest China[J]. Modern Tunnelling Technology, 2024, 61(2): 52-59. [2] WANG X T, LI S C, XU Z H, et al. Risk assessment of water inrush in Karst tunnels excavation based on normal cloud model[J]. Bulletin of Engineering Geology and the Environment, 2019, 78(5): 3783-3798. doi: 10.1007/s10064-018-1294-6 [3] XIAO Q F, LI S W, YE F, et al. Explicit analytical solution to the minimum safety thickness of waterproof-resistant slab in front of Karst tunnel face[J]. Engineering Failure Analysis, 2024, 157: 107941. doi: 10.1016/j.engfailanal.2023.107941 [4] HU H, ZHANG B W, ZUO Y Y, et al. The mechanism and numerical simulation analysis of water bursting in filling Karst tunnel[J]. Geotechnical and Geological Engineering, 2018, 36(2): 1197-1205. doi: 10.1007/s10706-017-0386-6 [5] 刘招伟, 何满潮, 王树仁. 圆梁山隧道岩溶突水机理及防治对策研究[J]. 岩土力学, 2006, 27(2): 228-232, 246. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2006.02.026LIU Zhaowei, HE Manchao, WANG Shuren. Study on Karst waterburst mechanism and prevention countermeasures in Yuanliangshan tunnel[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2006, 27(2): 228-232,246. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2006.02.026 [6] 钟昌桂, 张磊, 张慧玲, 等. 贵南高铁朝阳隧道出口岩溶突水灾害整治措施研究[J]. 工程技术研究, 2023, 8(3): 41-43.ZHONG Changgui, ZHANG Lei, ZHANG Huiling, et al. Research on treatment measures of Karst water inrush disaster at the exit of Chaoyang tunnel of Guiyang-Nanning high-speed railway[J]. Engineering and Technological Research, 2023, 8(3): 41-43. [7] LI S C, ZHOU Z Q, LI L P, et al. Risk assessment of water inrush in Karst tunnels based on attribute synthetic evaluation system[J]. Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology, 2013, 38: 50-58. doi: 10.1016/j.tust.2013.05.001 [8] 李利平. 高风险岩溶隧道突水灾变演化机理及其应用研究[D]. 济南: 山东大学, 2009. [9] 李术才, 袁永才, 李利平, 等. 钻爆施工条件下岩溶隧道掌子面突水机制及最小安全厚度研究[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2015, 37(2): 313-320.LI Shucai, YUAN Yongcai, LI Liping, et al. Water inrush mechanism and minimum safe thickness of rock wall of Karst tunnel face under blast excavation[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2015, 37(2): 313-320. [10] LI L P, XIONG Y F, WANG J, et al. Comprehensive influence analysis of multiple parameters on the safety thickness against water inrush in shield tunnel[J]. International Journal of Geomechanics, 2020, 20(12): 04020226. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)GM.1943-5622.0001870 [11] AN P T, LI M X, MA S K, et al. Analysis of the thickness of the outburst prevention layer in Karst tunnels under the control of compressive faults[J]. Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology, 2024, 147: 105710. doi: 10.1016/j.tust.2024.105710 [12] ZHANG L W, FU H, WU J, et al. Effects of Karst cave shape on the stability and minimum safety thickness of tunnel surrounding rock[J]. International Journal of Geomechanics, 2021, 21(9): 04021150. =. [13] LI S C, GAO C L, ZHOU Z Q, et al. Analysis on the precursor information of water inrush in Karst tunnels: a true triaxial model test study[J]. Rock Mechanics and Rock Engineering, 2019, 52(2): 373-384. doi: 10.1007/s00603-018-1582-2 [14] 曾艺. 岩溶隧道岩盘安全厚度计算方法及突水灾害发生机理研究[D]. 成都: 西南石油大学, 2015. [15] 郭佳奇. 岩溶隧道防突厚度及突水机制研究[D]. 北京: 北京交通大学, 2011. [16] 杨子汉, 杨小礼, 许敬叔, 等. 基于上限原理的两种岩溶隧道岩墙厚度计算方法[J]. 岩土力学, 2017, 38(3): 801-809. doi: 10.16285/j.rsm.2017.03.024YANG Zihan, YANG Xiaoli, XU Jingshu, et al. Two methods for rock wall thickness calculation in Karst tunnels based on upper bound theorem[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2017, 38(3): 801-809. doi: 10.16285/j.rsm.2017.03.024 [17] 孙谋, 刘维宁. 高风险岩溶隧道掌子面突水机制研究[J]. 岩土力学, 2011, 32(4): 1175-1180. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2011.04.037SUN Mou, LIU Weining. Research on water inrush mechanism induced by Karst tunnel face with high risk[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2011, 32(4): 1175-1180. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2011.04.037 [18] XIAO Q F, LI Y J, XUE P, et al. Face stability assessment for Karst tunnelling across a filling-type Karst cave[J]. KSCE Journal of Civil Engineering, 2024, 28(9): 4116-4128. doi: 10.1007/s12205-024-2162-5 [19] SHAN R L, ZHANG X N, LU M. Numerical application of safe thickness between a tunnel and surrounding concealed caves[J]. Geotechnical and Geological Engineering, 2018, 36(1): 95-104. doi: 10.1007/s10706-017-0309-6 [20] 陈帆. 岩溶隧道掌子面断续节理防突岩体突水演化规律[D]. 焦作: 河南理工大学, 2018. [21] WU W L, LIU X L, GUO J Q, et al. Upper limit analysis of stability of the water-resistant rock mass of a Karst tunnel face considering the seepage force[J]. Bulletin of Engineering Geology and the Environment, 2021, 80(7): 5813-5830. doi: 10.1007/s10064-021-02283-6 [22] XU Z H, HUANG X, LI S C, et al. A new slice-based method for calculating the minimum safe thickness for a filled-type Karst cave[J]. Bulletin of Engineering Geology and the Environment, 2020, 79(2): 1097-1111. doi: 10.1007/s10064-019-01609-9 [23] YE F, DUAN J C, FU W X, et al. Permeability properties of jointed rock with periodic partially filled fractures[J]. Geofluids, 2019, 2019(1): 4039024. doi: 10.1155/2019/4039024 [24] WU J, LI S C, XU Z H, et al. Determination of required rock thickness to resist water and mud inrush from Karst caves under earthquake action[J]. Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology, 2019, 85: 43-55. doi: 10.1016/j.tust.2018.11.048 [25] XU Z H, HUANG X, LI S C, et al. A new slice-based method for calculating the minimum safe thickness for a filled-type Karst cave[J]. Bulletin of Engineering Geology and the Environment, 2020, 79(2): 1097-1111. doi: 10.1007/s10064-019-01609-9 [26] 肖前丰, 李文龙, 符文熹, 等. 富水构造区圆形隧道抗突体最小安全厚度解析解[J]. 工程科学与技术, 2022, 54(3): 159-168.XIAO Qianfeng, LI Wenlong, FU Wenxi, et al. Analytical solution to the minimum safe thickness of circular tunnel anti-inrushing structure in water-rich area[J]. Advanced Engineering Sciences, 2022, 54(3): 159-168. -




 下载:
下载: