Metamodel-Driven Flexible Job Shop Embodied Agent and Its Scheduling System Construction
-
摘要:
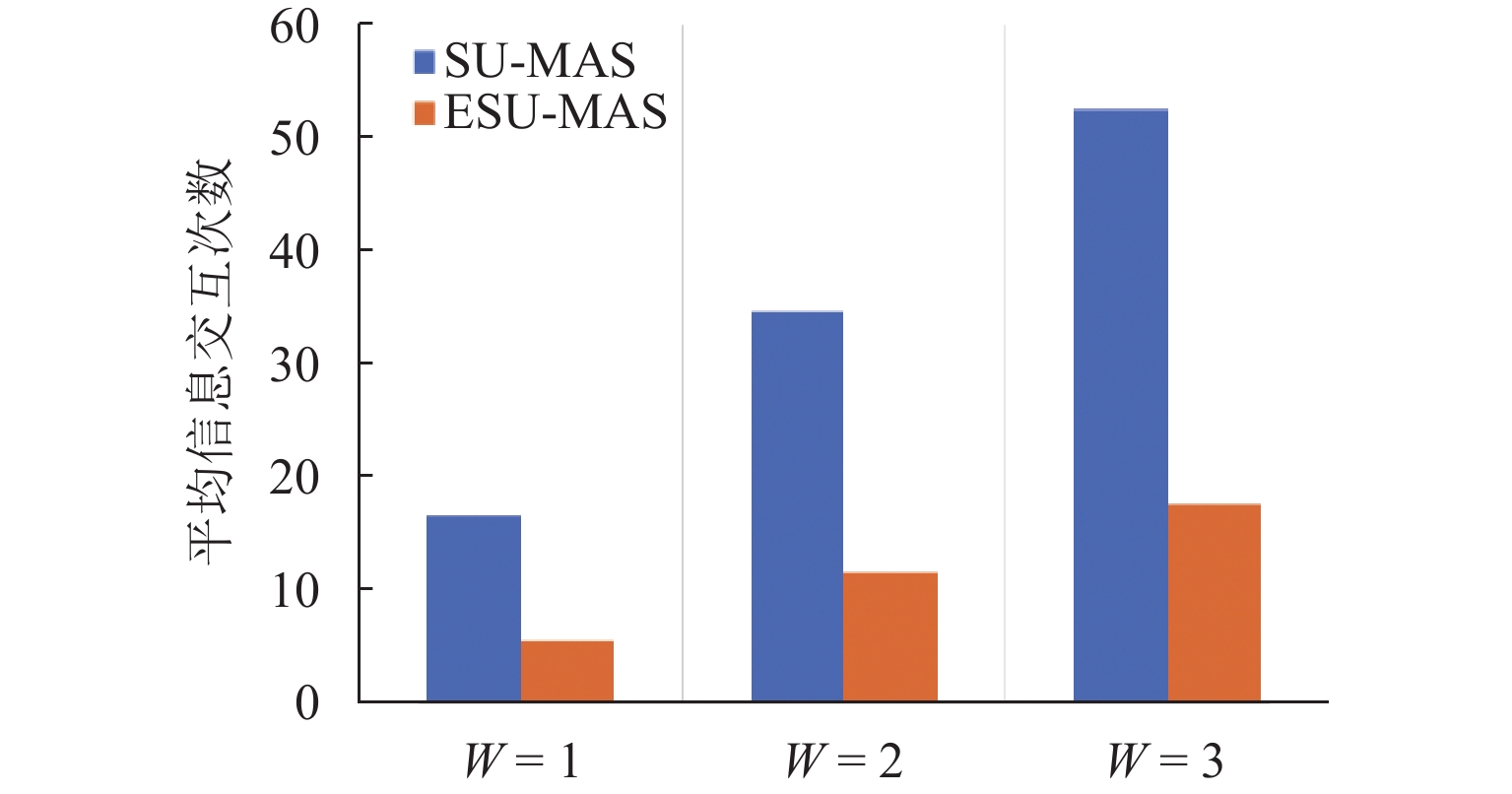
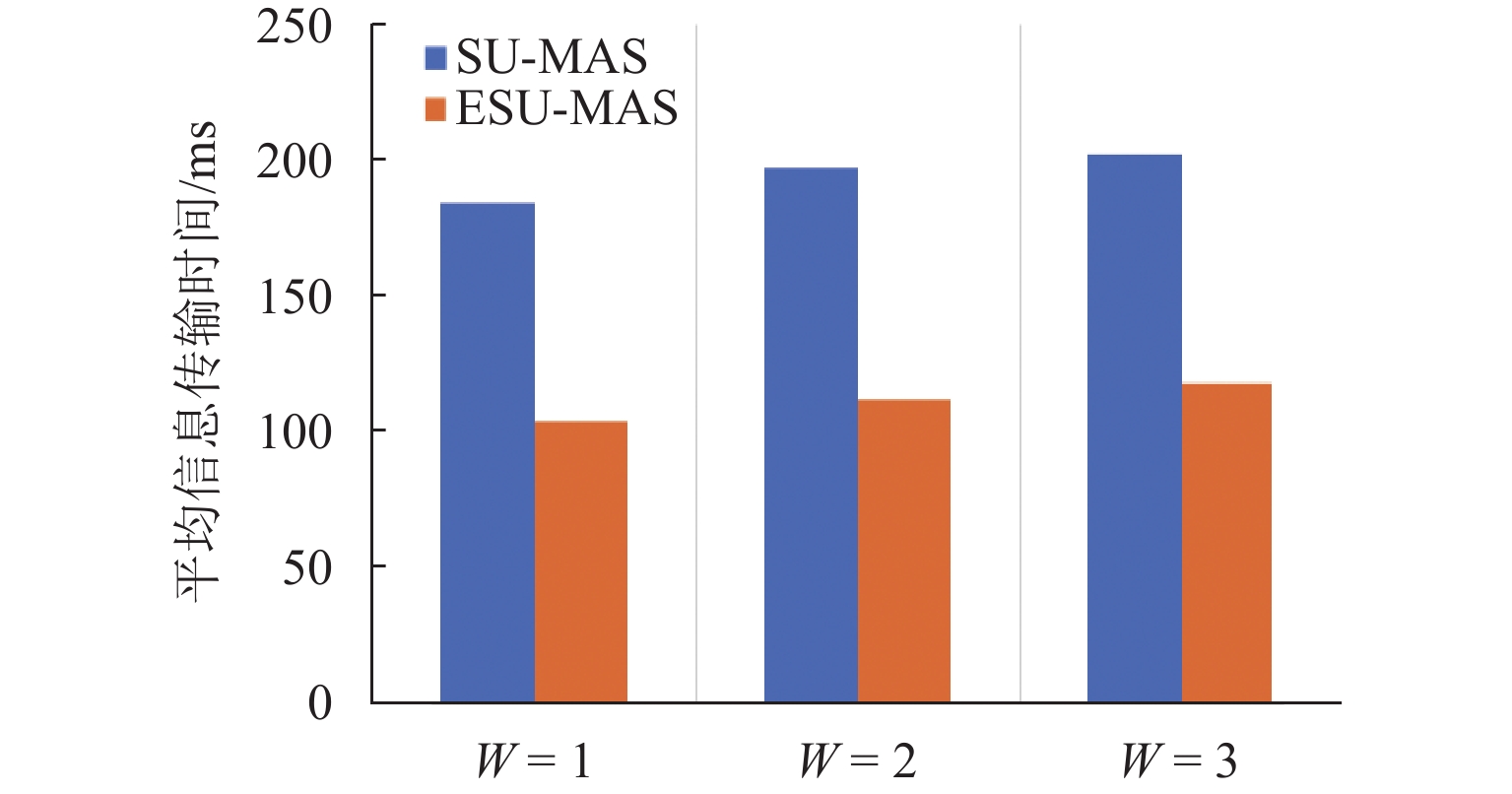
为提高柔性作业车间调度系统在扰动事件发生时的稳定性与响应效率,实现基于具身智能体的柔性作业车间多智能协同调度方法,首先,根据柔性作业车间调度问题特点,通过对具身智能体的构成要素、关系及属性的分析与抽象,提出柔性作业车间具身调度智能体元模型,实现具身调度智能体的统一建模;然后,在对元模型实例化后,设计分布式多智能体调度策略集合,构建具身多智能体调度系统,并结合Q博弈协商机制实现了多智能体的协同调度;最后,以某小型结构件车间为例,与现有多智能体调度方法进行对比. 研究结果表明:在新订单到达和机器故障扰动下,调度方案稳定性分别平均提高42.75%和42.88%,智能体间通讯量分别平均减少58.33%和62.5%,计算响应时间分别平均减少32.27%和33.28%.
Abstract:Objective Flexible job shop scheduling optimization is an important research topic in digital manufacturing science, especially the random occurrence of abnormal disturbances such as machine failures and order changes, which disrupt the original production plan, causing problems such as unreasonable resource allocation, delayed order delivery, and increased production costs. In recent years, distributed multi-agent scheduling methods have been considered to be one of the most effective ways to improve the response speed of manufacturing system disturbances and reduce the negative impact of uncertain disturbances in the production process. In the context of job shop scheduling, designing an embodied scheduling agent that integrates the dynamic behavior of physical entities enables real-time environmental perception and autonomous decision-making based on behavioral feedback during disturbances. This ensures the efficient operation of the production system.
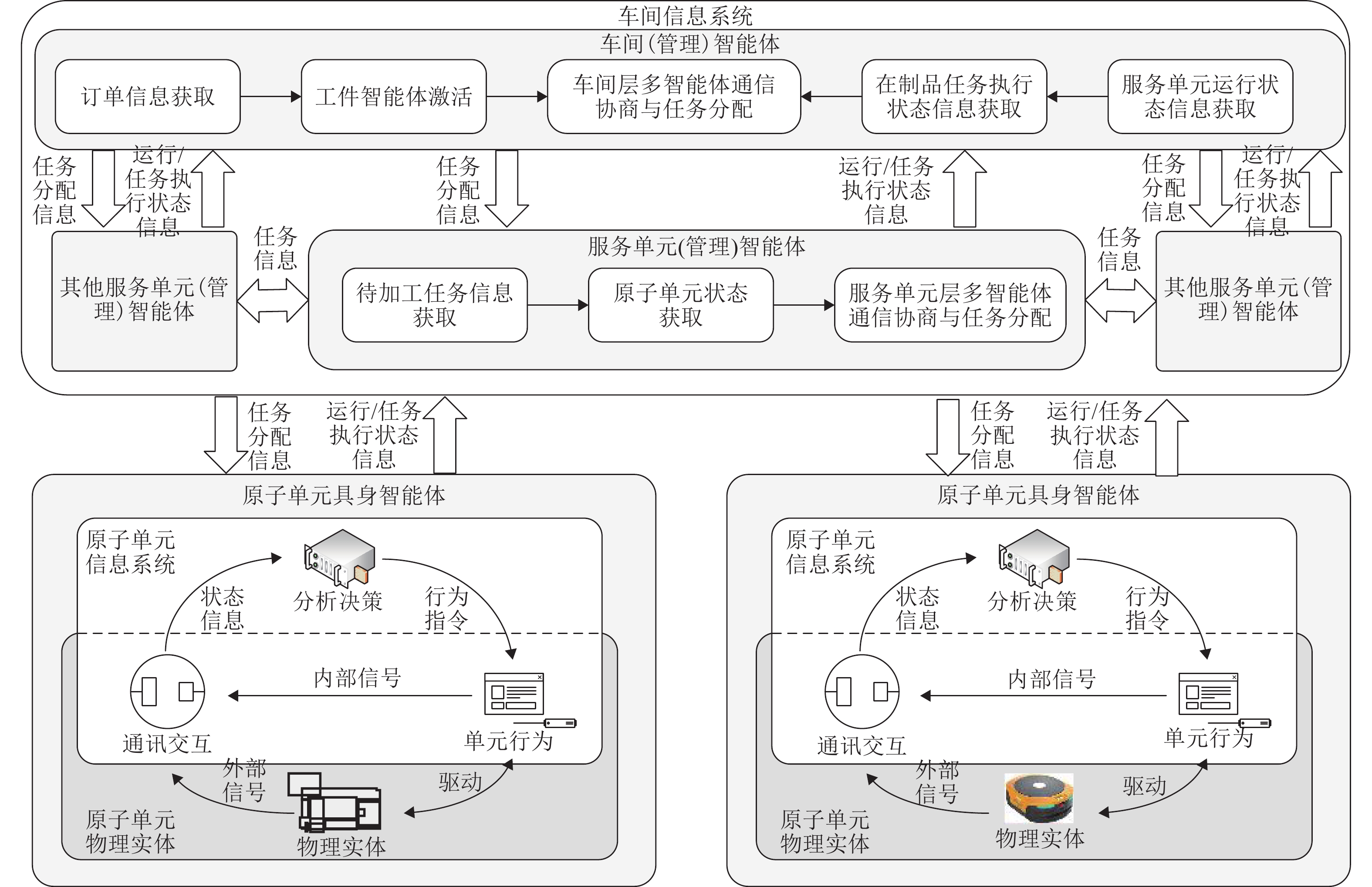
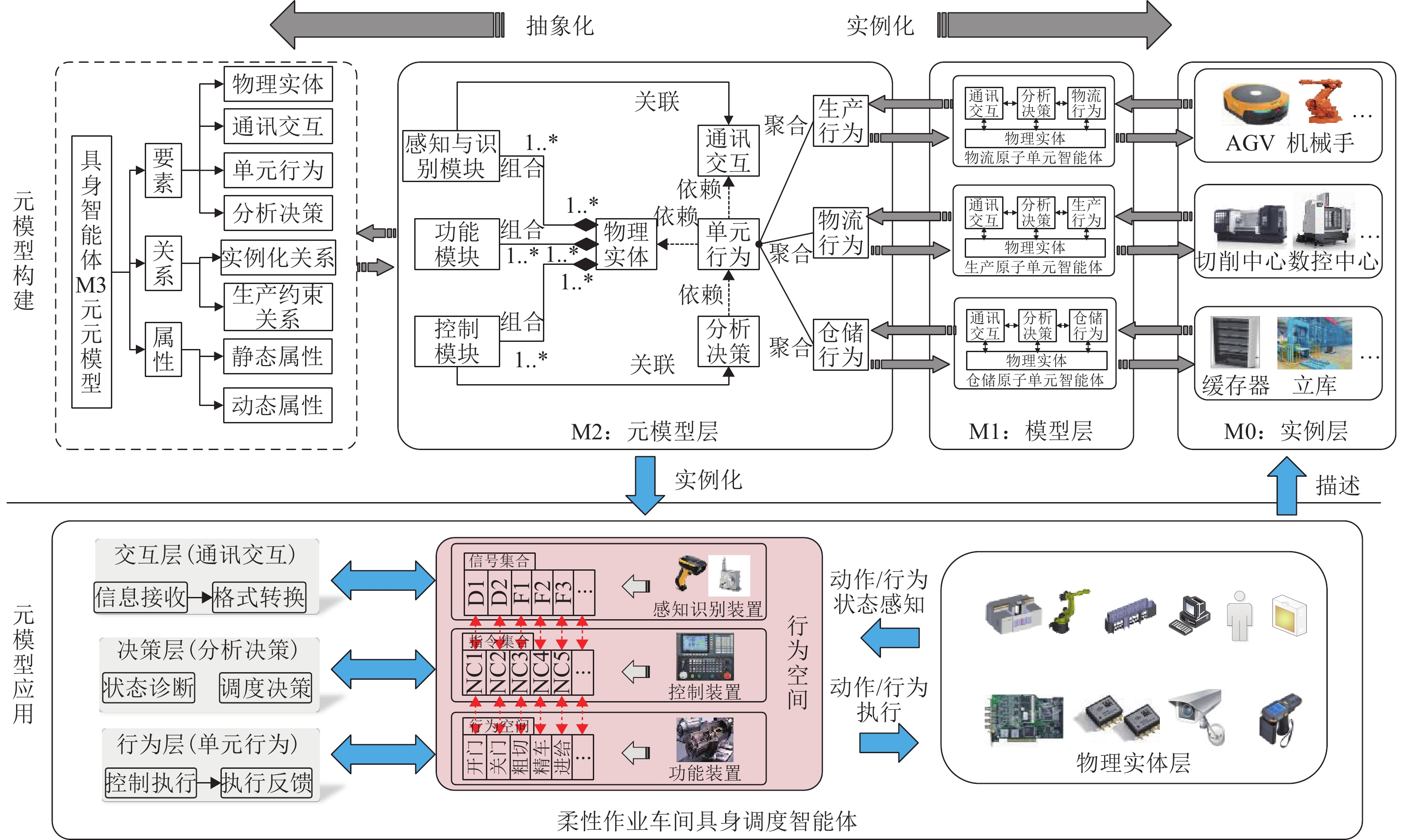
Method To develop a multi-agent scheduling method for flexible job shops based on embodied agents and to enhance the stability and responsiveness of the system during disruptive events, a metamodel-driven approach for constructing embodied agents in flexible job shops was proposed. By instantiating this model, a scheduling system with a unified structure of embodied agents was achieved. First, to enable agents to perform autonomous decision-making and real-time dynamic adjustments, the concept of embodied intelligence was applied. Based on the existing interaction layer, decision layer, and adaptation layer of job shop scheduling agents, their instruction sets, behavior spaces, and sensory signal sets were associated and encapsulated to form embodied agents with physical bodies and behavioral spaces. Based on the resource composition characteristics of flexible job shops, the elements, relationships, and attributes of embodied agents were analyzed and abstracted. A metamodel for embodied agents in flexible job shops was proposed, enabling the unified modeling of embodied scheduling agents and providing a foundational model for their collaborative scheduling. Second, through instantiation operations such as inheritance, composition, aggregation, dependency, and association applied to the metamodel, a distributed multi-agent scheduling system with a unified structure and self-organizing collaborative operation capability was developed. Finally, a set of distributed multi-agent scheduling strategies was designed based on the different functions of different agents and the different information they can obtain. By integrating these strategies with a Q-game negotiation mechanism, collaborative scheduling among multiple agents was realized, thereby improving the stability of the scheduling method and enhancing its responsiveness to disruptions. This scheduling system, based on embodied agents, enabled the adjustment of scheduling strategies at the individual level when disruptive events occur. This approach effectively reduced the number of information exchanges during the scheduling process, improving the stability of the multi-agent system and enhancing its scheduling optimization capabilities in the face of disruptions.
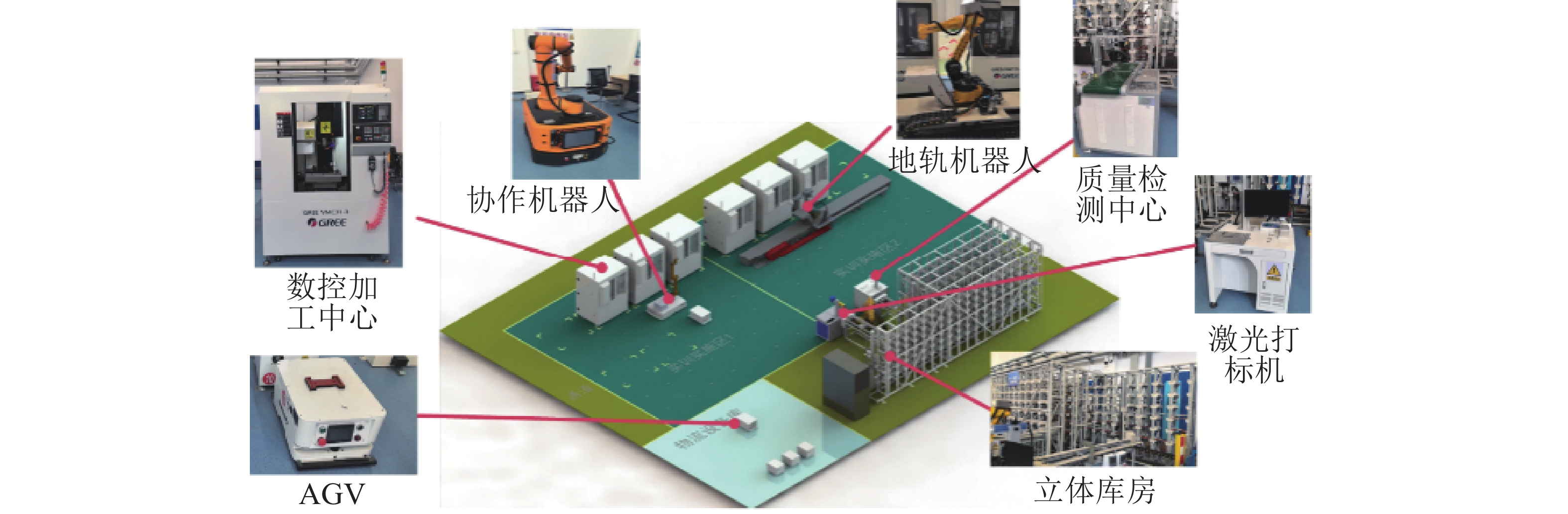
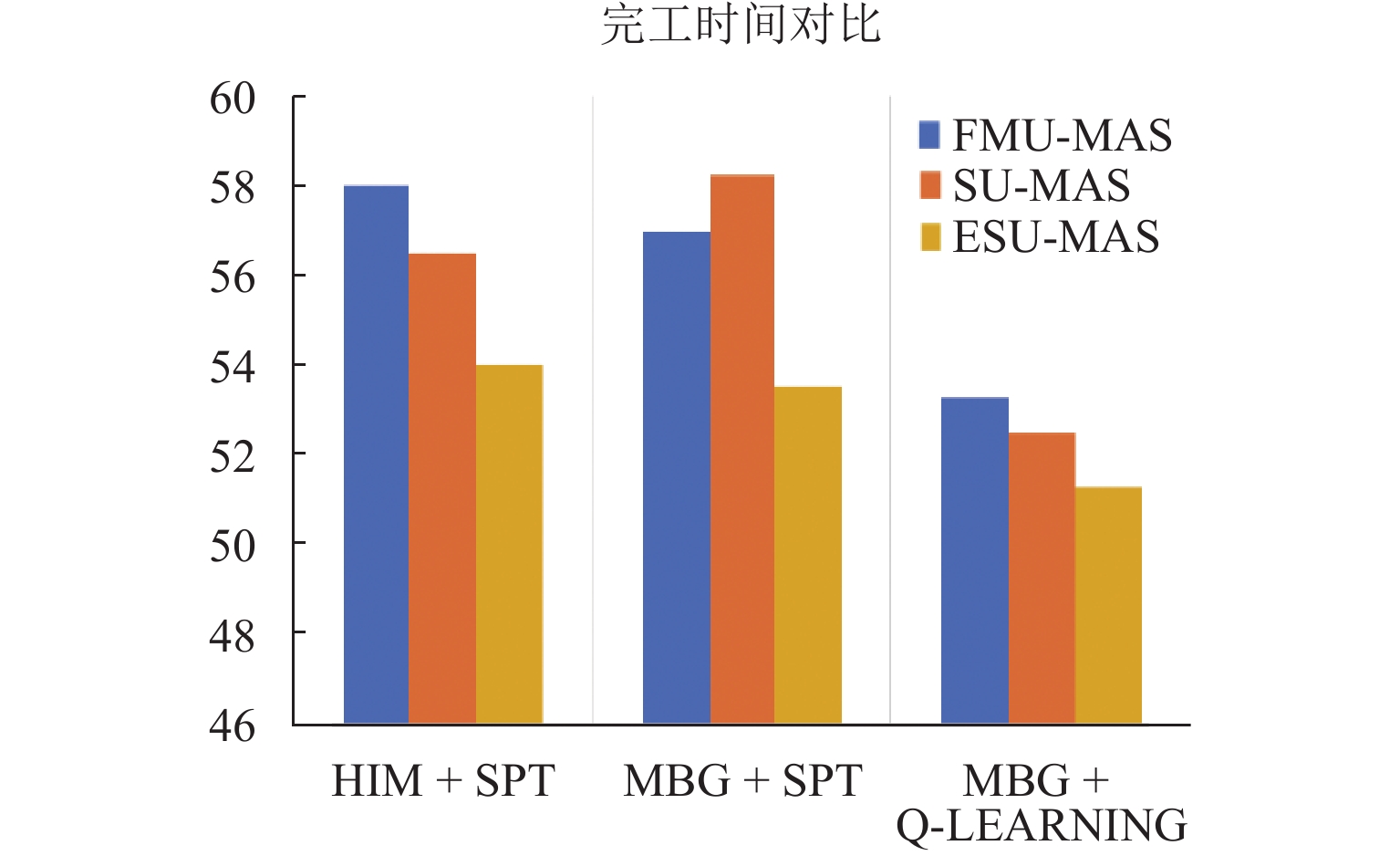
Result To validate the advantages of the proposed embodied scheduling agent modeling method and the multi-agent scheduling system, two small-scale manufacturing workshops producing structural components were used as case studies. The proposed method was compared with existing approaches in three aspects: embodied agent modeling, collaborative operation, and scheduling optimization. Experimental results demonstrate that the embodied agent modeling method proposed in this paper ensures model structure consistency, guaranteeing that the model adheres to predefined specifications and rules, thereby providing a unified modeling foundation for the collaborative scheduling of multi-agents. In the embodied multi-agent scheduling system, each agent generates a complete set of feasible individual strategies after evaluating all possible actions. Negotiation and interaction among agents are conducted based on these strategy sets. The number of interactions remains independent of the number of actions selected by the agents, resulting in an average reduction of 60.4% in communication volume and a 32.78% average decrease in computational response time. In terms of scheduling optimization performance, agents enhance the diversity of scheduling strategies during the negotiation process by adjusting their individual scheduling strategies, thereby improving the system’s global optimization capability. Compared to existing methods, the proposed approach achieves an improvement of more than 22.6%.
Conclusion In summary, the proposed multi-agent scheduling method based on embodied agents not only improves system responsiveness and stability in handling disruptive events but also significantly enhances global optimization performance. This provides an efficient and robust solution for scheduling optimization in flexible job shops and offers new research directions and technical support for intelligent scheduling and collaboration in future manufacturing systems. In the future, further research could focus on applying the proposed method to larger and more complex manufacturing scenarios, integrating real-time sensing technologies and advanced machine learning algorithms to further enhance the adaptability and intelligence of the scheduling system.
-
Key words:
- flexible job shop /
- dynamic scheduling /
- metamodel /
- embodied agent construction
-
表 1 具身调度智能体与非具身智能体对比
Table 1. Differences of embodied agents and non-embodied agents
类型 定义与结构形态 状态获取方式 调度方案生成策略 具身调度智能体 集成物理载体、与物理世界直接交互的智能体 与物理实体集成,实时感知/反馈,直接与物理设备交互 扰动事件发生时智能体通过主动决策的方式,动态调整自身行为、任务执行顺序等,系统稳定性强 非具身调度智能体 通常指软件层面的智能系统,没有物理实体或无直接与物理空间进行交互能力[13] 与信息系统交互感知/反馈,无法直接与物理空间交互 扰动事件发生后直接在全局/局部范围内进行重协商,依据运行状态数据被动决策,无个体调度方案调整能力 表 2 智能体分布式策略集合
Table 2. Distributed policy set of agents
智能体 策略特点 策略名称 描述 车间智能体 可直接获得订单全部信息 ATP 最早到达的工件优先 HUP 紧急度最高的工件优先 RPP 剩余代加工工序最多的优先 EDP 交付期最早的工件优先 服务单元智能体 可直接获得机器运行状态信息 STP 加工时间最短的机器优先 LRP 负载率最低的机器优先 SQP 剩余加工任务最少的机器优先 SWP 等待时间最短的机器优先 原子单元智能体 可直接获得机器已分配任务执行/未执行状态信息 TPX 随机选择队列/可选动作中的 2 个不相邻工序/动作进行交换 PFI 在任务队列/可选动作集合中随机选择 2 个工序/动作,将后一个工序/动作插入到另一个之前 NBE 随机选择任务队列/可选动作中相邻的 2 个工序/动作进行交换 HSE 将任务队列/可选动作分成 2 个等长的部分进行交换 SQI 随机选择任务队列/可选动作中的一段任务/动作进行逆序反转 表 3 案例1工件加工时间信息
Table 3. Processing time information of jobs in Case 1
min 工件号 工序号 CMU1 CMU2 工件号 工序号 CMU1 CMU2 MU1 MU2 MU3 MU4 MU5 MU6 MU1 MU2 MU3 MU4 MU5 MU6 J1 O11 3 3 5 J11 O111 5 3 5 O12 8 3 9 O112 7 7 7 J2 O21 5 7 3 J12 O121 5 7 3 O22 2 6 7 O122 2 6 7 J3 O31 5 6 5 J13 O131 7 6 5 O32 4 8 9 O132 4 8 9 J4 O41 7 5 8 J14 O141 7 5 6 O42 8 6 5 O142 8 6 5 J5 O51 5 7 6 J15 O151 8 8 6 O52 5 5 5 O152 5 5 5 J6 O61 7 4 4 J16 O161 3 3 5 O62 7 9 9 O162 8 3 9 J7 O71 5 6 5 J17 O171 5 7 3 O72 8 3 9 O172 2 6 7 J8 O81 4 5 3 J18 O181 5 6 5 O82 2 6 7 O182 4 8 9 J9 O91 7 6 9 J19 O191 7 5 8 O92 8 8 9 O192 8 6 5 J10 O101 5 8 6 J20 O201 5 7 6 O102 5 6 6 O202 5 5 5 表 4 案例2工件加工时间信息
Table 4. Processing time information of jobs in Case 2
min 工件号 工序号 CMU1 CMU2 CMU3 MU1 MU2 MU3 MU4 MU5 MU6 1 O11 3 3 5 O12 8 3 O13 3 2 O21 5 7 3 O22 2 6 O23 3 3 O31 5 6 O32 4 8 9 O33 3 4 O41 8 6 O42 7 5 8 O43 3 表 5 案例1智能体构成
Table 5. Agent composition of Case 1
智能体 物理实体 通讯交互 单元行为 分析决策 仓储原子单元智能体 立库、堆垛机、传送带 交互信息{X=1;Y=1;Z=0;HW=1;$\cdots $} 执行动作{X轴移动;Y轴移动;料叉取货;$\cdots $} 决策指令{X_1-9;Y_1-9;Z_1-2;$\cdots $} 视觉检测原则单元智能体 3D 摄像头、2D 摄像头、传送带 交互信息{CN=1;tp=1;} 执行动作{传送带启动;拍照} 决策指令{CN_S;CN_E;tp} AGV 原子单元智能体 驱动装置、位置识别装置等 交互信息{L=1,1,E=R;$\cdots $} 执行动作{从1,1点向2,2 移动;运行中$\cdots $} 决策指令{NC=1,1-2,2;E_R$\cdots $} 五轴原子单元智能体 数控机床驱动装置、进给装置等 交互信息{a1=1;b1=0;W=O;=$\cdots $} 执行动作{粗铣 a1 程序启动;粗车 b1 程序准备;安全门开;$\cdots $} 决策指令{NC_a1;NC_b1_S;D_O;$\cdots $} 表 6 案例2主要智能体构成
Table 6. Main agent composition of Case 2
智能体 物理实体 通讯交互 单元行为 分析决策 转运机械手原子单元智能体 驱动装置、夹取装置等 交互信息{1_X;0_Y;2_Z;Q=1$\cdots $} 执行动作{从1,0,0向2,0,0移动;机械手抓取;$\cdots $} 决策指令{1,1,0-2,2,0; ZQ_1;$\cdots $} 雕刻机原子单元智能体 切削装置、进给装置等 交互信息{a2=1;b2=0;$\cdots $} 执行动作{执行雕刻 a2 程序;雕刻 b2 程序准备;$\cdots $} 决策指令{NC_a2;NC_b2_S;$\cdots $} 传送带原子单元智能体 驱动电机、位置传感装置等 交互信息{CN=1;E=1;$\cdots $} 执行动作{传送带启动;传送带停止;点位 1 顶升} 决策指令{CN_S; CN_E; 1_DS;$\cdots $} 激光打标原子单元智能体 数控机床驱动装置、进给装置等 交互信息{a3=1;b3=0;$\cdots $} 执行动作{执行打标程序 a3;打标 b3 程序就绪;$\cdots $} 决策指令{NC_a3_1;NC_b3_0;$\cdots $} 表 7 新订单到达运行结果对比
Table 7. Comparison of operation results of new job arrival
类型 $ {P_{e}} $ $ {T_{{\mathrm{ave}}}} $/次 $ {L_{{\mathrm{ave}}}} $/ms 案例 1 案例 2 案例 1 案例 2 案例 1 案例 2 SU-MAS 0.486 0.525 16.5 6 184.17 95.26 ESU-MAS 0.235 0.347 5.5 3 104.17 65.63 表 8 机器故障运行结果对比
Table 8. Comparison of operation results of machine failure
类型 $ {P_{e}} $ $ {T_{{\mathrm{ave}}}} $/次 $ {L_{{\mathrm{ave}}}} $/ms 案例 1 案例 2 案例 1 案例 2 案例 1 案例 2 SU-MAS 0.1180 0.204 12 6.0 156.25 75.33 ESU-MAS 0.0625 0.125 3 1.5 89.75 57.25 表 9 多智能体协商调度方法对比
Table 9. Comparison with multi-agent scheduling methods
算例 规模 BKS NAM NIMASS EG GATS-HM ESU-MAS MK01 10 × 6 39 40 40 40 42 40 MK02 10 × 6 26 28 28 32 32 27 MK03 15 × 8 204 204 204 211 211 204 MK04 15 × 8 65 66 65 67 81 66 MK05 15 × 4 171 179 177 188 186 171 MK06 10 × 15 61 66 67 85 86 62 MK07 20 × 5 144 149 144 154 157 145 MK08 20 × 10 523 523 523 523 523 523 MK09 20 × 10 307 312 312 337 369 307 MK10 20 × 15 229 235 229 280 296 235 KM01 4 × 5 11 11 11 11 11 KM02 8 × 8 14 14 14 14 14 14 KM03 10 × 7 11 11 11 11 11 KM04 10 × 10 7 7 7 7 7 7 KM05 15 × 10 11 11 11 12 11 12 相对误差RE 32.4 28.3 129.5 167.1 21.9 -
[1] 庄存波, 刘检华, 熊辉. 分布式自主协同制造: 一种智能车间运行新模式[J]. 计算机集成制造系统, 2019, 25(8): 1865-1874.ZHUANG Cunbo, LIU Jianhua, XIONG Hui. Distributed initiative and collaborative manufacturing: new paradigm for intelligent shop-floor[J]. Computer Integrated Manufacturing Systems, 2019, 25(8): 1865-1874. [2] ZHANG J, DING G F, ZOU Y S, et al. Review of job shop scheduling research and its new perspectives under Industry 4.0[J]. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing, 2019, 30(4): 1809-1830. doi: 10.1007/s10845-017-1350-2 [3] PAL M, MITTAL M L, SONI G, et al. A multi-agent system for FJSP with setup and transportation times[J]. Expert Systems with Applications, 2023, 216: 119474. doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2022.119474 [4] ZHANG J, DENG T M, JIANG H F, et al. Bi-level dynamic scheduling architecture based on service unit digital twin agents[J]. Journal of Manufacturing Systems, 2021, 60: 59-79. doi: 10.1016/j.jmsy.2021.05.007 [5] WANG J, LIU Y, REN S, et al. Evolutionary game based real-time scheduling for energy-efficient distributed and flexible job shop[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2021, 293: 126093. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.126093 [6] 杨博见, 杜丽, 郭景仁. 基于多Agent的柔性作业车间动态调度方法研究[J]. 航空制造技术, 2023, 66(6): 99-107.YANG Bojian, DU Li, GUO Jingren. Research on dynamic scheduling of flexible job-shop based on multi-agent[J]. Aeronautical Manufacturing Technology, 2023, 66(6): 99-107. [7] 周毅君. 基于多智体的多资源约束车间调度技术与系统研究[D]. 武汉: 华中科技大学, 2021. [8] GU W B, LIU S Q, ZHANG Z Q, et al. A distributed physical architecture and data-based scheduling method for smart factory based on intelligent agents[J]. Journal of Manufacturing Systems, 2022, 65: 785-801. doi: 10.1016/j.jmsy.2022.11.006 [9] 李浩, 邢志远, 李琳利, 等. 基于多智能体的工业数字孪生系统云边端架构与关键技术[J]. 计算机集成制造系统, 2024, 30(11): 3755-3770.LI Hao, XING Zhiyuan, LI Linli, et al. Cloud-edge-device system architecture and key technologies of industrial digital twin system based on multi-agent[J]. Computer Integrated Manufacturing Systems, 2024, 30(11): 3755-3770. [10] 江海凡, 丁国富, 肖通, 等. 数字孪生演进模型及其在智能制造中的应用[J]. 西南交通大学学报, 2022, 57(6): 1386-1394.JIANG Haifan, DING Guofu, XIAO Tong, et al. Digital twin evolution model and its applications in intelligent manufacturing[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2022, 57(6): 1386-1394. [11] ZHAO Z K, WU Q X, WANG J, et al. Exploring embodied intelligence in soft robotics: a review[J]. Biomimetics, 2024, 9(4): 248. doi: 10.3390/biomimetics9040248 [12] 丁国富, 刘名远, 谢家翔, 等. 数字孪生制造装备高可用运行协同的计算方法[J]. 西南交通大学学报, 2025, 60(1): 194-204.DING Guofu, LIU Mingyuan, XIE Jiaxiang, et al. Collaborative computing method for highly available operation of digital twin manufacturing equipment[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2025, 60(1): 194-204. [13] 邓三鹏, 张香玲, 王凯, 等. 具身智能机器人关键技术及发展趋势研究[J]. 装备制造技术, 2024(6): 2-10.DENG Sanpeng, ZHANG Xiangling, WANG Kai, et al. Research on key technologies and development trend of intelligent robot with body[J]. Equipment Manufacturing Technology, 2024(6): 2-10. [14] YANG X L, LIU X M, ZHANG H, et al. Meta-model-based shop-floor digital twin architecture, modeling and application[J]. Robotics and Computer-Integrated Manufacturing, 2023, 84: 102595. doi: 10.1016/j.rcim.2023.102595 [15] 白辰甲, 许华哲, 李学龙. 大模型驱动的具身智能: 发展与挑战[J]. 中国科学: 信息科学, 2024, 54(9): 2035-2082. doi: 10.1360/SSI-2024-0076BAI Chenjia, XU Huazhe, LI Xuelong. Embodied-AI with large models: research and challenges[J]. Scientia Sinica (Informationis), 2024, 54(9): 2035-2082. doi: 10.1360/SSI-2024-0076 [16] ZHANG Y, ZHU H H, TANG D B, et al. Dynamic job shop scheduling based on deep reinforcement learning for multi-agent manufacturing systems[J]. Robotics and Computer-Integrated Manufacturing, 2022, 78: 102412. doi: 10.1016/j.rcim.2022.102412 [17] ZHAO F Q, DI S L, WANG L. A hyperheuristic with Q-learning for the multiobjective energy-efficient distributed blocking flow shop scheduling problem[J]. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2023, 53(5): 3337-3350. doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2022.3192112 [18] WEI L X, HE J X, GUO Z Y, et al. A multi-objective migrating birds optimization algorithm based on game theory for dynamic flexible job shop scheduling problem[J]. Expert Systems with Applications, 2023, 227: 120268. doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2023.120268 [19] 李奇, 艾钰璇, 孙彩, 等. 非合作博弈背景下基于BSA的配电网优化重构[J]. 西南交通大学学报, 2024, 59(2): 438-446.LI Qi, AI Yuxuan, SUN Cai, et al. Optimal reconfiguration of distribution network based on backtracking search algorithm under the background of non-cooperative game theory[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2024, 59(2): 438-446. [20] 陈鸣, 朱海华, 张泽群, 等. 基于信息素的多Agent车间调度策略[J]. 中国机械工程, 2018, 29(22): 2659-2665.CHEN Ming, ZHU Haihua, ZHANG Zequn, et al. Multi-agent job shop scheduling strategy based on pheromone[J]. China Mechanical Engineering, 2018, 29(22): 2659-2665. [21] BRANDIMARTE P. Routing and scheduling in a flexible job shop by tabu search[J]. Annals of Operations Research, 1993, 41(3): 157-183. doi: 10.1007/BF02023073 [22] KACEM I, HAMMADI S, BORNE P. Pareto-optimality approach for flexible job-shop scheduling problems: hybridization of evolutionary algorithms and fuzzy logic[J]. Mathematics and Computers in Simulation, 2002, 60(3/4/5): 245-276. [23] NOURI H E, BELKAHLA DRISS O, GHÉDIRA K. Solving the flexible job shop problem by hybrid metaheuristics-based multiagent model[J]. Journal of Industrial Engineering International, 2018, 14(1): 1-14. doi: 10.1007/s40092-017-0204-z -




 下载:
下载: